Abstract
Kidney disease and hypertension are interconnected, prevalent conditions that affect both pregnant women and children. Oxidative stress occurs when reactive oxygen species or reactive nitrogen species exceed the capacity of antioxidant systems. It plays a critical role in kidney development, resulting in kidney programming and increased risks for kidney disease and hypertension across the life course. Animal models have significantly advanced our understanding of oxidative stress-related kidney programming, the molecular mechanisms involved, and early-life antioxidant interventions to prevent kidney disease. This review critically examines the influence of perinatal oxidative stress on kidney development, highlighting its long-term effects on kidney outcomes and susceptibility to hypertension. It also explores the potential of antioxidant-based interventions in preventing kidney disease and hypertension. Furthermore, the review addresses the existing gap between insights gained from animal models and their translation into clinical practices, emphasizing the challenges and opportunities for future research in this area.
1. Introduction
The fetal and infant stages of life are decisive for future health. Adverse environmental exposures during this period can have lasting detrimental effects on offspring throughout their lifetime [1,2]. Developmental programming occurs when such exposures alter the structure and function of fetal organ systems, increasing the risk of diseases in adulthood [3]. These insights led to the emergence of the research field known as the Developmental Origins of Health and Disease (DOHaD) [4]. Remarkably, the life course approach informs high-risk prevention strategies for adult diseases, beginning in the prenatal and early postnatal stages [5]. This approach enables a shift in therapeutic interventions from adulthood to fetal or infant life, a process known as reprogramming [6,7]. As a result, reprogramming has the potential to work as an innovative preventive strategy, reducing the global burden of many chronic diseases.
Oxidative stress has emerged as a key link between adverse early-life environmental factors and disorders related to DOHaD [8,9,10]. This imbalance, resulting from the overproduction of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS and RNS) that exceed the capacity of cellular antioxidant defenses [11], has been observed in both human and experimental studies involving suboptimal in utero conditions during fetal development [12,13]. Conversely, findings from animal models indicate that antioxidants could hold potential for the early-life prevention and therapeutic intervention of diseases related to DOHaD in adult offspring [8,9,10].
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) and hypertension are highly prevalent conditions, including among pregnant women [14]. Globally, CKD affects an estimated 6% of women of reproductive age and occurs in approximately 3% of pregnancies [15]. Hypertensive disorders complicate 5–10% of pregnancies, significantly impacting maternal and offspring outcomes [16]. CKD and hypertension are closely interconnected [17], with both conditions often originating in early life [18,19,20]. Women with CKD face an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes [21], and hypertension is a major contributor to these risks.
Pregnancy heightens susceptibility to oxidative stress due to elevated ROS/RNS and systemic inflammation [22]. While enzymatic and non-enzymatic defense systems help counteract ROS/RNS, excessive levels can lead to adverse maternal and fetal outcomes [23]. Oxidative stress plays a crucial role in key pathophysiological processes during pregnancy, with its dysregulation contributing to hypertensive disorders and CKD.
Oxidative stress also plays a decisive role in shaping kidney development, eventually leading to kidney programming [24,25]. These morphological and functional changes can persist, increasing the risk of hypertension and adverse kidney outcomes in both mother and offspring. Given its impact, preclinical research suggests that antioxidant therapies during pregnancy and lactation may work as promising reprogramming strategies to avert kidney disease and hypertension in offspring [8].
This narrative review aims to summarize current knowledge on developmental programming mechanisms influencing maternal and offspring kidney health and hypertension, with a focus on the role of oxidative stress in preclinical models. Additionally, it explores the potential of antioxidant therapy as a reprogramming strategy for kidney disease and hypertension with developmental origins, while highlighting gaps that require further translational research.
The search was concluded in January 2025. We conducted searches in the Medline, PubMed, and Embase databases using the following keywords: “kidney disease”, “hypertension”, “nephrogenesis”, “blood pressure”, “life course”, “developmental programming”, “DOHaD”, “free radicals”, “offspring”, “progeny”, “mother”, “prenatal”, “nitric oxide”, “oxidative stress”, “pregnancy”, “lactation”, “breastfeeding”, “reprogramming”, “reactive oxygen species”, “reactive nitrogen species”, and “antioxidant”. The search was limited to English-language papers, and additional studies were identified from references of eligible articles.
2. Maternal–Fetal Interface and Oxidative Stress
2.1. Oxidative Stress in Pregnancy
During gestation, balancing ROS/RNS and antioxidants is vital for maintaining the maternal–fetal interface and promoting a healthy pregnancy [11,12]. ROS/RNS plays a role in redox signaling, but in significant concentration, they are highly reactive molecules that can cause oxidative damage. [13] Physiologically, ROS have a vital role in fetal development, contributing to processes such as oocyte development [26], blastocyst implantation [27], placental development [28], and organogenesis. ROS consist of free radicals like superoxide (O2−) and hydroxyl (OH−), along with non-radicals such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Superoxide initiates reactions generating other ROS. RNS, including nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2−), and peroxynitrite (ONOO−), contribute to cytotoxicity, with peroxynitrite forming from the reaction between superoxide and NO.
Fetal oxygen needs vary by trimester, starting low in the first and increasing in the second and third due to rapid growth and placental circulation [29,30]. High oxygen consumption and metabolism elevate ROS production, but excessive ROS can disrupt these processes, leading to pregnancy complications [12]. Oxidative damage occurs when antioxidant defenses fail, with adverse conditions in pregnancy like preeclampsia [31], gestational diabetes mellitus [32], obesity [33], placental disorders [34], and intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR) [35] known to induce oxidative stress.
NO has a crucial role in regulating maternal and fetal homeostasis, essential for feto-placental blood flow and placental development [36,37]. It contributes to vascular reactivity, placental bed resistance, and angiogenesis [38,39]. However, as a free radical and weak oxidant, NO can interact with redox intermediates, causing protein oxidation, lipid peroxidation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cell death, contributing to cytotoxic pathogenesis [40,41].
Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) catalyzes the conversion of L-arginine into NO and L-citrulline [42]. However, NOS uncoupling leads to NO depletion and increased superoxide production [43]. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), an endogenous NOS inhibitor, can disrupt NO synthesis, but L-arginine can displace ADMA, restoring NO production. Circulating ADMA levels decrease in the first trimester but rise as pregnancy progresses [44,45]. Early in gestation, low ADMA and high NO levels facilitate hemodynamic adaptation, enhanced organ blood flow, and uterine relaxation to support fetal growth. In contrast, elevated ADMA in later gestation promotes uterine contractility, essential for labor and delivery [46]. L-arginine supplementation can compete with ADMA to enhance NO production, potentially benefiting compromised pregnancy [36,37].
In high-risk pregnancies, including gestational diabetes [47], preeclampsia [48], and gestational hypertension [49], ADMA levels are meaningfully higher than in normal pregnancy. Overall, oxidative stress—stemming from a disruption in the ROS–NO balance—plays a critical role in fetal programming in these conditions.
2.2. Maternal Kidney Disease and Hypertension
Pregnancy can impact kidney disease, often leading to a decline in renal function, particularly in the presence of hypertension and proteinuria. Even mild CKD significantly increases the risk of pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia, small for gestational age, and preterm birth [15].
ROS contribute to kidney disease by directly damaging kidney cells, resulting in inflammation, dysfunction, and fibrosis [50,51]. ROS also trigger signaling pathways and transcription factors that worsen these processes. Hypertension is associated with renal oxidative stress and NOS uncoupling, disrupting the ROS–NO balance [43]. This imbalance leads to endothelial dysfunction, epithelial damage, glomerular hypertension, and albuminuria [50]. Animal studies indicate that targeting ROS/RNS with antioxidants could present a potential therapeutic strategy for managing kidney disease and hypertension [8,24,51].
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) affect 5–10% of pregnancies and pose risks to both maternal health and fetal development [52]. HDP encompasses pre-existing hypertension, gestational hypertension, and preeclampsia/eclampsia [53]. Endothelial dysfunction, driven by oxidative stress and NO deficiency, plays an essential role in these complications [54].
Preeclampsia originates at the maternal–fetal interface, leading to hypertension, proteinuria, and potential multi-organ dysfunction, fetal growth restriction, and maternal mortality. While its pathophysiology remains poorly understood, oxidative stress is a key factor [55]. ROS may activate platelet adhesion and aggregation, resulting in intravascular coagulopathy in preeclampsia. This disrupts uteroplacental blood flow, causing placental infarction and fetal growth restriction. Antioxidant enzymes like catalase and SOD protect against oxidative damage, but placental ischemia in preeclampsia reduces their activity, increasing oxidative stress. This contributes to hypertension and proteinuria, key features of preeclampsia [56].
2.3. Oxidative Stress and Human Kidney Development: A Missing Link?
Human kidney development begins at weeks 3–4 of gestation and completes by around 36 weeks [57]. It encompasses three structures derived from the posterior intermediate mesoderm: the pronephros and mesonephros, which undergo regression, and the metanephros, which develops into the definitive kidneys. The ureteric bud (UB) initiates metanephric kidney development by invading the metanephric mesenchyme (MM) [58]. The MM develops into nephrons, while UB branching gives rise to the collecting ducts. Renal vesicles, derived from mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition, serve as nephron precursors. UB branching is essential for the collecting duct system and nephron formation.
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney, with nephron endowment reflecting nephrogenesis success. Human kidneys typically have around 1 million nephrons, although this number can vary [59]. Nephrogenesis peaks between 18–32 weeks and completes by 36 weeks [60]. After birth, kidney growth continues [61]. Infants typically reach adult-like GFR between 6 and 24 months [62]. In rodents, kidney development is faster, with nephrogenesis continuing for 1–2 weeks postnatally [63]. Adverse prenatal and early postnatal conditions, such as oxidative stress, can significantly impact kidney development.
At full-term birth, neonates usually have a complete set of nephrons. However, preterm birth, IUGR, inadequate postnatal nutrition, and certain medications (such as gentamicin) may be associated with a reduced number of nephrons [20]. This deficiency contributes to glomerular hypertension, hyper-perfusion injury, and progressive nephron loss, increasing the risk of CKD [64].
Nevertheless, nephron numbers cannot be measured in vivo [60]. While prior autopsy studies estimate about 1 million nephrons per kidney, their exact count remains uncertain. Currently, human studies still lack clarity on perinatal oxidative stress-induced kidney disease and its molecular mechanisms [8,10]. Kidney biopsies in neonates are challenging, and the relationship between oxidative stress biomarkers and kidney pathologies remains unclear. As a result, much of our knowledge on renal programming and prevention comes from animal studies.
3. Animal Evidence for Oxidative Stress-Related Kidney Programming
Recent developments in animal models have greatly improved our understanding of the molecular mechanisms driving kidney programming. Beyond oxidative stress, key mechanisms include the abnormal activation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), dysregulated nutrient-sensing signals, reduced nephron number, and gut microbiota dysbiosis [6,7,8,18,19,20,25]. The strong interconnections between oxidative stress and these other core mechanisms highlight the prominent role of oxidative stress in kidney development [10].
Table 1 summarizes preclinical models of oxidative-stress-related kidney programming [65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89]. This review primarily focuses on adverse environmental factors that begin during gestation and lactation. A broad array of environmental stimuli can contribute to oxidative-stress-related kidney programming, including maternal nutritional imbalances [65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75], maternal diseases and pregnancy complications [76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86], medication use [87,88,89], and exposure to environmental toxins [90,91,92,93].

Table 1.
Overview of Animal Models of Kidney Programming Related to Oxidative Stress.
Although genetically engineered animal models can be utilized to explore the effects of prenatal oxidative stress modifications on offspring kidney outcomes [94,95], nearly all studies involving genetic alterations have focused on modifying the offspring’s genome rather than that of the parents. This makes it challenging to separate the effects of such manipulations during the prenatal period on kidney programming from the ongoing effects of genetic changes throughout the lifespan via epigenetic mechanisms. Consequently, most evidence comes from animal studies using dietary, surgical, pharmacological, or pollution interventions to induce antenatal oxidative stress programming (Table 1). Rats are the most commonly used species, followed by mice and sheep. Major adverse kidney outcomes associated with kidney programming include hypertension [67,68,69,70,71,72,73,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86], tubulointerstitial injury [65,66,77,83,91], renal hypertrophy [65,66,74,81,82], reduced nephron number [65,66,77,90], albuminuria [74,75,90] kidney dysfunction [73], and glomerulosclerosis [75]. The various models employing dietary, surgical, pharmacological, or pollution-related interventions to induce oxidative stress and kidney programming, along with their interconnections with kidney disease and hypertension in later life, are depicted in Figure 1.
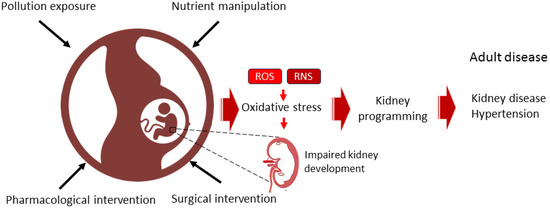
Figure 1.
Diagram illustrating the use of dietary, surgical, pharmacological, or pollution-related interventions during pregnancy to induce oxidative stress and kidney programming, thereby increasing the risk of developing kidney disease and hypertension throughout the lifespan.
3.1. Maternal Insults
Table 1 illustrates that nutritional imbalance is the most common factor inducing kidney programming. Nutritional manipulations can be categorized into various models, including those that manipulate maternal diets through reduced calorie intake [65,66], reduced protein intake [67], excessive fructose intake [68], altered methyl donor levels [69], restricted iron intake [70], and increased fat intake [71,72,73,74,75]. Additionally, maternal diseases and pregnancy complications, such as reduced uterine perfusion [76], diabetes [77,78], preeclampsia [79,80], chronic kidney disease (CKD) [81,82], endothelial dysfunction [83,84], inflammation [85,86], and maternal stress [87,88,89], can be induced by surgical or pharmacological interventions. Various other antenatal pollution exposures, such as nicotine [90], di-n-butyl phthalate [91], bisphenol A (BPA) [92], and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) [93], can also lead to kidney programming through oxidative stress.
Antenatal programmed oxidative stress modifications can also make both the mother and offspring more susceptible to subsequent programming insults that directly contribute to hypertension and CKD risk factors, often termed “second hits”. It is possible that many prenatal programming factors need further negative exposures throughout life to fully reveal kidney programming effects. This concept is supported by 2-hit models shown in Table 1, such as a rat model of antenatal BPA exposure followed by a high-fat diet [92] and antenatal TCDD exposure followed by dexamethasone exposure [93]. As a result, the heightened sensitivity of both the mother and offspring to future stressors represents a critical, yet frequently underestimated, consequence of prenatal oxidative stress manipulation.
3.2. Oxidative Stress Programming Mechanisms
Kidney programming can be linked to various oxidative stress-driven mechanisms, including increased ROS [76,83,89,90,91], decreased antioxidant capabilities [67,73,88], reduced NO bioavailability [65,66,68,71,77,80,81,82,84,87,89,92,93], and increased oxidative damage [65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,81,82,85,86,87,88,92,93].
Since assessing ROS in human kidneys is challenging, animal studies have provided substantial evidence linking elevated renal ROS levels to adverse kidney outcomes in models of reduced uterine perfusion [76], maternal angiotensin II administration [83], antenatal glucocorticoid administration [89], maternal nicotine exposure [90], and prenatal di-n-butyl phthalate exposure [91]. Conversely, impaired antioxidant defenses have also been implicated in kidney programming in models of low protein intake [67], high-fat diet [73], and antenatal glucocorticoid administration [87].
When an accumulation of ROS or RNS under detrimental intrauterine conditions exceeds antioxidant defenses, oxidative damage occurs, impairing kidney development. Oxidative damage is typically assessed by measuring lipid peroxidation products such as malondialdehyde (MDA), F2-isoprostanes (F2-IsoPs), and thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARSs) [96]. Elevated MDA levels have been observed in models of high-fat diet [72], LPS administration [86], and antenatal glucocorticoid administration [87]. Additionally, increased F2-IsoP levels have been linked to kidney programming in adult offspring in models of low-protein diet [67] and reduced uterine perfusion [76]. In a rat model of maternal diabetes induced by streptozotocin, elevated TBARSs have been associated with kidney oxidative damage and offspring hypertension [78].
In addition, oxidative DNA damage can be assessed by measuring 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), an oxidized nucleoside released during the repair of damaged DNA [97]. Elevated 8-OHdG expression in rat offspring kidneys has been associated with adverse kidney outcomes in various models, including caloric restriction [65,66], protein restriction [67], high-fructose diet [68], high-methyl-donor diet [69], methyl-deficient diet [69], iron deficiency diet [70], high-fat diet [73], maternal CKD [81,82], antenatal glucocorticoid administration [88], prenatal BPA exposure combined with a high-fat diet [92], and prenatal TCDD plus dexamethasone exposure [93].
Furthermore, several studies in Table 1 suggest that disruption of the ADMA–NO balance plays a role in oxidative stress-induced kidney programming [65,66,68,71,77,80,81,84,87,89,92]. Mounting evidence highlights the key role of epigenetic regulation in fetal programming [98]. ROS and NO influence key epigenetic processes, including DNA methylation, histone modifications, and microRNA regulation [99,100]. ADMA reduces NO production and increases ROS [42], leading to a dose-dependent reduction in nephron numbers in embryonic kidneys [101]. Transcriptome analysis of embryonic kidneys exposed to 10 µM ADMA identified 1221 differentially expressed genes (DEGs; 735 upregulated, 486 downregulated) [101], many linked to kidney development and epigenetic regulation. Similarly, maternal NO inhibition with L-NAME resulted in 2289 DEGs (1259 upregulated, 1030 downregulated) in neonatal kidneys [79]. These findings propose that oxidative stress during gestation contributes to kidney programming and increases the risk of kidney disease in offspring.
As shown in Table 1, different maternal insults can lead to similar adverse kidney outcomes in adult offspring, suggesting common mechanisms—such as oxidative stress—may underlie kidney programming. A deeper understanding of oxidative stress-induced kidney programming could help identify modifiable risk factors during pregnancy and facilitate the development of targeted interventions to prevent and treat kidney disease.
4. Antioxidants as a Strategy for Prevention and Treatment
As mentioned, perinatal oxidative stress plays a key role in kidney programming, increasing the risk of adult kidney disease. While antioxidant therapies may counteract excess ROS or RNS, their clinical benefits in kidney disease and hypertension remain inconclusive [102,103,104]. However, preclinical models in DOHaD-related disorders suggest potential benefits of early-life antioxidant therapy, which can be obtained through diet or synthetic sources.
For a substance to qualify as a dietary antioxidant, it must be commonly found in human diets and proven to reduce ROS and RNS in humans—not just in vitro. The Food and Nutrition Board of the U.S. National Institute of Medicine defines dietary antioxidants as food components that significantly reduce oxidative damage based on three criteria: presence in the human diet, measurable levels in common foods, and proven physiological effects [105].
Dietary antioxidants can be either water- or lipid-soluble. Lipid-soluble antioxidants protect cell membranes, while water-soluble ones act in the cytosol, mitochondria, or extracellular fluids. Common water-soluble antioxidants include vitamin C, glutathione, uric acid, and lipoic acid, while lipid-soluble antioxidants include vitamins A and E, coenzyme Q, carotenoids, and polyphenols. Synthetic antioxidants are man-made compounds designed to neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative damage. Examples include N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and MitoQ. Additionally, certain amino acids (e.g., L-arginine and L-citrulline) and hormones (e.g., melatonin) have been used in animal models of kidney programming due to their antioxidant properties. The following section briefly introduces antioxidants studied in kidney programming (Figure 2).
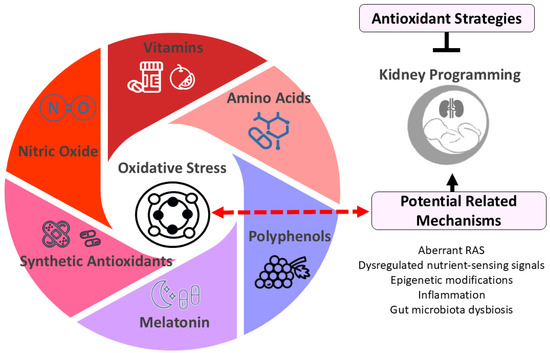
Figure 2.
Diagram illustrating potential antioxidant strategies for kidney programming. Oxidative stress plays a crucial role in kidney programming, potentially interacting with other factors such as dysregulated renin-angiotensin system (RAS) and nutrient-sensing signals to impact kidney development. Early-life antioxidant interventions have shown promise in preventing and treating kidney programming-related disorders. These antioxidant strategies include vitamins (e.g., vitamins C and E), amino acids (e.g., L-arginine and L-citrulline), polyphenols (e.g., resveratrol), melatonin, synthetic antioxidants (e.g., N-acetylcysteine), and therapies targeting nitric oxide pathways.
4.1. Vitamins
The antioxidant properties of various vitamins may provide potential benefits in CKD. These vitamins include vitamins A, C, and E, along with selenium and folic acid [106]. Among them, vitamins C and E are the most commonly used. Vitamin C neutralizes free radicals as a water-soluble antioxidant [107], while vitamin E, a lipid-soluble antioxidant, reduces ROS production by inhibiting oxidative enzymes [108].
In a rat model of maternal caloric restriction, offspring hypertension was prevented by the combined supplementation of vitamins C and E, selenium, and folic acid [109]. Additionally, gestational supplementation with vitamin C or E protected against hypertension in offspring exposed to maternal LPS administration [110,111].
However, a meta-analysis has linked high doses of vitamin A, β-carotene, and vitamin E to increased mortality [112], while excessive vitamin A intake has been related to birth defects [113]. Therefore, perinatal vitamin supplements should only be used in cases of deficiency, not routinely. Furthermore, contamination of vitamin supplements, particularly with heavy metals and toxins, poses a concern, especially for the vulnerable fetus. Ensuring these supplements are free from such contaminants is crucial for maternal and fetal health [114].
4.2. Polyphenols
Polyphenols are widely recognized dietary antioxidants. These naturally occurring plant compounds exhibit antioxidant properties and function as metal chelators, free radical scavengers, NOS activators, and stimulators of antioxidant enzymes [115]. Polyphenols have been studied for their potential role in improving kidney health [116,117]. While maternal polyphenol supplementation has shown potential benefits for pregnancy and fetal outcomes [118,119], evidence from human studies on its long-term effects on offspring kidney health remains limited [120,121].
Polyphenols are classified into flavonoids and nonflavonoids [115]. Quercetin, a flavonoid antioxidant, protected adult rat progeny from high-fat maternal-diet-induced kidney programming and hypertension [122]. Similarly, epigallocatechin gallate, used during gestation and lactation, moderated hypertension in a rat model of prenatal dexamethasone exposure [123].
Resveratrol is among the most extensively studied nonflavonoid polyphenols due to its broad spectrum of potential health benefits [124]. Its antioxidant properties include scavenging ROS and RNS, enhancing antioxidant enzyme activity, and increasing glutathione levels [125]. In rat models of kidney programming—such as high-fructose diet [71], maternal CKD [82], maternal ADMA administration [84], prenatal BPA exposure combined with a high-fat diet [92], and prenatal TCDD plus dexamethasone exposure [93]—resveratrol has demonstrated protective effects on kidney health in adult offspring.
For example, perinatal resveratrol therapy protected offspring from kidney programming induced by maternal CKD through reducing renal 8-OHdG expression and increasing NO production [66]. However, a key limitation of polyphenols in clinical applications is their low bioavailability [126]. Given the interindividual variability and the complexity of polyphenol pharmacokinetics, further research is crucial to clarify their effects on kidney health, particularly in pregnant women and their children.
The Mediterranean diet, one of the most widely studied dietary patterns with antioxidant properties, has been shown to be beneficial for cardiovascular and kidney health [127,128,129]. These effects are largely attributed to bioactive ingredients such as polyphenols [130]. The Mediterranean diet is characterized by high intakes of grains, vegetables, fruits, fish, legumes, and olive oil [127]. For example, polyphenol-rich olive oil has been found to counteract high-fat diet-induced oxidative stress, thereby preventing the progression of kidney disease and hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs) [131]. Thus, specific diets (e.g., the Mediterranean diet) or foods (e.g., olive oil) containing polyphenols may hold promise for the prevention and treatment of kidney programming-related disorders.
4.3. Amino Acids
Several amino acids exhibit antioxidant properties [132] and have demonstrated therapeutic and protective effects in kidney diseases [133]. L-arginine, a substrate for NOS, plays a crucial role in NO production, while L-citrulline serves as its precursor [105,106]. Given the impact of NO deficiency on kidney programming, the perinatal use of these amino acids has been explored for their potential to protect offspring against kidney disease later in life [134,135].
In human kidneys, L-citrulline is converted to L-arginine [135], and oral supplementation of L-citrulline bypasses hepatic metabolism, effectively increasing L-arginine and NO levels. Supplementation with L-citrulline during gestation and lactation has been shown to enhance NO bioavailability and protect adult offspring from kidney programming in oxidative stress-related models, including maternal caloric restriction [65], streptozotocin-induced diabetes [77], and antenatal dexamethasone exposure [88].
Moreover, L-tryptophan and L-cysteine have been evaluated as reprogramming interventions to mitigate oxidative stress and offspring hypertension in maternal CKD-induced kidney programming models [136,137]. Similarly, perinatal L-taurine supplementation prevented maternal diabetes-induced offspring hypertension by reducing oxidative stress [138]. Other amino acids, such as branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), show potential benefits for kidney health [134], but their specific role in reducing oxidative stress requires further investigation.
4.4. Melatonin
Melatonin is not typically classified as a dietary antioxidant, though it has strong antioxidant properties [139]. While small amounts can be obtained from food sources like eggs, fish, nuts, and some herbs [140], its primary source in humans is endogenous synthesis by the pineal gland, making it more accurately described as a biological antioxidant rather than a dietary one.
As a potent antioxidant derived from tryptophan [141], melatonin plays a crucial role in pregnancy and fetal development [142]. It neutralizes ROS and RNS, enhances antioxidant enzyme activity, and improves NO bioavailability [143,144]. Due to these properties, melatonin and its metabolites have been explored as antioxidant therapy for pregnant women and neonates [145,146].
Some human studies have shown that melatonin treatment helps reduce oxidative stress in newborns experiencing conditions such as sepsis, asphyxia, or other disorders associated with excessive ROS production [146]. Additionally, the urinary excretion of melatonin’s metabolite could act as a biomarker for infants with IUGR, indicating its involvement in fetal programming [147].
Animal studies indicate that perinatal melatonin therapy may prevent adult-onset diseases, including kidney disease [148]. Melatonin administration in mother dams has shown renal benefits in oxidative stress-related kidney programming models, including low caloric diet [66], methyl donor diet [69], maternal L-NAME administration [79], and high-fructose diet [149]. Its protective effects include reduced ADMA [66], lower 8-OHdG expression [69], decreased lipid peroxidation [79], and enhanced NO levels [149].
While melatonin is generally considered safe for children [145,146], its use during pregnancy remains unadvised due to a lack of sufficient evidence supporting its safety [150]. While animal studies suggest melatonin may protect kidney health by mitigating oxidative stress-related diseases, further research is required to confirm its safety, efficacy, and role as an epigenetic regulator before clinical recommendations can be made [151,152].
4.5. Synthetic Antioxidants
In addition to natural dietary antioxidants, several synthetic antioxidants have been studied in preclinical models of kidney programming. NAC is a widely studied synthetic antioxidant [153]. It serves as a precursor to glutathione and an L-cysteine analogue for hydrogen sulfide (H2S) synthesis [154]. NAC has demonstrated therapeutic potential in neonatal kidney disease in rat sepsis [155] and porcine neonatal asphyxia models [156], though human studies remain limited. NAC treatment during gestation and lactation protected rat offspring from maternal L-NAME-induced kidney programming by enhancing the expression and activity of renal H2S-generating enzymes [79]. In an antenatal dexamethasone and postnatal high-fat diet model [157], NAC’s protective effects were linked to increased plasma glutathione levels and upregulation of H2S-producing enzymes. Additionally, NAC prevented maternal suramin-induced offspring hypertension by boosting glutathione production, restoring NO levels, and activating the H2S pathway [80].
Other synthetic antioxidants, such as MitoQ and dimethyl fumarate (DMF), have also been explored in kidney disease models [158,159]. MitoQ, a coenzyme Q10 analogue, reduces oxidative stress by inhibiting superoxide production and lipid peroxidation [160]. Perinatal MitoQ treatment prevented hypertension, nephron loss, and kidney injury in a maternal nicotine exposure model [90]. DMF, an Nrf2 activator, reduced oxidative stress in a prenatal dexamethasone and postnatal high-fat diet model by lowering ADMA and 8-OHdG levels while increasing NO [161].
Additionally, SOD mimetics like tempol, when used during gestation, reduced proteinuria and BP in adult SHR offspring [162]. However, none of these synthetic antioxidants have been adopted in clinical practice, highlighting the need for further research.
4.6. Nitric Oxide-Targeted Therapies
Impaired NO action is linked to increased oxidative stress, making the restoration of NO bioavailability a key strategy for enhancing antioxidant defenses [163]. NO levels can be improved through NOS substrate supplementation, ADMA inhibition, NO donor or nitrodilator administration, and NOS enhancement [164].
As discussed earlier, supplementing L-arginine and L-citrulline can enhance NO production. Additionally, ADMA-lowering agents can help restore ROS/NO balance, although no specific drug is currently available [165,166]. Several clinically used drugs lower ADMA levels, including telmisartan [167], glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists [168], rosuvastatin [169], and epigallocatechin-3-gallate [170], which reduce ADMA-generating enzyme expression. Others, such as melatonin [66], NAC [80], metformin [171], atorvastatin [172], salvianolic acid A [173], telmisartan [167], oxymatrine [174], rosuvastatin [169], Farnesoid X receptor agonists [175], and nebivolol [176], enhance ADMA metabolism. Among them, only NAC and melatonin have been studied in kidney programming models to prevent offspring hypertension. Hence, further research is needed to explore their potential antioxidant benefits for kidney health.
Despite advancements in NO donors [177], their role in kidney programming remains largely unexplored. Similarly, few nitrodilators have been investigated in this context. Nitrodilators, such as pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN), nitroglycerin, and molsidomine, mimic NO’s vasodilatory effects by releasing NO from external sources [178,179]. PETN and molsidomine have shown benefits against hypertension in SHRs and fawn-hooded hypertensive rats, respectively [180,181].
While NO-related reprogramming interventions show promise in improving kidney health in preclinical studies, their interaction with oxidative stress mechanisms in kidney programming remains unclear. Further research is required to determine optimal dosage and duration before clinical translation.
4.7. Others
Evidence supports the beneficial effects of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in modulating oxidative stress, which plays a role in CKD pathogenesis and progression [182]. SCFAs, including acetate, propionate, and butyrate, are metabolites produced by gut bacteria during the fermentation of dietary fibers [183].
While SCFAs are not classified as traditional antioxidants, they possess indirect antioxidant properties. For instance, butyrate inhibits histone deacetylases (HDACs), promoting anti-inflammatory pathways and enhancing the expression of antioxidant enzymes such as SOD and glutathione peroxidase [184]. While SCFAs do not directly scavenge free radicals like conventional antioxidants, they help lower oxidative stress and support cellular health. Since SCFAs influence fetal development and programming in pregnancy [185], animal studies suggest that perinatal SCFA supplementation may prevent hypertension and kidney disease in adult offspring across various kidney programming models [186]. However, whether their protective effects stem primarily from antioxidant actions remains to be determined.
5. Research Gaps and Future Directions
Manipulating redox status during specific stages of gestation to influence offspring kidney development is challenging due to biological and technical complexities. Pregnancy involves dynamic redox changes, and disruptions can lead to multi-organ dysfunction in the developing fetus, impaired placental function, and pregnancy complications. Severe outcomes, including failed kidney development, may result, posing significant risks to offspring survival.
Animal studies suggest that oxidative stress—whether induced by dietary, surgical, pharmacological, or pollution interventions—contributes to kidney programming and increases the risk of kidney disease and hypertension. Since vulnerability to oxidative stress varies across organs, different maternal insults may lead to distinct programming effects. Key questions remain: (1) Does oxidative stress alone drive kidney programming, and when do changes occur? (2) Which free radical signals trigger lifelong redox alterations linked to kidney disease? (3) Are these changes organ-specific and reversible?
Although definitive answers remain elusive, emerging evidence provides some insights. Oxidative stress is a key contributor to kidney programming but not its sole determinant. Other factors, such as dysregulated nutrient-sensing signals [19], epigenetic modifications [98], inflammation [106], gut microbiota dysbiosis [186], and aberrant RAS [187], may interact with oxidative stress to influence kidney development. The timing of these changes likely occurs during critical windows of gestation, particularly in mid-to-late pregnancy when nephrogenesis is most active. However, oxidative stress in early pregnancy and the postnatal stage may also modify redox status and kidney programming.
Several key factors, such as superoxide and ADMA, can disrupt redox balance and alter gene expression related to nephron formation [10], though their relative importance requires further investigation. Some redox-induced changes may be reversible through postnatal interventions, such as antioxidant supplementation [8]. However, structural alterations in the kidney may have long-term consequences that are more difficult to reverse once nephrogenesis is complete [25]. Further research is needed to define critical developmental windows and redox-sensitive pathways that may serve as therapeutic targets.
Although rodents are widely used in kidney programming studies [188], their placentation and fetal development differ significantly from humans [189]. While non-human primates are the gold standard due to their genetic and biological similarity to humans, rodents remain the most commonly used models in DOHaD research [188] due to their low cost, short life cycle, and ease of genetic modification. Other species, such as rabbits, sheep, pigs, and cows, offer advantages depending on the study focus. Rabbits share similarities in lipid metabolism and placental structure with humans, pigs are ideal for early fertilization studies, sheep have a long gestation and fetal size comparable to humans, and cows, as large monotocous animals, also have a prolonged gestation period [190].
Non-rodent model organisms like zebrafish, Drosophila, and C. elegans provide valuable insights into oxidative stress research [191], offering advantages such as high reproduction rates, small size, live imaging capabilities, and ease of gene manipulation. However, their application in DOHaD research remains limited. When selecting an animal model, factors such as genetic background, anatomy, physiology, gestation length, litter size, life cycle, and relevance to study mechanisms must be considered. Findings from rodent studies should be interpreted with caution, and large animal models, which better mimic human physiology, should not be overlooked.
Another key research gap is the methodological limitations in assessing oxidative stress. Accurate quantification of redox components requires well-validated methods to ensure rigor, reproducibility, and comparability across studies. Analyzing isolated markers may misrepresent the functional status of the redox system, highlighting the need for comprehensive pathway analysis.
Currently, oxidative stress in kidney programming is assessed through biomarkers of ROS, NO, RNS, oxidation by-products, and antioxidants [192]. However, no universally accepted biomarker panel exists, leading to variability in study results. Many biomarkers (e.g., MDA, F2-isoprostanes, 8-OHdG) measure oxidative damage rather than oxidative stress itself. Additionally, the short half-lives of ROS/RNS make direct measurement difficult, forcing reliance on indirect markers that may not fully capture oxidative stress dynamics [193].
While preclinical studies support antioxidant strategies for kidney health, clinical validation is needed. Determining the optimal antioxidant and therapeutic dose remains crucial to translating animal research into human benefits. Extensive cohort studies involving pregnant women are necessary to determine the causal relationship between perinatal antioxidant supplementation and kidney outcomes in offspring. So far, there have been more than 200 trials studying the effects of antioxidants on pregnant women [194]. However, none of them focused on offspring kidney health. Given the challenges of recruiting pregnant women and neonates for research, breastmilk could serve as a starting point. Breastmilk has a strong antioxidant profile [195,196], and since the WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months [197], its potential role in protecting against renal programming warrants further investigation.
The safety of antioxidant supplements is another concern, as some may act as pro-oxidants under certain conditions [198]. For instance, vitamin E can become a radical if insufficient vitamin C is available for its regeneration [199]. The pro-oxidant effects of antioxidants depend on their concentration, highlighting the need for supplementation only when oxidative stress is confirmed. While oxidative damage can be assessed in animal models, human studies—especially in fetuses and neonates—are limited. Antioxidants may also affect healthy tissues, underscoring the importance of maintaining a balanced ROS/RNS state. Despite advances in oxidative stress biomarkers, their role in predicting adult-onset kidney diseases remains unclear [200]. These key research gaps are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Summary of Key Research Gaps.
6. Conclusions
Despite the high prevalence of hypertension and kidney disease, as well as increased perinatal mortality, global screening practices for pregnant women remain underutilized [201,202,203]. In humans, there is limited understanding of how early-life environmental factors influence oxidative stress and kidney programming, which may increase the risk of hypertension and CKD later in life. Although animal studies have provided valuable insights into adverse kidney outcomes in both dams and offspring, and antioxidant strategies show promise, further research is needed to translate these findings into clinical practice.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Writing—original draft, P.-C.L., Y.-L.T. and C.-N.H.; data curation, P.-C.L., Y.-L.T., Y.-J.L. and C.-N.H.; funding acquisition, Y.-L.T., Y.-J.L. and C.-N.H.; writing—review and editing, P.-C.L., Y.-L.T. and C.-N.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by financial assistance from the National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan, under grant number 113-2314-B-182A-118.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Barker, D.J.; Eriksson, J.G.; Forsen, T.; Osmond, C. Fetal origins of adult disease: Strength of effects and biological basis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 31, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Picó, C.; Reis, F.; Egas, C.; Mathias, P.; Matafome, P. Lactation as a programming window for metabolic syndrome. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13482. [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan, V.; Cardoso, R.C.; Puttabyatappa, M. Developmental Programming, a Pathway to Disease. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 1328–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, T.P.; Velazquez, M.A.; Eckert, J.J. Embryos, DOHaD and David Barker. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2015, 6, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wagner, C.; Carmeli, C.; Jackisch, J.; Kivimäki, M.; van der Linden, B.W.A.; Cullati, S.; Chiolero, A. Life course epidemiology and public health. Lancet Public. Health 2024, 9, e261–e269. [Google Scholar]
- Nüsken, E.; Dötsch, J.; Weber, L.T.; Nüsken, K.D. Developmental Programming of Renal Function and Re-Programming Approaches. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Paauw, N.D.; Van Rijn, B.B.; Lely, A.T.; Joles, J.A. Pregnancy as a critical window for blood pressure regulation in mother and child: Programming and reprogramming. Acta Physiol. 2016, 219, 241–259. [Google Scholar]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Oxidative Stress-Induced Hypertension of Developmental Origins: Preventive Aspects of Antioxidant Therapy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rodríguez, P.; Ramiro-Cortijo, D.; Reyes-Hernández, C.G.; López de Pablo, A.L.; González, M.C.; Arribas, S.M. Implication of Oxidative Stress in Fetal Programming of Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 602. [Google Scholar]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Metabolic Syndrome Programming and Reprogramming: Mechanistic Aspects of Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.P.; Al-Hasan, Y. Impact of oxidative stress in fetal programming. J. Pregnancy 2012, 2012, 582748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, T.; Murtaza, G.; Metwally, E.; Kalhoro, D.H.; Kalhoro, M.S.; Rahu, B.A.; Sahito, R.G.A.; Yin, Y.; Yang, H.; Chughtai, M.I.; et al. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Balance in Pregnancy. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 9962860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: A concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2017 Risk Factor Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1923–1994. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, M.L.; Herrera, C.A. Chronic Kidney Disease and Pregnancy. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2020, 27, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Wenger, N.K. Hypertension During Pregnancy. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2020, 22, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.G.; Bie, P. Role of the kidney in the pathogenesis of hypertension: Time for a neo-Guytonian paradigm or a paradigm shift? Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 310, R217–R229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyckx, V.A.; Bertram, J.F.; Brenner, B.M.; Fall, C.; Hoy, W.E.; Ozanne, S.E.; Vikse, B.E. Effect of fetal and child health on kidney development and long-term risk of hypertension and kidney disease. Lancet 2013, 382, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L. Advocacy for DOHaD research optimizing child kidney health. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2025, 66, S18–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyckx, V.A.; Chevalier, R.L. Impact of early life development on later onset chronic kidney disease and hypertension and the role of evolutionary trade-offs. Exp. Physiol. 2022, 107, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Khalaf, S.; Bodunde, E.; Maher, G.M.; O’Reilly, É.J.; McCarthy, F.P.; O’Shaughnessy, M.M.; O’Neill, S.M.; Khashan, A.S. Chronic kidney disease and adverse pregnancy outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 226, 656–670.e32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grzeszczak, K.; Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Malinowski, W.; Ziętek, P.; Kosik-Bogacka, D. Oxidative Stress in Pregnancy. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.; Khoo, M.I.; Ismail, E.H.E.; Hussain, N.H.N.; Zin, A.A.M.; Noordin, L.; Abdullah, S.; Mahdy, Z.A.; Lah, N.A.Z.N. Oxidative stress biomarkers in pregnancy: A systematic review. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2024, 22, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Tain, Y.L. Developmental Origins of Kidney Disease: Why Oxidative Stress Matters? Antioxidants 2020, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kett, M.M.; Denton, K.M. Renal programming: Cause for concern? Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 300, R791–R803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkolnik, K.; Tadmor, A.; Ben-Dor, S.; Nevo, N.; Galiani, D.; Dekel, N. Reactive oxygen species are indispensable in ovulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1462–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, P.; El Mouatassim, S.; Ménézo, Y. Oxidative stress and protection against reactive oxygen species in the pre-implantation embryo and its surroundings. Hum. Reprod. Update 2001, 7, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myatt, L. Review: Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and functional adaptation of the placenta. Placenta 2010, 31, S66–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennery, P.A. Oxidative stress in development: Nature or nurture? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.M. Placental oxygen consumption. Part, I. In vivo studies—A review. Placenta 2000, 21, S31–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrose, D.; Johansen, M.D.; Nikolic, V.; Karadzov Orlic, N.; Mikovic, Z.; Stefanovic, M.; Cakic, Z.; Hansbro, P.M.; McClements, L. Evaluating oxidative stress targeting treatments in in vitro models of placental stress relevant to preeclampsia. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2025, 13, 1539496. [Google Scholar]
- Saucedo, R.; Ortega-Camarillo, C.; Ferreira-Hermosillo, A.; Díaz-Velázquez, M.F.; Meixueiro-Calderón, C.; Valencia-Ortega, J. Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.X.W.; Candia, A.A.; Sferruzzi-Perri, A.N. Placental inflammation, oxidative stress, and fetal outcomes in maternal obesity. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 35, 638–647. [Google Scholar]
- Aouache, R.; Biquard, L.; Vaiman, D.; Miralles, F. Oxidative stress in preeclampsia and placental diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, E.H.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, N.; Jung, J.E.; Han, S.H.; Cho, H.Y. Effect of Endogenic and Exogenic Oxidative Stress Triggers on Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes: Preeclampsia, Fetal Growth Restriction, Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Preterm Birth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zullino, S.; Buzzella, F.; Simoncini, T. Nitric oxide and the biology of pregnancy. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2018, 110, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, B.J. Novel insights for the role of nitric oxide in placental vascular function during and beyond pregnancy. J. Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 7984–7999. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.T.; Hsieh, C.S.; Chang, K.A.; Tain, Y.L. Roles of nitric oxide and asymmetric dimethylarginine in pregnancy and fetal programming. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 14606–14622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Tain, Y.L. Impact of Arginine Nutrition and Metabolism during Pregnancy on Offspring Outcomes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, R. Oxygen radicals, nitric oxide, and peroxynitrite: Redox pathways in molecular medicine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5839–5848. [Google Scholar]
- Piacenza, L.; Zeida, A.; Trujillo, M.; Radi, R. The superoxide radical switch in the biology of nitric oxide and peroxynitrite. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 1881–1906. [Google Scholar]
- Baylis, C. Nitric oxide synthase derangements and hypertension in kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2012, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, C.S. Oxidative stress and nitric oxide deficiency in the kidney: A critical link to hypertension? Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 289, R913–R935. [Google Scholar]
- Fickling, S.A.; Williams, D.; Vallance, P.; Nussey, S.S.; Whitley, G.S. Plasma of endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis in normal pregnancy and pre-eclampsia. Lancet 1993, 342, 242–243. [Google Scholar]
- Holden, D.P.; Fickling, S.A.; Whitley, G.S.; Nussey, S.S. Plasma concentrations of asymmetric dimethylarginine, a natural inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, in normal pregnancy and preeclampsia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1998, 178, 551–556. [Google Scholar]
- Vida, G.; Sulyok, E.; Ertl, T.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Bode-Böger, S.M. Birth by cesarean section is associated with elevated neonatal plasma levels of dimethylarginines. Pediatr. Int. 2012, 54, 476–479. [Google Scholar]
- Akturk, M.; Altinova, A.; Mert, I.; Dincel, A.; Sargin, A.; Buyukkagnici, U.; Arslan, M.; Danisman, N. Asymmetric dimethylarginine concentrations are elevated in women with gestational diabetes. Endocrine 2010, 38, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Németh, B.; Murányi, E.; Hegyi, P.; Mátrai, P.; Szakács, Z.; Varjú, P.; Hamvas, S.; Tinusz, B.; Budán, F.; Czimmer, J.; et al. Asymmetric dimethylarginine levels in preeclampsia—Systematic review and meta-analysis. Placenta 2018, 69, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Rijvers, C.A.; Marzano, S.; Winkens, B.; Bakker, J.A.; Kroon, A.A.; Spaanderman, M.E.; Peeters, L.L. Early-pregnancy asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) levels in women prone to develop recurrent hypertension. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2013, 3, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- Kishi, S.; Nagasu, H.; Kidokoro, K.; Kashihara, N. Oxidative stress and the role of redox signalling in chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2024, 20, 101–119. [Google Scholar]
- Daenen, K.; Andries, A.; Mekahli, D.; Van Schepdael, A.; Jouret, F.; Bammens, B. Oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, J.; Vidaeff, A.; Pettker, C.M.; Simhan, H. Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 222. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 135, e237–e260. [Google Scholar]
- Cífková, R. Hypertension in Pregnancy: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Overview. High. Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2023, 30, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, P.O.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Cavalli, R.C.; Bengtsson, T.; Montenegro, M.F.; Sandrim, V.C. The Nitrate-Nitrite-Nitric Oxide Pathway: Potential Role in Mitigating Oxidative Stress in Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarello, D.I.; Abad, C.; Rojas, D.; Toledo, F.; Vázquez, C.M.; Mate, A.; Sobrevia, L.; Marín, R. Oxidative stress: Normal pregnancy versus preeclampsia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taysi, S.; Tascan, A.S.; Ugur, M.G.; Demir, M. Radicals, Oxidative/Nitrosative Stress and Preeclampsia. Mini. Rev. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchliffe, S.A.; Sargent, P.H.; Howard, C.V.; Chan, Y.F.; van Velzen, D. Human intrauterine renal growth expressed in absolute number of glomeruli assessed by the disector method and Cavalieri principle. Lab. Investig. 1991, 64, 777–784. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, M.M.; Sampogna, R.V.; Sakurai, H.; Bush, K.T.; Nigam, S.K. Branching morphogenesis and kidney disease. Development 2004, 131, 1449–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyckx, V.A.; Brenner, B.M. The clinical importance of nephron mass. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, J.F.; Douglas-Denton, R.N.; Diouf, B.; Hughson, M.; Hoy, W. Human nephron number: Implications for health and disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2011, 26, 1529–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, D.M.; Korngold, E.; Teele, R.L. Sonographic assessment of renal length in normal children. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1984, 142, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filler, G.; Lopes, L.; Awuku, M. The importance of accurately assessing renal function in the neonate and infant. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2015, 71, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Barajas, L. The rat renal nerves during development. Anat. Embryol. 1993, 188, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nenov, V.D.; Taal, M.W.; Sakharova, O.V.; Brenner, B.M. Multi-hit nature of chronic renal disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2000, 9, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsieh, C.S.; Lin, I.C.; Chen, C.C.; Sheen, J.M.; Huang, L.T. Effects of maternal L-citrulline supplementation on renal function and blood pressure in offspring exposed to maternal caloric restriction: The impact of nitric oxide pathway. Nitric Oxide 2010, 23, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Huang, L.T.; Hsu, C.N.; Lee, C.T. Melatonin therapy prevents programmed hypertension and nitric oxide deficiency in offspring exposed to maternal caloric restriction. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2014, 2014, 283180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambonie, G.; Comte, B.; Yzydorczyk, C.; Ntimbane, T.; Germain, N.; Lê, N.L.; Pladys, P.; Gauthier, C.; Lahaie, I.; Abran, D.; et al. Antenatal antioxidant prevents adult hypertension, vascular dysfunction, and microvascular rarefaction associated with in utero exposure to a low-protein diet. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R1236–R1245. [Google Scholar]
- Tain, Y.L.; Lee, W.C.; Wu, K.L.H.; Leu, S.; Chan, J.Y.H. Targeting arachidonic acid pathway to prevent programmed hypertension in maternal fructose-fed male adult rat offspring. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 38, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Chan, J.Y.H.; Lee, C.T.; Hsu, C.N. Maternal Melatonin Therapy Attenuates Methyl-Donor Diet-Induced Programmed Hypertension in Male Adult Rat Offspring. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.H.; Chen, W.H.; Su, C.H.; Yu, H.R.; Tain, Y.L.; Huang, L.T.; Sheen, J.M. Maternal Iron Deficiency Programs Rat Offspring Hypertension in Relation to Renin-Angiotensin System and Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Lee, W.C.; Wu, K.L.H.; Leu, S.; Chan, J.Y.H. Resveratrol Prevents the Development of Hypertension Programmed by Maternal Plus Post-Weaning High-Fructose Consumption through Modulation of Oxidative Stress, Nutrient-Sensing Signals, and Gut Microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 30, e1800066. [Google Scholar]
- Do Nascimento, L.C.P.; Neto, J.P.R.C.; de Andrade Braga, V.; Lagranha, C.J.; de Brito Alves, J.L. Maternal exposure to high-fat and high-cholesterol diet induces arterial hypertension and oxidative stress along the gut-kidney axis in rat offspring. Life Sci. 2020, 261, 118367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Lin, Y.J.; Sheen, J.M.; Yu, H.R.; Tiao, M.M.; Chen, C.C.; Tsai, C.C.; Huang, L.T.; Hsu, C.N. High Fat Diets Sex-Specifically Affect the Renal Transcriptome and Program Obesity, Kidney Injury, and Hypertension in the Offspring. Nutrients 2017, 9, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Nascimento, L.C.P.; de Souza, E.L.; de Luna Freire, M.O.; de Andrade Braga, V.; de Albuqeurque, T.M.R.; Lagranha, C.J.; de Brito Alves, J.L. Limosilactobacillus fermentum prevent gut-kidney oxidative damage and the rise in blood pressure in male rat offspring exposed to a maternal high-fat diet. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2022, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Mak, C.H.; Chen, H.; Zaky, A.A.; Wong, M.G.; Pollock, C.A.; Saad, S. SIRT1 Attenuates Kidney Disorders in Male Offspring Due to Maternal High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2019, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, N.B.; Hennington, B.S.; Williamson, D.T.; Hill, M.L.; Betson, N.E.; Sartori-Valinotti, J.C.; Reckelhoff, J.F.; Royals, T.P.; Alexander, B.T. Oxidative stress contributes to sex differences in blood pressure in adult growth-restricted offspring. Hypertension 2012, 60, 114–122. [Google Scholar]
- Tain, Y.L.; Lee, W.C.; Hsu, C.N.; Lee, W.C.; Huang, L.T.; Lee, C.T.; Lin, C.Y. Asymmetric dimethylarginine is associated with developmental programming of adult kidney disease and hypertension in offspring of streptozotocin-treated mothers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55420. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez Gascón, L.E.; Ortiz, M.C.; Galindo, M.; Sanchez, J.M.; Sancho-Rodriguez, N.; Albaladejo Otón, M.D.; Rodriguez Mulero, M.D.; Rodriguez, F. Role of heme oxygenase in the regulation of the renal hemodynamics in a model of sex dependent programmed hypertension by maternal diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2022, 322, R181–R191. [Google Scholar]
- Tain, Y.L.; Lee, C.T.; Chan, J.Y.; Hsu, C.N. Maternal melatonin or N-acetylcysteine therapy regulates hydrogen sulfide-generating pathway and renal transcriptome to prevent prenatal N(G)-Nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME)-induced fetal programming of hypertension in adult male offspring. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 215, 636. [Google Scholar]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N.; Lee, C.T.; Lin, Y.J.; Tsai, C.C. N-Acetylcysteine prevents programmed hypertension in male rat offspring born to suramin-treated mothers. Biol. Reprod. 2016, 95, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Yang, H.W.; Hou, C.Y.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Lin, S.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease Programs Hypertension in Adult Male Rat Offspring: Implications of Nitric Oxide and Gut Microbiome Derived Metabolites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.N.; Hou, C.Y.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Lin, S.; Yang, H.W.; Tain, Y.L. Perinatal Resveratrol Therapy Prevents Hypertension Programmed by Maternal Chronic Kidney Disease in Adult Male Offspring: Implications of the Gut Microbiome and Their Metabolites. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svitok, P.; Okuliarova, M.; Varga, I.; Zeman, M. Renal impairment induced by prenatal exposure to angiotensin II in male rat offspring. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2019, 244, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.N.; Hou, C.Y.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Lin, S.; Chan, J.Y.H.; Lee, C.T.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal resveratrol therapy protected adult rat offspring against hypertension programmed by combined exposures to asymmetric dimethylarginine and trimethylamine-N-oxide. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 93, 108630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, L.D.; Farias, J.S.; de Queiroz, D.B.; Cabral, E.V.; Lima-Filho, M.M.; Sant’Helena, B.R.M.; Aires, R.S.; Ribeiro, V.S.; SantosRocha, J.; Xavier, F.E.; et al. Oxidative stress induced by prenatal LPS leads to endothelial dysfunction and renal haemodynamic changes through angiotensin II/NADPH oxidase pathway: Prevention by early treatment with α-tocopherol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 3577–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Lan, C.; Chen, C.; Xu, Z.; Luo, H.; Zheng, S.; Gong, X.; Ren, H.; Li, Z.; Qu, S.; et al. Prenatal Lipopolysaccharides Exposure Induces Transgenerational Inheritance of Hypertension. Circulation. 2022, 146, 1082–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeje, S.O.; Akindele, O.O.; Ushie, G.; Rajil, Y. Changes in kidney function and oxidative stress biomarkers in offspring from dams treated with dexamethasone during lactation in Wistar rats. Afr. J. Med. Med. Sci. 2016, 45, 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Tain, Y.L.; Sheen, J.M.; Chen, C.C.; Yu, H.R.; Tiao, M.M.; Kuo, H.C.; Huang, L.T. Maternal citrulline supplementation prevents prenatal dexamethasone-induced programmed hypertension. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwathmey, T.M.; Shaltout, H.A.; Rose, J.C.; Diz, D.I.; Chappell, M.C. Glucocorticoid-induced fetal programming alters the functional complement of angiotensin receptor subtypes within the kidney. Hypertension 2011, 57, 620–626. [Google Scholar]
- Sukjamnong, S.; Chan, Y.L.; Zakarya, R.; Nguyen, L.T.; Anwer, A.G.; Zaky, A.A.; Santiyanont, R.; Oliver, B.G.; Goldys, E.; Pollock, C.A.; et al. MitoQ supplementation prevent long-term impact of maternal smoking on renal development, oxidative stress and mitochondrial density in male mice offspring. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6631. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.P.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.J.; Jiang, Q.H.; Bei, X.Y.; Sun, W.L.; Xia, S.J.; Jiang, J.T. Maternal exposure to di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) induces renal fibrosis in adult rat offspring. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 31101–31111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.N.; Lin, Y.J.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal exposure to bisphenol A combined with high-fat diet-induced programmed hypertension in adult male rat offspring: Effects of resveratrol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.N.; Lin, Y.J.; Lu, P.C.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal resveratrol therapy protects male rat offspring against programmed hypertension induced by TCDD and dexamethasone exposures: Is it relevant to aryl hydrocarbon receptor? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuczeriszka, M.; Wąsowicz, K. Animal models of hypertension: The status of nitric oxide and oxidative stress and the role of the renal medulla. Nitric Oxide 2022, 125–126, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubera, I.; Hummler, E.; Beermann, F. Transgenic mice and their impact on kidney research. Pflugers. Arch. 2009, 458, 211–222. [Google Scholar]
- Perrone, S.; Laschi, E.; Buonocore, G. Biomarkers of oxidative stress in the fetus and in the newborn. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 142, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Pilger, A.; Rüdiger, H.W. 8-Hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine as a marker of oxidative DNA damage related to occupational and environmental exposures. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2006, 80, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco-Miotto, T.; Craig, J.M.; Gasser, Y.P.; van Dijk, S.J.; Ozanne, S.E. Epigenetics and DOHaD: From basics to birth and beyond. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2017, 8, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.V.; Hora, S.; Pal, A.; Jha, S.; Taneja, R. Stressing the (Epi) Genome: Dealing with Reactive Oxygen Species in Cancer. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 1273–1292. [Google Scholar]
- Vasudevan, D.; Bovee, R.C.; Thomas, D.D. Nitric oxide, the new architect of epigenetic landscapes. Nitric Oxide 2016, 59, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Tain, Y.L.; Huang, L.T.; Chan, J.Y.; Lee, C.T. Transcriptome analysis in rat kidneys: Importance of genes involved in programmed hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 4744–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, R.G.; Lunkenbein, S.; Ströhle, A.; Hahn, A. Antioxidants in food: Mere myth or magic medicine? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, M.; Venkataraman, V.; Razavian, M.; Cooper, B.; Zoungas, S.; Ninomiya, T.; Webster, A.C.; Perkovic, V. Antioxidants for chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 10, CD008176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buonocore, G.; Groenendaal, F. Anti-oxidant strategies. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2007, 12, 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- National Academy of Sciences, Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids: A Report of the Panel on Dietary Antioxidants and Related Compounds, Subcommittees on Upper Reference Levels of Nutrients and on Interpretation and Use of Dietary Reference Intakes, and the Standing Committee on Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes, Food and Nutrition Board; Institute of Medicine, 17 National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rapa, S.F.; Di Iorio, B.R.; Campiglia, P.; Heidland, A.; Marzocco, S. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Chronic Kidney Disease-Potential Therapeutic Role of Minerals, Vitamins and Plant-Derived Metabolites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, H.M.; Nexo, E. Gastrointestinal Handling of Water-Soluble Vitamins. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1291–1311. [Google Scholar]
- Niki, E. Role of vitamin E as a lipid-soluble peroxyl radical scavenger: In vitro and in vivo evidence. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 66, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Franco Mdo, C.; Ponzio, B.F.; Gomes, G.N.; Gil, F.Z.; Tostes, R.; Carvalho, M.H.; Fortes, Z.B. Micronutrient prenatal supplementation prevents the development of hypertension and vascular endothelial damage induced by intrauterine malnutrition. Life Sci. 2009, 85, 327–333. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yin, N.; Deng, Y.; Wei, Y.; Huang, Y.; Pu, X.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, J.; Yu, J.; et al. Ascorbic Acid Protects against Hypertension through Downregulation of ACE1 Gene Expression Mediated by Histone Deacetylation in Prenatal InflammationInduced Offspring. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39469. [Google Scholar]
- Farias, J.S.; Santos, K.M.; Lima, N.K.S.; Cabral, E.V.; Aires, R.S.; Veras, A.C.; Paixão, A.D.; Vieira, L.D. Maternal endotoxemia induces renal collagen deposition in adult offspring: Role of NADPH oxidase/TGF-β1/MMP-2 signaling pathway. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 684, 108306. [Google Scholar]
- Bjelakovic, G.; Nikolova, D.; Gluud, L.L.; Simonetti, R.G.; Gluud, C. Antioxidant supplements for prevention of mortality in healthy participants and patients with various diseases. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 3, CD007176. [Google Scholar]
- Azaïs-Braesco, V.; Pascal, G. Vitamin A in pregnancy: Requirements and safety limits. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 1325S–1333S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwalfenberg, G.; Rodushkin, I.; Genuis, S.J. Heavy metal contamination of prenatal vitamins. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Souto, E.B.; Cicala, C.; Caiazzo, E.; Izzo, A.A.; Novellino, E.; Santini, A. Polyphenols: A concise over-view on the chemistry, occurrence, and human health. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 2221–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Peng, A. The Green Tea Polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and its beneficial roles in chronic kidney disease. J. Transl. Int. Med. 2016, 4, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, Í.; Ferreira-Pêgo, C.; Carregosa, D.; Santos, C.N.; Menezes, R.; Fernandes, A.S.; Costa, J.G. Polyphenols and Their Metabolites in Renal Diseases: An Overview. Foods 2022, 11, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacka-Aleksić, M.; Pirković, A.; Vilotić, A.; Bojić-Trbojević, Ž.; Jovanović Krivokuća, M.; Giampieri, F.; Battino, M.; Dekanski, D. The Role of Dietary Polyphenols in Pregnancy and Pregnancy-Related Disorders. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, J.R.T.; Mohd Dollah, M.H.B.; Regnault, T.R.H.; Williams, M.T.; Morrison, J.L. Systematic review: Impact of resveratrol exposure during pregnancy on maternal and fetal outcomes in animal models of human pregnancy complications-Are we ready for the clinic? Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 144, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ren, Y.; Yu, J.; Zeng, Y.; Ren, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X. The effect of maternal dietary polyphenol consumption on offspring metabolism. Crit. Rev. Food. Sci. Nutr. 2024, 19, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Maternal Polyphenols and Offspring Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Health. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Xu, H.; Lyv, Y.; Feng, X.; Fang, Y.; Xu, Y. Maternal quercetin administration during gestation and lactation decrease endoplasmic reticulum stress and related inflammation in the adult offspring of obese female rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 1669–1683. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lamothe, J.; Khurana, S.; Tharmalingam, S.; Williamson, C.; Byrne, C.J.; Lees, S.J.; Khaper, N.; Kumar, A.; Tai, T.C. Oxidative Stress Mediates the Fetal Programming of Hypertension by Glucocorticoids. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.P.; Singh, R.; Verma, S.S.; Rai, V.; Kaschula, C.H.; Maiti, P.; Gupta, S.C. Health benefits of resveratrol: Evidence from 926 clinical studies. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 1851–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, V.L.; Jun, M.; Jeong, W.S. Role of resveratrol in regulation of cellular defense systems against oxidative stress. Biofactors 2018, 44, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walle, T.; Hsieh, F.; DeLegge, M.H.; Oatis, J.E., Jr.; Walle, U.K. High absorption but very low bioavailability of oral resveratrol 957 in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippou, C.; Tatakis, F.; Polyzos, D.; Manta, E.; Thomopoulos, C.; Nihoyannopoulos, P.; Tousoulis, D.; Tsioufis, K. Overview of salt restriction in the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) and the Mediterranean diet for blood pressure reduction. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.; Kelly, J.; Tapsell, L. Dietary Modeling of Foods for Advanced CKD Based on General Healthy Eating Guidelines: What Should Be on the Plate? Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 436–450. [Google Scholar]
- Gantenbein, K.V.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C. Mediterranean Diet as an Antioxidant: The Impact on Metabolic Health and Overall Wellbeing. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Morze, J.; Hoffmann, G. Mediterranean diet and health status: Active ingredients and pharmacological mechanisms. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 1241–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarejo, A.B.; Ramírez-Sánchez, M.; Segarra, A.B.; Martínez-Cañamero, M.; Prieto, I. Influence of extra virgin olive oil on blood pressure and kidney angiotensinase activities in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Planta. Med. 2015, 81, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Ahsan, H.; Zia, M.K.; Siddiqui, T.; Khan, F.H. Understanding oxidants and antioxidants: Classical team with new players. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13145. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zheng, S.; Wu, G. Amino Acid Metabolism in the Kidneys: Nutritional and Physiological Significance. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1265, 71–95. [Google Scholar]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Amino Acids during Pregnancy and Offspring Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Health. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cynober, L.; Moinard, C.; De Bandt, J.P. The 2009 ESPEN Sir David Cuthbertson. Citrulline: A new major signaling molecule or just another player in the pharmaconutrition game? Clin. Nutr. 2010, 29, 545–551. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.N.; Lin, I.C.; Yu, H.R.; Huang, L.T.; Tiao, M.M.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal Tryptophan Supplementation Protects Adult Rat Offspring against Hypertension Programmed by Maternal Chronic Kidney Disease: Implication of Tryptophan-Metabolizing Microbiome and Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.N.; Hou, C.Y.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Lin, S.; Tain, Y.L. Dietary Supplementation with Cysteine during Pregnancy Rescues Maternal Chronic Kidney Disease-Induced Hypertension in Male Rat Offspring: The Impact of Hydrogen Sulfide and Microbiota-Derived Tryptophan Metabolites. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaeomor, A.; Teangphuck, P.; Chaisakul, J.; Seanthaweesuk, S.; Somparn, N.; Roysommuti, S. Perinatal Taurine Supplementation Prevents Metabolic and Cardiovascular Effects of Maternal Diabetes in Adult Rat Offspring. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 975, 295–305. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, R.J.; Mayo, J.C.; Tan, D.X.; Sainz, R.M.; Alatorre-Jimenez, M.; Qin, L. Melatonin as an antioxidant: Under promises but over delivers. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 61, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeland, R.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Kynuramines, metabolites of melatonin and other indoles: The resurrection of an almost forgotten class of biogenic amines. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 47, 109–126. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Gan, R.Y.; Xu, D.P.; Li, H.B. Dietary Sources and Bioactivities of Melatonin. Nutrients 2017, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Terron, M.P.; Flores, L.J.; Manchester, L.C.; Tan, D.X.; Sugino, N.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin and pregnancy in the human. Reprod. Toxicol. 2008, 25, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X.; Terron, M.P.; Flores, L.J.; Czarnocki, Z. Melatonin and its metabolites: New findings regarding their production and their radical scavenging actions. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2007, 54, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Melatonin Use during Pregnancy and Lactation Complicated by Oxidative Stress: Focus on Offspring’s Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Health in Animal Models. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aversa, S.; Pellegrino, S.; Barberi, I.; Reiter, R.J.; Gitto, E. Potential utility of melatonin as an antioxidant during pregnancy and in the perinatal period. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012, 25, 207–221. [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy, P.; Etcheverry, A.; Ia, J.; Witmans, M.; Tablizo, M.A. Melatonin Use in Pediatrics: A Clinical Review on Indications, Multisystem Effects, and Toxicity. Children 2024, 11, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marseglia, L.; D’Angelo, G.; Manti, S.; Reiter, R.J.; Gitto, E. Potential utility of melatonin in preeclampsia, intrauterine fetal growth retardation, and perinatal asphyxia. Reprod. Sci. 2016, 23, 970–977. [Google Scholar]
- Chitimus, D.M.; Popescu, M.R.; Voiculescu, S.E.; Panaitescu, A.M.; Pavel, B.; Zagrean, L.; Zagrean, A.M. Melatonin’s Impact on Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Reprogramming in Homeostasis and Disease. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Leu, S.; Wu, K.L.; Lee, W.C.; Chan, J.Y. Melatonin prevents maternal fructose intake-induced programmed hypertension in the offspring: Roles of nitric oxide and arachidonic acid metabolites. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 80–89. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, L.P.; Gögenur, I.; Rosenberg, J.; Reiter, R.J. The Safety of Melatonin in Humans. Clin. Drug Investig. 2016, 36, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Korkmaz, A.; Rosales-Corral, S.; Reiter, R.J. Gene regulation by melatonin linked to epigenetic phenomena. Gene 2012, 503, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Linowiecka, K.; Slominski, A.T.; Reiter, R.J.; Böhm, M.; Steinbrink, K.; Paus, R.; Kleszczyński, K. Melatonin: A Potential Regulator of DNA Methylation. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamon, S.; Kramar, B.; Marolt, T.P.; Poljšak, B.; Milisav, I. Medical and Dietary Uses of N-Acetylcysteine. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H. The physiological role of hydrogen sulfide and beyond. Nitric Oxide 2014, 41, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plotnikov, E.Y.; Pavlenko, T.A.; Pevzner, I.B.; Zorova, L.D.; Manskikh, V.N.; Silachev, D.N. The role of oxidative stress in acute renal injury of newborn rats exposed to hypoxia and endotoxin. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 3069–3078. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, S.T.; Bigam, D.L.; Emara, M.; Obaid, L.; Slack, G.; Korbutt, G. N-acetylcysteine improves the hemodynamics and oxidative stress in hypoxic newborn pigs reoxygenated with 100% oxygen. Shock 2007, 28, 484–490. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, I.H.; Sheen, J.M.; Lin, Y.J.; Yu, H.R.; Tiao, M.M.; Chen, C.C.; Huang, L.T.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal N-acetylcysteine therapy regulates hydrogen sulfide-generating pathway and prevents programmed hypertension in male offspring exposed to prenatal dexamethasone and postnatal high-fat diet. Nitric Oxide 2016, 53, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- James, A.M.; Smith, R.A.; Murphy, M.P. Antioxidant and prooxidant properties of mitochondrial Coenzyme Q. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 423, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Tintoré, M.; Sastre-Garriga, J. Multiple sclerosis: Dimethyl fumarate is coming of age. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 436–437. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.N.; Lin, Y.J.; Yu, H.R.; Lin, I.C.; Sheen, J.M.; Huang, L.T.; Tain, Y.L. Protection of Male Rat Offspring against Hypertension Programmed by Prenatal Dexamethasone Administration and Postnatal High-Fat Diet with the Nrf2 Activator Dimethyl Fumarate during Pregnancy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.C.; Corsi, D.; Cavi, N.; Bruni, N.; Dosio, F. Superoxide Dismutase Administration: A Review of Proposed Human Uses. Molecules 2021, 26, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeners, M.P.; Braam, B.; Joles, J.A. Perinatal inhibition of NF-kappaB has long-term antihypertensive effects in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goss, S.P.; Kalyanaraman, B.; Hogg, N. Antioxidant effects of nitric oxide and nitric oxide donor compounds on low-density lipoprotein oxidation. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 301, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andrabi, S.M.; Sharma, N.S.; Karan, A.; Shahriar, S.M.S.; Cordon, B.; Ma, B.; Xie, J. Nitric Oxide: Physiological Functions, Delivery, and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2303259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teerlink, T.; Luo, Z.; Palm, F.; Wilcox, C.S. Cellular ADMA: Regulation and action. Pharmacol. Res. 2009, 60, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltowski, J.; Kedra, A. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) as a target for pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol. Rep. 2006, 58, 159–178. [Google Scholar]
- Onozato, M.L.; Tojo, A.; Leiper, J.; Fujita, T.; Palm, F.; Wilcox, C.S. Expression of NG,NG-dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase and protein arginine N-methyltransferase isoforms in diabetic rat kidney: Effects of angiotensin II receptor blockers. Diabetes 2008, 57, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojima, A.; Ishibashi, Y.; Matsui, T.; Maeda, S.; Nishino, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Fukami, K.; Yamagishi, S. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist inhibits asymmetric dimethylarginine generation in the kidney of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by blocking advanced glycation end product-induced protein arginine methyltranferase-1 expression. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; Delemasure, S.; Korandji, C.; Segueira-Le Grand, A.; Lauzier, B.; Guilland, J.C.; Duvillard, L.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C.; et al. Anti-hypertensive effects of Rosuvastatin are associated with decreased inflammation and oxidative stress markers in hypertensive rats. Free Radic. Res. 2008, 42, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, K.Q.; Li, B.; Sun, D.Q.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Q. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorates erectile function in aged rats via regulation of PRMT1/DDAH/ADMA/NOS metabolism pathway. Asian J. Androl. 2017, 19, 291–297. [Google Scholar]
- Bal, F.; Bekpinar, S.; Unlucerci, Y.; Kusku-Kiraz, Z.; Önder, S.; Uysal, M.; Gurdol, F. Antidiabetic drug metformin is effective on the metabolism of asymmetric dimethylarginine in experimental liver injury. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 106, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Liang, Q.; Zeng, F.; Mai, Z.; Cai, A.; Qiu, R.; Xu, R.; Li, D.; Mai, W. Atorvastatin protects endothelium by decreasing asymmetric dimethylarginine in dyslipidemia rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, H.; Wang, S.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X. Effects of salvianolic acid A on plasma and tissue dimethylarginine levels in a rat model of myocardial infarction. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 61, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.K.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Dai, G. Cardioprotective effects of oxymatrine on isoproterenol-induced heart failure via regulation of DDAH/ADMA metabolism pathway in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 745, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Chouinard, M.; Cox, A.L.; Sipes, P.; Marcelo, M.; Ficorilli, J.; Li, S.; Gao, H.; Ryan, T.P.; Michael, M.D.; et al. Farnesoid X receptor agonist reduces serum asymmetric dimethylarginine levels through hepatic dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-1 gene regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 39831–39838. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M. The effect of nebivolol on asymmetric dimethylarginine system in spontaneously hypertension rats. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2011, 54, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Han, W. A Review of the Synthesis of Nitric Oxide Donor and Donor Derivatives with Pharmacological Activities. Mini. Rev. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 873–883. [Google Scholar]
- Bonini, M.G.; Stadler, K.; Silva, S.O.; Corbett, J.; Dore, M.; Petranka, J.; Fernandes, D.C.; Tanaka, L.Y.; Duma, D.; Laurindo, F.R.; et al. Constitutive nitric oxide synthase activation is a significant route for nitroglycerin-mediated vasodilation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8569–8574. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Schroeder, H.; Power, G.G.; Blood, A.B. A physiologically relevant role for NO stored in vascular smooth muscle cells: A novel theory of vascular NO signaling. Redox Biol. 2022, 53, 102327. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Siuda, D.; Xia, N.; Reifenberg, G.; Daiber, A.; Münzel, T.; Förstermann, U.; Li, H. Maternal treatment of spontaneously hypertensive rats with pentaerythritoltetranitrate reduces blood pressure in female offspring. Hypertension 2015, 65, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseling, S.; Essers, P.B.; Koeners, M.P.; Pereboom, T.C.; Braam, B.; van Faassen, E.E.; Macinnes, A.W.; Joles, J.A. Perinatal exogenous nitric oxide in fawn-hooded hypertensive rats reduces renal ribosomal biogenesis in early life. Front. Genet. 2011, 2, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliocca, G.; Mone, P.; Di Iorio, B.R.; Heidland, A.; Marzocco, S. Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Chronic Kidney Disease: Focus on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekha, K.; Venkidasamy, B.; Samynathan, R.; Nagella, P.; Rebezov, M.; Khayrullin, M.; Ponomarev, E.; Bouyahya, A.; Sarkar, T.; Shariati, M.A.; et al. Short-chain fatty acid: An updated review on signaling, metabolism, and therapeutic effects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 2461–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valvassori, S.S.; Dal-Pont, G.C.; Steckert, A.V.; Varela, R.B.; Lopes-Borges, J.; Mariot, E.; Resende, W.R.; Arent, C.O.; Carvalho, A.F.; Quevedo, J. Sodium butyrate has an antimanic effect and protects the brain against oxidative stress in an animal model of mania induced by ouabain. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 235, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziętek, M.; Celewicz, Z.; Szczuko, M. Short-Chain Fatty Acids, Maternal Microbiota and Metabolism in Pregnancy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Tain, Y.L. Chronic Kidney Disease and Gut Microbiota: What Is Their Connection in Early Life? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Tain, Y.L. Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System to Prevent Hypertension and Kidney Disease of Developmental Origins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavatte-Palmer, P.; Tarrade, A.; Rousseau-Ralliard, D. Diet before and during Pregnancy and Offspring Health: The Importance of Animal Models and What Can Be Learned from Them. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Kuroda, Y.; Sugiyama, A. A comparison of the histological structure of the placenta in experimental animals. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2014, 27, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, O.; Laporte-Broux, B.; Tarrade, A.; Chavatte-Palmer, P. The use of ruminant models in biomedical perinatal research. Theriogenology 2012, 78, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ren, T.; Duan, J.A.; Xiao, P. Promising tools into oxidative stress: A review of non-rodent model organisms. Redox Biol. 2024, 77, 103402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci-Çekiç, S.; Özkan, G.; Avan, A.N.; Uzunboy, S.; Çapanoğlu, E.; Apak, R. Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2022, 209, 114477. [Google Scholar]
- Suzen, S.; Gurer-Orhan, H.; Saso, L. Detection of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) Technique. Molecules 2017, 22, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Yuksel, S.; Yigit, A.A.; Cinar, M.; Atmaca, N.; Onaran, Y. Oxidant and Antioxidant Status of Human Breast Milk during Lactation Period. Dairy. Sci. Technol. 2015, 95, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.T.; Nadeem, M.; Imran, M.; Ullah, R.; Ajmal, M.; Jaspal, M.H. Antioxidant properties of Milk and dairy products: A comprehensive review of the current knowledge. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Section on Breastfeeding. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics 2012, 129, e827–e841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotler, R.; Poljšak, B.; Dahmane, R.; Jukić, T.; Pavan Jukić, D.; Rotim, C.; Trebše, P.; Starc, A. Prooxidant activities of antioxidants and their impact on health. Acta Clin. Croat. 2019, 58, 726–736. [Google Scholar]
- Carlisle, D.L.; Pritchard, D.E.; Singh, J.; Owens, B.M.; Blankenship, L.J.; Orenstein, J.M.; Patierno, S.R. Apoptosis and P53 induction in human lung fibroblasts exposed to chromium (VI): Effect of ascorbate and tocopherol. Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 55, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell, B. The antioxidant paradox. Lancet 2000, 355, 1179–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, J.T.; Thompson, J.H.; Burda, B.U.; Cantor, A. Preeclampsia Screening: Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2017, 317, 1668–1683. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, R.; Dunford, J.; Mehran, R.; Robson, S.; Kunadian, V. Pre-eclampsia and future cardiovascular risk among women: A review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar]
- Mosimann, B.; Amylidi-Mohr, S.K.; Surbek, D.; Raio, L. First trimester screening for preeclampsia—A systematic review. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2020, 39, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).