Shikonin-Loaded Nanoparticles Attenuate Particulate Matter-Induced Skin Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Shikonin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticle
2.2. Characterization of Shikonin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles
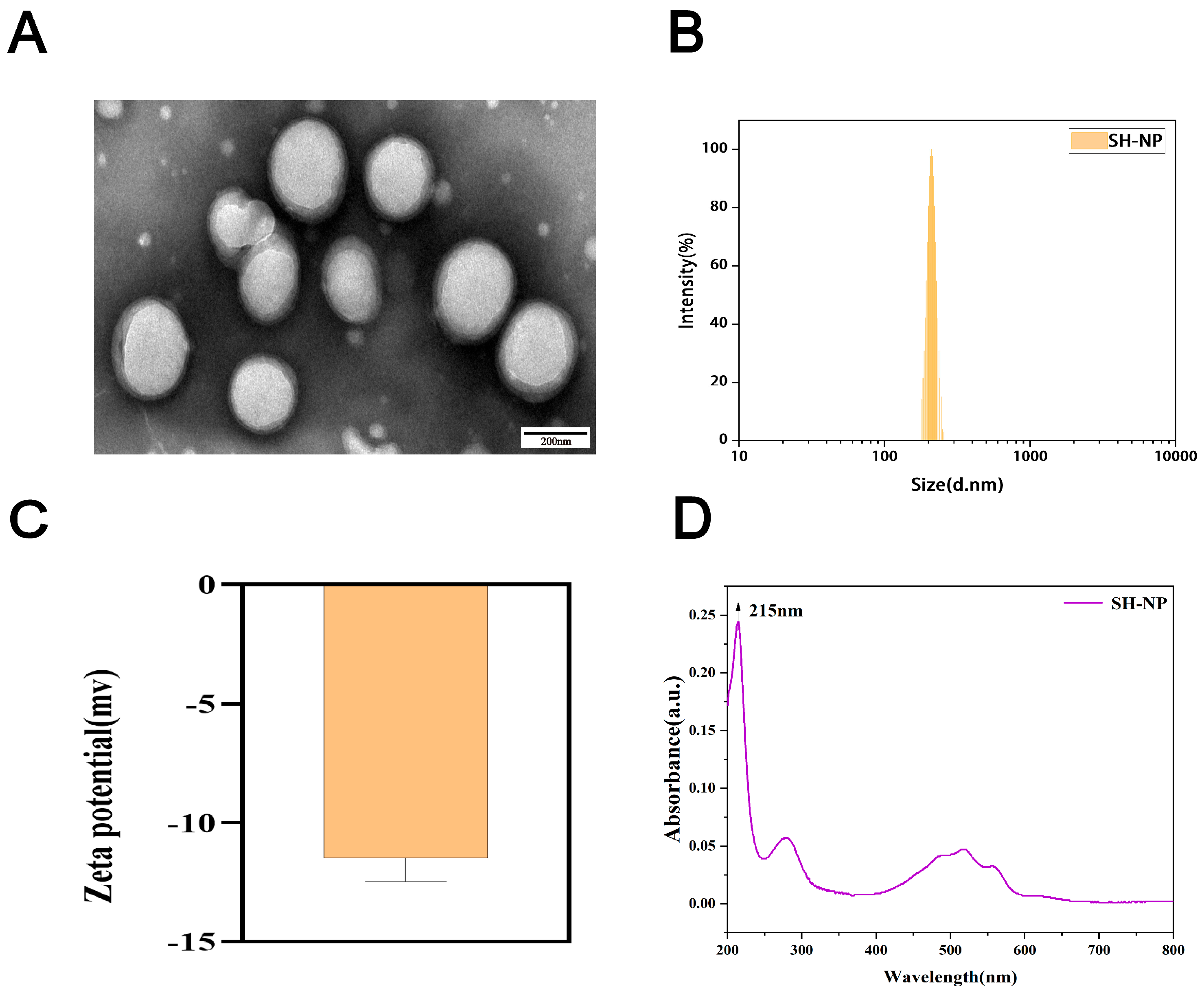
2.2.1. Particle Size and Zeta Potential
2.2.2. Morphology
2.2.3. Drug-Loading and Encapsulation Efficiency
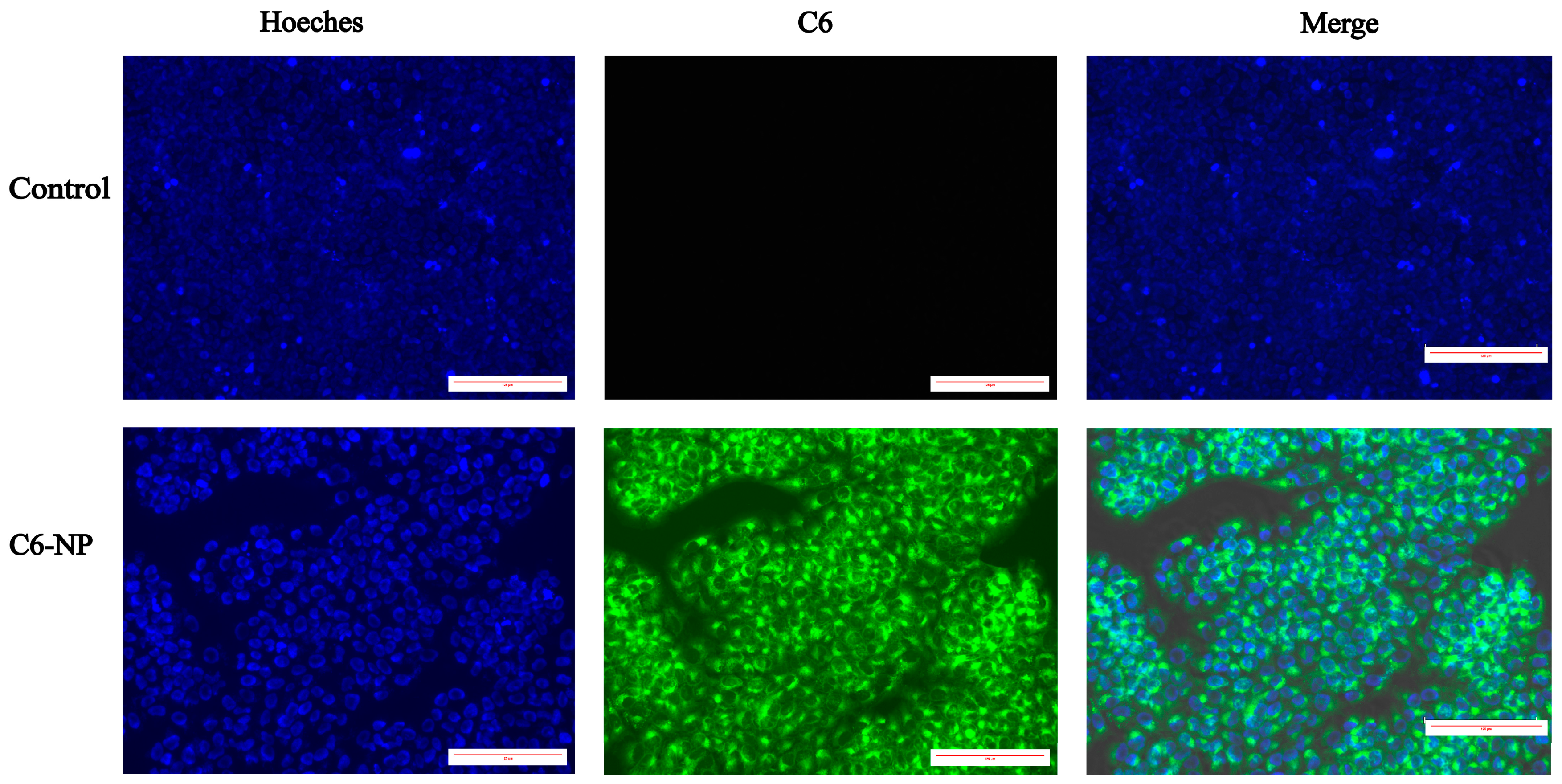
2.2.4. Evaluation of Cellular Uptake of Nanoparticles
2.3. Preparation of PM2.5
2.4. Experimental Animals
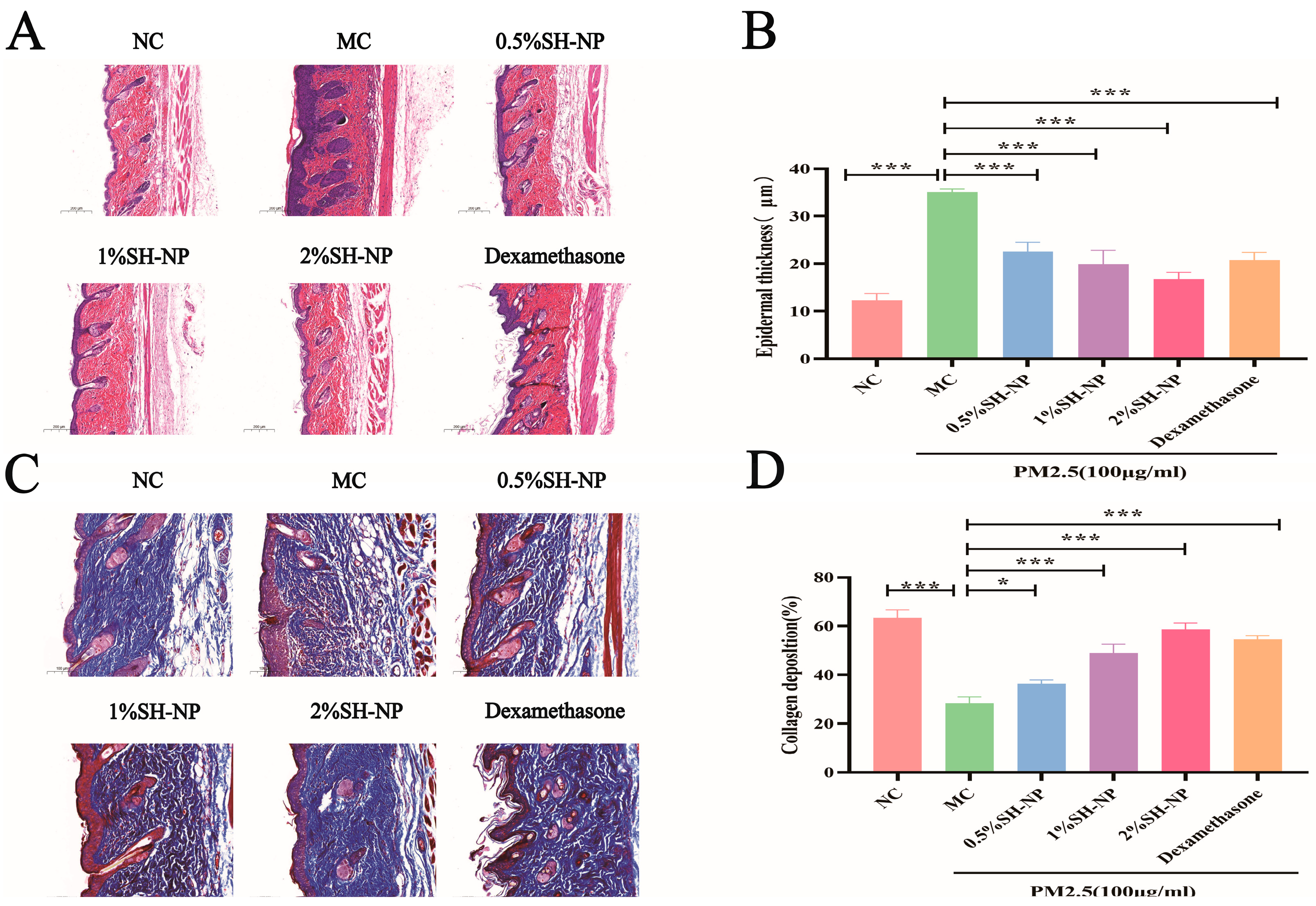
2.5. Histopathological Examination
2.6. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.8. Detection of MDA
2.9. Detection of Nitric Oxide (NO)
2.10. Biosafety Study
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Shikonin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles
3.2. Drug-Loading and Encapsulation Efficiency
3.3. Assessment of Cellular Uptake
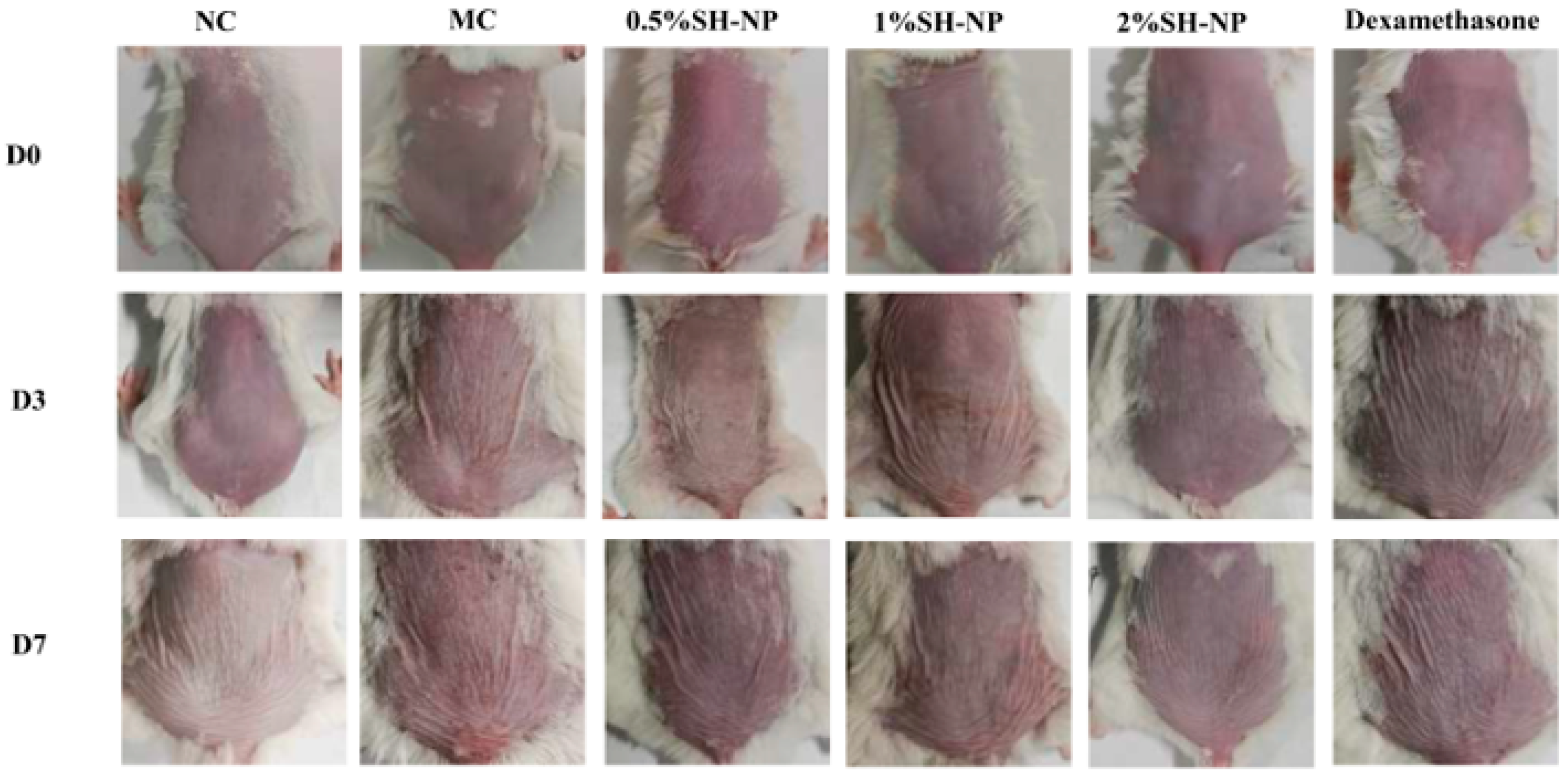
3.4. Shikonin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Attenuate PM2.5-Induced Skin Injury
3.5. Histopathological Examination of Skin Tissue
3.6. Immunohistochemical Analysis
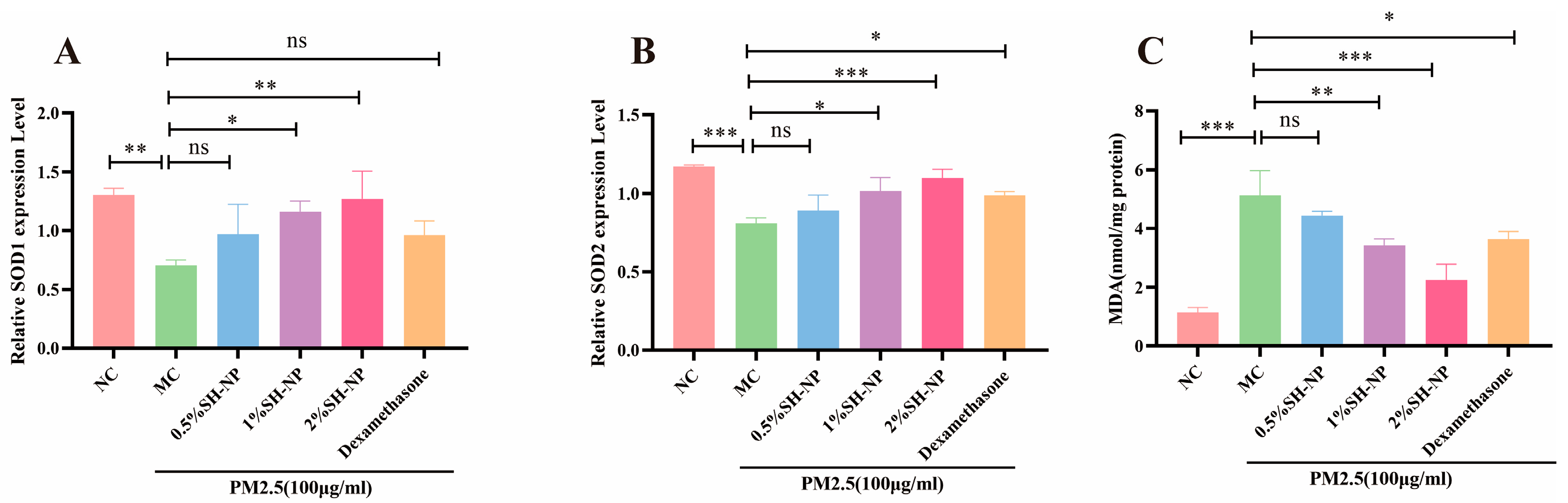
3.7. Shikonin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Alleviate PM2.5-Induced Oxidative Stress
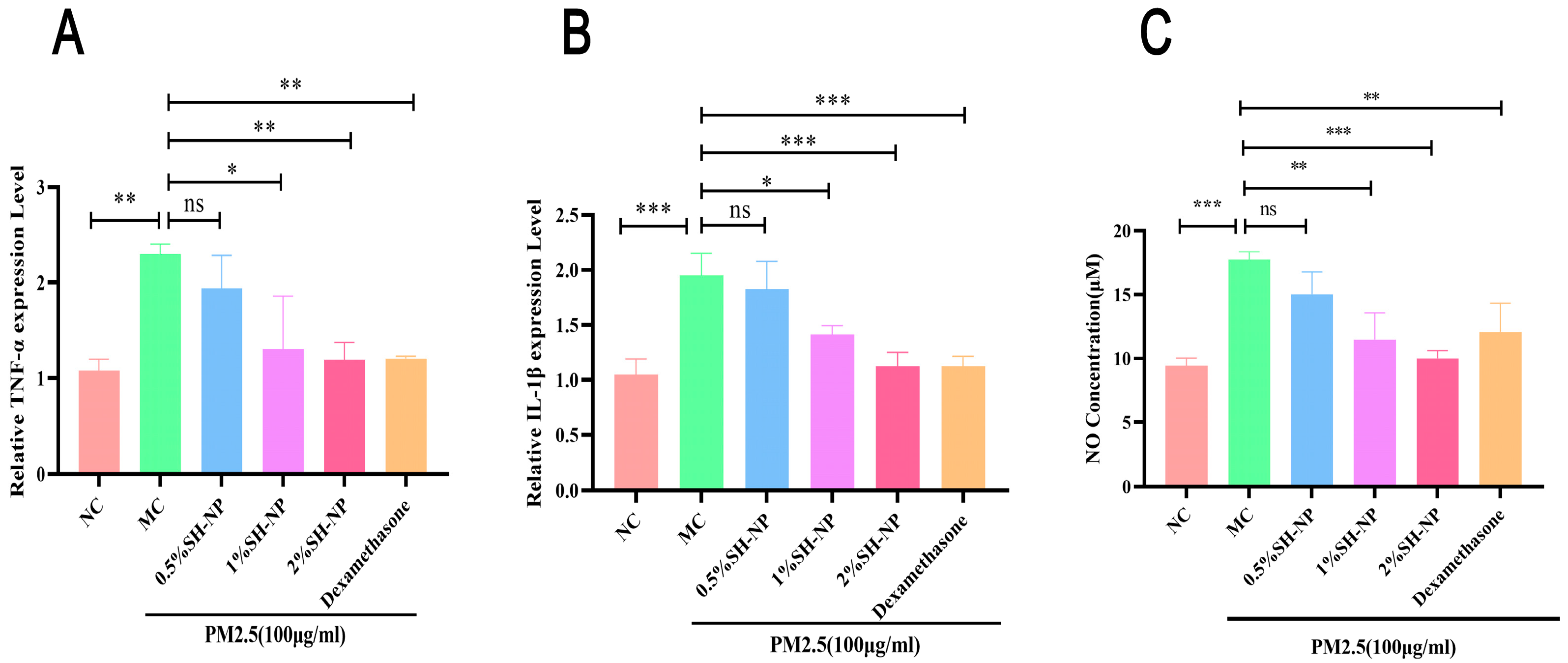
3.8. Shikonin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Reduce PM2.5-Induced Inflammatory Responses
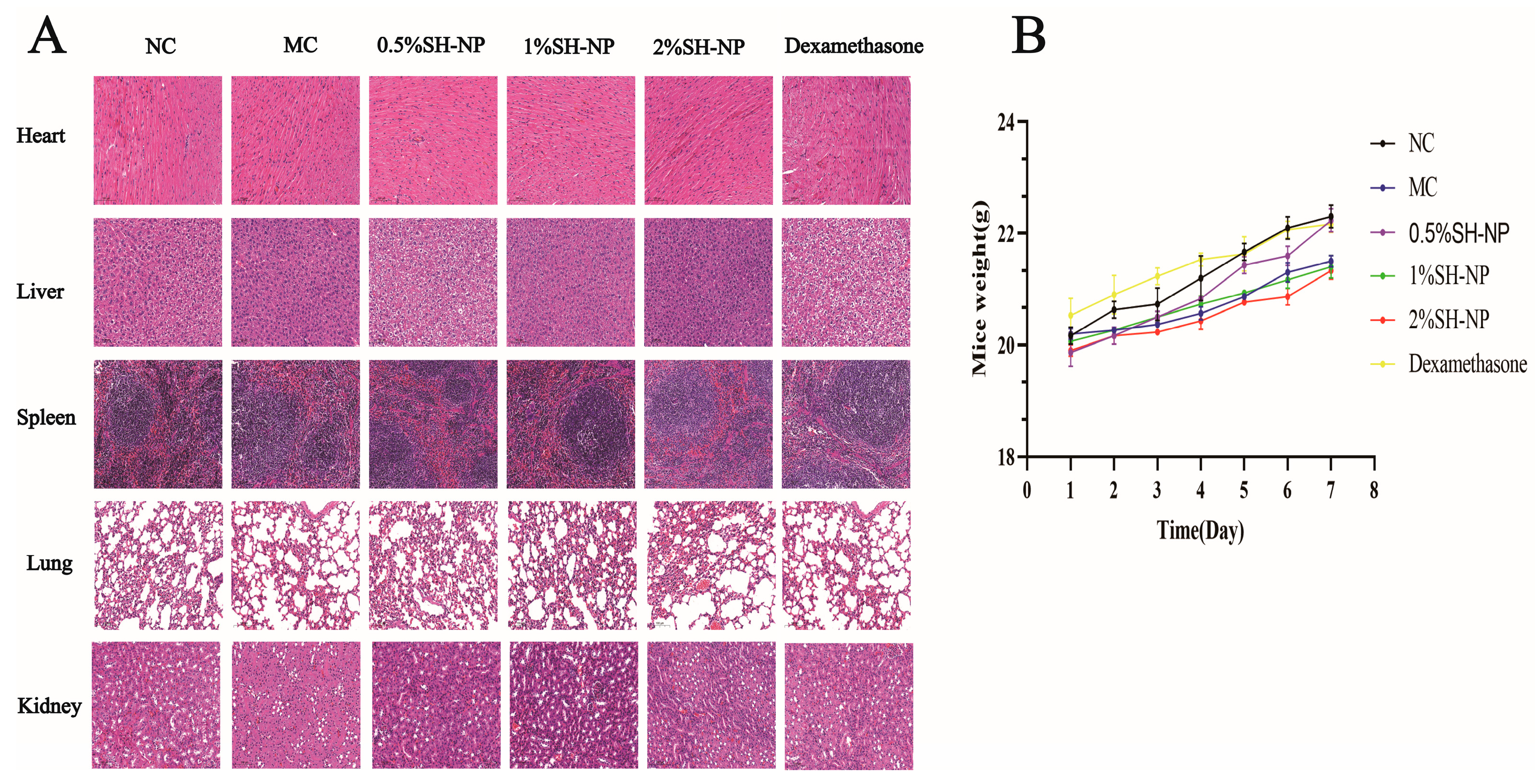
3.9. Biosafety Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thangavel, P.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.C. Recent Insights into Particulate Matter (PM2.5)-Mediated Toxicity in Humans: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.O.; Thundiyil, J.G.; Stolbach, A. Clearing the air: A review of the effects of particulate matter air pollution on human health. J. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Na, H.W.; Jang, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Kee, N.G.; Shin, D.Y.; Choi, H.; Kim, H.J.; Seo, Y.R. Integrative analysis to explore the biological association between environmental skin diseases and ambient particulate matter. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadelis, G.; Tourres, R.; Molinie, J. Short-term effects of the particulate pollutants contained in Saharan dust on the visits of children to the emergency department due to asthmatic conditions in Guadeloupe (French Archipelago of the Caribbean). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, K.; Johansson, C.; Forsberg, B. Estimated short-term effects of coarse particles on daily mortality in Stockholm, Sweden. Environ. Health Perspect 2012, 120, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Qiu, W.; Liao, R.; Cao, W.; Huang, F.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Li, Y. Subacute PM2.5 Exposure Induces Hepatic Insulin Resistance Through Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattignavong, E.; Neshatian, M.; Vaez, M.; Guillermin, A.; Tauer, J.T.; Odlyha, M.; Mittal, N.; Komarova, S.V.; Zahouani, H.; Bozec, L. Development of a facile method to compute collagen network pathological anisotropy using AFM imaging. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.F.; Hwang, E.; Leonard, C.E.; Cohen, J.M. Association between fine particulate matter and eczema: A cross-sectional study of the All of Us Research Program and the Center for Air, Climate, and Energy Solutions. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0310498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Shen, M.; Mao, R.; Zhang, C. Association of air pollution with incidence of late-onset seborrhoeic dermatitis: A prospective cohort study in UK Biobank. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 49, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.H.; Lee, C.C.; Hwang, M.M.; Jung, C.R.; Lai, I.H.; Chen, W.T.; Hwang, B.F. Fine particulate matter exposure and incident atopic dermatitis: A birth cohort study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2025, 192, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Yang, R.; Yu, H.; Shang, S.; Hu, Y. Short-term exposure to ambient fine particulate matter and psoriasis: A time-series analysis in Beijing, China. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1015197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, M.J.; Ahn, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Ryu, Y.S.; Hyun, Y.J.; Shilnikova, K.; Zhen, A.X.; Jeong, J.W.; Choi, Y.H.; Kang, H.K.; et al. Particulate matter 2.5 damages skin cells by inducing oxidative stress, subcellular organelle dysfunction, and apoptosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 2077–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharrhan, S.; Koul, A.; Chopra, K.; Rishi, P. Catechin suppresses an array of signalling molecules and modulates alcohol-induced endotoxin mediated liver injury in a rat model. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammeyer, A.; Luiten, R.M. Oxidation events and skin aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 21, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.P.; Chen, Q.; Dai, X.L.; Su, M.; Cheng, Y.H.; Chu, C.C.; Ren, Y.Q. Recent Trends in the Development and Application of Nano-Antioxidants for Skin-Related Disease. Antioxidants 2024, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, N.; Turpin, J.A.; Buckheit, R.W.; Osterling, C.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Howard, O.M. Shikonin, a component of chinese herbal medicine, inhibits chemokine receptor function and suppresses human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 2810–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Howard, M.Z. Cellular pharmacology studies of shikonin derivatives. Phytother Res. 2002, 16, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, D.L. Shikonin ameliorates isoproterenol (ISO)-induced myocardial damage through suppressing fibrosis, inflammation, apoptosis and ER stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 1343–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Yu, J. Shikonin attenuates kidney tubular epithelial cells apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammatory response through nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4/PTEN pathway in acute kidney injury of sepsis model. Drug Dev. Res. 2022, 83, 1111–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.J.; Xu, Y.Y.; Lan, X.O.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Gao, X.H.; Geng, L. Shikonin induces apoptosis and suppresses growth in keratinocytes via CEBP-δ upregulation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 72, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Bai, L.; Gong, R.; Chuan, J.; Duan, X.; Zhu, Y. Shikonin Protects PC12 Cells Against β-amyloid Peptide-Induced Cell Injury Through Antioxidant and Antiapoptotic Activities. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Qi, A.; Liu, L.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Cai, K.; Cai, C. Shikonin attenuates H2O2-induced oxidative injury in HT29 cells via antioxidant activities and the inhibition of mitochondrial pathway-mediated apoptosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maviah, M.B.J.; Farooq, M.A.; Mavlyanova, R.; Veroniaina, H.; Filli, M.S.; Aquib, M.; Kesse, S.; Boakye-Yiadom, K.O.; Wang, B. Food Protein-Based Nanodelivery Systems for Hydrophobic and Poorly Soluble Compounds. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Chu, G.E.; Park, S.; Park, C.; Aryal, S.; Kang, W.J.; Cho, W.G.; Key, J. Therapeutic Efficacy of Curcumin Enhanced by Microscale Discoidal Polymeric Particles in a Murine Asthma Model. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Fnu, G.; Bhatia, D.; Shahid, A.; Sutariya, V. Nanodelivery of Resveratrol-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for Age-Related Macular Degeneration. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.W. Formulation, Characterization And Evaluation Of Curcumin- Loaded PLGA- TPGS Nanoparticles For Liver Cancer Treatment. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 3569–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.A. The manufacturing techniques of various drug loaded biodegradable poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) devices. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2475–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshirsagar, S.M.; Shrestha, N.; Kipping, T.; Banga, A.K. Formulation development of tazarotene-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for follicular delivery in the treatment of inflammatory skin diseases. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2024, 200, 114346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leilei, L.; Wenke, Q.; Yuyuan, L.; Sihang, L.; Xue, S.; Weiqiang, C.; Lianbao, Y.; Ying, W.; Yan, L.; Ming, L. Oleanolic acid-loaded nanoparticles attenuate activation of hepatic stellate cells via suppressing TGF-β1 and oxidative stress in PM2.5-exposed hepatocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 437, 115891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Shang, C.; Li, Q.; Chen, L.; Yue, Z.; Ren, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W. Combined Shikonin-Loaded MPEG-PCL Micelles Inhibits Effective Transition of Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 4497–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Pan, W.; Pan, H. The reversion of anti-cancer drug antagonism of tamoxifen and docetaxel by the hyaluronic acid-decorated polymeric nanoparticles. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 126, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danhier, F.; Ansorena, E.; Silva, J.M.; Coco, R.; Le Breton, A.; Préat, V. PLGA-based nanoparticles: An overview of biomedical applications. J. Control. Release. 2012, 161, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mao, Z.; Gao, C. ROS-Responsive Nanoparticles for Suppressing the Cytotoxicity and Immunogenicity Caused by PM2.5 Particulates. Biomacromolecule 2019, 20, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.W.; Lin, Z.C.; Hu, S.C.; Chiang, Y.C.; Hsu, L.F.; Lin, Y.C.; Lee, I.T.; Tsai, M.H.; Fang, J.Y. Urban particulate matter down-regulates filaggrin via COX2 expression/PGE2 production leading to skin barrier dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Wang, H.; Huang, F.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Deng, W.; Chen, W. Investigation on the effects and mechanisms of novel peptide nanofiber gel to promote wound healing of deep second-degree burns in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 292, 139221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Hu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Feng, L.; Li, Y. Poly(ε-caprolactone)-block-poly(ethyl ethylene phosphate) micelles for brain-targeting drug delivery: In vitro and in vivo valuation. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 2657–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Yao, Q.; Ming, Y.; Li, Z.; Lu, L.; Shi, S. Ascorbyl palmitate-incorporated paclitaxel-loaded composite nanoparticles for synergistic anti-tumoral therapy. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1230–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhong, Q.; Zhong, R.; Huang, H.; Xia, Z.; Ke, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Song, J.; Jia, X. Preparation and antitumor evaluation of self-assembling oleanolic acid-loaded Pluronic P105/d-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate mixed micelles for non-small-cell lung cancer treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6337–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.W.; Zhao, P.; Khan, A.; Raza, F.; Raza, S.M.; Sarfraz, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, T.; Ma, X.; et al. Synergism of cisplatin-oleanolic acid co-loaded calcium carbonate nanoparticles on hepatocellular carcinoma cells for enhanced apoptosis and reduced hepatotoxicity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 3753–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intharuksa, A.; Arunotayanun, W.; Takuathung, M.N.; Boongla, Y.; Chaichit, S.; Khamnuan, S.; Prasansuklab, A. Therapeutic Potential of Herbal Medicines in Combating Particulate Matter (PM)-Induced Health Effects: Insights from Recent Studies. Antioxidants 2024, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.C.; Lin, S.; Wang, P.C.; Sridhar, R. Techniques for physicochemical characterization of nanomaterials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 711–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Md, S.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Rizwanullah, M.; Fatima, S.; Ahmed, N.; Alyazedi, F.M.; Karim, S.; Ahmad, J. Nanogels as Potential Delivery Vehicles in Improving the Therapeutic Efficacy of Phytopharmaceuticals. Polymers 2022, 14, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayoumi, M.; Arafa, M.G.; Nasr, M.; Sammour, O.A. Nobiletin-loaded composite penetration enhancer vesicles restore the normal miRNA expression and the chief defence antioxidant levels in skin cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; You, L.; Sun, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, P. Shikonin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: A promising strategy for psoriasis treatment. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craparo, E.F.; Musumeci, T.; Bonaccorso, A.; Pellitteri, R.; Romeo, A.; Naletova, I.; Cucci, L.M.; Cavallaro, G.; Satriano, C. mPEG-PLGA Nanoparticles Labelled with Loaded or Conjugated Rhodamine-B for Potential Nose-to-Brain Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoon, S.; Karim, S.; Bin Asad, M.H.; Akram, M.R.; Khan, A.K.; Malik, A.; Chen, C.; Murtaza, G. Anti-Aging Potential of Phytoextract Loaded-Pharmaceutical Creams for Human Skin Cell Longetivity. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 709628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Sun, X.Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Ze, K.; Chen, S.T.; Lu, Y.; Cai, X.C.; Chen, J.L.; et al. Evidence and Potential Mechanism of Action of Lithospermum erythrorhizon and Its Active Components for Psoriasis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 781850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Ren, A.; Li, T.; Jin, R.; Li, G.; Gu, X.; Shi, R.; Zhao, Y. Shikonin Suppresses Skin Carcinogenesis via Inhibiting Cell Proliferation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Huang, Z.; Weng, J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L. Effect and Mechanism of Tricholoma matsutake Extract on UVA and UVB Radiation-Induced Skin Aging. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 35, e2411085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qi, Y.; Yi, R.; Park, K.Y. Anti-ageing skin effects of Korean bamboo salt on SKH1 hairless mice. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 103, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.E.; Min, D.; Choi, J.Y.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.B.; Park, N.Y.; Jo, D.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Na, H.W.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. Primary Ciliogenesis by 2-Isopropylmalic Acid Prevents PM2.5-Induced Inflammatory Response and MMP-1 Activation in Human Dermal Fibroblasts and a 3-D-Skin Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Fang, Y.; Jia, R.; Cao, K.; Chen, X.; Xia, H.; Cheng, Z. Study on the Antioxidant Effect of Shikonin-Loaded β-Cyclodextrin Forming Host-Guest Complexes That Prevent Skin from Photoaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, G.; Dong, Q.; Duan, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; He, Q. NC2 complex is a key factor for the activation of catalase-3 transcription by regulating H2A.Z deposition. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 8332–8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovska, D.I.; Zhiponova, M.K.; Petrova, D.; Alipieva, K.; Bonchev, G.; Boycheva, I.; Evstatieva, Y.; Nikolova, D.; Tsacheva, I.; Simova, S.; et al. Exploring the Phytochemical Composition and Biological Potential of Balkan Endemic Species Stachys scardica Griseb. Plants 2023, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Xie, X.Y.; Xu, S.K.; Wang, Y.N.; Jiang, M.; Wen, L.R.; Lai, W.; Guan, L. PM2.5 Exposure Elicits Oxidative Stress Responses and Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway Activation in HaCaT Keratinocytes. Chin. Med. J. 2017, 130, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čakar, U.; Čolović, M.; Milenković, D.; Pagnacco, M.; Maksimović, J.; Krstić, D.; Đorđević, B. Strawberry and Drupe Fruit Wines Antioxidant Activity and Protective Effect Against Induced Oxidative Stress in Rat Synaptosomes. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.O.; Wang, H.X.; Qi, R.Q.; Xu, Y.Y.; Yu, Y.J.; Yang, Y.; Guo, H.; Gao, X.H.; Geng, L. Shikonin inhibits CEBPD downregulation in IL-17-treated HaCaT cells and in an imiquimod-induced psoriasis model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 2263–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, G.J.; Park, K.Y.; Lee, M.K.; Seo, S.J. Particulate matter induces pro-inflammatory cytokines via phosphorylation of p38 MAPK possibly leading to dermal inflammaging. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasarri, M.; Bergonzi, M.C.; Leri, M.; Castellacci, R.; Bucciantini, M.; De Marchi, L.; Degl’Innocenti, D. Protective Effects of Oleanolic Acid on Human Keratinocytes: A Defense Against Exogenous Damage. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.K.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, J.; Koo, J.I.; Kim, S.H. The Anti-Wrinkle Mechanism of Melatonin in UVB Treated HaCaT Keratinocytes and Hairless Mice via Inhibition of ROS and Sonic Hedgehog Mediated Inflammatory Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Sun, W.; Feng, L.; Wen, Z.; Yang, M.; Ma, Y.; Fu, J.; Ma, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Differential relieving effects of shikonin and its derivatives on inflammation and mucosal barrier damage caused by ulcerative colitis. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, P.; Wang, S.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, T.; Guo, S.; Jiang, K.; Wu, H.; Deng, G. Shikonin exerts anti-inflammatory effects in LPS-induced mastitis by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Name | Primer Sequence (5′–3′ Direction) | Genes Accession Numbers |
|---|---|---|
| SOD1 | F: AACCAGTTGTGTTGTCAGGAC | NM_011434.2 |
| R: CCACCATGTTTCTTAGAGTGAGG | ||
| SOD2 | F: CAGACCTGCCTTACGACTATGG | NM_013671.3 |
| R: CTCGGTGGCGTTGAGATTGTT | ||
| TNF-α | F: TAGCCCACGTCGTAGCAAAC | NM_013693.3 |
| R: TGTCTTTGAGATCCATGCCGT | ||
| IL-1β | F: TGCCACCTTTTGACAGTGATG | NM_008361.4 |
| R: TGATGTGCTGCTGCGAGATT | ||
| Actin | F: CGTTGACATCCGTAAAGACCTC | NM_007393.5 |
| R: TAGGAGCCAGGGCAGTAATCT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, F.; Tang, Q.; Wang, K.; Zhou, L.; Liao, R.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, M. Shikonin-Loaded Nanoparticles Attenuate Particulate Matter-Induced Skin Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14111301
Huang F, Tang Q, Wang K, Zhou L, Liao R, Wang Z, Li Y, Zhou L, Li M. Shikonin-Loaded Nanoparticles Attenuate Particulate Matter-Induced Skin Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(11):1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14111301
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Feifei, Qinghua Tang, Ke Wang, Lingmei Zhou, Ruiwei Liao, Zhuoya Wang, Yan Li, Lin Zhou, and Ming Li. 2025. "Shikonin-Loaded Nanoparticles Attenuate Particulate Matter-Induced Skin Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation" Antioxidants 14, no. 11: 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14111301
APA StyleHuang, F., Tang, Q., Wang, K., Zhou, L., Liao, R., Wang, Z., Li, Y., Zhou, L., & Li, M. (2025). Shikonin-Loaded Nanoparticles Attenuate Particulate Matter-Induced Skin Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Antioxidants, 14(11), 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14111301








