5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Depression-like Behaviors by Suppressing Hypothalamic Oxidative Stress and Regulating Neuroinflammation in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
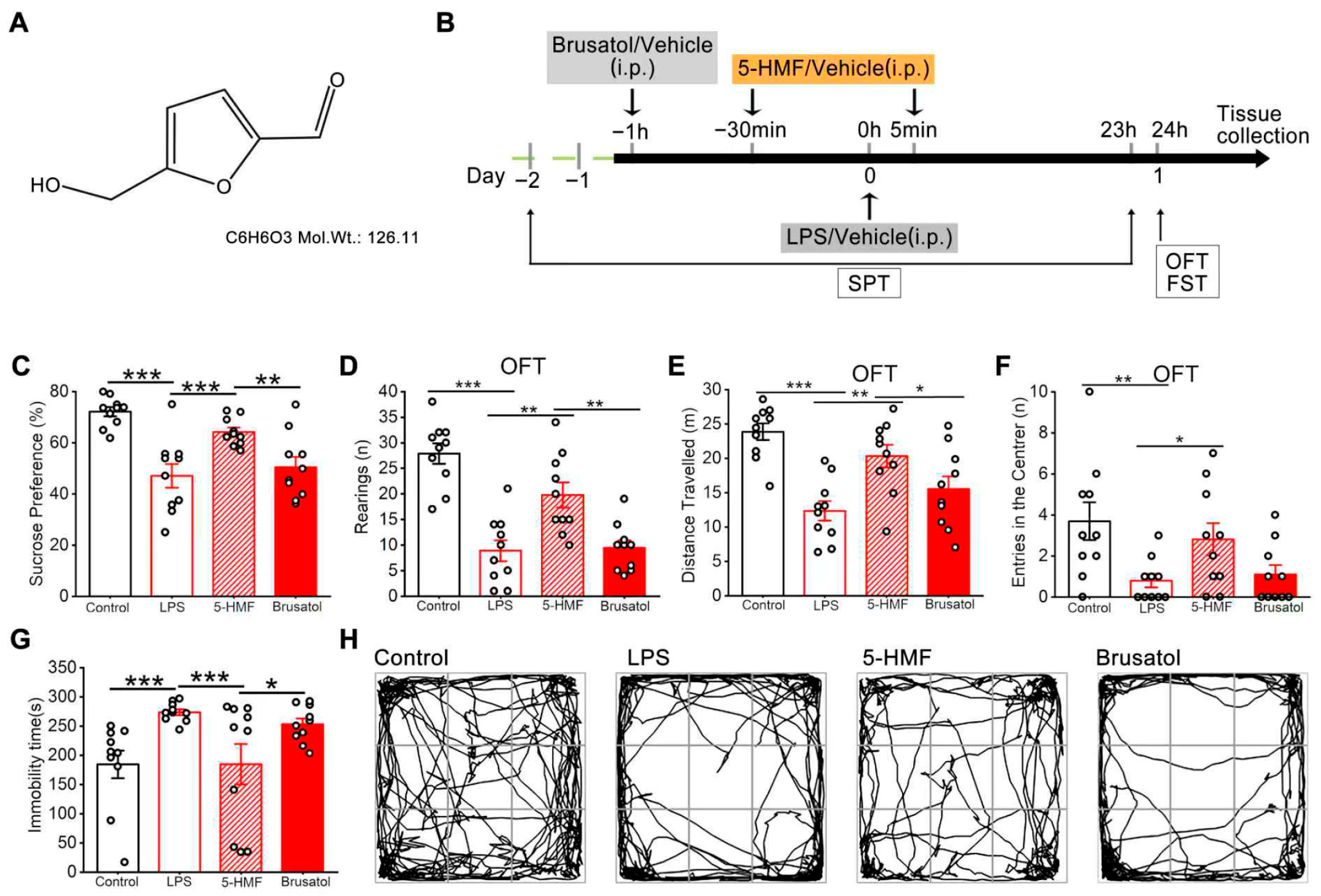
2.1. Drug Treatment and Experimental Design
2.2. Behavioral Assessments
2.2.1. Sucrose Preference Test (SPT)
2.2.2. Forced Swim Test (FST)
2.2.3. Open Field Test (OFT)
2.3. Immunofluorescence and Nissl Staining
2.4. Network Pharmacological Analysis
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Biochemical Analyses
2.7. Determination of Protein Oxidation and Lipid Peroxidation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. 5-HMF Reversed LPS-Induced Depression-like Behaviors in Mice
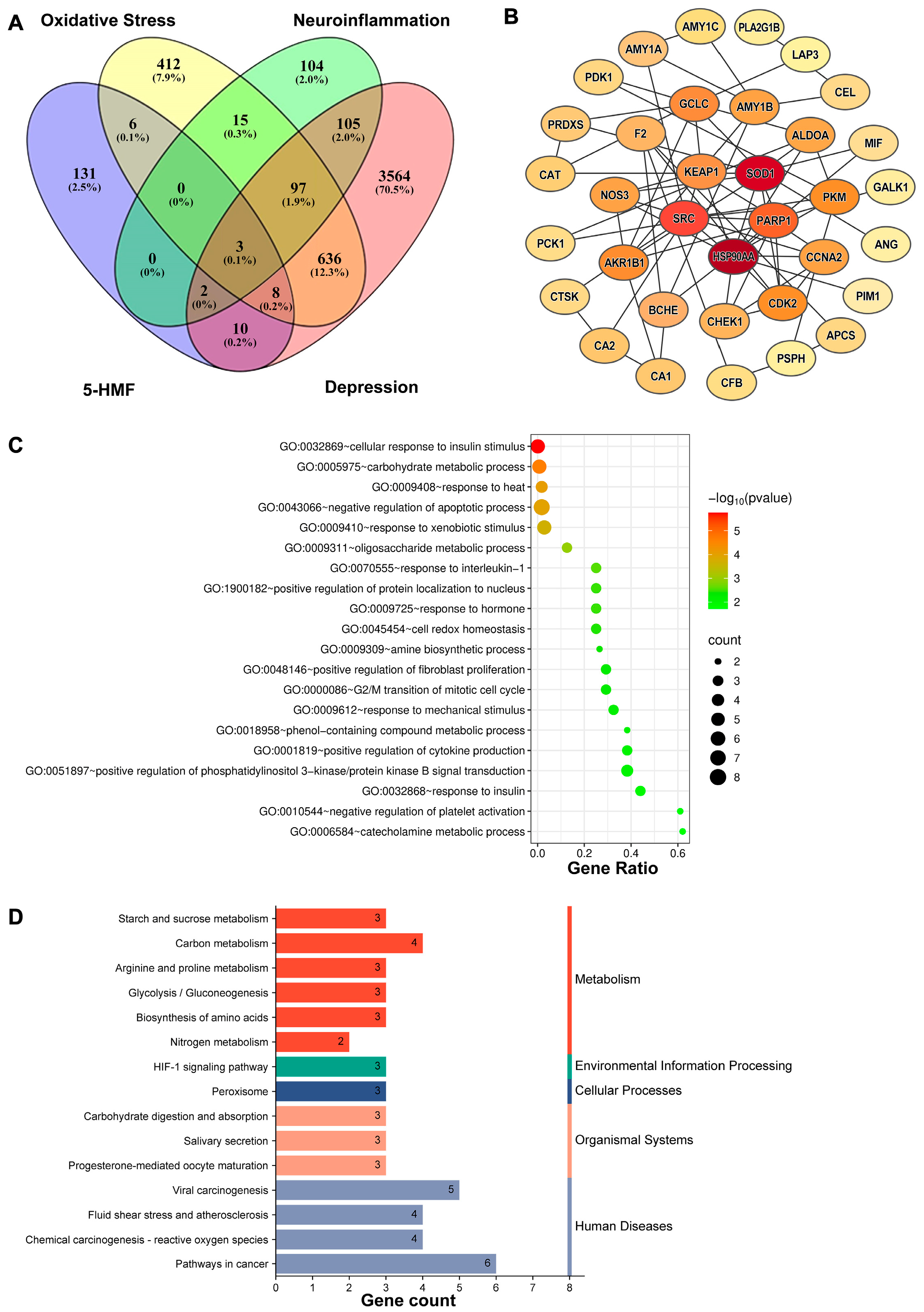
3.2. Network Pharmacology Analysis of 5-HMF in Depression Associated with Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation
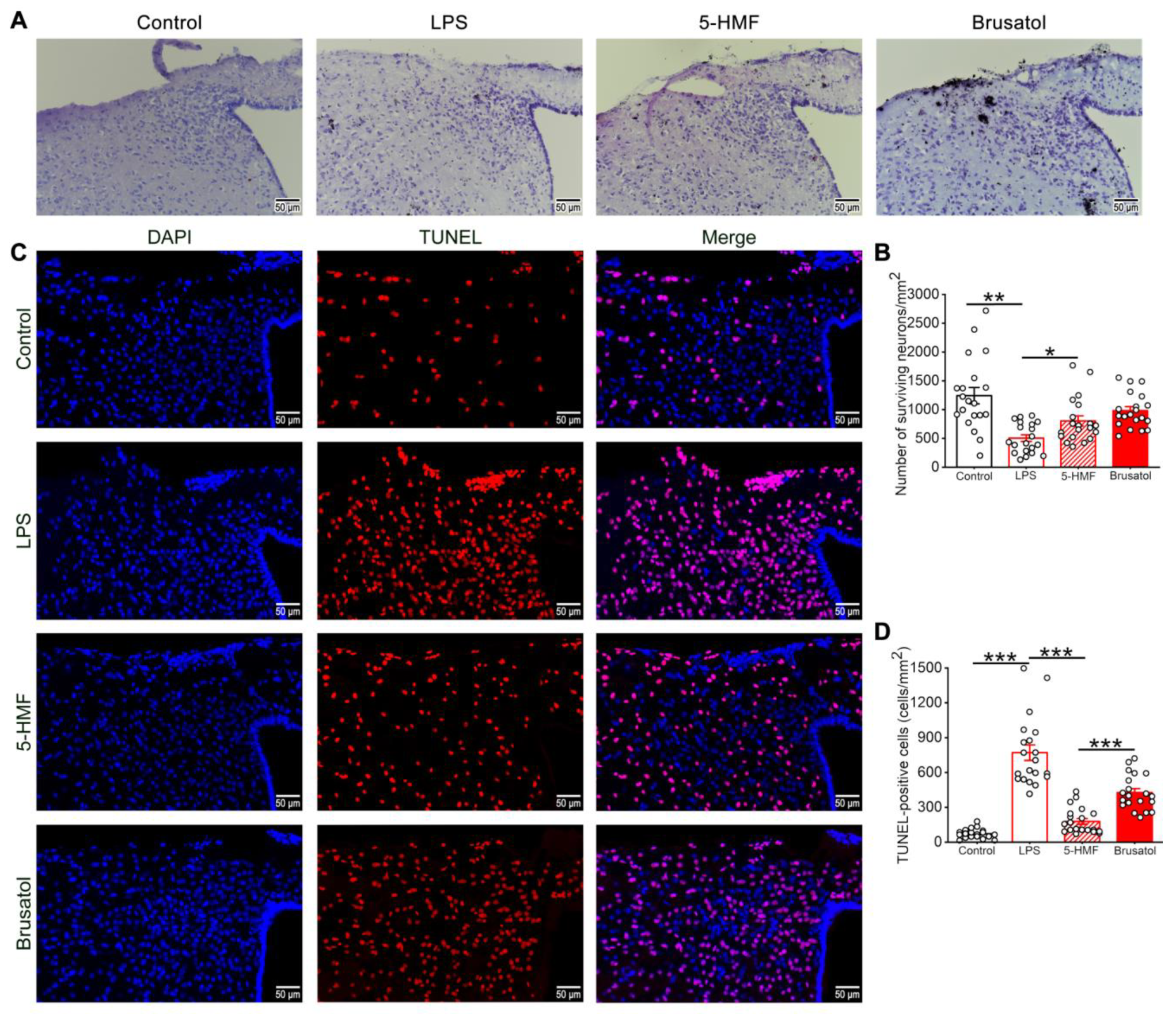
3.3. 5-HMF Attenuated Neuronal Injury in the Hypothalamic Region of LPS-Induced Mice
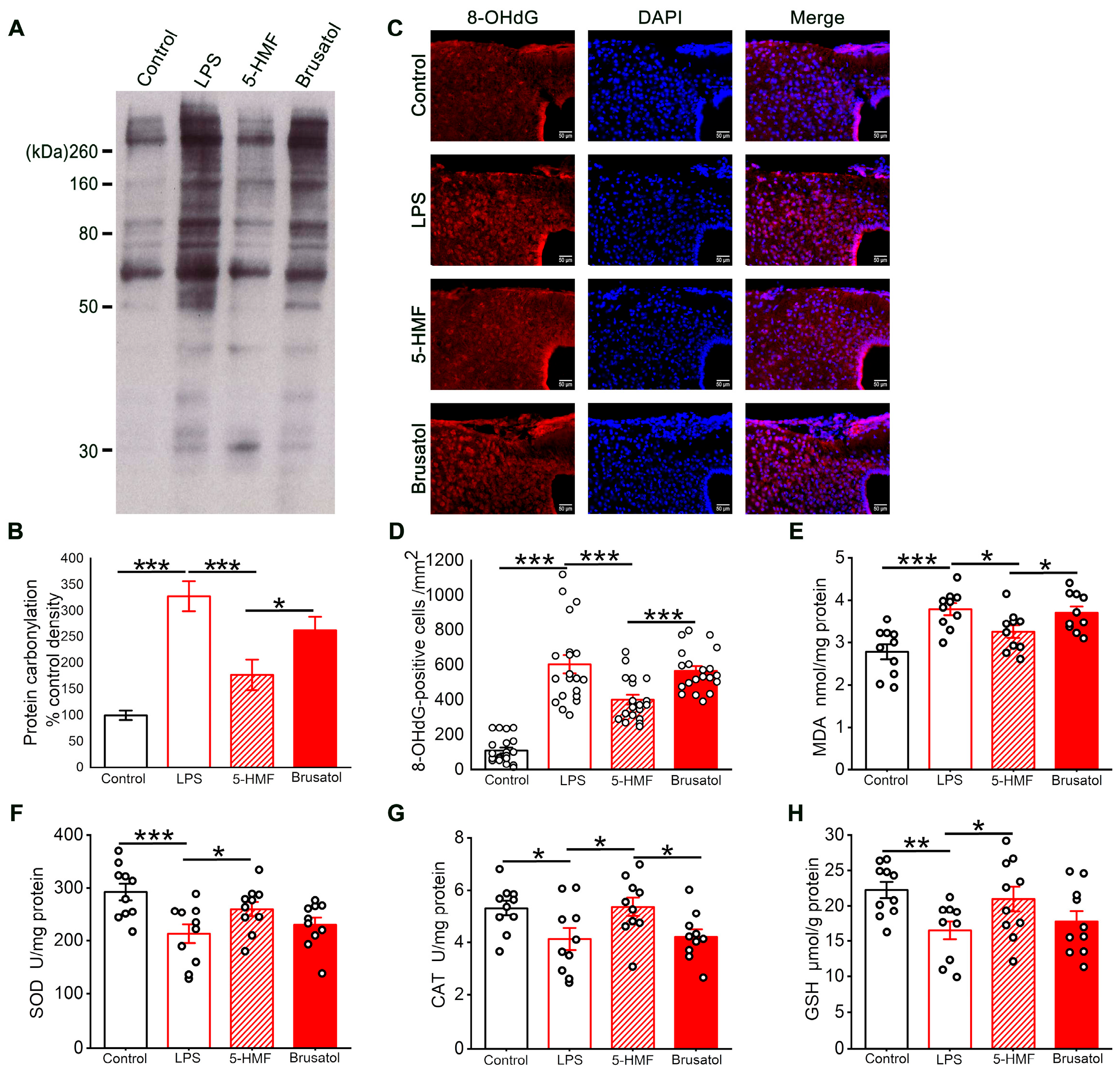
3.4. 5-HMF Alleviated Oxidative Stress in the Hypothalamic Region of LPS-Induced Mice
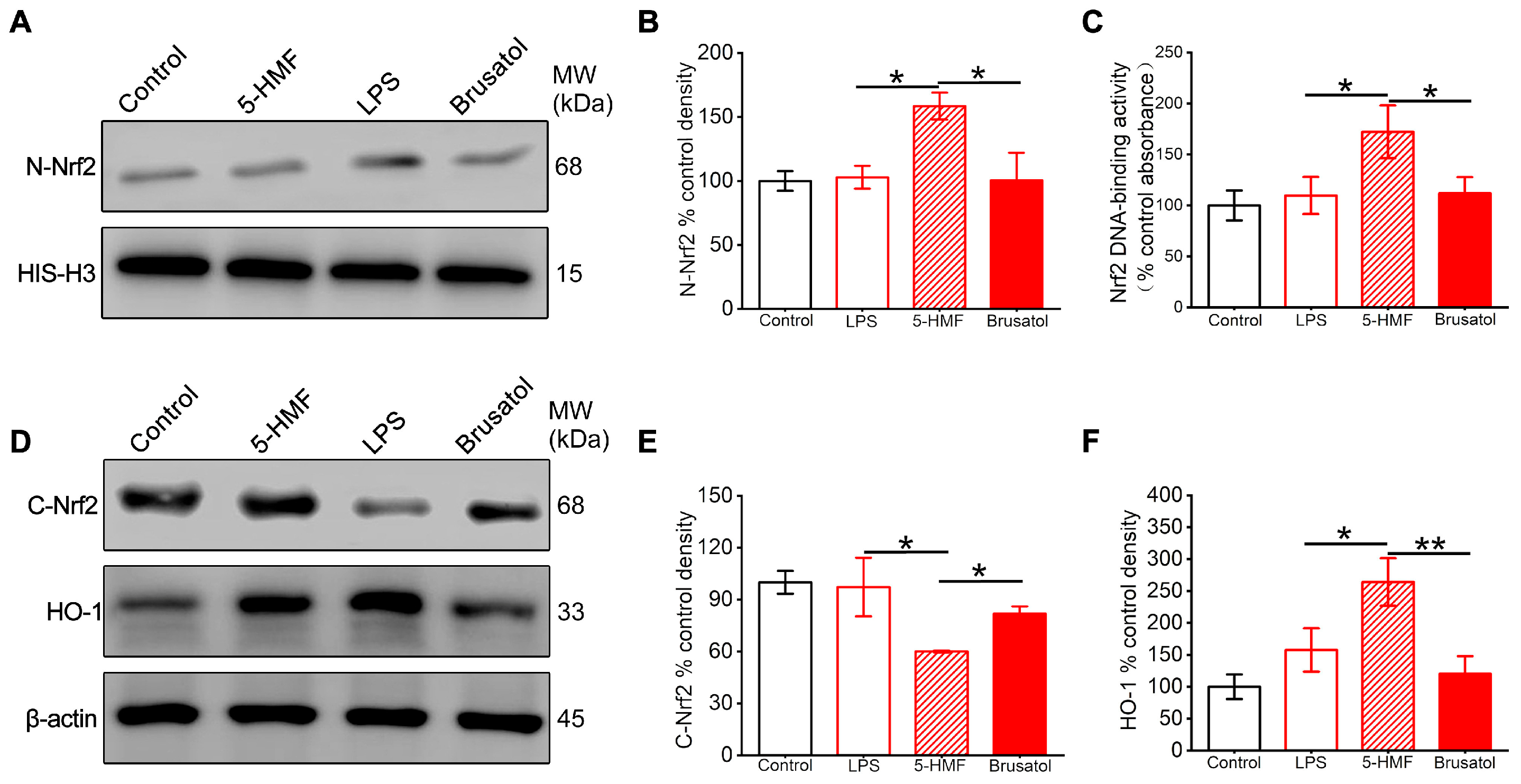
3.5. 5-HMF Activated the Nrf2 Pathway in the Hypothalamic Region of LPS-Induced Mice
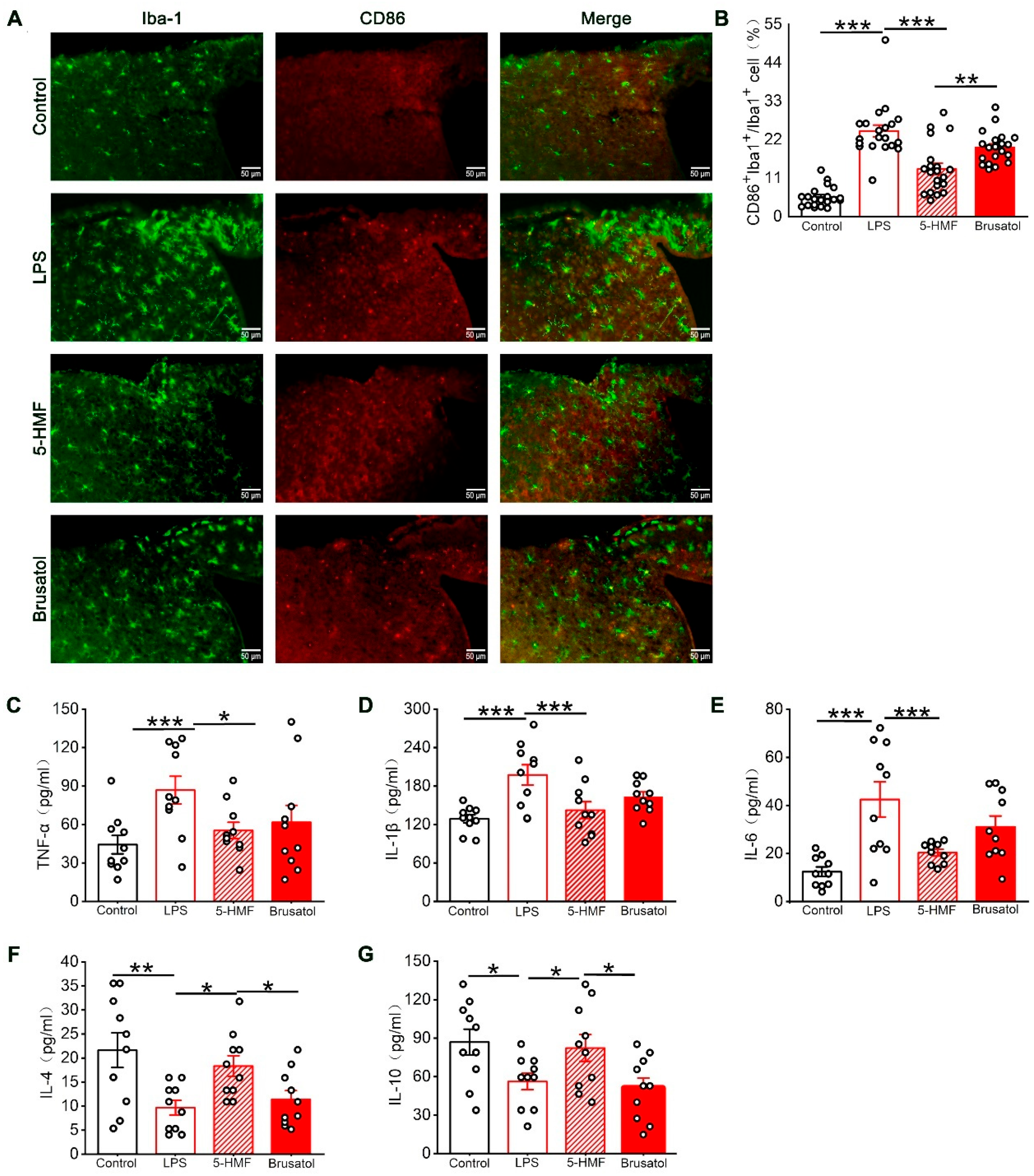
3.6. 5-HMF Suppressed Microglial M1 Polarization and Regulated Inflammatory Cytokine Levels in the Hypothalamic Region of LPS-Induced Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kennedy, S.H. Core symptoms of major depressive disorder: Relevance to diagnosis and treatment. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 10, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, A.S.; Cardoso, A.; Vale, N. Oxidative Stress in Depression: The Link with the Stress Response, Neuroinflammation, Serotonin, Neurogenesis and Synaptic Plasticity. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shiferaw, B.D.; Mackay, L.E.; Wang, J.; Tang, J.; et al. Chinese burden of depressive disorders from 1990 to 2021 and prediction for 2030: Analysis of data from the global burden of disease study 2021. BMC Psychol. 2025, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, R.G.; Adri, A.S.; Filgueiras, I.S.; Nóbile, A.L.; Barcelos, P.M.; Corrêa, Y.L.G.; de Oliveira, S.F.; Cabral-Miranda, G.; Dias, H.D.; Schimke, L.F.; et al. Modulation of neuroimmune cytokine networks by antidepressants: Implications in mood regulation. Transl. Psychiatry 2025, 15, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawani, N.S.; Chan, A.W.; Dursun, S.M.; Baker, G.B. The Underlying Neurobiological Mechanisms of Psychosis: Focus on Neurotransmission Dysregulation, Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, N.; Mandhare, A.; Tryphena, K.P.; Srivastava, S.; Shaikh, M.F.; Singh, S.B.; Khatri, D.K. Epigenetics in depression and gut-brain axis: A molecular crosstalk. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 1048333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Tayeb, A.E.K.; Poinsignon, V.; Chappell, K.; Bouligand, J.; Becquemont, L.; Verstuyft, C. Major Depressive Disorder and Oxidative Stress: A Review of Peripheral and Genetic Biomarkers According to Clinical Characteristics and Disease Stages. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarandol, A.; Sarandol, E.; Eker, S.S.; Erdinc, S.; Vatansever, E.; Kirli, S. Major depressive disorder is accompanied with oxidative stress: Short-term antidepressant treatment does not alter oxidative–antioxidative systems. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2007, 22, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogłodek, E.A. Changes in the concentrations of inflammatory and oxidative status biomediators (MIP-1 α, PMN elastase, MDA, and IL-12) in depressed patients with and without posttraumatic stress disorder. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018, 70, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquino, G.A.; Sousa, C.N.S.; Medeiros, I.S.; Almeida, J.C.; Filho, F.M.S.C.; Júnior, M.A.S.; Vasconcelos, S.M.M. Behavioral alterations, brain oxidative stress, and elevated levels of corticosterone associated with a pressure injury model in male mice. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2022, 33, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriani, L.O.; Silva, D.A.; Molina, M.d.C.B.; Mill, J.G.; Brunoni, A.R.; da Fonseca, M.d.J.M.; Moreno, A.B.; Benseñor, I.M.; de Aguiar, O.B.; Barreto, S.M.; et al. Associations of depression and intake of antioxidants and vitamin B complex: Results of the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil). J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 297, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazvinšćak Jembrek, M.; Oršolić, N.; Karlović, D.; Peitl, V. Flavonols in Action: Targeting Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Major Depressive Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, Y.; Sun, Z.; Ren, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Yang, J. Microglia in depression: An overview of microglia in the pathogenesis and treatment of depression. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosma, N.C.; Üsekes, B.; Otto, L.R.; Gerike, S.; Heuser, I.; Regen, F.; Hellmann-Regen, J. M1/M2 polarization in major depressive disorder: Disentangling state from trait effects in an individualized cell-culture-based approach. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 94, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Paone, E.; Rodríguez-Padrón, D.; Luque, R.; Mauriello, F. Recent catalytic routes for the preparation and the upgrading of biomass derived furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 4273–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Cai, H.; Cai, B.; Tu, S. Effect of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural derived from processed Cornus officinalis on the prevention of high glucose-induced oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and its mechanism. Food Chem. 2013, 140, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qu, X.-N.; Han, Y.; Zheng, S.-W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.-P. Ameliorative Effects of 5-Hydroxymethyl-2-furfural (5-HMF) from Schisandra chinensis on Alcoholic Liver Oxidative Injury in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 2446–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-N.; Jin, G.-Q.; Zhang, X.-L.; Gong, Z.-B.; Gu, C.-Y. Effects of 5-hydroxymethyl furfural extracted from Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch on the expression of signaling molecules relevant to learning and memory among hippocampal neurons exposed to high concentration of corticosterone. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2014, 20, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-H.; Di, Y.; Wu, L.-Y.; He, Y.-L.; Zhao, T.; Huang, X.; Ding, X.-F.; Wu, K.-W.; Fan, M.; Zhu, L.-L. 5-HMF prevents against oxidative injury via APE/Ref-1. Free Radic. Res. 2015, 49, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.; Lee, B.H.; Wei, K. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Mitigates Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Inflammation via Suppression of MAPK, NF-κB and mTOR Activation in RAW 264.7 Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, B.-L.; Li, H.-F.; Wang, H.-Y.; Wu, F.; Xin, Q.; Cheng, H.-J.; Li, W.-J.; Lin, N.; Ba, Z.-H.; Zhang, R.-J.; et al. 5-HMF attenuates striatum oxidative damage via Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway following transient global cerebral ischemia. Cell Stress Chaperones 2017, 22, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, R.; Kato, M.; Hattori, Y.; Kikuchi, H.; Watanabe, E.; Kobayashi, K.; Nishida, K. Identification of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (5-HMF) as an Active Component Citrus Jabara That Suppresses FcεRI-Mediated Mast Cell Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, L. 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfural prolongs survival and inhibits oxidative stress in a mouse model of forebrain ischemia☆. Neural Regen. Res. 2012, 7, 1722–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Nagalakshmi, D.; Sharma, K.K.; Ravichandiran, V. Natural antioxidants for neuroinflammatory disorders and possible involvement of Nrf2 pathway: A review. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Pan, W.; Shi, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Qi, D.; Li, L.; Ma, K.; et al. Depression-like behaviors and heme oxygenase-1 are regulated by Lycopene in lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2016, 298, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Wu, M.; Yin, X.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Bai, M.; Wang, B.; Xu, E. Modified Xiaoyao San reverses lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behavior through suppressing microglia M1 polarization via enhancing autophagy involved in PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 315, 116659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Zheng, R.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lei, N.; Xiong, L.; Guo, P.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like model in mice: Meta-analysis and systematic evaluation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1181973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKusick, V.A. Mendelian Inheritance in Man and its online version, OMIM. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 80, 588–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safran, M.; Dalah, I.; Alexander, J.; Rosen, N.; Iny Stein, T.; Shmoish, M.; Nativ, N.; Bahir, I.; Doniger, T.; Krug, H. GeneCards Version 3: The human gene integrator. Database 2010, 2010, baq020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Pan, W.; Qi, J.; et al. Midbrain FA initiates neuroinflammation and depression onset in both acute and chronic LPS-induced depressive model mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 117, 356–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasselin, J.; Lekander, M.; Benson, S.; Schedlowski, M.; Engler, H. Sick for science: Experimental endotoxemia as a translational tool to develop and test new therapies for inflammation-associated depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 3672–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Garza II, R. Endotoxin-or pro-inflammatory cytokine-induced sickness behavior as an animal model of depression: Focus on anhedonia. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005, 29, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Berk, M.; Goehler, L.; Song, C.; Anderson, G.; Gałecki, P.; Leonard, B. Depression and sickness behavior are Janus-faced responses to shared inflammatory pathways. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.K.; Budac, D.P.; Bisulco, S.; Lee, A.W.; Smith, R.A.; Beenders, B.; Kelley, K.W.; Dantzer, R. NMDA receptor blockade by ketamine abrogates lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior in C57BL/6J mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, A.K.; Wing, E.E.; Banks, W.A.; Dantzer, R. Leucine competes with kynurenine for blood-to-brain transport and prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behavior in mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yirmiya, R. Endotoxin produces a depressive-like episode in rats. Brain Res. 1996, 711, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custódio, C.S.; Mello, B.S.F.; Cordeiro, R.C.; de Araújo, F.Y.R.; Chaves, J.H.; Vasconcelos, S.M.M.; Júnior, H.V.N.; de Sousa, F.C.F.; Vale, M.L.; Carvalho, A.F.; et al. Time course of the effects of lipopolysaccharide on prepulse inhibition and brain nitrite content in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 713, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, F.; Hashemzehi, M.; Hosseini, M.; Marefati, N.; Memarpour, S. Inducible nitric oxide synthase plays a role in depression- and anxiety-like behaviors chronically induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats: Evidence from inflammation and oxidative stress. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 392, 112720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, A.V.; Rivier, C.L. Regulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis by Cytokines: Actions and Mechanisms of Action. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, M.G.; Muglia, L.M.; Laryea, G.; Muglia, L.J. Genetic Approaches to Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Regulation. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birmann, P.T.; Casaril, A.M.; Pesarico, A.P.; Caballero, P.S.; Smaniotto, T.Â.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Moreira, Â.N.; Conceição, F.R.; Sousa, F.S.S.; Collares, T.; et al. Komagataella pastoris KM71H modulates neuroimmune and oxidative stress parameters in animal models of depression: A proposal for a new probiotic with antidepressant-like effect. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 171, 105740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.D.; Zuluaga-Ramirez, V.; Gajghate, S.; Winfield, M.; Sriram, U.; Rom, S.; Persidsky, Y. Activation of GPR55 induces neuroprotection of hippocampal neurogenesis and immune responses of neural stem cells following chronic, systemic inflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 76, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.-l.; Chen, J.-g.; Wang, F. Microglia: A Central Player in Depression. Curr. Med. Sci. 2020, 40, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Gao, Q.; Kim, E.; Lee, Y.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.E.; Jang, D.S.; Ryu, J.H. Pretreatment with 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furaldehyde blocks scopolamine-induced learning deficit in contextual and spatial memory in male mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 134, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, Y.; Sarialioglu, I.; Armut, G.; Calmaz, E.; Orta Yilmaz, B. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural causes reproductive toxicity in male mice by increasing oxidative stress and apoptosis through the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2025, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural exerts negative effects on gastric mucosal epithelial cells by inducing oxidative stress, apoptosis, and tight junction disruption. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 3852–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtel, H.; Aydin, Y.; Orta Yilmaz, B. Modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway-and Apoptosis-Related Genes Following 5-hydroxymethylfurfural Induced Mouse Liver Injury. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2025, 39, e70385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Hahn, J.-S. Roles of the Yap1 transcription factor and antioxidants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae’s tolerance to furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, which function as thiol-reactive electrophiles generating oxidative stress. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5069–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scuto, M.; Rampulla, F.; Reali, G.M.; Spanò, S.M.; Trovato Salinaro, A.; Calabrese, V. Hormetic nutrition and redox regulation in gut–brain axis disorders. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuto, M.; Majzúnová, M.; Torcitto, G.; Antonuzzo, S.; Rampulla, F.; Di Fatta, E.; Trovato Salinaro, A. Functional food nutrients, redox resilience signaling and neurosteroids for brain health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ya, B.; Yin, H.; Yuan, L.; Jing, A.; Li, Y.; Yan, F.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, H.; Zhao, M. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Depression-like Behaviors by Suppressing Hypothalamic Oxidative Stress and Regulating Neuroinflammation in Mice. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14111366
Ya B, Yin H, Yuan L, Jing A, Li Y, Yan F, Zhang H, Xiong H, Zhao M. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Depression-like Behaviors by Suppressing Hypothalamic Oxidative Stress and Regulating Neuroinflammation in Mice. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(11):1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14111366
Chicago/Turabian StyleYa, Bailiu, Haiyan Yin, Lili Yuan, Aihong Jing, Yuxuan Li, Fenglian Yan, Hui Zhang, Huabao Xiong, and Mingsheng Zhao. 2025. "5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Depression-like Behaviors by Suppressing Hypothalamic Oxidative Stress and Regulating Neuroinflammation in Mice" Antioxidants 14, no. 11: 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14111366
APA StyleYa, B., Yin, H., Yuan, L., Jing, A., Li, Y., Yan, F., Zhang, H., Xiong, H., & Zhao, M. (2025). 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Depression-like Behaviors by Suppressing Hypothalamic Oxidative Stress and Regulating Neuroinflammation in Mice. Antioxidants, 14(11), 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14111366







