Evaluation of the Anti-Spike (RDB) IgG Titer among Workers Employed at the University of Pisa Vaccinated with Different Types of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Antibody Titer
2.3. Statistical Analysis
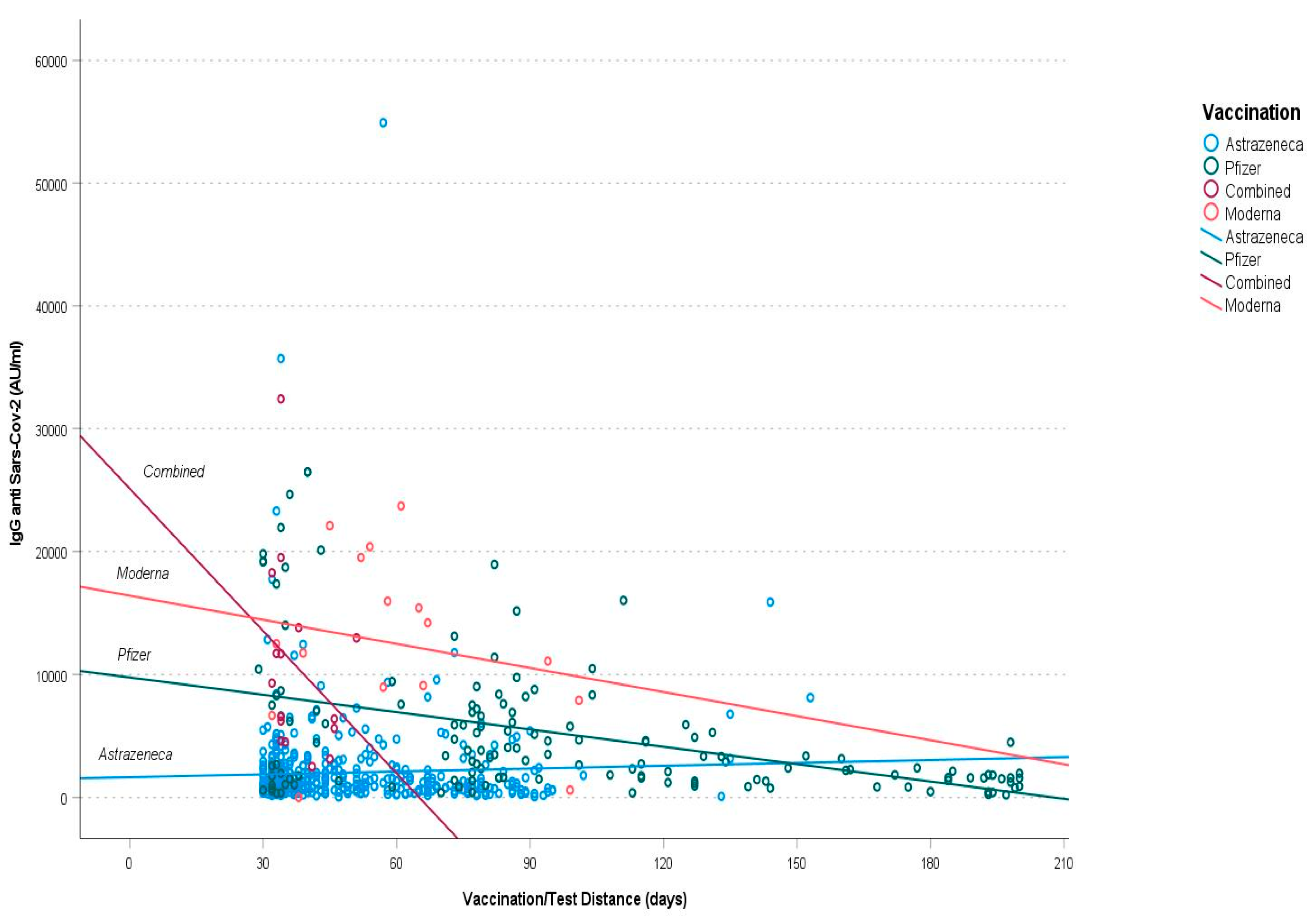
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Factors Affecting the Antibody Levels in Vaccinated People
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Favresse, J.; Bayart, J.-L.; Mullier, F.; Dogné, J.-M.; Closset, M.; Douxfils, J. Early Antibody Response in Health-Care Professionals after Two Doses of SARS-CoV-2 MRNA Vaccine (BNT162b2). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1351.e5–1351.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, M.N.; Minassian, A.M.; Ewer, K.J.; Flaxman, A.L.; Folegatti, P.M.; Owens, D.R.; Voysey, M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Babbage, G.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of ChAdOx1 NCoV-19 Vaccine Administered in a Prime-Boost Regimen in Young and Old Adults (COV002): A Single-Blind, Randomised, Controlled, Phase 2/3 Trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 1979–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laboratory Testing for 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-NCoV) in Suspected Human Cases. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/10665-331501 (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Laboratory Biosafety Guidance Related to Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Interim Guidance, 28 January 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/WHO-WPE-GIH-2021.1 (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Laboratory Biosafety Guidance Related to Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/laboratory-biosafety-guidance-related-to-coronavirus-disease-(covid-19) (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Mahallawi, W.; Alzahrani, M.; Alahmadey, Z. Durability of the Humoral Immune Response in Recovered COVID-19 Patients. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2802–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarrondo, F.J.; Hofmann, C.; Fulcher, J.A.; Goodman-Meza, D.; Mu, W.; Hausner, M.A.; Ali, A.; Balamurugan, A.; Taus, E.; Elliott, J.; et al. Primary, Recall, and Decay Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Antibody Responses. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 11180–11191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebinger, J.E.; Fert-Bober, J.; Printsev, I.; Wu, M.; Sun, N.; Figueiredo, J.C.; Eyk, J.E.V.; Braun, J.G.; Cheng, S.; Sobhani, K. Prior COVID-19 Infection and Antibody Response to Single Versus Double Dose MRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufloo, J.; Grzelak, L.; Staropoli, I.; Madec, Y.; Tondeur, L.; Anna, F.; Pelleau, S.; Wiedemann, A.; Planchais, C.; Buchrieser, J.; et al. Asymptomatic and Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections Elicit Polyfunctional Antibodies. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; To, K.K.-W.; Chan, K.-H.; Wong, Y.-C.; Zhou, R.; Kwan, K.-Y.; Fong, C.H.-Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Choi, C.Y.-K.; Lu, L.; et al. High Neutralizing Antibody Titer in Intensive Care Unit Patients with COVID-19. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Lam, E.C.; Astudillo, M.G.; Yang, D.; Miller, T.E.; Feldman, J.; Hauser, B.M.; Caradonna, T.M.; Clayton, K.L.; Nitido, A.D.; et al. COVID-19-Neutralizing Antibodies Predict Disease Severity and Survival. Cell 2021, 184, 476–488.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Pan, Z.; Yue, S.; Yu, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, B.; Yang, X.; Gao, L.; et al. Disease Severity Dictates SARS-CoV-2-Specific Neutralizing Antibody Responses in COVID-19. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurano, M.; Ohmiya, H.; Kishi, Y.; Okada, J.; Nakano, Y.; Yokoyama, R.; Qian, C.; Xia, F.; He, F.; Zheng, L.; et al. Measurement of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Titers Improves the Prediction Accuracy of COVID-19 Maximum Severity by Machine Learning in Non-Vaccinated Patients. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 811952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörschug, A.; Frickmann, H.; Schwanbeck, J.; Yilmaz, E.; Mese, K.; Hahn, A.; Groß, U.; Zautner, A.E. Comparative Assessment of Sera from Individuals after S-Gene RNA-Based SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination with Spike-Protein-Based and Nucleocapsid-Based Serological Assays. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyre, D.W.; Lumley, S.F.; Wei, J.; Cox, S.; James, T.; Justice, A.; Jesuthasan, G.; O’Donnell, D.; Howarth, A.; Hatch, S.B.; et al. Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 Anti-Spike Responses to Pfizer-BioNTech and Oxford-AstraZeneca Vaccines by Previous Infection Status. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1516.e7–1516.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvagno, G.L.; Henry, B.M.; di Piazza, G.; Pighi, L.; De Nitto, S.; Bragantini, D.; Gianfilippi, G.L.; Lippi, G. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Receptor-Binding Domain Total Antibodies Response in Seropositive and Seronegative Healthcare Workers Undergoing COVID-19 MRNA BNT162b2 Vaccination. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Sasso, B.; Giglio, R.V.; Vidali, M.; Scazzone, C.; Bivona, G.; Gambino, C.M.; Ciaccio, A.M.; Agnello, L.; Ciaccio, M. Evaluation of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD IgG Antibodies after COVID-19 MRNA BNT162b2 Vaccine. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, M.; Acquila, M.; Tripodi, G.; Spiazzi, R.; Castagnola, E. Antibodies against Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Induced by BNT162b2 Vaccine: Results from a Pragmatic, Real-Life Study. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1560–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masiá, M.; Fernández-González, M.; Telenti, G.; Agulló, V.; García, J.A.; Padilla, S.; García-Abellán, J.; Galiana, A.; Gonzalo-Jiménez, N.; Gutiérrez, F. Durable Antibody Response One Year after Hospitalization for COVID-19: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 123, 102703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterhoff, D.; Einhauser, S.; Beileke, S.; Niller, H.-H.; Günther, F.; Schachtner, M.; Asbach, B.; Steininger, P.; Tenbusch, M.; Peter, A.S.; et al. Comparative Immunogenicity of COVID-19 Vaccines in a Population-Based Cohort Study with SARS-CoV-2-Infected and Uninfected Participants. Vaccines 2022, 10, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.; Klemis, V.; Schub, D.; Mihm, J.; Hielscher, F.; Marx, S.; Abu-Omar, A.; Schneitler, S.; Becker, S.L.; Gärtner, B.C.; et al. Immunogenicity and Reactogenicity of a Heterologous COVID-19 Prime-Boost Vaccination Compared with Homologous Vaccine Regimens; Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS). Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1530–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahan, K.; Yu, J.; Mercado, N.B.; Loos, C.; Tostanoski, L.H.; Chandrashekar, A.; Liu, J.; Peter, L.; Atyeo, C.; Zhu, A.; et al. Correlates of Protection against SARS-CoV-2 in Rhesus Macaques. Nature 2021, 590, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Okba, N.M.A.; Igloi, Z.; Bogers, S.; Embregts, C.W.E.; Laksono, B.M.; Leijten, L.; Rokx, C.; Rijnders, B.; Rahamat-Langendoen, J.; et al. An Evaluation of COVID-19 Serological Assays Informs Future Diagnostics and Exposure Assessment. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.-Y.; Xue, J.-H.; Xiao, Y.; Jia, Z.-J.; Wu, M.-J.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Li, W.-L.; Liang, X.-M.; Yang, T.-C. Response and Duration of Serum Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies after Inactivated Vaccination within 160 Days. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 786554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, P.B.; Montefiori, D.C.; McDermott, A.; Fong, Y.; Benkeser, D.; Deng, W.; Zhou, H.; Houchens, C.R.; Martins, K.; Jayashankar, L.; et al. Immune Correlates Analysis of the MRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy Trial. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factor | Statistics |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 50 (41–57) |
| Sex | |
| M | 279 (41.6) |
| F | 391 (58.4) |
| Virus SARS-CoV-2 IgG_BAU | 205.2 (106.3–454.9) |
| Virus SARS-CoV-2 IgG AU | 1444.8 (748.7–3203.5) |
| Distance from booster dose (days) | 42 (34–74) |
| Vaccine type | |
| Unvaccinated | 3 (0.4) |
| Vaxzevria (Astrazeneca) | 493 (73.6) |
| Comirnaty (Pfizer) | 142 (21.2) |
| Spikevax (Moderna) | 16 (2.4) |
| Combined (Vaxzevria + Comirnaty or Spikevax) | 16 (2.4) |
| Vaccinated | 667 (99.6) |
| Contact with a SARS-CoV-2-positive subject | 76 (11.3) |
| Confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection | 19 (2.8) |
| Factor | Univariate Analysis | |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Factors | Spearman’s rho | p-value |
| Age | 0.046 | 0.239 |
| Distance from booster dose | 0.078 | 0.045 |
| Categorical Factors | Median (IQR) | p-value |
| Sex | 0.624 | |
| M | 1435.7 (759.1–2728.5) | |
| F | 1454.0 (748.4–3319.4) | |
| Type of vaccine | <0.001 | |
| (1) Unvaccinated | 1287.1 (820.5–1988.0) | |
| (2) Vaxzevria | 1141.9 (642.0–2208.2) | |
| (3) Comirnaty | 2933.0 (1438.2–6704.2) | |
| (4) Combined | 7935.7 (4854.0–13,602.5) | |
| (5) Spikevax | 12,127.5 (8167.8–18,624.8) | |
| SARS-CoV-2 infection | 0.002 | |
| No | 1390.8 (742.3–3132.2) | |
| Yes | 3003.0 (1759.8–8685.2) | |
| SARS-CoV-2 positivity | 0.06 | |
| Unvaccinated | 1287.1 (820.5–1988.0) | |
| Vaccinated | 5656.6 (2302.4–11,006.1) | |
| Symtoms | <0.001 | |
| No | 1373 (737–2869) | |
| Yes | 6336 (2691–11,780) | |
| Factor | Median (IQR) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | 0.047 | |
| No | 591.5 (413.6–769.4) | |
| Yes | 5415.6 (2410.0–10,232.0) | |
| Hospitalization | 0.254 | |
| No | 2846.9 (1405.2–8207.5) | |
| Yes | 8122.6 (5405.7–31,526.0) | |
| Dyspnoea | 0.536 | |
| No | 2846.9 (1405.2–8207.5) | |
| Yes | 5415.6 (2625.1–26,463.8) | |
| Fever > 38 °C | 0.604 | |
| No | 2658.0 (680.4–13,862.7) | |
| Yes | 5415.6 (2224.3–7729.9) | |
| Pneumonia | 0.109 | |
| No | 2846.9 (1405.3–7785.6) | |
| Yes | 26,463.8 (14,576.3–40,696.6) | |
| Headache | 0.701 | |
| No | 2688.9 (1028.2–14,398.3) | |
| Yes | 4450.3 (2458.1–8025.9) | |
| Ageusia/Anosmia | 1.000 | |
| No | 2690.9 (1482.1–14,398.3) | |
| Yes | 5656.6 (1641.6–8025.9) | |
| Cough | 0.592 | |
| No | 2690.9 (769.4–8685.2) | |
| Yes | 4209.3 (2302.4–17,114.2) |
| Vaccine | Median (IQR) | Vaccine | Median (IQR) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaxzevria | 1141.9 (642.0–2208.2) | Comiranty | 2933.0 (1438.2–6704.2) | <0.001 |
| Spikevax | 12,127.5 (8167.8–18,624.8) | <0.001 | ||
| Combined | 7935.7 (4854.0–13,602.5) | <0.001 | ||
| Comiranty | 2933.0 (1438.2–6704.2) | Spikevax | 12,127.5 (8167.8–18,624.8) | 0.018 |
| Combined | 7935.7 (4854.0–13,602.5) | 0.003 | ||
| Spikevax | 12,127.5 (8167.8–18,624.8) | Combined | 7935.7 (4854.0–13,602.5) | 0.653 |
| Factor | RC | 95% CI | SE | Beta | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccination | 4020 | 3507; 4534 | 261 | 0.525 | <0.001 |
| Distance from booster dose | −28 | −37; −19 | 4.6 | −0.210 | <0.001 |
| SARS-CoV-2 infection | −1053 | −6776; 4669 | 2914 | −0.033 | 0.718 |
| COVID-19 symptoms | 9914 | 3806; 16,024 | 3111 | 0.288 | 0.002 |
| Constant of the model | −4775 | −5961; −3589 | 604 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Foddis, R.; Marino, R.; Silvestri, R.; Fallahi, P.; Perretta, S.; Garaffa, C.; Morganti, R.; Corsi, M.; Mennucci, J.; Porciatti, F.; et al. Evaluation of the Anti-Spike (RDB) IgG Titer among Workers Employed at the University of Pisa Vaccinated with Different Types of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081244
Foddis R, Marino R, Silvestri R, Fallahi P, Perretta S, Garaffa C, Morganti R, Corsi M, Mennucci J, Porciatti F, et al. Evaluation of the Anti-Spike (RDB) IgG Titer among Workers Employed at the University of Pisa Vaccinated with Different Types of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines. Vaccines. 2022; 10(8):1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081244
Chicago/Turabian StyleFoddis, Rudy, Riccardo Marino, Roberto Silvestri, Poupak Fallahi, Salvio Perretta, Christian Garaffa, Riccardo Morganti, Martina Corsi, Jonathan Mennucci, Francesco Porciatti, and et al. 2022. "Evaluation of the Anti-Spike (RDB) IgG Titer among Workers Employed at the University of Pisa Vaccinated with Different Types of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines" Vaccines 10, no. 8: 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081244
APA StyleFoddis, R., Marino, R., Silvestri, R., Fallahi, P., Perretta, S., Garaffa, C., Morganti, R., Corsi, M., Mennucci, J., Porciatti, F., Nerli, G., Buselli, R., Veltri, A., Caldi, F., Guglielmi, G., Luchini, G., Briani, S., Talini, D., & Cipriani, F. (2022). Evaluation of the Anti-Spike (RDB) IgG Titer among Workers Employed at the University of Pisa Vaccinated with Different Types of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines. Vaccines, 10(8), 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081244








