Effects of Ingestion of Different Amounts of Carbohydrate after Endurance Exercise on Circulating Cytokines and Markers of Neutrophil Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Preliminary Testing
2.4. Experimental Protocol
2.5. Blood Sampling and Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physiological Variables
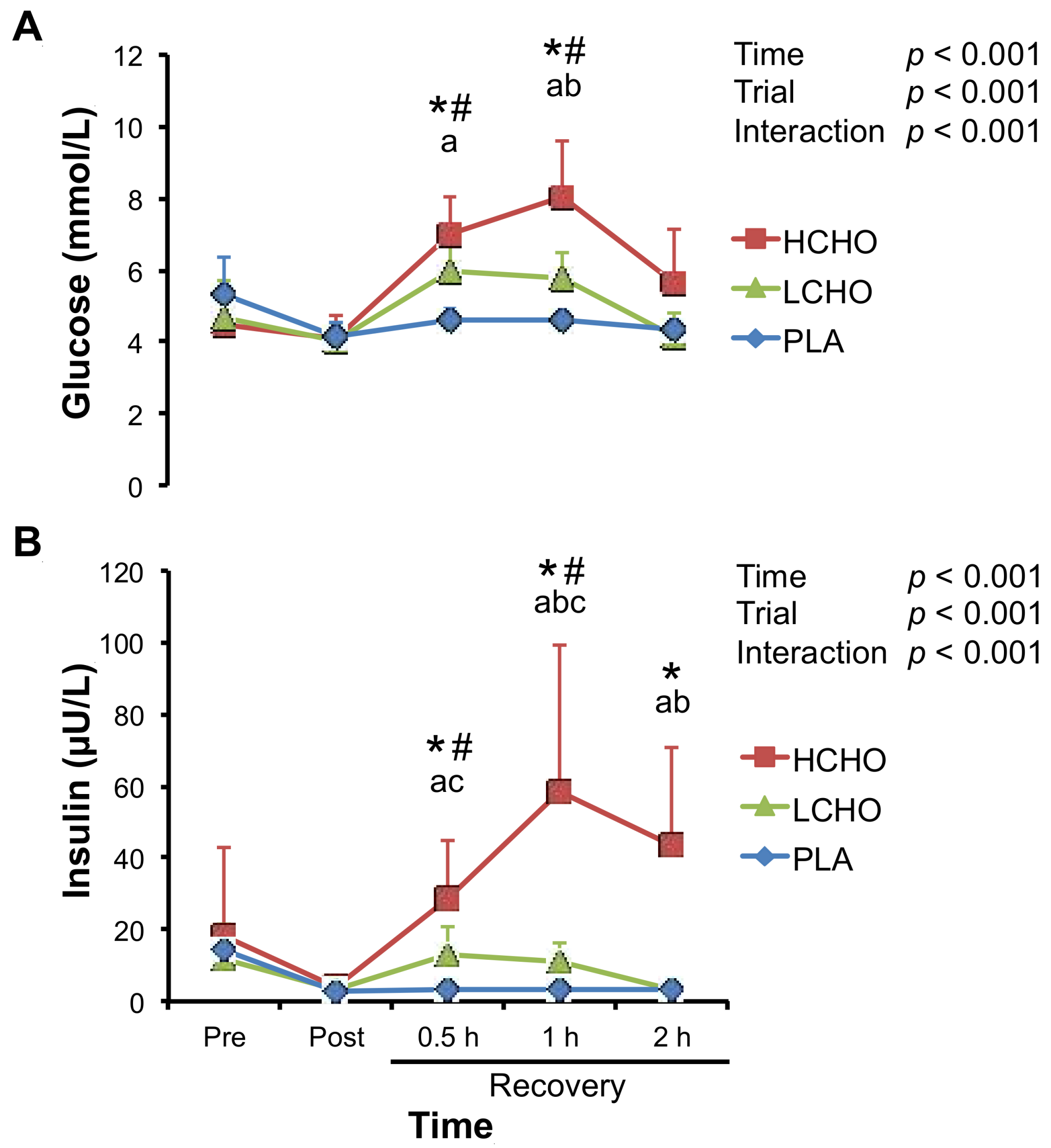
3.2. Glucose and Insulin
3.3. Leukocytes
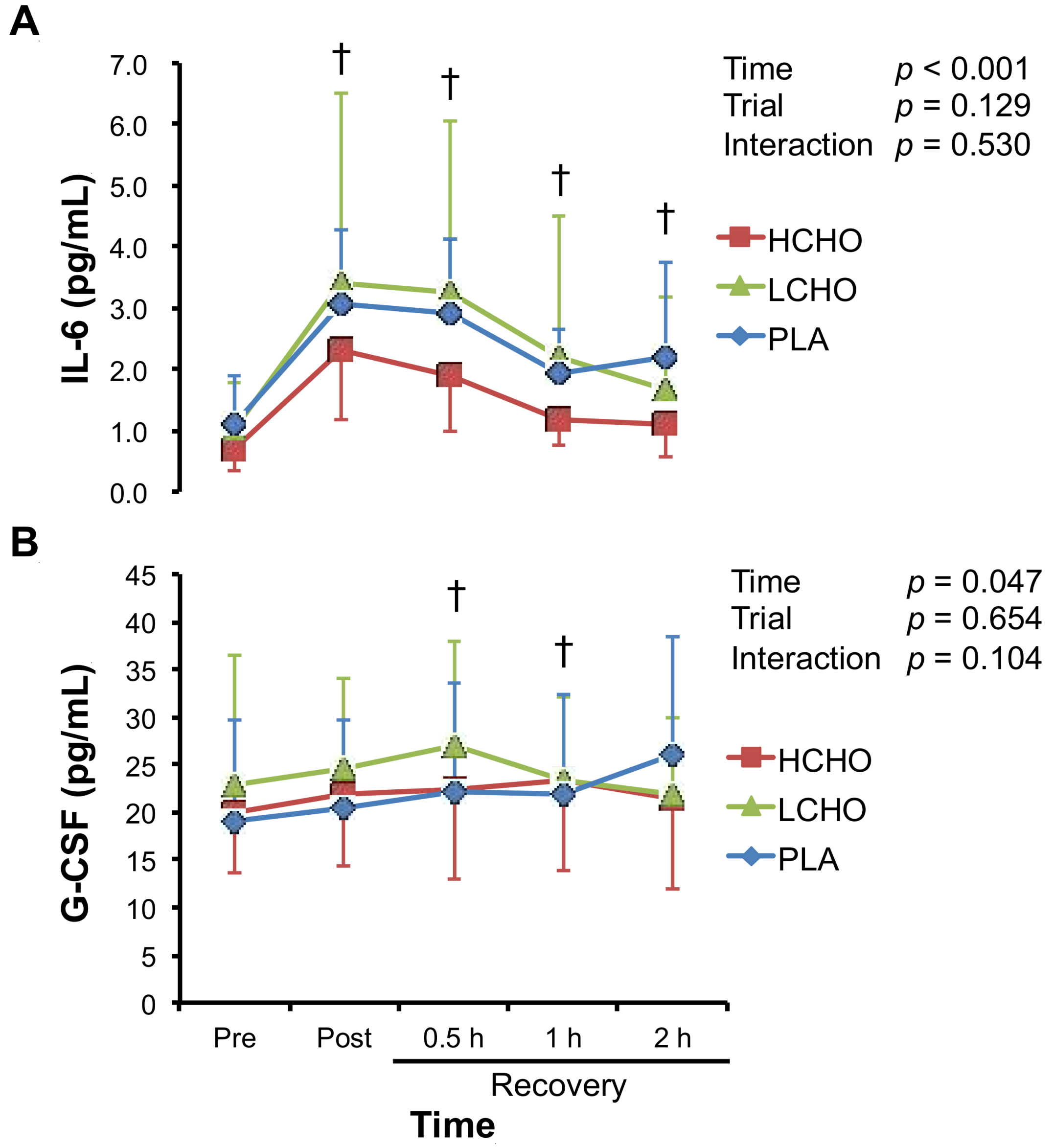
3.4. Neutrophil-Mobilizing Cytokines
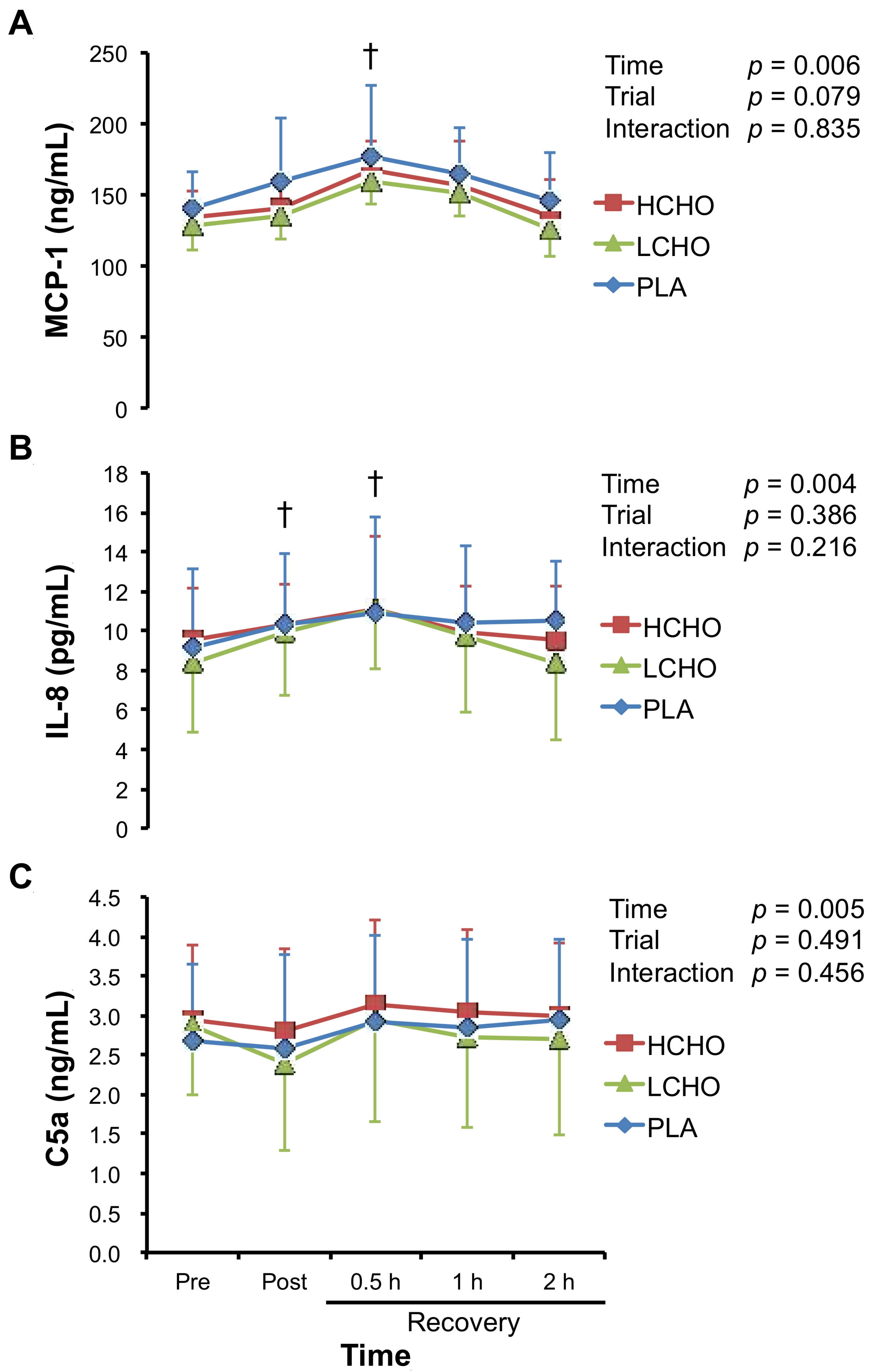
3.5. Chemotactic Factors
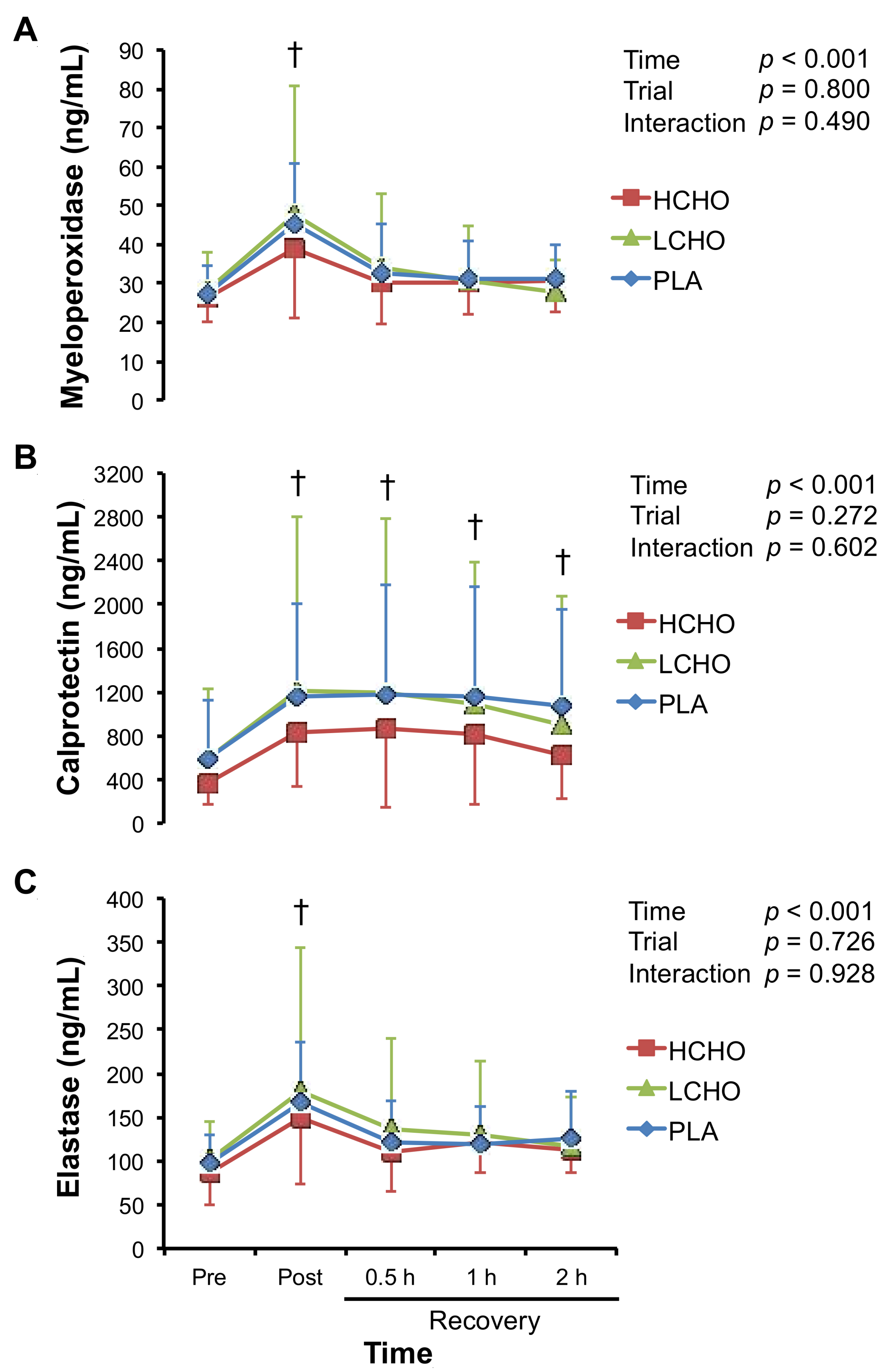
3.6. Markers of Neutrophil Activation
3.7. Indirect Markers of Muscle Damage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peake, J.; Nosaka, K.; Suzuki, K. Characterization of inflammatory responses to eccentric exercise in humans. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 11, 64–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Totsuka, M.; Nakaji, S.; Yamada, M.; Kudoh, S.; Liu, Q.; Sugawara, K.; Yamaya, K.; Sato, K. Endurance exercise causes interaction among stress hormones, cytokines, neutrophil dynamics, and muscle damage. J. Appl. Physiol. 1999, 87, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawanishi, N.; Mizokami, T.; Niihara, H.; Yada, K.; Suzuki, K. Neutrophil depletion attenuates muscle injury after exhaustive exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 1917–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawanishi, N.; Mizokami, T.; Niihara, H.; Yada, K.; Suzuki, K. Macrophage depletion by clodronate liposome attenuates muscle injury and inflammation following exhaustive exercise. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 5, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillon, N.J.; Bilan, P.J.; Fink, L.N.; Klip, A. Cross-talk between skeletal muscle and immune cells: Muscle-derived mediators and metabolic implications. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 304, E453–E465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tran, K.; Reddy, S.P.; Malik, A.B. Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1126–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, H.L.; Moots, R.J.; Bucknall, R.C.; Edwards, S.W. Neutrophil function in inflammation and inflammatory diseases. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2010, 49, 1618–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Sato, H.; Kikuchi, T.; Abe, T.; Nakaji, S.; Sugawara, K.; Totsuka, M.; Sato, K.; Yamaya, K. Capacity of circulating neutrophils to produce reactive oxygen species after exhaustive exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 81, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tidball, J.G. Inflammatory processes in muscle injury and repair. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 288, R345–R353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peake, J.; Suzuki, K.; Wilson, G.; Hordern, M.; Nosaka, K.; Mackinnon, L.; Coombes, J.S. Exercise-induced muscle damage, plasma cytokines, and markers of neutrophil activation. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, D.C.; Davis, J.M.; Henson, D.A.; Walberg-Rankin, J.; Shute, M.; Dumke, C.L.; Utter, A.C.; Vinci, D.M.; Carson, J.A.; Brown, A.; et al. Carbohydrate ingestion influences skeletal muscle cytokine mrna and plasma cytokine levels after a 3-h run. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 94, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, D.C.; Henson, D.A.; Smith, L.L.; Utter, A.C.; Vinci, D.M.; Davis, J.M.; Kaminsky, D.E.; Shute, M. Cytokine changes after a marathon race. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 91, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, D.C.; Nehlsen-Cannarella, S.L.; Fagoaga, O.R.; Henson, D.A.; Utter, A.; Davis, J.M.; Williams, F.; Butterworth, D.E. Effects of mode and carbohydrate on the granulocyte and monocyte response to intensive, prolonged exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 84, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peake, J.; Peiffer, J.J.; Abbiss, C.R.; Nosaka, K.; Laursen, P.B.; Suzuki, K. Carbohydrate gel ingestion and immunoendocrine responses to cycling in temperate and hot conditions. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2008, 18, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peake, J.; Wilson, G.; Mackinnon, L.; Coombes, J.S. Carbohydrate supplementation and alterations in neutrophils, and plasma cortisol and myoglobin concentration after intense exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 93, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehlsen-Cannarella, S.L.; Fagoaga, O.R.; Nieman, D.C.; Henson, D.A.; Butterworth, D.E.; Schmitt, R.L.; Bailey, E.M.; Warren, B.J.; Utter, A.; Davis, J.M. Carbohydrate and the cytokine response to 2.5 h of running. J. Appl. Physiol. 1997, 82, 1662–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Hashimoto, H.; Oh, T.; Ishijima, T.; Mitsuda, H.; Peake, J.M.; Sakamoto, S.; Muraoka, I.; Higuchi, M. The effects of sports drink osmolality on fluid intake and immunoendocrine responses to cycling in hot conditions. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo) 2013, 59, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Suzuki, K.; Nakaji, S.; Yamada, M.; Liu, Q.; Kurakake, S.; Okamura, N.; Kumae, T.; Umeda, T.; Sugawara, K. Impact of a competitive marathon race on systemic cytokine and neutrophil responses. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharhag, J.; Meyer, T.; Gabriel, H.H.; Auracher, M.; Kindermann, W. Mobilization and oxidative burst of neutrophils are influenced by carbohydrate supplementation during prolonged cycling in humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 87, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Valentine, R.J.; Saunders, M.J.; Todd, M.K.; St Laurent, T.G. Influence of carbohydrate-protein beverage on cycling endurance and indices of muscle disruption. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2008, 18, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, M.L.; Halson, S.L.; Suzuki, K.; Garnham, A.; Hawley, J.A.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Peake, J.M. Cytokine responses to carbohydrate ingestion during recovery from exercise-induced muscle injury. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010, 30, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afroundeh, R.; Siahkouhian, M.; Khalili, A. The effect of post-exercise carbohydrate ingestion on inflammatory responses to short time, high-force eccentric exercise. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2010, 50, 182–188. [Google Scholar]
- Depner, C.M.; Kirwan, R.D.; Frederickson, S.J.; Miles, M.P. Enhanced inflammation with high carbohydrate intake during recovery from eccentric exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, L.M.; Kiens, B.; Ivy, J.L. Carbohydrates and fat for training and recovery. J. Sports Sci. 2004, 22, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivy, J.L.; Katz, A.L.; Cutler, C.L.; Sherman, W.M.; Coyle, E.F. Muscle glycogen synthesis after exercise: Effect of time of carbohydrate ingestion. J. Appl. Physiol. 1988, 64, 1480–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.; Walters, R.; Bilzon, J.L.; Walsh, N.P. Effects of immediate postexercise carbohydrate ingestion with and without protein on neutrophil degranulation. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2011, 21, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.; Oliver, S.J.; Laing, S.J.; Waiters, R.; Bilzon, J.L.; Walsh, N.P. Influence of timing of postexercise carbohydrate-protein ingestion on selected immune indices. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2009, 19, 366–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dill, D.B.; Costill, D.L. Calculation of percentage changes in volumes of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J. Appl. Physiol. 1974, 37, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivy, J.L. Muscle glycogen synthesis before and after exercise. Sports Med. 1991, 11, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Yamada, M.; Kurakake, S.; Okamura, N.; Yamaya, K.; Liu, Q.; Kudoh, S.; Kowatari, K.; Nakaji, S.; Sugawara, K. Circulating cytokines and hormones with immunosuppressive but neutrophil-priming potentials rise after endurance exercise in humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 81, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hall, G.; Steensberg, A.; Sacchetti, M.; Fischer, C.; Keller, C.; Schjerling, P.; Hiscock, N.; Moller, K.; Saltin, B.; Febbraio, M.A.; et al. Interleukin-6 stimulates lipolysis and fat oxidation in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 3005–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, E.W.; Carey, A.L.; Sacchetti, M.; Steinberg, G.R.; Macaulay, S.L.; Febbraio, M.A.; Pedersen, B.K. Acute IL-6 treatment increases fatty acid turnover in elderly humans in vivo and in tissue culture in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 288, E155–E162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcanti, D.M.; Lotufo, C.M.; Borelli, P.; Ferreira, Z.S.; Markus, R.P.; Farsky, S.H. Endogenous glucocorticoids control neutrophil mobilization from bone marrow to blood and tissues in non-inflammatory conditions. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Poursine-Laurent, J.; Wu, H.Y.; Link, D.C. Interleukin-6 and the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor are major independent regulators of granulopoiesis in vivo but are not required for lineage commitment or terminal differentiation. Blood 1997, 90, 2583–2590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, H.; Ishijima, T.; Hayashida, H.; Suzuki, K.; Higuchi, M. Menstrual cycle phase and carbohydrate ingestion alter immune response following endurance exercise and high intensity time trial performance test under hot conditions. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2014, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, N.C.; Walsh, N.; Scanlon, G.A. Effect of prolonged exercise and carbohydrate on total neutrophil elastase content. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1326–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yui, S.; Nakatani, Y.; Mikami, M. Calprotectin (s100a8/s100a9), an inflammatory protein complex from neutrophils with a broad apoptosis-inducing activity. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peake, J.; Wilson, G.; Hordern, M.; Suzuki, K.; Yamaya, K.; Nosaka, K.; Mackinnon, L.; Coombes, J.S. Changes in neutrophil surface receptor expression, degranulation, and respiratory burst activity after moderate- and high-intensity exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 97, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Trial | Pre | Post | 0.5 h | 1 h | 2 h | Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) p-Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Trial | Interaction | |||||||
| † | † | † | |||||||
| Total leukocytes (×109 cells/L) | HCHO | 5.6 (1.4) | 6.8 (2.0) | 7.5 (3.1) | 8.5 (2.8) | 8.7 (2.2) | 0.001 | 0.608 | 0.685 |
| LCHO | 5.6 (1.8) | 7.0 (1.8) | 7.6 (2.9) | 8.9 (3.0) | 8.8 (2.3) | ||||
| PLA | 5.6 (1.3) | 7.6 (1.3) | 8.0 (3.1) | 8.7 (2.9) | 9.1 (2.2) | ||||
| † | |||||||||
| Lymphocytes (×109 cells/L) | HCHO | 2.0 (0.6) | 2.5 (0.8) | 1.7 (0.5) | 1.6 (0.4) | 1.7 (0.4) | <0.001 | 0.953 | 0.656 |
| LCHO | 1.9 (0.7) | 2.7 (0.5) | 1.7 (0.4) | 1.7 (0.4) | 1.8 (0.4) | ||||
| PLA | 1.8 (0.5) | 2.6 (0.8) | 1.8 (0.6) | 1.7 (0.4) | 1.7 (0.4) | ||||
| Monocytes (×109 cells/L) | HCHO | 0.7 (0.3) | 0.8 (0.4) | 0.7 (0.3) | 0.7 (0.2) | 0.7 (0.1) | 0.718 | 0.525 | 0.940 |
| LCHO | 0.7 (0.3) | 0.8 (0.4) | 0.7 (0.2) | 0.7 (0.3) | 0.7 (0.2) | ||||
| PLA | 0.7 (0.3) | 0.8 (0.3) | 0.8 (0.3) | 0.8 (0.3) | 0.7 (0.2) | ||||
| † | † | † | |||||||
| Neutrophils (×109 cells/L) | HCHO | 2.8 (0.9) | 3.5 (1.1) | 5.1 (2.9) | 6.2 (2.8) | 6.3 (2.2) | 0.001 | 0.691 | 0.624 |
| LCHO | 2.9 (1.0) | 3.5 (1.3) | 5.3 (2.6) | 6.5 (2.7) | 6.3 (2.3) | ||||
| PLA | 3.1 (0.8) | 4.2 (1.2) | 5.4 (2.9) | 6.3 (2.7) | 6.7 (2.2) | ||||
| † | † | ||||||||
| Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio | HCHO | 1.5 (0.5) | 1.5 (0.5) | 3.0 (1.6) | 3.9 (1.6) | 3.8 (1.6) | <0.001 | 0.840 | 0.784 |
| LCHO | 1.7 (0.6) | 1.3 (0.5) | 3.2 (1.3) | 3.9 (1.4) | 3.8 (1.5) | ||||
| PLA | 1.9 (1.1) | 1.8 (0.9) | 3.2 (1.7) | 3.8 (1.5) | 4.1 (1.5) | ||||
| Variables | Trial | Pre | Post | 0.5 h | 1 h | 2 h | ANOVA p-Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Trial | Interaction | |||||||
| † | † | † | |||||||
| Creatine kinase (IU/L) | HCHO | 181 (79) | 188 (80) | 198 (91) | 195 (86) | 192 (83) | <0.001 | 0.198 | 0.638 |
| LCHO | 185 (137) | 184 (128) | 206 (155) | 193 (136) | 195 (122) | ||||
| PLA | 175 (45) | 181 (43) | 190 (49) | 188 (50) | 186 (47) | ||||
| Myoglobin (ng/mL) | HCHO | 41 (5) | 40 (7) | 47 (14) | 47 (16) | 47 (24) | 0.031 | 0.033 | 0.471 |
| LCHO | 36 (8) | 30 (6) | 51 (32) | 60 (57) | 78 (112) | ||||
| PLA | 39 (8) | 36 (10) | 45 (12) | 54 (31) | 60 (46) | ||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanisawa, K.; Suzuki, K.; Ma, S.; Kondo, S.; Okugawa, S.; Higuchi, M. Effects of Ingestion of Different Amounts of Carbohydrate after Endurance Exercise on Circulating Cytokines and Markers of Neutrophil Activation. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7040051
Tanisawa K, Suzuki K, Ma S, Kondo S, Okugawa S, Higuchi M. Effects of Ingestion of Different Amounts of Carbohydrate after Endurance Exercise on Circulating Cytokines and Markers of Neutrophil Activation. Antioxidants. 2018; 7(4):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7040051
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanisawa, Kumpei, Katsuhiko Suzuki, Sihui Ma, Saki Kondo, Susumu Okugawa, and Mitsuru Higuchi. 2018. "Effects of Ingestion of Different Amounts of Carbohydrate after Endurance Exercise on Circulating Cytokines and Markers of Neutrophil Activation" Antioxidants 7, no. 4: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7040051
APA StyleTanisawa, K., Suzuki, K., Ma, S., Kondo, S., Okugawa, S., & Higuchi, M. (2018). Effects of Ingestion of Different Amounts of Carbohydrate after Endurance Exercise on Circulating Cytokines and Markers of Neutrophil Activation. Antioxidants, 7(4), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7040051







