Correlations between Cytokine Levels, Liver Function Markers, and Neuropilin-1 Expression in Patients with COVID-19
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Population
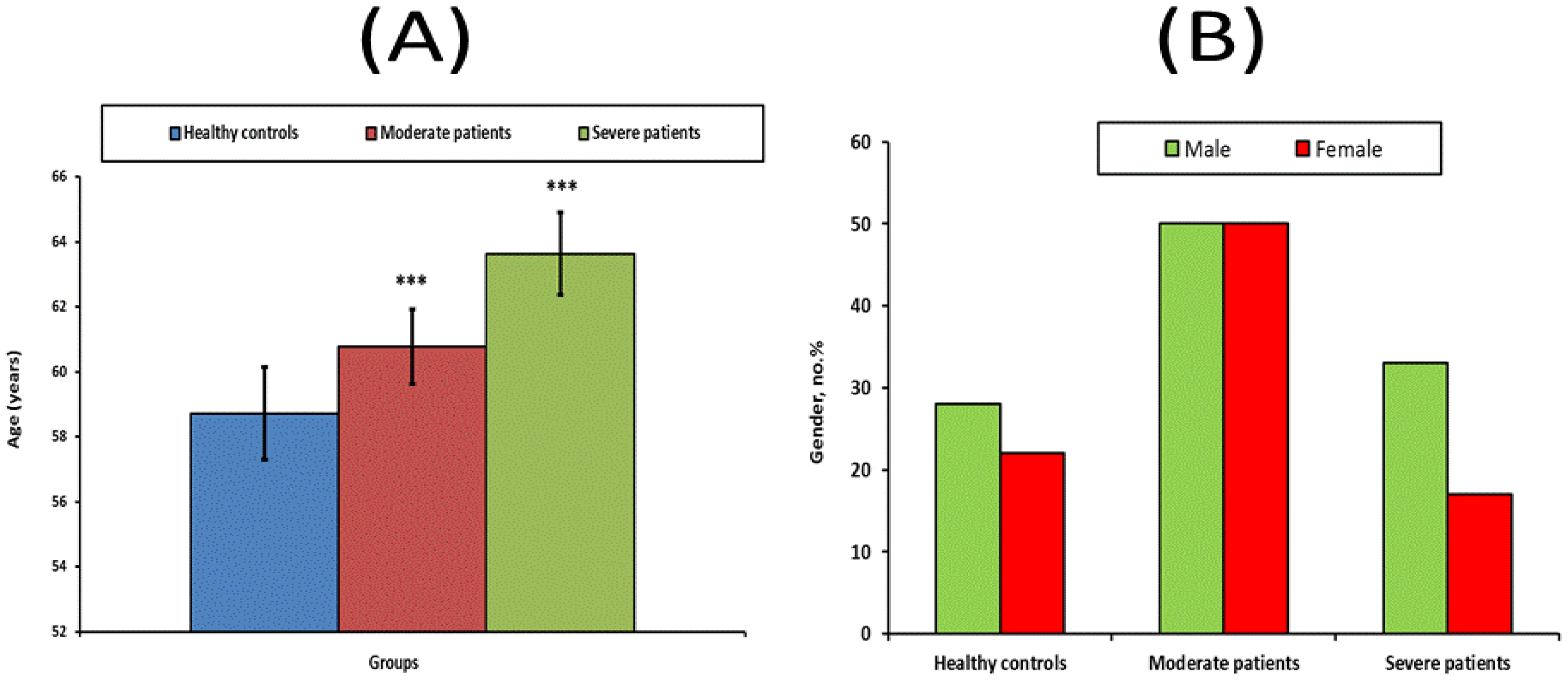
2.2. Patients
2.3. Laboratory Assay
2.4. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) qRT-PCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhama, K.; Khan, S.; Tiwari, R.; Sircar, S.; Bhat, S.; Malik, Y.S.; Singh, K.P.; Chaicumpa, W.; Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J. Coronavirus Disease 2019–COVID-19. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00028-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2020. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 3 March 2021).
- Keam, S.; Megawati, D.; Patel, S.K.; Tiwari, R.; Dhama, K.; Harapan, H. Immunopathology and immunotherapeutic strategies in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection. Rev. Med. Virol. 2020, 30, e2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fara, A.; Mitrev, Z.; Rosalia, R.A.; Assas, B.M. Cytokine storm and COVID-19: A chronicle of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, C.T.; Goepp, M.; Rossi, A.G.; Yao, C. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, prostaglandins, and COVID-19. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 4899–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A.; Huuskonen, J.; Ojala, J.; Kauppinen, A.; Kaarniranta, K.; Suuronen, T. Activation of innate immunity system during aging: NFkB signaling is the molecular culprit of inflamm-aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2008, 7, 83–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltimore, D. Discovering NF-kappaB. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000026.6. [Google Scholar]
- Cogswell, P.C.; Kashatus, D.F.; Keifer, J.A.; Guttridge, D.C.; Reuther, J.Y.; Bristow, C.; Roy, S.; Nicholson, D.W.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr. NF-kappa B and I kappa B alpha are found in the mitochondria. Evidence for regulation of mitochondrial gene expression by NF-kappa B. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2963–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lenardo, M.J.; Baltimore, D. 30 Years of NF-κB: A Blossoming of Relevance to Human Pathobiology. Cell 2017, 168, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.; Ji, J.; Wen, C. Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: The current evidence and treatment strategies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battagello, D.S.; Dragunas, G.; Klein, M.O.; Ayub, A.L.P.; Velloso, F.J.; Correa, R.G. Unpc COVID-19: Tissue-related signaling pathways associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 2137–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Zhou, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Tao, Y.; Xie, C.; Ma, K.; Shang, K.; Wang, W. Dysregulation of immune response in patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayi, B.S.; Leibowitz, J.A.; Woods, A.T.; Ammon, K.A.; Liu, A.E.; Raja, A. The role of Neuropilin-1 in COVID-19. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, R.H.; Elesawy, B.H.; Ali, T.M.; Abdallah, M.; Assal, H.H.; Ahmed, A.E.; Ahmed, O.M. Correlations between Kidney and Heart Function Bioindicators and the Expressions of Toll-Like, ACE2, and NRP-1 Receptors in COVID-19. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, R.H.; Abdallah, M.; Ali, T.M.; Ahmed, A.E.; Assal, H.H.; Elesawy, B.H.; Ahmed, O.M. The Associations between Cytokine Levels, Kidney and Heart Function Biomarkers, and Expression Levels of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2 and Neuropilin-1 in COVID-19 Patients. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lascarrou, J.B.; Colin, G.; Le Thuaut, A.; Serck, N.; Ohana, M.; Sauneuf, B.; Geri, G.; Mesland, J.-B.; Ribeyre, G.; Hussenet, C.; et al. Predictors of Negative First SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR despite Final Diagnosis of COVID-19 and Association with Outcome. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woloshin, S.; Patel, N.; Kesselheim, A.S. False Negative Tests for SARS-CoV-2 Infection—Challenges and Implications. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinloch, N.N.; Ritchie, G.; Brumme, C.J.; Dong, W.; Dong, W.; Lawson, T.; Jones, R.B.; Montaner, J.S.G.; Leung, V.; Romney, M.G.; et al. Suboptimal Biological Sampling as a Probable Cause of False-Negative COVID-19 Diagnostic Test Results. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 899–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harahwa, T.A.; Lai Yau, T.H.; Lim-Cooke, M.-S.; Al-Haddi, S.; Zeinah, M.; Harky, A. The Optimal Diagnostic Methods for COVID-19. Diagn. Berl. Ger. 2020, 7, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halalau, A.; Imam, Z.; Karabon, P.; Mankuzhy, N.; Shaheen, A.; Tu, J.; Carpenter, C. External Validation of a Clinical Risk Score to Predict Hospital Admission and In-Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. Ann. Med. 2021, 53, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynants, L.; Calster, B.V.; Collins, G.S.; Riley, R.D.; Heinze, G.; Schuit, E.; Bonten, M.M.J.; Dahly, D.L.; Damen, J.A.A.; Debray, T.P.A.; et al. Prediction Models for Diagnosis and Prognosis of COVID-19: Systematic Review and Critical Appraisal. BMJ 2020, 369, m1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, Y.; Yang, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, T.; Chen, Z.; Yao, R.; Liang, Z. Development and Validation a Nomogram for Predicting the Risk of Severe COVID-19: A Multi-Center Study in Sichuan, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haimovich, A.D.; Ravindra, N.G.; Stoytchev, S.; Young, H.P.; Wilson, F.P.; van Dijk, D.; Schulz, W.L.; Taylor, R.A. Development and Validation of the Quick COVID-19 Severity Index: A Prognostic Tool for Early Clinical Decompensation. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2020, 76, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Yang, P.; Xie, Y.; Woodruff, H.C.; Rao, X.; Guiot, J.; Frix, A.-N.; Louis, R.; Moutschen, M.; Li, J.; et al. Development of a Clinical Decision Support System for Severity Risk Prediction and Triage of COVID-19 Patients at Hospital Admission: An International Multicentre Study. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2001104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Wu, D.; Guo, W.; Cao, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Yu, H.; et al. Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2620–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gella, F.J.; Olivella, T.; Cruz, P.M.; Arenas, J.; Moreno, R.; Durban, R.; Gomez, J.A. A simple procedure for routine determination of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase with pyridoxal phosphate. Clin. Chim. Acta 1985, 153, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumas, B.T.; Watson, W.A.; Biggs, H.G. Determination of serum albumin. J. Clin. Chem. Acta 1971, 31, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 20.0; IBM Corp.: Armonk, NY, USA, 2011.
- Wolfel, R.; Corman, V.M.; Guggemos, W.; Seilmaier, M.; Zange, S.; Müller, M.A.; Niemeyer, D.; Jones, T.C.; Vollmar, P.; Rothe, C.; et al. Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature 2020, 581, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantuti-Castelvetri, L.; Ojha, R.; Pedro, L.D.; Djannatian, M.; Franz, J.; Kuivanen, S.; Kallio, K.; Kaya, T.; Anastasina, M.; Smura, T.; et al. Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and provides a possible pathway into the central nervous system. BioRxiv 2020, 10, 137802. [Google Scholar]
- Ghez, D.; Lepelletier, Y.; Lambert, S.; Fourneau, J.-M.; Blot, V.; Janvier, S.; Arnulf, B.; van Endert, P.; Heveker, N.; Pique, C.; et al. Neuropilin-1 is involved in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 entry. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6844–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaben, M.; Jae, L.; Herbert, A.S.; Kuehne, A.I.; Stubbs, S.H.; Chou, Y.-Y.; Blomen, V.A.; Kirchhausen, T.; Dye, J.M.; Brummelkamp, T.R.; et al. NRP2 and CD63 Are Host Factors for Lujo Virus Cell Entry. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 688–696.e685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teesalu, T.; Sugahara, K.N.; Kotamraju, V.R.; Ruoslahti, E. C-end rule peptides mediate neuropilin-1-dependent cell, vascular, and tissue penetration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16157–16162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wan, S.; Yi, Q.; Fan, S.; Lv, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, L.; Lang, C.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, K.; Yi, Z.; et al. Characteristics of lymphocyte subsets and cytokines in peripheral blood of 123 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (NCP). MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj, J.; Yatim, N.; Barnabei, L.; Corneau, A.; Boussier, J.; Pere, H.; Smith, N.; Charbit, B.; Bondet, V.; Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; et al. Impaired type I interferon activity and exacerbated inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients. Science 2020, 369, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates, J.A.; FitzGerald, G.A.; Branch, R.A.; Jackson, E.K.; Knapp, H.R.; Roberts, L.J. Clinical implications of prostaglandin and thromboxane A2 formation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 319, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricke-Hoch, M.; Stelling, E.; Lasswitz, L.; Gunesch, A.P.; Kasten, M.; Zapatero-Belinchon, F.J.; Brogden, G.; Gerold, G.; Pietschmann, T.; Montiel, V.; et al. Impaired immune response mediated by prostaglandin E2 promotes severe COVID-19 disease. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhodary, M.S.M. Treatment of COVID-19 by Controlling the Activity of the Nuclear Factor-Kappa, B. CellBio 2020, 9, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Takamori, M.; Shimoyama, Y.; Ishibashi, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Koshihara, Y. Regulation by PGE2 of the production of interleukin-6, macrophage colony stimulating factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor in human synovial fibroblasts. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 136, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-S.; Han, I.-H.; Lee, H.R.; Lee, H.-M. Prostaglandin E2 induces IL-6 and IL-8 production by the EP receptors/Akt/NF-κB pathways in nasal polyp-derived fibroblasts. Allergy Asthma. Immunol. Res. 2014, 6, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, P.; Bartle, L.; Barbacane, R.C.; Reale, M.; Placido, F.C.; Sipe, J. Synergistic activation ofserum amyloid A(SAA) by IL-6 and IL-1 in combination on human Hep 3B hepatoma cell line. Role of PGE2 and IL-1 receptor antagonist. Immunol. Investig. 1995, 24, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammock, B.D.; Wang, W.; Gilligan, M.M.; Panigrahy, D. Eicosanoids: The overlooked storm in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)? Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 1782–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notz, Q.; Schmalzing, M.; Wedekink, F.; Schlesinger, T.; Gernert, M.; Herrmann, J.; Sorger, L.; Weismann, D.; Schmid, B.; Sitter, M.; et al. Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Responses in Severe COVID-19-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome—An Observational Pilot Study. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 581338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, R.; Deng, X.; Li, F.; Liang, K.; Shi, Y. Immunopathological characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 cases in Guangzhou, China. Immunology 2020, 160, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prompetchara, E.; Ketloy, C.; Palaga, T. Immune responses in COVID-19 and potential vaccines: Lessons learned from SARS and MERS epidemic. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Campard, D.; Vasse, M.; Rose-John, S.; Poyer, F.; Lamacz, M.; Vannier, J.P. Multilevel regulation of IL-6R by IL-6-sIL-6R fusion protein according to the primitiveness of peripheral blood-derived CD133+cells. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 1302–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M. Clinical features of cytokine storm syndrome. In Cytokine Storm Syndrome; Cron, R., Behrens, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, D.A.; Adlimoghaddam, A.; Albensi, B.C. The Effect of COVID-19 on NF-κB and Neurological Manifestations of Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 4178–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giridharan, S.; Srinivasan, M. Mechanisms of NF-κB p65 and strategies for therapeutic manipulation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Zheng, K.I.; Yan, Q.Q.; Rios, R.S.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Van Poucke, S.; Liu, W.Y.; Zheng, M.H. COVID-19 and Liver Dysfunction: Current Insights and Emergent Therapeutic Strategies. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2020, 8, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, R.J.; Lv, G.Y.; Liu, H.-Q. The mechanisms and strategies to protect from hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 19, 2036–2047. [Google Scholar]
- Santa Cruz, A.; Mendes-Frias, A.; Oliveira, A.I.; Dias, L.; Matos, A.R.; Carvalho, A.; Capela, C.; Pedrosa, J.; Gil Castro, A.; Silvestre, R. Interleukin-6 Is a Biomarker for the Development of Fatal Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Pneumonia. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 613422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shabrawy, M.; Alsadik, M.E.; El-Shafei, M.; Abdelmoaty, A.A.; Alazzouni, A.S.; Esawy, M.M.; Shabana, M.A. Interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein/albumin ratio as predictors of COVID-19 severity and mortality. Egypt. J. Bronchol. 2021, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Healthy (n = 50) | Moderate Patients (n = 50) | Severe Patients (n = 50) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALT (U/I) | 16.35 ± 0.71 | 98.44 ± 7.64 ***,+++ | 152.72 ± 11.37 *** |
| AST(U/I) | 21.91 ± 1.00 | 83.54 ± 4.72 ***,+ | 100.82 ± 9.1 *** |
| Albumin (g/dl) | 4.00 ± 0.06 | 3.80 ± 0.14 ***,++ | 3.06 ± 0.05 *** |
| CRP(mg/dl) | 1.96 ± 0.20 | 51.75 ± 6.21 ***.+++ | 77.8 ± 3.33 *** |
| IL-1β (pg/mL) | 15.20 ± 0.51 | 35.57 ± 1.88 ***,+ | 29.96 ± 2.06 *** |
| IL-4 (pg/mL) | 4.07 ± 0.24 | 6.78 ± 0.27 *** | 6.48 ± 0.44 *** |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 10.37 ± 0.31 | 83.09 ± 5.25 ***,+++ | 110.37 ± 3.14 *** |
| IL-18 (pg/mL) | 116.08 ± 0.96 | 217.64 ± 7.47 *** | 229.68 ± 6.97 *** |
| IL-35 (pg/mL) | 76.30 ± 1.39 | 106.03 ± 1.57 *** | 105.05 ± 1.55 *** |
| PGE2(pg/mL) | 136.93 ± 1.45 | 260.44 ± 8.55 *** | 253.15 ± 8.78 *** |
| TXA2 (pg/mL) | 114.96 ± 0.73 | 241.74 ± 7.02 ***,+++ | 211.75 ± 6.91 *** |
| NF-κB p50 expression | 1.01 ± 0.002 | 2.29 ± 0.12 *** | 2.28 ± 0.09 *** |
| NF-κB p65 expression | 1.02 ± 0.003 | 4.38 ± 0.21 ***,+ | 3.89 ± 0.16 *** |
| NRP-1 expression | 1.01 ± 0.002 | 4.28 ± 0.16 *** | 3.98 ± 0.19 *** |
| CRP | PGE2 | TXA2 | NF-κB p50 | NF-κB p65 | NRP-1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | p | R | p | R | p | R | p | R | p | R | p | |
| ALT (U/L) | 0.421 *** | 0.000 | 0.303 ** | 0.002 | 0.407 *** | 0.000 | 0.370 *** | 0.000 | 0.362 *** | 0.000 | 0.417 *** | 0.000 |
| AST(U/L) | 0.477 *** | 0.000 | 0.305 ** | 0.002 | 0.331 ** | 0.001 | 0.253 * | 0.011 | 0.320 ** | 0.001 | 0.350 *** | 0.000 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | −0.646 *** | 0.000 | −0.162 | 0.106 | 0.001 | 0.994 | −0.082 | 0.417 | 0.036 | 0.722 | −0.161 | 0.110 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 1 | 0.540 *** | 0.000 | 0.515 *** | 0.000 | 0.421 *** | 0.000 | 0.461 *** | 0.000 | 0.627 *** | 0.000 | |
| IL-1β (pg/mL) | 0.504 *** | 0.000 | 0.464 *** | 0.000 | 0.637 *** | 0.000 | 0.481 *** | 0.000 | 0.629 *** | 0.000 | 0.604 *** | 0.000 |
| IL-4 (pg/mL) | 0.375 *** | 0.000 | 0.623 *** | 0.000 | 0.681 *** | 0.000 | 0.533 *** | 0.000 | 0.463 *** | 0.000 | 0.631 *** | 0.000 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 0.612 *** | 0.000 | 0.749 *** | 0.000 | 0.700 *** | 0.000 | 0.572 *** | 0.000 | 0.549 *** | 0.000 | 0.817 *** | 0.000 |
| IL-18 (pg/mL) | 0.634 *** | 0.000 | 0.692 *** | 0.000 | 0.718 *** | 0.000 | 0.590 *** | 0.000 | 0.611 *** | 0.000 | 0.778 *** | 0.000 |
| IL-35 (pg/mL) | 0.557 *** | 0.000 | 0.624 *** | 0.000 | 0.734 *** | 0.000 | 0.619 *** | 0.000 | 0.671 *** | 0.000 | 0.775 *** | 0.000 |
| PGE2 (pg/mL) | 0.540 *** | 0.000 | 1 | 0.657 *** | 0.000 | 0.487 *** | 0.000 | 0.610 *** | 0.000 | 0.711 *** | 0.000 | |
| TXA2 (pg/mL) | 0.515 *** | 0.000 | 0.657 *** | 0.000 | 1 | 0.773 *** | 0.000 | 0.850 *** | 0.000 | 0.835 *** | 0.000 | |
| NF-κB p50 expression | 0.421 *** | 0.000 | 0.487 *** | 0.000 | 0.773 *** | 0.000 | 1 | 0.571 *** | 0.000 | 0.726 *** | 0.000 | |
| NF-κB p65 expression | 0.461 *** | 0.000 | 0.610 *** | 0.000 | 0.850 *** | 0.000 | 0.571 *** | 0.000 | 1 | 0.706 *** | 0.000 | |
| NRP-1 expression | 0.627 *** | 0.000 | 0.711 *** | 0.000 | 0.835 *** | 0.000 | 0.726 *** | 0.000 | 0.706 *** | 0.000 | 1 | |
| IL1β | IL4 | IL6 | IL18 | IL35 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | p | R | p | R | p | R | p | R | p | |
| ALT (U/L) | R | 0.502 | 0.227 * | 0.023 | 0.308 ** | 0.002 | 0.452 *** | 0.000 | 0.328 ** | 0.001 |
| AST(U/L) | 0.068 | 0.541 | 0.218 * | 0.029 | 0.318 ** | 0.001 | 0.460 *** | .000 | 0.332 ** | 0.001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 0.062 | 0.216 | −0.025 | 0.808 | −0.187 | 0.063 | −0.218 * | 0.029 | −0.140 | 0.164 |
| CRP(mg/dL) | −0.125 | 0.000 | 0.375 *** | 0.000 | 0.612 *** | 0.000 | 0.634 *** | 0.000 | 0.557 *** | 0.000 |
| IL-1β (pg/mL) | 0.504 *** | 0.429 *** | 0.000 | 0.530 *** | 0.000 | 0.445 *** | 0.000 | 0.610 *** | 0.000 | |
| IL-4 (pg/mL) | 1 | 0.000 | 1 | 0.513 *** | 0.000 | 0.495 *** | 0.000 | 0.592 *** | 0.000 | |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 0.429 *** | 0.000 | 0.513 *** | 0.000 | 1 | 0.793 *** | 0.000 | 0.654 *** | 0.000 | |
| IL-18 (pg/mL) | 0.530 *** | 0.000 | 0.495 *** | 0.000 | 0.793 *** | 0.000 | 1 | 0.606 *** | 0.000 | |
| IL-35 (pg/mL) | 0.445 *** | 0.000 | 0.592 *** | 0.000 | 0.654 *** | 0.000 | 0.606 *** | 0.000 | 1 | |
| PGE2(pg/mL) | 0.610 *** | 0.000 | 0.623 *** | 0.000 | 0.749 *** | 0.000 | 0.692 *** | 0.000 | 0.624 *** | 0.000 |
| TXA2 (pg/mL) | 0.464 *** | 0.000 | 0.681 *** | 0.000 | 0.700 *** | 0.000 | 0.718 *** | 0.000 | 0.734 *** | 0.000 |
| NF-κB p50 expression | 0.637 *** | 0.000 | 0.533 *** | 0.000 | 0.572 *** | 0.000 | 0.590 *** | 0.000 | 0.619 *** | 0.000 |
| NF-κB p65 expression | 0.481 *** | 0.000 | 0.463 *** | 0.000 | 0.549 *** | 0.000 | 0.611 *** | 0.000 | 0.671 *** | 0.000 |
| NRP-1 expression | 0.629 *** | 0.000 | 0.631 ** | 0.000 | 0.817 *** | 0.000 | 0.778 *** | 0.000 | 0.775 *** | 0.000 |
| CRP | PGE2 | TXA2 | NF-κB p50 | NF-κB p50 | NRP-1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | p | R | p | R | p | R | p | R | p | R | p | |
| ALT (U/L) | 0.401 *** | 0.000 | 0.254 * | 0.011 | 0.361 *** | 0.000 | 0.299 ** | 0.002 | 0.423 *** | 0.000 | 0.103 | 0.309 |
| AST (U/L) | 0.334 ** | 0.001 | 0.155 | 0.123 | 0.340 ** | 0.001 | 0.318 ** | 0.001 | 0.397 *** | 0.000 | 0.092 | 0.361 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | −0.722 *** | 0.000 | −0.599 *** | 0.000 | −0.625-*** | 0.000 | −0.622 *** | 0.000 | −0.697 *** | 0.000 | −0.715 *** | 0.000 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 1 | 0.695 *** | 0.000 | 0.733 *** | 0.000 | 0.716 *** | 0.000 | 0.834 *** | 0.000 | 0.745 *** | 0.000 | |
| IL-1β (pg/mL) | 0.548 *** | 0.000 | 0.265 ** | 0.008 | 0.530 *** | 0.000 | 0.466 *** | 0.000 | 0.390 *** | 0.000 | 0.509 *** | 0.000 |
| IL4 (pg/mL) | 0.400 *** | 0.000 | 0.286 ** | 0.004 | 0.432 *** | 0.000 | 0.193 | 0.055 | 0.293 *** | 0.003 | 0.230 * | 0.021 |
| IL6 (pg/mL) | 0.838 *** | 0.000 | 0.799 *** | 0.000 | 0.775 *** | 0.000 | 0.773 *** | 0.000 | 0.838 *** | 0.000 | 0.811 *** | 0.000 |
| IL18 (pg/mL) | 0.737 *** | 0.000 | 0.754 *** | 0.000 | 0.670 *** | 0.000 | 0.707 *** | 0.000 | 0.785 *** | 0.000 | 0.731 *** | 0.000 |
| IL35 (pg/mL) | 0.685 *** | 0.000 | 0.640 *** | 0.000 | 0.632 *** | 0.000 | 0.728 *** | 0.000 | 0.669 *** | 0.000 | 0.708 *** | 0.000 |
| PGE2 (pg/mL) | 0.695 *** | 0.000 | 1 | 0.563 *** | 0.000 | 0.707 *** | 0.000 | 0.703 *** | 0.000 | 0.677 *** | 0.000 | |
| TXA2 (pg/mL) | 0.733 *** | 0.000 | 0.563 *** | 0.000 | 1 | 0.619 *** | 0.000 | 0.747 *** | 0.000 | 0.576 *** | 0.000 | |
| NF-κB p50 expression | 0.716 *** | 0.000 | 0.707 *** | 0.000 | 0.619 *** | 0.000 | 1 | 0.718 *** | 0.000 | 0.735 *** | 0.000 | |
| NF-κB p50 expression | 0.834 *** | 0.000 | 0.703 *** | 0.000 | 0.747 *** | 0.000 | 0.718 *** | 0.000 | 1 | 0.657 *** | 0.000 | |
| NRP-1 expression | 0.745 *** | 0.000 | 0.677 *** | 0.000 | 0.576 *** | 0.000 | 0.735 *** | 0.000 | 0.657 *** | 0.000 | 1 | |
| IL1β | IL4 | IL6 | IL18 | IL35 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | p | R | p | R | p | R | p | R | p | |
| ALT (U/L) | 0.268 ** | 0.007 | 0.313 ** | 0.002 | 0.288 ** | 0.004 | 0.258 ** | 0.009 | 0.199 * | 0.047 |
| AST (U/L) | 0.203 * | 0.043 | 0.204 * | 0.042 | 0.286 ** | 0.004 | 0.232 * | 0.020 | 0.200 * | 0.046 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | −0.495 *** | 0.000 | −0.330 ** | 0.001 | −0.722 *** | 0.000 | −0.694 *** | 0.000 | −0.631 *** | 0.000 |
| CRP(mg/dL) | 0.548 *** | 0.000 | 0.400 *** | 0.000 | 0.838 *** | 0.000 | 0.737 *** | 0.000 | 0.685 *** | 0.000 |
| IL-1β (pg/mL) | 1 | 0.348 *** | 0.000 | 0.544 *** | 0.000 | 0.466 *** | 0.000 | 0.450 *** | 0.000 | |
| IL-4 (pg/mL) | 0.348 *** | 0.000 | 1 | 0.387 *** | 0.000 | 0.341 ** | 0.001 | 0.425 *** | 0.000 | |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 0.544 *** | 0.000 | 0.387 *** | 0.000 | 1 | 0.805 *** | 0.000 | 0.763 *** | 0.000 | |
| IL-18 (pg/mL) | 0.466 *** | 0.000 | 0.341 ** | 0.001 | 0.805 *** | 0.000 | 1 | 0.706 *** | 0.000 | |
| IL-35 (pg/mL) | 0.450 *** | 0.000 | 0.425 *** | 0.000 | 0.763 *** | 0.000 | 0.706 *** | 0.000 | 1 | |
| PGE2 (pg/mL) | 0.265 *** | 0.008 | 0.286 ** | 0.004 | 0.799 *** | 0.000 | 0.754 *** | 0.000 | 0.640 *** | 0.000 |
| TXA2 (pg/mL) | 0.530 *** | 0.000 | 0.432 *** | 0.000 | 0.775 *** | 0.000 | 0.670 *** | 0.000 | 0.632 *** | 0.000 |
| NF-κB p50 expression | 0.466 *** | 0.000 | 0.193 | 0.055 | 0.773 *** | 0.000 | 0.707 *** | 0.000 | 0.728 *** | 0.000 |
| NF-κB p65 expression | 0.390 *** | 0.000 | 0.293 ** | 0.003 | 0.838 *** | 0.000 | 0.785 *** | 0.000 | 0.669 *** | 0.000 |
| NRP-1 expression | 0.509 *** | 0.000 | 0.230 * | 0.021 | 0.811 *** | 0.000 | 0.731 *** | 0.000 | 0.708 *** | 0.000 |
| AUC | CI 95% | p | Cut-Off Value | Sensitivity | Specificity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 0.656 | 0.517–0.742 | 0.002 | 24.3 pg/ml | 100% | 50% |
| TXA2 (pg/mL) | 0.843 | 0.782–0.904 | <0.001 | 213.95 pg/ml | 88% | 75% |
| NF-κB p50 expression | 0.735 | 0.657–0.814 | <0.001 | 1.47 (relative to control) | 80% | 56% |
| NF-κB p65 expression | 0.806 | 0.739–0.874 | <0.001 | 3.35 (relative to control) | 80% | 67% |
| AUC | CI 95% | p | Cut-Off Value | Sensitivity | Specificity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 0.844 | 0.783–0.904 | <0.001 | 51.0 pg/ml | 100% | 68% |
| TXA2 (pg/mL) | 0.657 | 0.571–0.742 | 0.002 | 148.7 pg/ml | 92% | 53% |
| NF-κB p50 expression | 0.765 | 0.690–0.839 | <0.001 | 1.84 (relative to control) | 74% | 74% |
| NF-κB p65 expression | 0.694 | 0.612–0.776 | <0.001 | 3.25 (relative to control) | 70% | 60% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Kazafy, S.A.; Fouad, Y.M.; Said, A.F.; Assal, H.H.; Ali, T.M.; Ahmed, A.E.; Elesawy, B.H.; Ahmed, O.M. Correlations between Cytokine Levels, Liver Function Markers, and Neuropilin-1 Expression in Patients with COVID-19. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101636
El Kazafy SA, Fouad YM, Said AF, Assal HH, Ali TM, Ahmed AE, Elesawy BH, Ahmed OM. Correlations between Cytokine Levels, Liver Function Markers, and Neuropilin-1 Expression in Patients with COVID-19. Vaccines. 2022; 10(10):1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101636
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Kazafy, Salma A., Yasser M. Fouad, Azza F. Said, Hebatallah H. Assal, Tarek M. Ali, Amr E. Ahmed, Basem H. Elesawy, and Osama M. Ahmed. 2022. "Correlations between Cytokine Levels, Liver Function Markers, and Neuropilin-1 Expression in Patients with COVID-19" Vaccines 10, no. 10: 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101636
APA StyleEl Kazafy, S. A., Fouad, Y. M., Said, A. F., Assal, H. H., Ali, T. M., Ahmed, A. E., Elesawy, B. H., & Ahmed, O. M. (2022). Correlations between Cytokine Levels, Liver Function Markers, and Neuropilin-1 Expression in Patients with COVID-19. Vaccines, 10(10), 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101636







