Saponin Formosanin C-Induced Ferritinophagy and Ferroptosis in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Database Analysis
2.4. Measurement of Cell Viability Inhibition
2.5. Measurement of Autophagy Level by Flow Cytometry
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Measurement of Cellular Lipid ROS by Flow Cytometry
2.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.9. Confocal Microscopy
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
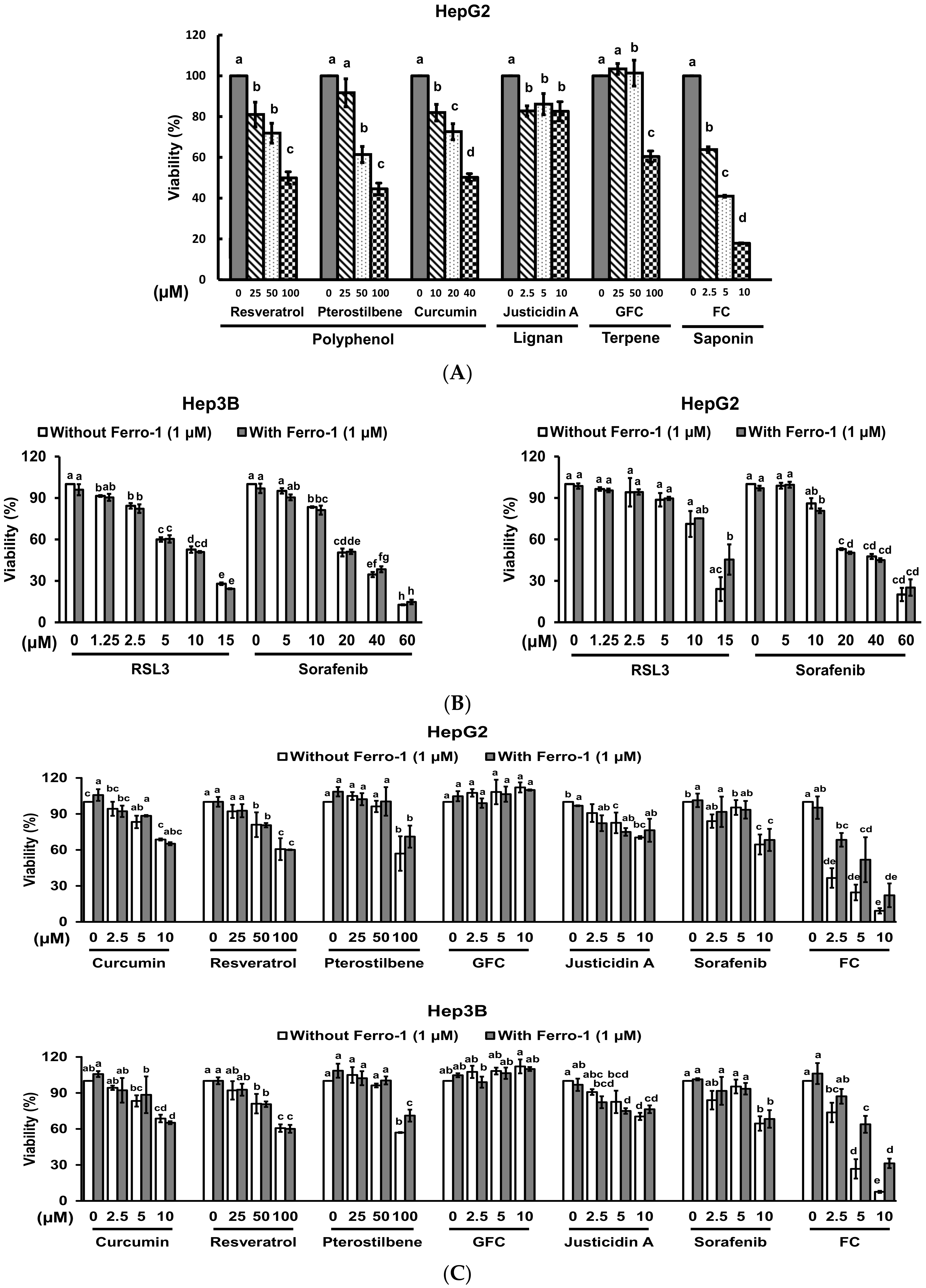
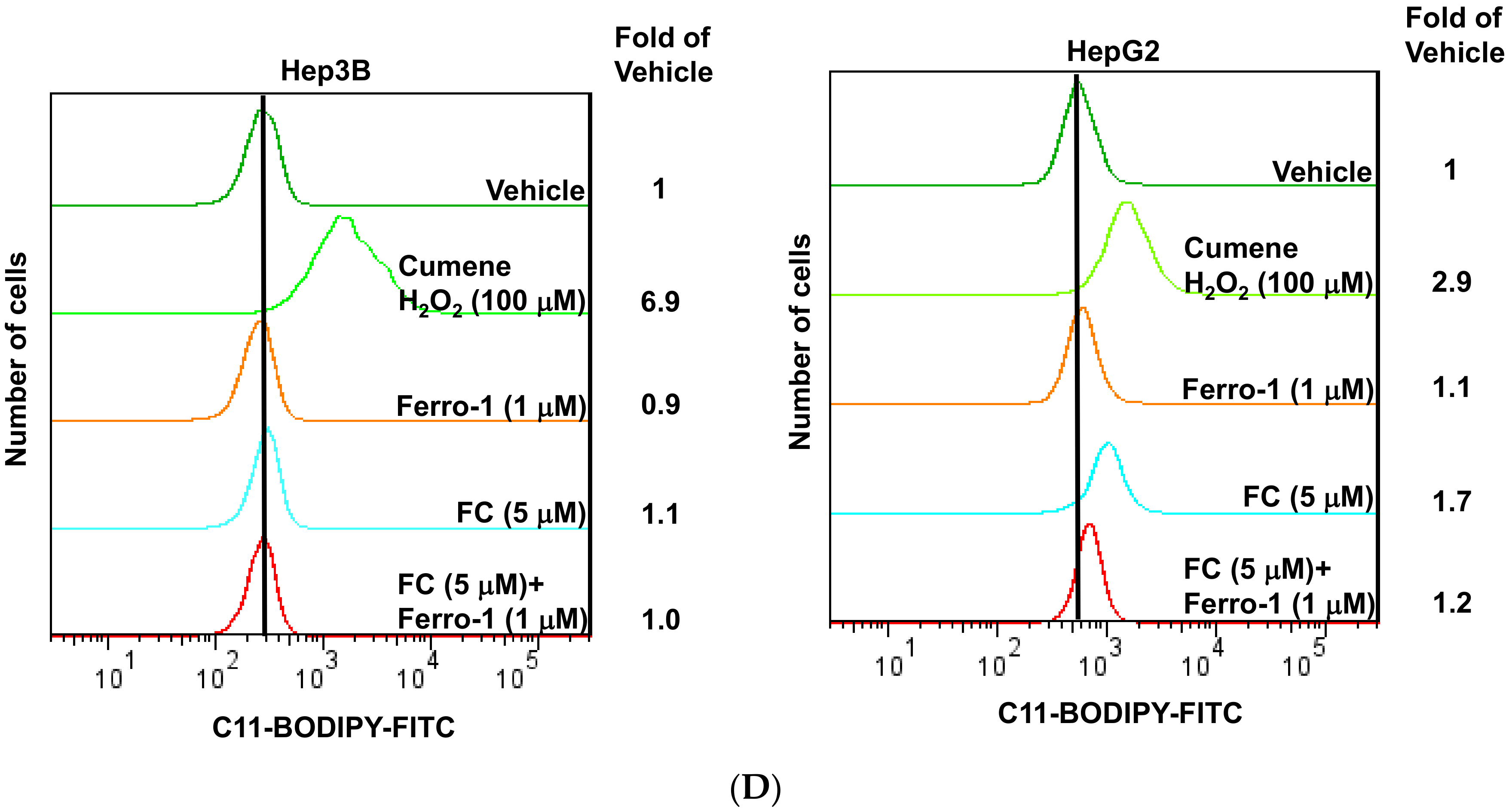
3.1. FC Induced Stronger Ferroptosis in HepG2 Cells Compared to Hep3B Cells
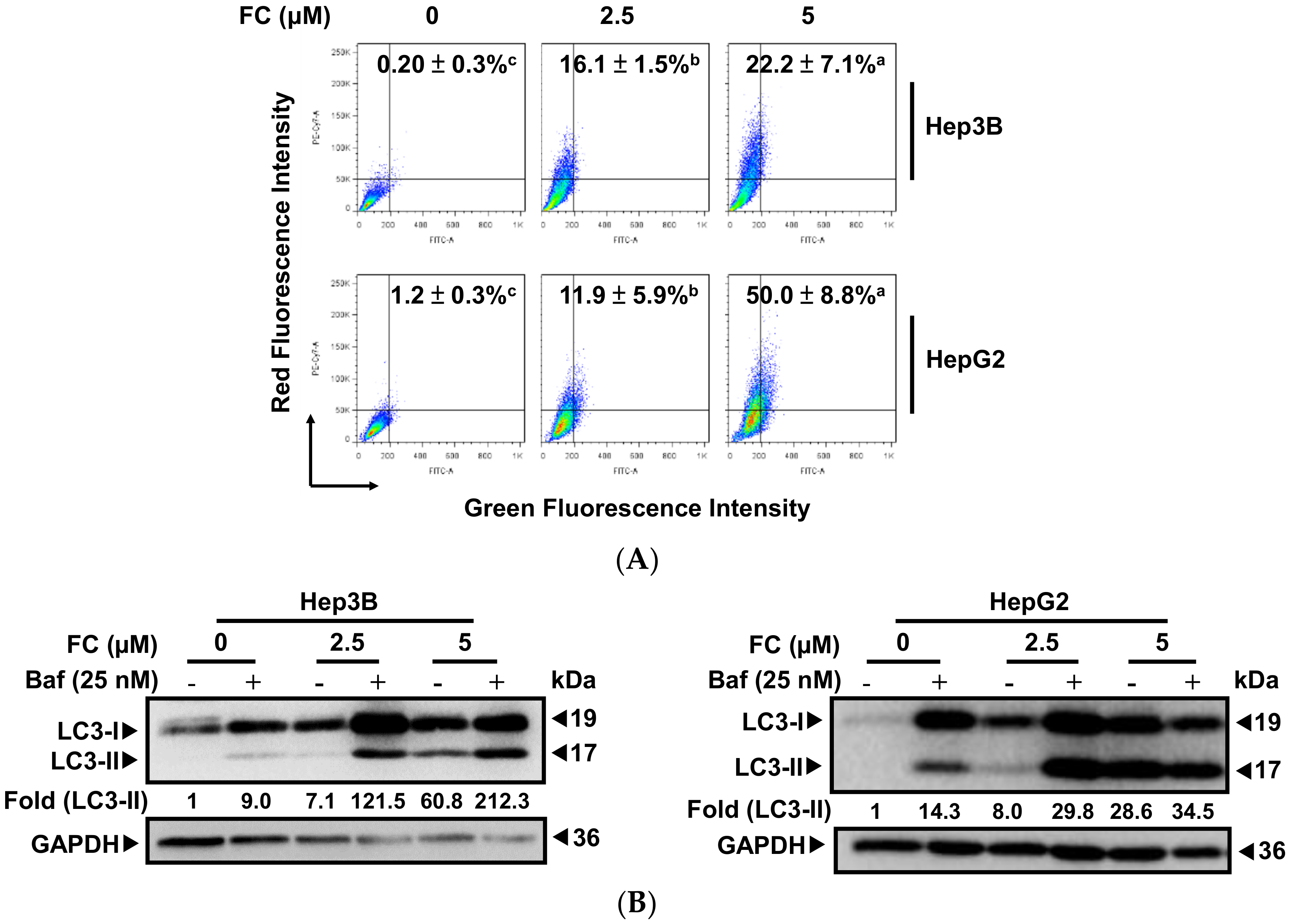
3.2. FC-Induced a Higher Degree of Autophagic Flux in HepG2 Cells
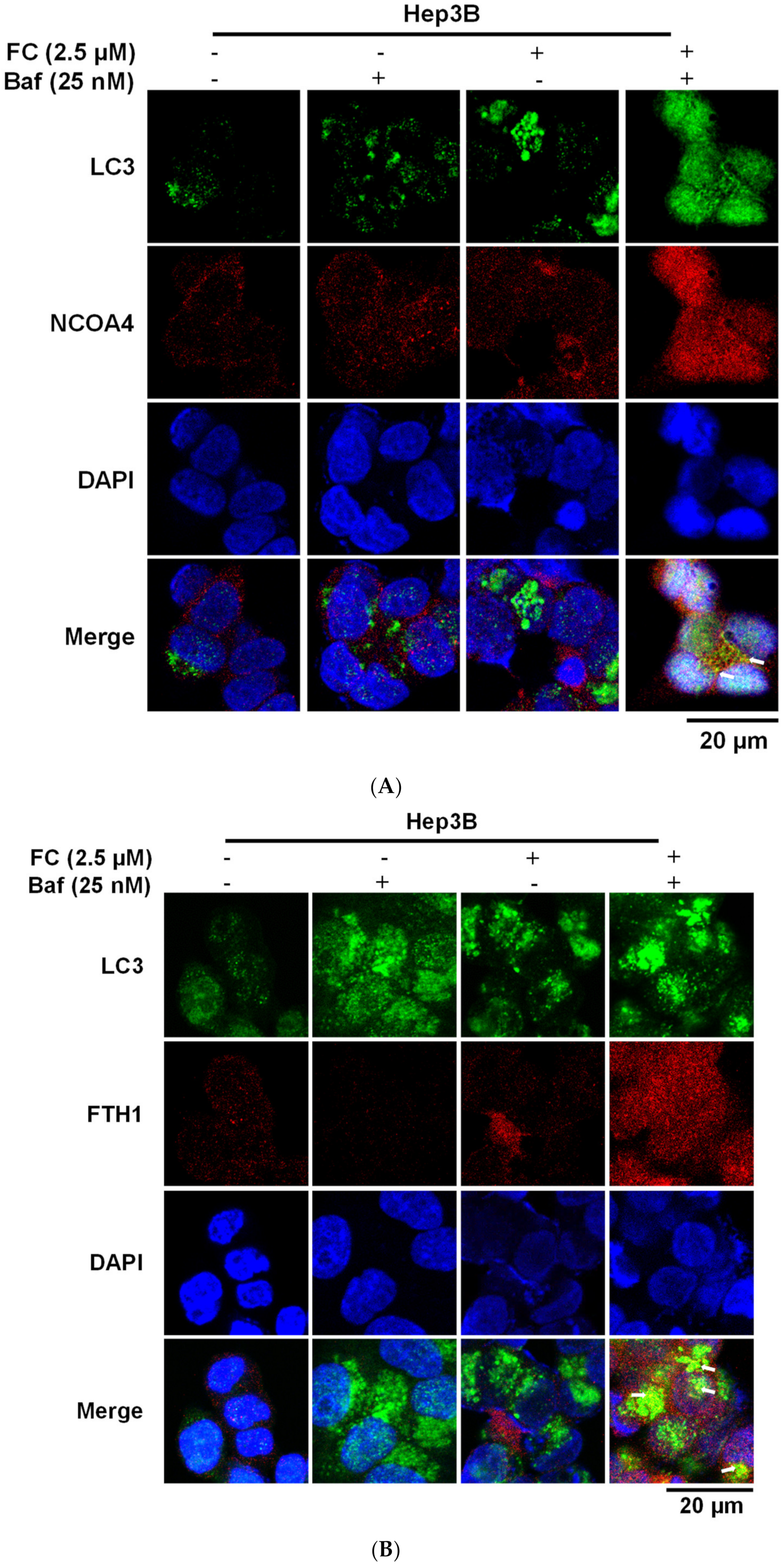
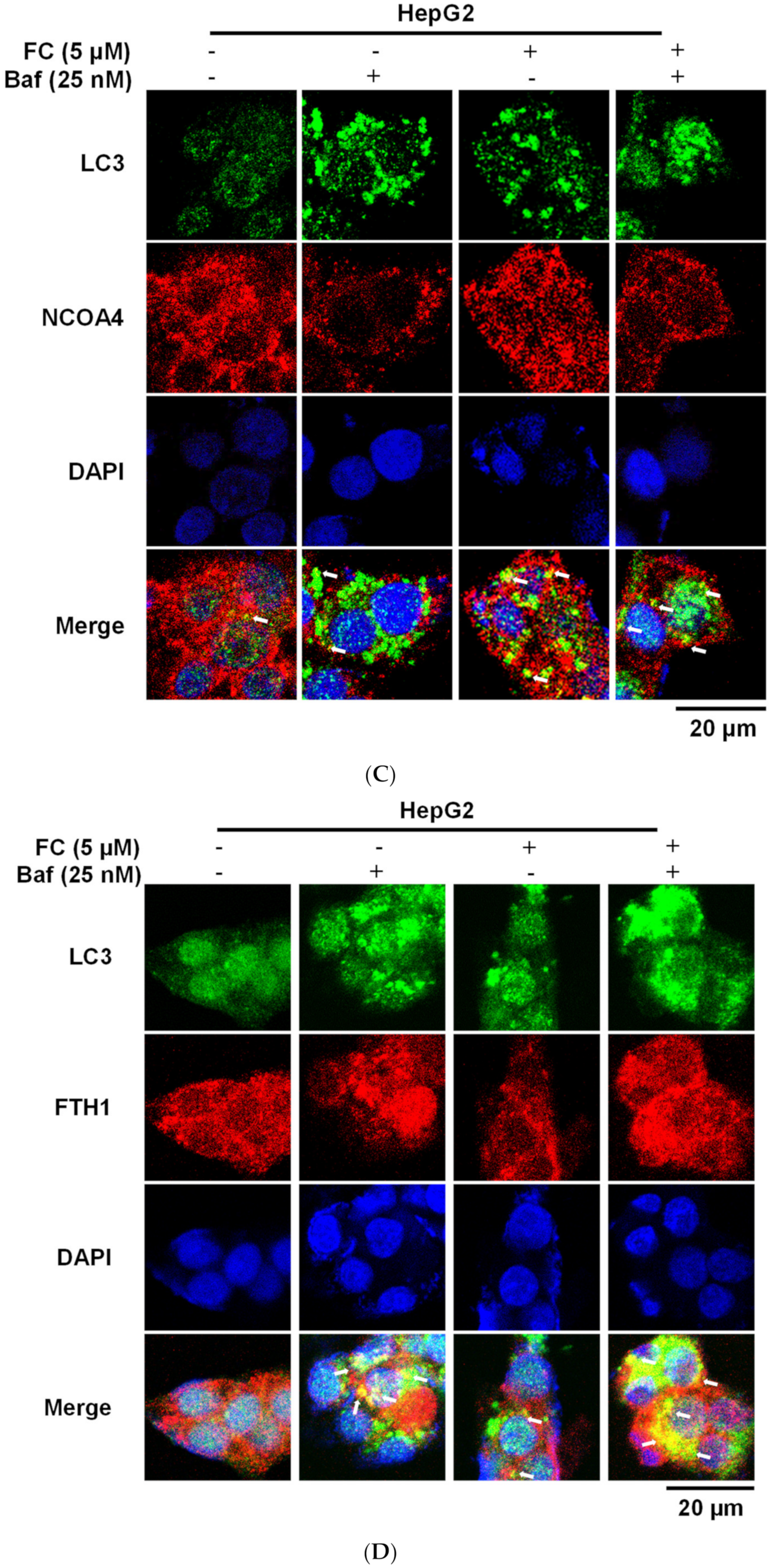
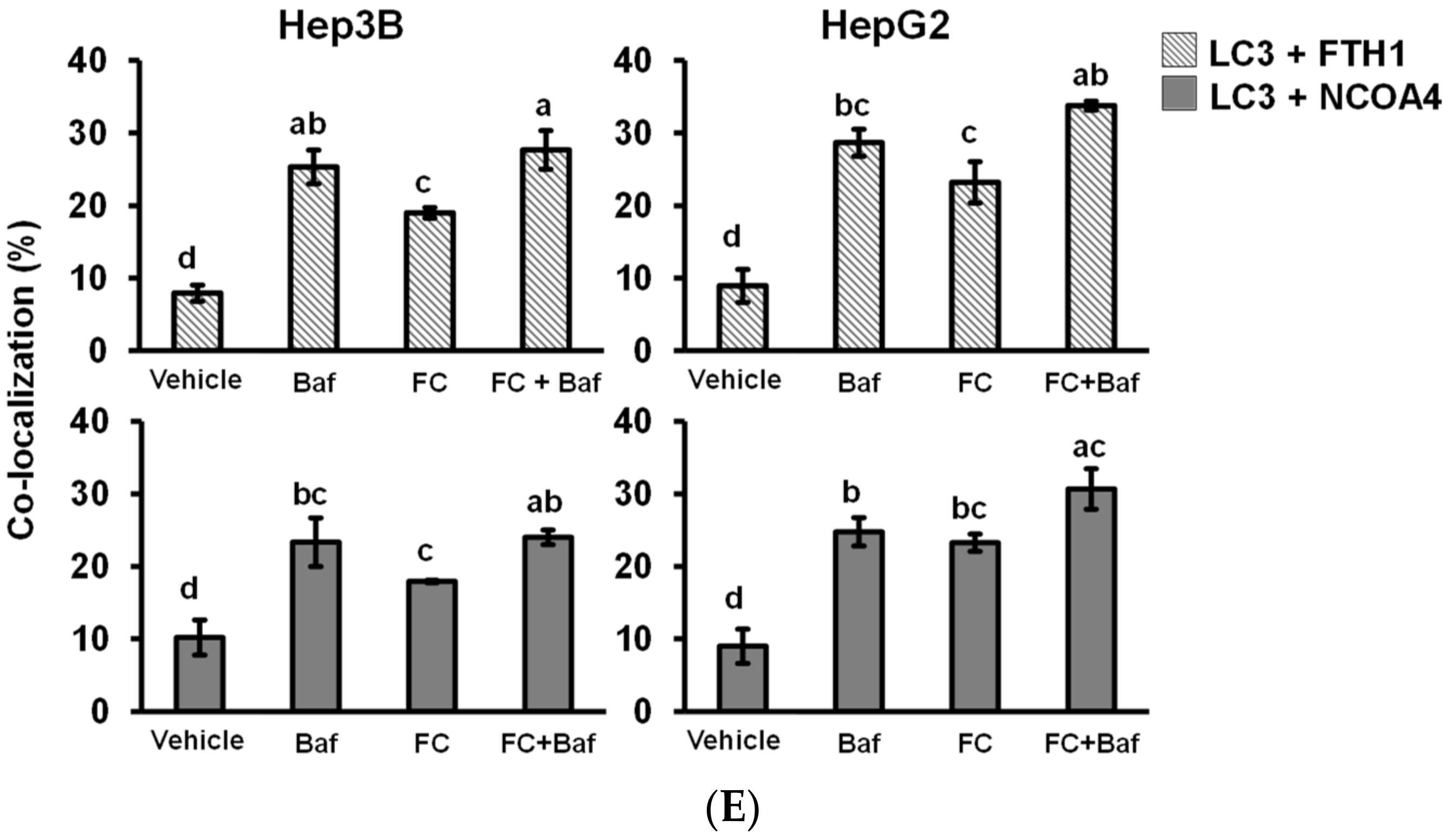
3.3. Cells Which Displayed a Higher Expression Level of NCOA4 were More Susceptible to Ferritinophagy
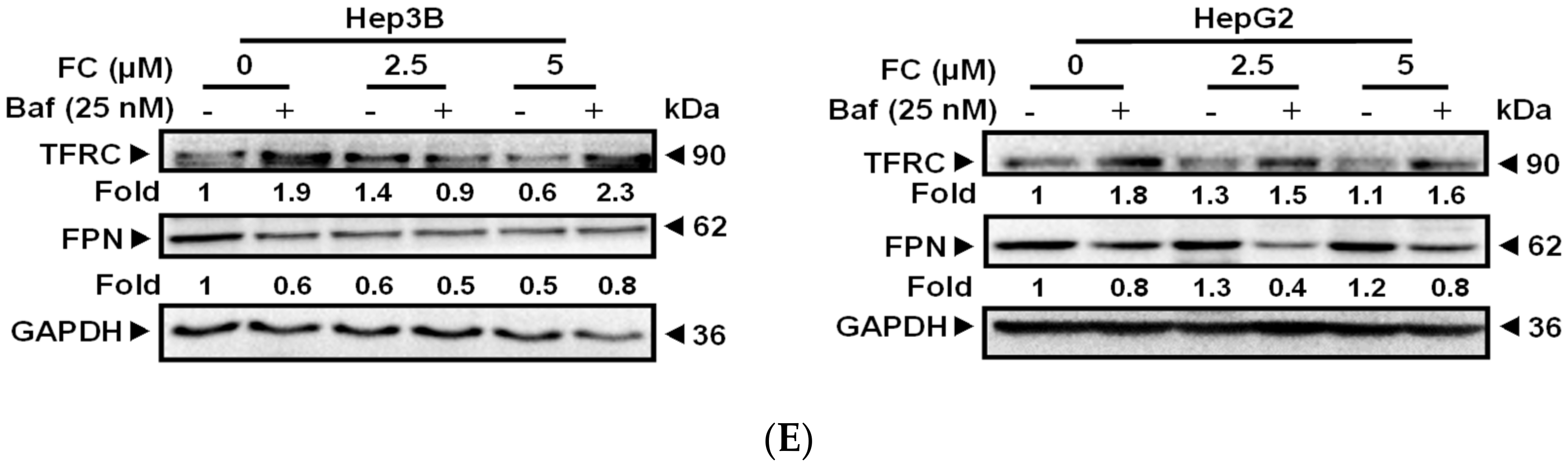
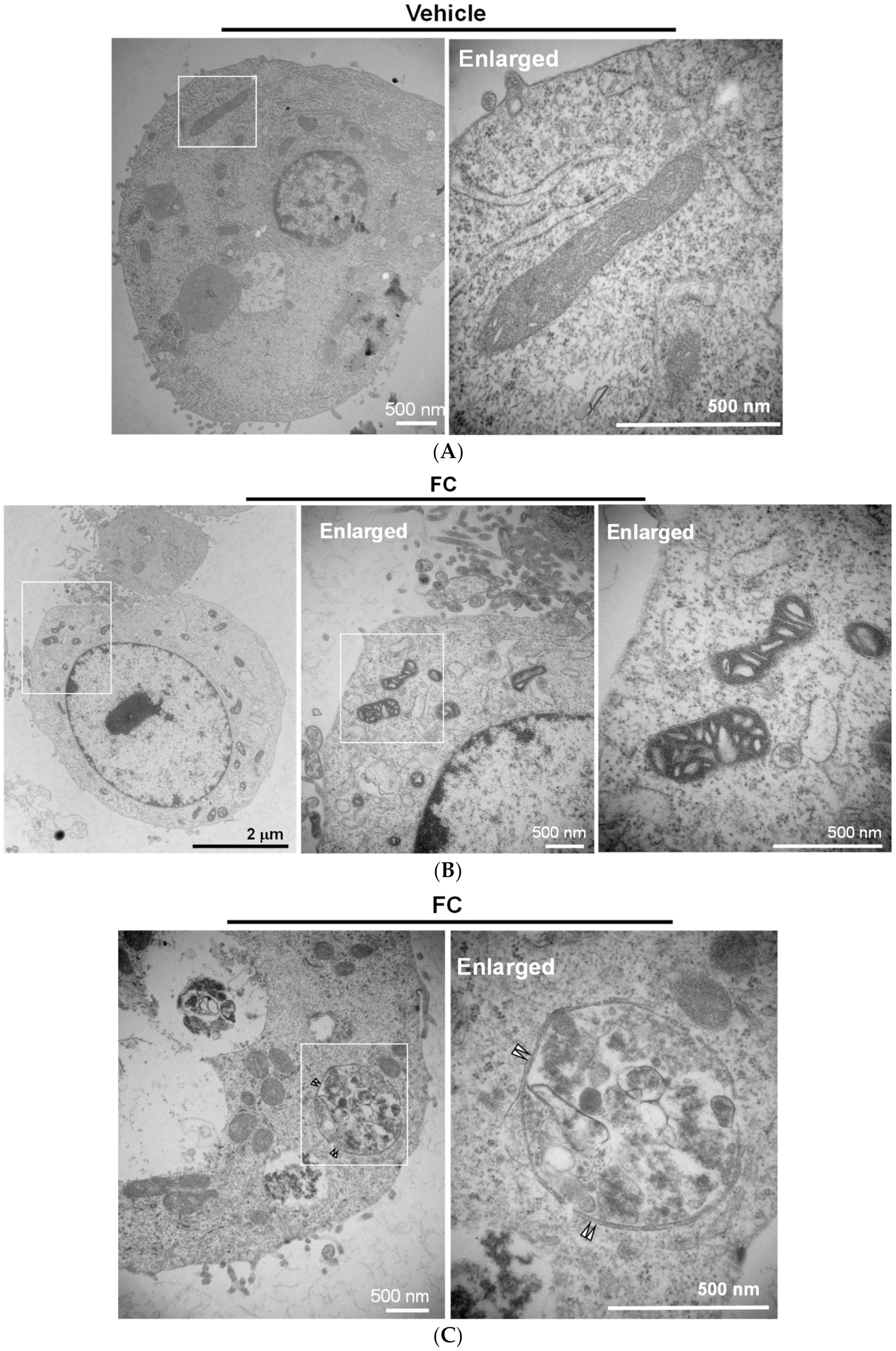
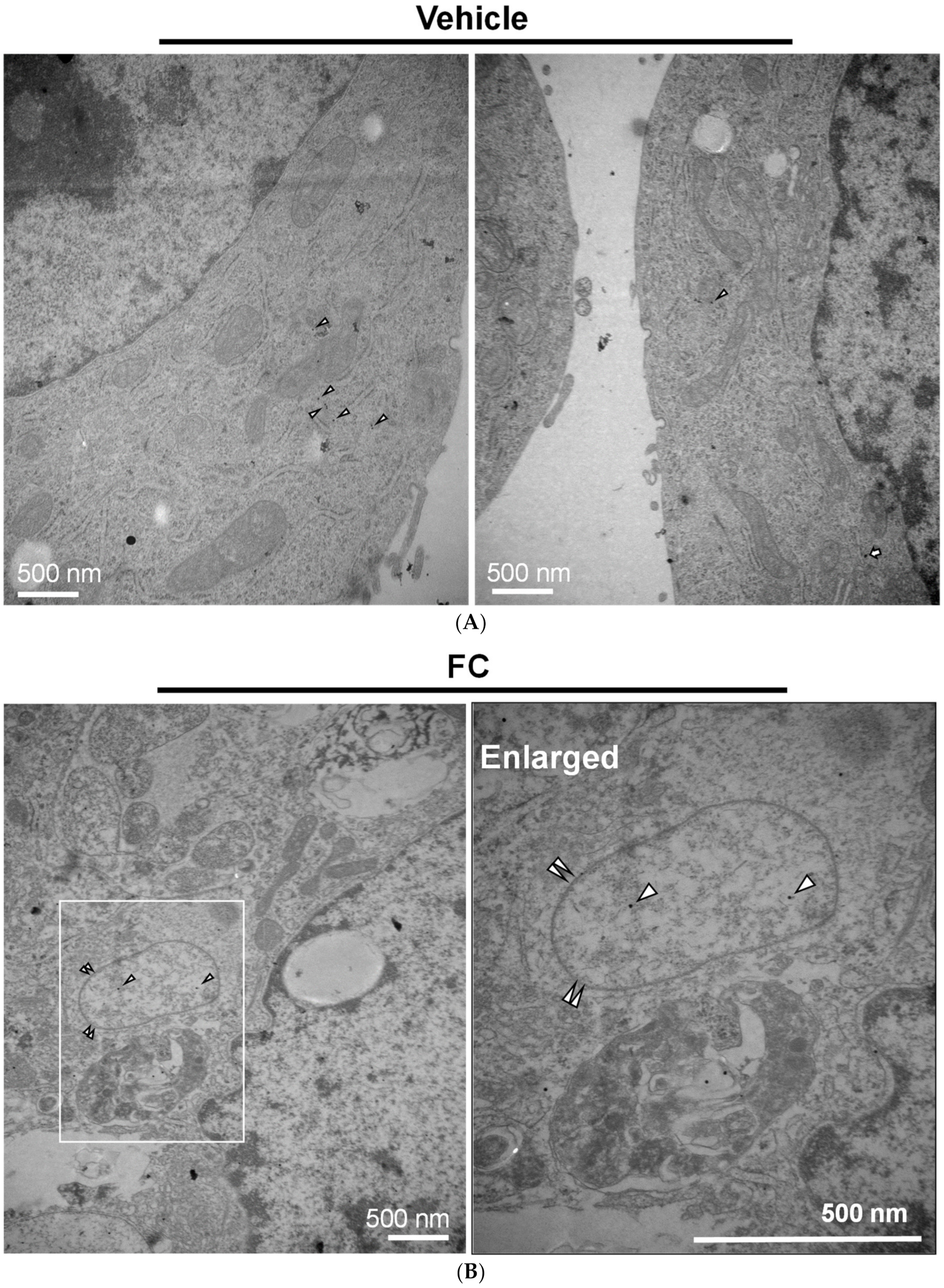
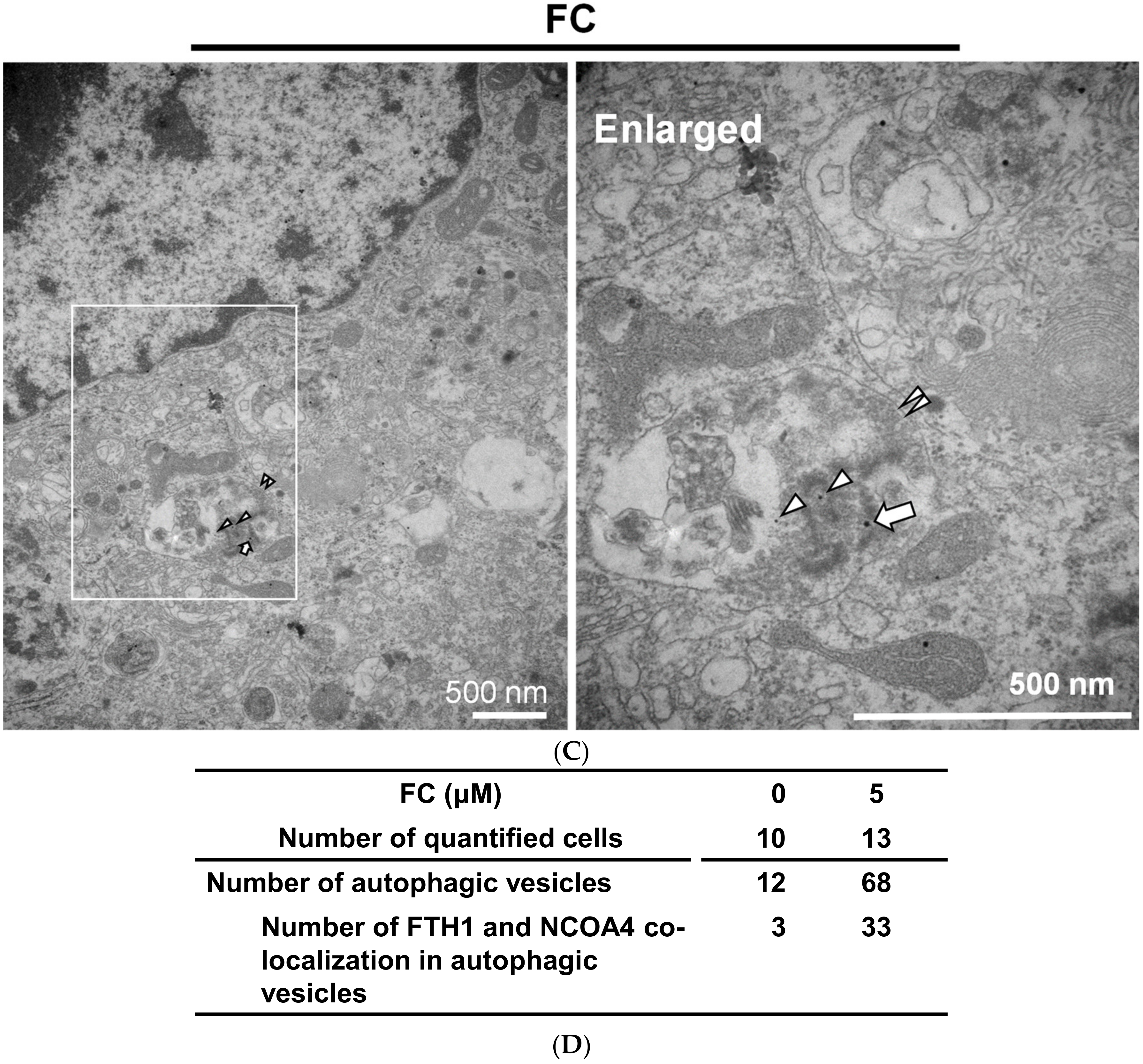
3.4. Confirmation of FC-Induced Ferritinophagy and Ferroptosis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Kazan, H.H.; Urfali-Mamatoglu, C.; Gunduz, U. Iron metabolism and drug resistance in cancer. Biometals Int. J. Role Met. Ions Biol. Biochem. Med. 2017, 30, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Dielschneider, R.F.; Henson, E.S.; Xiao, W.; Choquette, T.R.; Blankstein, A.R.; Chen, Y.; Gibson, S.B. Ferroptosis and autophagy induced cell death occur independently after siramesine and lapatinib treatment in breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancias, J.D.; Kimmelman, A.C. Mechanisms of Selective Autophagy in Normal Physiology and Cancer. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 1659–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Monian, P.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xiang, J.; Jiang, X. Ferroptosis is an autophagic cell death process. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancias, J.D.; Wang, X.; Gygi, S.P.; Harper, J.W.; Kimmelman, A.C. Quantitative proteomics identifies NCOA4 as the cargo receptor mediating ferritinophagy. Nature 2014, 509, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, D.H.; Blanchette, N.L.; Paul, B.T.; Torti, F.M.; Torti, S.V. Iron and cancer: Recent insights. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1368, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Lu, Y.H.; Wei, B.L.; Yang, S.C.; Won, S.J.; Lin, C.N. Phloroglucinols with prooxidant activity from Garcinia Subelliptica. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, S.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Tsai, M.L.; Tsao, L.T.; Ko, H.H.; Chung, M.I.; Lee, J.C.; Wang, J.P.; Won, S.J.; Lin, C.N. Potent cytotoxic lignans from Justicia procumbens and their effects on nitric oxide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in mouse macrophages. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Su, C.L.; Chen, L.L.; Won, S.J. Formosanin C-induced apoptosis requires activation of caspase-2 and change of mitochondrial membrane potential. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Lee, C.H.; Su, C.L.; Huang, C.W.; Liu, H.S.; Lin, C.N.; Won, S.J. Justicidin A decreases the level of cytosolic Ku70 leading to apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 1716–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skehan, P.; Storeng, R.; Scudiero, D.; Monks, A.; McMahon, J.; Vistica, D.; Warren, J.T.; Bokesch, H.; Kenney, S.; Boyd, M.R. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klionsky, D.J.; Cuervo, A.M.; Seglen, P.O. Methods for monitoring autophagy from yeast to human. Autophagy 2007, 3, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, S.J.; Yen, C.H.; Liu, H.S.; Wu, S.Y.; Lan, S.H.; Jiang-Shieh, Y.F.; Lin, C.N.; Su, C.L. Justicidin A-induced autophagy flux enhances apoptosis of human colorectal cancer cells via class III PI3K and Atg5 pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 930–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.J.; Yen, C.H.; Lin, T.Y.; Jiang-Shieh, Y.F.; Lin, C.N.; Chen, J.T.; Su, C.L. Autophagy mediates cytotoxicity of human colorectal cancer cells treated with garcinielliptone FC. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.S.; Ke, C.S.; Cheng, H.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Su, C.L. Curcumin-induced mitotic spindle defect and cell cycle arrest in human bladder cancer cells occurs partly through inhibition of Aurora A. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 80, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.Y.; Lan, S.H.; Cheng, D.E.; Chen, W.K.; Shen, C.H.; Lee, Y.R.; Zuchini, R.; Liu, H.S. Ras-related tumorigenesis is suppressed by BNIP3-mediated autophagy through inhibition of cell proliferation. Neoplasia N.Y. 2011, 13, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, A.N.; Xu, D.P.; Li, H.B. Antioxidant phytochemicals for the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases. Molecules 2015, 20, 21138–21156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, W.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V.; Hoskin, D.W. Dietary phytochemicals with anti-oxidant and pro-oxidant activities: A double-edged sword in relation to adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy? Cancer Lett. 2019, 452, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.E.; Zhang, L.; Ma, K.; Riegman, M.; Chen, F.; Ingold, I.; Conrad, M.; Turker, M.Z.; Gao, M.; Jiang, X.; et al. Ultrasmall nanoparticles induce ferroptosis in nutrient-deprived cancer cells and suppress tumour growth. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Synthetic lethal screening identifies compounds activating iron-dependent, nonapoptotic cell death in oncogenic-RAS-harboring cancer cells. Chem. Biol. 2008, 15, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Chen, S.; Huang, K.X.; Le, W.D. Why should autophagic flux be assessed? Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Xie, Y.; Song, X.; Sun, X.; Lotze, M.T.; Zeh, H.J., 3rd; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Autophagy promotes ferroptosis by degradation of ferritin. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowdle, W.E.; Nyfeler, B.; Nagel, J.; Elling, R.A.; Liu, S.; Triantafellow, E.; Menon, S.; Wang, Z.; Honda, A.; Pardee, G.; et al. Selective VPS34 inhibitor blocks autophagy and uncovers a role for NCOA4 in ferritin degradation and iron homeostasis in vivo. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancias, J.D.; Pontano Vaites, L.; Nissim, S.; Biancur, D.E.; Kim, A.J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Goessling, W.; Kimmelman, A.C.; Harper, J.W. Ferritinophagy via NCOA4 is required for erythropoiesis and is regulated by iron dependent HERC2-mediated proteolysis. Elife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellelli, R.; Federico, G.; Matte, A.; Colecchia, D.; Iolascon, A.; Chiariello, M.; Santoro, M.; de Franceschi, L.; Carlomagno, F. NCOA4 deficiency impairs systemic iron homeostasis. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, Y.; Kondo, S. Autophagy and cancer therapy. Autophagy 2006, 2, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskelinen, E.L.; Saftig, P. Autophagy: A lysosomal degradation pathway with a central role in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.; Noda, T.; Yoshimori, T. Dissection of the autophagosome maturation process by a novel reporter protein, tandem fluorescent-tagged LC3. Autophagy 2007, 3, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Sugita, Y.; Bannai, S. Regulation of glutathione levels in mouse spleen lymphocytes by transport of cysteine. J. Cell. Physiol. 1987, 133, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.A.; Yen, F.S.; Nicholson, S.P.V.; Alwaseem, H.; Bayraktar, E.C.; Alam, M.; Timson, R.C.; La, K.; Abu-Remaileh, M.; Molina, H.; et al. Maintaining iron homeostasis is the key role of lysosomal acidity for cell proliferation. Mol. Cell 2020, 77, 645–655.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G. Autophagy and NF-kappaB: Fight for fate. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007, 18, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Feng, P.; Ku, B.; Dotan, I.; Canaani, D.; Oh, B.H.; Jung, J.U. Autophagic and tumour suppressor activity of a novel Beclin1-binding protein UVRAG. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagoda, N.; von Rechenberg, M.; Zaganjor, E.; Bauer, A.J.; Yang, W.S.; Fridman, D.J.; Wolpaw, A.J.; Smukste, I.; Peltier, J.M.; Boniface, J.J.; et al. RAS-RAF-MEK-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels. Nature 2007, 447, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.T.; Chiang, H.C.; Fu, W.C.; Chien, K.Y.; Chung, Y.M.; Horng, L.Y. Formosanin-C, an immunomodulator with antitumor activity. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1990, 12, 777–786. [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick, D.E.; Oakenfull, D. Saponin content of food plants and some prepared foods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1983, 34, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zou, J.; Zhu, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Bai, P.; Xiao, X. Paris saponin II inhibits human ovarian cancer cell-induced angiogenesis by modulating NF-kappaB signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2190–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.C.; Wang, J.J.; Wu, R.T. Immunomodulating effects of the hydrolysis products of formosanin C and beta-ecdysone from Paris formosana Hayata. Anticancer. Res. 1992, 12, 1475–1478. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, G.; Sun, J.; Hou, Z.; Luan, W.; Wang, S.; Cui, S.; Cheng, M.; Liu, Y. Novel antitumor compound optimized from natural saponin Albiziabioside A induced caspase-dependent apoptosis and ferroptosis as a p53 activator through the mitochondrial pathway. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Man, S.; Liu, Z.; Ma, L.; Gao, W. A synergistic antitumor effect of polyphyllin I and formosanin C on hepatocarcinoma cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 4970–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Man, S.; Li, J.; Chai, H.; Fan, W.; Liu, Z.; Gao, W. The antitumor effect of formosanin C on HepG2 cell as revealed by 1H-NMR based metabolic profiling. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 220, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravikumar, P.R.; Hammesfahr, P.; Sih, C.J. Cytotoxic saponins from the Chinese herbal drug Yunnan Bai Yao. J. Pharm. Sci. 1979, 68, 900–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, R.; Tang, D. Autophagy and ferroptosis—What’s the connection? Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2017, 5, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krstic, J.; Galhuber, M.; Schulz, T.J.; Schupp, M.; Prokesch, A. p53 as a dichotomous regulator of liver disease: The dose makes the medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Kon, N.; Li, T.; Wang, S.J.; Su, T.; Hibshoosh, H.; Baer, R.; Gu, W. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature 2015, 520, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladner, S.K.; Otto, M.J.; Barker, C.S.; Zaifert, K.; Wang, G.H.; Guo, J.T.; Seeger, C.; King, R.W. Inducible expression of human hepatitis B virus (HBV) in stably transfected hepatoblastoma cells: A novel system for screening potential inhibitors of HBV replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Sun, Z.; Wang, X.J.; Jiang, T.; Huang, Z.; Fang, D.; Zhang, D.D. Direct interaction between Nrf2 and p21(Cip1/WAF1) upregulates the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response. Mol. Cell 2009, 34, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ou, Z.; Chen, R.; Niu, X.; Chen, D.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 2016, 63, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, S.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Panzilius, E.; Kobayashi, S.; Ingold, I.; Irmler, M.; Beckers, J.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Dave, K.B.; Doan, T.P.; Prescott, S.M. Fatty acid CoA ligase 4 is up-regulated in colon adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 8429–8434. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.J.; Xu, G.L. Overexpression of Acyl-CoA Ligase 4 (ACSL4) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and its prognosis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 4343–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Deng, F.; Li, Y.; Daniels, G.; Du, X.; Ren, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, V.; et al. ACSL4 promotes prostate cancer growth, invasion and hormonal resistance. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 44849–44863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ding, C.; Chen, Y.; Hu, W.; Lu, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Peng, C.; et al. ACSL4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via c-Myc stability mediated by ERK/FBW7/c-Myc axis. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, P.-L.; Tang, H.-H.; Wu, S.-Y.; Shaw, N.-S.; Su, C.-L. Saponin Formosanin C-Induced Ferritinophagy and Ferroptosis in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9080682
Lin P-L, Tang H-H, Wu S-Y, Shaw N-S, Su C-L. Saponin Formosanin C-Induced Ferritinophagy and Ferroptosis in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(8):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9080682
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Pin-Lun, Han-Hsuan Tang, Shan-Ying Wu, Ning-Sing Shaw, and Chun-Li Su. 2020. "Saponin Formosanin C-Induced Ferritinophagy and Ferroptosis in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells" Antioxidants 9, no. 8: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9080682
APA StyleLin, P.-L., Tang, H.-H., Wu, S.-Y., Shaw, N.-S., & Su, C.-L. (2020). Saponin Formosanin C-Induced Ferritinophagy and Ferroptosis in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Antioxidants, 9(8), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9080682




