Novel BC02 Compound Adjuvant Enhances Adaptive and Innate Immunity Induced by Recombinant Glycoprotein E of Varicella-Zoster Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Ethics Consideration
2.2. Materials and Reagents
2.3. Experimental Vaccine Preparation
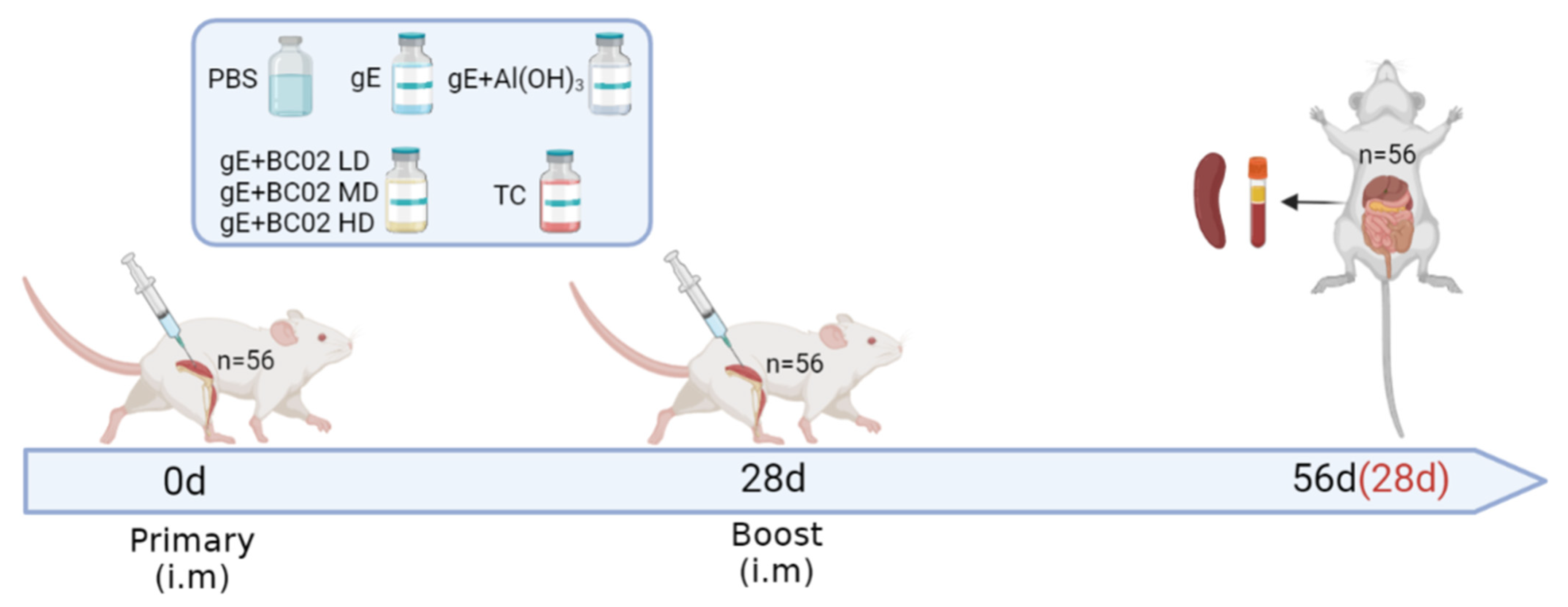
2.4. Immunization and Anatomy of Mice
2.5. gE-Specific IFN-γ and IL-2 ELISPOT Assays
2.6. VZV Fluorescent Antibody to Membrane Antigen (FAMA) Assays
2.7. Determination of VZV Neutralizing Antibody Titers by Plaque Reduction Test
2.8. Cell Culture Supernatant ELISA Assay
2.9. Cell Surface Costimulatory Molecules Flow Cytometry Assay
2.10. Cell Phagocytosis Confocal Microscopy Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
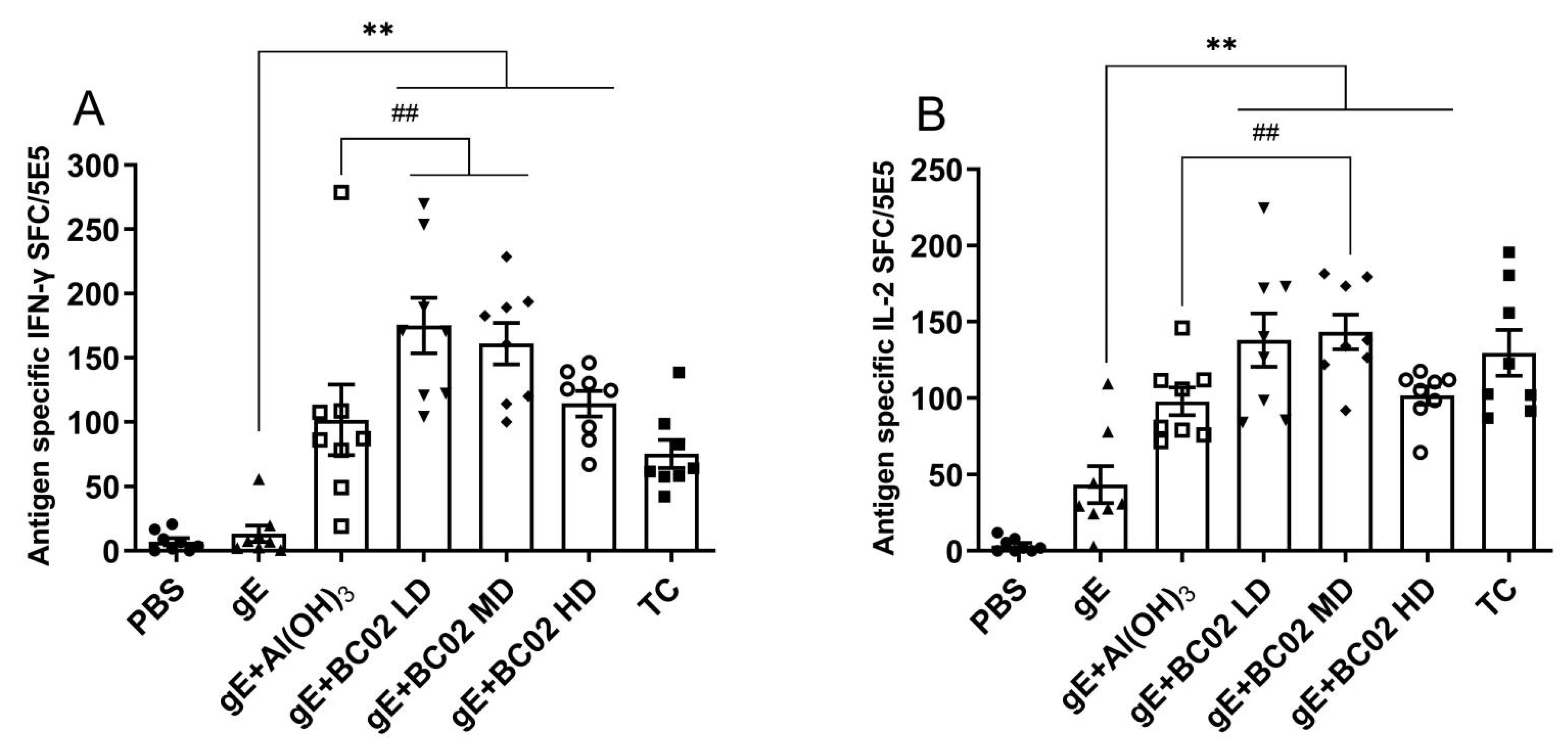
3.1. Higher Induction of gE Specific IFN-γ and IL-2 through the Experimental Vaccine with BC02
3.2. Efficient Induction of Anti-VZV Antibody by the Experimental Vaccine with BC02
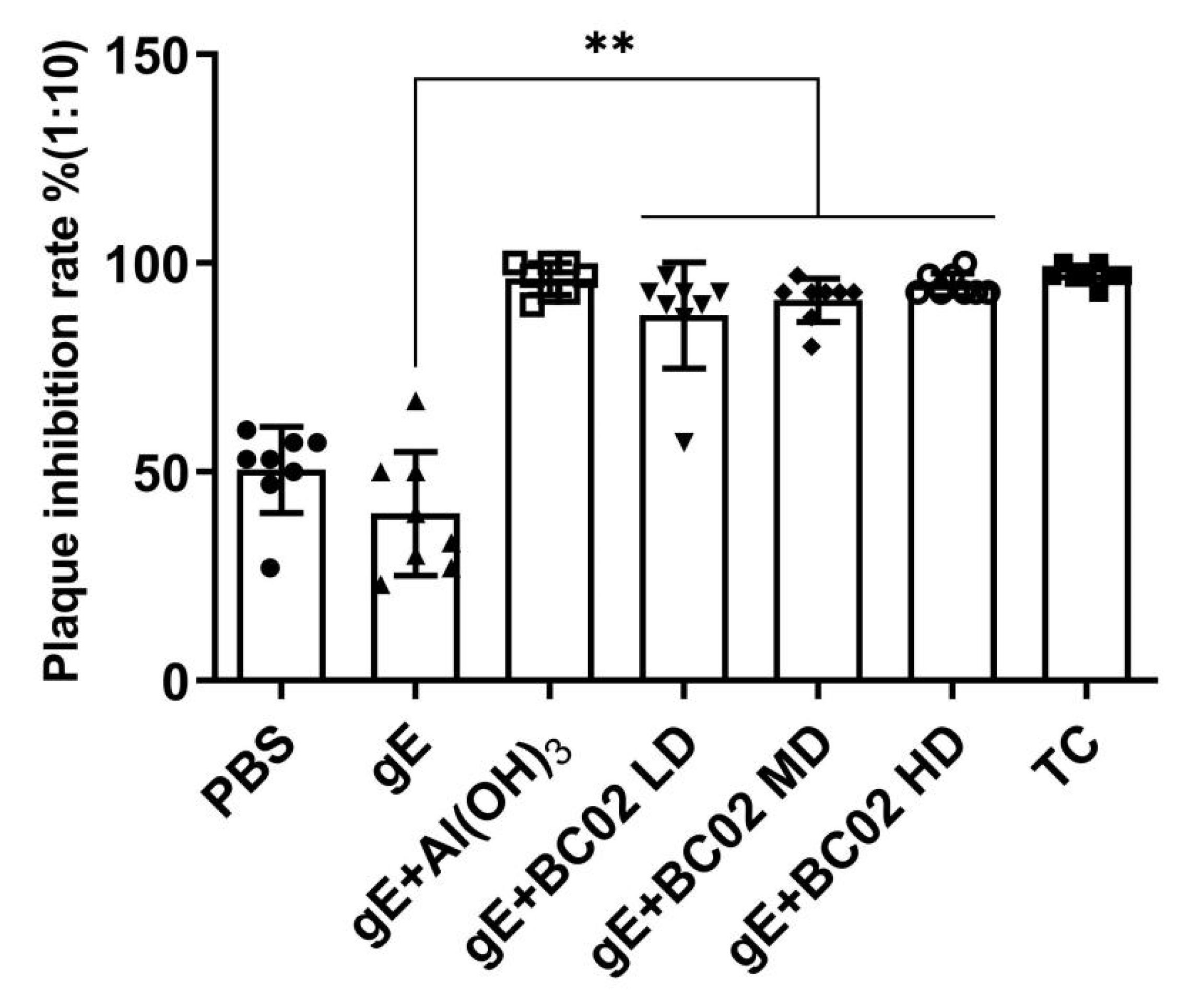
3.3. Efficient Induction of VZV Neutralizing Antibody through the Experimental Vaccine with BC02
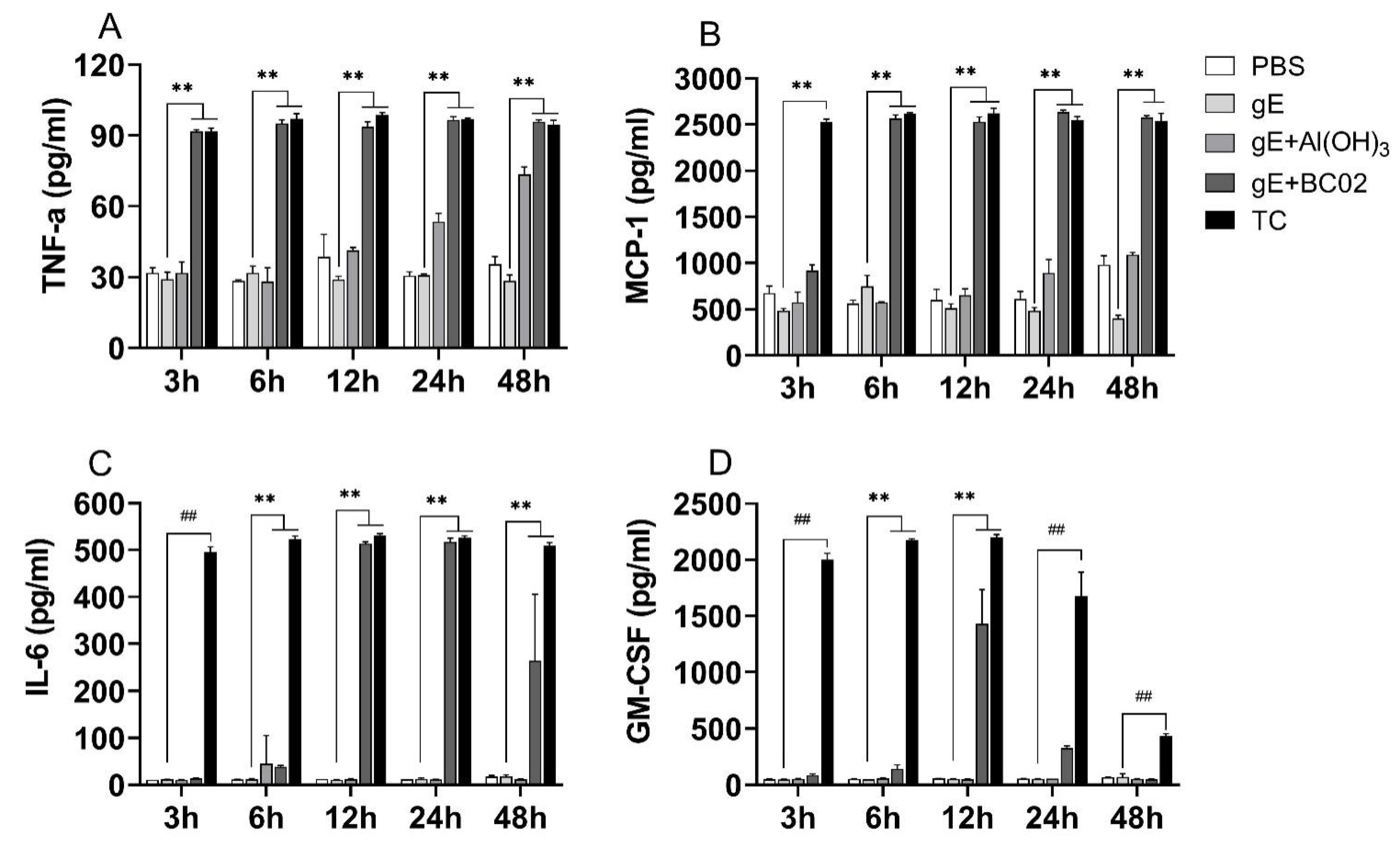
3.4. Higher Induction Cytokines of TNF-α, MCP-1, IL-6 and GM-CSF in RAW264.7 by the Experimental Vaccine with BC02
3.5. Higher Induction of Cell-Surface Costimulatory Molecules in RAW264.7 by the Experimental Vaccine with BC02
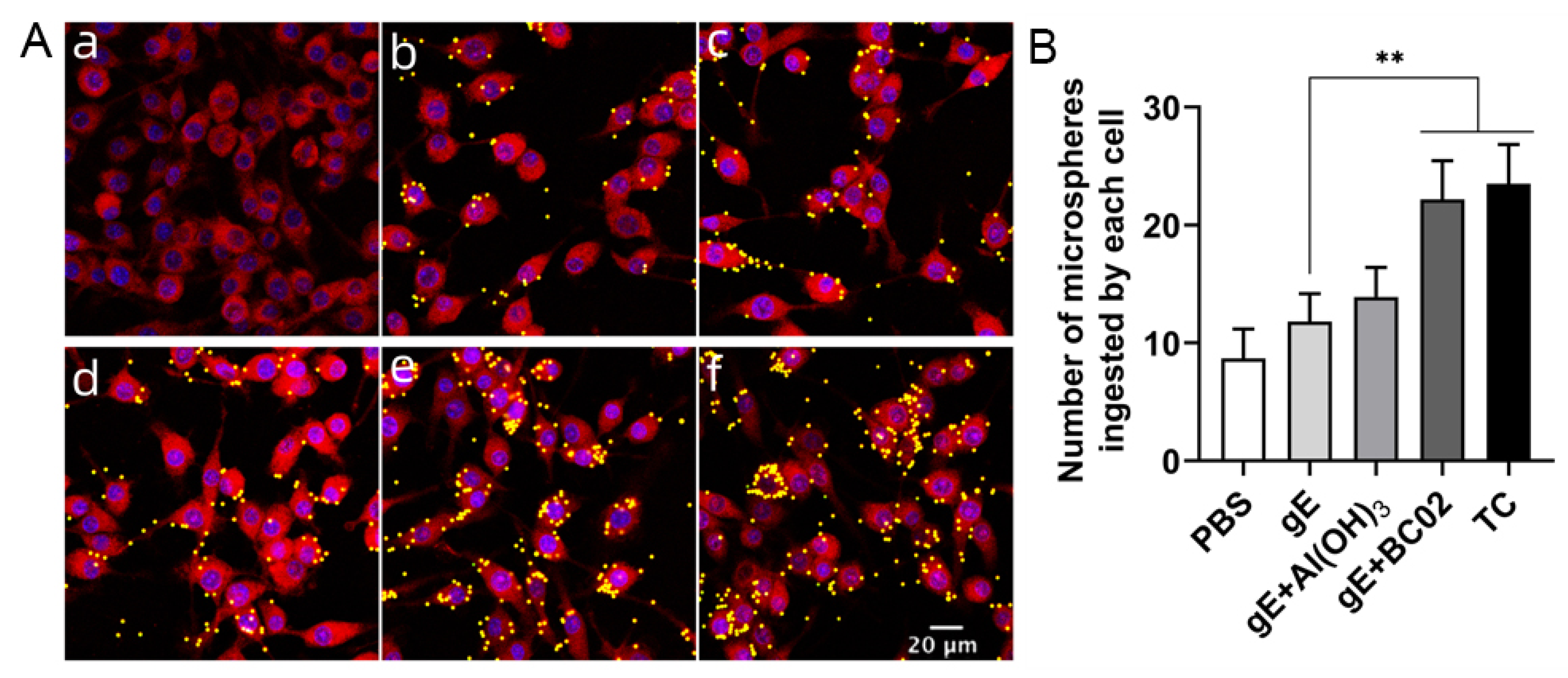
3.6. Enhancement of Phagocytosis in RAW264.7 by the Experimental Vaccine with BC02
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giudice, G.D.; Rappuoli, R.; Didierlaurent, A.M. Correlates of adjuvanticity: A review on adjuvants in licensed vaccines. Semin. Immunol. 2018, 39, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, T.J.; Zmolek, A.C.; Irvine, D.J. Beyond antigens and adjuvants: Formulating future vaccines. J. Clin. Investing 2016, 126, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, N.I.; Huis in’t Veld, L.G.M.; Raaijmakers, T.K.; Adema, G.J. Adjuvants Enhancing Cross-Presentation by Dendritic Cells: The Key to More Effective Vaccines? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, C.; Zhao, G.; Steinhagen, F.; Kinjo, T.; Klinman, D.M. CpG DNA as a vaccine adjuvant. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2011, 10, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Fu, L.; Wang, G.; Subbian, S.; Qin, C.; Zhao, A. Unmethylated CpG motif-containing genomic DNA fragment of Bacillus calmette-guerin promotes macrophage functions through TLR9-mediated activation of NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways. Innate Immun. 2020, 26, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmer, J.; Krieg, A.M. Immunotherapeutic applications of CpG oligodeoxynucleotide TLR9 agonists. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.; Lentino, J.; Kopp, J.; Murray, L.; Ellison, W.; Rhee, M.; Shockey, G.; Akella, L.; Erby, K.; Heyward, W.L.; et al. Immunogenicity of a two-dose investigational hepatitis B vaccine, HBsAg-1018, using a toll-like receptor 9 agonist adjuvant compared with a licensed hepatitis B vaccine in adults. Vaccines 2018, 36, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.M.; Chang, S.C.; Cheng, H.Y.; Shih, S.R.; Lien, C.E. Durability and Immunogenicity of Neutralizing Antibodies Response against Omicron Variants after Three Doses of Subunit SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine MVC-COV1901: An Extension to an Open-Label, Dose-Escalation Phase 1 Study. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2022, 11, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.M.; Liu, M.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Lee, W.S.; Hwang, S.J.; Cheng, S.H.; Ko, W.C.; Hwang, K.P.; Wang, N.C.; Lee, Y.L.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of CpG 1018 and aluminium hydroxide-adjuvanted SARS-CoV-2 S-2P protein vaccine MVC-COV1901: Interim results of a large-scale, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial in Taiwan. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 1396–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, L.; Smolenov, I.; Han, H.H.; Li, P.; Hosain, R.; Rockhold, F.; Clemens, S.A.C.; Roa, C., Jr.; Borja-Tabora, C.; Quinsaat, A.; et al. Efficacy of the adjuvanted subunit protein COVID-19 vaccine, SCB-2019: A phase 2 and 3 multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabarsi, P.; Anjidani, N.; Shahpari, R.; Roshanzamir, K.; Fallah, N.; Andre, G.; Petrovsky, N.; Barati, S. Immunogenicity and safety of SpikoGen®, an adjuvanted recombinant SARS-CoV-2 spike protein vaccine as a homologous and heterologous booster vaccination: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Immunology 2022, 167, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z.Y.; Chen, B.W.; Du, W.X.; Su, C.; Shen, X.B.; Zhao, A.H.; Dong, N.; Wang, Y.J.; et al. The development and preliminary evaluation of a new Mycobacterium tuberculosis vaccine comprising Ag85b, HspX and CFP-10:ESAT-6 fusion protein with CpG DNA and aluminum hydroxide adjuvants. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.C.; Zhang, J.; Bo, S.Y.; Xin, X.F.; Wang, G.Z. Immune effect of STAg combined with BCG-DNA and aluminum hydroxide adjuvant in mice. Chin. J. Biol. 2011, 24, 1177–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.L.; Fu, L.L.; Wang, G.Z.; Yang, X.M.; Zhao, A.H. Synergistic enhancement of macrophage innate immune response with BC02 complex adjuvant. Chin. J. Biol. 2018, 31, 941–948. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.L.; Fu, L.L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.Z.; Zhao, A.H. Analysis of synergistic enhancement of innate immune response by BC02 compound adjuvant components. Chin. J. Biol. 2022, 35, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.B.; Chen, B.W.; Den, H.Q.; Su, C.; Shen, X.B.; Du, W.X.; Yang, L.; Wang, G.Z.; Xu, M. Analysis of Koch phenomenon of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected guinea pigs vaccinated with recombinant tuberculosis vaccine AEC/BC02. Chin. J. Tuberc. Respir. 2016, 39, 524–528. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.B.; Yang, L.; Su, C.; Shen, X.B.; Chen, B.W.; Wang, G.Z.; Du, W.X. Therapeutic evaluation of antibiotics combined with recombinant tuberculosis vaccine AEC/BC02 in a guinea pig model of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Chin. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 38, 414–419. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, C.; Du, W.; Shen, X.; Su, C.; Wu, Y.; Xu, M. Therapeutic Effect of Subunit Vaccine AEC/BC02 on Mycobacterium tuberculosis Post-Chemotherapy Relapse Using a Latent Infection Murine Model. Vaccines 2022, 10, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.I. Clinical practice: Herpes zoster. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Zostavax [shingles (herpes zoster) vaccine (live)]: EU Summary of Product Characteristics. 2016. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/ (accessed on 14 March 2016).
- Harpaz, R.; Ortega-Sanchez, I.R.; Seward, J.F.; Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevention of herpes zoster: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2008, 57, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Dooling, K.L.; Guo, A.; Patel, M.; Lee, G.M.; Moore, K.; Belongia, E.A.; Harpaz, R. Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices for Use of Herpes Zoster Vaccines. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.K.; Riley, L.E.; Hunter, P.; Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices; Bridges, C.B.; Woods, L.; Wilson, A. Recommended Immunization Schedule for Adults Aged 19 Years or Older, United States, 2018. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 168, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, C.; Lee, J.; Sommer, M.; Grose, C.; Arvin, A.M. The requirement of varicella zoster virus glycoprotein E (gE) for viral replication and effects of glycoprotein I on gE in melanoma cells. Virology 2002, 304, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berarducci, B.; Rajamani, J.; Reichelt, M.; Sommer, M.; Zerboni, L.; Arvin, A.M. Deletion of the first cysteine-rich region of the varicella-zoster virus glycoprotein E ectodomain abolishes the gE and gI interaction and differentially affects cell-cell spread and viral entry. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berarducci, B.; Rajamani, J.; Zerboni, L.; Che, X.; Sommer, M.; Arvin, A.M. Functions of the unique N-terminal region of glycoprotein E in the pathogenesis of varicella-zoster virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garçon, N.; Chomez, P.; Van Mechelen, M. GlaxoSmithKline Adjuvant Systems in vaccines: Concepts, achievements and perspectives. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2007, 6, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garçon, N.; Van Mechelen, M. Recent clinical experience with vaccines using MPL- and QS-21-containing adjuvant systems. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2011, 10, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.; HogenEsch, H.; Hem, S.L. Relationship between the degree of antigen adsorption to aluminum hydroxide adjuvant in interstitial fluid and antibody production. Vaccines 2003, 21, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimaniol, A.C.; Gras, G.; Verdier, F.; Capel, F.; Grigoriev, V.B.; Porcheray, F.; Sauzeat, E.; Fournier, J.G.; Clayette, P.; Siegrist, C.A.; et al. Aluminum hydroxide adjuvant induces macrophage differentiation towards a specialized antigen-presenting cell type. Vaccines 2004, 22, 3127–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, A.; Asanuma, H.; Rinki, M.; Sharp, M.; Wong, R.M.; Blume, K.; Arvin, A.M. Use of an inactivated varicella vaccine in recipients of hematopoietic-cell transplants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.J.; Oxman, M.N.; Zhang, J.H.; Johnson, G.R.; Stanley, H.; Hayward, A.R.; Caulfield, M.J.; Irwin, M.R.; Smith, J.G.; Clair, J.; et al. Varicella-zoster virus-specific immune responses in elderly recipients of a herpes zoster vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, A.; Zhang, J.H.; Oxman, M.N.; Johnson, G.R.; Hayward, A.R.; Caulfield, M.J.; Irwin, M.R.; Clair, J.; Smith, J.G.; Stanley, H.; et al. Varicella-zoster virus-specific immune responses to herpes zoster in elderly participants in a trial of a clinically effective zoster vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxman, M.N. Zoster vaccine: Current status and future prospects. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fochesato, M.; Dendouga, N.; Boxus, M. Comparative preclinical evaluation of AS01 versus other Adjuvant Systems in a candidate herpes zoster glycoprotein E subunit vaccine. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2016, 12, 2092–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendouga, N.; Fochesato, M.; Lockman, L.; Mossman, S.; Giannini, S.L. Cell-mediated immune responses to a varicella-zoster virus glycoprotein E vaccine using both a TLR agonist and QS21 in mice. Vaccines 2012, 30, 3126–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, B.L.; Steele, R.W.; Beard, O.W.; Wood, J.S.; Cain, T.D.; Marmer, D.J. Immune responses to varicella-zoster in the aged. Arch. Intern. Med. 1982, 142, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Moriishi, E.; Okamoto, S.; Okuno, Y.; Iso, H.; Asada, H.; Yamanishi, K.; Mori, Y.; Shozu Herpes Zoster Study group. A community-based survey of varicella-zoster virus-specific immune responses in the elderly. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 55, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, H. VZV-specific cell-mediated immunity, but not humoral immunity, correlates inversely with the incidence of herpes zoster and the severity of skin symptoms and zoster-associated pain: The SHEZ study. Vaccines 2019, 37, 6776–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grose, C.; Edmond, B.J.; Brunell, P.A. Complement-enhanced neutralizing antibody response to varicella-zoster virus. J. Infect. Dis. 1979, 139, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, F.; Tritto, E.; Muzzi, A.; Monaci, E.; Bagnoli, F.; Iavarone, C.; O’Hagan, D.; Rappuoli, R.; De Gregorio, E. Molecular and cellular signatures of human vaccine adjuvants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10501–10506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabro, S.; Tortoli, M.; Baudner, B.C.; Pacitto, A.; Cortese, M.; O’Hagan, D.T.; De Gregorio, E.; Seubert, A.; Wack, A. Vaccine adjuvants alum and MF59 induce rapid recruitment of neutrophils and monocytes that participate in antigen transport to draining lymph nodes. Vaccines 2011, 29, 1812–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didierlaurent, A.M.; Collignon, C.; Bourguignon, P.; Wouters, S.; Fierens, K.; Fochesato, M.; Dendouga, N.; Langlet, C.; Malissen, B.; Lambrecht, B.N.; et al. Enhancement of adaptive immunity by the human vaccine adjuvant AS01 depends on activated dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, S.; Didierlaurent, A.; Bourguignon, P.; Delhaye, S.; Baras, B.; Jacob, V.; Planty, C.; Elouahabi, A.; Harvengt, P.; Carlsen, H.; et al. Adjuvant System AS03 containing α-tocopherol modulates innate immune response and leads to improved adaptive immunity. Vaccines 2011, 29, 2461–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didierlaurent, A.M.; Morel, S.; Lockman, L.; Giannini, S.L.; Bisteau, M.; Carlsen, H.; Kielland, A.; Vosters, O.; Vanderheyde, N.; Schiavetti, F.; et al. AS04, an aluminum salt- and TLR4 agonist-based adjuvant system, induces a transient localized innate immune response leading to enhanced adaptive immunity. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6186–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarosinski, K.W.; Carpenter, J.E.; Buckingham, E.M.; Jackson, W.; Knudtson, K.; Moffat, J.F.; Kita, H.; Grose, C. Cellular Stress Response to Varicella-Zoster Virus Infection of Human Skin Includes Highly Elevated Interleukin-6 Expression. In Open Forum Infectious Diseases; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018; Volume 5, p. ofy118. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Fu, L.; Guo, X.; Yang, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, G.; Zhao, A. Novel BC02 Compound Adjuvant Enhances Adaptive and Innate Immunity Induced by Recombinant Glycoprotein E of Varicella-Zoster Virus. Vaccines 2022, 10, 2155. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10122155
Li J, Fu L, Guo X, Yang Y, Dong J, Wang G, Zhao A. Novel BC02 Compound Adjuvant Enhances Adaptive and Innate Immunity Induced by Recombinant Glycoprotein E of Varicella-Zoster Virus. Vaccines. 2022; 10(12):2155. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10122155
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Junli, Lili Fu, Xiaonan Guo, Yang Yang, Jiaxin Dong, Guozhi Wang, and Aihua Zhao. 2022. "Novel BC02 Compound Adjuvant Enhances Adaptive and Innate Immunity Induced by Recombinant Glycoprotein E of Varicella-Zoster Virus" Vaccines 10, no. 12: 2155. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10122155
APA StyleLi, J., Fu, L., Guo, X., Yang, Y., Dong, J., Wang, G., & Zhao, A. (2022). Novel BC02 Compound Adjuvant Enhances Adaptive and Innate Immunity Induced by Recombinant Glycoprotein E of Varicella-Zoster Virus. Vaccines, 10(12), 2155. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10122155





