In Vitro Evaluation of Leuconostoc mesenteroides Cell-Free-Supernatant GBUT-21 against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Bacteria Growth
2.2. Bacteria Sample Preparation and Screening against SARS-CoV-2
2.3. Biochemical Characterization of LAB Isolate
2.4. Determination of Cytotoxity
2.5. MTT Assay
2.6. Estimation of Intracellular ROS
2.7. Immunofluorescent Assay
2.8. RT-qPCR
3. Results
3.1. Selection and Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolate
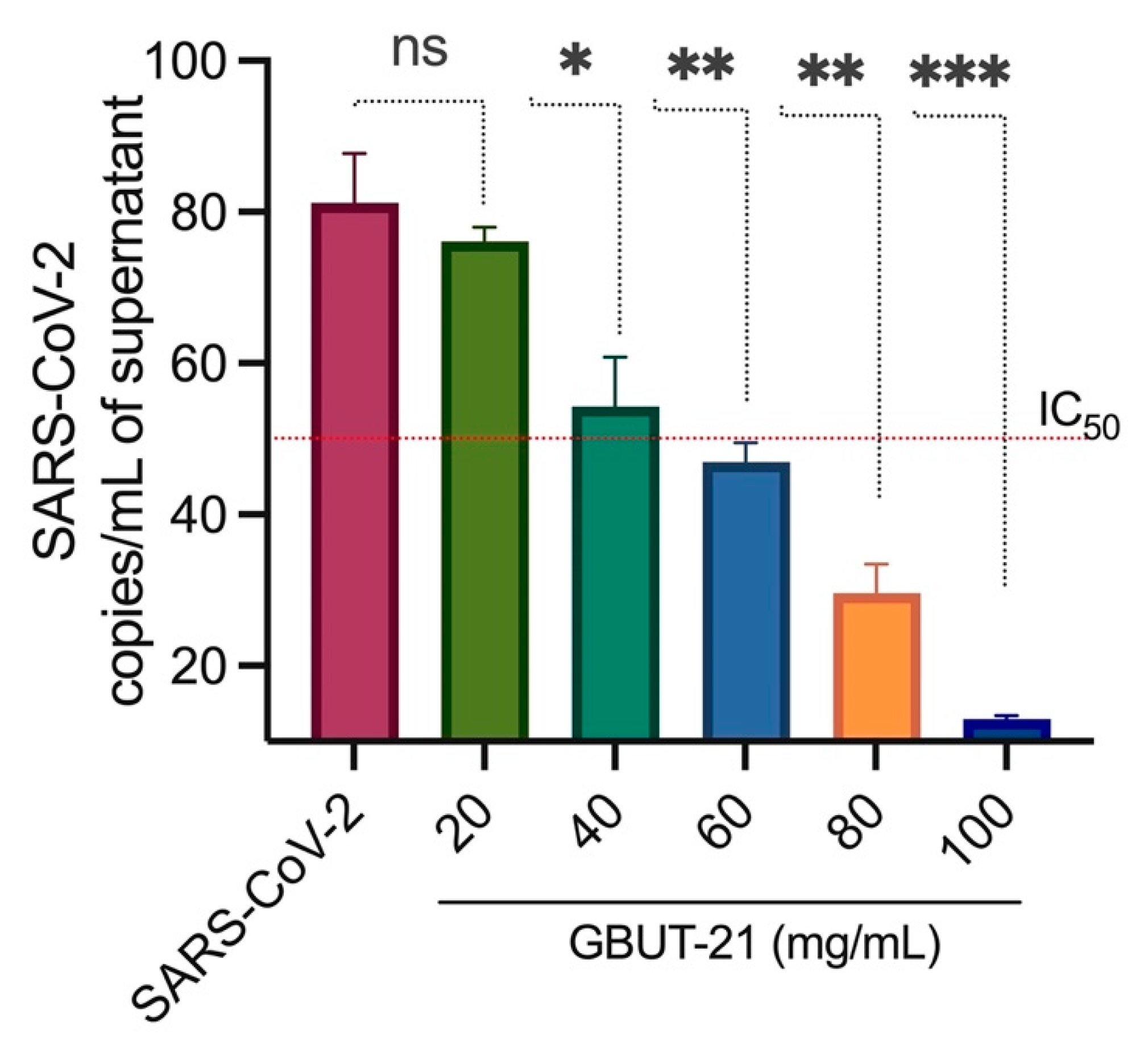
3.2. Virus Inhibition and Cell Viability
3.3. Estimation of Intracellular ROS
3.4. Antiviral Effect Depicted by Immunofluorescent Assay
3.5. Gene Expression Profile
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drosten, C.; Günther, S.; Preiser, W.; van der Werf, S.; Brodt, H.-R.; Becker, S.; Rabenau, H.; Panning, M.; Kolesnikova, L.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; et al. Identification of a Novel Coronavirus in Patients with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiris, J.S.M.; Lai, S.T.; Poon, L.L.M.; Guan, Y.; Yam, L.Y.C.; Lim, W.; Nicholls, J.; Yee, W.K.S.; Yan, W.W.; Cheung, M.T.; et al. Coronavirus as a Possible Cause of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. Lancet 2003, 361, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiken, T.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Schutten, M.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; van Amerongen, G.; van Riel, D.; Laman, J.D.; de Jong, T.; van Doornum, G.; Lim, W.; et al. Newly Discovered Coronavirus as the Primary Cause of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. Lancet 2003, 362, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.M.; van Boheemen, S.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Fouchier, R.A.M. Isolation of a Novel Coronavirus from a Man with Pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic Characterisation and Epidemiology of 2019 Novel Coronavirus: Implications for Virus Origins and Receptor Binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauer, S.A.; Grantz, K.H.; Bi, Q.; Jones, F.K.; Zheng, Q.; Meredith, H.R.; Azman, A.S.; Reich, N.G.; Lessler, J. The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) from Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases: Estimation and Application. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Ren, R.; Leung, K.S.M.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Wong, J.Y.; et al. Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Ni, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.; Ou, C.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Chakraborty, U.; Pal, J.; Karmakar, P. Silent Hypoxia: A Frequently Overlooked Clinical Entity in Patients with COVID-19. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e237207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Features of Patients Infected with 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of 99 Cases of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A Descriptive Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients with 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.J.; Choong, M.C.; Cheong, E.H.; Kalimuddin, S.; Duu Wen, S.; Phua, G.C.; Chan, K.S.; Haja Mohideen, S. Rapid Progression to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Review of Current Understanding of Critical Illness from COVID-19 Infection. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2020, 49, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriatopoulou, M.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Korompoki, E.; Fotiou, D.; Migkou, M.; Tzanninis, I.G.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Kastritis, E.; Terpos, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Emerging Treatment Strategies for COVID-19 Infection. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 21, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Marco, S.; Sichetti, M.; Muradyan, D.; Piccioni, M.; Traina, G.; Pagiotti, R.; Pietrella, D. Probiotic Cell-Free Supernatants Exhibited Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activity on Human Gut Epithelial Cells and Macrophages Stimulated with LPS. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 1756308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodaii, Z.; Ghaderian, S.M.H.; Natanzi, M.M. Probiotic Bacteria and Their Supernatants Protect Enterocyte Cell Lines from Enteroinvasive Escherichia Coli (EIEC) Invasion. Int. J. Mol. Cell Med. 2017, 6, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Izuddin, W.I.; Loh, T.C.; Foo, H.L.; Samsudin, A.A.; Humam, A.M.; Postbiotic, L. Plantarum RG14 Improves Ruminal Epithelium Growth, Immune Status and Upregulates the Intestinal Barrier Function in Post-Weaning Lambs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeyer, P.E.; Tang, H.; Ren, Y.; Bohannon, L.; Ramirez, Z.E.; Andermann, T.M.; Messina, J.A.; Sung, J.A.; Jensen, D.; Jung, S.-H.; et al. Daily Lactobacillus Probiotic versus Placebo in COVID-19-Exposed Household Contacts (PROTECT-EHC): A Randomized Clinical Trial. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, D.; Dimopoulou Agri, V.; Gibson, G.R.; Reid, G.; Giannoni, E. Using Probiotics to Flatten the Curve of Coronavirus Disease COVID-2019 Pandemic. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtoranta, L.; Latvala, S.; Lehtinen, M.J. Role of Probiotics in Stimulating the Immune System in Viral Respiratory Tract Infections: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasik, P.; Tomasik, P. Probiotics, Non-Dairy Prebiotics and Postbiotics in Nutrition. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, S.J.; Unnikrishnan, M.K.; Miraj, S.S.; Bagchi, D.; Banerjee, M.; Reddy, B.S.; Rodrigues, G.S.; Manu, M.K.; Saravu, K.; Mukhopadhyay, C.; et al. Probiotics in Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19: Current Perspective and Future Prospects. Arch. Med. Res. 2021, 52, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, C.A.; Lagier, J.C.; Raoult, D. New Insights into the Physiopathology of COVID-19: SARS-CoV-2-Associated Gastrointestinal Illness. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 640073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Fang, J.Y. 2019 Novel Coronavirus Infection and Gastrointestinal Tract. J. Dig. Dis. 2020, 21, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, M.M.; Beumer, J.; van der Vaart, J.; Knoops, K.; Puschhof, J.; Breugem, T.I.; Ravelli, R.B.; Paul van Schayck, J.; Mykytyn, A.Z.; Duimel, H.Q.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Productively Infects Human Gut Enterocytes. Science 2020, 369, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liu, P.; Shi, X.L.; Chu, Y.L.; Zhang, J.; Xia, J.; Gao, X.Z.; Qu, T.; Wang, M.Y. SARS-CoV-2 Induced Diarrhoea as Onset Symptom in Patient with COVID-19. Gut 2020, 69, 1143–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, J.P.; Mak, J.W.Y.; Mullish, B.H.; Alexander, J.L.; Ng, S.C.; Marchesi, J.R. The Gut Microbiome: An under-Recognised Contributor to the COVID-19 Pandemic? Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820974914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, D.; Mohanty, A. Gut Microbiota and Covid-19- Possible Link and Implications. Virus Res. 2020, 285, 198018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka, K.; Vitale, E.; Makarewicz, W. COVID-19—Gastrointestinal and Gut Microbiota-Related Aspects. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci 2020, 24, 10853–10859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, Y.K.; Zuo, T.; Lui, G.C.Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Q.; Li, A.Y.L.; Chung, A.C.K.; Cheung, C.P.; Tso, E.Y.K.; Fung, K.S.C.; et al. Gut Microbiota Composition Reflects Disease Severity and Dysfunctional Immune Responses in Patients with COVID-19. Gut 2021, 70, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Yang, J.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, V.N.; Chang, H. The Architecture of SARS-CoV-2 Transcriptome. Cell 2020, 181, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Teame, T.; Hao, Q.; Ding, Q.; Liu, H.; Ran, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Duan, M.; et al. Use of a Paraprobiotic and Postbiotic Feed Supplement (HWFTM) Improves the Growth Performance, Composition and Function of Gut Microbiota in Hybrid Sturgeon (Acipenser Baerii × Acipenser Schrenckii). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 104, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, T.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Lui, G.C.Y.; Tso, E.Y.K.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Chen, Z.; Boon, S.S.; Chan, F.K.L.; Chan, P.K.S.; et al. Depicting SARS-CoV-2 Faecal Viral Activity in Association with Gut Microbiota Composition in Patients with COVID-19. Gut 2021, 70, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angurana, S.K.; Bansal, A.; Singhi, S.; Aggarwal, R.; Jayashree, M.; Salaria, M.; Mangat, N.K. Evaluation of Effect of Probiotics on Cytokine Levels in Critically Ill Children with Severe Sepsis: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custodero, C.; Mankowski, R.T.; Lee, S.A.; Chen, Z.; Wu, S.; Manini, T.M.; Hincapie Echeverri, J.; Sabbà, C.; Beavers, D.P.; Cauley, J.A.; et al. Evidence-Based Nutritional and Pharmacological Interventions Targeting Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation in Middle-Age and Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2018, 46, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suez, J.; Zmora, N.; Segal, E.; Elinav, E. The Pros, Cons, and Many Unknowns of Probiotics. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilingiri, K.; Rescigno, M. Postbiotics: What Else? Benef. Microbes 2013, 4, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żółkiewicz, J.; Marzec, A.; Ruszczyński, M.; Feleszko, W. Postbiotics—A Step beyond Pre-and Probiotics. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paray, B.A.; Rather, I.A.; Al-Sadoon, M.K.; Fanar Hamad, A.-S. Pharmaceutical Significance of Leuconostoc Mesenteroides KS-TN11 Isolated from Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis Niloticus. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adedokun, E.O.; Rather, I.A.; Bajpai, V.K.; Choi, K.-H.; Park, Y.-H. Isolation and Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Nigerian Fermented Foods and Their Antimicrobial Activity. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 8, 3411–3420. [Google Scholar]
- Rather, I.A.; Choi, S.-B.; Kamli, M.R.; Hakeem, K.R.; Sabir, J.S.M.; Park, Y.-H.; Hor, Y.-Y. Potential Adjuvant Therapeutic Effect of Lactobacillus Plantarum Probio-88 Postbiotics against Sars-Cov-2. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, V.K.; Han, J.-H.; Nam, G.-J.; Majumder, R.; Park, C.; Lim, J.; Paek, W.K.; Rather, I.A.; Park, Y.-H. Characterization and Pharmacological Potential of Lactobacillus Sakei 1I1 Isolated from Fresh Water Fish Zacco Koreanus. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 24, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, B.J.; Rather, I.A.; Kumar, V.J.R.; Choi, U.H.; Moon, M.R.; Lim, J.H.; Park, Y.H. Evaluation of Leuconostoc Mesenteroides YML003 as a Probiotic against Low-Pathogenic Avian Influenza (H9N2) Virus in Chickens. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, I.A.; Seo, B.J.; Kumar, V.J.R.; Choi, U.-H.; Choi, K.-H.; Lim, J.; Park, Y.-H. Biopreservative Potential of Lactobacillus Plantarum YML007 and Efficacy as a Replacement for Chemical Preservatives in Animal Feed. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. Pathological Findings of COVID-19 Associated with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chousterman, B.G.; Swirski, F.K.; Weber, G.F. Cytokine Storm and Sepsis Disease Pathogenesis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimabukuro-Vornhagen, A.; Gödel, P.; Subklewe, M.; Stemmler, H.J.; Schlößer, H.A.; Schlaak, M.; Kochanek, M.; Böll, B.; von Bergwelt-Baildon, M.S. Cytokine Release Syndrome. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Yi, Q.; Fan, S.; Lv, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, L.; Lang, C.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, K.; Yi, Z.; et al. Characteristics of Lymphocyte Subsets and Cytokines in Peripheral Blood of 123 Hospitalized Patients with 2019 Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (NCP). medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battagello, D.S.; Dragunas, G.; Klein, M.O.; Ayub, A.L.P.; Velloso, F.J.; Correa, R.G. Unpuzzling COVID-19: Tissue-Related Signaling Pathways Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Transmission. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 2137–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchelle, E.; Zahm, J.M.; Tournier, J.M.; Coraux, C. Airway Epithelial Repair, Regeneration, and Remodeling after Injury in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2006, 3, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, C.; Zhou, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Tao, Y.; Xie, C.; Ma, K.; Shang, K.; Wang, W.; et al. Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients with Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Li, W.; Xie, J.; Hou, Y.; You, C. Cytokine Storm Induced by SARS-CoV-2. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 509, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Valle, D.M.; Kim-Schulze, S.; Huang, H.H.; Beckmann, N.D.; Nirenberg, S.; Wang, B.; Lavin, Y.; Swartz, T.H.; Madduri, D.; Stock, A.; et al. An Inflammatory Cytokine Signature Predicts COVID-19 Severity and Survival. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, P.C.; Richards, D.; Tanner, H.L.; Feldmann, M. Accumulating Evidence Suggests Anti-TNF Therapy Needs to Be given Trial Priority in COVID-19 Treatment. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e653–e655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, F.; Altayb, H.N.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Al-Malki, A.L.; Kamal, M.A.; Kumar, V. Antiviral Effects of Probiotic Metabolites on COVID-19. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 4175–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botić, T.; Danø, T.; Weingartl, H.; Cencič, A. A Novel Eukaryotic Cell Culture Model to Study Antiviral Activity of Potential Probiotic Bacteria. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2007, 115, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez-Brito, M.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Muñoz-Quezada, S.; Gómez-Llorente, C.; Gil, A. Probiotic Mechanisms of Action. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 61, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varyukhina, S.; Freitas, M.; Bardin, S.; Robillard, E.; Tavan, E.; Sapin, C.; Grill, J.P.; Trugnan, G. Glycan-Modifying Bacteria-Derived Soluble Factors from Bacteroides Thetaiotaomicron and Lactobacillus Casei Inhibit Rotavirus Infection in Human Intestinal Cells. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alzahrani, O.R.; Hawsawi, Y.M.; Alanazi, A.D.; Alatwi, H.E.; Rather, I.A. In Vitro Evaluation of Leuconostoc mesenteroides Cell-Free-Supernatant GBUT-21 against SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101581
Alzahrani OR, Hawsawi YM, Alanazi AD, Alatwi HE, Rather IA. In Vitro Evaluation of Leuconostoc mesenteroides Cell-Free-Supernatant GBUT-21 against SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines. 2022; 10(10):1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101581
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlzahrani, Othman R., Yousef M. Hawsawi, Abdullah D. Alanazi, Hanan E. Alatwi, and Irfan A. Rather. 2022. "In Vitro Evaluation of Leuconostoc mesenteroides Cell-Free-Supernatant GBUT-21 against SARS-CoV-2" Vaccines 10, no. 10: 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101581
APA StyleAlzahrani, O. R., Hawsawi, Y. M., Alanazi, A. D., Alatwi, H. E., & Rather, I. A. (2022). In Vitro Evaluation of Leuconostoc mesenteroides Cell-Free-Supernatant GBUT-21 against SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines, 10(10), 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101581







