High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Triglyceride and Oxidized HDL: New Lipid Biomarkers of Lipoprotein-Related Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
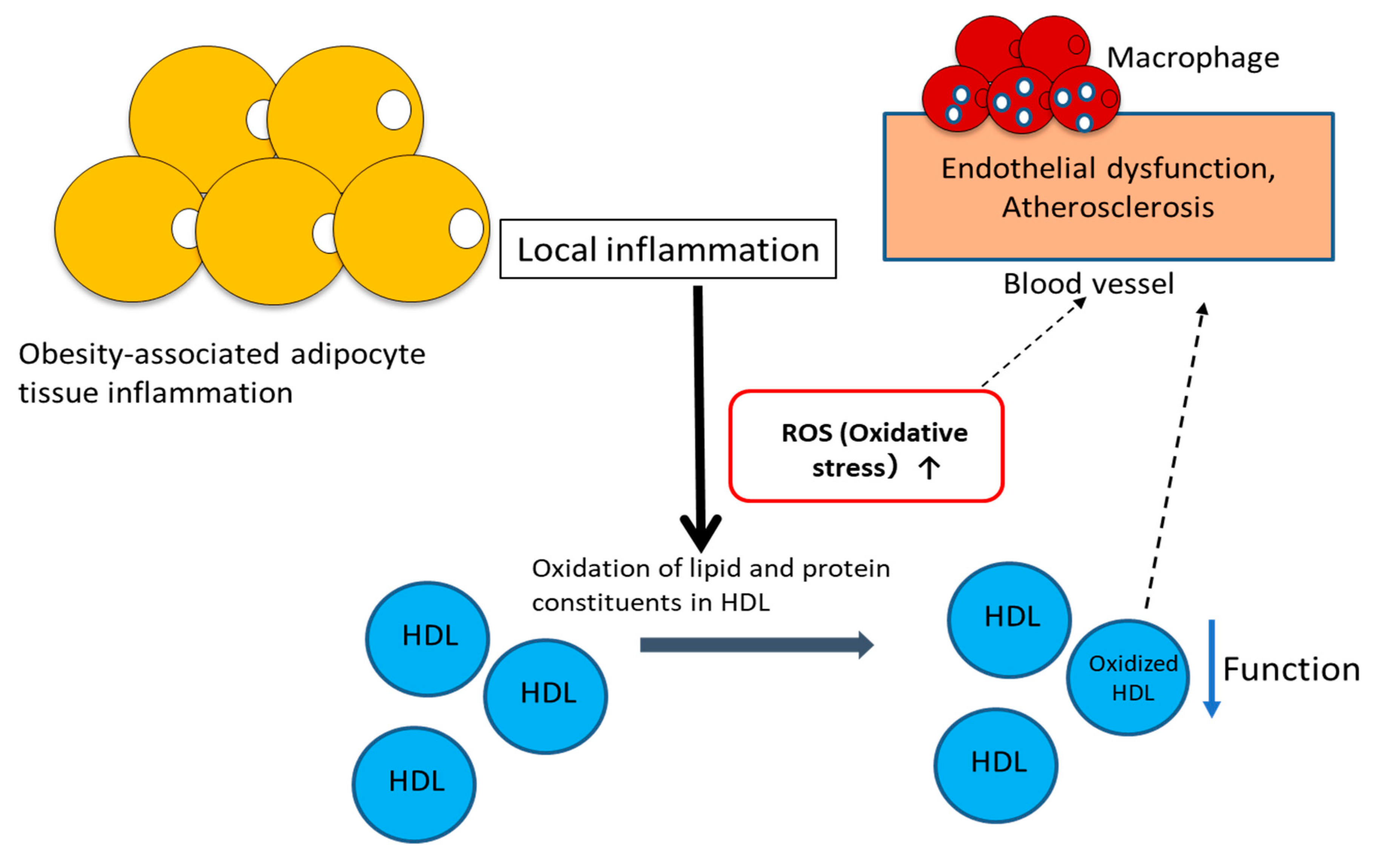
2. Dysfunctional HDL and Oxidative Stress
2.1. Dysfunctional HDL
2.2. Antiatherogenic Functions of HDL
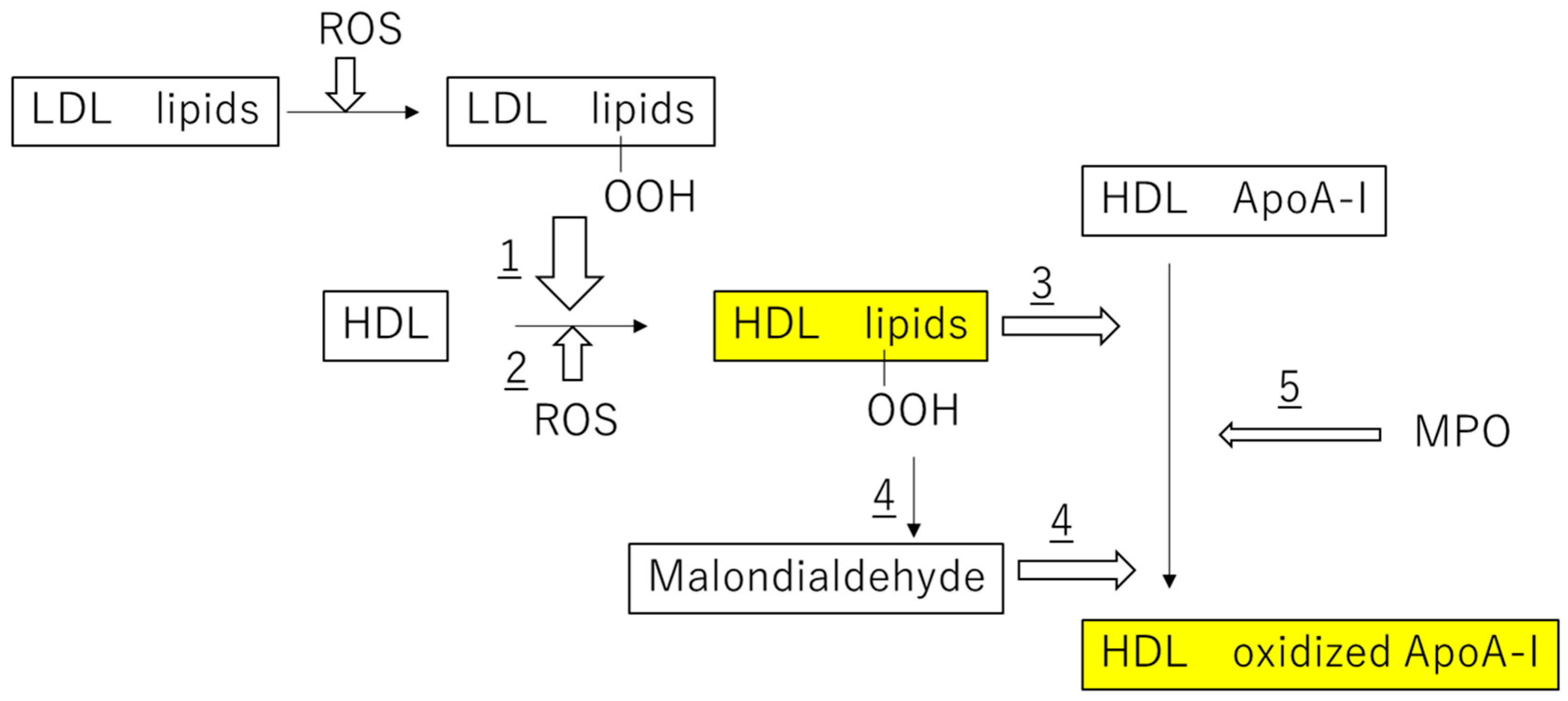
2.3. Oxidation of Lipids and apoA-I in HDL Particles
2.4. Association of HDL–LOOH with Arterial Stiffness and Chronic Inflammation
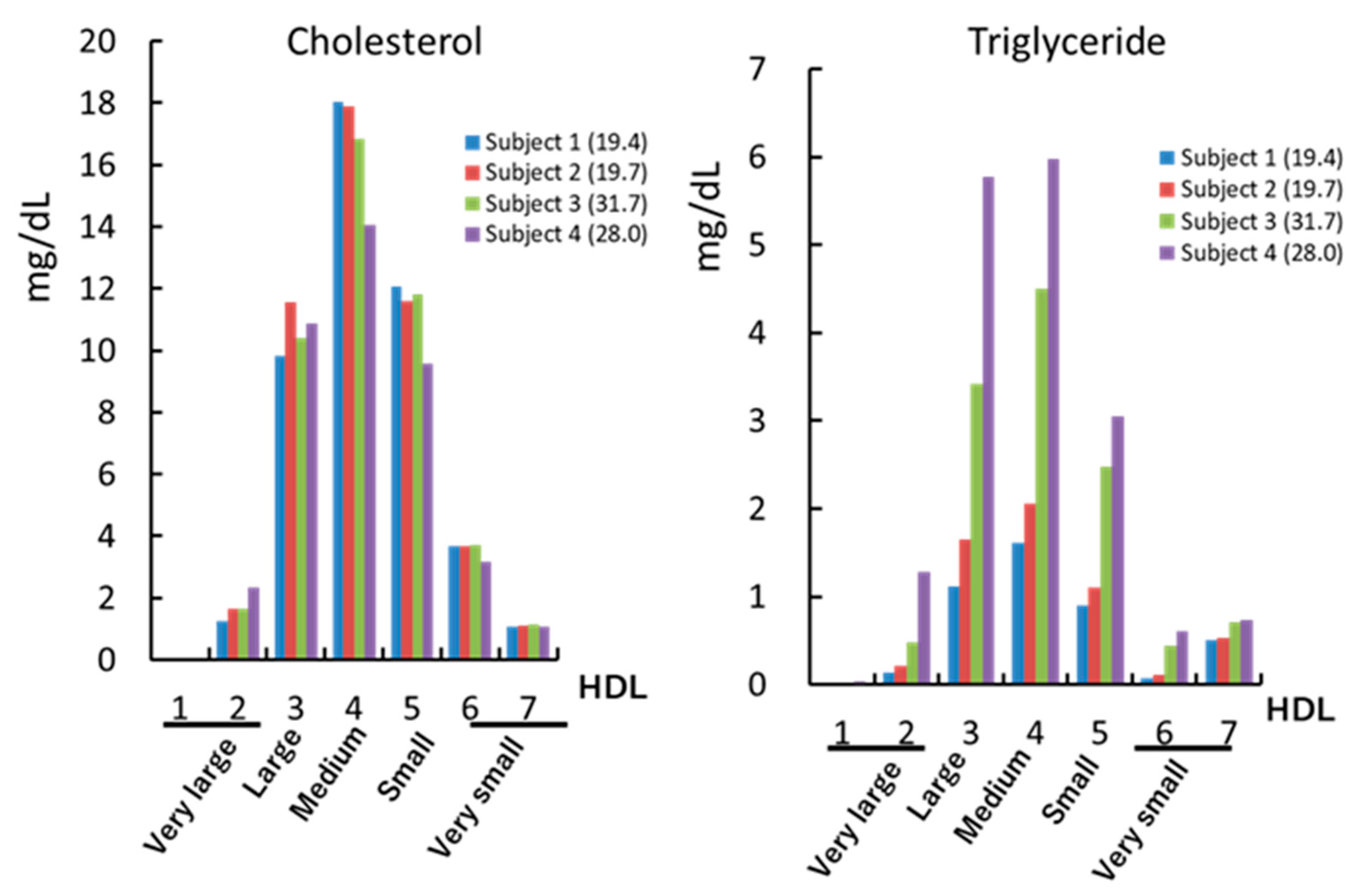
3. Dysfunctional HDL and Triglyceride Level
4. Lipid Panel
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ference:, B.A.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Graham, I.; Ray, K.K.; Packard, C.J.; Bruckert, E.; Hegele, R.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Raal, F.J.; Schunkert, H.; et al. Low-Density Lipoproteins Cause Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. 1. Evidence from Genetic, Epidemiologic, and Clinical Studies. A Consensus Statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2459–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. A Century of Cholesterol and Coronaries: From Plaques to Genes to Statins. Cell 2015, 161, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rader, D.J.; Hovingh, G.K. HDL and Cardiovascular Disease. Lancet 2014, 384, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutri, B.A.; Hime, N.J.; Nicholls, S.J. High-Density Lipoproteins: An Emerging Target in the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. Cell Res. 2006, 16, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Girona, J.; Amigó, N.; Ibarretxe, D.; Girona, J.; Amigó, N.; Ibarretxe, D.; Plana, N.; Rodríguez-Borjabad, C.; Heras, M.; Ferré, R.; et al. HDL Triglycerides: A New Marker of Metabolic and Cardiovascular Risk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riwanto, M.; Landmesser, U. High Density Lipoproteins and Endothelial Functions: Mechanistic Insights and Alterations in Cardiovascular Disease. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 3227–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrentino, S.A.; Besler, C.; Rohrer, L.; Meyer, M.; Heinrich, K.; Bahlmann, F.H.; Mueller, M.; Horváth, T.; Doerries, C.; Heinemann, M.; et al. Endothelial-Vasoprotective Effects of High-Density Lipoprotein Are Impaired in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus but Are Improved After Extended-Release Niacin Therapy. Circulation 2010, 121, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.A.K. Dysfunctional HDL in Diabetes Mellitus and Its role in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 440, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontush, A. HDL Particle Number and Size as Predictors of Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardner, M.; Yalcinkaya, M.; Goetze, S.; Luca, E.; Balaz, M.; Hunjadi, M.; Hartung, J.; Shemet, A.; Kränkel, N.; Radosavljevic, S.; et al. Structure-Function Relationships of HDL in Diabetes and Coronary Heart Disease. JCI Insight. 2020, 5, e131491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattlera, K.; Lehmanna, I.; Grälerb, M.; Bröcker-Preussc, M.; Erbeld, R.; Heuscha, G.; Levkaua, B. HDL-Bound Sphingosine 1-Phosphate (S1P) Predicts the Severity of Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irino, Y.; Toh, R.; Ishida, T. A Novel Indicator for HDL Functionality. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2019, 26, 945–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Variji, A.; Shokri, Y.; Fallahpour, S.; Zargari, M.; Bagheri, B.; Abediankenari, S.; Alizadeh, A.; Mahrooz, A. The Combined Utility of Myeloperoxidase (MPO) and Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) as Two Important HDL-Associated Enzymes in Coronary Artery Disease: Which Has a Stronger Predictive Role? Atherosclerosis 2019, 280, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Riwanto, M.; Rohrer, L.; von Eckardstein, A.; Landmesser, U. Dysfunctional HDL: From Structure-Function-Relationships to Biomarkers. Handb Exp. Pharmacol. 2015, 224, 337–366. [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann, U.; Xia, N.; Li, H. Roles of Vascular Oxidative Stress and Nitric Oxide in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 713–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, F. Polyphenols Can Potentially Prevent Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease by Modulating Macrophage Cholesterol Metabolism. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2020, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowry, V.W.; Stanley, K.K.; Stocker, R. High Density Lipoprotein Is the Major Carrier of Lipid Hydroperoxides in Human Blood Plasma from Fasting Donors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 10316–10320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christison, J.; Karjalainen, A.; Brauman, J.; Bygrave, F.; Stocker, R. Rapid Reduction and Removal of HDL- but not LDL-Associated Cholesteryl Ester Hydroperoxides by Rat Liver Perfused in situ. Biochem. J. 1996, 314, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Karlsson, H.; Kontush, A.; James, R.W. Functionality of HDL: Antioxidation and Detoxifying Effects. Handb Exp. Pharmacol. 2015, 224, 207–228. [Google Scholar]
- Zerrad-Saadi, A.; Therond, P.; Chantepie, S.; Couturier, M.; Rye, K.; Chapman, M.J.; Kontush, A. HDL3-Mediated Inactivation of LDL-Associated Phospholipid Hydroperoxides Is Determined by the Redox Status of Apolipoprotein A-I and HDL Particle Surface Lipid Rigidity: Relevance to Inflammation and Atherogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niki, E.; Yoshida, Y.; Saito, Y.; Noguchi, N. Lipid Peroxidation: Mechanisms, Inhibition, and Biological Effects. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 338, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalá, A. Lipid Peroxidation of Membrane Phospholipids Generates Hydroxy-Alkenals and Oxidized Phospholipids Active in Physiological and/or Pathological Conditions. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2009, 157, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, K.S.; Petersen, D.R. An Overview of the Chemistry and Biology of Reactive Aldehydes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 59, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzimenti, S.; Ciamporcero, E.; Daga, M.; Pettazzoni, P.; Arcaro, A.; Cetrangolo, G.; Minelli, R.; Dianzani, C.; Lepore, A.; Gentile, F.; et al. Interaction of Aldehydes Derived from Lipid Peroxidation and Membrane Proteins. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slatter, D.A.; Murray, M.; Bailey, A.J. Formation of a Dihydropyridine Derivative as a Potential Cross-Link Derived from Malondialdehyde in Physiological Systems. FEBS Lett. 1998, 421, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamore, S.D.; Azimian, S.; Hom, D.; Anglin, B.L.; Uchida, K.; Cabello, C.M.; Wondrak, G.T. The Malondialdehyde-Derived Fluorophore DHP-Lysine Is a Potent Sensitizer of UVA-Induced Photooxidative Stress in Human Skin Cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2010, 101, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, B.; Fu, X.; McDonald, T.O.; Green, P.S.; Uchida, K.; O’Brien, K.D.; Oram, J.F.; Heinecke, J.W. Acrolein Impairs ATP Binding Cassette Transporter A1-Dependent Cholesterol Export from Cells Through Site-specific Modification of Apolipoprotein A-I. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 36386–36396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadwick, A.C.; Holme, R.; Chen, Y.; Thomas, M.J.; Sorci-Thomas, M.G.; Silverstein, R.L.; Pritchard, K.A., Jr.; Sahoo, D. Acrolein Impairs the Cholesterol Transport Functions of High Density Lipoproteins. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, F.; Sono, Y.; Ito, T. Measurement and Clinical Significance of Lipid Peroxidation as a Biomarker of Oxidative Stress: Oxidative Stress in Diabetes, Atherosclerosis, and Chronic Inflammation. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Brewer, H.B., Jr.; Ansell, B.J.; Barter, P.; Chapman, M.J.; Heinecke, J.W.; Kontush, A.; Tall, A.R.; Webb, N.R. Dysfunctional HDL and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiDonato, J.A.; Aulak, K.; Huang, Y.; Wagner, M.; Gerstenecker, G.; Topbas, C.; Gogonea, V.; DiDonato, A.J.; Tang, W.H.W.; Mehl, R.A.; et al. Site-specific Nitration of Apolipoprotein A-I at Tyrosine 166 Is Both Abundant within Human Atherosclerotic Plaque and Dysfunctional. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 10276–10292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; DiDonato, J.A.; Levison, B.S.; Schmitt, D.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Buffa, J.; Kim, T.; Gerstenecker, G.S.; Gu, X.; et al. An Abundant Dysfunctional Apolipoprotein A1 in Human Atheroma. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, F.; Ito, T.; Suzuki, C.; Yahata, T.; Ikeda, K.; Hamaoka, K. The Application of a Modified d-ROMs Test for Measurement of Oxidative Stress and Oxidized High-Density Lipoprotein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Dai, J.L. Triglyceride to High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C) Ratio and Arterial Stiffness in Japanese Population: A Secondary Analysis Based on a Cross-Sectional Study. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.C.; Chuang, S.Y.; Lin, Y.P.; Chen, C.H. Brachial-Ankle vs Carotid-Femoral Pulse Wave Velocity as a Determinant of Cardiovascular Structure and Function. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2008, 22, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tani, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Nagao, K.; Hirayama, A. Association of Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins-Related Markers and Low-Density Lipoprotein Heterogeneity with Cardiovascular Risk: Effectiveness of Polyacrylamide-Gel Electrophoresis as a Method of Determining Low-Density Lipoprotein Particle Size. J. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sarwar, N.; Danesh, J.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Sigurdsson, G.; Wareham, N.; Bingham, S.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Khaw, K.T.; Gudnason, V. Triglycerides and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease: 10,158 Incident Cases Among 262,525 Participants in 29 Western Prospective Studies. Circulation 2007, 115, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, R.E.; Zilversmit, D.B. Inter-Relationship of Lipids Transferred by the Lipid-Transfer Protein Isolated from Human Lipoprotein-Deficient Plasma. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 11751–11757. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.; Stone, N.J.; Ballantyne, C.; Bittner, V.; Criqui, M.H.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Goldberg, A.C.; Howard, W.J.; Jacobson, M.S.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; et al. Triglycerides and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011, 123, 2292–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakoumakou, O.; Hatzigeorgiou, G.; Gontoras, N.; Boutsikou, M.; Kolovou, V.; Mavrogeni, S.; Giannakopoulou, V.; Kolovou, G.D. Severe/Extreme Hypertriglyceridemia and LDL Apheretic Treatment: Review of the Literature, Original Findings. Cholesterol 2014, 2014, 109263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packard, C.J. Triacylglycerol-Rich Lipoproteins and the Generation of Small, Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2003, 31, 1066–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.V.; Millwood, I.Y.; Kartsonaki, C.; Hill, M.R.; Bennett, D.A.; Boxall, R.; Guo, Y.; Xu, X.; Bian, Z.; Hu, R.; et al. Lipids, Lipoproteins, and Metabolites and Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Stroke. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigó, N.; Mallol, R.; Heras, M.; Martínez-Hervás, S.; Blanco Vaca, F.; Escolà-Gil, J.C.; Plana, N.; Yanes, Ó.; Masana, L.; Correig, X. Lipoprotein Hydrophobic Core Lipids Are Partially Extruded to Surface in Smaller HDL: “Herniated” HDL, A Common Feature in Diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pischon, T.; Girman, C.J.; Sacks, F.M.; Rifai, N.; Stampfer, M.J.; Rimm, E.B. Non-High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Apolipoprotein B in the Prediction of Coronary Heart Disease in Men. Circulation 2005, 112, 3375–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Flaws, J.; Whiteman, M.K.; Langenberg, P.; Bachorik, P.S.; Bush, T.L. Non-High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level as a Predictor of Cardiovascular Disease Mortality. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itabe, H.; Kato, R.; Sawada, N.; Obama, T.; Yamamoto, M. The Significance of Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein in Body Fluids as a Marker Related to Diseased Conditions. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 1576–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Zhu, L.; Cui, X.; Feng, L.; Zhao, X.; He, S.; Ping, F.; Li, W.; Li, Y. The Triglyceride to High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) Ratio as a Predictor of Insulin Resistance but not of β Cell Function in a Chinese Population with Different Glucose Tolerance Status. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharipour, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Nezafati, P.; Dianatkhah, M.; Sarrafzadegan, N. Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment: Triglyceride/High-Density Lipoprotein versus Metabolic Syndrome Criteria. J. Res. Health Sci. 2019, 19, e00442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Recommended Lipid Panel |
|---|
| • Total cholesterol |
| • HDL cholesterol |
| • Triglyceride |
| • LDL cholesterol |
| • Non-HDL cholesterol (calculated) |
| • HDL-LOOH (HDL-LOOH /HDL-cholesterol) |
| • HDL-Triglyceride (HDL-Triglyceride/HDL-cholesterol) |
Other markers
|
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ito, F.; Ito, T. High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Triglyceride and Oxidized HDL: New Lipid Biomarkers of Lipoprotein-Related Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050362
Ito F, Ito T. High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Triglyceride and Oxidized HDL: New Lipid Biomarkers of Lipoprotein-Related Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(5):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050362
Chicago/Turabian StyleIto, Fumiaki, and Tomoyuki Ito. 2020. "High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Triglyceride and Oxidized HDL: New Lipid Biomarkers of Lipoprotein-Related Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease" Antioxidants 9, no. 5: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050362
APA StyleIto, F., & Ito, T. (2020). High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Triglyceride and Oxidized HDL: New Lipid Biomarkers of Lipoprotein-Related Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Antioxidants, 9(5), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050362






