Molecular Hydrogen Affords Similar Neuroprotection to Therapeutic Hypothermia in a Porcine Model of Neonatal Hypoxic–Ischemic Encephalopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Animals
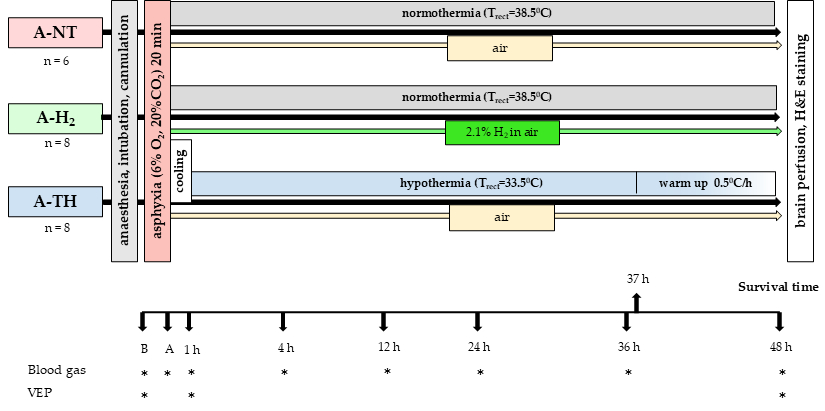
2.3. Experimental Protocol
2.3.1. Experimental Groups
2.3.2. Electrophysiology
2.3.3. Neuropathology
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
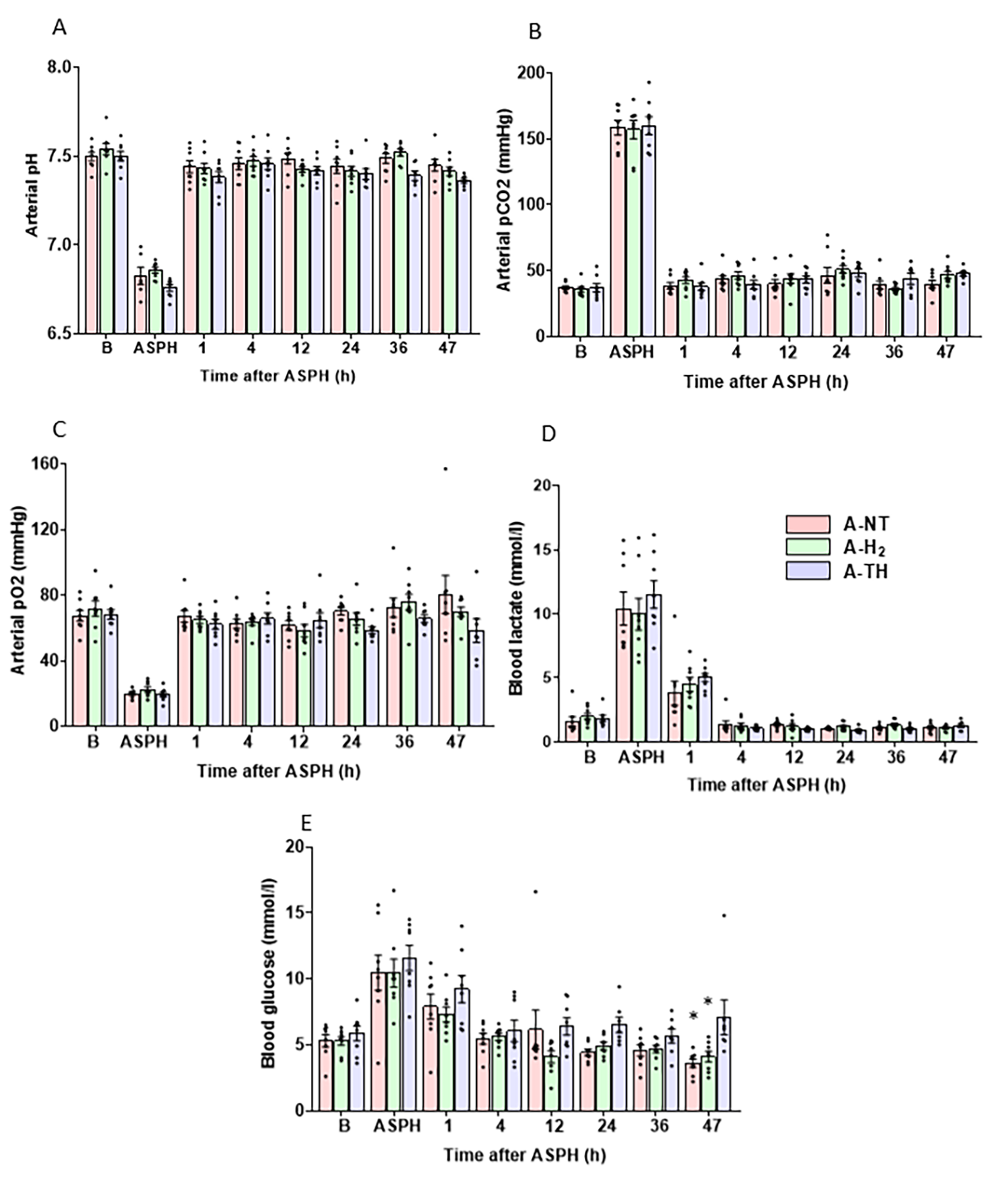
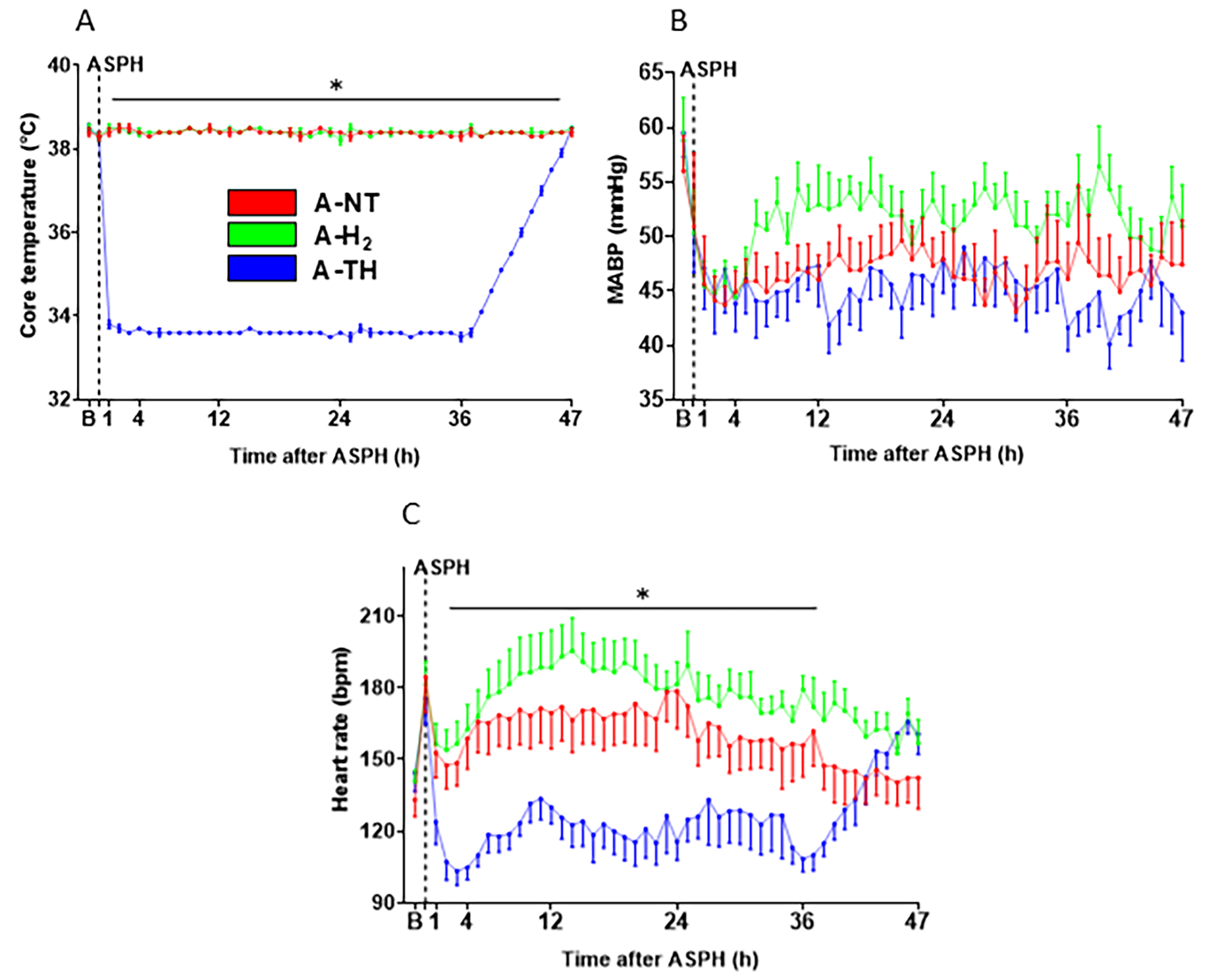
3.1. Physiological Parameters
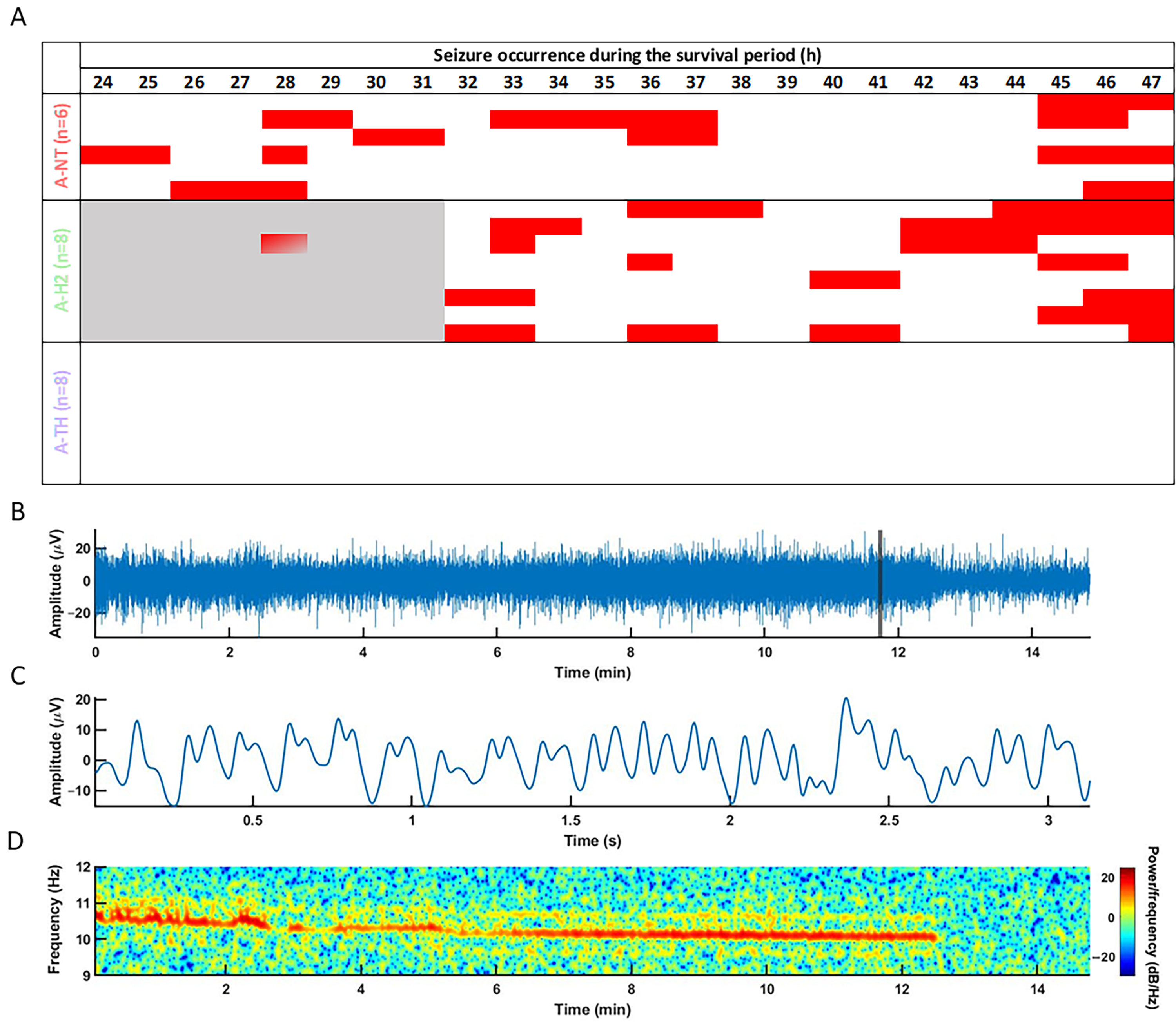
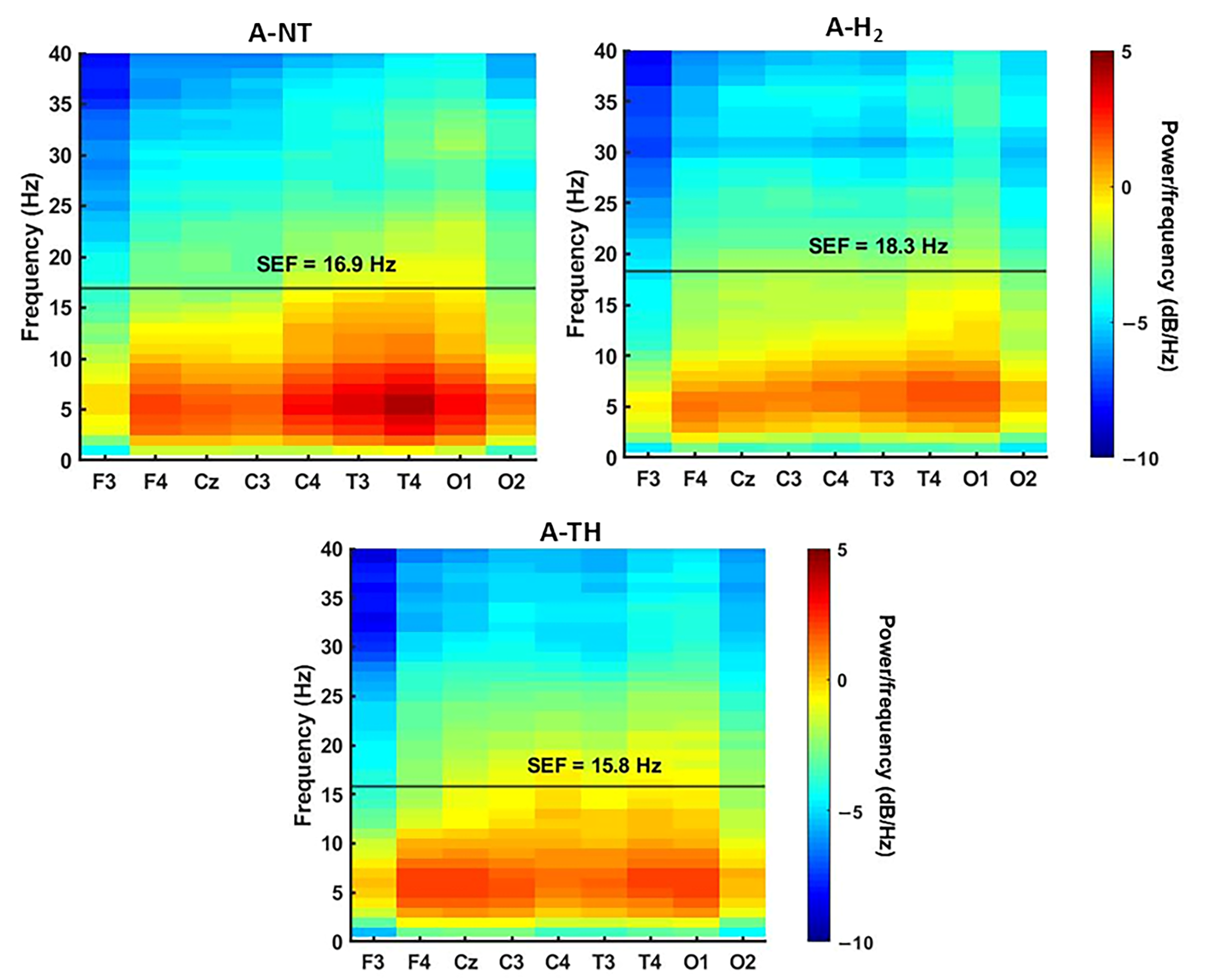
3.2. Electrophysiology
3.3. Neuropathology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A/ASPH | asphyxia |
| B | baseline |
| EEG | electroencephalography |
| FFT | fast Fourier transform |
| FiO2 | fraction of inspired oxygen |
| H&E | hematoxylin–eosin |
| HI | hypoxic-ischemic |
| HIE | hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy |
| HR | heart rate |
| InstSpEnt | Instantaneous Spectral Entropy |
| MABP | mean arterial blood pressure |
| PSD | power spectral densities |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| RR | respiratory rate |
| SEF | spectral edge frequency |
| SEM | standard error of the mean |
| spO2 | oxygen saturation |
| TH | therapeutic hypothermia |
| VEP | visual evoked potential |
References
- Kurinczuk, J.J.; White-Koning, M.; Badawi, N. Epidemiology of Neonatal Encephalopathy and Hypoxic-Ischaemic Encephalopathy. Early Hum. Dev. 2010, 86, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, K.A.; Brandon, D.H. Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy: Pathophysiology and Experimental Treatments. Newborn Infant Nurs. Rev. 2011, 11, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saugstad, O.D. Reducing Global Neonatal Mortality Is Possible. Neonatology 2011, 99, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gücüyener, K.; Ergenekon, E.; Demiryürek, T.; Erbaş, D.; Oztürk, G.; Koç, E.; Atalay, Y. Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels of Nitric Oxide and Nitrotyrosine in Neonates with Mild Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy. J. Child Neurol. 2002, 17, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, M.; Ramenghi, L.A.; Edwards, A.D.; Brocklehurst, P.; Halliday, H.; Levene, M.; Strohm, B.; Thoresen, M.; Whitelaw, A.; Azzopardi, D. Assessment of Brain Tissue Injury after Moderate Hypothermia in Neonates with Hypoxic-Ischaemic Encephalopathy: A Nested Substudy of a Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Lei, X.; Dong, W.; Li, Q. Benefits of Starting Hypothermia Treatment within 6 h vs. 6–12 h in Newborns with Moderate Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagin, M.A.; Woolcott, C.G.; Vincer, M.J.; Whyte, R.K.; Stinson, D.A. Hypothermia for Neonatal Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2012, 166, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Wang, K.; Liu, B.; Shen, Y.; Liu, G. Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy: Pathogenesis and Promising Therapies. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 2105–2122, Erratum in Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, J.; Toth-Szuki, V.; Varga, V.; Kovacs, V.; Remzso, G.; Domoki, F. Molecular Hydrogen Affords Neuroprotection in a Translational Piglet Model of Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 67, 677–689. [Google Scholar]
- Oláh, O.; Tóth-Szűki, V.; Temesvári, P.; Bari, F.; Domoki, F. Delayed Neurovascular Dysfunction Is Alleviated by Hydrogen in Asphyxiated Newborn Pigs. Neonatology 2013, 104, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, T.; Nakamura, S.; Sugiyama, Y.; Nakao, Y.; Mitsuie, T.; Inoue, K.; Inoue, E.; Htun, Y.; Arioka, M.; Ohta, K.; et al. Hydrogen Gas Can Ameliorate Seizure Burden during Therapeutic Hypothermia in Asphyxiated Newborn Piglets. Pediatr. Res. 2024, 95, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Kang, Z.; Liu, W.W.; Luo, X.; Qiang, S.; Zhang, J.H.; Ohta, S.; Sun, X.; Xu, W.; Tao, H.; et al. Hydrogen Therapy Reduces Apoptosis in Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia Rat Model. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 441, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Alconada, D.; Chillida, M.; Catalan, A.; Gressens, P.; Robertson, N.J. Sex Dimorphism in Brain Cell Death after Hypoxia-Ischemia in Newborn Piglets. Pediatr. Res. 2025, 98, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, V.; Remzső, G.; Tóth-Szűki, V.; Varga, V.; Németh, J.; Domoki, F. Inhaled H2 or CO2 Do Not Augment the Neuroprotective Effect of Therapeutic Hypothermia in a Severe Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Piglet Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domoki, F.; Oláh, O.; Zimmermann, A.; Németh, I.; Tóth-Szűki, V.; Hugyecz, M.; Temesvári, P.; Bari, F. Hydrogen Is Neuroprotective and Preserves Cerebrovascular Reactivity in Asphyxiated Newborn Pigs. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 68, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bobba, P.S.; Malhotra, A.; Sheth, K.N.; Taylor, S.N.; Ment, L.R.; Payabvash, S. Brain Injury Patterns in Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy of Term Neonates. J. Neuroimaging 2023, 33, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htun, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Nakao, Y.; Mitsuie, T.; Nakamura, M.; Yamato, S.; Jinnai, W.; Koyano, K.; Ohta, K.; Morimoto, A.; et al. Hydrogen Ventilation Combined with Mild Hypothermia Improves Short-Term Neurological Outcomes in a 5-Day Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischaemia Piglet Model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Nakao, Y.; Htun, Y.; Mitsuie, T.; Koyano, K.; Morimoto, A.; Konishi, Y.; Arioka, M.; Kondo, S.; Kato, I.; et al. Impact of Hydrogen Gas Inhalation during Therapeutic Hypothermia on Cerebral Hemodynamics and Oxygenation in the Asphyxiated Piglet. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, E.; Nakamura, S.; Sugiyama, Y.; Tsuchiya, T.; Nakao, Y.; Mitsuie, T.; Yokota, T.; Sakamoto, K.; Inoue, K.; Htun, Y.; et al. Six Hours of Hydrogen Gas Inhalation Has a Neuroprotective Effect Even in Piglets with Delayed Functional Recovery. Dev. Neurosci. 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, V.; Németh, J.; Oláh, O.; Tóth-Szűki, V.; Kovács, V.; Remzső, G.; Domoki, F. Molecular Hydrogen Alleviates Asphyxia-Induced Neuronal Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Newborn Pigs. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Tian, R.; Yan, H.; Pei, L.; Hou, Z.; Hao, S.; Li, Y.V.; Tian, Q.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q. Hydrogen-Rich Water Protects against Ischemic Brain Injury in Rats by Regulating Calcium Buffering Proteins. Brain Res. 2015, 1615, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Nasir, S.; Chau, C.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Bajgai, J.; Rahman, M.d.H.; Hwang-Un, K.; You, I.-S.; Kim, C.-S.; Seo, B.A.; Lee, K.-J. Hydrogen Gas Attenuates Toxic Metabolites and Oxidative Stress-Mediated Signaling to Inhibit Neurodegeneration and Enhance Memory in Alzheimer’s Disease Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, P.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Ding, Y.; Yang, F.; Luo, Y. Inhalation of Hydrogen Gas Attenuates Cognitive Impairment in Transient Cerebral Ischemia via Inhibition of Oxidative Stress. Neurol. Res. 2012, 34, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, I.; Ishikawa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Nishimaki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Katsura, K.-I.; Katayama, Y.; Asoh, S.; Ohta, S. Hydrogen Acts as a Therapeutic Antioxidant by Selectively Reducing Cytotoxic Oxygen Radicals. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S. Molecular Hydrogen as a Preventive and Therapeutic Medical Gas: Initiation, Development and Potential of Hydrogen Medicine. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 144, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihara, M.; Sobue, S.; Ito, M.; Ito, M.; Hirayama, M.; Ohno, K. Beneficial Biological Effects and the Underlying Mechanisms of Molecular Hydrogen-Comprehensive Review of 321 Original Articles. Med. Gas. Res. 2015, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Yue, L.; Du, M.; Geng, F.; Gao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, Q.; Pan, X. Molecular Hydrogen Therapy: Mechanisms, Delivery Methods, Preventive, and Therapeutic Application. MedComm 2025, 6, e70194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, H.-T.; Qin, S.-C. Neuroprotective Effects of Molecular Hydrogen: A Critical Review. Neurosci. Bull. 2020, 37, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, K.; Kodama, K.; Nagata, W.; Takahashi, S.; Satoh, Y.; Ishizuka, T. Molecular Hydrogen Inhibits Neuroinflammation and Ameliorates Depressive-like Behaviors and Short-Term Cognitive Impairment in Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Prone 8 Mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2025, 478, 115330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, G.; Nenov, A.; Kisher, H.; Hancock, J.T. Molecular Hydrogen as Medicine: An Assessment of Administration Methods. Hydrogen 2021, 2, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domoki, F. Hydrogen-Induced Neuroprotection in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xie, K.; Chen, H.; Dong, X.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, G.; Yu, Y. Inhalation of Hydrogen Gas Attenuates Brain Injury in Mice with Cecal Ligation and Puncture via Inhibiting Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Apoptosis. Brain Res. 2014, 1589, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Gonzalez-Islas, C.E.; Kang, Y.; Li, J.M.; Choi, I. Deletion of the Na/HCO3 Transporter NBCn1 Protects Hippocampal Neurons from NMDA-Induced Seizures and Neurotoxicity in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, E.; Liu, X.; Jary, S.; Cowan, F.; Thoresen, M. Cooling Neonates Who Do Not Fulfil the Standard Cooling Criteria–Short- and Long-Term Outcomes. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemyre, B.; Chau, V. Hypothermia for Newborns with Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy. Paediatr. Child Health 2018, 23, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polderman, K.H. Mechanisms of Action, Physiological Effects, and Complications of Hypothermia. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, S186–S202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, W.D.; Bramlett, H.M. Therapeutic Hypothermia and Targeted Temperature Management in Traumatic Brain Injury: Clinical Challenges for Successful Translation. Brain Res. 2016, 1640, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, T. Hydrogen Therapy in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases: From Bench to Bedside. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, S. Recent Progress Toward Hydrogen Medicine: Potential of Molecular Hydrogen for Preventive and Therapeutic Applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Broek, M.P.H.; Groenendaal, F.; Egberts, A.C.G.; Rademaker, C.M.A. Effects of Hypothermia on Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2010, 49, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belur, A.D.; Sedhai, Y.R.; Truesdell, A.G.; Khanna, A.K.; Mishkin, J.D.; Belford, P.M.; Zhao, D.X.; Vallabhajosyula, S. Targeted Temperature Management in Cardiac Arrest: An Updated Narrative Review. Cardiol. Ther. 2023, 12, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollo, L.L.; Mirasso, C.; Villa, A.E.P. Dynamic Control for Synchronization of Separated Cortical Areas through Thalamic Relay. Neuroimage 2010, 52, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drury, P.P.; Gunn, E.R.; Bennet, L.; Gunn, A.J. Mechanisms of Hypothermic Neuroprotection. Clin. Perinatol. 2014, 41, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharoshankaya, L.; Stevenson, N.J.; Livingstone, V.; Murray, D.M.; Murphy, B.P.; Ahearne, C.E.; Boylan, G.B. Seizure Burden and Neurodevelopmental Outcome in Neonates with Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2016, 58, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-K.; Pai, M.-S.; Yeh, K.-C.; Hung, C.-F.; Wang, S.-J. Hydrogen Inhalation Exerts Anti-Seizure Effects by Preventing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in the Hippocampus in a Rat Model of Kainic Acid-Induced Seizures. Neurochem. Int. 2025, 183, 105925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balog, E.; Remzső, G.; Tóth-Szűki, V.; Rózsa, É.; Kovács, V.; Domoki, F. Molecular Hydrogen Affords Similar Neuroprotection to Therapeutic Hypothermia in a Porcine Model of Neonatal Hypoxic–Ischemic Encephalopathy. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14121405
Balog E, Remzső G, Tóth-Szűki V, Rózsa É, Kovács V, Domoki F. Molecular Hydrogen Affords Similar Neuroprotection to Therapeutic Hypothermia in a Porcine Model of Neonatal Hypoxic–Ischemic Encephalopathy. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(12):1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14121405
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalog, Emma, Gábor Remzső, Valéria Tóth-Szűki, Éva Rózsa, Viktória Kovács, and Ferenc Domoki. 2025. "Molecular Hydrogen Affords Similar Neuroprotection to Therapeutic Hypothermia in a Porcine Model of Neonatal Hypoxic–Ischemic Encephalopathy" Antioxidants 14, no. 12: 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14121405
APA StyleBalog, E., Remzső, G., Tóth-Szűki, V., Rózsa, É., Kovács, V., & Domoki, F. (2025). Molecular Hydrogen Affords Similar Neuroprotection to Therapeutic Hypothermia in a Porcine Model of Neonatal Hypoxic–Ischemic Encephalopathy. Antioxidants, 14(12), 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14121405







