Defining the Functional Targets of Cap‘n’collar Transcription Factors NRF1, NRF2, and NRF3
Abstract
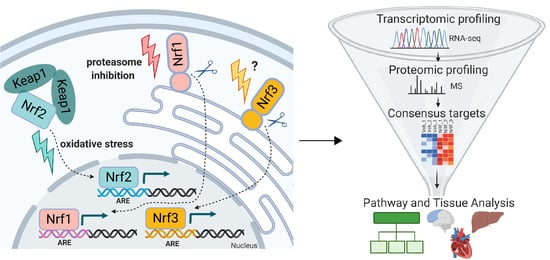
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Cloning
2.3. Immunoblotting
2.4. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Luciferase Reporter Assays
2.6. RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) Experiments
2.7. Mass Spectrometry-Based Quantitative Proteomics Experiments
3. Results
3.1. Design and Validation of an NRF Transgene Overexpression Platform
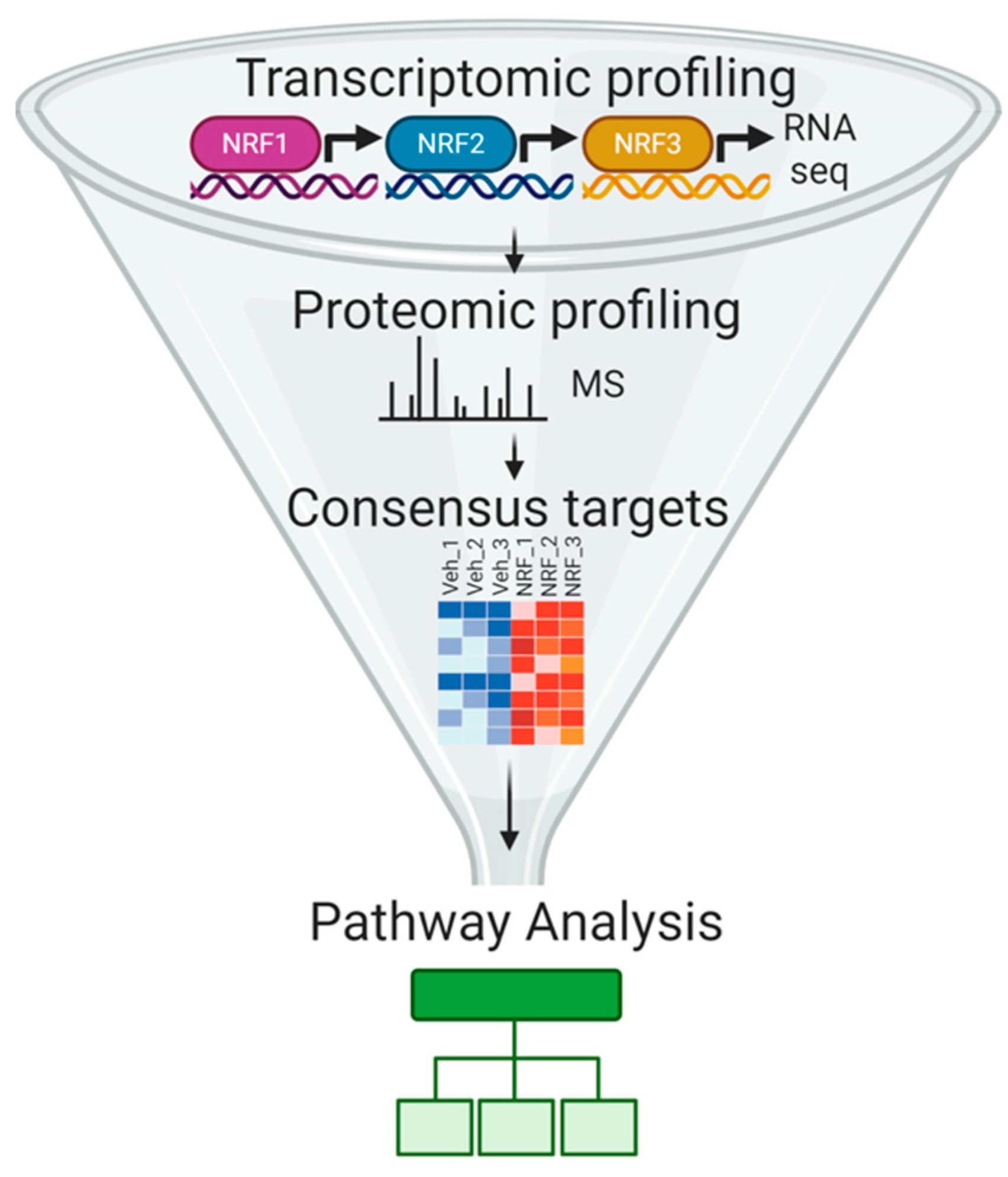
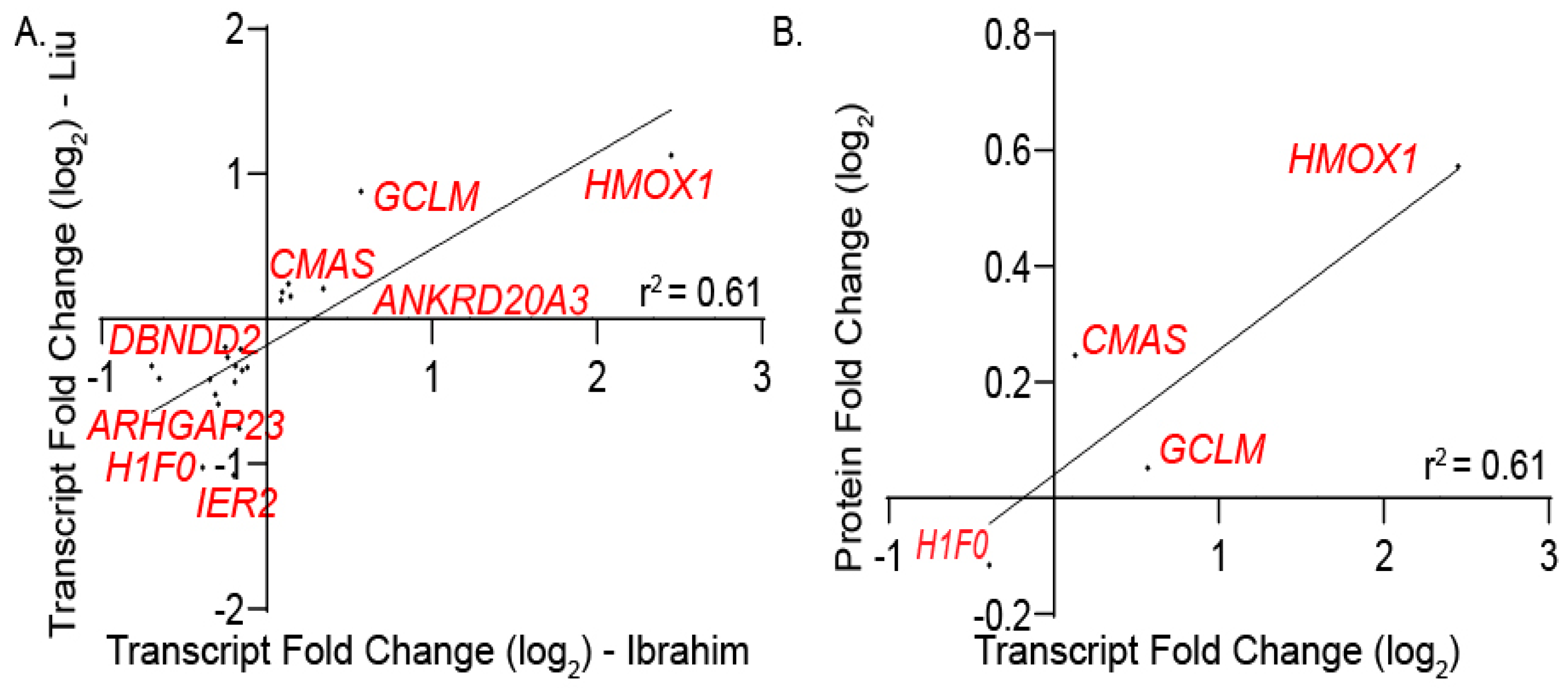
3.2. Defining Transcriptomic and Proteomic Targets of NRF Family Members
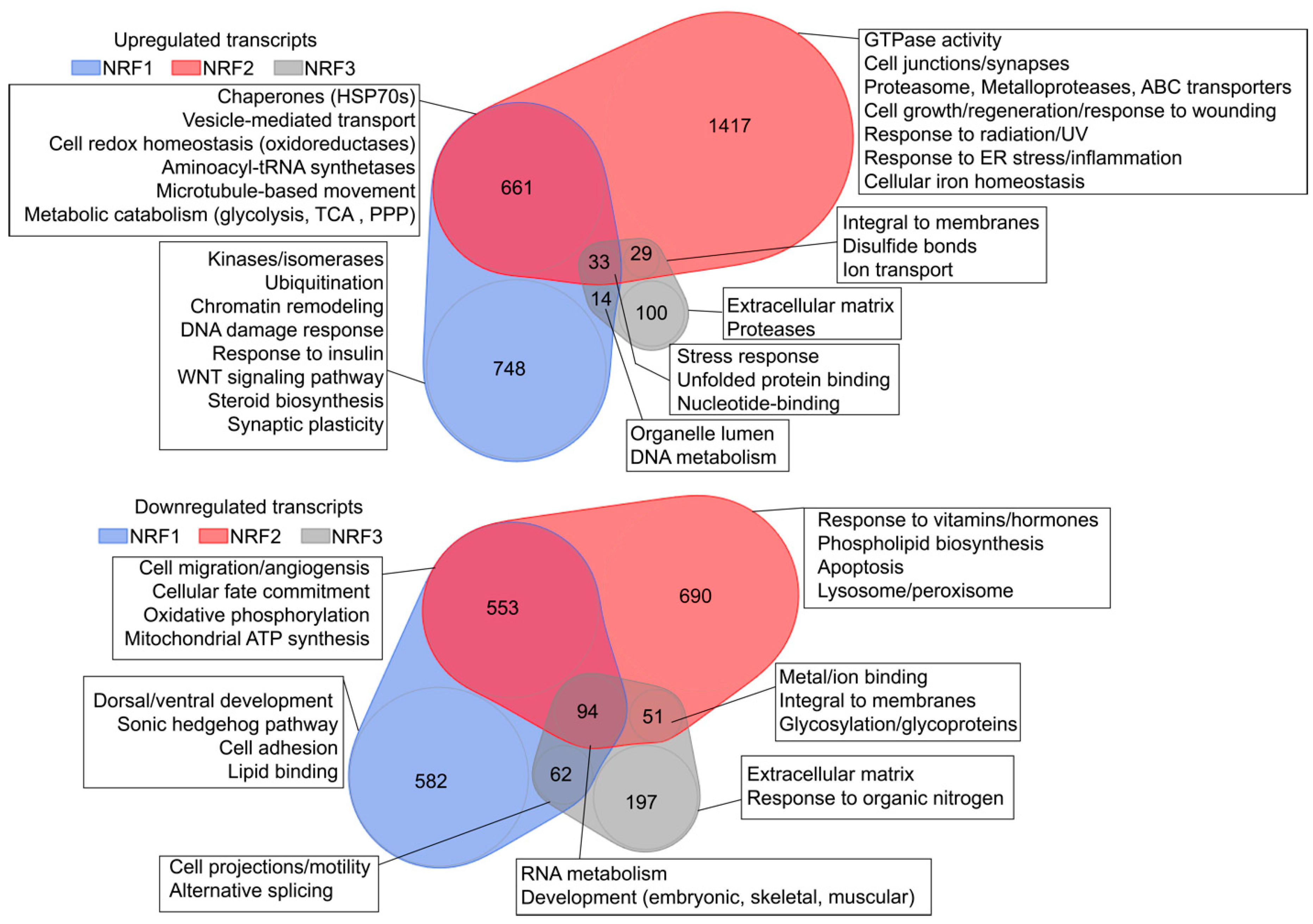
3.2.1. RNA Sequencing-Based Analysis of NRF Transcriptional Targets
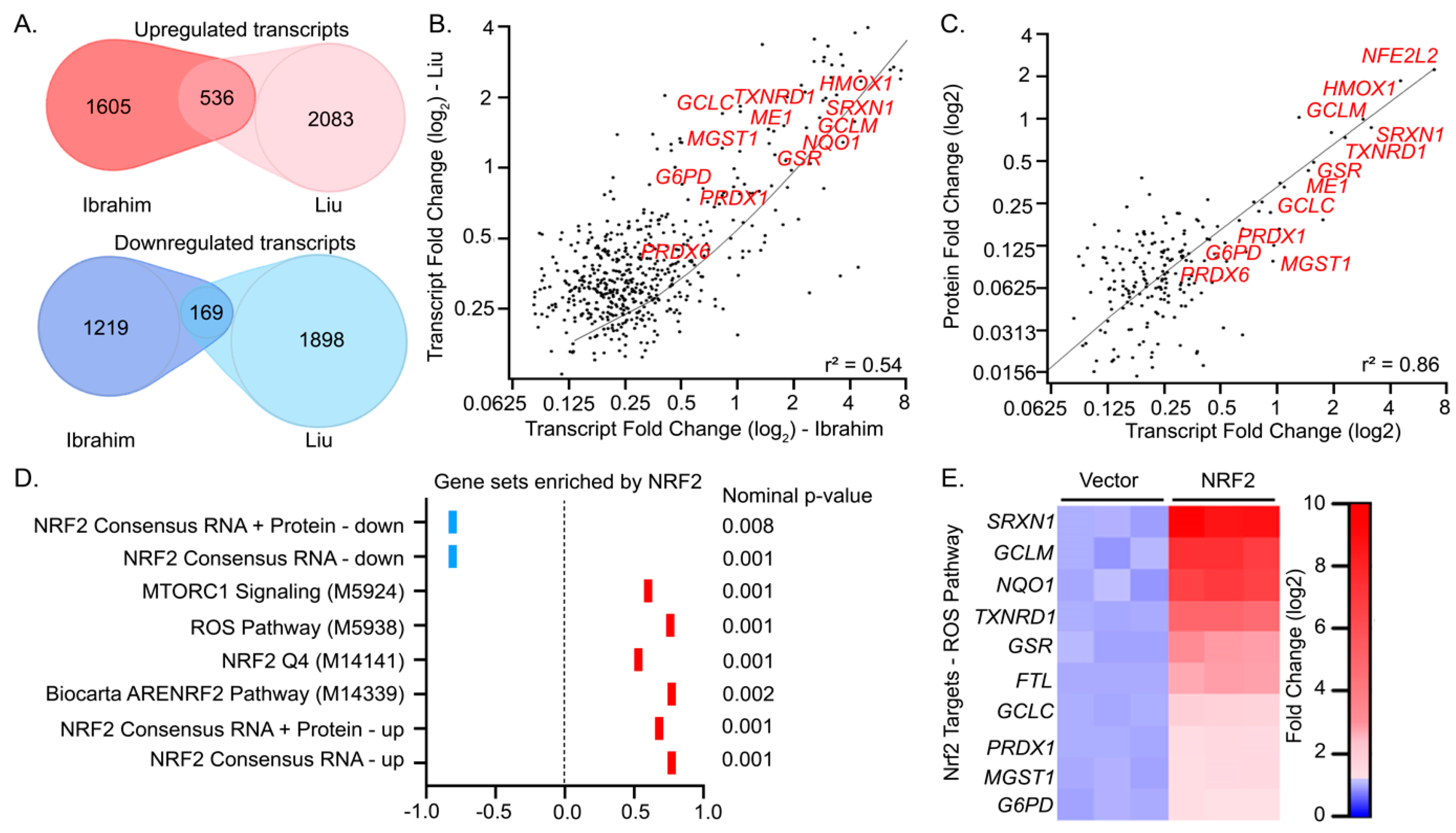
3.2.2. Defining a Core Set of NRF2 Target Genes
3.2.3. Defining a Core Set of NRF1 Target Genes
3.2.4. Defining a Core Set of NRF3 Target Genes
3.3. Identifying the Co-Expression Patterns of NRF Target Genes across Human Tissues
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sykiotis, G.P.; Bohmann, D. Stress-activated cap‘n’collar transcription factors in aging and human disease. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, re3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivdasani, R.A.; Rosenblatt, M.F.; Zucker-Franklin, D.; Jackson, C.W.; Hunt, P.; Saris, C.J.; Orkin, S.H. Transcription factor NF-E2 is required for platelet formation independent of the actions of thrombopoietin/MGDF in megakaryocyte development. Cell 1995, 81, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Chiba, T.; Takahashi, S.; Ishii, T.; Igarashi, K.; Katoh, Y.; Oyake, T.; Hayashi, N.; Satoh, K.; Hatayama, I.; et al. An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 236, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celentano, S.; Capolongo, G.; Pollastro, R.M. Bardoxolone: A new potential therapeutic agent in the treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease? Giornale Italiano di Nefrologia 2019, 36, 2019-vol5. [Google Scholar]
- Wakkee, M.; Thio, H.B. Drug evaluation: BG-12, an immunomodulatory dimethylfumarate. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 8, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jaramillo, M.C.; Zhang, D.D. The emerging role of the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway in cancer. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 2179–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastres-Becker, I.; García-Yagüe, A.J.; Scannevin, R.H.; Casarejos, M.J.; Kügler, S.; Rábano, A.; Cuadrado, A. Repurposing the NRF2 Activator Dimethyl Fumarate as Therapy Against Synucleinopathy in Parkinson’s Disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 25, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, T.O.; Huang, M.T.; Kwon, K.H.; Chan, J.Y.; Reddy, B.S.; Kong, A.N. Nrf2-Deficient Mice Have an Increased Susceptibility to Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11580–11584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uruno, A.; Furusawa, Y.; Yagishita, Y.; Fukutomi, T.; Muramatsu, H.; Negishi, T.; Sugawara, A.; Kensler, T.W.; Yamamoto, M. The Keap1-Nrf2 System Prevents Onset of Diabetes Mellitus. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 2996–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, S.K.; Lee, C.S.; Young, P.; Beskow, A.; Chan, J.Y.; Deshaies, R.J. Transcription factor Nrf1 mediates the proteasome recovery pathway after proteasome inhibition in mammalian cells. Mol. Cell. 2010, 38, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; Han, J.W.; Chan, J.Y. Nuclear Factor Erythroid-2 Like 1 (NFE2L1): Structure, function and regulation. Gene 2016, 584, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, A.; Katoh, H.; Hatanaka, A.; Iwanari, H.; Nakamura, N.; Hamakubo, T.; Natsume, T.; Waku, T.; Kobayashi, A. Multiple regulatory mechanisms of the biological function of NRF3 (NFE2L3) control cancer cell proliferation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waku, T.; Katayama, H.; Hiraoka, M.; Hatanaka, A.; Nakamura, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Tamura, N.; Watanabe, A.; Kobayashi, A. NFE2L1 and NFE2L3 Complementarily Maintain Basal Proteasome Activity in Cancer Cells through CPEB3-Mediated Translational Repression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, A.; Ito, E.; Toki, T.; Kogame, K.; Takahashi, S.; Igarashi, K.; Hayashi, N.; Yamamoto, M. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a new Cap’n’ collar family transcription factor Nrf3. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 6443–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackwell, T.K.; Steinbaugh, M.J.; Hourihan, J.M.; Ewald, C.Y.; Isik, M. SKN-1/Nrf, stress responses, and aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitoniak, A.; Bohmann, D. Mechanisms and functions of Nrf2 signaling in Drosophila. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, J.M.D.; Plate, L.; Morimoto, R.I.; Bollong, M.J.; Powers, E.T.; Wiseman, R.L. Deconvoluting Stress-Responsive Proteostasis Signaling Pathways for Pharmacologic Activation Using Targeted RNA Sequencing. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Kerins, M.J.; Tian, W.; Neupane, D.; Zhang, D.D.; Ooi, A. Differential and overlapping targets of the transcriptional regulators NRF1, NRF2, and NRF3 in human cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 18131–18149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauniyar, N.; Yates, J.R. Isobaric Labeling-Based Relative Quantification in Shotgun Proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 5293–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, J.K.; McCormack, A.L.; Yates, J.R. An approach to correlate tandem mass spectral data of peptides with amino acid sequences in a protein database. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1994, 5, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Park, S.K.; Venable, J.D.; Wohlschlegel, J.A.; Diedrich, J.K.; Cociorva, D.; Lu, B.; Liao, L.; Hewel, J.; Han, X.; et al. ProLuCID: An improved SEQUEST-like algorithm with enhanced sensitivity and specificity. J. Proteom. 2015, 129, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, S.K.; den Besten, W.; Deshaies, R.J. p97-dependent retrotranslocation and proteolytic processing govern formation of active Nrf1 upon proteasome inhibition. Elife 2014, 3, e01856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canning, P.; Sorrell, F.J.; Bullock, A.N. Structural basis of Keap1 interactions with Nrf2. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, S.-C.; Li, X.; Henzl, M.T.; Beamer, L.J.; Hannink, M. Structure of the Keap1:Nrf2 interface provides mechanistic insight into Nrf2 signaling. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3605–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaconelli, J.; Ibrahim, L.; Chen, E.; Hull, M.; Schultz, P.G.; Bollong, M.J. Small-Molecule Stimulators of NRF1 Transcriptional Activity. Chembiochem 2020, 21, 1816–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mootha, V.K.; Lindgren, C.M.; Eriksson, K.-F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstråle, M.; Laurila, E.; et al. PGC-1α-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Lee, C.; Hu, T.; Nguyen, J.M.; Zhang, J.; Martin, M.V.; Vawter, M.P.; Huang, E.J.; Chan, J.Y. Loss of nuclear factor E2-related factor 1 in the brain leads to dysregulation of proteasome gene expression and neurodegeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8408–8413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Brain | Liver | Heart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlated | Anti-Correlated | Correlated | Anti-Correlated | Correlated | Anti-Correlated |
| NQO1 | TBK1 | NQO1 | MGST1 | NQO1 | TXNRD1 |
| HMOX1 | MAP2 | TXNRD1 | CBR1 | HMOX1 | SQSTM1 |
| MGST1 | PRKCI | HMOX1 | EPHX1 | MGST1 | GCLM |
| CBR1 | CSNK2A2 | SQSTM1 | GCLC | CBR1 | GSR |
| EPHX1 | MAP1A | GCLM | FERMT2 | TBK1 | PRDX1 |
| PRDX1 | PPP3R1 | GSR | IL6R | FERMT2 | GCLC |
| FERMT2 | ARPC2 | PRDX1 | PPP3R1 | PRKCI | RB1CC1 |
| IL6R | KIF3B | WARS | ZEB1 | CLIP1 | |
| LIFR | AFG3L2 | TBK1 | IL6R | MAP1A | |
| SERINC3 | RB1CC1 | CSNK2A2 | AFG3L2 | ||
| CLIP1 | PPP3R1 | SET | |||
| PRKCI | ARPC2 | ME1 | |||
| CSNK2A2 | KIF3B | ||||
| ARPC2 | SERINC3 | ||||
| KIF3B | |||||
| AFG3L2 | |||||
| SERINC3 | |||||
| SET | |||||
| ME1 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, L.; Mesgarzadeh, J.; Xu, I.; Powers, E.T.; Wiseman, R.L.; Bollong, M.J. Defining the Functional Targets of Cap‘n’collar Transcription Factors NRF1, NRF2, and NRF3. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9101025
Ibrahim L, Mesgarzadeh J, Xu I, Powers ET, Wiseman RL, Bollong MJ. Defining the Functional Targets of Cap‘n’collar Transcription Factors NRF1, NRF2, and NRF3. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(10):1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9101025
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Lara, Jaleh Mesgarzadeh, Ian Xu, Evan T. Powers, R. Luke Wiseman, and Michael J. Bollong. 2020. "Defining the Functional Targets of Cap‘n’collar Transcription Factors NRF1, NRF2, and NRF3" Antioxidants 9, no. 10: 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9101025
APA StyleIbrahim, L., Mesgarzadeh, J., Xu, I., Powers, E. T., Wiseman, R. L., & Bollong, M. J. (2020). Defining the Functional Targets of Cap‘n’collar Transcription Factors NRF1, NRF2, and NRF3. Antioxidants, 9(10), 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9101025