Abstract
Cyanidioschyzon merolae, an extremophilic unicellular red alga thriving in acidic hot springs at temperatures of 40–56 °C and pH 0.5–4.0, faces extreme oxidative stress conditions. This study presents a comprehensive genomic analysis of the carotenoid and vitamin E biosynthetic pathways, which are essential for antioxidant defense in this organism. Through comparative genomics using Arabidopsis thaliana sequences as queries, we identified and characterized genes encoding key enzymes involved in their metabolism. Our analysis reveals that C. merolae exclusively utilizes the methylerythritol-4-phosphate (MEP) pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis and lacks a complete mevalonate (MVA) pathway. We identified eleven genes involved in terpenoid metabolism and seven genes specifically for carotenoid biosynthesis. Pigment analysis confirmed a streamlined carotenoid profile consisting solely of β-carotene, β-cryptoxanthin, and zeaxanthin, lacking the entire β,ε-branch and part of the β,β-branch. The complete tocopherol biosynthetic pathway produces exclusively α-tocopherol. The absence of the β,ε-carotenoid branch and the exclusive production of α-tocopherol demonstrate metabolic streamlining while maintaining antioxidant efficacy. These findings provide molecular blueprints for biotechnological applications, enabling targeted strategies to enhance antioxidant production through pathway optimization and metabolic engineering, while offering insights into developing stress-tolerant organisms and enhancing nutritional content in crops.
1. Introduction
Algae represent one of the most diverse and promising groups of organisms for sustainable bioresource development [1]. They offer exceptional versatility in producing high-value compounds, including proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, pigments, and bioactive molecules, while addressing global challenges related to food security, renewable energy, and environmental sustainability [2,3]. Microalgae such as Chlorella and Spirulina have already established themselves in the production of essential amino acids and vitamins, while Dunaliella salina serves as the primary commercial source of natural β-carotene, and Haematococcus pluvialis produces the potent antioxidant astaxanthin [4,5,6,7]. Beyond nutraceuticals, algae exhibit great potential for biofuel production, carbon dioxide sequestration, wastewater treatment, and the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds [8,9]. Their autotrophic nature, rapid growth, minimal land requirements, and ability to thrive in non-arable environments make algae particularly attractive for sustainable biotechnology applications that do not compete with traditional agriculture.
Over the course of evolution, some algae have developed unique adaptations to extreme environments. For example, the unicellular red alga Cyanidioschyzon merolae was first isolated from an acidic hot spring and can survive under extreme conditions, including temperatures ranging from 40 °C to 56 °C and pH levels of 0.5 to 4.0 [10,11]. This unique feature suggests that C. merolae can serve as a robust chassis for bioproduction. The extreme conditions for its optimal growth effectively reduce the need for contamination management. Notably, like other photosynthetic organisms, C. merolae naturally produces high-value antioxidants, including provitamin A carotenoids (β-carotene, β-cryptoxanthin, and zeaxanthin) and α-tocopherol (vitamin E), compounds of significant commercial value in the pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmetic industries [12,13].
Unlike most eukaryotes, C. merolae possesses one of the smallest genomes, a single chloroplast, and a single mitochondrion [10]. The compact genome and simple cell structure enable the elucidation and further modification of its relatively simple metabolic network for the production of high-value products, without interference from multiple competing metabolic branches, as is often observed in green algae and higher plants.
The availability of complete genome sequences serves as a foundational resource that revolutionizes our ability to identify and characterize the complete sets of genes involved in specific metabolic pathways. Homologous genes can be identified through sequence similarity searches against well-characterized model organisms. This genomic foundation is particularly critical for non-model organisms with limited prior research, such as extremophilic algae. Furthermore, complete genome sequences are indispensable for developing genetic tools, designing targeted knockouts or overexpression systems, and applying synthetic biology approaches to enhance or redirect metabolic flux toward desired products.
Both carotenoids and vitamin E are essential antioxidant compounds synthesized in plastids, and geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP) produced via the plastidial 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathway serves as a common substrate for their biosynthesis [14]. While carotenoids and vitamin E are crucial for human health, most animals, including humans, are unable to synthesize these essential nutrients and must rely on dietary sources for their intake [15]. Although metabolic pathways for synthesizing carotenoids and vitamin E have been extensively studied in higher plants, where their constituent profiles and corresponding genes are relatively conserved, very limited information is currently available in algae, which display significant diversity [16,17]. For example, Euglenophyta contain diadinoxanthin and diatoxanthin, Dinophyta (dinoflagellates) are characterized by the presence of peridinin, and some classes of Heterokontophyta have fucoxanthin as their unique carotenoid [18,19]. In addition to these examples, C. merolae, as a member of the most primitive lineage of red algae, is able to synthesize only β-carotene, β-cryptoxanthin, and zeaxanthin, which represent the simplest repertoire of carotenoids among all eukaryotic photosynthetic organisms [20].
Although the genome of C. merolae has been sequenced, there are only limited reports on its metabolic pathways [20]. This study focuses specifically on genes involved in carotenoid and vitamin E biosynthesis. By identifying these genes and outlining potential metabolic branches, we establish a foundation for transforming C. merolae from a biological curiosity into a tractable biotechnological platform with predictable and modifiable metabolic capabilities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material and Growth Conditions
C. merolae strain 10D was a gift from Dr. Jianren Shen. The alga was cultivated in 2× Allen’s medium (pH 2.5) at 42 °C under 55 μmol photon m–2 s–1 and a 12 h/12 h light/dark regime [21]. The culture was shaking at 100 rpm. Cells were harvested by centrifugation at 8000× g for 5 min for chemical analysis. Three batches of cultivated cells were used as repeats for chemical analysis below.
2.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
We used the tblastx algorithm and functionally identified sequences of the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana’s and the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae’s genes as queries. Sequence similarities of the C. merolae genes with their A. thaliana and S. cerevisiae homologs were calculated using the online sequence alignment tool (https://en.vectorbuilder.com/tool/sequence-alignment.html, accessed on 1 May 2025). All sequence information is presented in Table 1. The C. merolae genome sequence was from http://merolae.biol.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp (accessed on 1 May 2025).

Table 1.
Genes encoding enzymes involved in carotenoid and vitamin E metabolism in C. merolae.
Table 1.
Genes encoding enzymes involved in carotenoid and vitamin E metabolism in C. merolae.
| Gene 1 | C. merolae Gene ID | A. thaliana | S. cerevisiae | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homolog ID | Similarity | Homolog ID | Similarity | ||
| DXS | CMF089C | At4g15560 | 67.17% | - | - |
| DXR | CMG148C | At5g62790 | 64.77% | - | - |
| MCT | CMH115C | At2g02500 | 54.30% | - | - |
| CMK | CMS444C | At2g26930 | 50.84% | - | - |
| MDS | CMT435C | At1g63970 | 29.21% | - | - |
| HDS | CML284C | At5g60600 | 38.39% | - | - |
| HDR | CMJ152C | At4g34350 | 68.67% | - | - |
| IDI | CMB062C | At3g02780 | 55.31% | BK006949.2 | 48.45% |
| HMGS | CMM189C | At4g11820 | 50.64% | NM_001182489.1 | 51.73% |
| AACT1 | CMA042C | At5g47720 | 51.26% | BK006942.2 | 60.22% |
| AACT2 | CME087C | At5g48230 | 62.39% | BK006949.2 | 48.33% |
| AACT3 | CMR380C | At5g47720 | 21.54% | BK006942.2 | 23.77% |
| FPPS | CMM269C | At4g17190 | 63.21% | BK006943.2 | 61.22% |
| GGPPS | CMK058C | At4g36810 | 61.27% | BK006936.2 | 21.32% |
| PSY | CMM166C | At5g17230 | 46.95% | - | - |
| PDS | CMK151C | At4g14210 | 68.72% | - | - |
| ZDS | CMT061C | At3g04870 | 63.71% | - | - |
| ZISO | CMQ364C | At1g10830 | 47.80% | - | - |
| CRTISO | CMN268C | At1g06820 | 52.75% | - | - |
| LCYB | CMK050C | At3g10230 | 53.44% | - | - |
| CrtR | CMV041C | - | - | - | - |
| HPPD | CMI063C | At1g06570 | 50.31% | - | - |
| GGR | CMJ154C | At1g74470 | 71.46% | - | - |
| VTE1 | CML326C | At4g32770 | 41.07% | - | - |
| VTE2.1 | CMN202C | At2g18950 | 55.88% | - | - |
| VTE2.2 | CMS413C | At2g18950 | 47.86% | - | - |
| VTE3 | CMD011C | At3g63410 | 62.83% | - | - |
| VTE4 | CMT560C | At1g64970 | 43.03% | - | - |
| VTE5 | CMR252C | At5g04490 | 39.42% | - | - |
| VTE6 | CMS030C | At1g78620 | 52.28% | - | - |
1 Full names of the genes are provided in the legend of Figure 1.

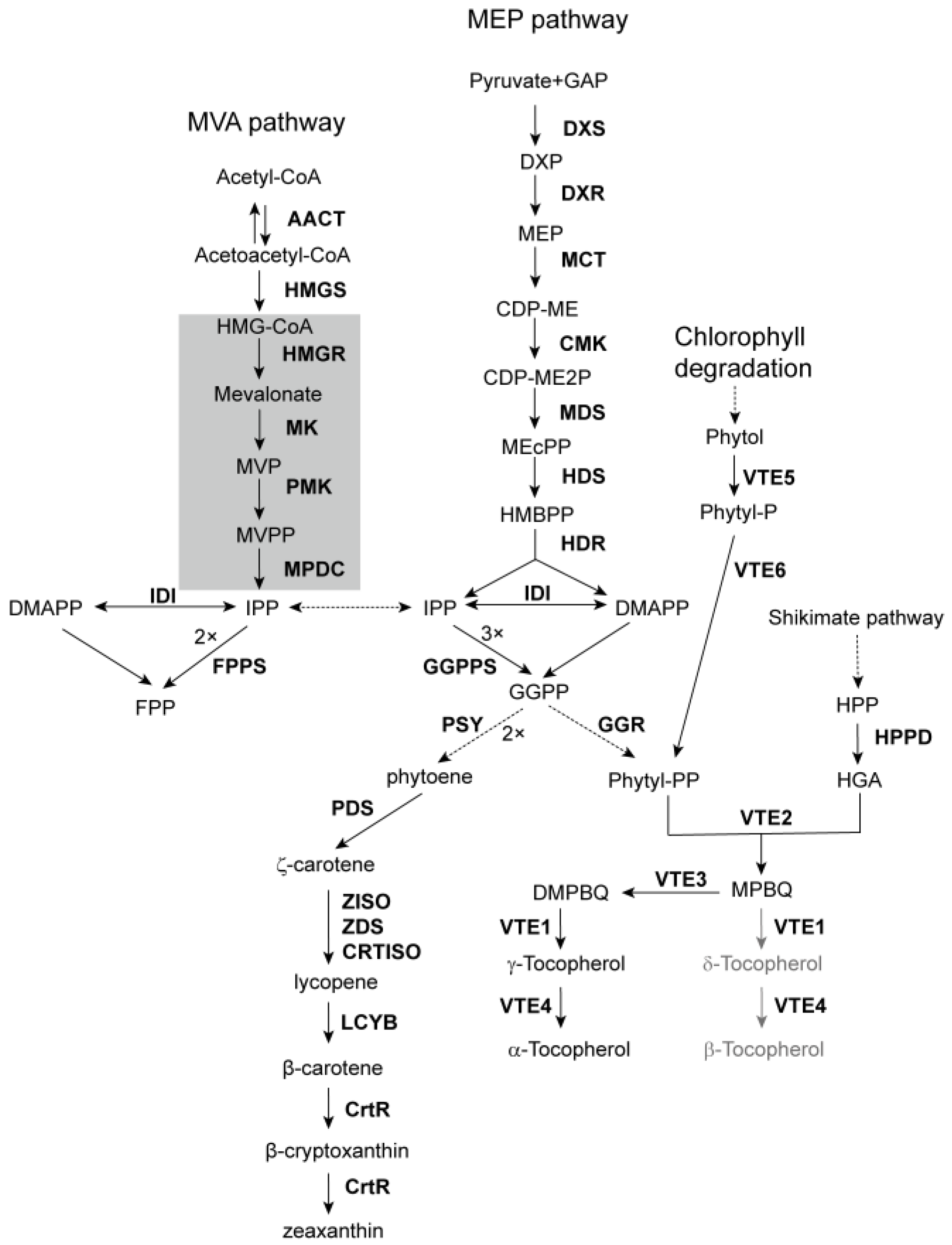
Figure 1.
Carotenoid and tocopherol biosynthetic pathways in C. merolae. The shadowed area indicates the metabolic steps that are absent in C. merolae. Dashed arrows indicate multiple steps. Gray arrows and products indicate undiscovered metabolic steps. Abbreviations of the metabolites are: GAP, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; DXP, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate; MEP, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate; CDP-ME, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-d-erythritol; CDP-ME2P, 4-cytidinediphospho-2-C-methylerythritol 2-phosphate; MEcPP, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclo-diphosphate; HMBPP, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate; HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA; MVP, mevalonate phosphate; MVPP, mevalonate diphosphate; IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate; DMAPP, dimethylallyl diphosphate; GGPP, geranylgeranyl diphosphate; HPP, 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate; HGA, homogentisic acid; MPBQ, 2-methyl-6-phytyl-1,4-benzoquinol; DMPBQ, 2,3-dimethyl-6-phytyl-1,4-benzoquinone (DMPBQ); and for the enzymes (in bold) are: AACT, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase; HMGS, HMG-CoA synthase; HMGR, HMG-CoA reductase; MK, mevalonate kinase; PMK, phosphomevalonate kinase; MPDC, mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase; DXS, DXP synthase; DXR, DXP reductoisomerase; MCT, MEP cytidylyltransferase; CMK, CDP-ME kinase; MDS, MEcPP synthase; HDS, HMBPP synthase; HDR, HMBPP reductase; IDI, IPP/DMAPP isomerase; GGPPS, GGPP synthase; PSY, phytoene synthase; PDS, phytoene desaturase; ZISO, ζ-carotene isomerase; ZDS, ζ-carotene desaturase; CRTISO, carotene isomerase; LCYB, lycopene β-cyclase; CrtR, carotene hydroxylase; GGR, geranylgeranyl reductase; VTE5, phytol kinase; VTE6, phytyl phosphate kinase; HPPD, 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase; VTE2, HGA phytyltransferase; VTE3, MPBQ methyltransferase; VTE1, tocopherol cyclase; VTE4, γ-tocopherol methyltransferase.
Figure 1.
Carotenoid and tocopherol biosynthetic pathways in C. merolae. The shadowed area indicates the metabolic steps that are absent in C. merolae. Dashed arrows indicate multiple steps. Gray arrows and products indicate undiscovered metabolic steps. Abbreviations of the metabolites are: GAP, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; DXP, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate; MEP, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate; CDP-ME, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-d-erythritol; CDP-ME2P, 4-cytidinediphospho-2-C-methylerythritol 2-phosphate; MEcPP, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclo-diphosphate; HMBPP, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate; HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA; MVP, mevalonate phosphate; MVPP, mevalonate diphosphate; IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate; DMAPP, dimethylallyl diphosphate; GGPP, geranylgeranyl diphosphate; HPP, 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate; HGA, homogentisic acid; MPBQ, 2-methyl-6-phytyl-1,4-benzoquinol; DMPBQ, 2,3-dimethyl-6-phytyl-1,4-benzoquinone (DMPBQ); and for the enzymes (in bold) are: AACT, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase; HMGS, HMG-CoA synthase; HMGR, HMG-CoA reductase; MK, mevalonate kinase; PMK, phosphomevalonate kinase; MPDC, mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase; DXS, DXP synthase; DXR, DXP reductoisomerase; MCT, MEP cytidylyltransferase; CMK, CDP-ME kinase; MDS, MEcPP synthase; HDS, HMBPP synthase; HDR, HMBPP reductase; IDI, IPP/DMAPP isomerase; GGPPS, GGPP synthase; PSY, phytoene synthase; PDS, phytoene desaturase; ZISO, ζ-carotene isomerase; ZDS, ζ-carotene desaturase; CRTISO, carotene isomerase; LCYB, lycopene β-cyclase; CrtR, carotene hydroxylase; GGR, geranylgeranyl reductase; VTE5, phytol kinase; VTE6, phytyl phosphate kinase; HPPD, 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase; VTE2, HGA phytyltransferase; VTE3, MPBQ methyltransferase; VTE1, tocopherol cyclase; VTE4, γ-tocopherol methyltransferase.
2.3. Metabolite Analysis
For terpenoid analysis, pelleted algal cells were extracted with methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE). The sample was subjected to gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) analysis using a GC-MS-TQ8050 NX system (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) and an HP-5MS (30 m × 0.25 mm; film thickness, 0.25 μm) column (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Helium was used as the carrier gas. The GC oven temperature was programmed as follows: the initial temperature was 45 °C and held for 2 min, increased at a rate of 10 °C min–1 up to 250 °C and held for 5 min. The ion source temperature was set to 280 °C. The acquisition was made in scan mode (60 to 300 m/z).
Carotenoid detection is carried out according to the previous report [22]. In brief, to 100 mg pelleted cells, 400 μL 80% acetone, 250 μL ethyl acetate, and 250 μL distilled water were added sequentially, with a 30 s vortex after each addition to mix thoroughly. After centrifugation at 15,000× g for 10 min, the upper organic phase was collected for high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis. An Agilent 1260 HPLC system (Agilent) with a Spherisorb ODS2 column (5 μm, 4.6 mm × 250 mm) (Waters, Milford, MA, USA) and a 2998 photodiode array detector (PDA, Agilent) was used. A 30 min gradient of ethyl acetate (0–66.7%) in mobile phase A (acetonitrile:water:trimethylamine = 9:1:0.01, v/v/v) at 35 °C was used.
For vitamin E analysis, 1 mL hexane containing 0.01% butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) as an antioxidant was mixed thoroughly with 100 mg pelleted algal cells by vortex. The extract was left at room temperature for 20 min and then centrifuged at 4000× g for 10 min. The pellet was repeatedly extracted once. The upper organic phase was combined and dried under a stream of nitrogen. The dried samples were redissolved in 200 μL of methanol for HPLC analysis. An Agilent 1260 HPLC system equipped with an Eclipse Plus C18 (4.6 × 250 mm, 5 μm) column and a 2998 PDA was used for separation. The elution conditions were 100% mobile phase (methanol:water = 98:2) at 1 mL min–1, and the detection wavelength was 292 nm. The retention times of each peak were compared with those of authentic chemicals that were analyzed in parallel for identification [23,24].
For each batch of cultivated algal cells, three repeats were performed for each of the GC-MS assay of terpenoids, and the HPLC assay of carotenoids and vitamin E.
3. Results
3.1. Terpenoid Metabolism
Terpenoids represent the largest class of natural products, which are ubiquitously synthesized in all organisms, with more than 80,000 structures characterized to date [25]. Although the structures and functions of terpenoids are highly diverse, all of them share the same C5 isoprenoid precursors, isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and its isomer dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP). In vascular plants, these precursors are synthesized through two parallel pathways: the cytosolic mevalonate (MVA) pathway and the plastidial MEP pathway [26]. However, algae display a great diversity in the operation of these two pathways. For example, while green algae and most multicellular red algae exclusively use the MEP pathway, some unicellular red algae have been reported to possess both pathways [27].
Our comprehensive search of the C. merolae genome revealed a total of 13 genes involved in terpenoid biosynthesis, including all eight genes of the MEP pathway, the first 3 of the MVA pathway, and 3 short-chain prenyltransferases (PTs) (Table 1). For the MEP pathway, there is one gene copy for each of the following eight enzymes: (1) 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP) synthase (DXS), which catalyzes the condensation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and pyruvate to produce DXP; (2) DXP reductoisomerase (DXR), which converts DXP to MEP as the first rate-limiting step in terpenoid metabolism; (3) MEP cytidyltransferase (MCT), which converts MEP into 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol (CDP-ME); (4) CDP-ME kinase (CMK), which further phosphorylates CDP-ME into 4-cytidinediphospho-2-C-methylerythritol 2-phosphate (CDP-ME2P); (5) 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclo-diphosphate (MEcPP) synthase (MDS), which uses CDP-ME2P as a substrate to synthesize MEcPP; (6) 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate (HMBPP) synthase (HDS), which converts MEcPP to HMBPP; (7) HMBPP reductase (HDR), which produces both IPP and DMAPP simultaneously, with a preference for IPP; and (8) IPP/DMAPP isomerase (IPI), which interconverts IPP and DMAPP to maintain their balance (Figure 1) [14].
Using A. thaliana genes of the MVA pathway as queries, we identified only three C. merolae homologous genes: two genes encoding acetyl-CoA acetyltransferases (AACTs), which catalyze the condensation of acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl-CoA, and one gene encoding 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) synthase (HMGS), which catalyzes the biosynthesis of HMG-CoA as the first rate-limiting step of the pathway, as reported in vascular plants (Table 1, Figure 1) [28,29]. No homologous genes encoding enzymes beyond HMG-CoA in this pathway could be identified using the corresponding A. thaliana sequences as queries. However, considering the extreme evolutionary distance between these two organisms, the C. merolae homologs may have sequence similarities too low to be detected by the A. thaliana queries. For this reason, we used the annotated HMGS, HMGR, MK, and MPDC sequences from the green alga Mesostigma viride, which has been proposed as an ancient streptophyte, as queries for another round of blast search [28]. However, our BLAST (ver. 2.16.0) search identified only one HMGS gene from the C. merolae genome, which was identical to the one obtained using AtHMGS as a query (Table S1). Moreover, because the M. viride gene sequences deposited in GenBank are incomplete, the sequence similarity between C. merolae and M. viride HMGS homologs was slightly lower than that between the C. merolae homolog and AtHMGS (Table S1).
Because most of the algal genes related to terpenoid metabolism have been actually annotated or predicted using A. thaliana and other model land plants genes as queries [30,31,32], there is a possibility that C. merolae genes of the MVA pathway have an alternative origin. Therefore, we further used genes from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as queries to search the C. merolae genome. Again, no homologous genes beyond HMGS could be identified (Table 1). However, an additional AACT (CmAACT3) was identified, sharing 23.77% and 21.54% sequence similarities with its S. cerevisiae (BK006942.2) and A. thaliana (At5g47720) homologs, respectively (Table 1). Encouraged by this result, we further used HMGR sequences from a bacterium (Pediococcus pentosaceus, NC_008525.1) and an animal (Mus musculus, XM_146397.3) as queries. However, no C. merolae homolog could be identified from the genome (Table S1). Taken together, it is unlikely that C. merolae operates both MVA and MEP pathways as does another unicellular red alga, Galdieria sulphuraria [33]. Its IPP and DMAPP required for terpenoid biosynthesis are probably derived exclusively from the MEP pathway. According to the endosymbiosis theory, red algae evolved after an ancestral cyanobacterium operating the MEP pathway was engulfed by a eukaryotic host operating the MVA pathway [34]. Therefore, the ancestral red alga might have harbored both pathways, as reflected by modern G. sulphuraria and a few other unicellular red algae. Both G. sulphuraria and C. merolae have highly compact genomes with low gene numbers and are proposed to have experienced extensive gene reduction [35]. It is possible that different repertoires of genes were lost during the evolution of these two species, both of which belong to the most primitive red algal class Cyanidiophyceae.
PTs are a class of enzymes that catalyze the sequential condensation of different numbers of IPP molecules to one molecule of DMAPP, generating prenyl diphosphates with varying chain lengths. These enzymes are typically named after their respective products [36]. For instance, geranyl diphosphate (GPP, C10) synthase (GPPS) utilizes IPP and DMAPP at a 1:1 ratio to produce GPP, the immediate precursor of monoterpenoids; farnesyl diphosphate (FPP, C15) synthase (FPPS) utilizes a 2:1 ratio to produce FPP, a common substrate for synthesizing sesquiterpenoids and sterols (C30); and geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP, C20) synthases (GGPPS) utilizes a 3:1 ratio to produce GGPP, a central intermediate shared among multiple downstream pathways, including those for diterpenoid products, tetraterpenoids (C40, e.g., carotenoids and their derivatives), and the side chains of chlorophylls and vitamin E. Sequence analysis has shown that GPPS and GGPPS share a high degree of similarity and are generally classified within the same enzyme family. In contrast, FPPS constitutes a distinct evolutionary lineage [37].
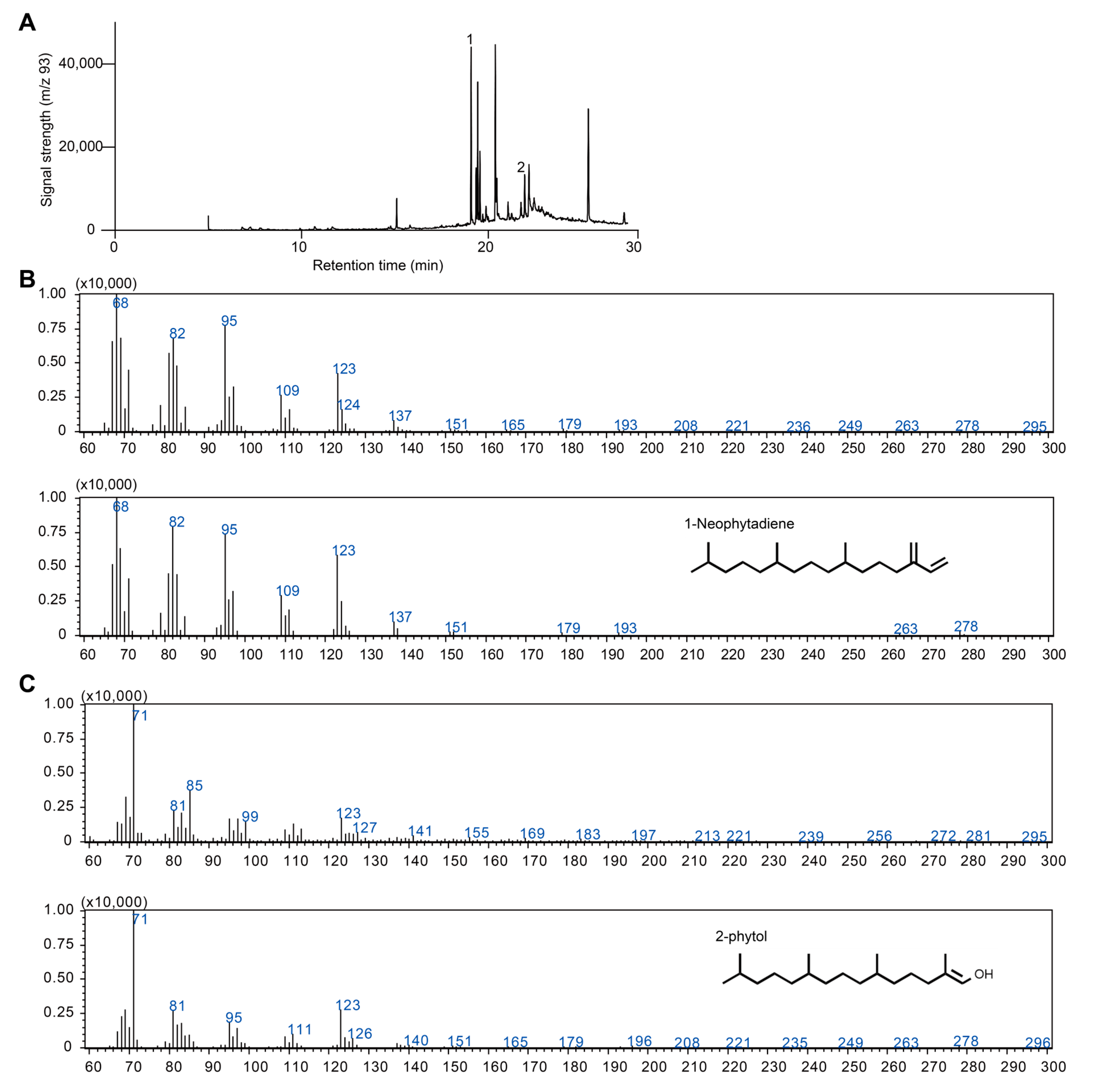
In our genome-wide analysis, we identified one gene homologous to the FPPS family and another belonging to the GPPS/GGPPS family (Table 1; Figure 1). The presence of both genes might suggest the capability of synthesizing monoterpenoids and sesquiterpenoids, and occasional reports have described such constituents in red algae [38,39]. However, several lines of evidence challenge these findings. First, the biosynthesis of monoterpenoids and sesquiterpenoids typically requires specific terpene synthases (TPSs) that utilize GPP and FPP as substrates [40]. Recent evolutionary analyses indicate that plant-type TPS enzymes only emerged after the divergence of land plants from their charophytic algal ancestors. Moreover, no microbial-type TPS homologs have been detected in the C. merolae genome [41,42,43]. In addition, previous studies revealed that members of the GPPS/GGPPS family in red algae are bona fide GGPPSs that produce only GGPP. The capability of these enzymes to generate GPP appears to have originated in early land plants such as bryophytes [37,44,45]. Taken together, these findings suggest that C. merolae is unlikely to synthesize mono- or sesquiterpenoid products, at least not through the canonical metabolic pathway observed in other plant lineages. To further confirm our conclusion, we cultivated C. merolae and extracted its volatile constituents for GC-MS analysis. From this analysis, only two diterpenoid compounds, 1-neophytadiene and 2-phytol, were identified, which appear to be generated from chlorophyll degradation (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
GC-MS analysis and identification of terpenoid compounds in C. merolae. (A) GC-MS profile of C. merolae extract. Only peaks 1 and 2 were identified as terpenoids. (B) Comparison of the mass spectrum of peak 1 (top) and the standard spectrum of 1-neophytadiene (bottom). (C) Comparison of the mass spectrum of peak 2 (top) and the standard spectrum of 2-phytol.
3.2. Carotenoid Biosynthesis
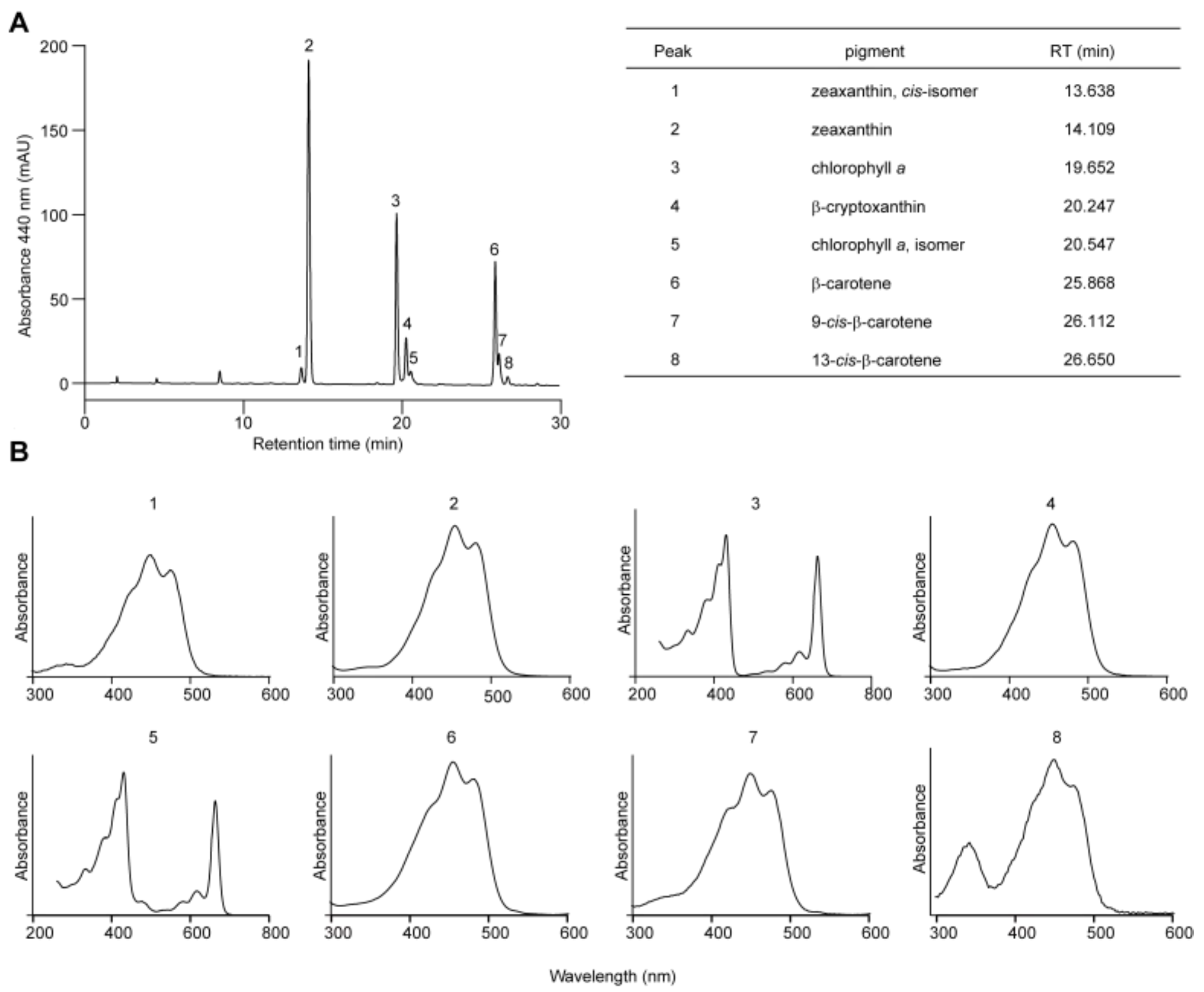
Carotenoid biosynthesis begins with the condensation of two molecules of GGPP by phytoene synthase (PSY) to form phytoene, which acts as the entry enzyme channeling GGPP flux into the carotenoid pathways (Figure 1). Vascular plants share a common carotenoid profile that includes constituents containing either two β-rings (the β,β-branch, e.g., β-carotene, zeaxanthin, antheraxanthin, violaxanthin, etc.) or one β- and one ε-rings (the β,ε-branch, e.g., α-carotene and lutein). Since the 1990s, the genes and enzymes involved in carotenoid biosynthesis in plants and microorganisms have been gradually elucidated [16]. Generally, phytoene undergoes two desaturation and two isomerization steps catalyzed sequentially by phytoene desaturase (PDS), ζ-carotene isomerase (ZISO), ζ-carotene desaturase (ZDS), and carotene isomerase (CRTISO), to produce linear lycopene (Figure 1). Lycopene represents the first branching point in carotenoid metabolism. It may be cyclized by lycopene β-cyclase (LCYB) alone, introducing two β-rings to both open ends to form β-carotene and its derivatives in the β,β-branch, or by LCYB together with lycopene ε-cyclase (LCYE), introducing one β- and one ε-ring to form α-carotene and its derivatives in the β,ε-branch (Figure 1). In rare species, lycopene can also be cyclized by LCYE alone to produce ε-carotene and its derivatives that have two ε-rings on both ends. Consistent with the previous report [20], our HPLC analysis revealed only β-carotene, zeaxanthin, and their metabolic intermediates in C. merolae, suggesting that it possesses the simplest carotenoid repertoire among photosynthetic eukaryotes, similar to that of the prokaryotic cyanobacteria (Figure 3).

Figure 3.
Pigment profile of C. merolae. (A) HPLC separation of pigments extracted from C. merolae culture. Retention times of numbered peaks (1–8) are provided. (B) UV-Vis absorption spectra for each numbered peak.
From our search, we identified a total of seven homolog genes encoding enzymes for carotenoid biosynthesis in C. merolae, including PSY, PDS, ZDS, ZISO, CRTISO, LCYB, and a non-heme CrtR-type carotene hydroxylase (Table 1, Figure 1). Interestingly, whereas previous studies in red algae identified only a single gene for PDS and ZDS in Porphyra umbilicalis, we found two separate genes encoding these two enzymes in C. merolae (Table 1) [46]. We further performed a BLAST search of their homologs in other red algal species with complete genomes and identified homologs for both enzymes in most of them. The lack of additional homologous desaturase genes in the carotenoid pathway in P. umbilicalis may be due to a genome assembly issue.
LCYB has been previously characterized. Recent studies of other lycopene cyclases demonstrated a duplication and neofunctionalization of LCYE within red algae, parallelling a similar event in the green lineage [47]. The absence of the complete β,ε-branch of carotenoids is in agreement with the absence of LCYE in C. merolae. Conversion of β-carotene to zeaxanthin requires carotene β-hydroxylase, which is typically mediated by non-heme and/or P450-type enzymes in vascular plants. A P450-type enzyme was previously cloned and characterized as carotene β-hydroxylase from the multicellular red algal seaweed P. umbilicalis; however, no homolog was found in the C. merolae genome [46]. Although a gene encoding a CrtR-type hydroxylase was identified and cloned from C. merolae, its cognate protein has not yet been functionally characterized, leaving the mechanism of zeaxanthin formation unclear [20]. Nevertheless, the combination of zeaxanthin accumulation, the absence of the entire β,ε-branch, and a minimal β,β-branch strongly suggests that C. merolae represents a metabolically streamlined system for carotenoid biosynthesis. This minimal carotenoid network makes it an ideal chassis for metabolic engineering, offering a clean background for the heterologous production of high-value carotenoids such as capsanthin and astaxanthin, without interference from competing endogenous pathways.
3.3. Vitamin E Biosynthesis
Vitamin E comprises a family of lipid-soluble antioxidants, including tocopherols and tocotrienols, all of which share a homogentisic acid (HGA) aromatic head group derived from the shikimate pathway. The two classes are distinguished by their side chains: tocotrienols carry an unsaturated geranylgeranyl side chain, whereas tocopherols possess a saturated phytyl side chain. The geranylgeranyl side chain is derived directly from GGPP. The phytyl side chain can arise via two routes suppling phytyl diphosphate (Phytyl-PP): one through direct reduction of GGPP by geranylgeranyl reductase (GGR) as an extension of the MEP pathway, and the other through chlorophyll degradation, in which the released phytol is sequentially re-phosphorylated by two kinases, phytol kinase (namely VTE5 in A. thaliana) and phytyl phosphate kinase (VTE6) (Table 1, Figure 1) [48].
Key genes for vitamin E biosynthesis were initially cloned and characterized in A. thaliana and the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 [17]. Besides VTE5 and VTE6 mentioned above, 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) catalyzes the initial ring-cleavage steps leading to the production of HGA (Figure 1) [49]. HGA phytyltransferase (HPT/VTE2) and HGA geranylgeranyltransferase (HGGT) catalyze the condensation of HGA with Phytyl-PP or GGPP, producing 2-methyl-6-phytyl-1,4-benzoquinol (MPBQ) or 2-methyl-6-geranylgeranyl-1,4-benzoquinol (MGGBQ), respectively (Figure 1) [50]. MPBQ can be methylated to produce 2,3-dimethyl-6-phytyl-1,4-benzoquinone (DMPBQ) by methyltransferase (VTE3) [51]. Both MPBQ and DMPBQ can be catalyzed by a cyclase (VTE1) and a methylase (VTE4) to produce α-tocopherol and β-tocopherol, respectively (Figure 1) [24,52,53]. In parallel, similar reactions starting from MGGBQ produce α- and β-tocotrienols, respectively. Tocopherols are universal compounds in most higher plants, whereas tocotrienols occur primarily in the seeds of monocot species, such as barley, wheat, oat, rye, rice, palm tree, and coconut [54].
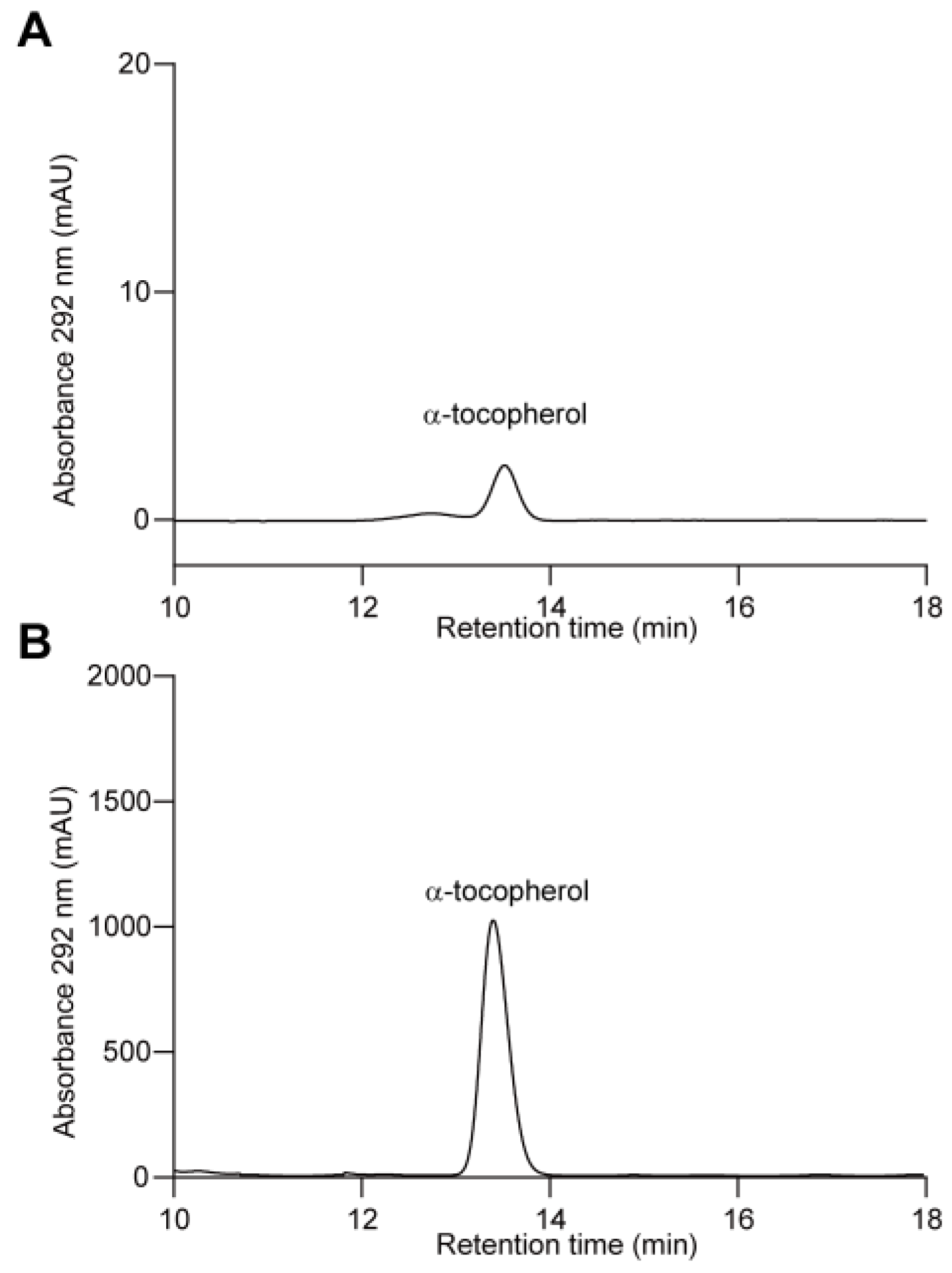
No previous studies have reported vitamin E in C. merolae before. In this study, we extracted vitamin E from cultivated algal cells and performed HPLC analysis. From our results, it was clear that only α-tocopherol could be detected, indicating that C. merolae solely uses the phytyl side chain (Figure 4 and Figure S1). However, two homologous copies of VTE2 were identified in the C. merolae genome, in contrast to A. thaliana, which has a single copy of the VTE2 gene (Table 1). It remains unclear how the two genes evolved and whether one of them was neofunctionalized to utilize GGPP for tocotrienol production [55]. In addition, the absence of β-tocopherol suggests that VTE1 preferentially utilizes DMPBQ as a substrate in C. merolae.

Figure 4.
HPLC separation of vitamin E in C. merolae. (A) HPLC separation of vitamin E extracted from C. merolae. The absorbance at 292 nm was monitored. (B) A separation of authentic α-tocopherol in parallel with (A).
4. Discussion and Conclusions
The availability of complete genome sequences provides an unprecedented opportunity for metabolic engineering. Such a strategy has been successfully applied to a wide range of microbes, crops, medicinal and industrial plants, etc. However, identifying gene homologs in primitive red algae presents significant challenges compared to land plants. The bottleneck probably lies in the limited information on the genomics and molecular biology of red algae, compared with the extensively sequenced genomes and well-studied traits of model plants and major crops such as Arabidopsis, rice, and maize. In this study, our analysis revealed complete sets of genes for the biosynthesis of carotenoids and tocopherols, two major classes of antioxidants, as well as their upstream terpenoids, in C. merolae. Our analysis has the following three main findings.
First, C. merolae has an incomplete MVA pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis. The incomplete MVA pathway without enzymes beyond HMGS (Table 1) exemplifies metabolic efficiency through evolutionary gene reduction. By exclusively utilizing the MEP pathway, the alga avoids energy-intensive cytosolic steps, optimizing isoprenoid flux toward plastidial antioxidants under stressed conditions such as high temperature and low pH. This streamlining reduces metabolic redundancy, as seen in compact genomes of extremophiles, enabling rapid adaptation to oxidative bursts in its acidic hot spring habitat [14]. Moreover, in plants, HMG-CoA functions not only as a precursor for the mevalonate pathway but also as a reversible reservoir of acetoacetyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA [56,57,58]. It is currently unclear whether the incomplete MVA pathway in C. merolae participates in the redistribution of carbon flux.
Second, C. merolae can synthesize only a limited group of carotenoids. Our genome analysis failed to identify a gene homolog for LCYE, consistent with chemical analysis indicating the absence of lutein and other carotenoid species of the β,ε-branch (Table 1, Figure 3). Moreover, there are no homologous genes for ZEP and beyond in the C. merolae genome (Table 1). This also supports our result that zeaxanthin of the β,β-branch is the end product in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway (Figure 3). Both the gene repertoire and carotenoid profile of C. merolae resemble those of prokaryotic cyanobacteria, reflecting the primitive nature of this unicellular red alga [18].
Third, α-tocopherol is the only vitamin E constituent in C. merolae. Enzymes like VTE2 (with promiscuous duplicates VTE2.1 and VTE2.2) and VTE3 exhibit mechanistic versatility. VTE2 catalyzes HGA–phytyl condensation, but its dual copies may allow substrate promiscuity, enabling further functional divergence toward handling GGPP for tocotrienol biosynthesis during evolution. Methylation of MPBQ by VTE3 ensures efficient DMPBQ formation, favoring a prompt metabolic flux from VTE2 to VTE1. This likely enhances pathway resilience by buffering against substrate fluctuations [17]. Functional assays could further elucidate these roles.
Similar to the promiscuous functions of genes for VTE2.1/2.2 and VTE3, the unresolved evolutionary relationship of AACT1/2 and PDS/ZDS with their homologs across different linages of photosynthetic organisms, as well as the puzzle surrounding the production of mono- and sesquiterpenoids, also merits further analysis.
This comprehensive identification of carotenoid and vitamin E biosynthetic genes in C. merolae provides an essential molecular blueprint for antioxidant synthesis that underpins its resilience in extreme niches. Simplified pathways (e.g., MEP-exclusive isoprenoids leading to zeaxanthin and α-tocopherol) minimize energy diversion and channel resources toward ROS scavenging. In acidic hot springs, these antioxidants may help stabilize membranes and protect photosystems from thermal and oxidative damage, enabling survival where other algae fail [10,11]. Insights gained from C. merolae’s streamlined yet efficient antioxidant machinery can guide efforts to enhance stress tolerance and nutritional value in agricultural and industrial crops, contributing to food security and sustainable agriculture under increasingly challenging environmental conditions. This study also offers strategies for advancing bioresource development and metabolic engineering applications in sustainable biotechnology. Targeted pathway optimization, gene overexpression, metabolic flux redirection, and rational synthetic biology design could help transform C. merolae into an efficient production platform for commercially valuable antioxidants.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antiox14111303/s1. Figure S1: HPLC separation of authentic standards of tocopherols in C. merolae. Table S1: Genes encoding enzymes in the MVA pathway in C. merolae identified using non-Arabidopsis queries.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.H., D.L., C.H., L.-E.Y., S.L. (Shan Lu) and Y.D.; methodology, Y.H., D.L., C.H., L.-E.Y., P.L., S.L. (Shan Lu) and Y.D.; investigation, Y.H., D.L., N.H., S.L. (Shan Luo), L.Z. (Libao Zheng), L.Z. (Linyuan Zheng) and P.L.; data curation, Y.H., D.L., N.H., S.L. (Shan Luo), L.Z. (Libao Zheng), L.Z. (Linyuan Zheng), P.L., S.L. (Shan Lu) and Y.D.; writing—original draft preparation, D.L. and S.L. (Shan Lu); writing—review and editing, D.L., S.L. (Shan Lu) and Y.D.; supervision, P.L.; project administration, C.H., S.L. (Shan Lu) and Y.D.; funding acquisition, C.H., S.L. (Shan Lu) and Y.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Seed Industry Revitalization Project of Jiangsu Province of China (No. JBGS [2021]033), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 42206134, and 32470271), and the support from the Key Laboratory of Saline-Alkali Vegetation Ecology Restoration of the Ministry of Education, College of Life Science, Northeast Forestry University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We thank Kui Li (Nanjing University) for his help with the bioinformatic analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AACT | acetyl-CoA acetyltransferases |
| BHT | butylated hydroxytoluene |
| CDP-ME | 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol |
| CDP-ME2P | 4-cytidinediphospho-2-C-methylerythritol 2-phosphate |
| CMK | CDP-ME kinase |
| CRTISO | carotene isomerase |
| DMAPP | dimethylallyl diphosphate |
| DMPBQ | 2,3-dimethyl-6-phytyl-1,4-benzoquinone |
| DXP | 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate |
| DXR | DXP reductoisomerase |
| DXS | DXP synthase |
| FPP | farnesyl diphosphate |
| FPPS | FPP synthase |
| GC-MS | gas chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| GGPP | geranylgeranyl diphosphate |
| GGPPS | GGPP synthase |
| GGR | geranylgeranyl reductase |
| GPP | geranyl diphosphate |
| GPPS | GPP synthase |
| HDR | HMBPP reductase |
| HDS | HMBPP synthase |
| HGA | homogentisic acid |
| HGGT | HGA geranylgeranyltransferase |
| HMBPP | 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate |
| HMG-CoA | 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA |
| HMGS | HMG-CoA synthase |
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| HPPD | 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase |
| HPT | HGA phytyltransferase |
| IPI | IPP/DMAPP isomerase |
| IPP | isopentenyl diphosphate |
| LCYB | lycopene β-cyclase |
| LCYE | lycopene ε-cyclase |
| MCT | MEP cytidyltransferase |
| MDS | MEcPP synthase |
| MEcPP | 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclo-diphosphate |
| MEP | 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate |
| MGGBQ | 2-methyl-6-geranylgeranyl-1,4-benzoquinol |
| MPBQ | 2-methyl-6-phytyl-1,4-benzoquinol |
| MTBE | methyl tert-butyl ether |
| MVA | mevalonate |
| PDA | photodiode array detector |
| PDS | phytoene desaturase |
| PSY | phytoene synthase |
| TPS | terpene synthase |
| ZDS | ζ-carotene desaturase |
| ZISO | ζ-carotene isomerase |
References
- Pulz, O.; Gross, W. Valuable products from biotechnology of microalgae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 65, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Ghosh, S.; Dubinsky, Z.; Verdelho, V.; Iluz, D. Unconventional high-value products from microalgae: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 329, 124895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, K.W.; Yap, J.Y.; Show, P.L.; Suan, N.H.; Juan, J.C.; Ling, T.C.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. Microalgae biorefinery: High value products perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 229, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, E.W. Micro-algae as a source of protein. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Amotz, A.; Avron, M. The biotechnology of cultivating the halotolerant alga Dunaliella. Trends Biotechnol. 1990, 8, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, J.C.; Phuc, A.P.; Dubacq, J.P. Nutritional value of the alga Spirulina. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 1995, 77, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, R.T.; Cysewski, G.R. Commercial potential for Haematococcus microalgae as a natural source of astaxanthin. Trends Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.A.V.; de Morais, M.G. The role of biochemical engineering in the production of biofuels from microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, I.; Kumar, R.R.; Mutanda, T.; Bux, F. Dual role of microalgae: Phycoremediation of domestic wastewater and biomass production for sustainable biofuels production. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3411–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, M.; Misumi, O.; Shin, I.T.; Maruyama, S.; Takahara, M.; Miyagishima, S.Y.; Mori, T.; Nishida, K.; Yagisawa, F.; Nishida, K.; et al. Genome sequence of the ultrasmall unicellular red alga Cyanidioschyzon merolae 10D. Nature 2004, 428, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seckbach, J. Algae and Cyanobacteria in Extreme Environments; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Krinsky, N.I.; Mayne, S.T.; Sies, H. Carotenoids in Health and Disease; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Packer, L.; Fuchs, J. Vitamin E in Health and Disease; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Vranová, E.; Coman, D.; Gruissem, W. Network analysis of the MVA and MEP pathways for isoprenoid synthesis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 665–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, R.; Nowicka, B.; Kruk, J. Vitamin E—Occurrence, biosynthesis by plants and functions in human nutrition. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, F.X., Jr.; Gantt, E. Genes and enzymes of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 49, 557–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DellaPenna, D.; Pogson, B.J. Vitamin synthesis in plants: Tocopherols and carotenoids. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 711–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaichi, S. Distribution, biosynthesis, and function of carotenoids in oxygenic phototrophic algae. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakahama, T.; Laza-Martínez, A.; Bin Haji Mohd Taha, A.I.; Okuyama, H.; Yoshida, K.; Kogame, K.; Awai, K.; Kawachi, M.; Maoka, T.; Takaichi, S. Structural confirmation of a unique carotenoid lactoside, P457, in Symbiodinium sp. strain NBRC 104787 isolated from a sea anemone and its distribution in dinoflagellates and various marine organisms. J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, F.X., Jr.; Lee, H.; Gantt, E. Carotenoid biosynthesis in the primitive red alga Cyanidioschyzon merolae. Eukaryot. Cell 2007, 6, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parys, E.; Krupnik, T.; Kułak, I.; Kania, K.; Romanowska, E. Photosynthesis of the Cyanidioschyzon merolae cells in blue, red, and white light. Photosynth. Res. 2021, 147, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, D.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.-E.; Hu, C.; Lu, S.; Deng, Y. Diurnal rhythm of carotenoid metabolism in the intertidal red algal seaweed Neoporphyra haitanensis. Algal Res. 2025, 85, 103846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X.; Tang, K. Engineering tocopherol biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis leaves and its effect on antioxidant metabolism. Plant Sci. 2010, 178, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, S.E.; Cahoon, E.B.; Coughlan, S.J.; DellaPenna, D. Characterization of tocopherol cyclases from higher plants and cyanobacteria. Evolutionary implications for tocopherol synthesis and function. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 2184–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, D.W. Structural and chemical biology of terpenoid cyclases. Chem Rev. 2017, 117, 11570–11648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, B.M.; Rujan, T.; Martin, W.; Croteau, R. Isoprenoid biosynthesis: The evolution of two ancient and distinct pathways across genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13172–13177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. The non-mevalonate DOXP/MEP (deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate/methylerythritol 4-phosphate) pathway of chloroplast isoprenoid and pigment biosynthesis. In The Chloroplast: Basics Applications; Rebeiz, C.A., Benning, C., Bohnert, H.J., Daniell, H., Hoober, J.K., Lichtenthaler, H.K., Portis, A.R., Tripathy, B.C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 95–118. [Google Scholar]
- Grauvogel, C.; Petersen, J. Isoprenoid biosynthesis authenticates the classification of the green alga Mesostigma viride as an ancient streptophyte. Gene 2007, 396, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Yoon, H.S.; Bhattacharya, D. Red algal phylogenomics provides a robust framework for inferring evolution of key metabolic pathways. PLoS Curr. 2016, 8, e4567. [Google Scholar]
- Blanc, G.; Duncan, G.; Agarkova, I.; Borodovsky, M.; Gumon, J.; Kuo, A.; Lindquist, E.; Lucas, S.; Pangilinan, J.; Polle, J.; et al. The Chlorella variabilis NC64A genome reveals adaptation to photosymbiosis, coevolution with viruses, and cryptic sex. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2943–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, X.; Dong, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L. An update on the function and regulation of methylerythritol phosphate and mevalonate pathways and their evolutionary dynamics. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 1211–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Dehesh, K. The eukaryotic MEP-pathway genes are evolutionarily conserved and originated from Chlaymidia and cyanobacteria. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönknecht, G.; Chen, W.-H.; Ternes, C.M.; Barbier, G.G.; Shrestha, R.P.; Stanke, M.; Bräutigam, A.; Baker, B.J.; Banfield, J.F.; Garavito, R.M.; et al. Gene transfer from bacteria and archaea facilitated evolution of an extremophilic eukaryote. Science 2013, 339, 1207–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. The 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 50, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Bautista, J.M. Red algal genomics: A synopsis. In Red Algae in the Genomic Age; Seckbach, J., Chapman, D.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- Vandermoten, S.; Haubruge, É.; Cusson, M. New insights into short-chain prenyltransferases: Structural features, evolutionary history and potential for selective inhibition. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3685–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Jin, R.; Chen, Y.; He, S.; Li, K.; Tang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Kong, M.; Dudareva, N.; et al. The functional evolution of architecturally different plant geranyl diphosphate synthases from geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 2293–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, T.S.; Burkhardt, I.; Moore, M.L.; de Rond, T.; Bone, H.K.; Barry, K.; Bunting, V.M.; Grimwood, J.; Handley, L.H.; Rajasekar, S.; et al. Biosynthesis of haloterpenoids in red algae via microbial-like type I terpene synthases. ACS Chem. Biol. 2024, 19, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, L.-Y.; Ding, L.-P.; Liang, H.; Tu, P.-F.; Zhang, Q.-Y. Antioxidant terpenoids from the red alga Laurencia tristicha. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 5048–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tholl, D. Terpene synthases and the regulation, diversity and biological roles of terpene metabolism. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Brown, R.; Köllner, T.G.; Fu, J.; Chen, X.; Wong, G.K.-S.; Gershenzon, J.; Peters, R.J.; Chen, F. Origin and early evolution of the plant terpene synthase family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2100361119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.L.; Köllner, T.G.; Yin, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, H.; Xu, Y.; Gershenzon, J.; Pichersky, E.; Chen, F. Nonseed plant Selaginella moellendorfii has both seed plant and microbial types of terpene synthases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14711–14715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Jia, Q.; Chen, X.; Köllner, T.G.; Bhattacharya, D.; Wong, G.K.-S.; Gershenzon, J.; Chen, F. Terpene biosynthesis in red algae is catalyzed by microbial type but not typical plant terpene synthases. Plant Physiol. 2019, 179, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.-Y.; Wang, Q.; Cao, T.-J.; Zheng, H.; Ge, Z.-H.; Yang, L.-E.; Lu, S. Cloning and functional characterization of the bona fide geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase from the red algal seaweed Bangia fuscopurpurea. Algal Res. 2020, 48, 101935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-E.; Huang, X.-Q.; Lu, Q.-Q.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Lu, S. Cloning and characterization of the geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase (GGPS) responsible for carotenoid biosynthesis in Pyropia umbilicalis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 28, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-E.; Huang, X.-Q.; Hang, Y.; Deng, Y.-Y.; Lu, Q.-Q.; Lu, S. The P450-type carotene hydroxylase PuCHY1 from Porphyra suggests the evolution of carotenoid metabolism in red algae. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.-Y.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Q.; Ge, Z.-H.; Zheng, H.; Cao, T.-J.; Lu, Q.-Q.; Yang, L.-E.; Lu, S. Functional characterization of lycopene cyclases illustrates the metabolic pathway toward lutein in red algal seaweeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- vom Dorp, K.; Hölzl, G.; Plohmann, C.; Eisenhut, M.; Abraham, M.; Weber, A.P.M.; Hanson, A.D.; Dörmann, P. Remobilization of phytol from chlorophyll degradation is essential for tocopherol synthesis and growth of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 2846–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritze, I.M.; Linden, L.; Freigang, J.; Auerbach, G.; Huber, R.; Steinbacher, S. The crystal structures of Zea mays and Arabidopsis 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 1388–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schledz, M.; Seidler, A.; Beyer, P.; Neuhaus, G. A novel phytyltransferase from Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 involved in tocopherol biosynthesis. FEBS Lett. 2001, 499, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motohashi, R.; Ito, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Taji, T.; Nagata, N.; Asami, T.; Yoshida, S.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Functional analysis of the 37 kDa inner envelope membrane polypeptide in chloroplast biogenesis using a Ds-tagged Arabidopsis pale-green mutant. Plant J. 2003, 34, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porfirova, S.; Bergmüller, E.; Tropf, S.; Lemke, R.; Dörmann, P. Isolation of an Arabidopsis mutant lacking vitamin E and identification of a cyclase essential for all tocopherol biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12495–12500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, D.; DellaPenna, D. Elevating the vitamin E content of plants through metabolic engineering. Science 1998, 282, 2098–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, G.; Wessjohann, L.; Bigirimana, J.; Jansen, M.; Guisez, Y.; Caubergs, R.; Horemans, N. Differential distribution of tocopherols and tocotrienols in photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic tissues. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collakova, E.; DellaPenna, D. Isolation and functional analysis of homogentisate phytyltransferase from Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, T.J. Some new aspects of isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants—A review. Lipids 1995, 30, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, T.J.; Boronat, A.; Campos, N.; Ferrer, A.; Vollack, K.-U. Mevalonate biosynthesis in plants. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 34, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Concepción, M.; Boronat, A. Elucidation of the methylerythritol phosphate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis in bacteria and plastids. A metabolic milestone achieved through genomics. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).