Highly Soluble Mussel Foot Protein Enhances Antioxidant Defense and Cytoprotection via PI3K/Akt and Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
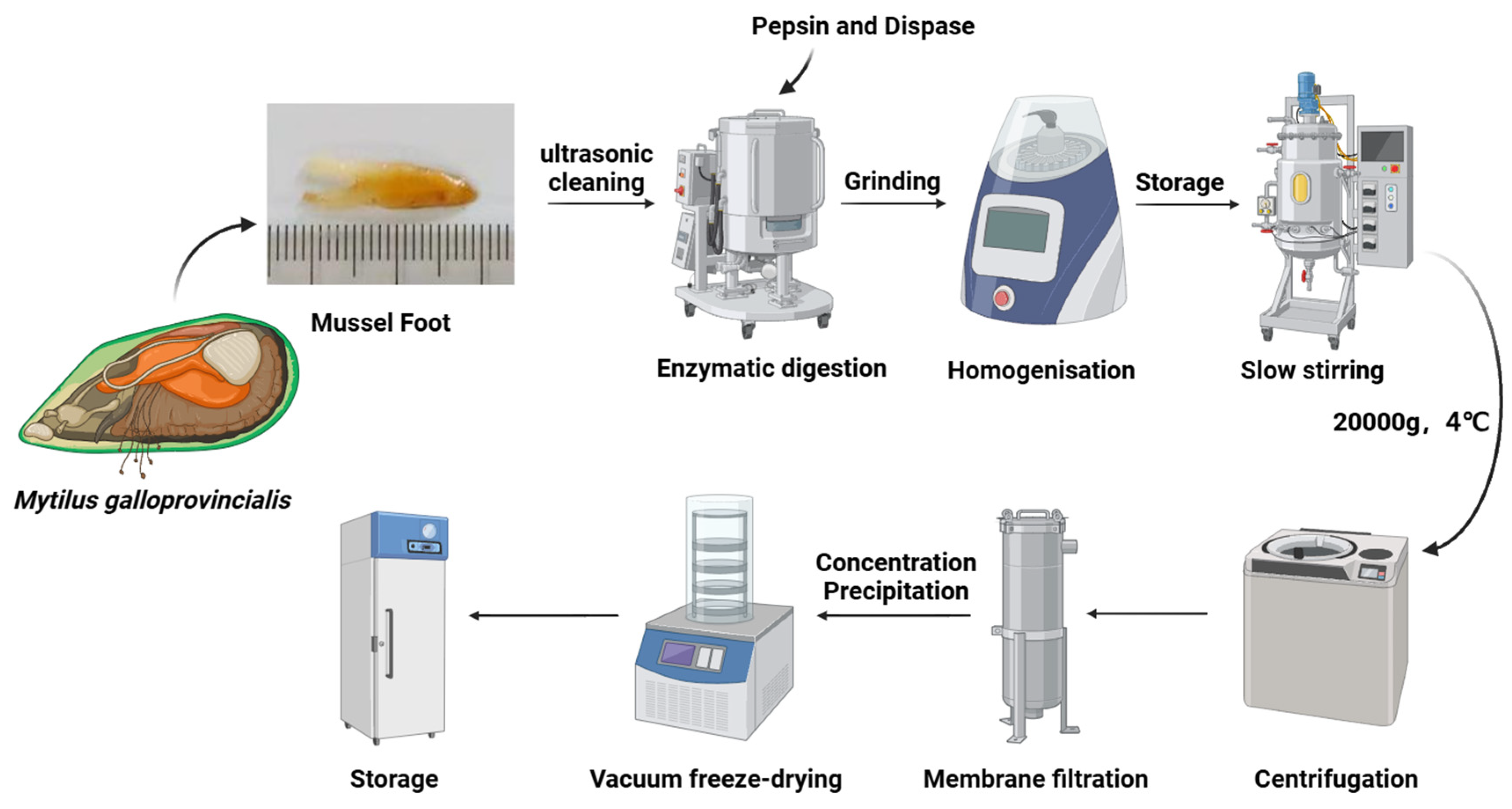
2.2. Extraction of Highly Soluble Mussel Foot Protein (HMFP) from Foot Gland of Mytilus galloprovincialis
2.3. Gel Filtration Chromatography Using Sephadex G-50
2.4. SDS-PAGE
2.5. Determination of DOPA Content in HMFP
2.6. PEGylation of Highly Soluble Mussel Foot Protein Using NHS-PEG-MAL
2.7. FTIR Analysis of HMFP
2.8. Thermogravimetric Analysis of HMFP and HMFP-PEG
2.9. Morphological Characterization of HMFP and HMFP-PEG via SEM
2.10. Cell Activity Assay
2.11. Evaluation of In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of HMFP and HMFP-PEG Using DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
2.12. Assessment of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
2.13. Assessment of Cell Apoptosis
2.14. Western Blotting Analysis
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. SDS-PAGE Analysis of HMFP
3.2. FTIR and Secondary Structure Analysis of PEG-Modified Mussel Foot Protein
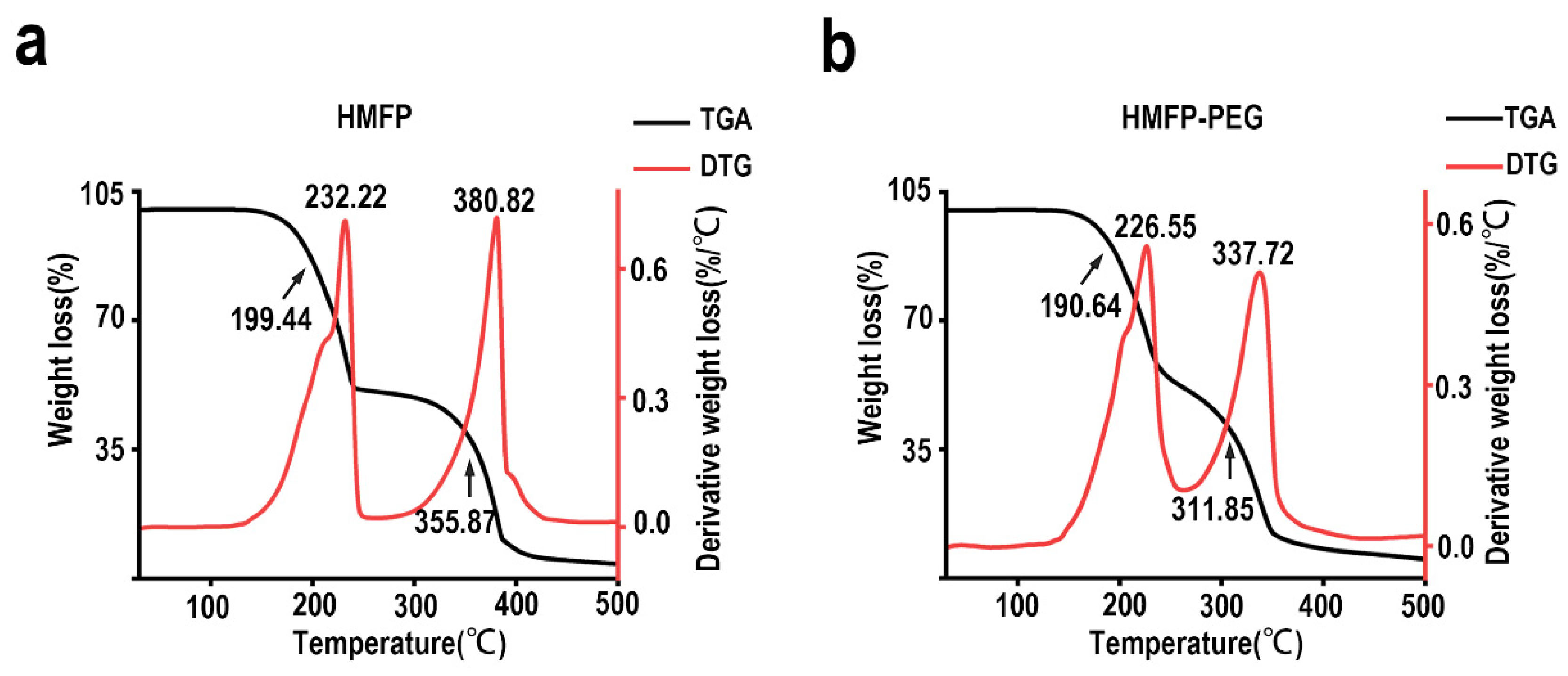
3.3. Thermal Stability Analysis of HMFP and HMFP-PEG by TGA and DTG
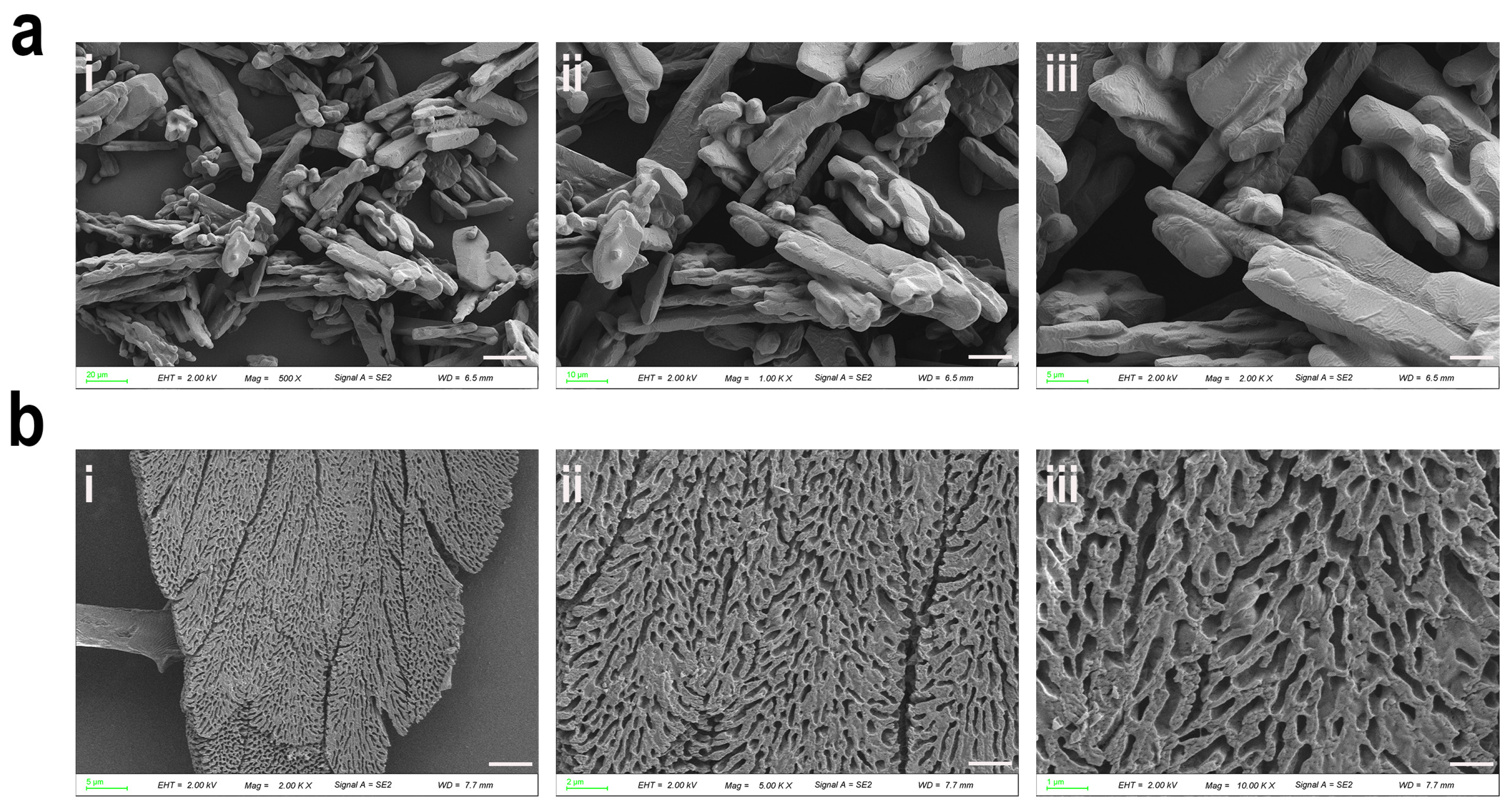
3.4. SEM Analysis of Dried-State Surface Morphology of HMFP and HMFP-PEG
3.5. Protective Effects of HMFP and HMFP-PEG Against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress in Fibroblasts
3.6. The Effects of HMFP and HMFP-PEG on Antioxidant Enzymes and MDA in Oxidative Stress Fibroblasts
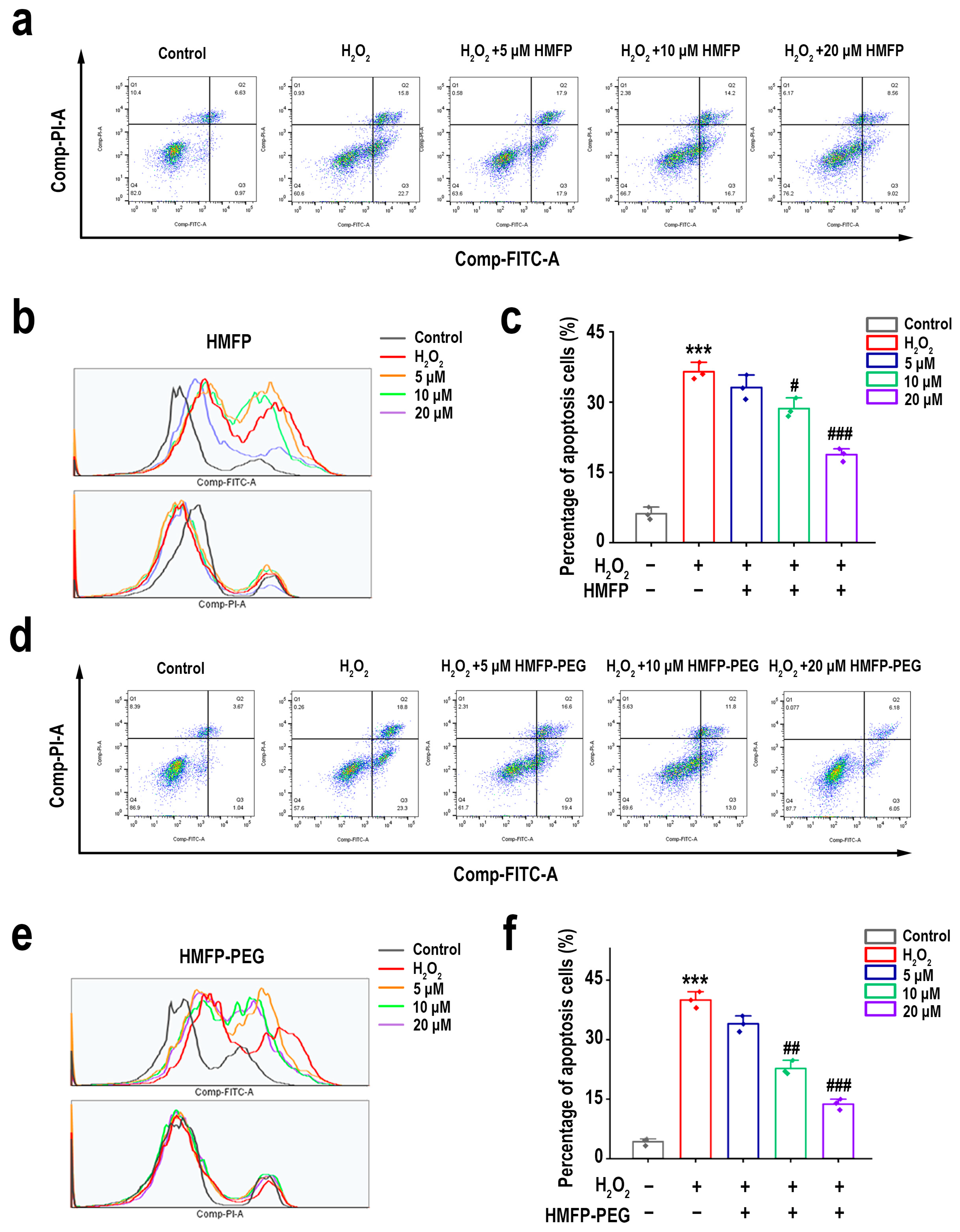
3.7. HMFP and HMFP-PEG Reduce Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Apoptosis of Fibroblasts
3.8. Regulation of Bcl-2/Bax Ratio by HMFP and HMFP-PEG in H2O2-Induced Fibroblast Apoptosis
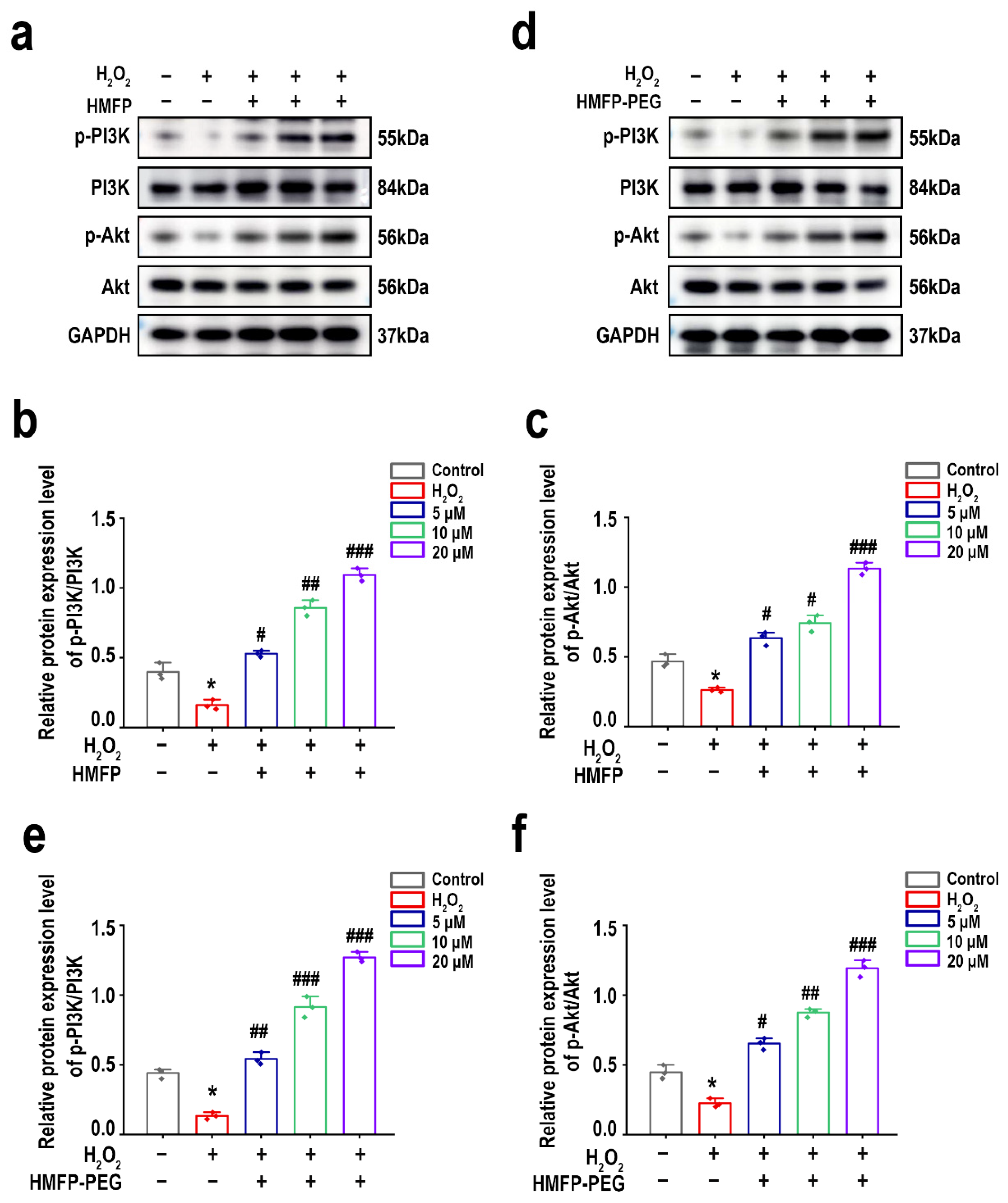
3.9. HMFP and HMFP-PEG Activate the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway to Enhance Cell Proliferation
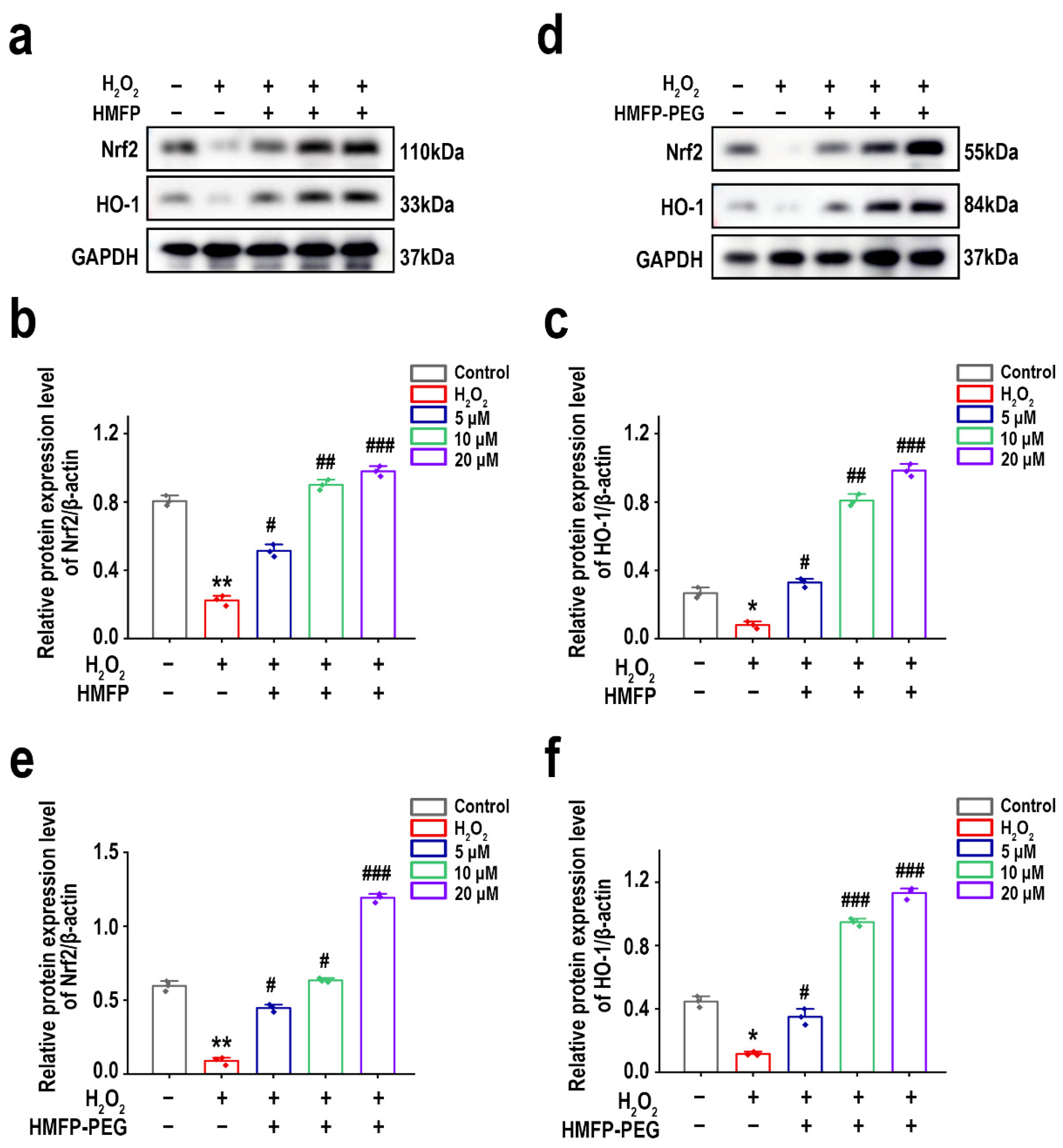
3.10. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway by HMFP and HMFP-PEG in Enhancing Antioxidant Defenses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forrester, S.J.; Kikuchi, D.S.; Hernandes, M.S.; Xu, Q.; Griendling, K.K. Reactive Oxygen Species in Metabolic and Inflammatory Signaling. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 877–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redza-Dutordoir, M.; Averill-Bates, D.A. Activation of Apoptosis Signalling Pathways by Reactive Oxygen Species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 2977–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tran, K.; Reddy, S.P.; Malik, A.B. Reactive Oxygen Species in Inflammation and Tissue Injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2014, 20, 1126–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Ali, R.; Faisal, A.B. Chapter 9—Oxidative Stress and Cardiovascular Diseases. In Fundamental Principles of Oxidative Stress in Metabolism and Reproduction; Alam, F., Rehman, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 139–149. ISBN 978-0-443-18807-7. [Google Scholar]
- Niedzielska, E.; Smaga, I.; Gawlik, M.; Moniczewski, A.; Stankowicz, P.; Pera, J.; Filip, M. Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 4094–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Tew, K.D. Oxidative Stress in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 167–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelic, M.D.; Mandic, A.D.; Maricic, S.M.; Srdjenovic, B.U. Oxidative Stress and Its Role in Cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2021, 17, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungvari, Z.; Sosnowska, D.; Podlutsky, A.; Koncz, P.; Sonntag, W.E.; Csiszar, A. Free Radical Production, Antioxidant Capacity, and Oxidative Stress Response Signatures in Fibroblasts From Lewis Dwarf Rats: Effects of Life Span-Extending Peripubertal GH Treatment. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2011, 66A, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, A.; Seluanov, M.; Hwang, C.; Tam, J.; Khan, T.; Morgenstern, A.; Wiener, L.; Vazquez, J.M.; Zafar, H.; Wen, R.; et al. Sensitivity of Primary Fibroblasts in Culture to Atmospheric Oxygen Does Not Correlate with Species Lifespan. Aging 2016, 8, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Plikus, M.V.; Wang, X.; Sinha, S.; Forte, E.; Thompson, S.M.; Herzog, E.L.; Driskell, R.R.; Rosenthal, N.; Biernaskie, J.; Horsley, V. Fibroblasts: Origins, Definitions, and Functions in Health and Disease. Cell 2021, 184, 3852–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Onitsuka, Y.; Koito, T. Mussel Biology: From the Byssus to Ecology and Physiology, Including Microplastic Ingestion and Deep-Sea Adaptations. Fish. Sci. 2021, 87, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, N.R.; Chen, Y.; Hosseini, V.; Wang, W.; Nasiri, R.; Mahmoodi, M.; Yalcintas, E.P.; Haghniaz, R.; Mecwan, M.M.; Karamikamkar, S.; et al. Recent Developments in Mussel-Inspired Materials for Biomedical Applications. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 6653–6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardim Lessa, R.; Ebrahimi, B.; Jury, J.; Sewell, M.; Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, J. Characterising Bioactive Components of Green-Lipped Mussel via Two Extraction Methods: In Vitro Assessment of Antioxidant and Immunomodulatory Effects. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 4546–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zeng, H. Mussel-Inspired Reversible Molecular Adhesion for Fabricating Self-Healing Materials. Langmuir 2022, 38, 12999–13008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Cui, P.; Lu, S. Mussel-Inspired Hydrogel Applied to Wound Healing: A Review and Future Prospects. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Wang, J.; Huang, W.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, R.; Li, S. Efficient Production of Recombinant Hybrid Mussel Proteins with Improved Adhesion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 289, 139937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Jin, Q.; Zhi, J.; Luo, Y.; Yuan, J.; Pi, L.; Nan, M.; Jin, Z.; Jin, C. Mussel Adhesive Protein Treatment Delivered by Microneedling for Sensitive Skin: A Clinical Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Liu, H.; Gao, C.; Sun, W.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W.; Qiao, H.; Jin, A.; Wang, Y.; et al. Advances in Mussel Adhesion Proteins and Mussel-Inspired Material Electrospun Nanofibers for Their Application in Wound Repair. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 6097–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xia, J.; Hou, Z.; Wu, P.; Yang, Y.; Cui, L.; Xiang, Z.; Sun, S.; Yang, L. Natural Polysaccharides Combined with Mussel-Inspired Adhesion for Multifunctional Hydrogels in Wound Hemostasis and Healing: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 136965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J. Antioxidant Is a Key Factor in Mussel Protein Adhesion. In Adhesive Interactions of Mussel Foot Proteins; Yu, J., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 31–41. ISBN 978-3-319-06031-6. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, Y.S.; Yang, B.; Yang, B.; Shin, M.; Seong, J.; Cha, H.J.; Kwon, I. Enhanced Production of Dopa-Incorporated Mussel Adhesive Protein Using Engineered Translational Machineries. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyra Recky, J.R.; Serrano, M.P.; Dántola, M.L.; Lorente, C. Oxidation of Tyrosine: Antioxidant Mechanism of l-DOPA Disclosed. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 165, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurth, M.; Barayeu, U.; Gharibi, H.; Kuzhelev, A.; Riedmiller, K.; Zilke, J.; Noack, K.; Denysenkov, V.; Kappl, R.; Prisner, T.F.; et al. DOPA Residues Endow Collagen with Radical Scavenging Capacity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202216610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndayiragije, E.; Caumul, P.; Joondan, N.; Akerman, M.P.; Bhowon, M.G.; Jhaumeer-Laulloo, S. Radical Scavenging Abilities of L-Tyrosine and L-DOPA Schiff Bases and Their Fluorescence Binding Studies and Molecular Docking Interactions with Bovine Serum Albumin. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1284, 135352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilakka Veedu, A.; Nakashima, K.; Shiga, H.; Sato, T.; Godigamuwa, K.; Hiroyoshi, N.; Kawasaki, S. Functional Modification of Mussel Adhesive Protein to Control Solubility and Adhesion Property. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2023, 136, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Xue, R.; Xu, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, L.; Li, S. Promoting Soluble Expression of Hybrid Mussel Foot Proteins by SUMO-TrxA Tags for Production of Mussel Glue. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 225, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, L.; McClements, D.J. Current Insights into Protein Solubility: A Review of Its Importance for Alternative Proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Wu, X.; Pei, D.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, D.; Wan, X. Contribution of the Polarity of Mussel-Inspired Adhesives in the Realization of Strong Underwater Bonding. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 3133–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, A.; Wu, J. Improving the Adhesion Forces of Mussel-Inspired Peptides through Inverse Design. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2025, 64, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, F.; Gong, Y.; Wan, X.; Zhou, L.-M. Protective Effects of Recombined Mussel Adhesive Protein against AD Skin Inflammation in Mice. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Liao, Z.; Liu, M.; Ye, M.; Tan, L.; Wang, R.-X. Identification of Mussel Foot Proteins with Low Molecular Mass From Mytilus coruscus Plaques. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2011, 35, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, J.H.; Benedict, C.V. Assay of Dihydroxyphenylalanine (Dopa) in Invertebrate Structural Proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 107, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Lei, Y.; Li, N.; Wei, M.; Wang, S.; Rahman, S.U.; Bao, C.; Bao, B.; Elango, J.; Wu, W. Collagen from Iris Squid Grafted with Polyethylene Glycol and Collagen Peptides Promote the Proliferation of Fibroblast through PI3K/AKT and Ras/RAF/MAPK Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 247, 125772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Waite, J.H. Linking Adhesive and Structural Proteins in the Attachment Plaque of Mytilus californianus. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 26150–26158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Gourdon, D.; Sun, C.; Holten-Andersen, N.; Anderson, T.H.; Waite, J.H.; Israelachvili, J.N. Adhesion Mechanisms of the Mussel Foot Proteins Mfp-1 and Mfp-3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3782–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodko-Piórecka, K.; Litwinienko, G. Antioxidant Activity of Dopamine and L-DOPA in Lipid Micelles and Their Cooperation with an Analogue of α-Tocopherol. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciatore, I.; Marinelli, L.; Di Stefano, A.; Di Marco, V.; Orlando, G.; Gabriele, M.; Gatta, D.M.P.; Ferrone, A.; Franceschelli, S.; Speranza, L.; et al. Chelating and Antioxidant Properties of L-Dopa Containing Tetrapeptide for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neuropeptides 2018, 71, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Cao, S.; Chen, S.; Guo, Y.; Chen, N.; Zheng, Y.; Jin, B. Salvianolic Acid A Alleviates H2O2-Induced Endothelial Oxidative Injury via miR-204-5p. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Liu, W.-W.; Shi, A.-W.; Gu, N. Salidroside Suppresses HUVECs Cell Injury Induced by Oxidative Stress through Activating the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2016, 21, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense. World Allergy Organ. J. 2012, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panday, S.; Talreja, R.; Kavdia, M. The Role of Glutathione and Glutathione Peroxidase in Regulating Cellular Level of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species. Microvasc. Res. 2020, 131, 104010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. Assessment of Lipid Peroxidation by Measuring Malondialdehyde (MDA) and Relatives in Biological Samples: Analytical and Biological Challenges. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 524, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci-Çekiç, S.; Özkan, G.; Avan, A.N.; Uzunboy, S.; Çapanoğlu, E.; Apak, R. Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 209, 114477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianciulli, A.; Calvello, R.; Porro, C.; Trotta, T.; Salvatore, R.; Panaro, M.A. PI3k/Akt Signalling Pathway Plays a Crucial Role in the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Curcumin in LPS-Activated Microglia. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 36, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Sun, L.; Tu, L. GABAB Receptor-Mediated PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Cell Injury in a Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 76, 1513–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein-Goldberg, A.; Voloshin, T.; Zemer Tov, E.; Paz, R.; Somri-Gannam, L.; Volodin, A.; Koren, L.; Lifshitz, L.; Meir, A.; Shabtay-Orbach, A.; et al. Role of the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in the Cellular Response to Tumor Treating Fields (TTFields). Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loboda, A.; Damulewicz, M.; Pyza, E.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 System in Development, Oxidative Stress Response and Diseases: An Evolutionarily Conserved Mechanism. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3221–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Buttari, B.; Panieri, E.; Profumo, E.; Saso, L. An Overview of Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Inflammation. Molecules 2020, 25, 5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, T.; Hallis, S.P.; Kwak, M.-K. Hypoxia, Oxidative Stress, and the Interplay of HIFs and NRF2 Signaling in Cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yan, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liu, H. Mussel Foot Protein Inspired Tough Tissue-Selective Underwater Adhesive Hydrogel. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, A.C.; Pereira, P.R.; Alves, N.M. Polymeric Biomaterials Inspired by Marine Mussel Adhesive Proteins. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 159, 104802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liao, Z.; Yang, Q.; Ye, Y.; Shen, W.; Liu, H.; Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Characterization of a Novel Antioxidant Byssal Protein from Mytilus coruscus Foot. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 133095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xie, J.; Ma, B.; Bartlett, D.E.; Xu, A.; Wang, C.-H. Mussel-Inspired Protein-Mediated Surface Functionalization of Electrospun Nanofibers for pH-Responsive Drug Delivery. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.J.; Cheong, H.; Hwang, B.H.; Cha, H.J. Mussel-Inspired Protein Nanoparticles Containing Iron(III)-DOPA Complexes for pH-Responsive Drug Delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 7318–7322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Tan, Y.; Martinez Rodriguez, N.R.; Yu, J.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Waite, J.H. A Mussel-Derived One Component Adhesive Coacervate. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, J.H. Mussel Adhesion—Essential Footwork. J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, J.H.; Qin, X. Polyphosphoprotein from the Adhesive Pads of Mytilus edulis. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 2887–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirshafian, R.; Wei, W.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Waite, J.H. α,β-Dehydro-Dopa: A Hidden Participant in Mussel Adhesion. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.K.; Lee, D.W.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Waite, J.H. Surface-Initiated Self-Healing of Polymers in Aqueous Media. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Xue, B.; Lao, Y.; Wutthinitikornkit, Y.; Tian, R.; Zou, A.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.; Cao, Y.; Li, J. Structure and Sequence Features of Mussel Adhesive Protein Lead to Its Salt-Tolerant Adhesion Ability. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, P.; Melendez, C.; Paris, I.; Segura-Aguilar, J. Molecular and Neurochemical Mechanisms Dopamine Oxidation To O-Quinones in Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis. In Toxicity and Autophagy in Neurodegenerative Disorders; Fuentes, J.M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 205–223. ISBN 978-3-319-13939-5. [Google Scholar]
- Soni, J.; Sahiba, N.; Sethiya, A.; Agarwal, S. Polyethylene Glycol: A Promising Approach for Sustainable Organic Synthesis. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 315, 113766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, H.; Fu, H. Protective Effect of Resveratrol Combined with Levodopa Against Oxidative Damage in Dopaminergic Neurons. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 82, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, H.J.; Zhang, H. Targeting Oxidative Stress in Disease: Promise and Limitations of Antioxidant Therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 689–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Sun, M.M.; Zhang, G.G.; Yang, J.; Chen, K.S.; Xu, W.W.; Li, B. Targeting PI3K/Akt Signal Transduction for Cancer Therapy. Sig Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaviano, A.; Foo, A.S.C.; Lam, H.Y.; Yap, K.C.H.; Jacot, W.; Jones, R.H.; Eng, H.; Nair, M.G.; Makvandi, P.; Geoerger, B.; et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Transduction Pathway and Targeted Therapies in Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, N.; Xu, J.; Liu, B.; Elango, J.; Wu, W. Highly Soluble Mussel Foot Protein Enhances Antioxidant Defense and Cytoprotection via PI3K/Akt and Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14060644
Li N, Xu J, Liu B, Elango J, Wu W. Highly Soluble Mussel Foot Protein Enhances Antioxidant Defense and Cytoprotection via PI3K/Akt and Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(6):644. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14060644
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Na, Jiren Xu, Boheng Liu, Jeevithan Elango, and Wenhui Wu. 2025. "Highly Soluble Mussel Foot Protein Enhances Antioxidant Defense and Cytoprotection via PI3K/Akt and Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways" Antioxidants 14, no. 6: 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14060644
APA StyleLi, N., Xu, J., Liu, B., Elango, J., & Wu, W. (2025). Highly Soluble Mussel Foot Protein Enhances Antioxidant Defense and Cytoprotection via PI3K/Akt and Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways. Antioxidants, 14(6), 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14060644








