Comparison of Phenolic Compounds and the Antioxidant Activities of Fifteen Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat cv. ‘Hangbaiju’ in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Sample Extraction
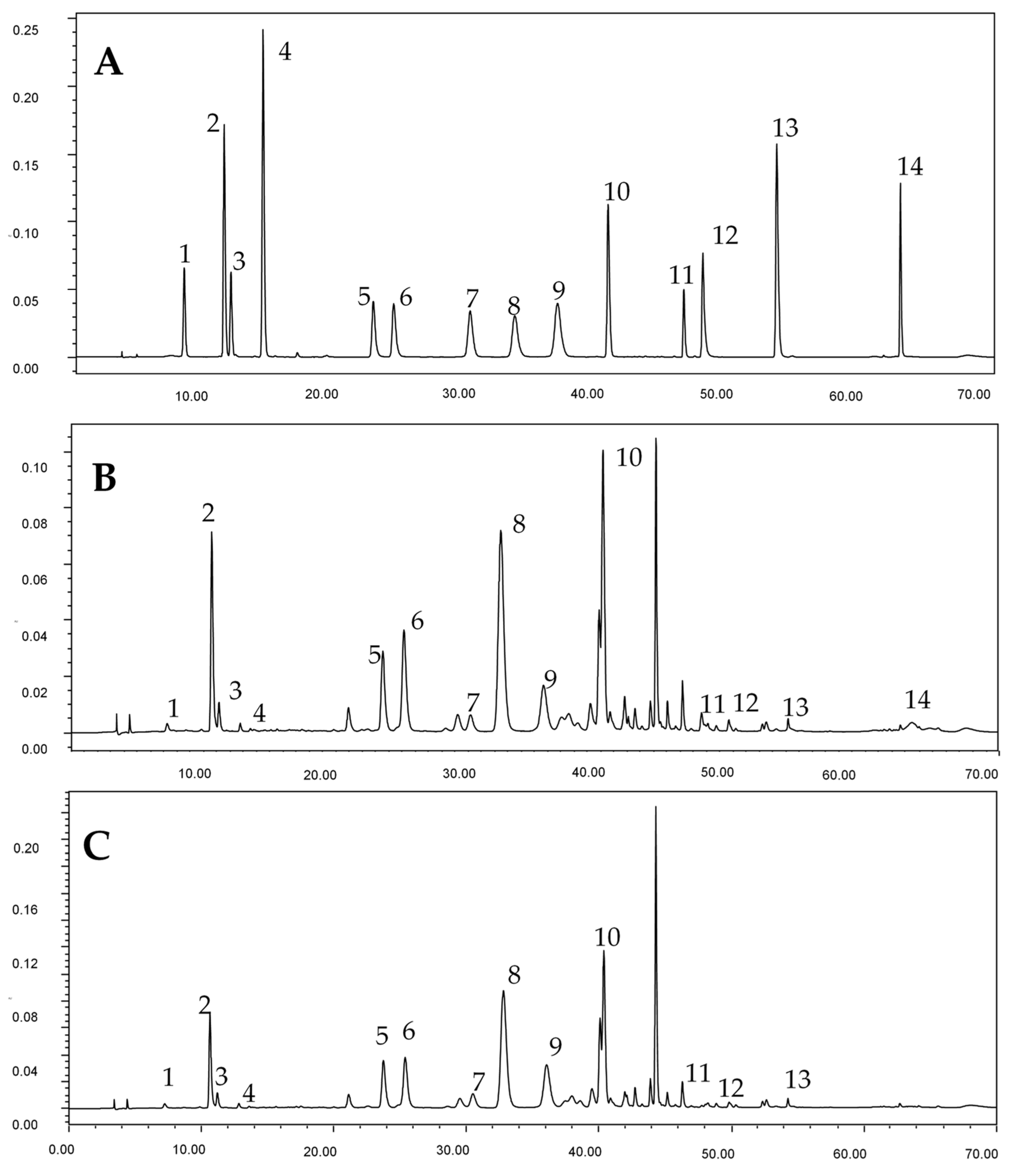
2.4. HPLC-DAD Analysis
2.5. DPPH Assay
2.6. ABTS Assay
2.7. Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phenolic Composition
3.2. Antioxidant Activity
3.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.; Kotani, A.; Kusu, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Hakamata, H. Quantitative comparison of caffeoylquinic acids and flavonoids in Chrysanthemum morifolium flowers and their sulfur-fumigated products by three-channel liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 63, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, L.; Ruan, J.Y.; Jin, L.J.; Shi, W.Z.; Li, X.X.; Han, L.F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T. Xanthine oxidase inhibitory effects of the constituents of Chrysanthemum morifolium stems. Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 19, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hao, L.J.; Zhu, J.J.; Zhang, Q.W.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhang, X.; Song, X. Study on the effects of sulfur fumigation on chemical constituents and antioxidant activity of Chrysanthemum morifolium cv. Hang-ju. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Wako, Y. Evaluation of phenolic compounds and neurotrophic/neuroprotective activity of cultivar extracts derived from Chrysanthemum morifolium flowers. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2017, 23, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.Z.; Harnly, J.M. Identification of the phenolic components of chrysanthemum flower (Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat.). Food Chem. 2010, 120, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Guo, Q.S.; Mao, P.F. Flavonoid accumulation during florescence in three Chrysanthemum morifolium ramat cv. ‘Hangju’ genotypes. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 55, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Chinese Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 310–311. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.X.; Ru, X.C.; Wen, L.; Wen, Y.C.; Jiang, H.D.; Bruce, I.C.; Jin, J.; Ma, X.; Xia, Q. Total flavonoids of Flos Chrysanthemi protect arterial endothelial cells againstoxidative stress. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; He, Z.; He, S.; Jing, P. Insights into the importance of dietary chrysanthemum flower (Chrysanthemum morifolium cv. Hangju)-wolfberry (Lycium barbarum fruit) combination in antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.Y.; Qu, J.L.; Wang, Q.L.; Wang, Y.; Yoshikawa, M.; Yuan, D. Comparative evaluation of cultivars of Chrysanthemum morifolium flowers by HPLC-DAD-ESI/MS analysis and antiallergic assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 12574–12583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ning, Z.; Li, S. Extraction and purification of isochlorogenic acid c from Chrysanthemum morifolium using ionic liquid-based ultrasound-assisted extraction and aqueous two-phase system. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2113–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Luo, Y.; Gao, B.; Sun, J.; Lu, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L. Chemical compositions of chrysanthemum teas and their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Hao, L.J.; Wu, G.; Wang, S.; Duan, J.A.; Xie, G.Y.; Qin, M.J. Effects of drying methods on the phytochemicals contents and antioxidant properties of Chrysanthemum flower heads harvested at two developmental stages. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.Y.; Gong, J.Y.; Liu, J.E.; Wu, X.Q.; Zhang, Y. Antioxidant capacity of extract from edible flowers of Prunus mume in China and its active components. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Paek, J.H.; Lim, S.S. Simultaneous ultra performance liquid chromatography determination and antioxidant activity of linarin, luteolin, chlorogenic acid and apigenin in different parts of compositae species. Molecules 2016, 21, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Simultaneous determination of five flavonoids components in different parts of Callistephus chinensis by HPLC. Chin. Trad. Herbal Drugs 2015, 43, 428–432. [Google Scholar]
- Turkoglu, A.; Duru, M.E.; Mercan, N.; Kivrak, I.; Gezer, K. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Laetiporus sulphureus (bull.) murrill. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yanga, M.; Rice-Evansa, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 6, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. Uric acid: Friend or foe? Redox Rep. 1996, 2, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudonné, S.; Vitrac, X.; Coutière, P.; Woillez, M.; Mérillon, J.M. Comparative study of antioxidant properties and total phenolic content of 30 plant extracts of industrial interest using DPPH, ABTS, FRAP, SOD, and ORAC assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1768–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Z.W.; Du, G.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, D.T.; et al. Analysis of methanolic extracts and crude polysaccharides from the leaves of Chuanminshen violaceum and their antioxidant activities. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaipong, K.; Boonprakob, U.; Crosby, K.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Byrne, D.H. Comparison of ABTS, DPPH, FRAP, and ORAC assays for estimating antioxidant activity from guava fruit extracts. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 19, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.Y.; Xia, D.Z.; Huang, J.; Ge, Q.; Mao, J.W.; Liu, S.W.; Zhang, Y. Functional components of bamboo shavings and bamboo leaf extracts and their antioxidant activities in Vitro. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Huang, J.; Xiao, G.; Chen, F.; Lee, B.; Ge, Q.; You, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. Antioxidant capacities of fractions of bamboo shaving extract and their antioxidant components. Molecules 2016, 21, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djebbar, A.; Nassima, C.; Dina, A.; Meriem, B.; Nadjet, D.; Hania, B. Flavonoids in human health: From structure to biological activity. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2009, 5, 225–237. [Google Scholar]
- Taira, J.; Uehara, M.; Tsuchida, E.; Ohmine, W. Inhibition of the β-catenin/Tcf signaling by caffeoylquinic acids in sweet potato leaf through down regulation of the Tcf-4 transcription. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šamec, D.; Maretic’, M.; Lugaric’, I.; Mešic’, A.; Salopek-Sondi, B.; Duralija, B. Assessment of the differences in the physical, chemical and phytochemical properties of four strawberry cultivars using principal component analysis. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawidowicz, A.L.; Typek, R. Transformation of 5-O-Caffeoylquinic acid in blueberries during high-temperature processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10889–10895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.; Jaiswal, R.; Matei, M.F.; Kuhnert, N. Investigation of acyl migration in mono- and dicaffeoylquinic acids under aqueous basic, aqueous acidic, and dry roasting conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 9160–9170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Shi, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.Q.; Guan, J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ma, Q. Stability and degradation of caffeoylquinic acids under different storage conditions studied by high-performance liquid chromatography with photo diode array detection and high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization collision-induced dissociation tandem mass spectrometry. Molecules 2016, 21, 948. [Google Scholar]
- Nishihara, M.; Nakatsuka, T.; Yamamura, S. Flavonoid components and flower color change in transgenic tobacco plants by suppression of chalcone isomerase gene. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 6074–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobilya, D.J. Flavonoid antioxidants: Chemistry, metabolism and structure-activity relationships. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 572–584. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, G.; Sofic, E.; Prior, R.L. Antioxidant and prooxidant behavior of flavonoids: Structure-activity relationship. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 22, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzo, F.A. Antioxidant and antidiabetic effects of flavonoids: A structure-activity relationship based study. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 8386065. [Google Scholar]

| Phenolic Compound | DJ1 | DJ2 | DJ3 | DJ4 | DJ5 | DJ6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 691.48 ± 21.98 d | 889.07 ± 25.98 c | 597.64 ± 19.87 e | 644.24 ± 30.34 e | 965.49 ± 38.17 b | 1167.59 ± 16.22 a |
| 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 1745.29 ± 55.86 c | 2083.55 ± 81.66 b | 1413.66 ± 65.66 d | 1370.96 ± 54.98 d | 2189.24 ± 58.96 b | 2392.17 ± 136.86 a |
| 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 640.83 ± 30.17 b | 765.78 ± 36.74 a | 540.74 ± 15.36 c | 521.76 ± 19.27 c | 764.92 ± 20.67 a | 792.53 ± 13.98 a |
| TMAC | 3077.60 ± 70.87 c | 3738.40 ± 108.99 b | 2552.04 ± 70.11 d | 2536.96 ± 58.78 d | 3919.65 ± 69.86 b | 4352.29 ± 140.11 a |
| 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 282.62 ± 9.94 c | 379.66 ± 15.67 b | 259.12 ± 6.98 d | 289.24 ± 18.27 c | 385.30 ± 17.18 b | 530.91 ± 9.85 a |
| 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 5275.20 ± 210.76 c | 6460.38 ± 201.38 a | 4736.66 ± 286.99 d | 4918.72 ± 229.38 cd | 5796.97 ± 198.35 b | 6421.88 ± 298.67 a |
| 4,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 3156.97 ± 96.38 c | 3702.25 ± 109.26 b | 3158.17 ± 157.88 c | 3087.61 ± 69.20 c | 3880.21 ± 158.29 ab | 4022.14 ± 156.76 a |
| TDAC | 8714.80 ± 250.49 a | 10542.71 ± 240.56 a | 8153.62 ± 300.37 a | 8295.57 ± 248.27 a | 10062.48 ± 210.85 a | 10974.94 ± 371.48 a |
| caffeic acid | 10.85±0.36a | 9.11 ± 0.33 b | 3.92 ± 0.55 c | - | 10.71 ± 0.32 a | - |
| TPAC | 11803.25 ± 281.19 ab | 14290.22 ± 281.01 a | 10709.58 ± 328.27 b | 10832.53 ± 260.99 b | 13992.84 ± 241.33 ab | 15327.22 ± 430.98 ab |
| hyperoside | 655.32 ± 25.11 c | 739.11 ± 30.64 b | 613.70 ± 40.48 c | 628.19 ± 12.36 c | 813.68 ± 20.66 a | 666.99 ± 10.38 c |
| luteoloside | 1135.19 ± 40.14 d | 1335.69 ± 42.11 c | 1524.16 ± 65.83 a | 1476.67 ± 45.21 ab | 1407.85 ± 50.74 bc | 1369.87 ± 20.18 c |
| apigenin-7-O-glucoside | 1293.56 ± 30.85 bc | 1264.53 ± 49.76 bc | 1302.82 ± 89.27 b | 1593.54 ± 40.16 a | 1211.42 ± 30.34 c | 1234.12 ± 31.73 c |
| linarin | 2057.88 ± 87.21 c | 1955.80 ± 59.75 c | 1647.05 ± 61.85 d | 2194.81 ± 39.11 b | 2605.87 ± 87.83 a | 1675.81 ± 20.11 d |
| luteolin | 200.10 ± 8.86 cd | 238.37 ± 9.28 a | 191.73 ± 3.59 d | 219.25 ± 4.19 b | 247.09 ± 15.22 a | 207.07 ± 4.76 bc |
| apigenin | 63.36 ± 1.87 b | - | - | 36.44 ± 0.54 c | 73.87 ± 2.27 a | - |
| acacetin | 4.67 ± 0.13 c | - | 13.87 ± 0.40 b | 3.9 ± 0.10 c | 15.07 ± 0.41 b | 29.48 ± 0.67 a |
| TFC | 5410.06 ± 98.37 bc | 5533.50 ± 25.87 b | 5293.33 ± 78.28b c | 6152.90 ± 50.38 a | 6374.85 ± 63.19 a | 5183.35 ± 50.67 c |
| TKPC | 8155.68 ± 321.12 c | 9880.04 ± 438.21 ab | 7674.15 ± 381.37 c | 7766.35 ± 391.5 c | 9394.06 ± 411.82 b | 10183.92 ± 501.02 a |
| Phenolic Compound | TJ1 | TJ2 | TJ3 | TJ4 | TJ5 | TJ6 | TJ7 | TJ8 | TJ9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 1555.13 ± 50.01 c | 1246.00 ± 40.11 e | 2844.64 ± 66.38 a | 1117.50 ± 37.88 f | 1641.14 ± 47.32 b | 1589.85 ± 59.38 bc | 673.09 ± 28.93 g | 1403.69 ± 38.29 d | 1560.38 ± 50.21 c |
| 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 2649.68 ± 60.19 cd | 2180.97 ± 182.93 e | 3193.04 ± 167.95 a | 2205.75 ± 129.84 e | 2759.82 ± 164.23 bc | 2941.23 ± 156.82 b | 1487.40 ± 36.865 f | 2482.32 ± 136.75 d | 2519.96 ± 163.76 cd |
| 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 981.08 ± 63.18 bcd | 869.65 ± 48.95 e | 1365.16 ± 89.10 a | 882.50 ± 57.89 de | 1018.33 ± 87.85 b | 990.22 ± 64.72 bc | 512.62 ± 37.16 f | 916.21 ± 66.84 ce | 940.69 ± 67.09 be |
| TMAC | 5185.89 ± 89.28 bc | 4296.62 ± 199.25 e | 7402.83 ± 196.27 a | 4205.75 ± 152.57 e | 5419.29 ± 211.27 bc | 5521.29 ± 195.845 b | 2673.11 ± 52.17 f | 4802.21 ± 157.28 d | 5021.03 ± 211.27 cd |
| 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 718.39 ± 39.28 bc | 517.04 ± 15.73 d | 782.14 ± 23.18 a | 498.48 ± 38.93 d | 743.78 ± 28.33 ab | 719.32 ± 47.38 bc | 229.17 ± 17.03 e | 677.70 ± 13.98 c | 685.30 ± 20.17 c |
| 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 7156.41 ± 301.27 b | 5913.21 ± 392.83 c | 8119.70 ± 503.27 a | 7090.86 ± 411.28 b | 8259.63 ± 367.86 a | 7305.74 ± 522.86 b | 4489.29 ± 289.78 d | 7251.88 ± 298.39 b | 6717.60 ± 363.18 b |
| 4,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 4820.02 ± 110.37 ab | 4217.64 ± 207.81 b | 4520.06 ± 167.28 ab | 4360.67 ± 112.13 ab | 4956.98 ± 165.32 a | 4791.11 ± 226.83 ab | 3000.33 ± 162.18 cd | 3250.84 ± 255.35 c | 4551.21 ± 182.86 ab |
| TDAC | 12694.82 ± 398.37 bc | 10647.89 ± 458.76 e | 13421.90 ± 637.81 ab | 11950.01 ± 502.85 cd | 13960.39 ± 411.15 a | 12816.17 ± 628.75 bc | 7718.79 ± 327.27 f | 12515.29 ± 428.63 de | 11998.11 ± 463.37 cd |
| caffeic acid | - | 4.29 ± 0.11 f | 23.03 ± 0.98 a | 7.43 ± 0.26 e | 11.39 ± 0.28 c | 13.50 ± 0.09 b | 13.40 ± 0.36 b | 4.70 ± 0.12 f | 9.92 ± 0.81 d |
| TPAC | 17880.71 ± 411.8 c | 14948.80 ± 583.67 e | 20847.76 ± 762.17 a | 16163.18 ± 598.17 de | 19391.07 ± 512.28 b | 18350.97 ± 703.84 bc | 10405.31 ± 356.83 f | 17322.21 ± 501.25 de | 17029.06 ± 581.25 cd |
| hyperoside | 919.83 ± 38.19 ab | 875.45 ± 58.91 bcd | 994.81 ± 67.73 a | 865.66 ± 33.83 bcd | 797.63 ± 68.39 d | 919.97 ± 57.38 abc | 708.80 ± 46.86 e | 860.22 ± 50.09 bcd | 875.19 ± 58.96 bcd |
| luteoloside | 1939.73 ± 60.8 b | 1878.94 ± 97.95 bc | 2331.10 ± 96.06 a | 1775.10 ± 72.81 bcd | 1711.19 ± 87.27 cd | 1881.30 ± 99.96 b | 1614.81 ± 118.19 d | 1923.38 ± 148.71 b | 2416.07 ± 99.26 a |
| apigenin-7-O-glucoside | 2651.70 ± 56.38 cd | 2461.46 ± 162.84 def | 1553.48 ± 98.98 h | 2493.06 ± 83.87 cf | 2143.65 ± 48.78 g | 2522.15 ± 138.39 cde | 2905.07 ± 57.81 b | 2662.34 ± 187.29 c | 3539.55 ± 163.83 a |
| linarin | 2816.67 ± 67.38 cd | 2623.92 ± 162.18 def | 3470.66 ± 207.48 ab | 2795.03 ± 156.27 ce | 3239.20 ± 187.53 b | 3573.51 ± 165.78 a | 2518.28 ± 89.96 f | 2726.28 ± 127.28 cf | 2898.40 ± 120.53 c |
| luteolin | 40.11 ± 1.99 e | 52.47 ± 1.08 c | 70.68 ± 2.83 a | 55.18 ± 1.87 b | 46.99 ± 0.99 d | 24.08 ± 0.57 f | 41.32 ± 1.28 e | 51.55 ± 0.98 c | 53.15 ± 2.55 bc |
| apigenin | - | 94.36 ± 2.76 a | 43.29 ± 0.27 b | 8.90 ± 0.26 e | 17.83 ± 1.01 d | 10.67 ± 0.72 e | 23.88 ± 0.92 c | - | 9.65 ± 0.39 e |
| acacetin | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| TFC | 8368.04 ± 98.25 bc | 7986.60 ± 212.38 c | 8464.01 ± 198.26 bc | 7992.93 ± 178.84 c | 7956.49 ± 223.17 c | 8931.68 ± 256.27 b | 7812.16 ± 172.38 c | 8223.77 ± 167.83 c | 9792.01 ± 187.22 a |
| TKPC | 11745.82 ± 421.72 cd | 9973.12 ± 472.46 e | 13144.12 ± 652.89 a | 11071.71 ± 541.23 d | 12730.64 ± 328.48 ab | 12128.27 ± 331.34 bc | 7591.50 ± 198.62 f | 11657.58 ± 348.80 cd | 11653.63 ± 351.28 cd |
| Antioxidant Capacity | DJ1 | DJ2 | DJ3 | DJ4 | DJ5 | DJ6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPPH * | 2.47 ± 0.05 c | 1.75 ± 0.04 f | 3.04 ± 0.08 a | 2.68 ± 0.03 b | 2.10 ± 0.08 e | 2.23 ± 0.04 d |
| ABTS * | 2.77 ± 0.06 ab | 2.30 ± 0.05 d | 2.83 ± 0.04 a | 2.71 ± 0.03 b | 2.13 ± 0.06 e | 2.39 ± 0.03 c |
| FRAP * | 222.28 ± 4.10 d | 247.73 ± 8.45 b | 236.82 ± 3.19 c | 255.00 ± 8.20 b | 266.82 ± 4.16 a | 273.64 ± 7.10 a |
| Antioxidant Capacity | TJ1 | TJ2 | TJ3 | TJ4 | TJ5 | TJ6 | TJ7 | TJ8 | TJ9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPPH * | 1.74 ± 0.06 e | 2.13 ± 0.06 b | 2.05 ± 0.10 bc | 1.70 ± 0.7 e | 1.93 ± 0.10 cd | 1.69 ± 0.04 e | 2.56 ± 0.20 a | 1.78 ± 0.07 de | 1.97 ± 0.09 bc |
| ABTS * | 1.84 ± 0.07 de | 2.09 ± 0.06 b | 1.94 ± 0.10 cd | 1.82 ± 0.03 ef | 1.88 ± 0.08 cde | 1.91 ± 0.04 cde | 2.42 ± 0.06 a | 1.88 ± 0.07 cde | 1.98 ± 0.08 bc |
| FRAP * | 387.73 ± 3.28 b | 390.15 ± 2.78 b | 362.87 ± 8.45 cd | 362.88 ± 9.72 cd | 352.88 ± 1.89 d | 368.94 ± 4.30 c | 320.15 ± 4.58 e | 436.51 ± 5.91 a | 318.93 ± 8.25 e |
| Phenolic Compound | DPPH (EC50 μmol/L) | ABTS (EC50 μmol/L) | FRAP (mg TEAC/g DW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 22.81 ± 0.22 de | 18.41 ± 0.43 d | 255.92 ± 13.29 de |
| 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 17.62 ± 0.33 ef | 10.27 ± 0.21 de | 366.00 ± 21.13 a |
| 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 20.30 ± 0.20 de | 12.52 ± 0.10 de | 273.25 ± 14.30 cd |
| caffeic acid | 16.73 ± 0.31 ef | 11.57 ± 0.18 de | 224.23 ± 16.56 gh |
| hyperoside | 8.44 ± 0.10 ef | 14.01 ± 0.37 de | 235.00 ± 0.10 fg |
| luteoloside | 9.99 ± 0.42 ef | 14.22 ± 0.65 de | 212.17 ± 0.10 h |
| 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 10.43 ± 0.33 ef | 6.14 ± 0.33 e | 297.02 ± 9.18 b |
| 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 10.48 ± 0.22 ef | 7.14 ± 0.47 e | 249.94 ± 25.16 ef |
| apigenin-7-O-glucoside | 307.44 ± 13.10 b | 158.24 ± 6.22 b | 53.87 ± 3.89 j |
| 4,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 9.40 ± 0.31 ef | 5.47 ± 0.43 e | 279.09 ± 15.80 bc |
| linarin | - | 256.03 ± 10.18 a | 6.56 ± 0.34 k |
| luteolin | 9.81 ± 0.45 ef | 8.06 ± 0.50 e | 229.93 ± 5.87 g |
| apigenin | 199.38 ± 19.11 c | 144.55 ± 7.36 c | 54.62 ± 1.98 j |
| acacetin | 706.27 ± 35.90 a | 254.17 ± 16.75 a | 51.08 ± 1.20 j |
| Positive Control (Vitamin C) | 34.69 ± 1.47 d | 11.77 ± 0.33 de | 168.93 ± 8.30i |
| Phenolic Compound | DPPH | ABTS | FRAP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duoju | Taiju | Duoju | Taiju | Duoju | Taiju | |
| 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 0.8231 | 0.5808 | 0.7966 | 0.6304 | 0.2733 | 0.5166 |
| 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 0.7134 | 0.5761 | 0.6871 | 0.6147 | 0.0831 | 0.4985 |
| luteoloside | 0.6063 | 0.5687 | 0.5455 | 0.6339 | 0.0369 | 0.1208 |
| TMAC | 0.8101 | 0.5279 | 0.6871 | 0.5704 | 0.3318 | 0.6051 |
| TDAC | 0.8433 | 0.5917 | 0.7982 | 0.6599 | 0.2568 | 0.4081 |
| TPAC | 0.8655 | 0.5886 | 0.8118 | 0.6480 | 0.2686 | 0.4987 |
| TFC | 0.7165 | 0.5810 | 0.6686 | 0.6522 | 0.0245 | 0.0835 |
| TKPC | 0.8761 | 0.5963 | 0.8224 | 0.6602 | 0.2139 | 0.4265 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, J.; Chu, B.; Gong, L.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, S.; Wang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Xiao, G.; Yuan, H.; et al. Comparison of Phenolic Compounds and the Antioxidant Activities of Fifteen Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat cv. ‘Hangbaiju’ in China. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8080325
Gong J, Chu B, Gong L, Fang Z, Zhang X, Qiu S, Wang J, Xiang Y, Xiao G, Yuan H, et al. Comparison of Phenolic Compounds and the Antioxidant Activities of Fifteen Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat cv. ‘Hangbaiju’ in China. Antioxidants. 2019; 8(8):325. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8080325
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Jinyan, Bingquan Chu, Lingxiao Gong, Zhongxiang Fang, Xiaoxu Zhang, Shaoping Qiu, Jingjing Wang, Yali Xiang, Gongnian Xiao, Haina Yuan, and et al. 2019. "Comparison of Phenolic Compounds and the Antioxidant Activities of Fifteen Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat cv. ‘Hangbaiju’ in China" Antioxidants 8, no. 8: 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8080325
APA StyleGong, J., Chu, B., Gong, L., Fang, Z., Zhang, X., Qiu, S., Wang, J., Xiang, Y., Xiao, G., Yuan, H., & Zheng, F. (2019). Comparison of Phenolic Compounds and the Antioxidant Activities of Fifteen Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat cv. ‘Hangbaiju’ in China. Antioxidants, 8(8), 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8080325





