Green Extraction of Antioxidant Polyphenols from Green Tea (Camellia sinensis)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Preparation of DESs
2.4. Extraction of Tea Polyphenols
2.5. Determination of Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.6. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
2.7. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
2.8. Experimental Design
2.8.1. Single-Factor Experiments
2.8.2. Response Surface Methodology
2.9. Morphology
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Selection of DES
3.2. Effects of Extraction Parameters on TPC
3.2.1. Liquid to Solid Ratio
3.2.2. ChCl/Glycerol Molar Ratio
3.2.3. Water Content in the DES-1(ChCl-glycerol)
3.2.4. Ultrasonic Power
3.2.5. Ultrasonic Time
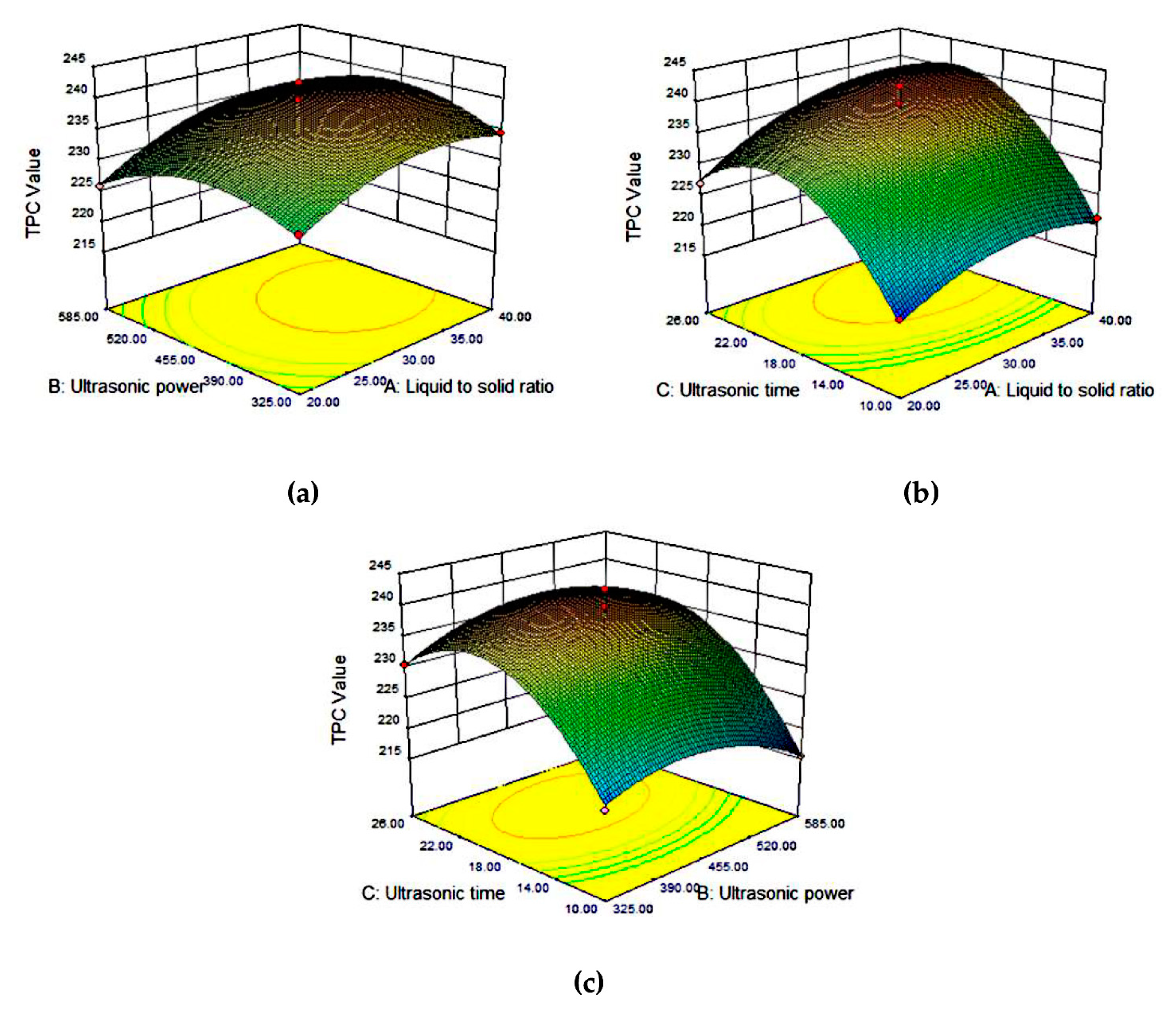
3.3. Optimization of the Extraction Conditions Using the UAE-DES Method
3.3.1. Model Adequacy
3.3.2. TPC in Tea Extracts
3.3.3. Verification of the Predicted TPC Value
3.4. Comparison of Extraction Methods on TPC and Antioxidant Activity in Green Tea Extracts
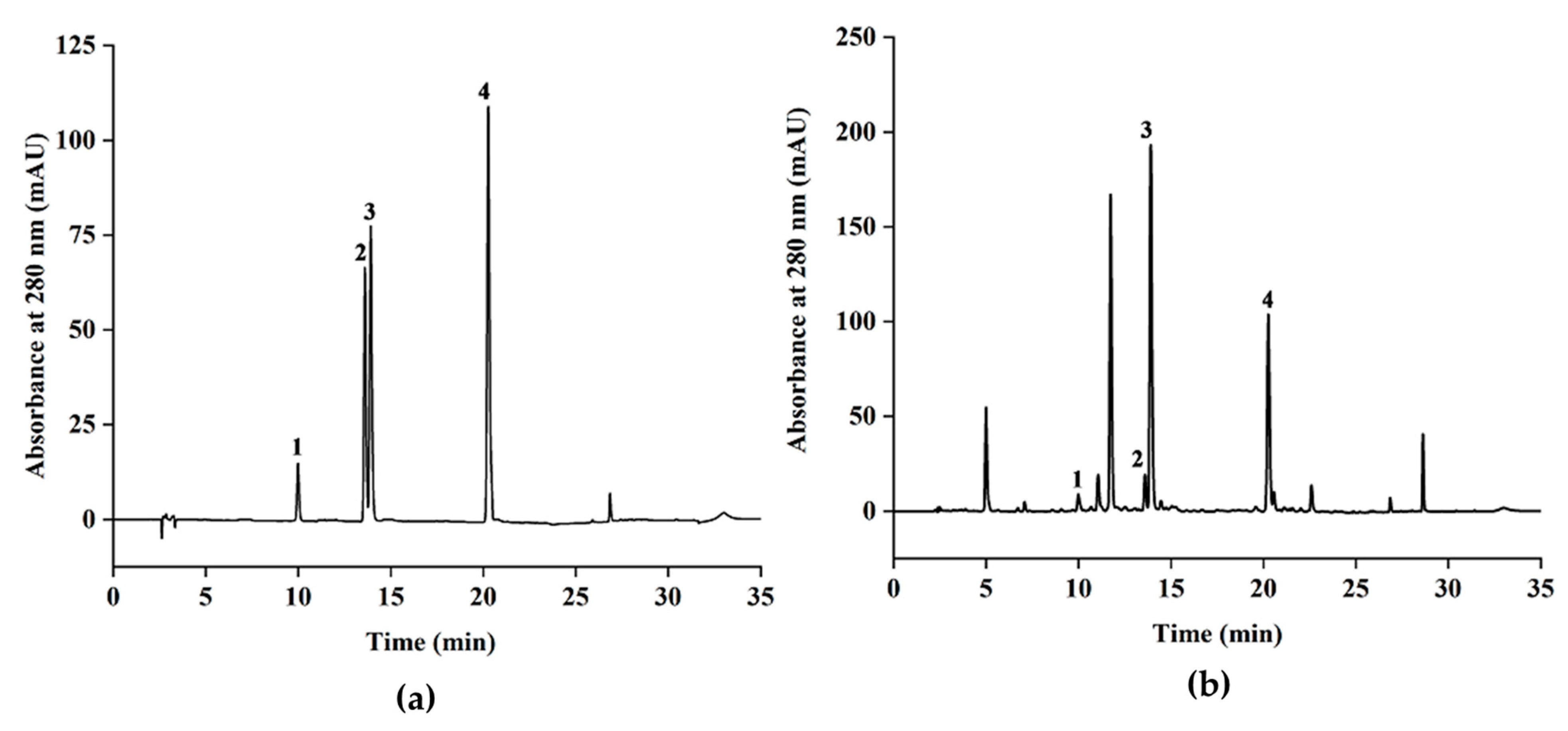
3.5. HPLC Quantification of the Major Catechins in Green Tea Extracts
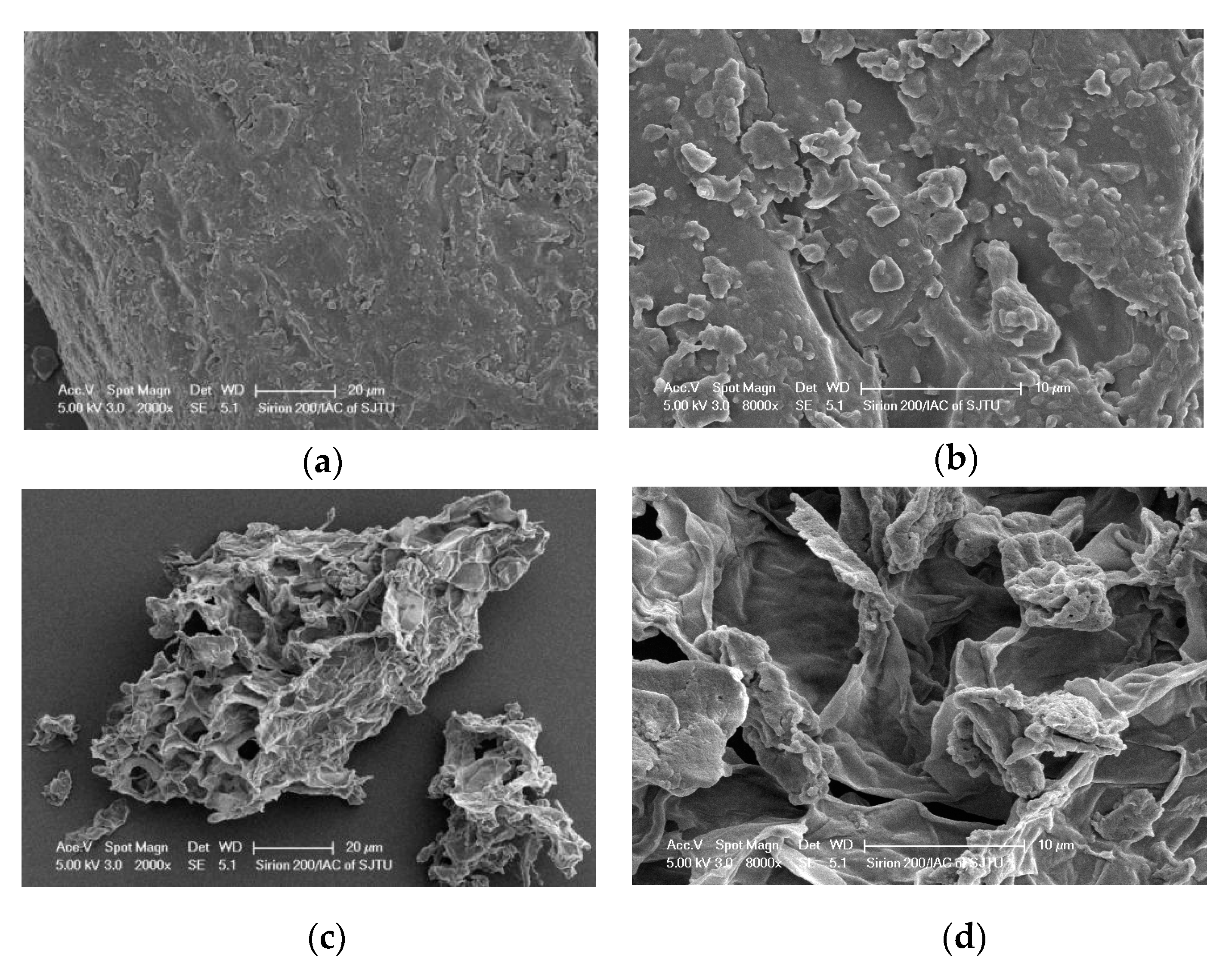
3.6. SEM Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, H. Polysaccharides from Chinese tea: Recent advance on bioactivity and function. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.V.; Golding, J.B.; Nguyen, M.; Roach, P.D. Extraction and isolation of catechins from tea. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 3415–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saklar Ayyildiz, S.; Karadeniz, B.; Sagcan, N.; Bahar, B.; Us, A.A.; Alasalvar, C. Optimizing the extraction parameters of epigallocatechin gallate using conventional hot water and ultrasound assisted methods from green tea. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 111, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, N.; Tanabe, H.; Suzuki, T.; Saeki, K.; Hara, Y. Applications of a standardized green tea catechin preparation for viral warts and human papilloma virus-related and unrelated cancers. Molecules 2020, 25, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.Y.; Zhao, C.N.; Cao, S.Y.; Tang, G.Y.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, H.B. Effects and mechanisms of tea for the prevention and management of cancers: An updated review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1693–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.-M.; Cao, S.-Y.; Wei, X.-L.; Gan, R.-Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; Cai, S.-X.; Xu, X.-Y.; Zhang, P.-Z.; Li, H.-B. Effects and mechanisms of tea for the prevention and management of diabetes mellitus and diabetic complications: An updated review. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.-Y.; Zhao, C.-N.; Gan, R.-Y.; Xu, X.-Y.; Wei, X.-L.; Corke, H.; Atanasov, A.G.; Li, H.-B. Effects and mechanisms of tea and its bioactive compounds for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases: An updated review. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.-Y.; Meng, X.; Gan, R.-Y.; Zhao, C.-N.; Liu, Q.; Feng, Y.-B.; Li, S.; Wei, X.-L.; Atanasov, A.G.; Corke, H.; et al. Health functions and related molecular mechanisms of tea components: An update review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Lin, X. Deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasonic-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from Moringa oleifera L. leaves: Optimization, comparison and antioxidant activity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 247, 117014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruesgas-Ramon, M.; Figueroa-Espinoza, M.C.; Durand, E. Application of deep eutectic solvents (DES) for phenolic compounds extraction: Overview, challenges, and opportunities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3591–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as a new extraction media for phenolic metabolites in Carthamus tinctorius L. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6272–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, G.; Aparicio, S.; Ullah, R.; Atilhan, M. Deep eutectic solvents: Physicochemical properties and gas separation applications. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 2616–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural deep eutectic solvents-solvents for the 21st century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, V.Z.; Wu, T.Y.; Lee, C.; Cheong, N.W.R.; Shak, K.P.Y. Sequential ultrasonication and deep eutectic solvent pretreatment to remove lignin and recover xylose from oil palm fronds. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.S.; Lobo, H.R.; Pinjari, D.V.; Jarag, K.J.; Pandit, A.B.; Shankarling, G.S. Ultrasound and deep eutectic solvent (DES): A novel blend of techniques for rapid and energy efficient synthesis of oxazoles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, A.; Aghaie, M. Ultrasonic-assisted environmentally-friendly synergetic synthesis of nitroaromatic compounds in core/shell nanoreactor: A green protocol. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 39, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurob, E.; Cabezas, R.; Villarroel, E.; Rosas, N.; Merlet, G.; Quijada-Maldonado, E.; Romero, J.; Plaza, A. Design of natural deep eutectic solvents for the ultrasound-assisted extraction of hydroxytyrosol from olive leaves supported by COSMO-RS. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezeli, T.; Daneshfar, A. Synthesis and application of magnetic deep eutectic solvents: Novel solvents for ultrasound assisted liquid-liquid microextraction of thiophene. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Li, F.; Liu, L.; Tan, Z. Deep eutectic solvents used as the green media for the efficient extraction of caffeine from Chinese dark tea. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 227, 115723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, Z.; Zou, Y.; Yu, B. Efficient extraction of major catechins in Camellia sinensis leaves using green choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 93937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.-Y.; Xu, P.; Yang, F.-X.; Wu, H.; Zong, M.-H.; Lou, W.-Y. Biocompatible deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride: Characterization and application to the extraction of rutin from Sophora japonica. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacci, S.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Costanzo, P.; Maiuolo, L.; Tallarico, S.; Nardi, M. Natural deep eutectic solvent as extraction media for the main phenolic compounds from Olive Oil processing wastes. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraige, K.; Arrua, R.D.; Sutton, A.T.; Funari, C.S.; Cavalheiro, A.J.; Hilder, E.F.; Bolzani, V.D.S. Using natural deep eutectic solvents for the extraction of metabolites in Byrsonima intermedia leaves. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Curko, N.; Tomasevic, M.; Kovacevic Ganic, K.; Radojcic Redovnikovic, I. Green extraction of grape skin phenolics by using deep eutectic solvents. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosiljkov, T.; Dujmić, F.; Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Hribar, J.; Vidrih, R.; Brnčić, M.; Zlatic, E.; Radojčić Redovniković, I.; Jokić, S. Natural deep eutectic solvents and ultrasound-assisted extraction: Green approaches for extraction of wine lees anthocyanins. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 102, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Soylak, M. Ultrasound assisted-deep eutectic solvent based on emulsification liquid phase microextraction combined with microsample injection flame atomic absorption spectrometry for valence speciation of chromium (III/VI) in environmental samples. Talanta 2016, 160, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, M. Optimization of deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasound-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Dioscorea opposita Thunb. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 95, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-N.; Tang, G.-Y.; Cao, S.-Y.; Xu, X.-Y.; Gan, R.-Y.; Liu, Q.; Mao, Q.-Q.; Shang, A.; Li, H.-B. Phenolic profiles and antioxidant activities of 30 tea infusions from green, black, oolong, white, yellow and dark teas. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.-Y.; Zhao, C.-N.; Xu, X.-Y.; Gan, R.-Y.; Cao, S.-Y.; Liu, Q.; Shang, A.; Mao, Q.-Q.; Li, H.-B. Phytochemical composition and antioxidant capacity of 30 Chinese teas. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.-Q.; Cheng, L.; Long, Z.-Y.; Li, H.-B.; Gunaratne, A.; Gan, R.-Y.; Cork, H. Comparison of the phenolic profiles of soaked and germinated peanut cultivars via UPLC-QTOF-MS. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, H.C.; Liang, H.J.; Chen, S.T.; Lin, W.Y.; Wu, K.Y.; Chiang, S.Y.; Lin, C.Y. Nuclear magnetic resonance- and mass spectrometry-based metabolomics to study maleic acid toxicity from repeated dose exposure in rats. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banu, A.; Marcu, M.; Juganaru, C.; Osiceanu, P.; Anastasescu, M.; Capra, L. Corrosion behavior of CoCrMoW cast alloy in lactic acid environment for surgical applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaha, Y.N.; Darsono, N.; Utomo, M.S.; Sajuti, D.; Kartika, I. The effect of malonic acid and succinic acid on the corrosion behavior of Mg-5Zn in (Nh4)3PO4 and NaF. Int. J. Technol. 2019, 10, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidlak, A.M.; Marino, R.T.; Van Meerbeke, J.P.; Pizon, A.F. Single versus continued dosing of fomepizole during hemodialysis in ethylene glycol toxicity. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Tailoring properties of natural deep eutectic solvents with water to facilitate their applications. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaram, S.; Mirhosseini, H.; Tan, C.P.; Ghazali, H.M.; Bordbar, S.; Serjouie, A. Optimisation of ultrasound-assisted extraction of oil from papaya seed by response surface methodology: Oil recovery, radical scavenging antioxidant activity, and oxidation stability. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maran, J.P.; Priya, B. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of polysaccharide from Nephelium lappaceum L. fruit peel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 70, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zheng, J.; Gan, R.Y.; Zhou, T.; Xu, D.P.; Li, H.B. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of antioxidants from the Mung Bean Coat. Molecules 2017, 22, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.Y.; Gan, R.Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Xu, D.P.; Li, H.B. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of antioxidant polyphenols from the seed coats of Red Sword Bean (Canavalia gladiate (Jacq.) DC.). Antioxidants 2019, 8, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, A.R.; Song, N.E.; Jang, H.W.; Lim, T.G.; Yoo, M.; Nam, T.G. Optimizing the ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvent extraction of flavonoids in common buckwheat sprouts. Food Chem. 2019, 293, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Wang, M.; Guo, H.; Xu, J.; Ye, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, L. Ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvent as green and efficient media for the extraction of flavonoids from Radix scutellariae. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, A.; Li, G.; Ren, X.; Yin, W. Ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvent extraction of echinacoside and oleuropein from Syringa pubescens Turcz. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 151, 112442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xue, X.-J.; Li, H.; Apandi, S.N.; Tay-Chan, S.C.; Ong, S.P.; Tian, E.F. The relative antioxidant activity and steric structure of green tea catechins-a kinetic approach. Food Chem. 2018, 257, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peluso, I.; Serafini, M. Antioxidants from black and green tea: From dietary modulation of oxidative stress to pharmacological mechanisms. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Jia, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Influence of ultrasonic pretreatment on the yield of bio-oil prepared by thermo-chemical conversion of rice husk in hot-compressed water. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dranca, F.; Oroian, M. Total monomeric anthocyanin, total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of extracts from eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) peel using ultrasonic treatments. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 40, 12312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
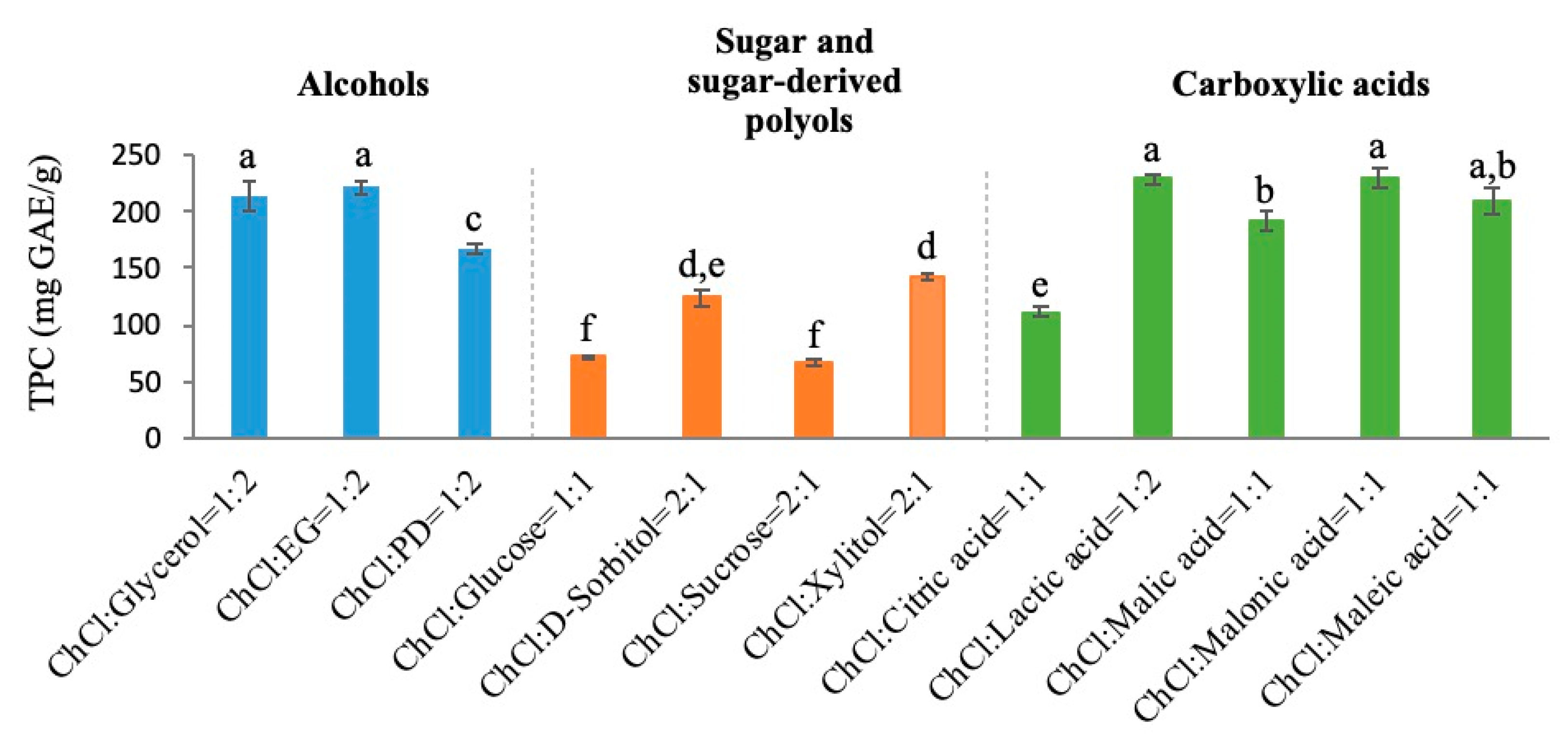

| No. | HBD | Molar Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Glycerol | 1:2 |
| 2 | EG | 1:2 |
| 3 | PD | 1:2 |
| 4 | Glucose | 1:1 |
| 5 | D-sorbitol | 2:1 |
| 6 | Sucrose | 2:1 |
| 7 | Xylitol | 2:1 |
| 8 | Citric acid | 1:1 |
| 9 | Lactic acid | 1:2 |
| 10 | Malic acid | 1:1 |
| 11 | Malonic acid | 1:1 |
| 12 | Maleic acid | 1:1 |
| Independent Variables | Coded Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | +1 | |
| X1 (liquid to solid ratio, mL/g) | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| X2 (ultrasonic power, W) | 325 | 455 | 585 |
| X3 (ultrasonic time, min) | 10 | 18 | 26 |
| Run | X1 (Liquid to Solid Ratio, mL/g) | X2 (Ultrasonic Power, W) | X3 (Ultrasonic Time, min) | Response Y (TPC, mg GAE/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 * | 0 | 0 | 0 | 239 ± 2 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 221 ± 3 |
| 3 * | 0 | 0 | 0 | 238 ± 1 |
| 4 * | 0 | 0 | 0 | 237 ± 5 |
| 5 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 229 ± 5 |
| 6 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 234.6 ± 0.6 |
| 7 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 227 ± 2 |
| 8 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 217 ± 1 |
| 9 * | 0 | 0 | 0 | 243 ± 3 |
| 10 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 215 ± 2 |
| 11 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 226 ± 3 |
| 12 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 234 ± 4 |
| 13 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 218.9 ± 0.7 |
| 14 * | 0 | 0 | 0 | 240 ± 2 |
| 15 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 237 ± 4 |
| 16 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 231 ± 2 |
| 17 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 233.5 ± 0.4 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | Significant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 1117.99 | 9 | 124.22 | 37.18 | <0.0001 | significant |
| X1 | 95.91 | 1 | 95.91 | 28.71 | 0.0011 | |
| X2 | 2.53 | 1 | 2.53 | 0.76 | 0.4129 | |
| X3 | 383.64 | 1 | 383.64 | 114.84 | <0.0001 | |
| X1X2 | 1.69 | 1 | 1.69 | 0.51 | 0.4999 | |
| X1X3 | 8.70 | 1 | 8.70 | 2.61 | 0.1506 | |
| X2X3 | 10.56 | 1 | 10.56 | 3.16 | 0.1186 | |
| X12 | 56.25 | 1 | 56.25 | 16.84 | 0.0046 | |
| X22 | 89.29 | 1 | 89.29 | 26.73 | 0.0013 | |
| X32 | 419.37 | 1 | 419.37 | 125.54 | <0.0001 | |
| Residual | 23.38 | 7 | 3.34 | |||
| Lack of fit | 3.65 | 3 | 1.22 | 0.25 | 0.8601 | not significant |
| Pure error | 19.73 | 4 | 4.93 | |||
| Cor total | 1141.37 | 16 | ||||
| R2 | 0.9795 | |||||
| Adj. R2 | 0.9532 |
| Extraction Methods | Extraction Time | TPC (mg GAE/g) | FRAP (mmol Fe (II)/100 g DW) | DPPH (mmol Trolox/100 g DW) | ABTS (mmol Trolox/100 g DW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UAE-DES | 21 min | 243 ± 7 a | 332 ± 9 a | 215 ± 6 a | 99 ± 3 a |
| UAE with Ethanol | 21 min | 219 ± 3 b | 285 ± 6 c | 195 ± 3 c | 77 ± 1 c |
| Ethanol Extraction | 24 h | 242 ± 2 a | 300 ± 3 b | 205 ± 5 b | 84 ± 3 b |
| Hot Water Extraction | 21 min | 152 ± 2 c | 174 ± 5 d | 99.0 ± 0.8 d | 46 ± 1 d |
| Compound | Concentration (mg/g DW) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGC | EC | EGCG | ECG | |
| UAE-DES | 24.4 ± 0.6 a | 8.5 ± 0.4 a | 94 ± 2 a | 36.2 ± 0.7 a |
| UAE-Ethanol | 19.6 ± 0.5 c | 6.8 ± 0.6 b | 92.3 ± 0.8 a | 35.3 ± 0.7 a |
| Ethanol Extraction | 22 ± 1 b | 6.9 ± 0.2 b | 92 ± 2 a | 35.4 ± 0.4 a |
| Hot Water Extraction | 12.5 ± 0.2 d | 4.1 ± 0.1 c | 36.8 ± 0.4 b | 11.7 ± 0.1 b |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Q.; Zhang, J.-R.; Li, H.-B.; Wu, D.-T.; Geng, F.; Corke, H.; Wei, X.-L.; Gan, R.-Y. Green Extraction of Antioxidant Polyphenols from Green Tea (Camellia sinensis). Antioxidants 2020, 9, 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9090785
Luo Q, Zhang J-R, Li H-B, Wu D-T, Geng F, Corke H, Wei X-L, Gan R-Y. Green Extraction of Antioxidant Polyphenols from Green Tea (Camellia sinensis). Antioxidants. 2020; 9(9):785. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9090785
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Qiong, Jia-Rong Zhang, Hua-Bin Li, Ding-Tao Wu, Fang Geng, Harold Corke, Xin-Lin Wei, and Ren-You Gan. 2020. "Green Extraction of Antioxidant Polyphenols from Green Tea (Camellia sinensis)" Antioxidants 9, no. 9: 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9090785
APA StyleLuo, Q., Zhang, J.-R., Li, H.-B., Wu, D.-T., Geng, F., Corke, H., Wei, X.-L., & Gan, R.-Y. (2020). Green Extraction of Antioxidant Polyphenols from Green Tea (Camellia sinensis). Antioxidants, 9(9), 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9090785