Abstract
Ischemic stroke remains a leading cause of mortality and disability, with proinflammatory, metabolic, and oxidative stress-related factors contributing to outcome variability. We conducted a retrospective cross-sectional study of 124 consecutive patients (53 women, 71 men; median age 71 [62–76]) discharged with ICD-10 code I69.3 from the Neurology Department of the Clinical Rehabilitation Hospital in Cluj-Napoca (January 2023–September 2024). Men were younger (median age of 69 vs. 73 years, p-value = 0.010), more frequently smokers (42% vs. 9%, p < 0.001), and alcohol consumers (21% vs. 4%, p-value = 0.007) than women. In contrast, women were more frequently sedentary (68% vs. 49%, p-value = 0.038) and had higher LDL cholesterol (89 vs. 74 mg/dL, p = 0.026) than men. Patients with at least moderate disability (n = 84) presented higher levels of C-Reactive Protein (CRP), 1.4 vs. 1.1 mg/L, p-value = 0.027) and more frequently low HDL cholesterol serum levels (29.8% vs. 7.5%, p-value = 0.006) compared to those with minor disability. In multivariable regression, low HDL was the sole independent predictor of disability severity (OR = 4.58, 95% CI 1.21–17.41; AUC = 0.78, sensitivity = 88%, specificity = 42%), while CRP and age did not retain the significance obtained in univariable regression. Our findings highlight sex-specific risk profiles and underline the contribution of proinflammatory, metabolic, and oxidative pathways to ischemic stroke severity, underscoring the need for prospective validation in larger cohorts.
1. Introduction
Oxidative stress is defined as an imbalance between the excessive generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) and the antioxidant defense mechanisms that counteract them [1]. Mitochondria, which produce nearly 90% of cellular ATP and regulate calcium homeostasis and thermogenesis, are a major source of ROS [1]. Under mitochondrial dysfunction, excessive ROS and RNS accumulate, causing oxidative damage of lipids, proteins, and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). Free radicals may arise from exogenous stressors such as air pollution or smoking, or from endogenous metabolic processes when antioxidant defenses are overwhelmed [2]. At physiological levels, ROS act as secondary messengers in signaling pathways regulating proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis [3]. However, excessive or mislocalized ROS production disrupts homeostasis and contributes to chronic degenerative and cardiovascular diseases through cumulative biomolecular damage [3].
The brain is particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress due to its high metabolic rate and oxygen demand. During ischemic stroke, reduced cerebral blood flow deprives neurons of oxygen and glucose, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction, ROS overproduction, excitotoxicity, and neuroinflammation, ultimately exacerbating neuronal injury and blood–brain barrier disruption [1,4]. In the subacute and chronic phases, persistent oxidative stress—together with systemic risk factors such as dyslipidemia, diabetes, and smoking—sustains vascular dysfunction and impairs recovery, underscoring the central role of oxidative pathways in stroke pathophysiology [5].
Research has recently focused on integrating inflammatory, metabolic, and oxidative pathways into a unified model of cerebrovascular injury. Biomarkers such as high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), oxidized low-density lipoproteins (ox-LDL), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) have been shown to predict poor outcomes and recurrent events, reflecting a state of persistent low-grade inflammation that bridges metabolic and vascular dysfunction [5,6]. Moreover, studies establish the role of adipokines, such as leptin and adiponectin, and oxidative enzymes including myeloperoxidase and paraoxonase-1, in modulating endothelial reactivity and plaque stability [7]. Understanding the interplay between these molecular mediators and classical risk factors such as hypertension and diabetes will help refine patient stratification and open up new therapeutic perspectives targeting redox balance and vascular repair mechanisms.
Stroke remains the second leading cause of mortality and the third leading cause of disability worldwide [8]. Ischemic stroke, together with acute myocardial infarction, accounts for nearly 85% of cardiovascular disease-related deaths [9]. In Europe, the prevalence is highest in Eastern regions, with Romania reporting an incidence of 262 cases per 100,000 inhabitants and 38,725 hospital admissions in 2022, resulting in an in-hospital mortality rate of 12% [10]. According to the TOAST classification, ischemic stroke is divided into five categories, of which large-artery atherosclerosis and cardioembolism are the most frequent [11]. Atherogenesis, driven by hypertension, dyslipidemia, smoking, and diabetes, involves endothelial injury, lipid accumulation, inflammation, and plaque rupture, followed by thrombus formation and arterial occlusion [12,13,14]. These processes trigger excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, and inflammation, collectively defined as neuroinflammation [15,16].
Neuroinflammation extends beyond the acute stage, persisting into the subacute and chronic phases, where it maintains oxidative stress, promotes vascular dysfunction, and drives secondary neuronal damage [11,17,18]. This prolonged inflammatory–metabolic state is shaped by both modifiable (e.g., hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, smoking, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, hyperhomocysteinemia, periodontal disease) and non-modifiable (e.g., age, sex, race, genetics) risk factors [11]. In Romania, stroke imposes a substantial societal burden, with average first-year costs of EUR 5227 per patient, more than 80% being direct medical expenses [19]. Aphasia-related costs exceed EUR 3 million annually [20], and between 2007 and 2015, stroke incidence nearly doubled, with yearly expenditures surpassing EUR 650 million [21]. Beyond these economic aspects, Romanian studies highlighted genetic and metabolic determinants: a case–control study found no significant association between the TNFα-308G>A polymorphism and ischemic stroke [22], while a prospective analysis linked lipid profile abnormalities, particularly low HDL cholesterol, with worse outcomes [23]. In this context, our study focused on circulating inflammatory and lipid markers as potential modulators of post-stroke outcomes.
Building on previous evidence, our study focuses on inflammatory and metabolic pathways as central drivers of sustained neuroinflammation and variability in ischemic stroke outcomes. We hypothesized that distinct patterns would emerge according to sex and level of disability. By examining these determinants in patients hospitalized for rehabilitation in the Neurology Department of the Clinical Rehabilitation Hospital in Cluj-Napoca, we aimed to provide an exploratory analysis of their contribution to stroke severity and recovery.
2. Materials and Methods
The study adhered to the Helsinki Declaration and had received approval from the Ethics Committee of the Scientific Research Ethics Commission of the “Iuliu-Haţieganu” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Cluj-Napoca (Approval number 37/2 April 2025). The Scientific Research Ethics Commission of the Cluj-Napoca Clinical Recovery Hospital also approved the study (Approval number 20/23 October 2024). The ethics committees approved a waiver of consent since the study used only de-identified, historical medical data.
2.1. Study Design and Setting
We conducted an observational, retrospective, cross-sectional study at the Cluj-Napoca, Clinical Rehabilitation Hospital, including patients admitted to the Neurology Department between January 2023 to September 2024.
2.2. Participants
Patients were selected based on the diagnosis of ischemic stroke (ICD 10-I69.3—Sequelae of cerebral infarction). Although no formal local validation has been conducted in Romania, international studies have reported good accuracy for this code, with positive predictive values generally above 80% and sensitivity reaching over 90% when used as the principal diagnosis [24,25]. All cases were documented with neurologic examination, using National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS ≥ 0), assessed at the time of hospital admission, recorded by the attending neurologist [26], and imagistic criteria (native or angio-cranial Computer Tomography—ruling out hemorrhage or tumors) [27]. Patients hospitalized for other neurological pathologies, without a diagnosis of ischemic stroke documented by imaging, septic, or with any known inflammatory disease in acute flare-up, were excluded. Patient’s neurological and functional status at the time of transfer to the rehabilitation department, corresponding to the subacute phase after ischemic stroke, was evaluated by NIHSS score.
2.3. Data Extraction and Preparation
Medical records and the computer data system of the hospital, “Atlas Med” were the source of our data. Patients were selected using a filter based on the primary diagnosis at discharge (ICD-I69.3). Subsequently, from the patients’ follow-up sheets, we obtained data on hereditary collateral history (HCA), medical history, consumption of toxic substances, clinical examination, and laboratory tests. Biomarkers were measured at the time of admission to the hospital following the same protocol. The eligible patients were those admitted for neurological rehabilitation after an ischemic stroke, so, the timing from the acute event to the admission varied depending on the patient’s functional prognosis and transfer logistics. Information on the presence of comorbidities (e.g., hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, chronic kidney disease) was collected from the medical charts; diagnoses were established based on clinical records and laboratory criteria as described above. Information regarding chronic medication use, including statin therapy, was inconsistently reported in hospital charts and, therefore, not included in the present analysis.
To reduce potential bias, we included all consecutive patients with ICD-10 I69.3 discharge diagnosis during the study period, confirmed by both clinical and imaging criteria. Data was extracted from a single hospital electronic system to minimize information bias (Figure 1). Potential confounding was addressed in the statistical analysis.
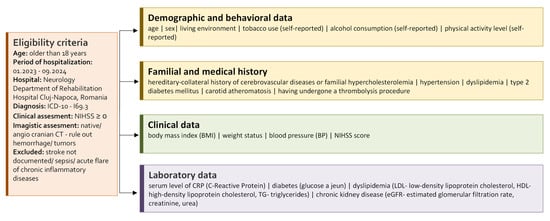
Figure 1.
Baseline characteristics and clinical data of the study cohort.
The study size was determined by the number of consecutive patients meeting inclusion criteria during the study period, without a priori sample size calculation.
Concerning the laboratory examinations, we evaluated the presence of diabetes mellitus type 2 (a-jeun blood glucose > 126 mg/dL), dyslipidemia (LDL-cholesterol > 100 mg/dL or HDL-cholesterol < 40 mg/dL or triglycerides (TG) > 150 mg/dL), chronic kidney disease (estimated glomerular filtration rate—eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2). Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated using CKD-EPI Formula [28]. Border values for evaluation were obtained from several guidelines [29,30,31,32]. These markers were also considered relevant due to their previously reported associations with systemic inflammation, oxidative stress, and vascular dysfunction in ischemic stroke.
2.4. Data Analysis
Primary data were obtained from the electronic system (Atlas Med) and patients’ charts. Data cleaning involved verification of the extracted variables against the original patient records to ensure accuracy. Given the exploratory nature of this study, particular attention was paid to markers reflecting inflammatory and oxidative stress-related pathways (e.g., CRP, HDL). Data was collected in Microsoft Excel and processed in search of different associations between specific groups, sex, and level of disability (NIHSS categories). Continuous variables are reported as median [first quartile (Q1) to third quartile (Q3)], and comparisons between groups were performed using the Mann–Whitney U test according to the evaluation of distribution by groups. Categorical variables are reported as counts and percentages, and differences between groups were assessed using the Chi-squared test or Fisher’s exact test, as appropriate. Bivariate associations were examined using Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient. Univariable logistic regression analyses were conducted to evaluate the association between potential predictors and the outcome of interest. Variables with a p-value < 0.10 in univariable analyses were entered into forward stepwise multivariable logistic regression models to adjust for potential confounders. Results are presented as odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Considering an exploratory approach, a two-tailed p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using Jamovi [version 2.6.26.0].
3. Results
Our cohort consisted of 124 patients, aged from 24 to 94, with a high proportion of men (57.3%). Subjects’ selection process is illustrated in Figure 2. Half of the cohort were overweight or obese, with the presence of carotid atherosclerosis observed in three-quarters of participants (Table 1).
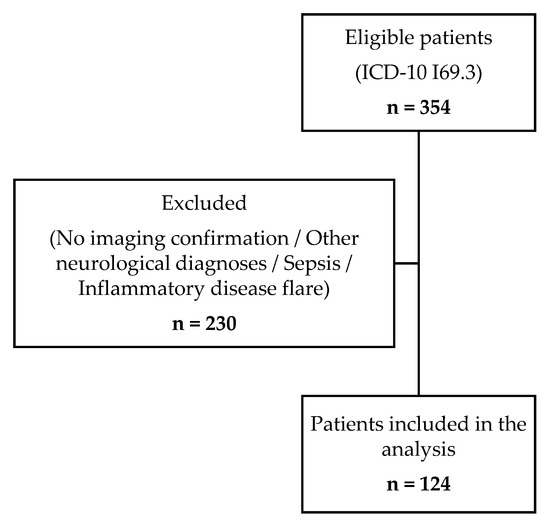
Figure 2.
Flow diagram of patient selection process.

Table 1.
Patients’ characteristics by sex.
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics by Sex
Most of the evaluated patients were male, with statistically significant differences between men and women (Table 1). Only nine patients received embolization treatment, 5/53 women and 4/71 men (Fisher’s exact test: p-value = 0.4949). Men and women had similar characteristics except for age (younger men), smoking and self-declared alcohol consumption status (higher frequency among men), sedentarism (higher frequency among women), higher serum levels of LDL in women, and lower HDL serum levels in men, and higher levels of creatinine in men (Table 1).
Most participants had LDL levels in the normal range, with similar frequencies of higher levels (7.5% in women and 7.0% in men), but the frequency of men with lower LDL levels was higher (28.2%) than in women (9.4%) (Fisher’s exact test: p-value = 0.0320). Lower serum levels of HDL were similar among men (23.9%) and women (18.9%) (Fisher’s exact test: p-value = 0.7230). A higher frequency of men showed higher values of serum creatinine levels (21.1%) than women (9.4%), while lower levels were more frequently seen in women (9.4%) than men (2.8%), but the differences only reach a tendency to statistical significance (Fisher’s exact test: p-value = 0.092).
3.2. Patients’ Characteristics by Disability Class
Eighty-four patients had a NIHSS score of at least moderate, with no patient classified with a severe deficit. Thrombolysis was applied in one patient with a mild disability score and in eight patients with at least a moderate disability score. Patients with a mild disability score were older, had a lower frequency of atheromatosis, lower serum values of CRP and eGFR, and a higher serum creatinine level (Table 2).

Table 2.
Patients’ characteristics by different disability class: minor vs. at least moderate.
Lacunarism is more frequent among patients with minor disability (62.5%) than those with at least moderate disability (47.6%), but the difference did not reach the significance threshold (Chi-squared test: p-value = 0.1209). Patients with at least a moderate disability had more frequently lower levels of HDL cholesterol (29.8%) than patients with minor disability (7.5%), the difference being statistically significant (Fisher’s exact test: p-value = 0.0056).
Among characteristics that showed statistically significant differences between groups, the abnormal value of HDL cholesterol proved the strongest predictor in univariable regression analysis (Table 3). The presence of abnormal values of HDL remains also in the multivariable logistic regression analysis the most important factor, but the model can correctly classify 88.1% of patients with at least moderate disability and 42.5% of those with minor disability (Acc—accuracy = 73%, Se—sensibility = 88%, Sp—specificity = 42%, AUC—area under the curve = 0.78). Inclusion of eGFR in the multivariable model led to only HDL class as a statistically significant predictor.

Table 3.
Logistic regression analysis: risk factors for association with disability level.
3.3. Bivariate Association of Quantitative Factors
Age showed a statistically significant association with eGFR, eGFR with serum level of creatinine, HDL with CRP, and LDL and TG with BMI and HDL cholesterol (Figure 3).
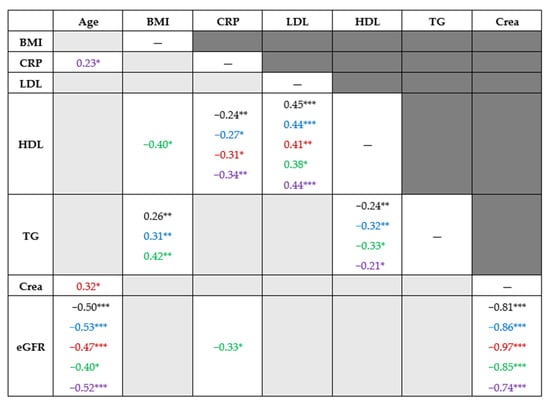
Figure 3.
Bivariate association of quantitative factors. Note. * p-value < 0.05, ** p-value < 0.01, *** p-value < 0.001. Light gray background indicates the absence of statistically significant correlations. The reported values represent Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients. Blue indicates the values for men, red for women, green for patients with minor disability and violet for patients with at least a moderate disability. BMI—body mass index; CRP—C-reactive protein, LDL—low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL—high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, TG—triglycerides, CRE—creatinine, eGFR—estimated glomerular filtration rate.
Similar monotonic association was observed in the whole cohort (Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients in black), in men (blue), in women (red), in patients with minor disability (green), and those with at least moderate disability (violet) (Figure 3).
4. Discussions
4.1. Key Results
Our findings partially support the initial hypothesis by highlighting distinct patterns of demographic and proinflammatory risk factors within ischemic stroke patients and their association with disability severity. Men were younger and more frequently auto-reported tobacco and alcohol consumption, whereas women were more sedentary and had higher LDL cholesterol levels (Table 1). Patients with more severe disability presented higher CRP values and a greater prevalence of low HDL cholesterol, while those with minor disability tended to be older and showed reduced renal function (Table 2). In multivariable regression, low HDL cholesterol emerged as the sole independent predictor of disability severity (Table 3). Together with elevated CRP levels, this profile reflects not only systemic inflammation but also an altered oxidative balance, reinforcing the concept of oxidative stress as a key determinant of stroke severity and recovery [33,34].
4.2. Interpretation
Beyond its biochemical implications, the observed pattern supports the hypothesis of a crosslink between systemic metabolic disorders and localized neurovascular injury of that oxidative stress. Experimental studies demonstrated that excess ROS could alter the permeability of the blood–brain barrier and activate microglia, perpetuating neuronal apoptosis and white matter damage [35,36]. Furthermore, metabolic conditions such as diabetes and dyslipidemia amplify this oxidative burden through mitochondrial dysfunction and lipid peroxidation [37], leading to a self-sustaining proinflammatory environment. This integrative framework aligns with recent translational models that emphasize “metabolic inflammation” as a key driver of post-stroke neurodegeneration and reduced functional recovery.
Sex-related differences in vascular risk factors have been documented in stroke populations [38,39,40]. Our findings are consistent with studies showing that men are more frequently exposed to behavioral risks such as tobacco and alcohol consumption, whereas women often present with metabolic abnormalities, including higher LDL cholesterol (Table 1). These patterns may contribute to sex-specific differences in stroke incidence, severity, and recovery reported across various cohorts.
The independent association between low HDL cholesterol and disability severity underscores the potential role of lipid metabolism in post-stroke outcomes (Table 3). Prior studies have highlighted the anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and vasoprotective effects of HDL [41,42], and our findings are in line with this evidence. Beyond lipid transport, HDL neutralizes oxidized LDL, reduces lipid peroxidation, and protects endothelial nitric oxide availability, thereby counteracting oxidative stress and vascular dysfunction [42]. Elevated CRP levels in patients with more severe disability (Table 2) emphasize the contribution of systemic inflammation and oxidative stress to stroke severity, as CRP can activate NADPH oxidase, enhance ROS production, and impair endothelial nitric oxide signaling, thereby amplifying neuroinflammation [6]. While rare, inborn errors of immunity have been associated with vascular inflammation and thrombotic complications, potentially predisposing to ischemic stroke in selected patients [43]. These mechanisms, however, were not investigated in the present cohort and warrant further dedicated research.
Although our dataset did not include information on statin therapy, we acknowledge that statin therapy may influence both lipid fractions and inflammatory profiles. Evidence indicates that statin treatment improves outcomes in specific subtypes of ischemic stroke, such as Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source (ESUS), a well-defined form of cryptogenic stroke characterized by prominent inflammatory and endothelial dysfunction mechanisms [44]. These findings reinforce the importance of integrating medication history and stroke subtype data in future studies exploring inflammatory and oxidative mechanisms. Renal dysfunction is an established predictor of adverse outcomes after ischemic stroke, with several studies demonstrating associations between reduced eGFR, higher creatinine levels, and greater disability or mortality [45,46]. In our cohort, impaired renal function was paradoxically more common among patients with minor disability. This discrepancy may reflect selection bias, survival effects, or residual confounding inherent to retrospective designs (Table 2). Impaired renal function is associated with increased oxidative stress due to reduced clearance of reactive metabolites and accumulation of uremic toxins, which may further aggravate vascular injury and compromise neurological recovery [47]. Nevertheless, the integration of renal markers with lipid and inflammatory parameters highlights the complex interplay of metabolic and systemic factors in ischemic stroke, supporting the need for multifactorial risk assessment.
Although low HDL cholesterol remained the sole independent predictor of disability severity in the multivariable model (Table 3), its clinical utility appears limited. The model achieved good sensitivity but poor specificity, correctly classifying most patients with more severe disability but failing to discriminate those with minor deficits. This imbalance suggests that HDL alone cannot serve as a reliable prognostic biomarker in clinical practice. Rather, it may be better interpreted as part of a broader inflammatory–metabolic profile. At the same time, the paradoxical finding regarding renal function underlines the need for cautious interpretation and further validation in larger, prospective studies.
By providing evidence from a Romanian stroke cohort, our study highlights the importance of further research to validate these associations and to develop multifactorial prognostic models with clinical relevance.
4.3. Generalizability
Our findings should be interpreted with caution regarding external validity. The analysis was conducted in a single rehabilitation hospital in Romania, and the demographic and clinical characteristics of the included patients may not fully reflect ischemic stroke populations in other regions or healthcare systems. The observed sex-related differences and the association of low HDL cholesterol with disability severity are consistent with international evidence, suggesting that these patterns may be broadly applicable. In contrast, the findings regarding renal function diverge from prior studies, indicating that local factors, study design, or sample characteristics may have influenced the results. Confirmation in larger, multicenter, and prospective cohorts is therefore required to establish the extent to which our results can be generalized.
4.4. Limitations
We acknowledge several limitations in our study. The applied study design as retrospective and cross-sectional study of routinely collected healthcare data limits the possibility to establish causal relationships of the reported patterns. The absence of follow-up data further restricts the evaluation of long-term outcomes. The analysis was conducted in a single rehabilitation hospital, which may not fully capture the variability of ischemic stroke populations in other clinical or geographic contexts. Consequently, the external validity of the findings is limited.
The source of data was represented by the routinely collected hospital data. In this context, certain variables, such as tobacco and alcohol consumption, were self-reported and may be subject to social desirability and acquiescence bias. The absence of data regarding statin use, not routinely collected, is a major limitation of our study. Statin therapy can modulate both lipid profiles and inflammatory responses, factors that are closely linked to stroke outcomes. Therefore, not accounting for this variable may have introduced confounding effects affecting the associations observed between HDL cholesterol, CRP, and disability severity as stroke outcome.
Another limitation is that most patients included in our study did not undergo thrombolytic therapy. Consequently, our results mainly reflect risk factor patterns and outcomes in non-thrombolyzed ischemic stroke patients. It remains uncertain whether patients treated with thrombolysis might present distinct inflammatory, metabolic, or oxidative profiles, and further studies comparing thrombolyzed versus non-thrombolyzed cohorts are warranted.
The absence of a control group restricts the possibility of comparing the prevalence of behavioral and metabolic risk factors in our cohort with those observed in the general population. For instance, smoking and alcohol consumption patterns reported in Table 1 cannot be directly contextualized outside the evaluated sample.
Only a limited set of biomarkers was assessed, focusing primarily on CRP and lipid profile parameters. We did not include direct markers of oxidative stress (e.g., malondialdehyde, 8-iso-PGF2α, glutathione, superoxide dismutase, catalase), which limits our ability to capture the redox imbalance associated with ischemic stroke. Future prospective studies integrating oxidative stress and cytokine biomarkers, along with imaging markers of vascular dysfunction, may further clarify causal pathways.
As shown in Table 3, HDL cholesterol emerged as an independent predictor of disability severity; however, the lack of additional inflammatory and metabolic markers (e.g., cytokines, adipokines, genetic factors) may have introduced residual confounding. Furthermore, although low HDL cholesterol emerged as a statistically significant predictor in the multivariable model (Table 3), the modest specificity observed limits its immediate clinical applicability. Moreover, the association between low HDL cholesterol and disability severity (Table 3) might also be partially explained by lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity. As shown in Table 1, women were significantly more sedentary than men, and sedentarism itself is a known determinant of reduced HDL levels, which could have contributed to the observed differences.
5. Conclusions
In our retrospective cross-sectional study, we identified distinct demographic and biochemical patterns among ischemic stroke patients during rehabilitation. Sex-related differences were evident, with men more frequently reporting behavioral risk factors and women presenting metabolic imbalances. Among biochemical markers, low HDL cholesterol remained the sole independent predictor of disability severity, although its clinical utility appeared limited due to modest specificity. The results underline the possible contribution of metabolic, inflammatory, and oxidative pathways to functional outcomes in ischemic stroke, highlighting the need for integrated risk factor management and for prospective studies including redox biomarkers to validate the observed associations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.G., S.D.B., C.A.N. and A.-E.B.; Methodology, A.G. and S.D.B.; Formal analysis, A.G., I.C.S., C.M.M., S.D.B. and A.-E.B.; Investigation, A.G., I.C.S., C.-A.G. and A.-E.B.; Writing—original draft preparation, A.G., G.B.D., P.M.B. and C.-A.G.; Writing—review and editing, S.D.B., C.M.M., G.B.D., C.A.N., P.M.B. and A.-E.B.; Supervision, A.-E.B. (lead supervision), S.D.B., I.C.S., C.M.M. and C.A.N.; Correspondence, S.D.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Scientific Research Ethics Commission of the “Iuliu Hațieganu” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Cluj-Napoca (approval no. 37/2 April 2025) and by the Ethics Committee of the Clinical Rehabilitation Hospital, Cluj-Napoca (approval no. 20/23 October 2024).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived because the study involved a retrospective review of anonymized medical records.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author. The data is not publicly available due to privacy and ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this manuscript, the authors used OpenAI’s ChatGPT (GPT-5, July, August and September 2025) to support language refinement. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Acc | Accuracy |
| AF | Atrial Fibrillation |
| ATP | Adenosine–triphosphate |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CKD-EPI | Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (formula) |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| CVD | Cardiovascular Diseases |
| eGFR | Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| ESUS | Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source |
| FHC | Familial Hypercholesterolemia |
| HCA | Hereditary-Collateral History |
| HDL | High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| ICD-10 | International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision |
| LDL | Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| NIHSS | National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| Se | Sensitivity |
| Sp | Specificity |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| TNFα | Alpha Tumor Necrosis Factor |
References
- Dash, U.C.; Bhol, N.K.; Swain, S.K.; Samal, R.R.; Nayak, P.K.; Raina, V.; Panda, S.K.; Kerry, R.G.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Neurological Disorders: Mechanisms and Implications. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2025, 15, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ściskalska, M.; Zalewska, M.; Grzelak, A.; Milnerowicz, H. The Influence of Occupational Exposure to Heavy Metals and Tobacco Smoke on Selected Oxidative Stress Markers in Smelters. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 159, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, S.; Abramov, A.Y. Mechanism of Oxidative Stress in Neurodegeneration. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2012, 2012, 428010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, M.U.; Wali, A.F.; Ahmad, A.; Shakeel, S.; Rasool, S.; Ali, R.; Majid, S.; Madkhali, H.; Ganaie, M.A.; Khan, R. Neuroprotective Strategies for Neurological Disorders by Natural Products: An Update. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluk, H.; Tafelska-Kaczmarek, A.; Sopońska, M.; Porzych, M.; Modrzejewska, M.; Pawluk, M.; Kurhaluk, N.; Tkaczenko, H.; Kołodziejska, R. The Influence of Oxidative Stress Markers in Patients with Ischemic Stroke. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Li, L.; Xu, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, A.; Liao, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, Z.; et al. The relationship between systemic inflammation index, systemic immune-inflammatory index, and inflammatory prognostic index and 90-day outcomes in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, E.; Martorell, J.; Riambau, V. Review of serum biomarkers in carotid atherosclerosis. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 71, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs). World Health Organization, 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- European Stroke Organisation (ESO). Stroke in Numbers—Romania, 2022–2021. Stroke Action Plan for Europe—Stroke Incidence. Available online: https://actionplan.eso-stroke.org/stroke-incidence?country=romania&years%5B%5D=2022&years%5B%5D=2021 (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Adams, H.P., Jr.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E., 3rd. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke: Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R. Atherosclerosis—An inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 2002, 420, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuster, V.; Moreno, P.R.; Fayad, Z.A.; Corti, R.; Badimon, J.J. Atherothrombosis and high-risk plaque: Part I: Evolving concepts. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 937–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskowitz, M.A.; Lo, E.H.; Iadecola, C. The science of stroke: Mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron 2010, 67, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, H.L.; Selkoe, D.J. Inflammation and therapeutic vaccination in CNS diseases. Nature 2002, 420, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Maida, C.; Pinto, A. Inflammation and inflammatory cell recruitment in acute cerebrovascular diseases. Curr. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 11, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, S.; Raz, E.; Yang, D.; Cutting, S.; Mac Grory, B.; Elkind, M.S.; de Havenon, A. Lacunar stroke: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strilciuc, S.; Grad, D.A.; Mixich, V.; Stan, A.; Buzoianu, A.D.; Vlădescu, C.; Vintan, M.A. Societal cost of ischemic stroke in Romania: Results from a retrospective county-level study. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stan, A.; Strilciuc, S.; Gherghel, N.; Cozma, A.; Cristian, A.; Ilut, S.; Blesneag, A.; Vacaras, V.; Stanca, D.; Stan, H.; et al. Aphasia after acute ischemic stroke: Epidemiology and impact on tertiary care resources. Balneo PRM Res. J. 2021, 12, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloj, F.A.; Buicu, F.C.; Filep, C.R.; Suciu, B.A.; Vunvulea, V.; Mărginean, L. A cost effectiveness analysis of stroke management in Romania. Gazz. Med. Ital. Arch. Sci. Med. 2022, 181, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felicia, P.; Popp, R.A.; Cătană, A.; Porojan, M.; Pop, I.V. Genetic polymorphism TNFα −308 G>A and ischemic stroke in Northern Romania. Acta Med. Marisiensis 2013, 59, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hutanu, A.; Iancu, M.; Dobreanu, M.; Oprea, O.R.; Barbu, Ș.; Maier, S.; Tero-Vescan, A.; Băjko, Z.; Bălașa, R. Extended lipid profile in Romanian ischemic stroke patients in relation to stroke severity and outcome: A path analysis model. Arch. Med. Sci. 2021, 17, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.T.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Tsai, T.T.; Wang, Y.C.; Sung, S.F. Performance of ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes for identifying acute ischemic stroke in a national health insurance claims database. Clin. Epidemiol. 2020, 12, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, N.; Bhole, V.; Lacaille, D.; Avina-Zubieta, J.A. Validity of diagnostic codes for acute stroke in administrative databases: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brott, T.; Adams, H.P., Jr.; Olinger, C.P.; Marler, J.R.; Barsan, W.G.; Biller, J.; Spilker, J.; Holleran, R.; Eberle, R.; Hertzberg, V.; et al. Measurements of acute cerebral infarction: A clinical examination scale. Stroke 1989, 20, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.P.; Liebeskind, D.S. Imaging of ischemic stroke. Continuum (Minneap Minn.) 2016, 22, 1399–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Kidney Foundation. CKD-EPI Creatinine Equation. 2021. Available online: https://www.kidney.org/ckd-epi-creatinine-equation-2021-0 (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Pappan, N.; Awosika, A.O.; Rehman, A. Dyslipidemia. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560891/ (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Goyal, R.; Singhal, M.; Jialal, I. Type 2 diabetes. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513253/ (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Timar, R. Noțiuni de Diabet, Nutriție și Boli Metabolice; Eurobit: Timișoara, Romania, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.K.; Knicely, D.H.; Grams, M.E. Chronic kidney disease diagnosis and management: A review. JAMA 2019, 322, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Yang, L.; Chen, G.; Ding, P.; Yu, D.; Liao, H.; Liu, J.; Yue, W. National Institute of Health Stroke Scale Score Mediated the Relationship between Systemic Inflammatory Response Index, High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein, and Functional Prognosis of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Prospective Cross-Sectional Study. Heart Mind. 2025, 9, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyurászová, M.; Kovalčíková, A.; Gaál, E.; Renczés, E.; Kmeťová, K.; Celec, P.; Bábíčková, J.; Tóthová, Ľ. Oxidative Stress in Animal Models of Acute and Chronic Renal Failure. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 8690805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yoshioka, H.; Kim, G.S.; Jung, J.E.; Okami, N.; Sakata, H.; Maier, C.M.; Narasimhan, P.; Goeders, C.E.; Chan, P.H. Oxidative stress in ischemic brain damage: Mechanisms of cell death and potential molecular targets for neuroprotection. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jung, U.J.; Kim, S.R. Role of oxidative stress in blood–brain barrier disruption and neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, J.S.; Bhatti, G.K.; Reddy, P.H. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in metabolic disorders—A step towards mitochondria-based therapeutic strategies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1066–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimjee, S.M.; Akhter, A.S.; Zakeri, A.; Herson, P.S. Sex differences in thrombosis as it affects acute ischemic stroke. Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 165, 105647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Kwan, A.C.; Chen, M.T.; Ouyang, D.; Ebinger, J.E.; Bell, S.P.; Niiranen, T.J.; Bello, N.A.; Cheng, S. Sex differences in myocardial and vascular aging. Circ. Res. 2022, 130, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebchuk, A.D.; Hill, M.D.; Goyal, M.; Demchuk, A.; Coutts, S.B.; Asdaghi, N.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Holodinsky, J.K.; Fainardi, E.; Shankar, J.; et al. Exploring sex differences for acute ischemic stroke clinical, imaging and thrombus characteristics in the INTERRSeCT study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2023, 43, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkhoff, M.; Polzin, A. Lipoprotection in cardiovascular diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 264, 108747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beazer, J.D.; Patanapirunhakit, P.; Gill, J.M.R.; Graham, D.; Karlsson, H.; Ljunggren, S.; Mulder, M.T.; Freeman, D.J. High-density lipoprotein’s vascular protective functions in metabolic and cardiovascular disease—Could extracellular vesicles be at play? Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2020, 134, 2977–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortesi, M.; Dotta, L.; Cattalini, M.; Lougaris, V.; Soresina, A.; Badolato, R. Unmasking inborn errors of immunity: Identifying the red flags of immune dysregulation. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1497921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitturi, B.K.; Gagliardi, R.J. Effectiveness of statins on outcomes of patients with Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source (ESUS). J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2024, 33, 107469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojs Fabjan, T.; Hojs, R. Stroke and renal dysfunction. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 25, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Tian, X.; Chen, S.; Xing, A.; Wang, A.; He, Y. Association of stroke with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease with and without CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2024, 83, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshagh, K.; Khorvash, F.; Sahebkar, A.; Askari, G.; Karimi, A.; Pishva, H.; Nikbakht, F.; Dehnavi, Z.; Jafari, E.; Entezari-Maleki, T.; et al. The Effects of Curcumin-Piperine Supplementation on Inflammatory, Oxidative Stress and Metabolic Indices in Patients with Ischemic Stroke in the Rehabilitation Phase: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2023, 22, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).