The Influence of Diabetes Mellitus and Kidney Dysfunction on Oxidative Stress, a Reflection of the Multisystem Interactions in Aortic Stenosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Serum Free Thiol Levels
2.3. Immunodetection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
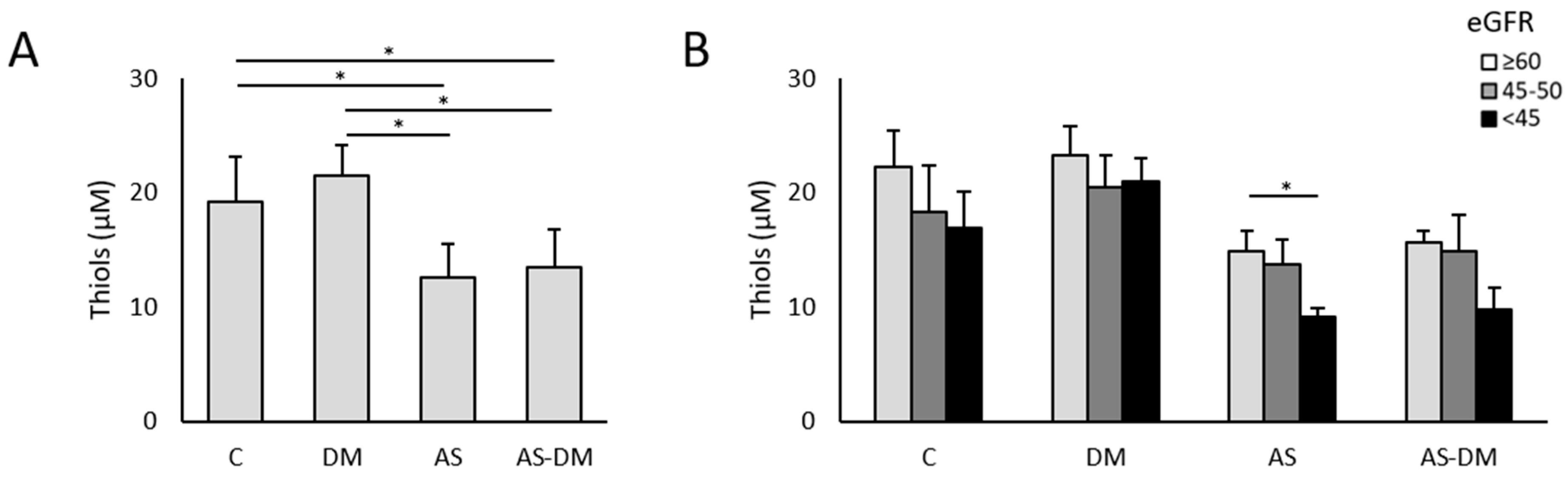
3.2. Plasma Thiol Levels and Albumin Redox State
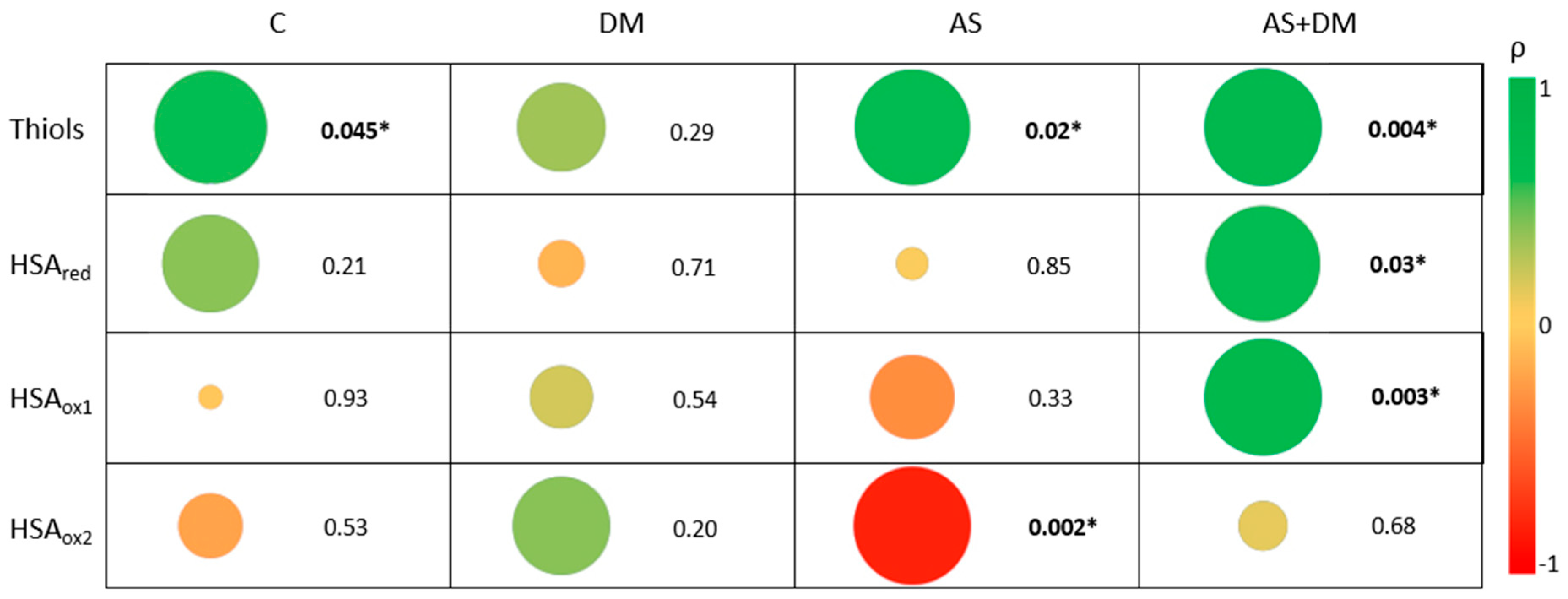
3.3. The Relationship Between Free Reduced Thiols and Albumin Oxidation
3.4. Relationship Between Kidney Function, Free Thiols, and the Albumin Redox State
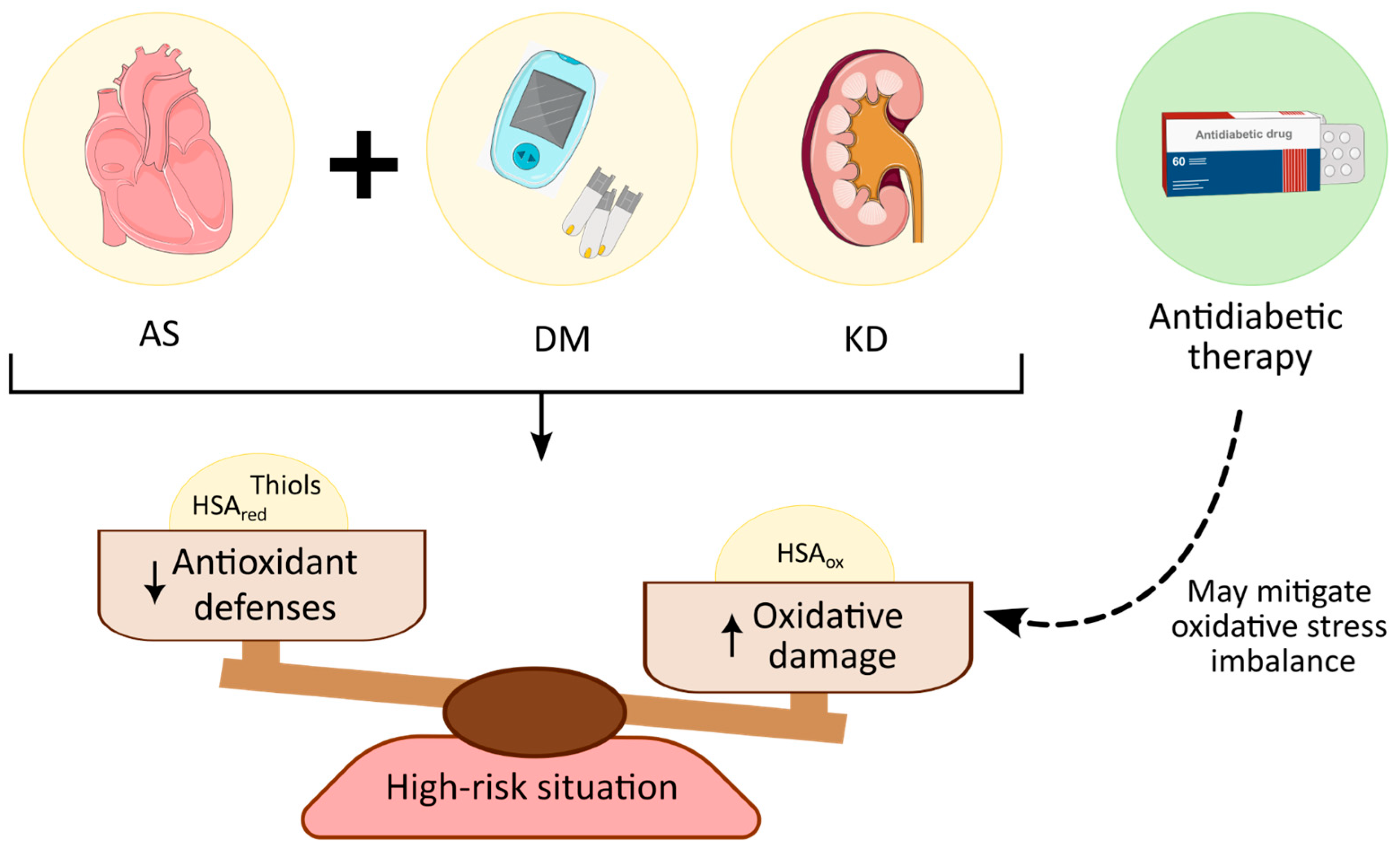
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coffey, S.; Roberts-Thomson, R.; Brown, A.; Carapetis, J.; Chen, M.; Enriquez-Sarano, M.; Zühlke, L.; Prendergast, B.D. Global epidemiology of valvular heart disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goody, P.R.; Hosen, M.R.; Christmann, D.; Niepmann, S.T.; Zietzer, A.; Adam, M.; Bönner, F.; Zimmer, S.; Nickenig, G.; Jansen, F. Aortic Valve Stenosis: From basic mechanisms to novel therapeutic targets. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahanian, A.; Beyersdorf, F.; Praz, F.; Milojevic, M.; Baldus, S.; Bauersachs, J.; Capodanno, D.; Conradi, L.; De Bonis, M.; De Paulis, R.; et al. 2021 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 561–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saku, K.; Tahara, N.; Takaseya, T.; Otsuka, H.; Takagi, K.; Shojima, T.; Shintani, Y.; Zaima, Y.; Kikusaki, S.; Fukuda, T.; et al. Pathological role of receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products in calcified aortic valve stenosis. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2020, 9, e015261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Lv, J.; Ye, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; et al. Prevalence and impact of diabetes in patients with valvular heart disease. iScience 2024, 27, 109084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderburg, C.; Loosen, S.H.; Luedde, T.; Kostev, K.; Luedde, M. Diabetes mellitus is associated with an increased incidence of aortic valve stenosis. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2021, 18, 14791641211033819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, H.Z.E.; Zhao, G.; Shah, A.M.; Zhang, M. Role of oxidative stress in calcific aortic valve disease and its therapeutic implications. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 1433–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Han, K.; Kim, M.K.; Koh, E.S.; Kim, E.S.; Nam, G.E.; Kwon, H.S. Changes in metabolic syndrome and its components and the risk of type 2 diabetes: A nationwide cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwick, T.H.; Amann, K.; Bangalore, S.; Cavalcante, J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Craig, J.C.; Gill, J.S.; Hlatky, M.A.; Jardine, A.G.; Landmesser, U.; et al. Chronic kidney disease and valvular heart disease: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungberg, J.; Johansson, B.; Bergdahl, I.A.; Holmgren, A.; Näslund, U.; Hultdin, J.; Söderberg, S. Mild impairment of renal function (shrunken pore syndrome) is associated with increased risk for future surgery for aortic stenosis. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2019, 79, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.C.; Cooper, M.E.; Zimmet, P. Changing epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and associated chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Adeli, A.; Kylhammar, D.; Swahn, E.; E Engvall, J.; Lind, L.; Söderberg, S.; Blomberg, A.; Engström, G.; Spaak, J.; et al. Prevalence and common cardiovascular risk factors in aortic valve calcification in the middle-aged general population. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2025, zwaf157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Yuan, Z.; Li, F.; Cai, Z. Oxidative stress and valvular endothelial cells in aortic valve calcification. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase, D.M.; Valasciuc, E.; Gosav, E.M.; Floria, M.; Costea, C.F.; Dima, N.; Tudorancea, I.; Maranduca, M.A.; Serban, I.L. Contribution of Oxidative Stress (OS) in Calcific Aortic Valve Disease (CAVD): From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Targets. Cells 2022, 11, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbacho-Alonso, N.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, E.; Sastre-Oliva, T.; Mercado-García, E.; Perales-Sánchez, I.; Juarez-Alia, C.; López-Almodovar, L.F.; Padial, L.R.; Tejerina, T.; Mourino-Alvarez, L.; et al. Global oxidative status is linked to calcific aortic stenosis: The differences due to Diabetes Mellitus and the effects of metformin. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Anil Kumar, N.V.; Zucca, P.; Varoni, E.M.; Dini, L.; Panzarini, E.; Rajkovic, J.; Tsouh Fokou, P.V.; Azzini, E.; Peluso, I.; et al. Lifestyle, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants: Back and Forth in the Pathophysiology of Chronic Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammisotto, V.; Nocella, C.; Bartimoccia, S.; Sanguigni, V.; Francomano, D.; Sciarretta, S.; Pastori, D.; Peruzzi, M.; Cavarretta, E.; D’amico, A.; et al. The Role of Antioxidants Supplementation in Clinical Practice: Focus on Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daenen, K.; Andries, A.; Mekahli, D.; Van Schepdael, A.; Jouret, F.; Bammens, B. Oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortese-Krott, M.M.; Koning, A.; Kuhnle, G.G.C.; Nagy, P.; Bianco, C.L.; Pasch, A.; Wink, D.A.; Fukuto, J.M.; Jackson, A.A.; Van Goor, H.; et al. The Reactive Species Interactome: Evolutionary Emergence, Biological Significance, and Opportunities for Redox Metabolomics and Personalized Medicine. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 684–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, P.R.; Pasch, A.; van Ockenburg-Brunet, S.L.; Waanders, F.; Abdulle, A.E.; Muis, M.J.; Hillebrands, J.L.; Bilo, H.J.G.; van Goor, H. Thiols as markers of redox status in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 11, 2042018820903641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, T.; Minnion, M.; Barbarino, F.; Koster, G.; Fernandez, B.; Cumpstey, A.; Wischmann, P.; Madhani, M.; Frenneaux, M.; Postle, A.; et al. A robust and versatile mass spectrometry platform for comprehensive assessment of the thiol redox metabolome. Redox Biol. 2018, 16, 359–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turell, L.; Radi, R.; Alvarez, B. The thiol pool in human plasma: The central contribution of albumin to redox processes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimaru, Y.; Adachi, T.; Ashikawa, H.; Hori, M.; Shimozato, T.; Ohtake, H.; Shimizu, S.; Ueyama, J.; Yamada, S. Association between the redox state of human serum albumin and exercise capacity in patients with cardiac disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2023, 189, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magzal, F.; Sela, S.; Szuchman-Sapir, A.; Tamir, S.; Michelis, R.; Kristal, B.; Aguilera, A.I. In-vivo oxidized albumin—A pro-inflammatory agent in hypoalbuminemia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastre-Oliva, T.; Corbacho-Alonso, N.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, E.; Mercado-García, E.; Perales-Sanchez, I.; Hernandez-Fernandez, G.; Juarez-Alia, C.; Tejerina, T.; López-Almodóvar, L.F.; Padial, L.R.; et al. Albumin Redox Modifications Promote Cell Calcification Reflecting the Impact of Oxidative Status on Aortic Valve Disease and Atherosclerosis. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre-Oliva, T.; Corbacho-Alonso, N.; Albo-Escalona, D.; Lopez, J.A.; Lopez-Almodovar, L.F.; Vázquez, J.; Padial, L.R.; Mourino-Alvarez, L.; Barderas, M.G. The influence of coronary artery disease in the development of aortic stenosis and the importance of the albumin redox state. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgonje, A.R.; Abdulle, A.E.; Bourgonje, M.F.; Binnenmars, S.H.; Gordijn, S.J.; Bulthuis, M.L.; Gemert, S.l.B.-V.; Kieneker, L.M.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Bakker, S.J.; et al. Serum free sulfhydryl status associates with new-onset chronic kidney disease in the general population. Redox Biol. 2021, 48, 102211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirichen, H.; Yaigoub, H.; Xu, W.; Wu, C.; Li, R.; Li, Y. Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species and Their Contribution in Chronic Kidney Disease Progression Through Oxidative Stress. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 627837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachofeiro, V.; Goicochea, M.; de Vinuesa, S.G.; Oubiña, P.; Lahera, V.; Luño, J. Oxidative stress and inflammation, a link between chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopytek, M.; Ząbczyk, M.; Mazur, P.; Undas, A.; Natorska, J. Accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) is associated with the severity of aortic stenosis in patients with concomitant type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, S.P.; Bhatnagar, A. Role of thiols in oxidative stress. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, T. All About Albumin: Biochemistry, Genetics, and Medical Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima, F.; Shibata, T.; Kamiya, K.; Yoshitake, J.; Kikuchi, R.; Matsushita, T.; Ishii, I.; Giménez-Bastida, J.A.; Schneider, C.; Uchida, K. Structural and functional insights into S-thiolation of human serum albumins. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocedi, A.; Cattani, G.; Stella, L.; Massoud, R.; Ricci, G. Thiol disulfide exchange reactions in human serum albumin: The apparent paradox of the redox transitions of Cys34. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 3225–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Yasukawa, K.; Oba, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Yatomi, Y.; Kadowaki, T. Oxidized albumin in blood reflects the severity of multiple vascular complications in diabetes mellitus. Metab. Open 2020, 6, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramasivan, S.; Adav, S.S.; Ngan, S.C.; Dalan, R.; Leow, M.K.-S.; Ho, H.H.; Sze, S.K. Serum albumin cysteine trioxidation is a potential oxidative stress biomarker of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imafuku, T.; Watanabe, H.; Oniki, K.; Yoshida, A.; Kato, H.; Nakano, T.; Tokumaru, K.; Fujita, I.; Arimura, N.; Maeda, H.; et al. Cysteinylated Albumin as a Potential Biomarker for the Progression of Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, e115–e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Slikke, E.C.; Boekhoud, L.; Bourgonje, A.R.; Olgers, T.J.; ter Maaten, J.C.; Henning, R.H.; van Goor, H.; Bouma, H.R. Plasma Free Thiol Levels during Early Sepsis Predict Future Renal Function Decline. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Aylor, K.W.; Chai, W.; Barrett, E.J.; Liu, Z. Metformin prevents endothelial oxidative stress and microvascular insulin resistance during obesity development in male rats. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2022, 322, E293–E306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadi, A.; Bellia, A.; Di Daniele, N.; Meloni, M.; Lauro, R.; Della-Morte, D.; Lauro, D. The molecular link between oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes: A target for new therapies against cardiovascular diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2022, 62, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposeiras-Roubin, S.; Amat-Santos, I.J.; Rossello, X.; Ferreiro, R.G.; Bermúdez, I.G.; Otero, D.L.; Nombela-Franco, L.; Gheorghe, L.; Diez, J.L.; Zorita, C.B.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Implantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 1396–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Clinical Characteristics | C (n = 12) | T2DM (n = 12) | AS (n = 12) | AS+T2DM (n = 12) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 79.7 ± 9.8 | 78.8 ± 8.2 | 79.5 ± 5.0 | 76.0 ± 4.1 | 0.273 |
| Gender (M/F) | 8/4 | 9/3 | 7/5 | 7/5 | 0.801 |
| %AHT | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | - |
| %Dyslipidemia | 42 | 83 | 83 | 67 | 0.090 |
| %Diabetes | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0.000 |
| %Smokers | 8.3 | 0 | 8.3 | 25 | 0.237 |
| %Obesity | 8.3 | 8.3 | 25 | 25 | 0.494 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 164.7 ± 60.1 | 163.1 ± 367 | 156.7 ± 41.5 | 135.6 ± 24.6 | 0.301 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 111.7 ± 52.9 | 139.8 ± 52.9 | 101.5 ± 37.0 | 101.1 ± 27.9 | 0.179 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 51.06 ± 13.6 | 46.2 ± 16.8 | 46.8 ± 12.9 | 42.5 ± 14.2 | 0.334 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 88.0 ± 45.8 | 88.8 ± 31.5 | 89.6 ± 30.0 | 74.2 ± 21.6 | 0.455 |
| Glycemia (mg/dL) | 96.2 ± 10.9 | 119.4 ± 34.0 | 97.1 ± 18.9 | 136.9 ± 54.7 | 0.030 |
| eGFR | 53.1 ± 17.7 | 54.4 ± 17.4 | 56.9 ± 17.7 | 49.3 ± 20.2 | 0.90 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.34 ± 0.34 | 1.29 ± 0.39 | 1.16 ± 0.29 | 1.35 ± 0.55 | 0.47 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 6.37 ± 2.00 | 6.04 ± 1.62 | 5.74 ± 1.32 | 6.69 ± 1.61 | 0.32 |
| Group | Mean ± SD | p-Value | Adj. p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thiol (µM) | Control | 19.13 ± 3.94 | 0.000 * | AS+T2DM vs. AS AS vs. C AS vs. T2DM AS+T2DM vs. C AS+T2DM vs. DM C vs. T2DM | 1.000 0.005 0.000 0.023 0.000 1.000 |
| T2DM | 21.53 ± 2.58 | ||||
| AS | 12.53 ± 3.02 | ||||
| AS+T2DM | 13.46 ± 3.34 | ||||
| HSAred (Band volume) | Control | 146.871 ± 49.361 | 0.019 * | AS+T2DM vs. AS AS vs. C AS vs. T2DM AS+T2DM vs. C AS+T2DM vs. DM C vs. T2DM | 1.000 0.186 0.086 0.284 0.138 1.000 |
| T2DM | 171.749 ± 7.1120 | ||||
| AS | 97.037 ± 33.570 | ||||
| AS+T2DM | 109.596 ± 70.194 | ||||
| HSAox1 (Band volume) | Control | 486.392 ± 10.9618 | 0.046 * | AS+T2DM vs. AS AS vs. C AS vs. T2DM AS+T2DM vs. C AS+T2DM vs. DM C vs. T2DM | 1.000 0.275 0.059 1.000 0.496 1.000 |
| T2DM | 528.408 ± 14.6578 | ||||
| AS | 366.031 ± 115.268 | ||||
| AS+T2DM | 430.884 ± 164.350 | ||||
| HSAox2 (Band volume) | Control | 237.165 ± 101.422 | 0.146 | NA | |
| T2DM | 193.445 ± 51.137 | ||||
| AS | 237.780 ± 79.305 | ||||
| AS+T2DM | 215.880 ± 33.788 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mourino-Alvarez, L.; Perales-Sánchez, I.; Hernández-Fernández, G.; Blanco-López, G.; Blanco-López, E.; Eiros, R.; Herrera-Flores, C.; González-Cebrian, M.; Tejerina, T.; Piqueras-Flores, J.; et al. The Influence of Diabetes Mellitus and Kidney Dysfunction on Oxidative Stress, a Reflection of the Multisystem Interactions in Aortic Stenosis. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070888
Mourino-Alvarez L, Perales-Sánchez I, Hernández-Fernández G, Blanco-López G, Blanco-López E, Eiros R, Herrera-Flores C, González-Cebrian M, Tejerina T, Piqueras-Flores J, et al. The Influence of Diabetes Mellitus and Kidney Dysfunction on Oxidative Stress, a Reflection of the Multisystem Interactions in Aortic Stenosis. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(7):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070888
Chicago/Turabian StyleMourino-Alvarez, Laura, Inés Perales-Sánchez, Germán Hernández-Fernández, Gabriel Blanco-López, Emilio Blanco-López, Rocío Eiros, Cristian Herrera-Flores, Miryam González-Cebrian, Teresa Tejerina, Jesús Piqueras-Flores, and et al. 2025. "The Influence of Diabetes Mellitus and Kidney Dysfunction on Oxidative Stress, a Reflection of the Multisystem Interactions in Aortic Stenosis" Antioxidants 14, no. 7: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070888
APA StyleMourino-Alvarez, L., Perales-Sánchez, I., Hernández-Fernández, G., Blanco-López, G., Blanco-López, E., Eiros, R., Herrera-Flores, C., González-Cebrian, M., Tejerina, T., Piqueras-Flores, J., Sánchez, P. L., López-Almodóvar, L. F., Padial, L. R., & Barderas, M. G. (2025). The Influence of Diabetes Mellitus and Kidney Dysfunction on Oxidative Stress, a Reflection of the Multisystem Interactions in Aortic Stenosis. Antioxidants, 14(7), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070888










