The Safety and Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Japanese Patients after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Sample Collection and Measurement of Antibody Titers
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
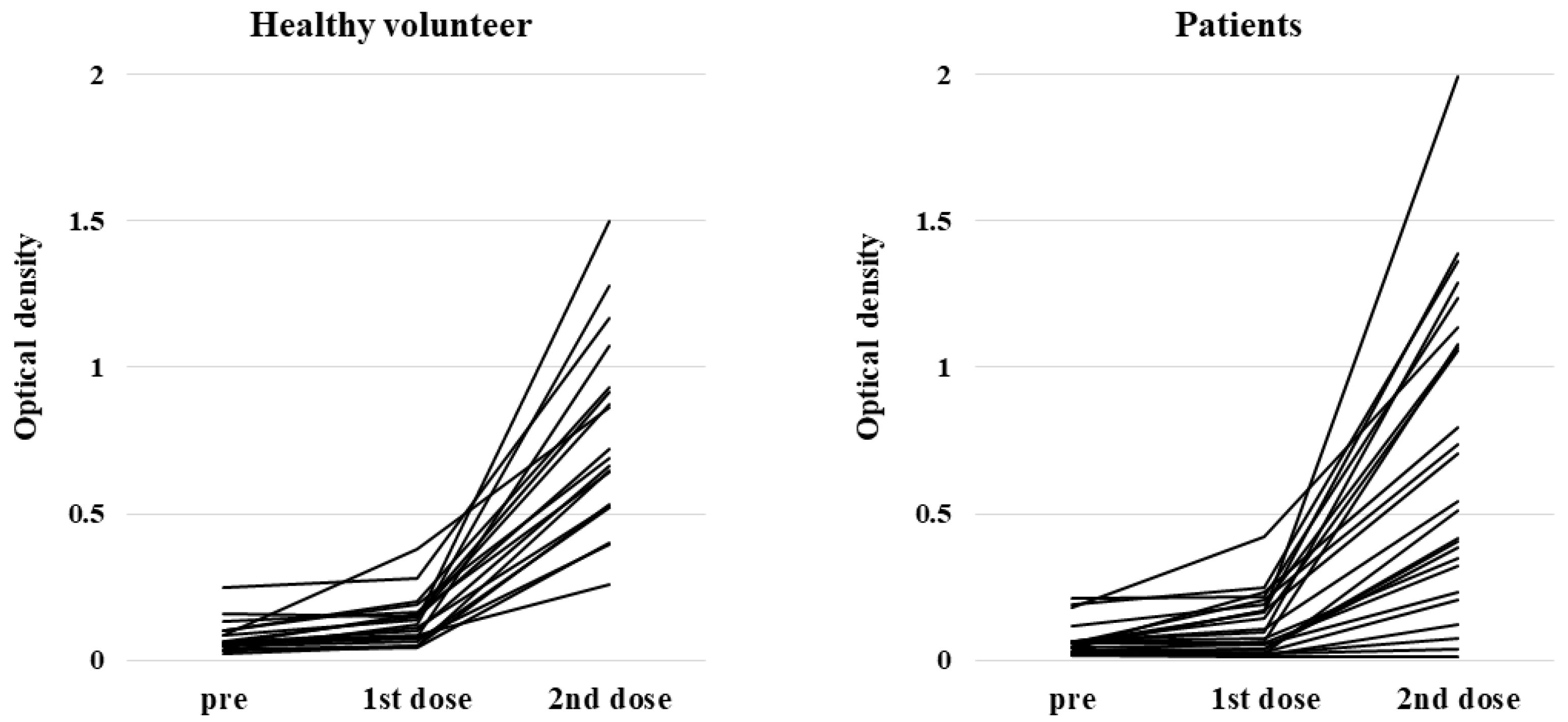
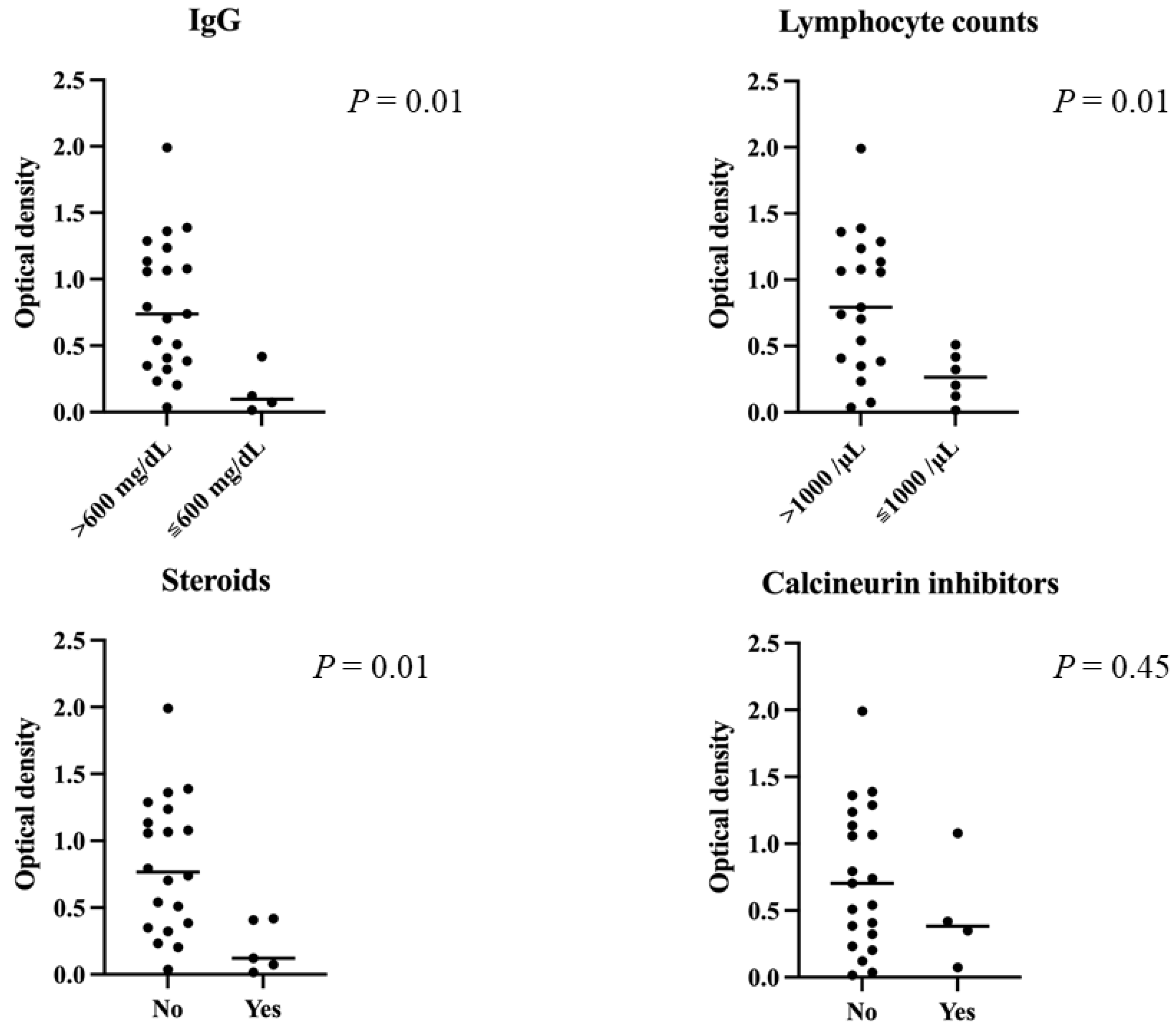
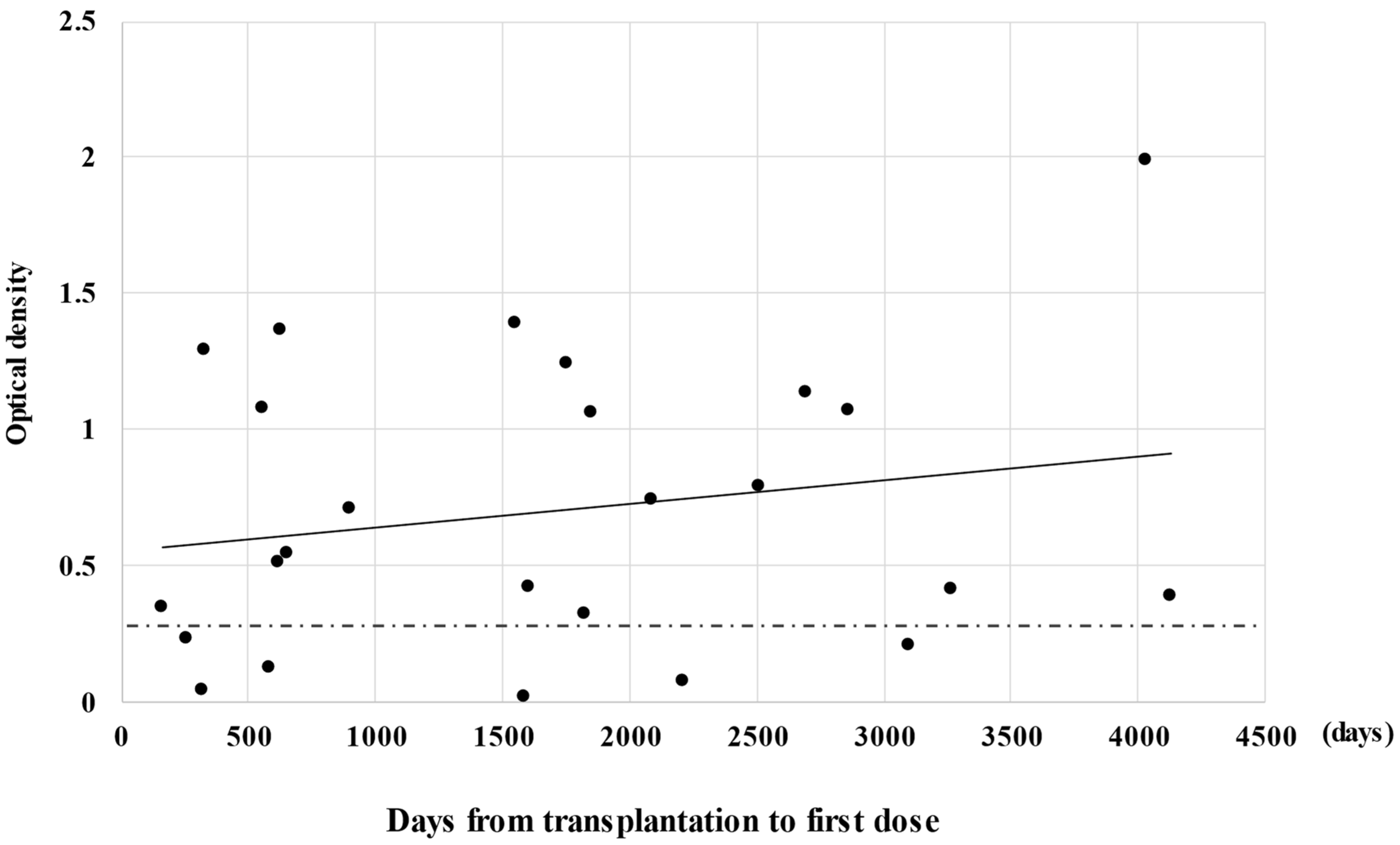
3.2. Serological Outcomes
3.3. Safety
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, A.; Bhatt, N.S.; Martin, A.S.; Abid, M.B.; Bloomquist, J.; Chemaly, R.F.; Dandoy, C.; Gauthier, J.; Gowda, L.; Perales, M.-A.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 in haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation recipients: An observational cohort study. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e185–e193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Bhattacharya, M.; Agoramoorthy, G.; Lee, S.-S. The Drug Repurposing for COVID-19 Clinical Trials Provide Very Effective Therapeutic Combinations: Lessons Learned From Major Clinical Studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 704205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zmievskaya, E.; Valiullina, A.; Ganeeva, I.; Petukhov, A.; Rizvanov, A.; Bulatov, E. Application of CAR-T Cell Therapy beyond Oncology: Autoimmune Diseases and Viral Infections. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunachalam, P.S.; Scott, M.K.D.; Hagan, T.; Li, C.; Feng, Y.; Wimmers, F.; Grigoryan, L.; Trisal, M.; Edara, V.V.; Lai, L.; et al. Systems vaccinology of the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in humans. Nature 2021, 596, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Ngo, D.; Aribi, A.; Arslan, S.; Dadwal, S.; Marcucci, G.; Nakamura, R.; Forman, S.J.; Chen, J.; Al Malki, M.M. Safety and Tolerability of SARS-CoV2 Emergency-Use Authorized Vaccines for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Transpl. Cell. Ther. 2021, 27, 938.e1–938.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, J.A. Humoral Immunity After mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Allogeneic HCT Recipients-Room for Improvement and Much to Learn. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2127454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhakal, B.; Abedin, S.; Fenske, T.; Chhabra, S.; Ledeboer, N.; Hari, P.; Hamadani, M. Response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients after hematopoietic cell transplantation and CAR T-cell therapy. Blood 2021, 138, 1278–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishima, Y.; Kawase, T.; Malkki, M.; Morishima, S.; Spellman, S.; Kashiwase, K.; Kato, S.; Cesbron, A.; Tiercy, J.-M.; Senitzer, D.; et al. Significance of ethnicity in the risk of acute graft-versus-host disease and leukemia relapse after unrelated donor hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2013, 19, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, S.J.; Moreira, E.D., Jr.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Marc, G.P.; Polack, F.P.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine through 6 Months. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1761–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Carter, B.; Gifford, D.K. Predicted Cellular Immunity Population Coverage Gaps for SARS-CoV-2 Subunit Vaccines and Their Augmentation by Compact Peptide Sets. Cell Syst. 2021, 12, 102–107.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, R.; Hagin, D.; Kikozashvilli, N.; Freund, T.; Amit, O.; Bar-On, Y.; Beyar-Katz, O.; Shefer, G.; Moshiashvili, M.M.; Karni, C.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Patients after Allogeneic HCT or CD19-based CART therapy-A Single-Center Prospective Cohort Study. Transpl. Cell. Ther. 2021, 27, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, K.; Kitagawa, Y.; Tabata, S.; Kubota, K.; Nagura-Ikeda, M.; Matsuoka, M.; Miyoshi, K.; Sakai, J.; Ishibashi, N.; Tarumoto, N.; et al. Antibody response patterns in COVID-19 patients with different levels of disease severity in Japan. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 3211–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Attolico, I.; Tarantini, F.; Carluccio, P.; Schifone, C.; Delia, M.; Gagliardi, V.P.; Perrone, T.; Gaudio, F.; Longo, C.; Giordano, A.; et al. Serological response following BNT162b2 anti-SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in haematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 138, 4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canti, L.; Humblet-Baron, S.; Desombere, I.; Neumann, J.; Pannus, P.; Heyndrickx, L.; Henry, A.; Servais, S.; Willems, E.; Ehx, G.; et al. Predictors of neutralizing antibody response to BNT162b2 vaccination in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarucci, M.; Paolasini, S.; Isidori, A.; Guiducci, B.; Loscocco, F.; Capalbo, M.; Visani, G. Immunological Response Against SARS-CoV-2 After BNT162b2 Vaccine Administration Is Impaired in Allogeneic but Not in Autologous Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 737300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shem-Tov, N.; Yerushalmi, R.; Danylesko, I.; Litachevsky, V.; Levy, I.; Olmer, L.; Lusitg, Y.; Avigdor, A.; Nagler, A.; Shimoni, A.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in haematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients. Br. J. Haematol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bourgeois, A.; Coste-Burel, M.; Guillaume, T.; Peterlin, P.; Garnier, A.; Imbert, B.-M.; Drumel, T.; Mahé, B.; Dubruille, V.; Blin, N.; et al. Interest of a third dose of BNT162b2 anti-SARS-CoV-2 messenger RNA vaccine after allotransplant. Br. J. Haematol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Median Age at Vaccination (Range, Years) | 55 (23–71) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | n | % |
| Female | 11 | 44 |
| Male | 14 | 56 |
| Conditioning | ||
| MAC | 9 | 36 |
| RIC | 16 | 64 |
| Disease | ||
| AML | 11 | 44 |
| ALL | 6 | 24 |
| ML | 5 | 20 |
| Others | 3 | 12 |
| Immunosuppressants | ||
| Tacrolimus alone | 2 | 8 |
| Tacrolimus + steroid | 1 | 4 |
| Cyclosporine A +steroid | 1 | 4 |
| Steroid alone | 3 | 12 |
| No use | 18 | 72 |
| IgG | ||
| ≥600 mg/dL | 21 | 84 |
| <600 mg/dL | 4 | 16 |
| Absolute lymphocyte counts | ||
| ≥1000/μL | 19 | 76 |
| <1000/μL | 6 | 24 |
| 1st Dose | Patients, n (%) | HV, n (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fever | 1 (4) | 1 (5) | 1 |
| Pain | 20 (80) | 12 (63) | 0.308 |
| Redness | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 |
| Swelling | 2 (8) | 2 (11) | 1 |
| Headache | 4 (16) | 0 (0) | 0.122 |
| Fatigue | 5 (20) | 4 (21) | 1 |
| Chills | 2 (8) | 0 (0) | 0.498 |
| Muscle pain | 3 (12) | 1 (5) | 0.622 |
| Joint pain | 2 (8) | 0 (0) | 0.498 |
| Vomiting | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 |
| Diarrhea | 1 (4) | 1 (5) | 1 |
| 2nd dose | |||
| Fever | 1 (4) | 2 (11) | 0.181 |
| Pain | 17 (68) | 13 (68) | 1 |
| Redness | 2 (8) | 1 (5) | 1 |
| Swelling | 6 (24) | 2 (11) | 0.433 |
| Headache | 7 (28) | 1 (5) | 0.111 |
| Fatigue | 13 (52) | 6 (32) | 0.227 |
| Chills | 2 (8) | 1 (5) | 1 |
| Muscle pain | 3 (12) | 1 (5) | 0.622 |
| Joint pain | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 |
| Vomiting | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 |
| Diarrhea | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 |
| Skin rash | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watanabe, M.; Yakushijin, K.; Funakoshi, Y.; Ohji, G.; Hojo, W.; Sakai, H.; Saeki, M.; Hirakawa, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Sakai, R.; et al. The Safety and Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Japanese Patients after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Vaccines 2022, 10, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020158
Watanabe M, Yakushijin K, Funakoshi Y, Ohji G, Hojo W, Sakai H, Saeki M, Hirakawa Y, Matsumoto S, Sakai R, et al. The Safety and Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Japanese Patients after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Vaccines. 2022; 10(2):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020158
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatanabe, Marika, Kimikazu Yakushijin, Yohei Funakoshi, Goh Ohji, Wataru Hojo, Hironori Sakai, Miki Saeki, Yuri Hirakawa, Sakuya Matsumoto, Rina Sakai, and et al. 2022. "The Safety and Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Japanese Patients after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation" Vaccines 10, no. 2: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020158
APA StyleWatanabe, M., Yakushijin, K., Funakoshi, Y., Ohji, G., Hojo, W., Sakai, H., Saeki, M., Hirakawa, Y., Matsumoto, S., Sakai, R., Nagao, S., Kitao, A., Miyata, Y., Koyama, T., Saito, Y., Kawamoto, S., Ito, M., Murayama, T., Matsuoka, H., & Minami, H. (2022). The Safety and Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Japanese Patients after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Vaccines, 10(2), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020158







