Subclinical Atherosclerosis Is Associated with Discrepancies in BAFF and APRIL Levels and Altered Breg Potential of Precursor-like Marginal Zone B-Cells in Long-Term HIV Treated Individuals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimens and Clinical Data Collection
2.2. Characterisation of Atherosclerosis Plaques
2.3. Measure of Soluble BAFF, APRIL and CD83 Blood Levels
2.4. Flow Cytometry Characterisation of Breg Markers and Membrane BAFF Expression Levels
2.5. Culture of Blood Human B-Cells with Recombinant APRIL and BAFF
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Socio-Demographic Characteristics of the Study Cohort
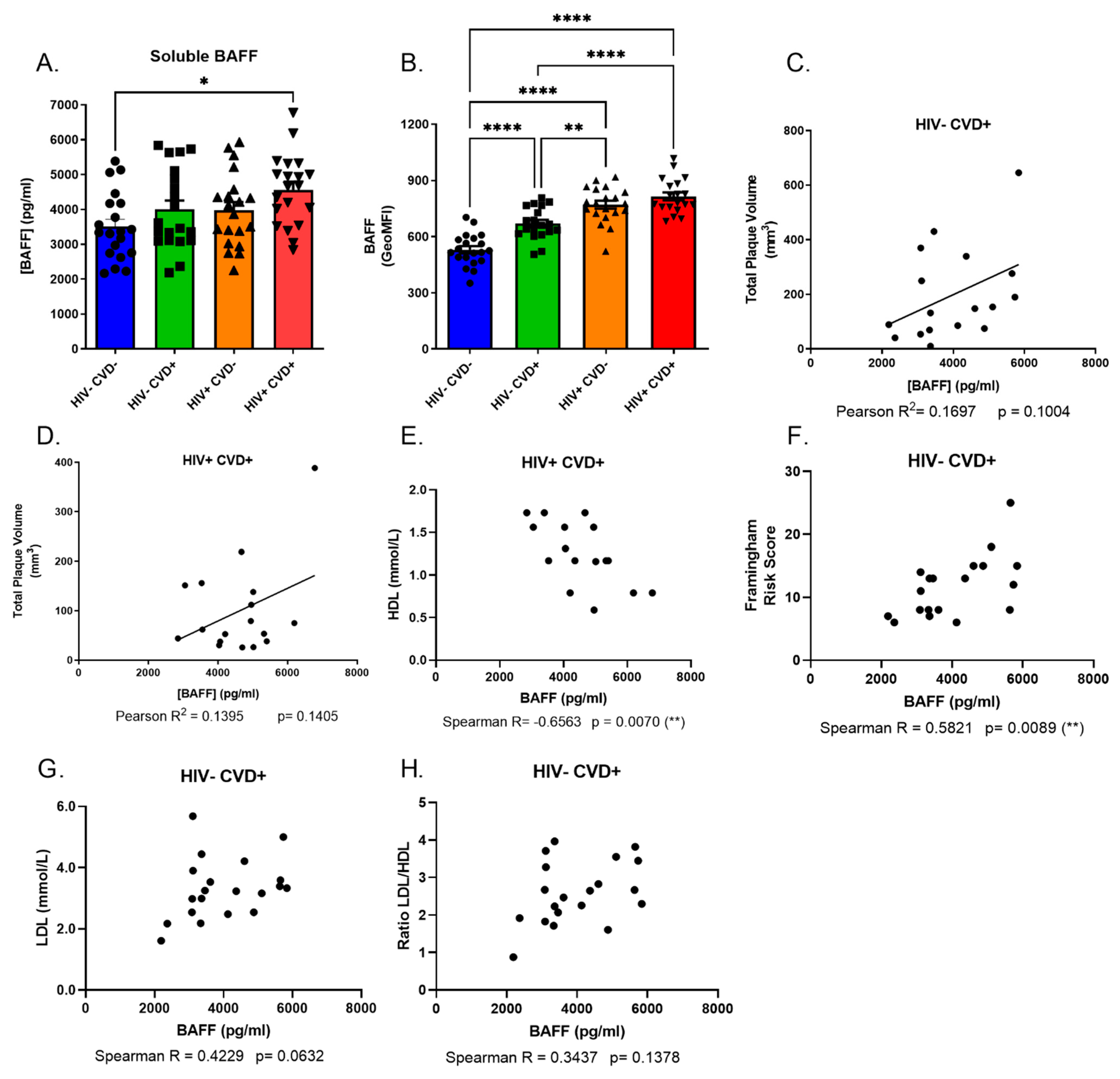
3.2. Excess BAFF Levels in the Blood of PLHIV from the CHACS Correlates with Atherosclerosis Risk Factors
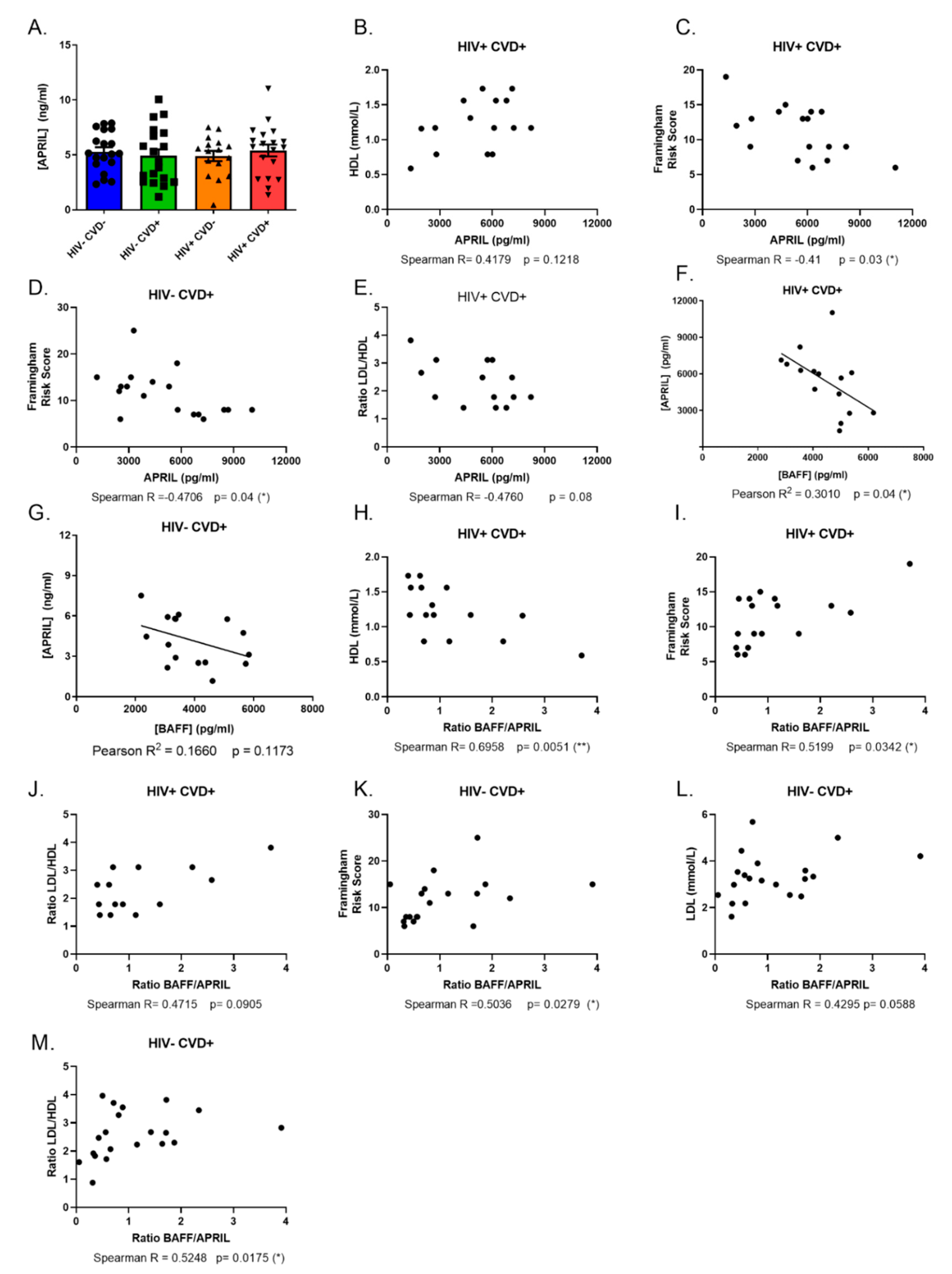
3.3. APRIL Levels Correlate Negatively with BAFF and Atherosclerosis Biomarkers in the Blood of PLHIV from the CHACS
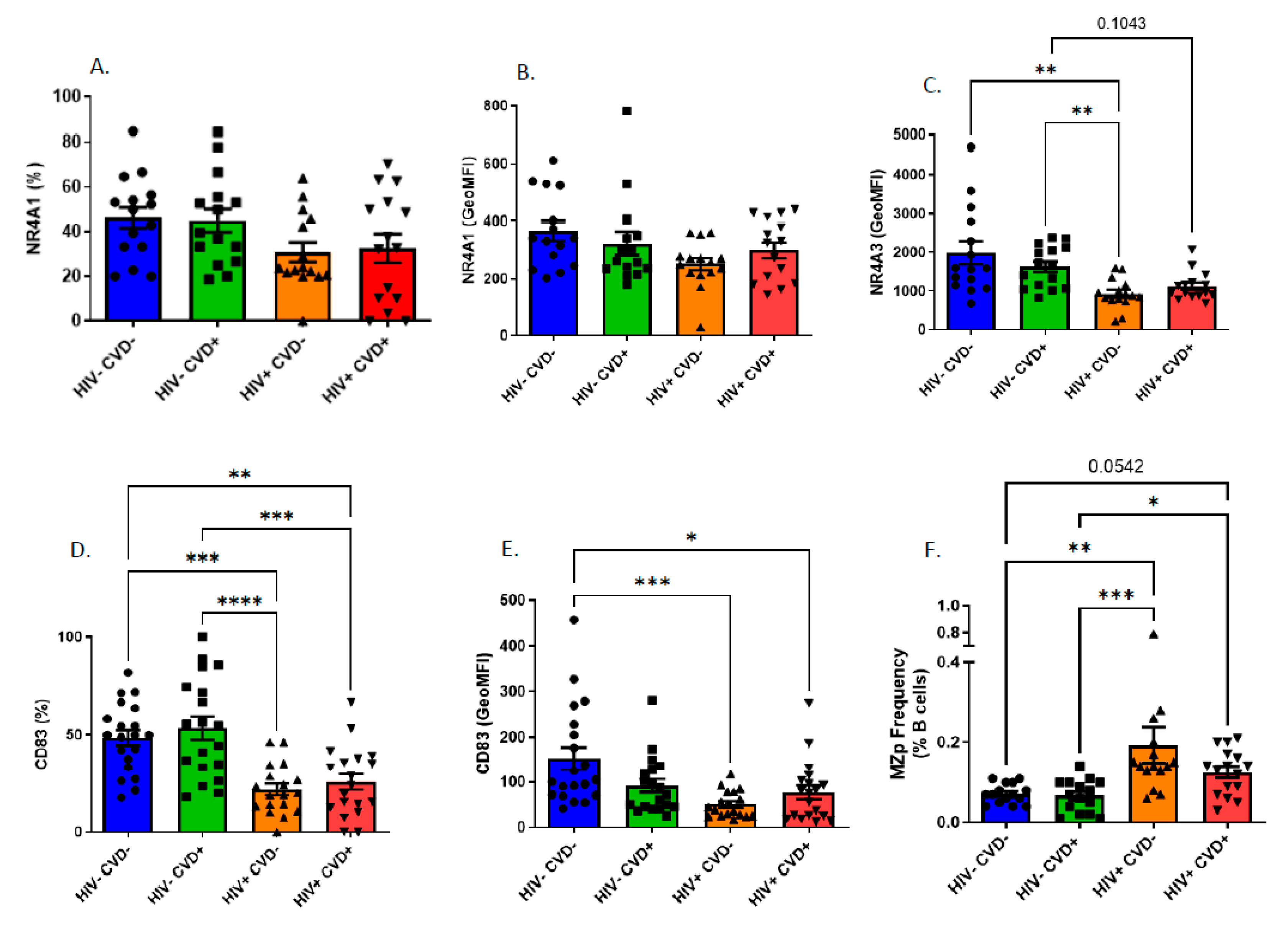
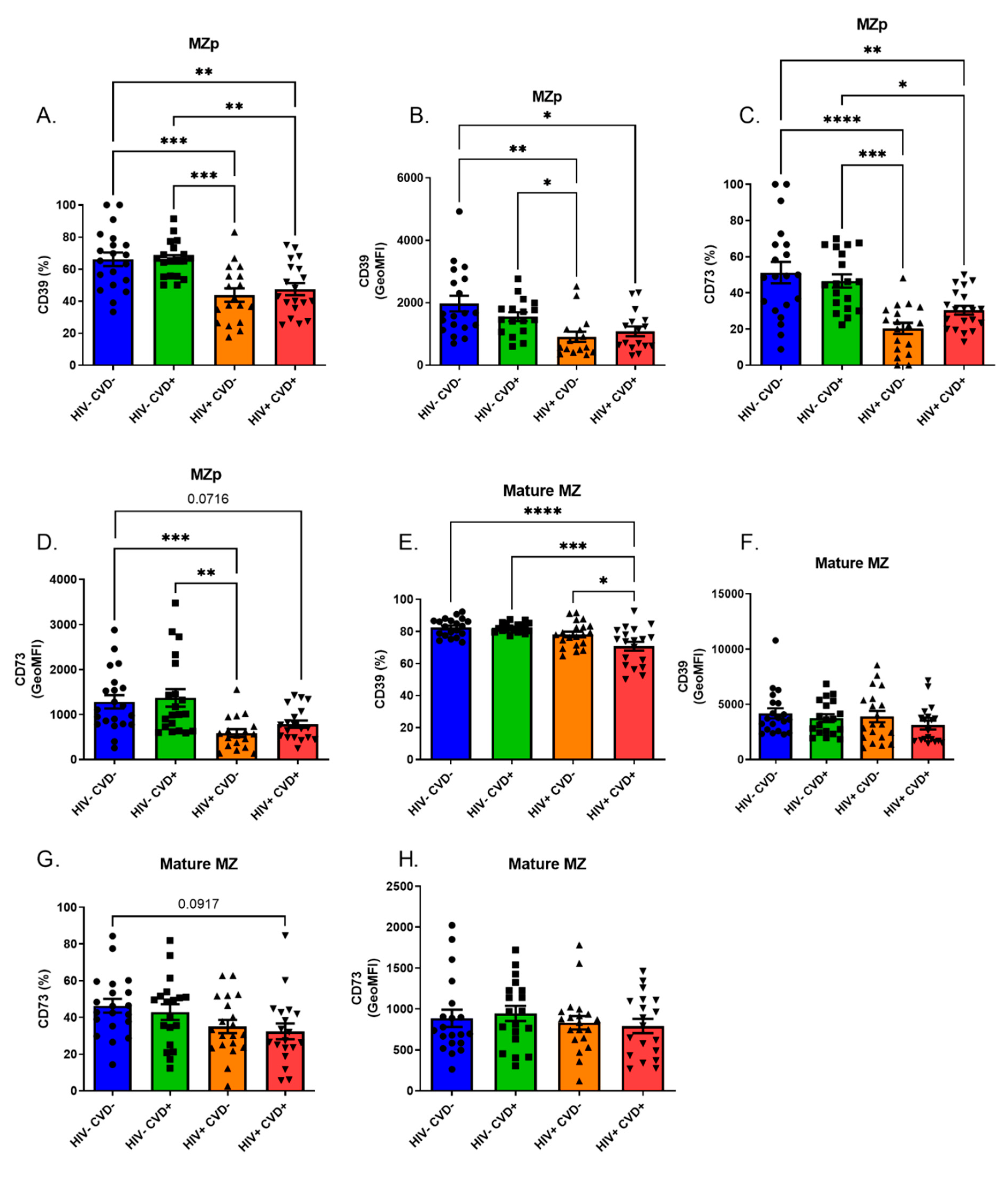
3.4. Altered Blood MZp Breg Capacities in PLHIV from the CHACS
3.5. APRIL Upregulates Expression Levels of Breg Markers by Blood MZp
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewden, C.; Chene, G.; Morlat, P.; Raffi, F.; Dupon, M.; Dellamonica, P.; Pellegrin, J.-L.; Katlama, C.; Dabis, F.; Leport, C. HIV-infected adults with a CD4 cell count greater than 500 cells/mm3 on long-term combination antiretroviral therapy reach same mortality rates as the general population. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2007, 46, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, M.; Covinsky, K.; Valcour, V.; Miao, Y.; Madamba, J.; Lampiris, H.; Cenzer, I.S.; Martin, J.; Steven, G. Deeks Geriatric Syndromes in Older HIV-Infected Adults. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. (1999) 2015, 69, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlandson, K.M.; Schrack, J.A.; Jankowski, C.M.; Brown, T.T.; Campbell, T.B. Functional impairment, disability, and frailty in adults aging with HIV-infection. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2014, 11, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triant, V.A.; Lee, H.; Hadigan, C.; Grinspoon, S.K. Increased acute myocardial infarction rates and cardiovascular risk factors among patients with human immunodeficiency virus disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 2506–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, S.; Mary-Krause, M.; Cotte, L.; Gilquin, J.; Partisani, M.; Simon, A.; Boccara, F.; Bingham, A.; Costagliola, D. Increased risk of myocardial infarction in HIV-infected patients in France, relative to the general population. Aids 2010, 24, 1228–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, M.; For the investigators of the Canadian HIV and Aging Cohort Study; Chartrand-Lefebvre, C.; Baril, J.-G.; Trottier, S.; Trottier, B.; Harris, M.; Walmsley, S.; Conway, B.; Wong, A.; et al. The Canadian HIV and aging cohort study-determinants of increased risk of cardio-vascular diseases in HIV-infected individuals: Rationale and study protocol. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, A.G.; Idris, N.S.; Barth, R.E.; Klipstein-Grobusch, K.; Grobbee, D.E. Pro-inflammatory markers in relation to cardiovascular disease in HIV infection. A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisterå, A.; Hansson, G.K. The immunology of atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenchley, J.M.; Price, D.A.; Schacker, T.W.; Asher, T.E.; Silvestri, G.; Rao, S.; Kazzaz, Z.; Bornstein, E.; Lambotte, O.; Altmann, D.; et al. Microbial translocation is a cause of systemic immune activation in chronic HIV infection. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, S.G. HIV infection, inflammation, immunosenescence, and aging. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011, 62, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, S.G. Immune dysfunction, inflammation, and accelerated aging in patients on antiretroviral therapy. Top. HIV Med. 2009, 17, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chagnon-Choquet, J.; Gauvin, J.; Roger, J.; Fontaine, J.; Poudrier, J.; Roger, M. HIV Nef Promotes Expression of B-Lymphocyte Stimulator by Blood Dendritic Cells During HIV Infection in Humans. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 211, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontaine, J.; Chagnon-Choquet, J.; Valcke, H.S.; Poudrier, J.; Roger, M. High expression levels of B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) by dendritic cells correlate with HIV-related B-cell disease progression in humans. Blood 2011, 117, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyon-Laliberté, K.; Aranguren, M.; Byrns, M.; Chagnon-Choquet, J.; Paniconi, M.; Routy, J.-P.; Tremblay, C.; Quintal, M.-C.; Brassard, N.; Kaufmann, D.E.; et al. Excess BAFF Alters NR4As Expression Levels and Breg Function of Human Precursor-like Marginal Zone B-Cells in the Context of HIV-1 Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti, A.; Cols, M.; Puga, I. Marginal zone B cells: Virtues of innate-like antibody-producing lymphocytes. Nat. Rev. Immunology 2013, 13, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, F.; Schneider, P. Cracking the BAFF code. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudrier, J.; Soulas, C.; Chagnon-Choquet, J.; Burdo, T.; Autissier, P.; Oskar, K.; Williams, K.C.; Roger, M. High expression levels of BLyS/BAFF by blood dendritic cells and granulocytes are associated with B-cell dysregulation in SIV-infected rhesus macaques. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabourin-Poirier, C.; Fourcade, L.; Chagnon-Choquet, J.; Labbé, A.-C.; Alary, M.; Guédou, F.; Poudrier, J.; Roger, M. Blood B Lymphocyte Stimulator (BLyS)/BAFF levels may reflect natural immunity to HIV in highly exposed uninfected Beninese Commercial Sex Workers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudrier, J.; Weng, X.; Kay, D.G.; Paré, G.; Calvo, E.L.; Hanna, Z.; Kosco-Vilbois, M.H.; Jolicoeur, P. The AIDS Disease of CD4C/HIV Transgenic Mice Shows Impaired Germinal Centers and Autoantibodies and Develops in the Absence of IFN-γ and IL-6. Immunity 2001, 15, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castigli, E.; Scott, S.; Dedeoglu, F.; Bryce, P.; Jabara, H.; Bhan, A.; Mizoguchi, E.; Geha, R. Impaired IgA class switching in APRIL-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varfolomeev, E.; Kischkel, F.; Martin, F.; Seshasayee, D.; Wang, H.; Lawrence, D.; Olsson, C.; Tom, L.; Erickson, S.; French, D.; et al. APRIL-Deficient Mice Have Normal Immune System Development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyon-Laliberté, K.; Chagnon-Choquet, J.; Byrns, M.; Aranguren, M.; Memmi, M.; Chrobak, P.; Stagg, J.; Poudrier, J.; Roger, M. NR4A Expression by Human Marginal Zone B-Cells. Antibodies 2019, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagnon-Choquet, J.; Fontaine, J.; Poudrier, J.; Roger, M. IL-10 and lymphotoxin-α expression profiles within marginal zone-like B-cell populations are associated with control of HIV-1 disease progression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duren, R.P.; Boudreaux, S.P.; Conneely, O.M. Genome Wide Mapping of NR4A Binding Reveals Cooperativity with ETS Factors to Promote Epigenetic Activation of Distal Enhancers in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, B.; Allard, D.; Buisseret, L.; Stagg, J. The adenosine pathway in immuno-oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sage, A.P.; Tsiantoulas, D.; Binder, C.J.; Mallat, Z. The role of B cells in atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Clopton, P.; Ayers, C.; Khera, A.; de Lemos, J.; Witztum, J.; Tsimikas, S. Relationship of Autoantibodies to MDA-LDL and ApoB-Immune Complexes to Sex, Ethnicity, Subclinical Atherosclerosis, and Cardiovascular Events. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, C.; Liu, Y.-H.; Kanellakis, P.; Kallies, A.; Li, Y.; Cao, A.; Hosseini, H.; Tipping, P.; Toh, B.-H.; Bobik, A.; et al. Follicular B Cells Promote Atherosclerosis via T Cell-Mediated Differentiation Into Plasma Cells and Secreting Pathogenic Immunoglobulin G. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, e71–e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikakulapu, P.; Hu, D.; Yin, C.; Mohanta, S.; Bontha, S.V.; Peng, L.; Beer, M.; Weber, C.; McNamara, C.; Grassia, G.; et al. Artery Tertiary Lymphoid Organs Control Multilayered Territorialized Atherosclerosis B-Cell Responses in Aged ApoE-/- Mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nus, M.; Sage, A.; Lu, Y.; Masters, L.; Lam, B.; Newland, S.; Weller, S.; Tsiantoulas, D.; Raffort, J.; Marcus, D.; et al. Marginal zone B cells control the response of follicular helper T cells to a high-cholesterol diet. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nus, M.; Basatemur, G.; Galan, M.; Cros-Brunsó, L.; Zhao, T.; Masters, L.; Harrison, J.; Figg, N.; Tsiantoulas, D.; Geissmann, F.; et al. NR4A1 Deletion in Marginal Zone B Cells Exacerbates Atherosclerosis in Mice-Brief Report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 2598–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldeanu, I.; Sadouni, M.; Mansour, S.; Baril, J.-G.; Trottier, B.; Soulez, G.; Chin, A.S.; Leipsic, J.; Tremblay, C.; Durand, M.; et al. Prevalence and Characterization of Subclinical Coronary Atherosclerotic Plaque with CT among Individuals with HIV: Results from the Canadian HIV and Aging Cohort Study. Radiology 2021, 299, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Boldeanu, I.; Nepveu, S.; Durand, M.; Chin, A.; Kauffmann, C.; Mansour, S.; Soulez, G.; Tremblay, C.; Chartrand-Lefebvre, C. In vivo coronary artery plaque assessment with computed tomography angiography: Is there an impact of iterative reconstruction on plaque volume and attenuation metrics? Acta Radiol. 2017, 58, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Far, M.; Durand, M.; Turcotte, I.; Larouche-Anctil, E.; Sylla, M.; Zaidan, S.; Chartrand-Lefebvre, C.; Bunet, R.; Ramani, H.; Sadouni, M.; et al. Upregulated IL-32 Expression And Reduced Gut Short Chain Fatty Acid Caproic Acid in People Living With HIV With Subclinical Atherosclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 664371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ju, X.; Silveira, P.A.; Abadir, E.; Hsu, W.-H.; Hart, D.N.J.; Clark, G. CD83: Activation Marker for Antigen Presenting Cells and Its Therapeutic Potential. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Audo, R.; Yeremenko, N.; Baeten, D.; Hahne, M.; Combe, B.; Morel, J.; Daïen, C. A proliferation inducing ligand (APRIL) promotes IL-10 production and regulatory functions of human B cells. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 73, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehres, C.M.; Van Uden, N.O.; Yeremenko, N.G.; Fernandez, L.; Salinas, G.F.; Van Duivenvoorde, L.M.; Huard, B.; Morel, J.; Spits, H.; Hahne, M.; et al. APRIL Induces a Novel Subset of IgA(+) Regulatory B Cells That Suppress Inflammation via Expression of IL-10 and PD-L1. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, P.A.; Leib, C.; Goddard, M.E.; Rosser, E.C.; Park, I.; Nilsson, A.H.; Nilsson, J.; Strom, A.C.; Cross, A.J.; Cole, J.E.; et al. B regulatory cells are increased in hypercholesterolaemic mice and protect from lesion development via IL-10. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 114, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiantoulas, D.; Eslami, M.; Obermayer, G.; Clement, M.; Smeets, D.; Mayer, F.; Kiss, M.; Enders, L.; Weißer, J.; Göderle, L.; et al. APRIL limits atherosclerosis by binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Nature 2021, 597, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, N.G.; Sereti, I. Can early therapy reduce inflammation? Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2014, 9, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.W.; Scharping, N.; Jacobs, H.; Wang, S.; Chait, A.; Rawlings, D. Cutting Edge: BAFF Overexpression Reduces Atherosclerosis via TACI-Dependent B Cell Activation. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiantoulas, D.; Sage, A.; Göderle, L.; Ozsvar-Kozma, M.; Murphy, D.; Porsch, F.; Pasterkamp, G.; Menche, J.; Schneider, P.; Mallat, Z.; et al. B Cell-Activating Factor Neutralization Aggravates Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2018, 138, 2263–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, W.C.; Sanguankeo, A.; Upala, S. Association between primary Sjogren’s syndrome, arterial stiffness, and subclinical atherosclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, E.; Nezos, A.; Antypa, E.; Ioakeimidis, D.; Koutsilieris, M.; Tektonidou, M.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Mavragani, C.P. B-cell activating factor and related genetic variants in lupus related atherosclerosis. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 92, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Do, M.-S. BAFF knockout improves systemic inflammation via regulating adipose tissue distribution in high-fat diet-induced obesity. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Choi, B.-H.; Cheon, H.-G.; Do, M.-S. B cell activation factor (BAFF) is a novel adipokine that links obesity and inflammation. Exp. Mol. Med. 2009, 41, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, F.R.; Barbati, C.; Cecarelli, F.; Morello, F.; Colasanti, T.; Vomero, M.; Massaro, L.; Orefice, V.; Alessandri, C.; Valesini, G.; et al. B lymphocyte stimulator modulates number and function of endothelial progenitor cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, R.B., Sr.; Vasan, R.; Pencina, M.; Wolf, P.; Cobain, M.; Massaro, J.; Kannel, W. General cardiovascular risk profile for use in primary care: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2008, 117, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.; Huot-Marchand, S.; Gombault, A.; Panek, C.; Bourinet, M.; Fanny, M.; Savigny, F.; Schneider, P.; Le Bert, M.; Ryffel, B.; et al. B-Cell Activating Factor Secreted by Neutrophils Is a Critical Player in Lung Inflammation to Cigarette Smoke Exposure. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, F.B.; Saulep-Easton, D.; Figgett, W.A.; Fairfax, K.A.; Mackay, F. The BAFF/APRIL system: Emerging functions beyond B cell biology and autoimmunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013, 24, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvestutto, C.D.; Aberg, J. Management of dyslipidemia in HIV-infected patients. Clin. Lipidol. 2011, 6, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Song, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Feng, K.; Liu, L.; et al. High APRIL Levels Are Associated With Slow Disease Progression and Low Immune Activation in Chronic HIV-1-Infected Patients. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.-X.; Huang, H.-H.; Huang, L.; Shi, J.-J.; Jiao, Y.-M.; Zhang, C.; Jin, L.; Yang, T.; Shi, M.; Tu, B.; et al. Skewed CD39/CD73/adenosine pathway in B cells is associated with innate immune hyperactivation in chronic HIV-1 infection. Transl. Med. Commun. 2019, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-S.; Ackermann, C.; Tóth, I.; Dierks, P.; Eberhard, J.M.; Wroblewski, R.; Scherg, F.; Geyer, M.; E Schmidt, R.; Beisel, C.; et al. Down-regulation of CD73 on B cells of patients with viremic HIV correlates with B cell activation and disease progression. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheiser, A.; Ebner, A.; Burghoff, S.; Ding, Z.; Romio, M.; Viethen, C.; Lindecke, A.; Köhrer, K.; Fischer, J.W.; Schrader, J. Inactivation of CD73 promotes atherogenesis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 92, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Koupenova, M.; Johnston-Cox, H.; Ravid, K. Regulation of atherosclerosis and associated risk factors by adenosine and adenosine receptors. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2012, 14, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rothan, C.; Yero, A.; Shi, T.; Farnos, O.; Chartrand-Lefebvre, C.; El-Far, M.; Costiniuk, C.T.; Tsoukas, C.; Tremblay, C.; Durand, M.; et al. Antiretroviral therapy-treated HIV-infected adults with coronary artery disease are characterized by a distinctive regulatory T-cell signature. Aids 2021, 35, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, A.-M.; Stengaard-Pedersen, K.; Hetland, M.L.; Hørslev-Petersen, K.; Junker, P.; Østergaard, M.; Höllsberg, P.; Deleuran, B.; Hvid, M. Expression of soluble CD83 in plasma from early-stage rheumatoid arthritis patients is not modified by anti-TNF-α therapy. Cytokine 2017, 96, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hock, B.D.; O’Donnell, J.L.; Taylor, K.; Steinkasserer, A.; McKenzie, J.L.; Rothwell, A.G.; Summers, K.L. Levels of the soluble forms of CD80, CD86, and CD83 are elevated in the synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Tissue Antigens 2006, 67, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hock, B.D.; Haring, L.F.; Steinkasserer, A.; Taylor, K.G.; Patton, W.N.; McKenzie, J.L. The soluble form of CD83 is present at elevated levels in a number of hematological malignancies. Leuk. Res. 2004, 28, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hock, B.; Fernyhough, L.; Gough, S.; Steinkasserer, A.; Cox, A.; McKenzie, J. Release and clinical significance of soluble CD83 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2009, 33, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
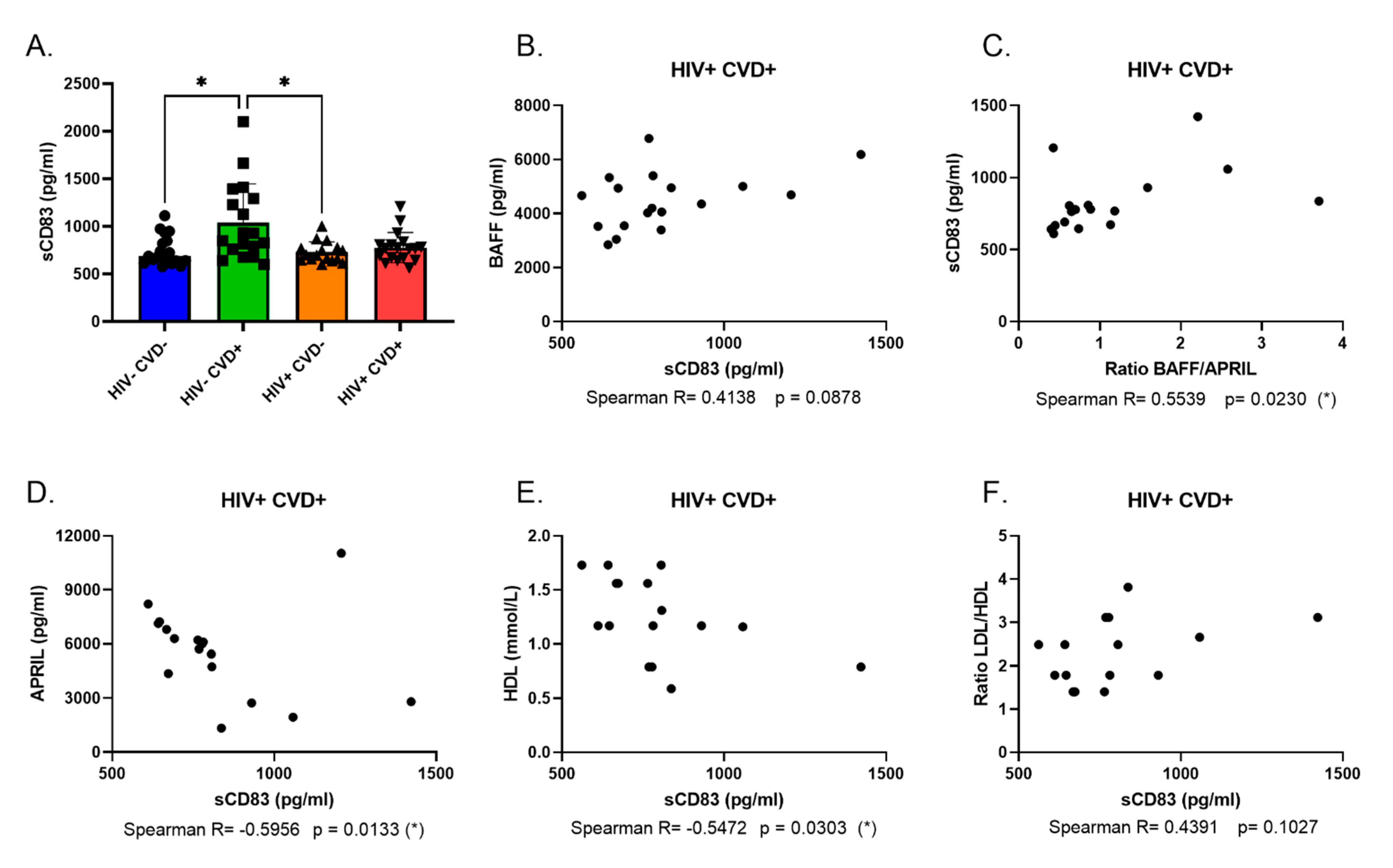
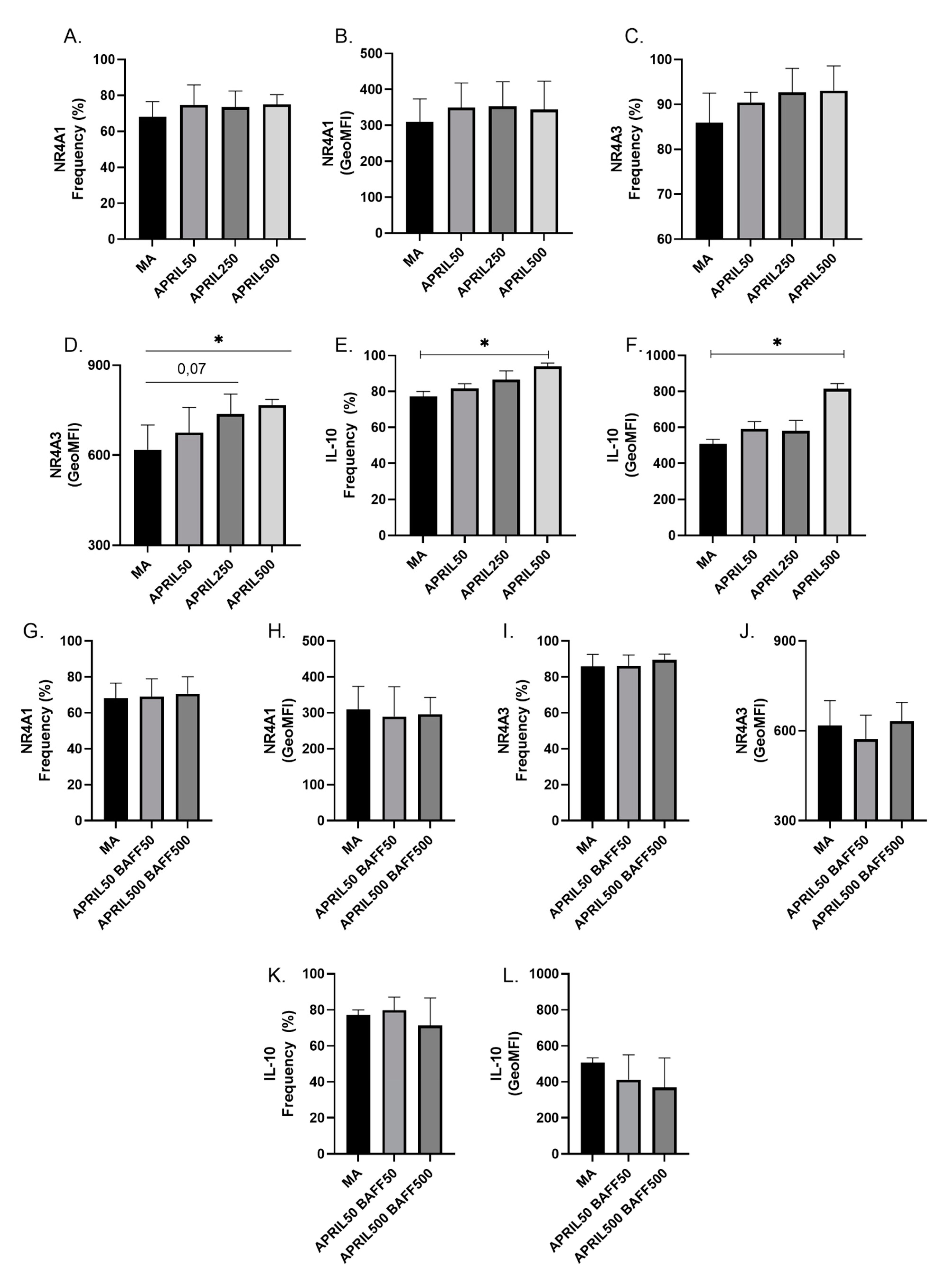
| Group | HIV− CVD− (n = 20) | HIV− CVD+ (n = 20) | HIV+ CVD− (n = 20) | HIV+ CVD+ (n = 19) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 54.64 (40.5–66.5) | 61.93 (42.8–74.5) | 54.66 (44.3–65.8) | 57.08 (44.8–72.8) | 0.0085 1 |
| No. of male participants | 16 | 13 | 19 | 17 | 0.0700 |
| TPV (mm3) | 0 | 314.1 (10.3–2253) | 0 | 269.1 (25.7–1725) | 0.2829 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.404 (1.910–5.280) | 3.310 (1.610–5.680) | 2.449 (1.820–4.300) | 2.726 (2.090–4.300) | 0.0024 2 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.492 (0.94–2.67) | 1.320 (0.89–1.84) | 1.168 (0.79–1.73) | 1.235 (0.59–1.73) | 0.0394 3 |
| Median 10 years Framingham Risk Score (%) | 8.474 (2.0–18.0) | 11.68 (6.0–25.0) | 10.70 (6.0–17.0) | 10.95 (6.0–19.0) | 0.0969 |
| Participants undergoing statin therapy (%) | 0 | 2 (10%) | 4 (20%) | 2 (10.5%) | 0.2319 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aranguren, M.; Doyon-Laliberté, K.; El-Far, M.; Chartrand-Lefebvre, C.; Routy, J.-P.; Barril, J.-G.; Trottier, B.; Tremblay, C.; Durand, M.; Poudrier, J.; et al. Subclinical Atherosclerosis Is Associated with Discrepancies in BAFF and APRIL Levels and Altered Breg Potential of Precursor-like Marginal Zone B-Cells in Long-Term HIV Treated Individuals. Vaccines 2023, 11, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010081
Aranguren M, Doyon-Laliberté K, El-Far M, Chartrand-Lefebvre C, Routy J-P, Barril J-G, Trottier B, Tremblay C, Durand M, Poudrier J, et al. Subclinical Atherosclerosis Is Associated with Discrepancies in BAFF and APRIL Levels and Altered Breg Potential of Precursor-like Marginal Zone B-Cells in Long-Term HIV Treated Individuals. Vaccines. 2023; 11(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010081
Chicago/Turabian StyleAranguren, Matheus, Kim Doyon-Laliberté, Mohamed El-Far, Carl Chartrand-Lefebvre, Jean-Pierre Routy, Jean-Guy Barril, Benoît Trottier, Cécile Tremblay, Madeleine Durand, Johanne Poudrier, and et al. 2023. "Subclinical Atherosclerosis Is Associated with Discrepancies in BAFF and APRIL Levels and Altered Breg Potential of Precursor-like Marginal Zone B-Cells in Long-Term HIV Treated Individuals" Vaccines 11, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010081
APA StyleAranguren, M., Doyon-Laliberté, K., El-Far, M., Chartrand-Lefebvre, C., Routy, J.-P., Barril, J.-G., Trottier, B., Tremblay, C., Durand, M., Poudrier, J., & Roger, M., on behalf of the Canadian HIV and Aging Cohort Study. (2023). Subclinical Atherosclerosis Is Associated with Discrepancies in BAFF and APRIL Levels and Altered Breg Potential of Precursor-like Marginal Zone B-Cells in Long-Term HIV Treated Individuals. Vaccines, 11(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010081





