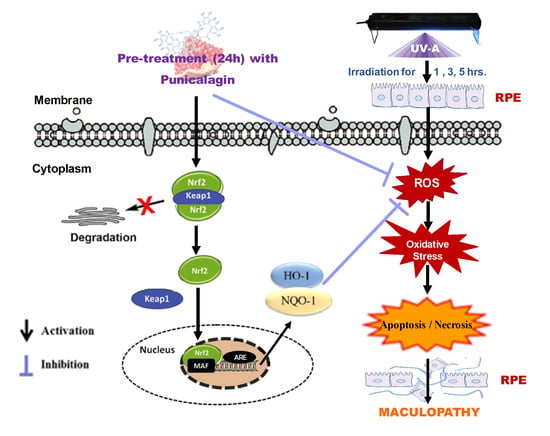
Punicalagin Protects Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells from Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Oxidative Damage by Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway and Reducing Apoptosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture Conditions and UV Exposure
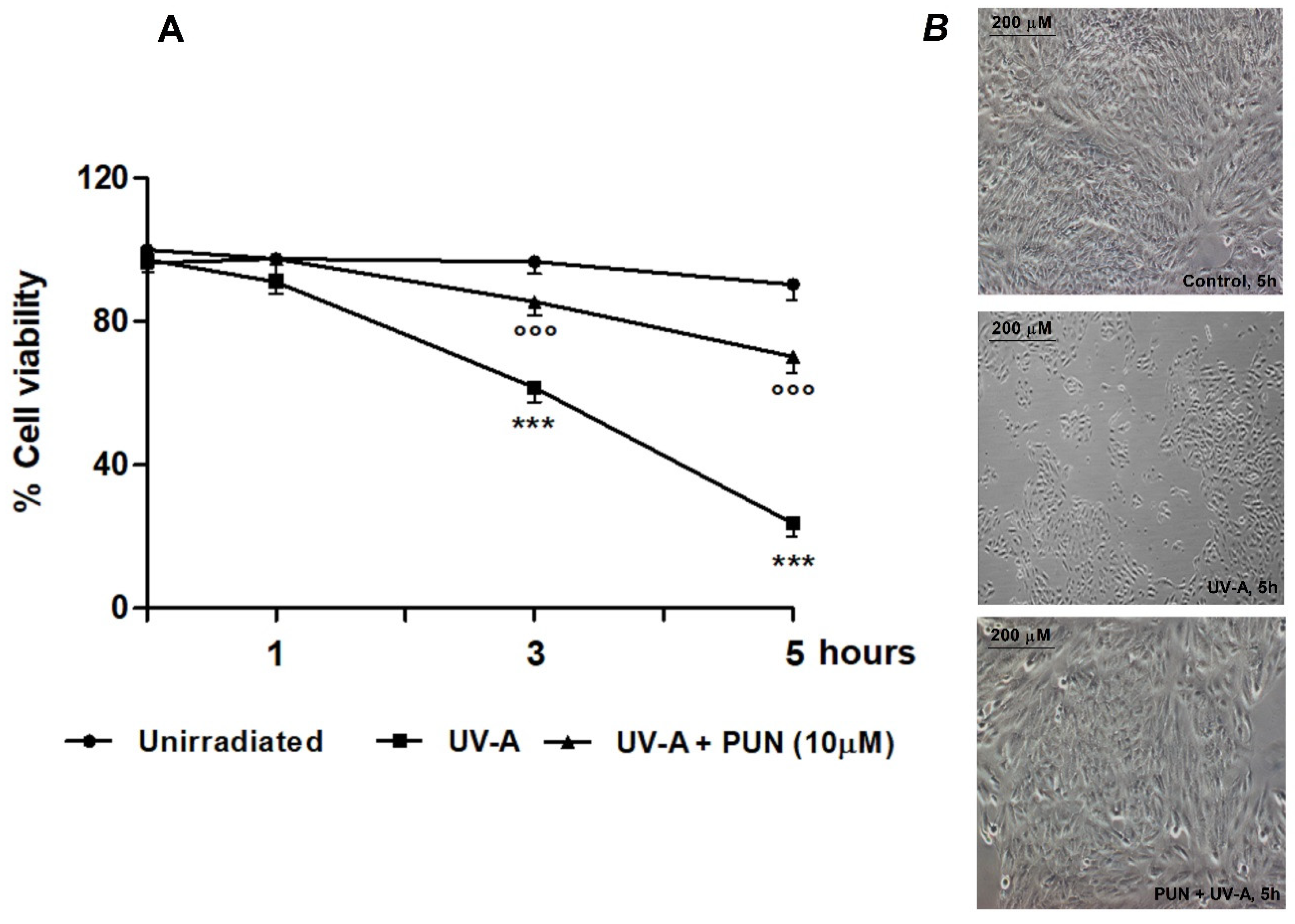
2.2. Cell Viability
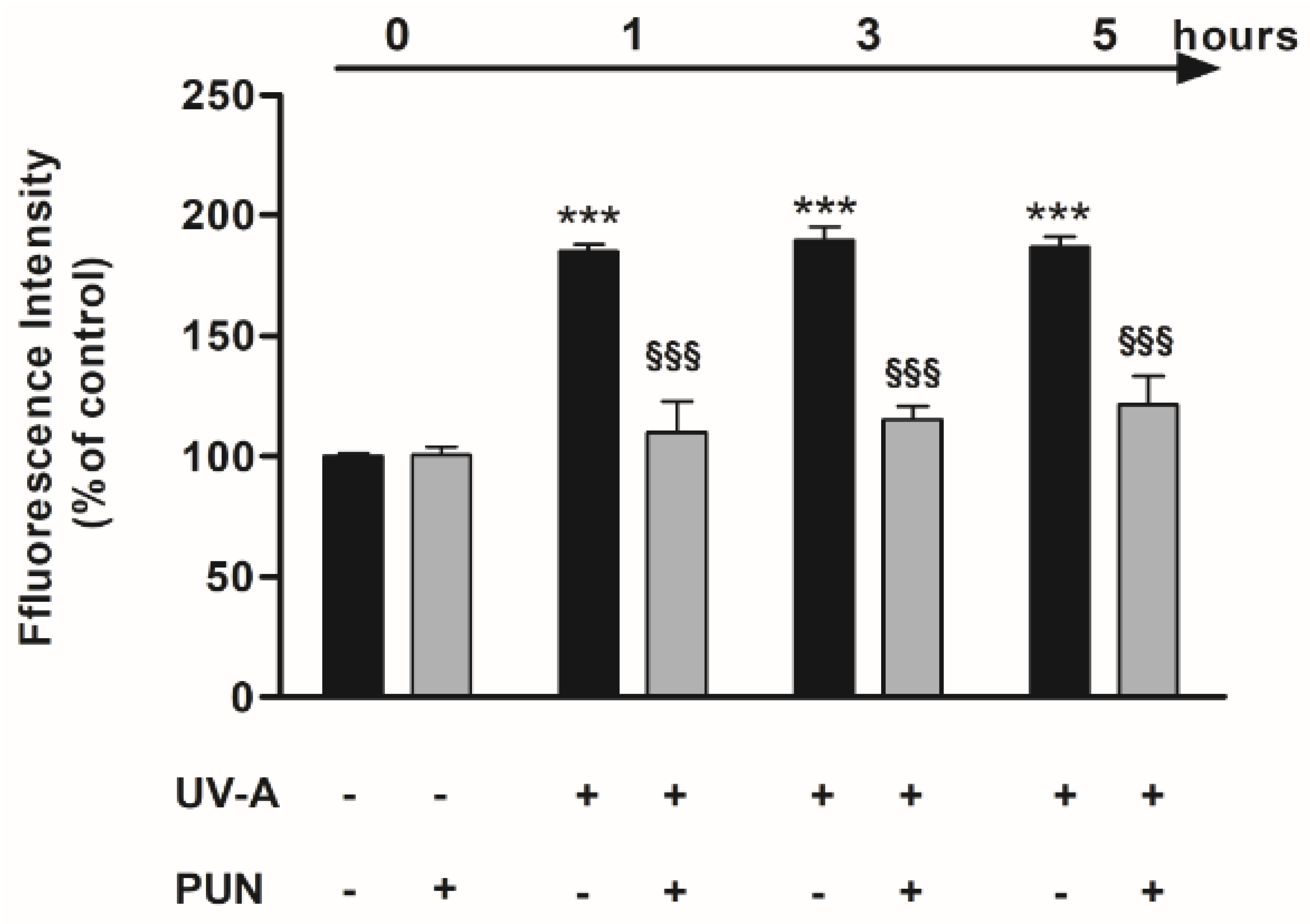
2.3. Detection of ROS
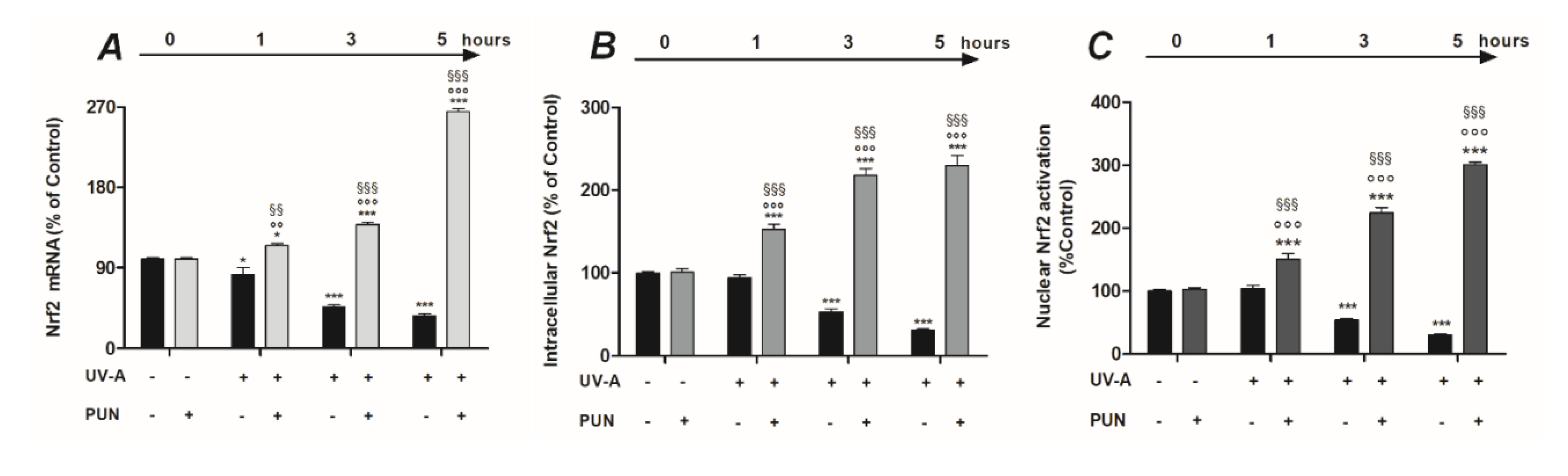
2.4. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR
2.5. Quantification of Intracellular Levels and Nuclear Activation of Nrf2
2.6. Bax and Bcl-2 Detection
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Protective Role of PUN against UV-A-Induced Oxidative Stress and Cell Death
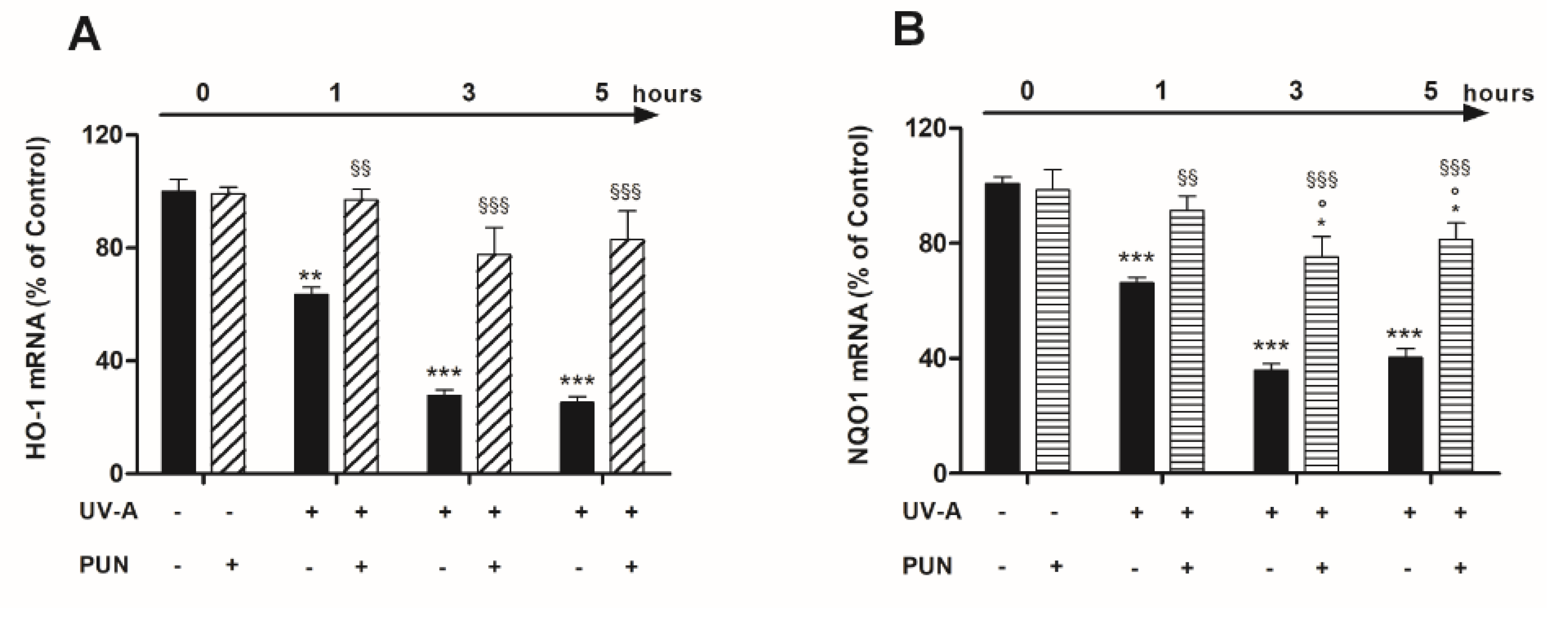
3.2. PUN Protects ARPE-19 Cells from UV Damages by Activating Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 Signaling
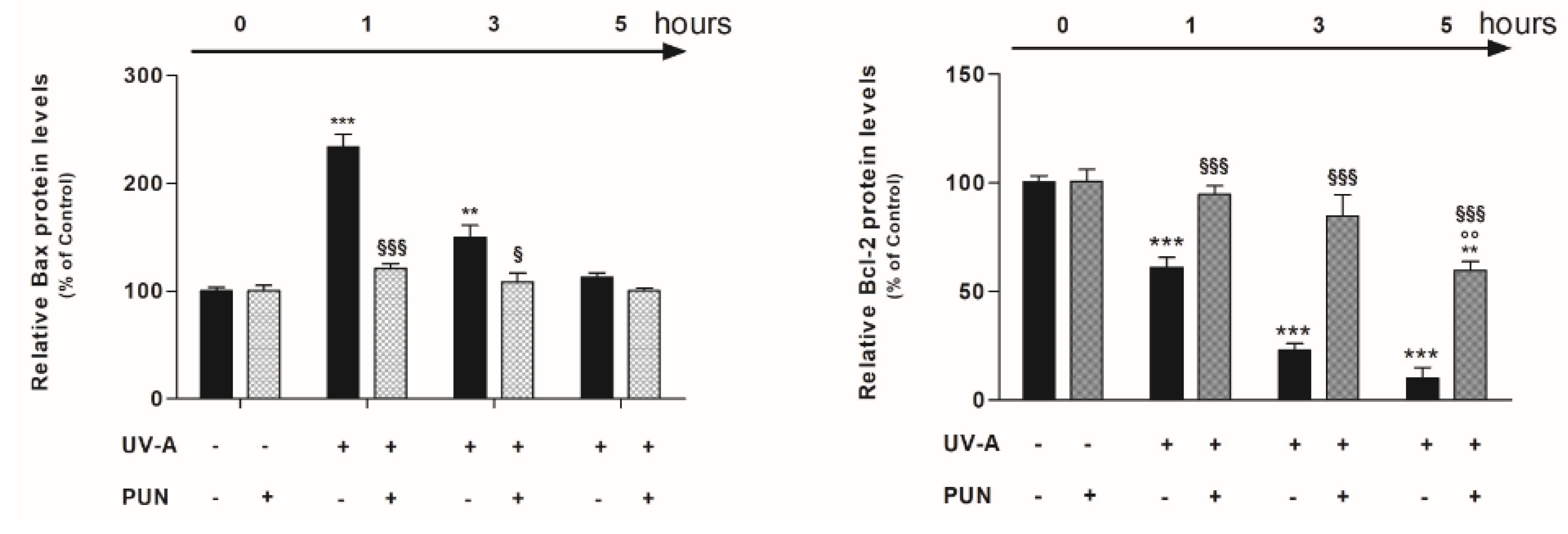
3.3. PUN Modulates UV-A-Induced Bax and Bcl-2 Protein Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strauss, O. The retinal pigment epithelium in visual function. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 845–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauß, O. Pharmacology of the retinal pigment epithelium, the interface between retina and body system. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 787, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, B.; Dalpiaz, A. Retinal pigment epithelial cells as a therapeutic tool and target against retinopathies. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaarniranta, K.; Tokarz, P.; Koskela, A.; Paterno, J.; Blasiak, J. Autophagy regulates death of retinal pigment epithelium cells in age-related macular degeneration. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2017, 33, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.; Krebs, M.P.; Mao, H.; Jones, K.; Conners, M.; Lewin, A.S. Pathological Consequences of Long-Term Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress in the Mouse Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Exp. Eye Res. 2012, 101, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tringali, G.; Sampaolese, B.; Clementi, M.E. Expression of early and late cellular damage markers by ARPE-19 cells following prolonged treatment with UV-A radiation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 3485–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defence. World Allergy Organ. J. 2012, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorusupudi, A.; Nelson, K.; Bernstein, P.S. The Age-Related Eye Disease 2 Study: Micronutrients in the Treatment of Macular Degeneration. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardi, M.; Marangoni, D.; Minnella, A.; Savastano, M.C.; Valentini, P.; Ambrosio, L.; Capoluongo, E.; Maccarone, R.; Bisti, S.; Falsini, B. A longitudinal follow-up study of saffron supplementation in early age-related macular degeneration: Sustained benefits to central retinal function. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2012, 2012, 429124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiri, S. Evaluation of antioxidant and antiradical properties of Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) seed and defatted seed extracts. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeram, N.P.; Aviram, M.; Zhang, Y.; Henning, S.M.; Feng, L.; Dreher, M.; Heber, D. Comparison of antioxidant potency of commonly consumed polyphenol-rich beverages in the United States. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, M.I.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Hess-Pierce, B.; Holcroft, D.M.; Kader, A.A. Antioxidant activity of pomegranate juice and its relationship with phenolic composition and processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4581–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.P.; Mahal, H.S.; Kapoor, S.; Aradhya, S.M. In vitro studies on the binding, antioxidant, and cytotoxic actions of punicalagin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Tuuli, M.G.; Longtine, M.S.; Shin, J.S.; Lawrence, R.; Inder, T.; Michael Nelson, D. Pomegranate juice and punicalagin attenuate oxidative stress and apoptosis in human placenta and in human placental trophoblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E1142–E1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Hsu, Y.F.; Lin, T.C.; Hsu, H.Y. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of punicalagin and punicalin on acetaminophen-induced liver damage in rats. Phytother. Res. 2001, 15, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementi, M.E.; Pani, G.; Sampaolese, B.; Tringali, G. Punicalagin reduces H2O2-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in PC12 cells by modulating the levels of reactive oxygen species. Nutr. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Kuse, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Hara, H.; Shimazawa, M. Transient acceleration of autophagic degradation by pharmacological Nrf2 activation is important for retinal pigment epithelium cell survival. Redox Biol. 2018, 19, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambros, M.L.; Plafker, S.M. Oxidative Stress and the Nrf2 Anti-Oxidant Transcription Factor in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 854, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kleszczyński, K.; Zillikens, D.; Fischer, T.W. Melatonin enhances mitochondrial ATP synthesis, reduces reactive oxygen species formation, and mediates translocation of the nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2 resulting in activation of phase-2 antioxidant enzymes (γ-GCS, HO-1, NQO1) in ultraviolet radiation-treated normal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHEK). J. Pineal Res. 2016, 61, 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Bucolo, C.; Drago, F.; Maisto, R.; Romano, G.L.; D’Agata, V.; Maugeri, G.; Giunta, S. Curcumin Prevents High Glucose Damage in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Through ERK1/2-mediated Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 17295–17304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlich, F. BCL-2 proteins and apoptosis: Recent insights and unknowns. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; He, S.; Yin, P.; Li, D.; Mei, C.; Yu, X.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liu, F. Punicalagin induces Nrf2 translocation and HO-1 expression via PI3K/Akt, protecting rat intestinal epithelial cells from oxidative stress. Int. J. Hyperth. 2016, 32, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, J.; He, S.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, Q. Punicalagin, a PTP1B inhibitor, induces M2c phenotype polarization via up-regulation of HO-1 in murine macrophages. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 110, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.; Kim, C.Y.; Hwang, J.; Jo, K.; Kim, S.; Suh, H.J.; Choi, H.S. Punicalagin, a Pomegranate-Derived Ellagitannin, Suppresses Obesity and Obesity-Induced Inflammatory Responses Via the Nrf2/Keap1 Signaling Pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Peng, X.; Wei, Z.F.; Wei, F.Y.; Wang, W.; Ma, W.D.; Yao, L.P.; Fu, Y.J.; Zu, Y.G. Geraniin Exerts Cytoprotective Effect Against Cellular Oxidative Stress by Upregulation of Nrf2-mediated Antioxidant Enzyme Expression via PI3K/AKT and ERK1/2 Pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 1751–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Singh, J.P.; Kaur, A.; Singh, N. Phenolic compounds as beneficial phytochemicals in pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) peel: A review. Food Chem. 2018, 261, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, J.; Qin, H.; Yang, L. A new possible mechanism by which punicalagin protects against liver injury induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus: Upregulation of autophagy via the Akt/FoxO3a signaling pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13948–13959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Yao, X.; Xu, S.; Pan, J.; Yu, H.; Bao, J.; Guan, H.; Lu, R.; Zahng, L. Punicalagin induces senescent growth arrest in human papillary thyroid carcinoma BCPAP cells via NF-κB signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Y.; Chang, S.F.; Chau, S.F.; Chiu, S.C. The Protective Effect of Hispidin against Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress in ARPE-19 Cells via Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.W.; Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.D.; Hu, Z.L. S-allyl cysteine protects retinal pigment epithelium cells from hydroquinone-induced apoptosis through mitigating cellular response to oxidative stress. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 2120–2128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, Z.; Han, J.; Wei, G.; Yi, B.; Li, Z. Rhizoma Paridis total saponins alleviate H2O2 induced oxidative stress injury by upregulating the Nrf2 pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nita, M.; Grzybowski, A. The Role of the Reactive Oxygen Species and Oxidative Stress in the Pathomechanism of the Age-Related Ocular Diseases and Other Pathologies of the Anterior and Posterior Eye Segments in Adults. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 3164734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparrrow, J.R.; Hicks and Hamel, C.P. The retinal pigment epithelium in health and disease. Curr. Mol. Med. 2010, 10, 802–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanus, J.; Anderson, C.; Wang, S. RPE necroptosis in response to oxidative stress and in AMD. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 24 Pt B, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Cano, M.; Ebrahimi, K.; Wang, L.; Handa, J.T. The impact of oxidative stress and inflammation on RPE degeneration in non-neovascular AMD. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2017, 60, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batliwala, S.; Xavier, C.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Pang, I.H. Involvement of Nrf2 in Ocular Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1703810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W.; Motohashi, H. The KEAP1-NRF2 system: A thiol-based sensor-effector apparatus for maintaining redox homeostasis. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1169–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Li, J.; Johnson, D.A.; Stein, T.D.; Kraft, A.D.; Calkins, M.J.; Jakel, R.J.; Johnson, J.A. Nrf2, a multi-organ protector? FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niture, S.K.; Jaiswal, A.K. Nrf2 protein up-regulates antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 and prevents cellular apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 9873–9886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, F.; Tian, H.; Li, W.; Hung, H.; Sun, F. Potential role of punicalagin against oxidative stress induced testicular damage. Asian J. Androl. 2016, 18, 627–632. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Li, H.; Hou, X.; Li, D.; He, S.; Wan, C.; Yin, P.; Liu, M.; Liu, F.; Xu, J. Punicalagin Induces Nrf2/HO-1 Expression via Upregulation of PI3K/AKT Pathway and Inhibits LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 380218. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.R.; Gao, Z.H.; Qu, X.J. Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway and natural products for cancer chemoprevention. Cancer Epidemiol. 2010, 34, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Genes | Forward | Reverse | Product Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nrf2 (NM_006164.5) | GTCACATCGAGAGCCCAGTC | ACCATGGTAGTCTCAACCAGC | 193 |
| HO-1 (NM_002133.3) | CTGGAGGAGGAGATTGAGCG | ATGGCTGGTGTGTAGGGGAT | 152 |
| NQO1 (NM_000903.3) | GGTTTGAGCGAGTGTTCATAGG | GCAGAGAGTACATGGAGCCAC | 129 |
| GAPDH (NM_002046.7) | AACGGATTTGGTCGTATTG | GGAAGATGGTGATGGGATT | 208 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clementi, M.E.; Sampaolese, B.; Sciandra, F.; Tringali, G. Punicalagin Protects Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells from Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Oxidative Damage by Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway and Reducing Apoptosis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060473
Clementi ME, Sampaolese B, Sciandra F, Tringali G. Punicalagin Protects Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells from Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Oxidative Damage by Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway and Reducing Apoptosis. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(6):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060473
Chicago/Turabian StyleClementi, Maria Elisabetta, Beatrice Sampaolese, Francesca Sciandra, and Giuseppe Tringali. 2020. "Punicalagin Protects Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells from Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Oxidative Damage by Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway and Reducing Apoptosis" Antioxidants 9, no. 6: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060473
APA StyleClementi, M. E., Sampaolese, B., Sciandra, F., & Tringali, G. (2020). Punicalagin Protects Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells from Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Oxidative Damage by Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway and Reducing Apoptosis. Antioxidants, 9(6), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060473