Comparing SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses after Various COVID-19 Vaccinations in Healthcare Workers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Measurement
2.2.1. Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2
2.2.2. Alinity SARS-CoV-2 IgG
2.2.3. R-FIND SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody
2.3. Ethical Approvals
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics of Subjects
3.2. Antibody-Positive Rate and Quantity in Each Assay
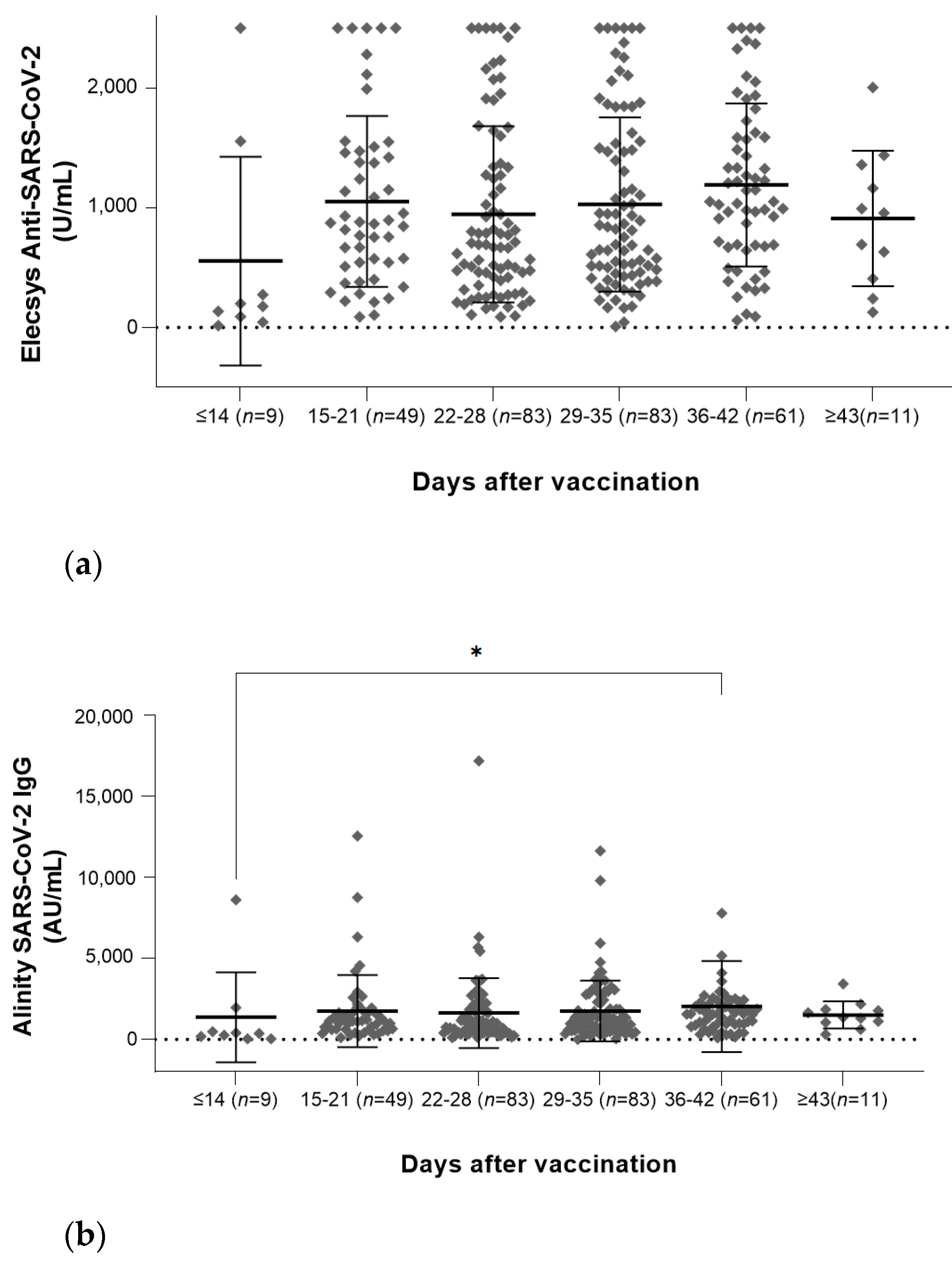
3.2.1. Results of Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Assay
3.2.2. Results of Alinity SARS-CoV-2 IgG
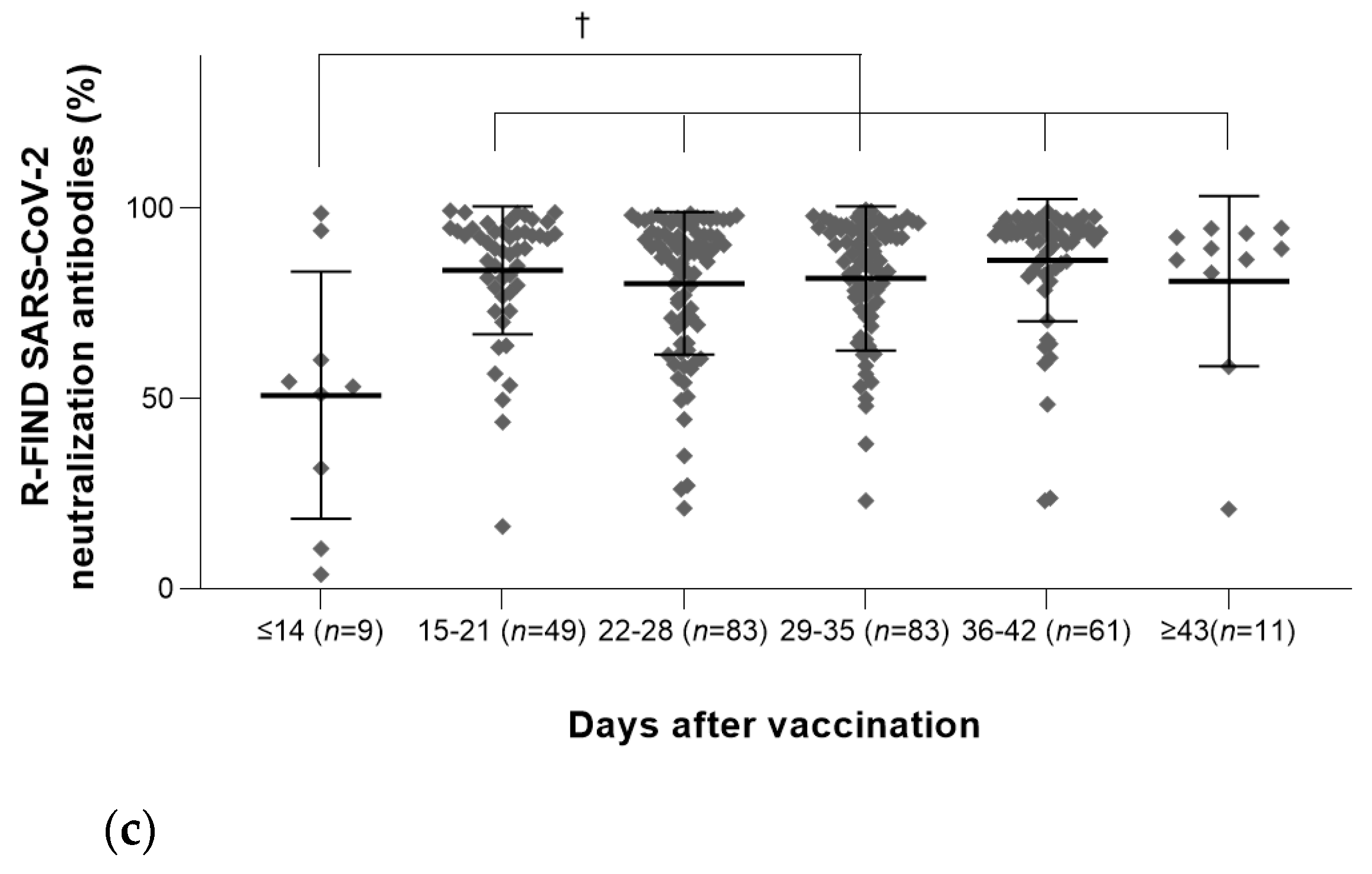
3.2.3. Results of R-FIND SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody
3.3. Antibody Quantities According to the Elapsed Day
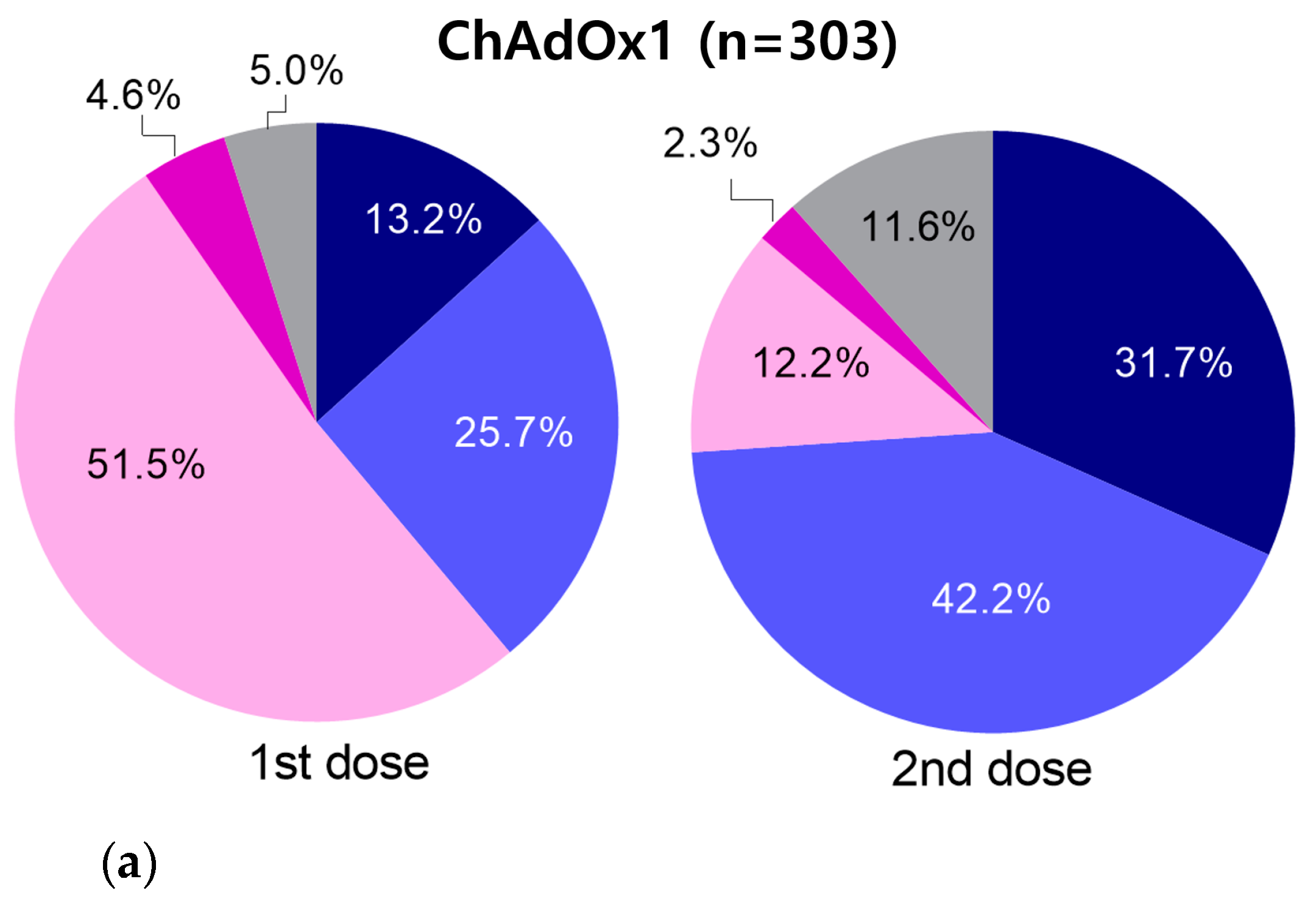
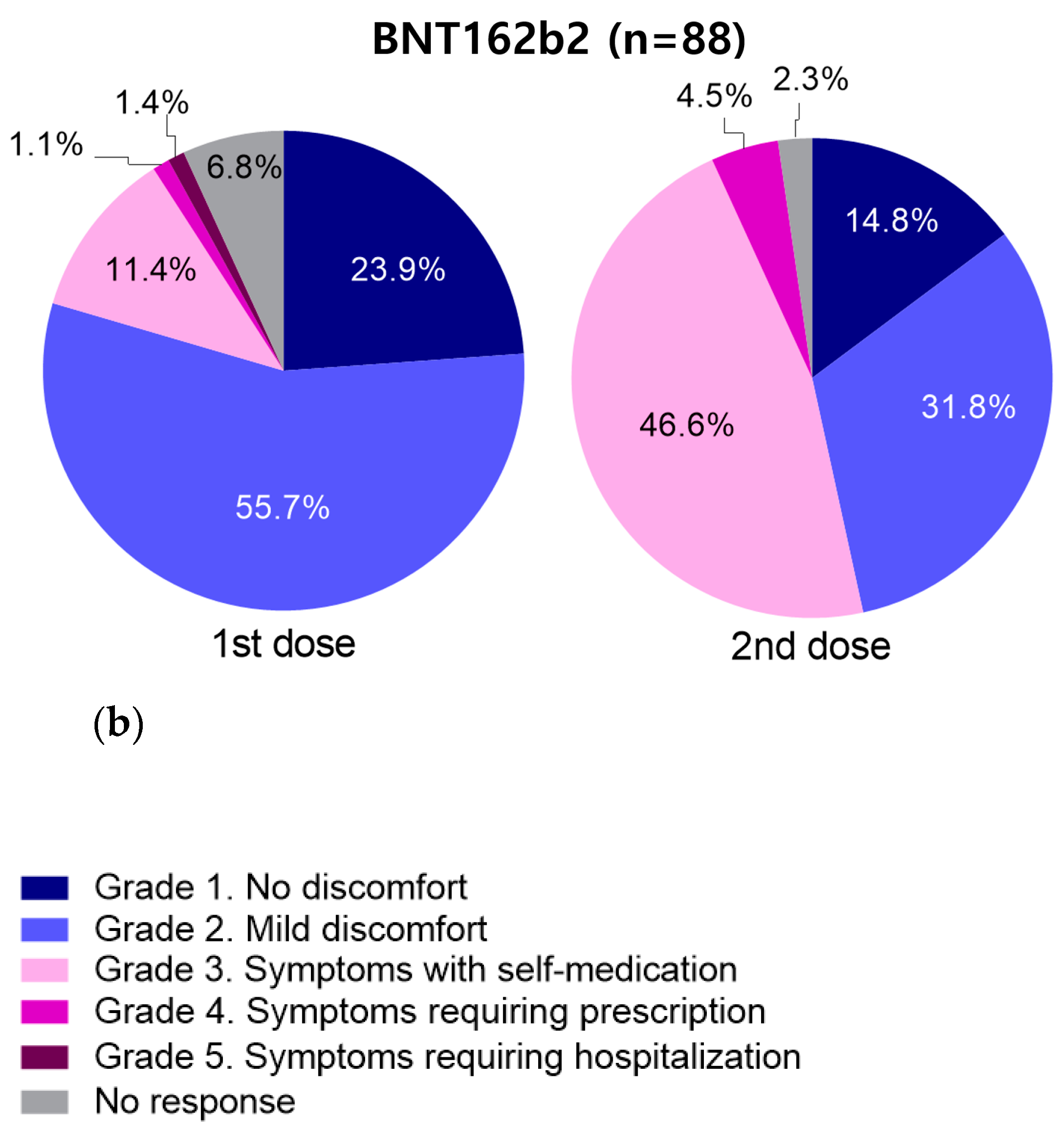
3.4. Incidence of Adverse Events According to Vaccine Type
3.5. Association between Antibody Quantities and Adverse Events
3.5.1. Results of ChAdOx1
3.5.2. Results of BNT162b2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kandimalla, R.; Chakraborty, P.; Vallamkondu, J.; Chaudhary, A.; Samanta, S.; Reddy, P.H.; De Feo, V.; Dewanjee, S. Counting on COVID-19 vaccine: Insights into the current strategies, progress and future challenges. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Marc, G.P.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J. Preparing for the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) vaccination: Evidence, plans, and implications. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, V.; Fabros, A.; Kulasingam, V. Quantitative measurement of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies: Analytical and clinical evaluation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e03149-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkerke, H.; Horwath, M.; Saeedi, B.; Boyer, D.; Allen, J.W.; Owens, J.; Arthur, C.M.; Nakahara, H.; Rha, J.; Patel, K.; et al. Comparison of antibody class-specific SARS-CoV-2 serologies for the diagnosis of acute COVID-19. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e02026-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Lee, N.; Lee, S.K.; Cho, E.J.; Hyun, J.; Park, M.J.; Song, W.; Jung, E.J.; Woo, H.; Seo, Y.B.; et al. Comparing results of five SARS-CoV-2 antibody assays before and after the first dose of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine among health care workers. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0110521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Minn, D.; Park, S.; Roh, E.Y.; Yoon, J.H.; Park, H.; Shin, S. Positivity of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies among Korean healthy healthcare workers 1 and 2 weeks after second dose of Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36, e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyre, D.W.; Lumley, S.F.; Wei, J.; Cox, S.; James, T.; Justice, A.; Jesuthasan, G.; O’Donnell, D.; Howarth, A.; Hatch, S.B.; et al. Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike responses to Pfizer-BioNTech and Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccines by previous infection status. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1516.e7–1516.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, M.; Seo, J.D.; Moon, H.W.; Kim, H.; Hur, M.; Yun, Y.M. Evaluation of humoral immune response after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination using two binding antibody assays and a neutralizing antibody assay. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0120221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tretyn, A.; Szczepanek, J.; Skorupa, M.; Jarkiewicz-Tretyn, J.; Sandomierz, D.; Dejewska, J.; Ciechanowska, K.; Jarkiewicz-Tretyn, A.; Koper, W.; Pałgan, K. Differences in the concentration of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies post-COVID-19 recovery or post-vaccination. Cells 2021, 10, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, B.; Rubey, H.; Treipl, A.; Gromann, M.; Hemedi, B.; Zehetmayer, S.; Kirsch, B. Haemodialysis patients show a highly diminished antibody response after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination compared with healthy controls. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Stoesser, N.; Matthews, P.C.; Ayoubkhani, D.; Studley, R.; Bell, I.; Bell, J.I.; Newton, J.N.; Farrar, J.; Diamond, I.; et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in 45,965 adults from the general population of the United Kingdom. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.H.; Song, K.H.; Choi, Y.; Go, S.; Choi, S.J.; Jung, J.; Kang, C.K.; Choe, P.G.; Kim, N.J.; Park, W.B.; et al. Can reactogenicity predict immunogenicity after COVID-19 vaccination? Korean J. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 1486–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Number | % |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| 20–29 | 131 | 26.4 |
| 30–39 | 87 | 17.5 |
| 40–49 | 108 | 21.7 |
| 50–59 | 134 | 27.0 |
| ≥60 | 31 | 6.2 |
| Not available | 6 | 1.2 |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 402 | 80.9 |
| Male | 93 | 18.7 |
| Not available | 2 | 0.4 |
| Vaccination | ||
| Completion | ||
| ChAdOx1 (1st and 2nd dose) | 303 | 61.0 |
| BNT162b2 (1st and 2nd dose) | 88 | 17.7 |
| JNJ-78436735 (1st dose) | 4 | 0.8 |
| ChAdOx1 (1st dose) and BNT162b2 (2nd dose) | 2 | 0.4 |
| Incompletion | ||
| mRNA-1273 (1st dose) | 62 | 12.5 |
| AZD1222 (1st dose) | 22 | 4.4 |
| BNT162b2 (1st dose) | 1 | 0.2 |
| Not available | 15 | 3.0 |
| Number | Days after the Final Vaccination * (Range) | Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 | Alinity SARS-CoV-2 IgG | R-FIND SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Positive Cases | Antibody Quantities (U/mL) * | Number of Positive Cases | Antibody Quantities (AU/mL) * | Number of Positive Cases | Neutralization Rates (%) * | |||
| Completed vaccination (N = 397) | ||||||||
| ChAdOx1 (1st and 2nd dose) | 303 | 29.3 ± 9.1 (0–58) | 303 (100%) | 1017.4 ± 718.4 | 300 (99.0%) | 1742.6 ± 2205.4 | 291 (96.0%) | 81.6 ± 19.5 |
| BNT162b2 (1st and 2nd dose) | 88 | 94.7 ± 2.2 (88–102) | 88 (100%) | 948.5 ± 533.9 | 88 (100%) | 3558.9 ± 2308.0 | 88 (100%) | 90.8 ± 7.0 |
| JNJ-78436735 (1st dose) | 4 | 22.8 ± 2.1 (20–25) | 4 (100%) | 15.2 ± 17.4 | 4 (100%) | 335.4 ± 324.2 | 4 (100%) | 43.3 ± 25.1 |
| ChAdOx1 (1st dose) and BNT162b2 (2nd dose) | 2 | 2.0 ± 2.8 (0–4) | 2 (100%) | 17.4 ± 4.9 | 1 (50.0%) | 50.7 ± 30.5 | 0 | 7.0 ± 5.9 |
| Incomplete vaccination (N = 85) | ||||||||
| mRNA-1273 (1st dose) | 62 | 9.9 ± 4.0 (4–18) | 35 (56.5%) | 54.5 ± 316.8 | 36 (58.1%) | 1925.6 ± 8661.8 | 33 (53.2%) | 35.4 ± 39.2 |
| ChAdOx1 (1st dose) | 22 | 66.2 ± 31.3 (7–117) | 22 (100%) | 90.1 ± 212.6 | 20 (91.0%) | 409.7 ± 365.2 | 15 (68.2%) | 39.7 ± 24.0 |
| BNT162b2 (1st dose) | 1 | 8 | 0 | 0.4 | 0 | 9.6 | 0 | 11.7 |
| Variable | Mean ± SD | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Event Group | No Discomfort Group | ||
| ChAdOx1 (n = 277) | |||
| Number | 174 | 103 | |
| Age | 41.9 ± 10.9 | 47.2 ± 10.9 | <0.01 |
| Days after the last vaccination | 30.7 ± 8.0 | 29.1 ± 7.7 | NS |
| Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 (U/mL) | 1037.1 ± 708.8 | 1051.6 ± 733.8 | NS |
| Alinity SARS-CoV-2 IgG (AU/mL) | 1817.8 ± 2175.4 | 1718.7 ± 2365.0 | NS |
| R-FIND SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody (%) | 82.3 ± 19.6 | 83.0 ± 15.8 | NS |
| BNT162b2 (n = 83) | |||
| Number | 46 | 37 | |
| Age | 35.4 ± 11.5 | 41.0 ± 13.7 | NS |
| Days after the last vaccination | 94.5 ± 1.9 | 94.9 ± 2.5 | NS |
| Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 (U/mL) | 1065.8 ± 611.6 | 871.2 ± 392.7 | NS |
| Alinity SARS-CoV-2 IgG (AU/mL) | 4118.0 ± 2736.8 | 3111.8 ± 1538.3 | <0.05 |
| R-FIND SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody (%) | 92.2 ± 5.6 | 90.4 ± 7.2 | NS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-K.; Minn, D.; Chang, S.-H.; Suh, J.-S. Comparing SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses after Various COVID-19 Vaccinations in Healthcare Workers. Vaccines 2022, 10, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020193
Kim Y-K, Minn D, Chang S-H, Suh J-S. Comparing SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses after Various COVID-19 Vaccinations in Healthcare Workers. Vaccines. 2022; 10(2):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020193
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yu-Kyung, Dohsik Minn, Soon-Hee Chang, and Jang-Soo Suh. 2022. "Comparing SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses after Various COVID-19 Vaccinations in Healthcare Workers" Vaccines 10, no. 2: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020193
APA StyleKim, Y.-K., Minn, D., Chang, S.-H., & Suh, J.-S. (2022). Comparing SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses after Various COVID-19 Vaccinations in Healthcare Workers. Vaccines, 10(2), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020193







