Abstract
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has caused an exceptional setback to the global economy and health. Vaccination is one of the most effective interventions to markedly decrease severe illness and death from COVID-19. In recent years, there have been increasingly more reports of new acute kidney injury (AKI) after COVID-19 vaccination. Podocyte injury, IgA nephropathy, vasculitis, tubulointerstitial injury, and thrombotic microangiopathy appear to be the main pathological phenotypes. Nonetheless, whether the link between the COVID-19 vaccine and acute kidney disease (AKD) is causal or coincidental remains to be verified. Here, we generalize some hypotheses for the emergence of AKD and its pathogenesis in response to certain COVID-19 vaccines. In fact, the enormous benefits of mass vaccination against COVID-19 in preventing COVID-19 morbidity and mortality cannot be denied. The purpose of this review is to assist in the clinical assessment and management of AKD following COVID-19 vaccination.
1. Introduction
With the ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic and the emergence of new variants of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the rapid development of effective and safe preventive vaccines is urgently required to control disease outbreaks [1,2]. Over the past 2 years, hundreds of COVID-19 vaccine candidates have been developed, tested, and finally rolled out, including protein-based vaccines (Novavax), inactivated vaccines (Sinovac Life Science), viral vector vaccines (Janssen, Oxford-AstraZeneca), and mRNA vaccines (Pfizer/BioNtech, Moderna, CureVac) (Figure 1) [2,3]. Among them, mRNA-based drugs are new but not unknown [4]. mRNA vaccines deliver transgenic mRNA through lipid nanoparticles, which act as carriers. Once injected, the mRNA is translated into the target protein in vivo, resulting in a strong immune response, and a 2-dose regimen confers 95% protection against COVID-19 [5]. To date, large phase III and IV trials have found these vaccines to have a good safety profile, with few serious reactions [3,6,7,8,9]. Common short-term adverse events include local injection site reactions, fever, fatigue, generalized pain, and headache [6,10].
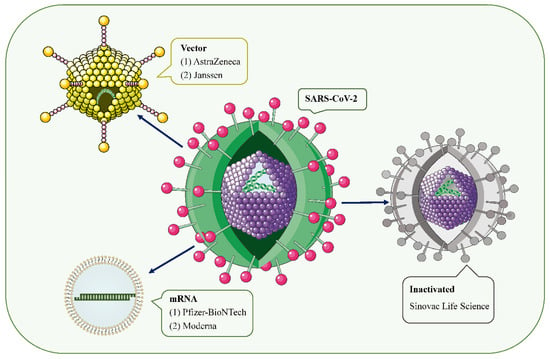
Figure 1.
SARS-CoV-2 and the main types of vaccines that may trigger AKD. SARS-CoV-2 is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus with a lipid bilayer consisting of the spike S protein and membrane and envelope proteins. mRNA vaccines deliver transgenic mRNA through lipid nanoparticles as carriers. Viral vector vaccines utilize adenovirus and integrate genetic material from SARS-CoV-2 into its genome. Inactivated vaccines involve SARS-CoV-2 that has been killed by physical or chemical means.
However, since mass vaccination, there have been a few case reports of acute kidney injury (AKI), acute kidney disease (AKD), proteinuria, edema, gross hematuria, and other renal side effects requiring hospitalization after COVID-19 vaccinations [11]. Serum creatinine (Scr) levels and proteinuria recovered within 3 months of treatment in most patients. The vast majority of cases occurred after mRNA vaccine and adenoviral vector injection, and a few cases of glomerulonephritis associated with inactivated virus vaccines have also been reported.
In this review, we summarize the clinical features of AKD after vaccination, and elaborate on the possible mechanisms of AKD after COVID-19 vaccination.
2. Clinical Characteristics of Patients
In this review, we performed a literature search through the electronic database, including Medline/PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science (WOS) before February 2022, using the following keywords: (“acute kidney injury” OR “acute kidney disease” OR “glomerulonephritis”) AND (“COVID-19” OR 2019-nCoV” OR “novel corona virus” OR “SARS-CoV-2” OR “coronavirus”) AND (“vaccine” OR “vaccination”).
According to the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) criteria, AKI stage 1 is defined as a 0.3 mg/dL increase in Scr within 48 h or a 1.5 to 1.9 times increase in Scr from baseline within 7 days, AKI stage 2 is defined as a 2 to 2.9 times increase in Scr within 7 days from baseline, and AKI stage 3 is defined as a 3 times or more increase in Scr within 7 days from baseline or initiation of renal replacement therapy (RRT) [12,13]. AKD is defined as a condition of acute or subacute damage and/or loss of renal function between 7 and 90 days after exposure to an AKI initiating event [14]. AKD lasting more than 90 days is considered to be chronic kidney disease (CKD) [14]. The baseline Scr was determined by a median Scr within 8 to 365 days prior to admission. Because of inaccurate and missing urine output records in electronic health records, we did not use the urine output criteria in the KDIGO guidelines to define AKI [15].
As of 28 February 2022, we found a total of 38 published articles (53 cases) on AKI after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination (Table 1) [11,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52]. Only one case clearly identified an increase in Scr and a resolve within 7 days after vaccination [30]. Scr returned to baseline within 90 days in 37 patients, and no outcomes were recorded in 6 patients. Seven patients did not respond.

Table 1.
Summary of published cases of newly diagnosed acute kidney disease.
There were 53 cases in total, including 47 (89%) cases of new kidney involvements and 6 (11%) cases of relapse. Minimal change disease (MCD) was the most common pathology (13 (25%): 11 new, 2 relapse), followed by IgA nephropathy (IgAN) (11 (21%): 9 new, 2 relapse), acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP) (8 (15%): all new), and anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies (ANCA) vasculitis (8 (15%): all new). Other diagnosed diseases included acute interstitial nephritis (AIN) in four new cases, membranous nephropathy (MN) in four cases (two new, two relapse), anti-glomerular basement membrane (anti-GBM) nephritis in three cases (all new), ANCA-negative granulomatous vasculitis in one new case, and leukocytoclastic vasculitis in one new case. The mean age was 58 years (standard deviation 18), and 64% were male.
The Pfizer-BioNTech (mRNA) vaccine was the most common vaccine used (27/53 patients, 51%), followed by Moderna (mRNA) (16/53 patients, 30%), AstraZeneca (Adenovirus vector) (5/53 patients, 9%), Sinovac Life Science (Inactivated virus) (3/53 patients, 6%), and Janssen (Adenovirus vector) (3/53 patients, 6%). Of the 53 patients, 26 patients (49%) had an increase in Scr after the first dose, 25 patients (47%) after the second dose, and 2 patients (4%) after both doses.
3. Clinical Characteristics and Follow-Up of Patients by Disease
3.1. Minimal Change Disease (MCD)
Of all the cases reported in the literature, MCD was the most common pathological type of AKD after COVID-19 vaccinations, with a total of 13 cases (11 new and 2 relapse). Six patients had acute renal tubular and/or interstitial injury. Ten patients developed AKD after the first vaccination, and three developed AKD after the second dose. Edema is the most common symptom. All patients received steroids therapy, and one patient also underwent hemodialysis [16]. A patient with relapsed MCD who did not respond to high-dose steroids received rituximab (RTX), to which the patient responded [11]. In total, 11 patients achieved complete remission (CR) or partial remission (PR) within 3 months of treatment, 1 had no response [20], and 1 had no follow-up records [21].
3.2. IgA Nephropathy (IgAN)
Eleven cases of IgAN (nine new onset, two relapse) were reported in the literature, of which only one patient could be identified with AKI without AKD [30]. One case was complicated with AIN [11]. Gross hematuria was the most common presentation. Six patients (four new, two relapse) received conservative treatment, four achieved CR, one did not achieve normal Scr, and one had no follow-up records. The other five new-onset patients were treated with steroids, three patients responded to treatment, and two patients had no follow-up records.
3.3. Membranous Nephropathy (MN)
MN developed in four patients (two new and two relapse), and three were serum anti-phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) antibody positive. All patients had symptoms of edema. One new-onset patient received conservative treatment with no remission within 60 days [26]. The other new case developed MN and AKD after the first mRNA (Pfizer-BioNTech) vaccination, achieved partial remission after administration of renin-angiotensin system blockade (RASB), and Scr did not return to baseline levels. Edema reappeared after the second mRNA (Moderna) vaccination, and Scr remained at 1.15 mg/dL [27]. The patient was subsequently given rituximab (RTX) and achieved a PR. One relapse case responded to tacrolimus (TAC), and Scr did not return to baseline during the last follow-up [11]. The other relapsed patient had no records of treatment or follow-up [42].
3.4. Anti-Glomerular Basement Membrane (Anti-GBM) and Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibodies (ANCA) Vasculitis
According to reports in the literature, there have been three cases of typical new-onset anti-GBM nephritis, accompanied by gross hematuria, hypertension, anorexia, nausea, fever, and other symptoms. One case did not respond to mycophenolate and steroids, and his Scr level continued to rise [11]. Two patients received cyclophosphamide (CyC), plasma exchange (PLEX), and pulse methylprednisolone therapy, one patient did not respond and continued dialysis [32], and the other one patient had no follow-up records [29].
In the literature, eight cases were new-onset ANCA-associated vasculitis, five cases were associated with myeloperoxidase (MPO), and three cases with proteinase 3 (PR3). In addition, there was one report of ANCA-negative granulomatous vasculitis following the first dose of adenoviral vector (AstraZeneca) vaccination, and the patient’s Scr returned to normal within 2 months [39]. All 3 patients with confirmed PR3-ANCA vasculitis developed symptoms within 1 week after the second dose of mRNA vaccine and were then admitted to hospital for treatment. One case received RTX, CyC, PSL, and hemodialysis treatment, and received hemodialysis without remission. Further, 1 case received high-dose glucocorticoids, CyC, and PLEX, and achieved Scr remission within 3 weeks, and 1 case received pulse methylprednisolone therapy, RTX, CyC, and PLEX, and Scr decreased to 1.5 mg/dL within 10 weeks. From the literature, both MPO-ANCA and ANCA-negative patients with granulomatous vasculitis show improved Scr after treatment.
3.5. Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (aTTP)
According to the statistics, only one of the eight patients was reported after the second vaccination [47]. The main symptoms included fever, headache, fatigue, ecchymosis on the limbs, and gastrointestinal reactions, which usually appeared 1 to 2 weeks after vaccination. Except for the one case reported by Al Rawahi et al. [51], all other cases were immediately treated with PLEX and immunosuppressive therapy, such as corticosteroids, RTX, etc., and the clinical effects were generally good. Additionally, in three cases, the first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine induced high titers of neutralizing IgG against SARS-CoV-2 [45,49,51]. ADAMTS13 (A Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase with a ThromboSpondin type 1 motif, member 13) activity levels were markedly reduced and its inhibitor’s titer was increased in some cases [45,46,47,49]. Hence, some researchers speculated that in patients without underlying diseases, de novo aTTP was associated with COVID-19 vaccination [49,51].
4. Inducing AKD through COVID-19 Vaccine: Hypotheses
4.1. Podocyte Damage
The temporal association between intramuscular vaccination and the development of MCD speculates that a cell-mediated immune response may be a trigger for podocyte injury [20,53]. All 12 patients with MCD reported in the literature were over 60 years of age, developed AKD within 2 weeks of vaccination, and steroids appeared to be effective in achieving rapid remission (Table 1). Typically, following vaccination, the vaccine’s antigens are taken up by dendritic cells and then presented to T cell receptors on naive T cells [54]. This leads to the activation of antigen-specific effector T cells, peaking 7 to 14 days after vaccination [55]. Studies have also confirmed that during viral infection, cellular immune responses can be observed within about 1 week after infection, but T cell activation can occur 2–3 days earlier [56,57]. This answers the question of whether it is reasonable for a COVID-19 vaccine to elicit a cell-mediated response 3–4 days after administration.
Although the exact pathogenesis of MCD remains unclear, podocyte damage caused by circulating factors released by activated T lymphocytes appears to be decisive (Figure 2) [58,59]. During active stages of MCD, T cell subsets are imbalanced, and circulating CD8+ suppresses the prevalence of T cells, which is exacerbated by cytokine-induced damage [60]. Compared with conventional vaccines, mRNA vaccines are expected to provoke higher antibody responses and stronger CD8+ T and CD4+ T cell reactions, including higher chemokine and cytokine production [61,62]. The resulting irregular permeability factors can alter glomerular permeability and lead to marked proteinuria and kidney injury [53].
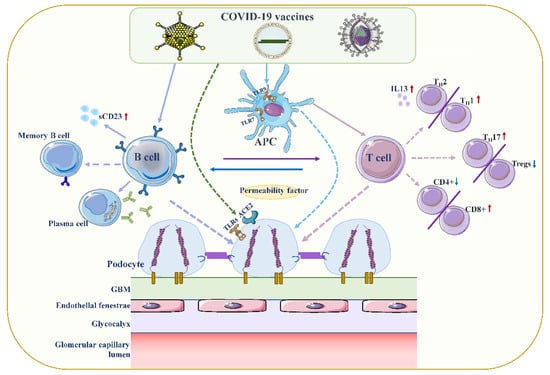
Figure 2.
Proposed mechanisms of podocyte injury caused by COVID19 vaccination. Vaccination stimulates antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and B cells, which in turn activate T cells through antigen presentation and cytokine production. A decrease in CD4+ T helper (Th) cells is associated with the prevalence of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, and an imbalance between Th2 and Th1 cells is associated with an increase in Th2-specific interleukin-13 (IL-13) production, and Th17. In contrast to increased cellular activity, the frequency and function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) decreased. Permeability proteins, such as cytokines and autoantibodies, can directly affect podocytes, leading to loss of foot processes and disruption of the glomerular permeability barrier. In addition, the vaccine can also affect podocytes through specific toll-like receptors (TLRs), and angiotensin conversion enzyme 2 (ACE2). The figure refers to the pathogenesis of minimal change disease by Vivarelli et al [53].
Another hypothesis we speculate might be relevant is that type 2 helper T cells (Th2) indirectly induce tissue cell damage through hypersensitivity reactions via nucleic acid (NA) sensors. Previous study has demonstrated that T cells sensing their own NAs can trigger and amplify allergic inflammation independent of known NA sensors in innate immunity [63]. Muscle cells presenting viral mRNA-derived products on major histocompatibility complex class I are eliminated by CD8+ T cells, and self-NA released by dead muscle cells may directly induce T cell co-stimulation. This may be followed by Th2 differentiation and Th2-mediated allergic inflammation, causing podocytopathy [23]. Nevertheless, the study by Sahin et al. found that the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine elicited a cytokine response involving Th1 T cell responses [62,64].
Furthermore, SARS-CoV-2 can penetrate proximal tubular cells through ligation with angiotensin conversion enzyme 2 (ACE2) and CD147-spike protein to cause severe AKI, and can also penetrate podocytes through ligation with ACE2, resulting in podocyte dysfunction [65,66]. In addition, SARS-CoV-2 can also unbalance renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) activation, promoting inflammation, glomerular dysfunction, fibrosis, and vasoconstriction [66]. However, whether the vaccine is related to ACE2 and RAAS is unclear.
4.2. Increased Production of Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibodies (ANCAs)
Influenza and rabies vaccines based on viral mRNAs have been described to possibly lead to an increase in ANCA, contributing to the development of ANCA-associated vasculitis [67]. Moreover, it was confirmed that the ANCA response was significantly reduced after the treatment of vaccinees with ribonuclease. Scientists have found that in the context of COVID-19, a host response to viral RNA can directly cause ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) and an autoimmune response [68,69,70]. COVID-19 mRNA vaccination induced a stronger response of the innate immune system after the second booster compared with primary immunization [71]. The heightened innate immune response observed after the second vaccination with BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine may be an inducer of MPO-ANCA and PR3 autoantibodies [34]. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) can be expressed on leukocyte membranes and play an important role in inflammatory responses, recognizing viral antigens and promoting immune system activation. In AAV, major toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) activation can provoke autoimmunity [72]. Interestingly, Kumar et al. suggested that TLR2 was activated by a robust and specific immune response of immunodominant cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) to the spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV2 (also produced by the COVID-19 vaccine) [73]. Messenger RNA vaccines could act as both antigen and adjuvant due to their intrinsic immunostimulatory properties of RNA; thus, they can be recognized by endosomal TLRs and cytosolic inflammasome components [64]. Therefore, the occurrence of AAV in the context of COVID-19 mRNA is highly relevant compared with non-mRNA vaccinations, but further experiments are required to verify the mechanism of the link between autoimmunity and a COVID-19 vaccine.
4.3. Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia (VITT)
Some scholars have speculated that antiphospholipid antibodies (APLs) may be part of the cause of thrombosis after COVID-19 vaccination, by triggering the type I interferon response associated with APLs’ production [74,75]. It binds directly to platelets by inhibiting the anticoagulant pathway of protein C, triggers the coagulation cascade, and appears to be associated with abnormal activation of immune responses involving the complement cascade [74]. Thrombocytopenia and platelet activation have been reported following the administration of adenoviral gene transfer vectors [76]. Thrombocytopenia also occurred after treatment with some anti-sense oligonucleotides [77]. Based on the above background, another hypothesis speculates that the activation of platelets by adenovirus-platelet-leukocyte complexes, mediated by von Willebrand factor (VWF) and P-selectin, may lead to accelerated clearance of platelets in the liver [75,78].
However, the virus in viral vector vaccines is replication-incomparable and the circulating virus disappears 7–14 days after vaccination, so the viral localization to the central nervous system and digestive system causing thrombosis is unlikely [79]. In addition, Greinacher et al. suggested that the rare occurrence of VITT was mediated by platelet factor 4 (PF4)-dependent platelet-activating antibodies, which in turn stimulate platelets via their Fcγ receptors [80,81]. Immune complexes containing PF4 can be recognized by C1q, which binds to the Fc portion of IgG molecules. This results in C3 activation, expansion of the complement response, and production of downstream proinflammatory mediators and effectors, ultimately leading to enhanced thrombus inflammation.
4.4. Direct Induction of Myositis
A previous case reported that a patient who presented with profound left upper arm pain after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination had an increased serum creatine kinase concentration, indicating skeletal muscle damage and inflammation (myositis) [82]. There is also evidence of renal biopsies from post-vaccination patients showing massive rhabdomyolysis-induced myoglobin casting, which may contribute to worsening renal function [34].
5. Discussion
This review has limitations. First, most of the literature is from reported single-case studies, and we cannot infer a causal relationship between vaccines and AKD. There may be potential undetected confounding factors. Second, there may be many unreported cases that may not represent the true incidence of AKD. Third, the mechanism is unproven, with only a combination of hypotheses derived from case reports and literature.
6. Conclusions
Despite these reported cases of AKD, the protective role of COVID-19 vaccination far outweighs any risks identified so far. In conclusion, the occurrence of AKD is relatively rare following COVID-19 vaccination. If some symptoms, such as hematuria, foamy urine, and edema, can be detected in an early phase, patients will benefit from a timely treatment of the primary disease, such as steroids. Further research is warranted to better understand the causes and mechanisms of AKD after COVID-19 vaccination.
Author Contributions
Y.L. conducted data collection and wrote the manuscript. M.R. conducted data collection. G.X. was responsible for the idea, funds, and paper revision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81970583 & 82060138), the Nature Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (No. 20202BABL206025).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Abbreviations
| AAV | ANCA-associated vasculitis |
| ACE2 | angiotensin conversion enzyme 2 |
| ADAMTS13 | A Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase with a ThromboSpondin type 1 motif, member 13 |
| AIN | acute interstitial nephritis |
| AKD | acute kidney disease |
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| ANCA | anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies |
| anti-GBM | anti-glomerular basement membrane |
| anti-PLA2R | anti-phospholipase A2 receptor |
| APLs | antiphospholipid antibodies |
| aTTP | acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| COVID-19 | coronavirus disease 2019 |
| CR | complete remission |
| CTL | cytotoxic T-lymphocyte |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CyC | cyclophosphamide |
| PF4 | platelet factor 4 |
| GN | glomerulonephritis |
| IgAN | IgA nephropathy |
| KDIGO | Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes |
| MCD | minimal change disease |
| MN | membranous nephropathy |
| MPO | myeloperoxidase |
| NAs | nucleic acids |
| PLEX | plasma exchange |
| PR | partial remission |
| PR3 | proteinase 3 |
| RAAS | renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system |
| RASB | renin-angiotensin system blockade |
| RRT | renal replacement therapy |
| RTX | rituximab |
| SARS-CoV-2 | severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| Scr | serum creatinine |
| TAC | tacrolimus |
| TLRs | toll-like receptors |
| TLR2 | toll-like receptor 2 |
| TLR9 | toll-like receptor 9 |
| VITT | vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia |
| VWF | von Willebrand factor |
References
- Sahin, U.; Muik, A.; Vogler, I.; Derhovanessian, E.; Kranz, L.M.; Vormehr, M.; Quandt, J.; Bidmon, N.; Ulges, A.; Baum, A.; et al. BNT162b2 vaccine induces neutralizing antibodies and poly-specific T cells in humans. Nature 2021, 595, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, O.; Sultan, A.A.; Ding, H.; Triggle, C.R. A Review of the Progress and Challenges of Developing a Vaccine for COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 585354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiolet, T.; Kherabi, Y.; MacDonald, C.J.; Ghosn, J.; Peiffer-Smadja, N. Comparing COVID-19 vaccines for their characteristics, efficacy and effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern: A narrative review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 28, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, J.A.; Malone, R.W.; Williams, P.; Chong, W.; Acsadi, G.; Jani, A.; Felgner, P.L. Direct gene transfer into mouse muscle in vivo. Science 1990, 247 Pt 1, 1465–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Perez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.J.; Moreira, E.D., Jr.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Perez Marc, G.; Polack, F.P.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine through 6 Months. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1761–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emary, K.R.W.; Golubchik, T.; Aley, P.K.; Ariani, C.V.; Angus, B.; Bibi, S.; Blane, B.; Bonsall, D.; Cicconi, P.; Charlton, S.; et al. Efficacy of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern 202012/01 (B.1.1.7). an exploratory analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voysey, M.; Clemens, S.A.C.; Madhi, S.A.; Weckx, L.Y.; Folegatti, P.M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Baillie, V.L.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2. an interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet 2021, 397, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Clemens, S.A.; Weckx, L.; Clemens, R.; Almeida Mendes, A.V.; Ramos Souza, A.; Silveira, M.B.V.; da Guarda, S.N.F.; de Nobrega, M.M.; de Moraes Pinto, M.I.; Gonzalez, I.G.S.; et al. Heterologous versus homologous COVID-19 booster vaccination in previous recipients of two doses of CoronaVac COVID-19 vaccine in Brazil (RHH-001). a phase 4, non-inferiority, single blind, randomised study. Lancet 2022, 399, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomjit, N.; Alexander, M.P.; Fervenza, F.C.; Zoghby, Z.; Garg, A.; Hogan, M.C.; Nasr, S.H.; Minshar, M.A.; Zand, L. COVID-19 Vaccination and Glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 2969–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Eckardt, K.U.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Levin, A.; Coresh, J.; Rossert, J.; De Zeeuw, D.; Hostetter, T.H.; Lameire, N.; Eknoyan, G. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease. a position statement from Kidney Disease. Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kellum, J.A.; Lameire, N.; Group, K.A.G.W. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of acute kidney injury. a KDIGO summary (Part 1). Crit. Care 2013, 17, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chawla, L.S.; Bellomo, R.; Bihorac, A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Siew, E.D.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bittleman, D.; Cruz, D.; Endre, Z.; Fitzgerald, R.L.; et al. Acute kidney disease and renal recovery. consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 16 Workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirsch, J.S.; Ng, J.H.; Ross, D.W.; Sharma, P.; Shah, H.H.; Barnett, R.L.; Hazzan, A.D.; Fishbane, S.; Jhaveri, K.D.; Northwell, C.-R.C.; et al. Acute kidney injury in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclerc, S.; Royal, V.; Lamarche, C.; Laurin, L.P. Minimal Change Disease With Severe Acute Kidney Injury Following the Oxford-AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccine. A Case Report. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Han, M.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, M.S.; Jung, H.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, C.D.; Kim, Y.L.; Park, S.H. New-onset Nephrotic Syndrome after Janssen COVID-19 Vaccination. a Case Report and Literature Review. J. Korean Med. Sci 2021, 36, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, L.; Sapojnikov, M.; Wechsler, A.; Varadi-Levi, R.; Zamir, D.; Tobar, A.; Levin-Iaina, N.; Fytlovich, S.; Yagil, Y. Minimal Change Disease Following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, R.J.; Gianotten, S.; van der Meijden, W.A.G. An Additional Case of Minimal Change Disease Following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agati, V.D.; Kudose, S.; Bomback, A.S.; Adamidis, A.; Tartini, A. Minimal change disease and acute kidney injury following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 461–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzworth, A.; Couchot, P.; Cruz-Knight, W.; Brucculeri, M. Minimal change disease following the Moderna mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 463–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weijers, J.; Alvarez, C.; Hermans, M.M.H. Post-vaccinal minimal change disease. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Fugo, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Terawaki, H. Minimal change disease soon after Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 2606–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, J.; Ingram, A.; Shao, T. Minimal Change Disease After First Dose of Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine. A Case Report and Review of Minimal Change Disease Related to COVID-19 Vaccine. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2021, 8, 20543581211058271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unver, S.; Haholu, A.; Yildirim, S. Nephrotic syndrome and acute kidney injury following CoronaVac anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 2608–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da, Y.; Goh, G.H.; Khatri, P. A case of membranous nephropathy following Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccination against COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 938–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueguen, L.; Loheac, C.; Saidani, N.; Khatchatourian, L. Membranous nephropathy following anti-COVID-19 mRNA vaccination. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 1140–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudose, S.; Friedmann, P.; Albajrami, O.; D’Agati, V.D. Histologic correlates of gross hematuria following Moderna COVID-19 vaccine in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 468–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.Z.; Tan, R.Y.; Choo, J.C.J.; Lim, C.C.; Tan, C.S.; Loh, A.H.L.; Tien, C.S.; Tan, P.H.; Woo, K.T. Is COVID-19 vaccination unmasking glomerulonephritis? Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, C.; Herrera Hernandez, L.P.; Bu, L.; Kizilbash, S.; Najera, L.; Rheault, M.N.; Czyzyk, J.; Kouri, A.M. IgA nephropathy presenting as macroscopic hematuria in 2 pediatric patients after receiving the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 705–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderegg, M.A.; Liu, M.; Saganas, C.; Montani, M.; Vogt, B.; Huynh-Do, U.; Fuster, D.G. De novo vasculitis after mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccination. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacker, A.; Kung, V.; Andeen, N. Anti-GBM nephritis with mesangial IgA deposits after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 471–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, M.; Diaz-Crespo, F.; Perez de Jose, A.; Verdalles, U.; Verde, E.; Almeida Ruiz, F.; Acosta, A.; Mijaylova, A.; Goicoechea, M. A case of ANCA-associated vasculitis after AZD1222 (Oxford-AstraZeneca) SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. casualty or causality? Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 937–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakroush, S.; Tampe, B. Case Report. ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Presenting With Rhabdomyolysis and Pauci-Immune Crescentic Glomerulonephritis After Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 762006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, A.; Campbell, R.; Tabbara, J.; Rastogi, P. ANCA glomerulonephritis after the Moderna COVID-19 vaccination. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakoor, M.T.; Birkenbach, M.P.; Lynch, M. ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Following Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dube, G.K.; Benvenuto, L.J.; Batal, I. Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody-Associated Glomerulonephritis Following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 3087–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feghali, E.J.; Zafar, M.; Abid, S.; Santoriello, D.; Mehta, S. De-novo Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis Following the mRNA-1273 (Moderna) Vaccine for COVID-19. Cureus 2021, 13, e19616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillion, V.; Jadoul, M.; Demoulin, N.; Aydin, S.; Devresse, A. Granulomatous vasculitis after the AstraZeneca anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 706–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, F.S.; Costa Carvalho, J.; de Almeida, P.A.; Pimenta, A.C.; Alen Coutinho, I.; Figueiredo, C.; Rodrigues, L.; Sousa, V.; Ferreira, E.; Pinto, H.; et al. A Case of Acute Interstitial Nephritis After Two Doses of the BNT162b2 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2021, 14, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancianti, N.; Guarnieri, A.; Tripodi, S.; Salvo, D.P.; Garosi, G. Minimal change disease following vaccination for SARS-CoV-2. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34, 1039–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, M.F.; Yildiz, A.; Oruc, A.; Sezen, M.; Dilek, K.; Gullulu, M.; Yavuz, M.; Ersoy, A. Relapse of primary membranous nephropathy after inactivated SARS-CoV-2 virus vaccination. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 464–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, P.; Bassand, X.; Benotmane, I.; Bouvier, N. Gross hematuria following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yocum, A.; Simon, E.L. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura after Ad26.COV2-S Vaccination. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 49, 441.e443–441.e444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhe, J.; Schnetzke, U.; Kentouche, K.; Prims, F.; Baier, M.; Herfurth, K.; Schlosser, M.; Busch, M.; Hochhaus, A.; Wolf, G. Acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura after first vaccination dose of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. Ann. Hematol. 2022, 101, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanodja, B.; Schreiber, A.; Schrezenmeier, E.; Seelow, E. First diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura after SARS-CoV-2 vaccine—Case report. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamarti, K.; Dar, K.; Reddy, A.; Gundlapalli, A.; Mourning, D.; Bajaj, K. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Presentation in an Elderly Gentleman Following COVID Vaccine Circumstances. Cureus 2021, 13, e16619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alislambouli, M.; Veras Victoria, A.; Matta, J.; Yin, F. Acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura following Pfizer COVID-19 vaccination. EJHaem 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Sakaki, A.; Matsuyama, Y.; Mushino, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Sonoki, T.; Tamura, S. Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Following BNT162b2 mRNA Coronavirus Disease Vaccination in a Japanese Patient. Intern. Med. 2022, 61, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missoum, S.; Lahmar, M.; Khellaf, G. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis and acute renal failure following inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Nephrol. Ther. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rawahi, B.; BaTaher, H.; Jaffer, Z.; Al-Balushi, A.; Al-Mazrouqi, A.; Al-Balushi, N. Vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia following AstraZeneca (ChAdOx1 nCOV-19) vaccine-A case report. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost 2021, 5, e12578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.H.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Han, M.H.; Jung, H.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, C.D.; Kim, Y.L.; Park, S.H. New-Onset Kidney Diseases after COVID-19 Vaccination. A Case Series. Vaccines 2022, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivarelli, M.; Massella, L.; Ruggiero, B.; Emma, F. Minimal Change Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, M.A.; Bevan, M.J. Effector and memory CTL differentiation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudd, P.A.; Minervina, A.A.; Pogorelyy, M.V.; Turner, J.S.; Kim, W.; Kalaidina, E.; Petersen, J.; Schmitz, A.J.; Lei, T.; Haile, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination elicits a robust and persistent T follicular helper cell response in humans. Cell 2021, 185, 603–613.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, H.; Hollenbaugh, J.A.; Zand, M.S.; Holden-Wiltse, J.; Mosmann, T.R.; Perelson, A.S.; Wu, H.; Topham, D.J. Quantifying the early immune response and adaptive immune response kinetics in mice infected with influenza A virus. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 6687–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sette, A.; Crotty, S. Adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Cell 2021, 184, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci, M.; Corpetti, G.; Emma, F.; Vivarelli, M. Immunology of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieson, P.W. Immune dysregulation in minimal change nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2003, 18 (Suppl. S6), vi26–vi29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Berre, L.; Herve, C.; Buzelin, F.; Usal, C.; Soulillou, J.P.; Dantal, J. Renal macrophage activation and Th2 polarization precedes the development of nephrotic syndrome in Buffalo/Mna rats. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 2079–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Porter, F.W.; Weissman, D. mRNA vaccines—A new era in vaccinology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahin, U.; Muik, A.; Derhovanessian, E.; Vogler, I.; Kranz, L.M.; Vormehr, M.; Baum, A.; Pascal, K.; Quandt, J.; Maurus, D.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b1 elicits human antibody and TH1 T cell responses. Nature 2020, 586, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imanishi, T.; Ishihara, C.; Badr Mel, S.; Hashimoto-Tane, A.; Kimura, Y.; Kawai, T.; Takeuchi, O.; Ishii, K.J.; Taniguchi, S.; Noda, T.; et al. Nucleic acid sensing by T cells initiates Th2 cell differentiation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teijaro, J.R.; Farber, D.L. COVID-19 vaccines: Modes of immune activation and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Bhargava, R.; Shaukat, A.A.; Albert, E.; Leggat, J. Spectrum of podocytopathies in new-onset nephrotic syndrome following COVID-19 disease. a report of 2 cases. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarre, P.; Dumas, G.; Dupont, T.; Darmon, M.; Azoulay, E.; Zafrani, L. Acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Intens. Care Med. 2020, 46, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffs, L.S.; Nitschke, J.; Tervaert, J.W.; Peh, C.A.; Hurtado, P.R. Viral RNA in the influenza vaccine may have contributed to the development of ANCA-associated vasculitis in a patient following immunisation. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppal, N.N.; Kello, N.; Shah, H.H.; Khanin, Y.; De Oleo, I.R.; Epstein, E.; Sharma, P.; Larsen, C.P.; Bijol, V.; Jhaveri, K.D. De Novo ANCA-Associated Vasculitis With Glomerulonephritis in COVID-19. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 2079–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.G.; Magira, E.; Alexopoulos, H.; Jahaj, E.; Theophilopoulou, K.; Kotanidou, A.; Tzioufas, A.G. Autoantibodies related to systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases in severely ill patients with COVID-19. Ann. Rheum Dis. 2020, 79, 1661–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izci Duran, T.; Turkmen, E.; Dilek, M.; Sayarlioglu, H.; Arik, N. ANCA-associated vasculitis after COVID-19. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, P.S.; Scott, M.K.D.; Hagan, T.; Li, C.; Feng, Y.; Wimmers, F.; Grigoryan, L.; Trisal, M.; Edara, V.V.; Lai, L.; et al. Systems vaccinology of the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in humans. Nature 2021, 596, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, S.A.; Steinmetz, O.M.; Gan, P.Y.; Ooi, J.D.; Odobasic, D.; Kitching, A.R.; Holdsworth, S.R. Toll-like receptor 2 induces Th17 myeloperoxidase autoimmunity while Toll-like receptor 9 drives Th1 autoimmunity in murine vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum 2011, 63, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Admane, N.; Kumari, A.; Sood, D.; Grover, S.; Prajapati, V.K.; Chandra, R.; Grover, A. Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte elicited vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 employing immunoinformatics framework. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talotta, R.; Robertson, E.S. Antiphospholipid antibodies and risk of post-COVID-19 vaccination thrombophilia. The straw that breaks the camel’s back? Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2021, 60, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, X.M.; Shuai, Z.W.; Ye, D.Q.; Pan, H.F. New-onset autoimmune phenomena post-COVID-19 vaccination. Immunology 2021, 165, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.Y.; Au, S.Y.; Fong, K.M. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e11. [Google Scholar]
- Pasin, F.; Calabrese, A.; Pelagatti, L. Immune thrombocytopenia following COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. casuality or causality? Intern. Emerg. Med. 2022, 17, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, M.; Labelle, A.; Mazzetti, I.; Elbatarny, H.S.; Lillicrap, D. Adenovirus-induced thrombocytopenia. the role of von Willebrand factor and P-selectin in mediating accelerated platelet clearance. Blood 2007, 109, 2832–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichinger, S.; Warkentin, T.E.; Greinacher, A. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccination. Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e11. [Google Scholar]
- Greinacher, A.; Thiele, T.; Warkentin, T.E.; Weisser, K.; Kyrle, P.A.; Eichinger, S. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCov-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2092–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinacher, A.; Selleng, K.; Mayerle, J.; Palankar, R.; Wesche, J.; Reiche, S.; Aebischer, A.; Warkentin, T.E.; Muenchhoff, M.; Hellmuth, J.C.; et al. Anti-platelet factor 4 antibodies causing VITT do not cross-react with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Blood 2021, 138, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorou, D.J.; Theodorou, S.J.; Axiotis, A.; Gianniki, M.; Tsifetaki, N. COVID-19 vaccine-related myositis. QJM 2021, 114, 424–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).