Aging and Progression of Beta-Amyloid Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease Correlates with Microglial Heme-Oxygenase-1 Overexpression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Tissue Immunofluorescence
2.3. RNAscope in Situ Hybridization
2.4. Human Samples
2.5. Image Analysis
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
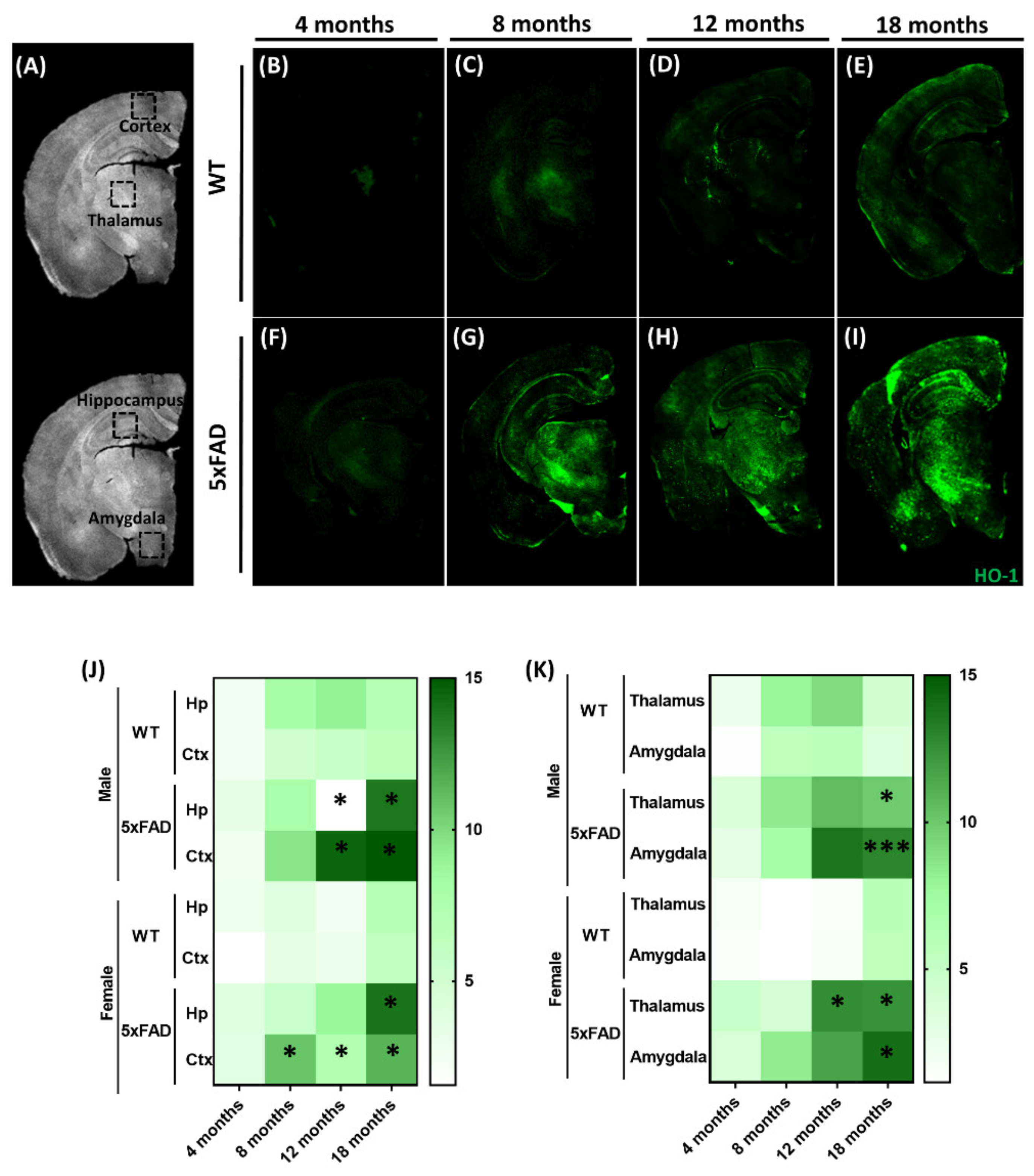
3.1. Expression of Brain HO-1 with Aging in the Alzheimer’s 5xFAD Animal Model
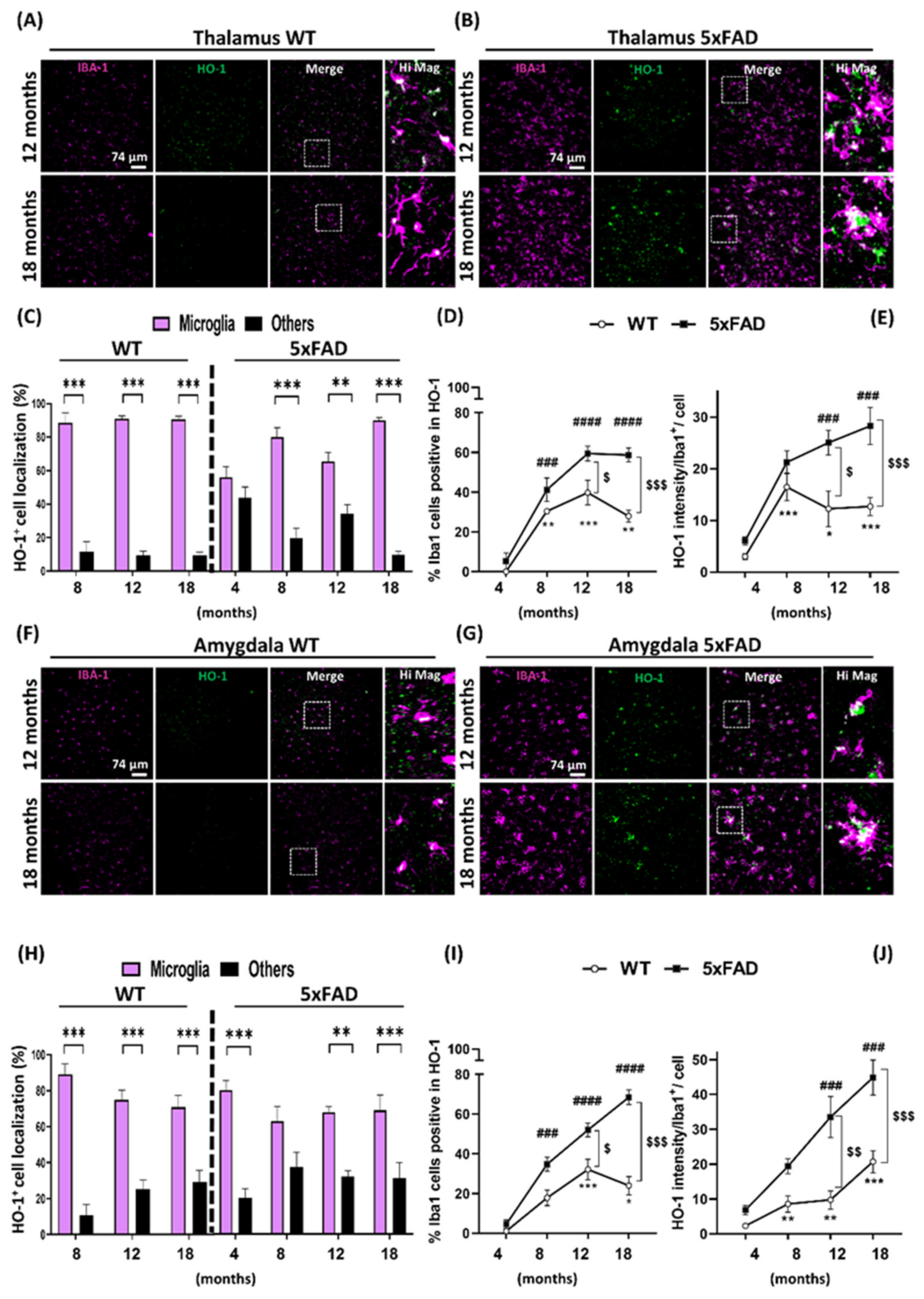
3.2. Microglia HO-1 Expression Profile in WT and 5xFAD Mice with Aging
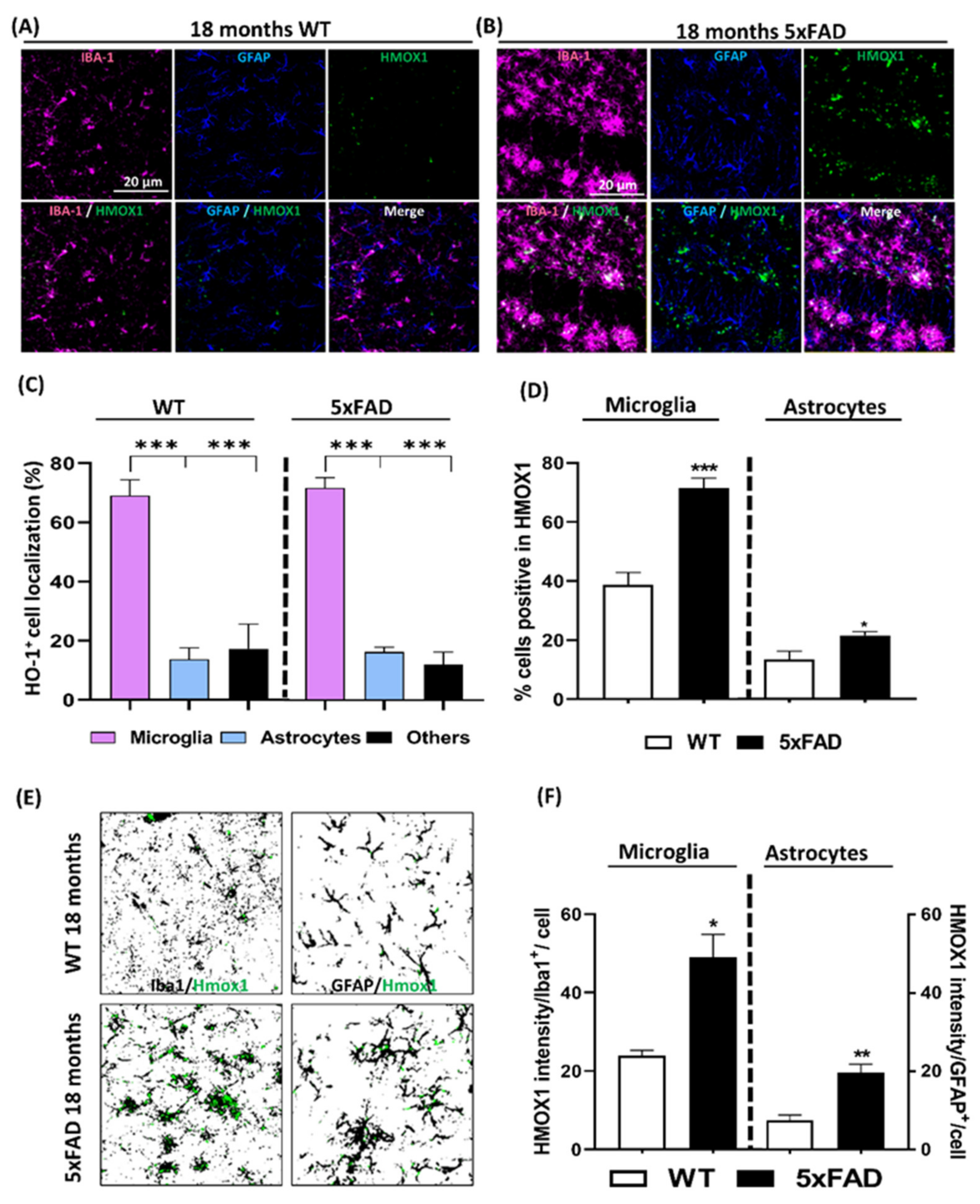
3.3. Localization Analysis of RNA Hmox1 in Glial Cells in Aged 5xFAD Mice
3.4. Localization of Microglia Overexpressing HO-1 Surrounding Aβ Plaques
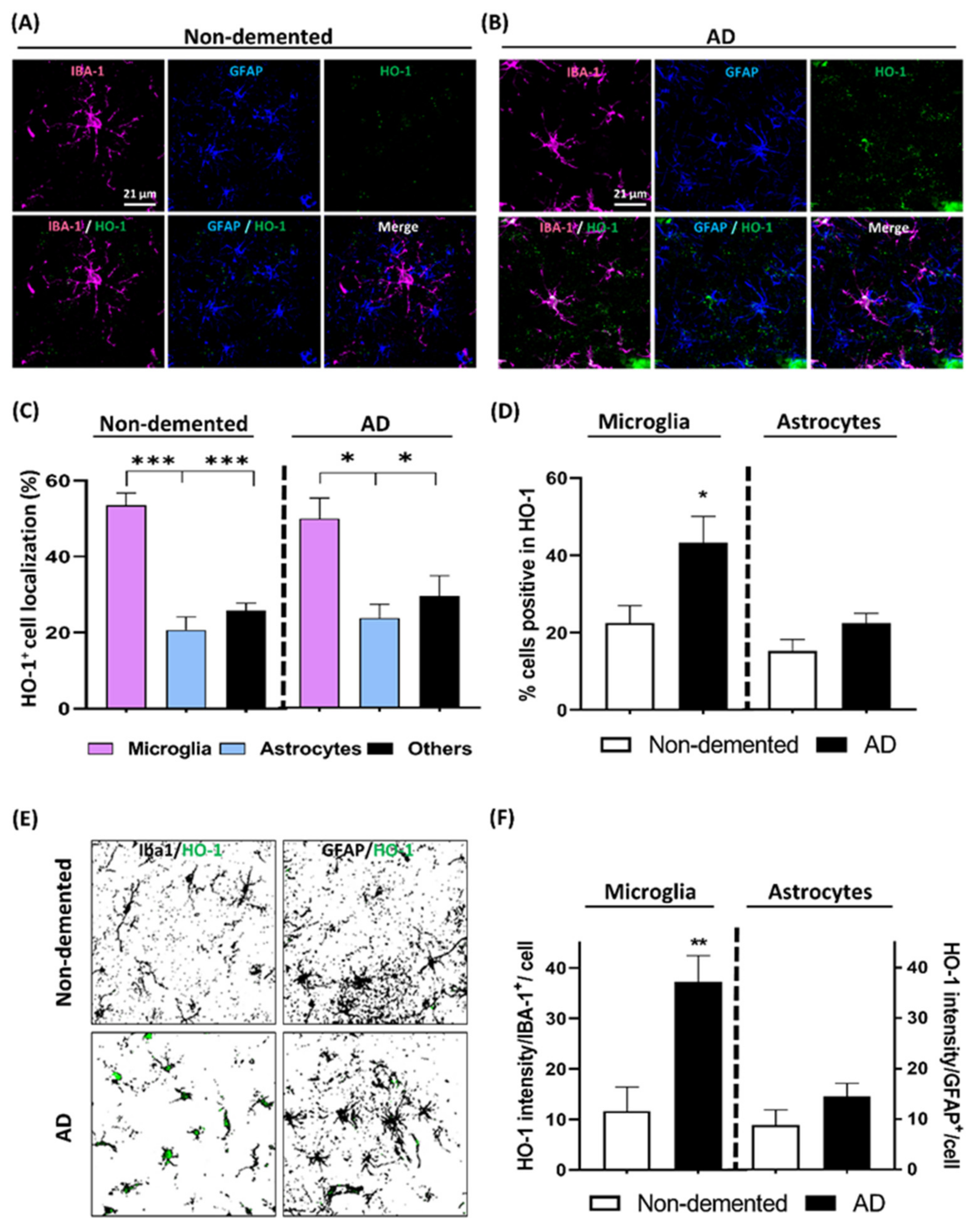
3.5. HO-1 Expression Analysis in the Cortex of AD Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lane, C.A.; Hardy, J.; Schott, J.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2017, 25, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.-P.; Xie, Y.; Meng, X.-Y.; Kang, J.-S. History and progress of hypotheses and clinical trials for Alzheimer’s disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiss, A.B.; Arain, H.A.; Stecker, M.M.; Siegart, N.M.; Kasselman, L.J. Amyloid toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 29, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, T.; Shakeri, A.; Rao, P.P.N. Amyloid cascade in Alzheimer’s disease: Recent advances in medicinal chemistry. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 113, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panza, F.; Lozupone, M.; Logroscino, G.; Imbimbo, B.P. A critical appraisal of amyloid-β-targeting therapies for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawhar, S.; Trawicka, A.; Jenneckens, C.; Bayer, T.A.; Wirths, O. Motor deficits, neuron loss, and reduced anxiety coinciding with axonal degeneration and intraneuronal Aβ aggregation in the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 196.e29–196.e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, B.C.; Kurdakova, A.; Baches, S.; Bayer, T.A.; Weggen, S.; Wirths, O. Gene Dosage Dependent Aggravation of the Neurological Phenotype in the 5XFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 45, 1223–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, M.W.; Stevens, B. Microglia emerge as central players in brain disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritzel, R.M.; Patel, A.R.; Pan, S.; Crapser, J.; Hammond, M.; Jellison, E.; McCullough, L.D.; Crapser, J. Age- and location-related changes in microglial function. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 2153–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, D.V.; Hanson, J.E.; Sheng, M. Microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 217, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-W.; Zong, Y.; Cao, X.-P.; Tan, L.; Tan, L. Microglial priming in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Holtzman, D.M. Interplay between innate immunity and Alzheimer disease: APOE and TREM2 in the spotlight. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitti, M.; Piras, S.; Brondolo, L.; Marinari, U.M.; Pronzato, M.A.; Furfaro, A.L. Heme Oxygenase 1 in the Nervous System: Does It Favor Neuronal Cell Survival or Induce Neurodegeneration? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schipper, H.M.; Song, W.; Tavitian, A.; Cressatti, M. The sinister face of heme oxygenase-1 in brain aging and disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 172, 40–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, J.; Den, Z. Distal AP-1 binding sites mediate basal level enhancement and TPA induction of the mouse heme oxygenase-1 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 21894–21900. [Google Scholar]
- Wijayanti, N.; Huber, S.; Samoylenko, A.; Kietzmann, T.; Immenschuh, S. Role of NF-kB and p38 MAP Kinase Signaling Pathways in the Lipopolysaccharide-Dependent Activation of Heme Oxygenase-1 Gene Expression. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2004, 6, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, K.; Men, F.; Wang, W.-C.; Zhou, Y.-Q.; Zhang, H.-W.; Ye, D.-W. Carbon Monoxide and Its Controlled Release: Therapeutic Application, Detection, and Development of Carbon Monoxide Releasing Molecules (CORMs). J. Med. Chem. 2017, 61, 2611–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikam, A.; Ollivier, A.; Rivard, M.; Wilson, J.L.; Mebarki, K.; Martens, T.; Dubois-Randé, J.-L.; Motterlini, R.; Foresti, R. Diverse Nrf2 Activators Coordinated to Cobalt Carbonyls Induce Heme Oxygenase-1 and Release Carbon Monoxide in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motterlini, R.; Nikam, A.; Manin, S.; Ollivier, A.; Wilson, J.L.; Djouadi, S.; Muchova, L.; Martens, T.; Rivard, M.; Foresti, R. HYCO-3, a dual CO-releaser/Nrf2 activator, reduces tissue inflammation in mice challenged with lipopolysaccharide. Redox Biol. 2018, 20, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, N.; Dallas, M.L.; Al-Owais, M.; Jarosz-Griffiths, H.H.; Hooper, N.M.; Scragg, J.; Boyle, J.; Peers, C. Heme oxygenase-1 protects against Alzheimer’s amyloid-β(1-42)-induced toxicity via carbon monoxide production. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, W.; Ikematsu, K.; Tsuda, R. Age-associated increases in heme oxygenase-1 and ferritin immunoreactivity in the autopsied brain. Leg. Med. 2003, 5, S360–S366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, H.M.; Cisse, S.; Stopa, E.G. Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in the senescent and alzheimer-diseased brain. Ann. Neurol. 1995, 37, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, H.; Liberman, A.; Stopa, E. Neural Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression in Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease. Exp. Neurol. 1998, 150, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyman, B.T.; Phelps, C.H.; Beach, T.G.; Bigio, E.H.; Cairns, N.J.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dickson, D.W.; Duyckaerts, C.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; et al. National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2012, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuadrado, A.; Rojo, A. Heme Oxygenase-1 as a Therapeutic Target in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Brain Infections. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Sykiotis, G.P.; Nishimura, M.; Bodmer, R.; Bohmann, D. Declining signal dependence of Nrf2-MafS-regulated gene expression correlates with aging phenotypes. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.H.; Shenvi, S.V.; Dixon, B.M.; Liu, H.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Liu, R.M.; Hagen, T.M. Decline in transcriptional activity of Nrf2 causes age-related loss of glutathione synthesis, which is reversible with lipoic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3381–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Shen, D.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z. Early induction of oxidative stress in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease with heme oxygenase activity. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.A.; Kutty, R.K.; Richey, P.L.; Yan, S.D.; Stern, D.; Chader, G.J.; Wiggert, B.; Petersen, R.B.; Perry, G. Heme oxygenase-1 is associated with the neurofibrillary pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 145, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perry, V.H.; Holmes, C. Microglial priming in neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Sloan, S.A.; Bennett, M.L.; Scholze, A.R.; O’Keeffe, S.; Phatnani, H.P.; Guarnieri, P.; Caneda, C.; Ruderisch, N.; et al. An RNA-Sequencing Transcriptome and Splicing Database of Glia, Neurons, and Vascular Cells of the Cerebral Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 11929–11947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sloan, S.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Caneda, C.; Plaza, C.A.; Blumenthal, P.D.; Vogel, H.; Steinberg, G.K.; Edwards, M.S.B.; Li, G.; et al. Purification and Characterization of Progenitor and Mature Human Astrocytes Reveals Transcriptional and Functional Differences with Mouse. Neuron 2016, 89, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakimura, J.-I.; Kitamura, Y.; Takata, K.; Umeki, M.; Suzuki, S.; Shibagaki, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Nomura, Y.; Gebicke-Haerter, P.J.; Smith, M.A.; et al. Microglial activation and amyloid-β clearance induced by exogenous heat-shock proteins. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, A.; Mela, V.; Harty, C.; Minogue, A.M.; Costello, D.; Kerskens, C.; Lynch, M.A. Iron accumulation in microglia triggers a cascade of events that leads to altered metabolism and compromised function in APP/PS1 mice. Brain Pathol. 2019, 29, 606–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheignon, C.; Tomas, M.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Faller, P.; Hureau, C.; Collin, F. Oxidative stress and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Redox Biol. 2017, 14, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.-N.; Qian, Z.-M.; Wu, K.-C.; Yung, W.-H.; Ke, Y. Expression of Iron Transporters and Pathological Hallmarks of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Diseases in the Brain of Young, Adult, and Aged Rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 54, 5213–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaidi, A.A.; Bush, I.A. Iron neurochemistry in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease: Targets for therapeutics. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, H.; Gupta, A.; Szarek, W. Suppression of Glial HO-1 Activitiy as a Potential Neurotherapeutic Intervention in AD. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2009, 6, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Sun, C.; et al. Heme Oxygenase 1 Induces Tau Oligomer Formation and Synapse Aberrations in Hippocampal Neurons. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 65, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hui, Y.; Peng, Y.; Tang, L.; Jin, J.; He, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Overexpression of Heme Oxygenase 1 Causes Cognitive Decline and Affects Pathways for Tauopathy in Mice. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 43, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Peng, Y.; Hui, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Si, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, D.; et al. Overexpression of Heme Oxygenase 1 Impairs Cognitive Ability and Changes the Plasticity of the Synapse. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 47, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.Y.; Choi, B.-O.; Jeong, J.H.; Kong, K.A.; Hwang, J.; Ahn, J.-H. Amyloid Beta-Mediated Hypomethylation of Heme Oxygenase 1 Correlates with Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Lacoste, B.; Pistel, P.J.; Ingram, D.K.; Hamel, E.; Alaoui-Jamali, M.A.; Szarek, W.A.; Vlahakis, J.Z.; Jie, S.; Song, W.; et al. Neurotherapeutic effects of novel HO-1 inhibitorsin vitroand in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2014, 131, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, D.G.; Caruso, M.; Murchison, C.F.; Zhu, J.Y.; Wright, K.M.; Harris, C.J.; Gray, N.E.; Quinn, J.F.; Soumyanath, A. Centella Asiatica Improves Memory and Promotes Antioxidative Signaling in 5XFAD Mice. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettiarachchi, N.T.; Boyle, J.P.; Dallas, M.L.; Al-Owais, M.M.; Scragg, J.L.; Peers, C. Heme oxygenase-1 derived carbon monoxide suppresses Aβ1-42 toxicity in astrocytes. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morroni, F.; Sita, G.; Graziosi, A.; Turrini, E.; Fimognari, C.; Tarozzi, A.; Hrelia, P. Neuroprotective Effect of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester in A Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease Involves Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, C. Upregulation of Heme Oxygenase-1 by Acteoside Through ERK and PI3 K/Akt Pathway Confer Neuroprotection Against Beta-Amyloid-Induced Neurotoxicity. Neurotox. Res. 2011, 21, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, F.U.; Shah, S.A.; Kim, M.O. Vanillic acid attenuates Aβ1-42-induced oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagone, P.; Patti, F.; Mangano, K.; Mammana, S.; Coco, M.; Touil-Boukoffa, C.; Chikovani, T.; Di Marco, R.; Nicoletti, F. Heme oxygenase-1 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells correlates with disease activity in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 261, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pan, K.; Chen, L.; Ning, J.; Li, X.; Yang, T.; Terrando, N.; Gu, J.; Tao, G. Deferoxamine regulates neuroinflammation and iron homeostasis in a mouse model of postoperative cognitive dysfunction. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblanc, R.H.; Chen, R.; Selim, M.H.; Hanafy, K.A. Heme oxygenase-1-mediated neuroprotection in subarachnoid hemorrhage via intracerebroventricular deferoxamine. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, L.-M.; Li, Y.-F.; Mi, W.-D. Deferoxamine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and memory impairment in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanella, L.; Barbagallo, I.; Tibullo, D.; Forte, S.; Zappalá, A.; Volti, G.L. The non-canonical functions of the heme oxygenases. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 69075–69086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murohashi, K.; Hara, Y.; Shinada, K.; Nagai, K.; Shinkai, M.; Kawana, A.; Kaneko, T. Clinical Significance of Serum Hemeoxygenase-1 as a New Biomarker for the Patients with Interstitial Pneumonia. Can. Respir. J. 2018, 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, K. Heme oxygenase-1 and acute kidney injury. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2014, 23, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, T.; Saiki, S.; Okuzumi, A.; Mohney, R.P.; Hattori, N. Identification of novel biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease by metabolomic technologies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 87, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Kothari, V.; Velly, A.M.; Cressatti, M.; Liberman, A.; Gornitsky, M.; Schipper, H.M. Evaluation of salivary heme oxygenase-1 as a potential biomarker of early Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, I.; Infante, J.; Sánchez-Juan, P.; García-Gorostiaga, I.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, E.; Vázquez-Higuera, J.L.; Berciano, J.; Combarros, O. Serum heme oxygenase-1 levels are increased in Parkinson’s disease but not in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2010, 121, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, H.M. Biomarker potential of heme oxygenase-1 in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Biomarkers Med. 2007, 1, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Mendívil, C.; Arreola, M.A.; Hohsfield, L.A.; Green, K.N.; Lopez, M.G. Aging and Progression of Beta-Amyloid Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease Correlates with Microglial Heme-Oxygenase-1 Overexpression. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9070644
Fernández-Mendívil C, Arreola MA, Hohsfield LA, Green KN, Lopez MG. Aging and Progression of Beta-Amyloid Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease Correlates with Microglial Heme-Oxygenase-1 Overexpression. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(7):644. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9070644
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Mendívil, Cristina, Miguel A. Arreola, Lindsay A. Hohsfield, Kim N. Green, and Manuela G. Lopez. 2020. "Aging and Progression of Beta-Amyloid Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease Correlates with Microglial Heme-Oxygenase-1 Overexpression" Antioxidants 9, no. 7: 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9070644
APA StyleFernández-Mendívil, C., Arreola, M. A., Hohsfield, L. A., Green, K. N., & Lopez, M. G. (2020). Aging and Progression of Beta-Amyloid Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease Correlates with Microglial Heme-Oxygenase-1 Overexpression. Antioxidants, 9(7), 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9070644





