Associations between Brain Alpha-Tocopherol Stereoisomer Profile and Hallmarks of Brain Aging in Centenarians
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. GCS Decedents, Demographic Data, and Brain Collection
2.2. Brain and Serum Tocopherol Analysis
2.3. Diffuse Plaque, Neuritic Plaque, and Neurofibrillary Tangle Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Description
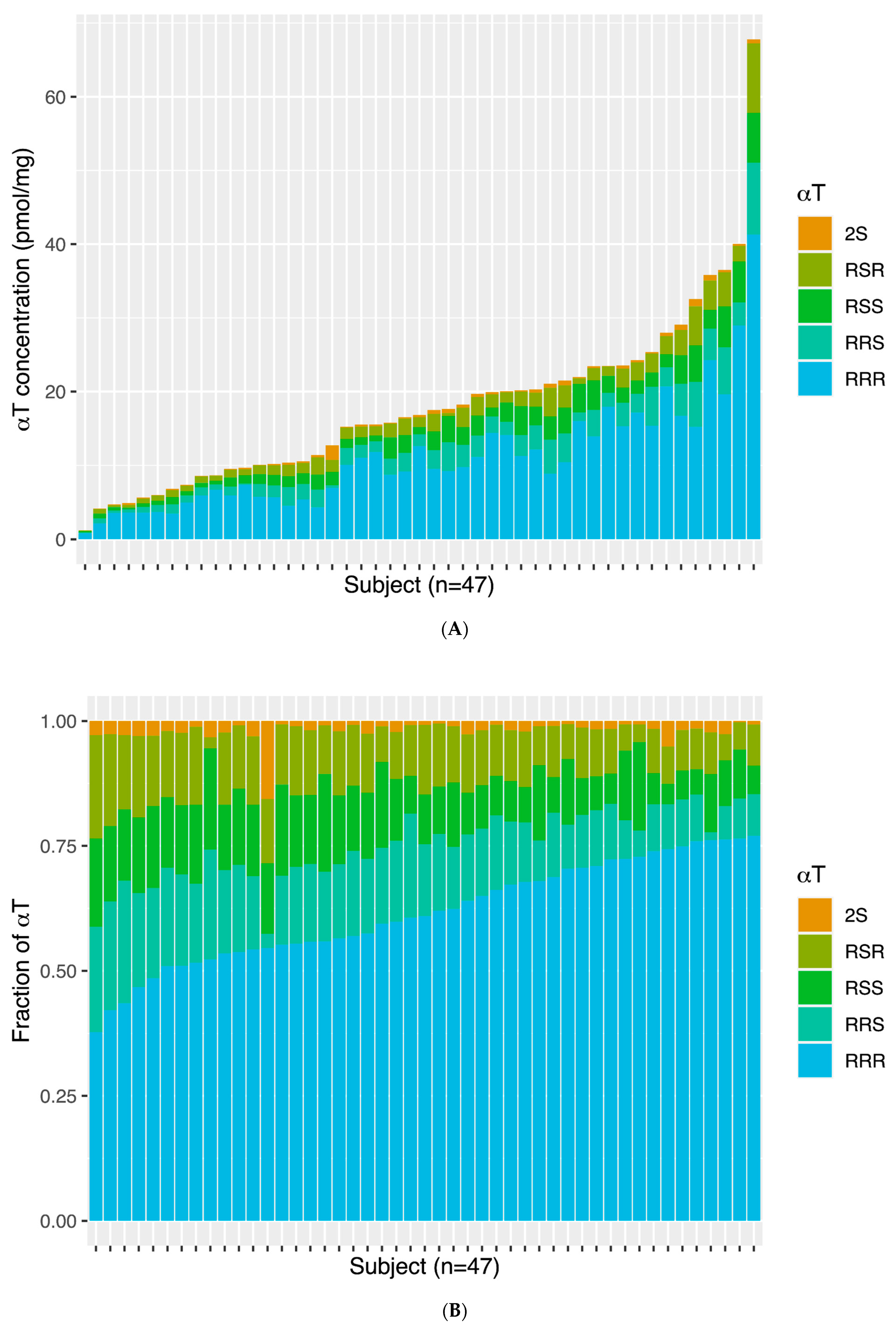
3.2. Temporal Cortex αT and γT and αT Stereoisomer Distribution
3.3. Temporal Cortex Tocopherol and Global Deterioration Scale (GDS)
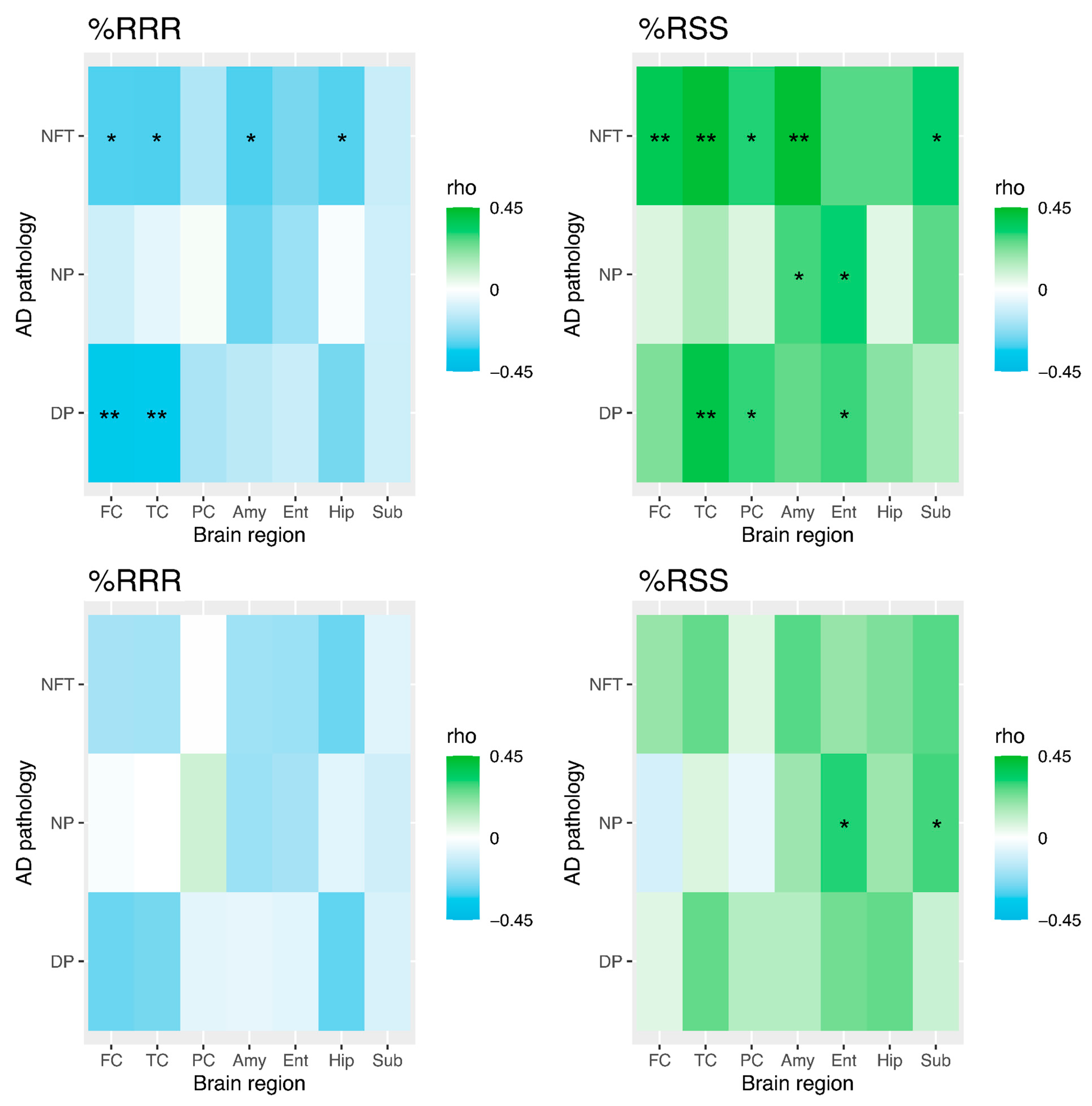
3.4. Temporal Cortex Tocopherol and Diffuse Plaques, Neuritic Plaques, and Neurofibrillary Tangles
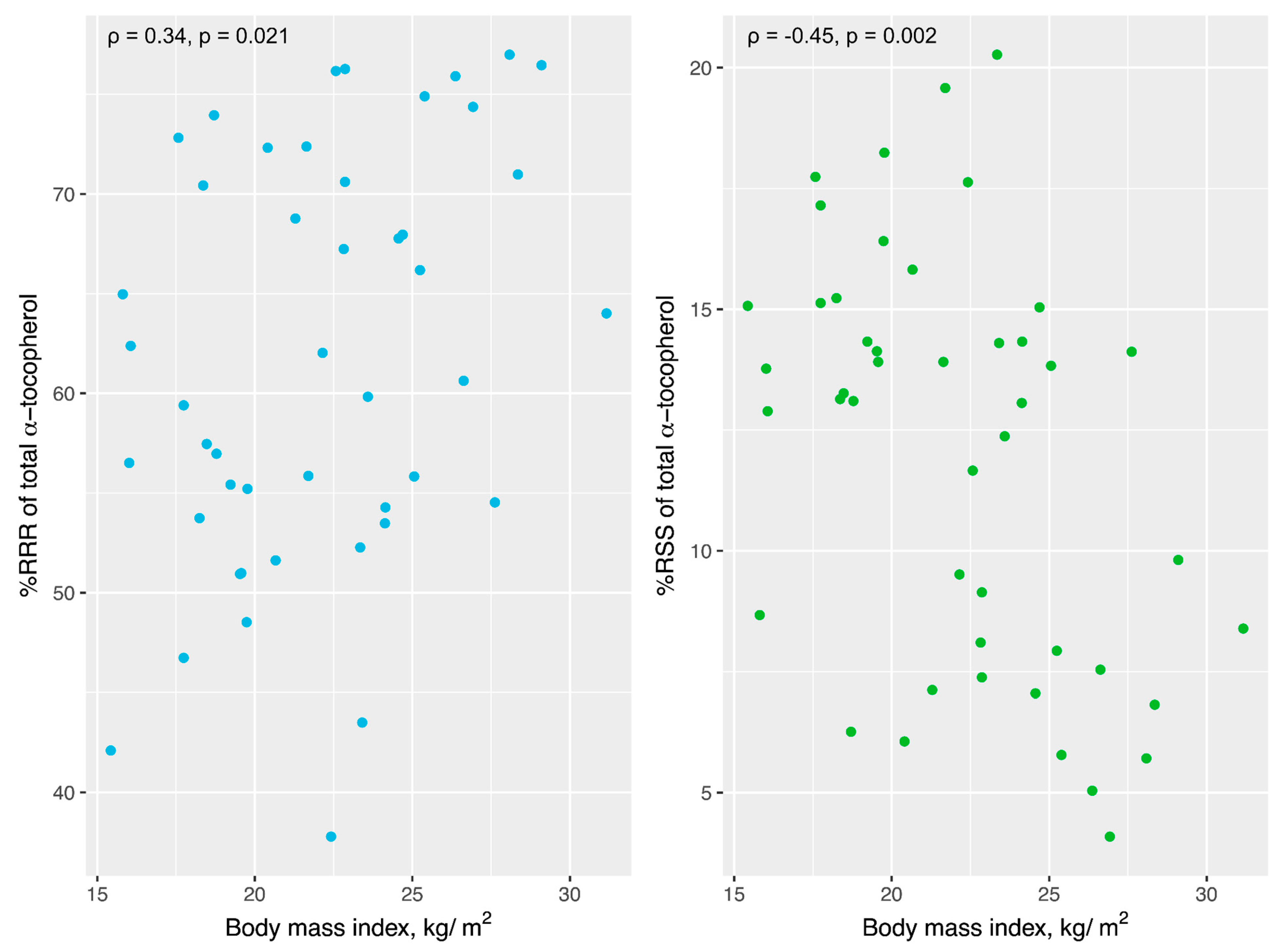
3.5. Temporal Cortex Tocopherols and BMI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Traber, M.G.; Sokol, R.J.; Ringel, S.P.; Neville, H.E.; Thellman, C.A.; Kayden, H.J. Lack of Tocopherol in Peripheral Nerves of Vitamin E-Deficient Patients with Peripheral Neuropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 317, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, R.J.; Guggenheim, M.A.; Iannaccone, S.T.; Barkhaus, P.E.; Miller, C.; Silverman, A.; Balistreri, W.F.; Heubi, J.E. Improved Neurologic Function after Long-Term Correction of Vitamin E Deficiency in Children with Chronic Cholestasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 313, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niki, E.; Traber, M.G. A History of Vitamin, E. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 61, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, D.P.R.; Lloyd, J.; Wolff, O.H. Molecular Nutrition and Food Research. Lancet 1983, 321, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.; Ulatowski, L.M. Vitamin E: Mechanism of Transport and Regulation in the CNS. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Panel on Dietary Antioxidants and Related Compounds. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0-309-06949-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hosomi, A.; Arita, M.; Sato, Y.; Kiyose, C.; Ueda, T.; Igarashi, O.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K. Affinity for Alpha-Tocopherol Transfer Protein as a Determinant of the Biological Activities of Vitamin E Analogs. FEBS Lett. 1997, 409, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranard, K.M.; Erdman, J.W. Effects of Dietary RRR α-Tocopherol vs All-Racemic α-Tocopherol on Health Outcomes. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, S.W.; Terasawa, Y.; Farese, R.V., Jr.; Traber, M.G. Incorporation of Deuterated RRR- or All-Rac-α-Tocopherol in Plasma and Tissues of α-Tocopherol Transfer Protein–Null Mice123. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 75, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, H.; Kono, N. α-Tocopherol Transfer Protein (α-TTP). Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 176, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchan, M.J.; Jensen, S.K.; Johnson, E.J.; Lieblein-Boff, J.C. The Naturally Occurring α-Tocopherol Stereoisomer RRR-α-Tocopherol Is Predominant in the uchan Brain. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.L.; Morris, J.C. Tangles and Plaques in Nondemented Aging and “Preclinical” Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 45, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denver, P.; McClean, P.L. Distinguishing Normal Brain Aging from the Development of Alzheimer’s Disease: Inflammation, Insulin Signaling and Cognition. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.L. Tangles and Plaques in Healthy Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease: Independence or Interaction? Semin. Neurosci. 1994, 6, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek-Ahmadi, M. Reversion From Mild Cognitive Impairment to Normal Cognition: A Meta-Analysis. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2016, 30, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillozet, A.L.; Weintraub, S.; Mash, D.C.; Mesulam, M.M. Neurofibrillary Tangles, Amyloid, and Memory in Aging and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ganz, A.B.; Rohde, S.; Rozemuller, A.J.M.; Bank, N.B.; Reinders, M.J.T.; Scheltens, P.; Hulsman, M.; Hoozemans, J.J.M.; Holstege, H. Resilience and Resistance to the Accumulation of Amyloid Plaques and Neurofibrillary Tangles in Centenarians: An Age-Continuous Perspective. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 2831–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrada, M.M.; Berlau, D.J.; Kawas, C.H. A Population-Based Clinicopathological Study in the Oldest-Old: The 90+ Study. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2012, 9, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, A.B.; Beker, N.; Hulsman, M.; Sikkes, S.; Netherlands Brain Bank; Scheltens, P.; Smit, A.B.; Rozemuller, A.J.M.; Hoozemans, J.J.M.; Holstege, H. Neuropathology and Cognitive Performance in Self-Reported Cognitively Healthy Centenarians. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, M.H.; Newell, K.; Brady, C.; Hedley-White, E.T.; Perls, T.T. Distinguishing between Neurodegenerative Disease and Disease-Free Aging: Correlating Neuropsychological Evaluations and Neuropathological Studies in Centenarians. Psychosom. Med. 2002, 64, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Neltner, J.H.; Abner, E.L.; Jicha, G.A.; Schmitt, F.A.; Patel, E.; Poon, L.W.; Marla, G.; Green, R.C.; Davey, A.; Johnson, M.A.; et al. Brain Pathologies in Extreme Old Age. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanprasertsuk, J.; Johnson, E.J.; Johnson, M.A.; Poon, L.W.; Nelson, P.T.; Davey, A.; Martin, P.; Barbey, A.K.; Barger, K.; Wang, X.-D.; et al. Clinico-Neuropathological Findings in the Oldest Old from the Georgia Centenarian Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. JAD 2019, 70, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klímová, B.; Vališ, M. Nutritional Interventions as Beneficial Strategies to Delay Cognitive Decline in Healthy Older Individuals. Nutrients 2018, 10, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, G.K.; Reddy, A.P.; Reddy, P.H.; Bhatti, J.S. Lifestyle Modifications and Nutritional Interventions in Aging-Associated Cognitive Decline and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, T.M.; Manosso, L.M.; Yau, S.; Gil-Mohapel, J.; Brocardo, P.S. In Pursuit of Healthy Aging: Effects of Nutrition on Brain Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaliszewska, A.; Allison, J.; Martini, M.; Arias, N. The Interaction of Diet and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Aging and Cognition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steindler, D.A.; Reynolds, B.A. Perspective: Neuroregenerative Nutrition. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pan, M.; Sun, M.; Shi, H.; Feng, R. Nutritional Status and Physical Exercise Are Associated with Cognitive Function in Chinese Community-Dwelling Older Adults: The Role of Happiness. Nutrients 2024, 16, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Ascherio, A.; Grodstein, F. Fruit and Vegetable Consumption and Cognitive Decline in Aging Women. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 57, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, G.S.; Scarmeas, N. Dietary Interventions in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 21, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, M.C.; Evans, D.A.; Bienias, J.L.; Tangney, C.C.; Wilson, R.S. Vitamin E and Cognitive Decline in Older Persons. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valls-Pedret, C.; Sala-Vila, A.; Serra-Mir, M.; Corella, D.; de la Torre, R.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Martínez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Fitó, M.; Pérez-Heras, A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; et al. Mediterranean Diet and Age-Related Cognitive Decline: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arjmand, G.; Abbas-Zadeh, M.; Eftekhari, M.H. Effect of MIND Diet Intervention on Cognitive Performance and Brain Structure in Healthy Obese Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauretti, E.; Iuliano, L.; Praticò, D. Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Ameliorates Cognition and Neuropathology of the 3xTg Mice: Role of Autophagy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2017, 4, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, R.L.; Fulgoni, V.L.; Keast, D.R.; Dwyer, J.T. Examination of Vitamin Intakes among US Adults by Dietary Supplement Use. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 657–663.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydoun, M.A.; Fanelli-Kuczmarski, M.T.; Kitner-Triolo, M.H.; Beydoun, H.A.; Kaufman, J.S.; Mason, M.A.; Evans, M.K.; Zonderman, A.B. Dietary Antioxidant Intake and Its Association With Cognitive Function in an Ethnically Diverse Sample of US Adults. Psychosom. Med. 2015, 77, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, M.; Mett, J.; Hartmann, T. The Impact of Vitamin E and Other Fat-Soluble Vitamins on Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontush, A.; Schekatolina, S. Vitamin E in Neurodegenerative Disorders: Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1031, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.-J.; Shen, L.; Ji, H.-F. Dietary Intakes of Vitamin E, Vitamin C, and β-Carotene and Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 31, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Luo, J.; Xiao, Z.; Wu, W.; Liang, X.; Ding, S.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Ding, D. Low Dietary Vitamin E Intake Is Associated with High Risk of Incident Dementia among Older Adults: The Shanghai Aging Study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1036795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dysken, M.W.; Sano, M.; Asthana, S.; Vertrees, J.E.; Pallaki, M.; Llorente, M.; Love, S.; Schellenberg, G.D.; McCarten, J.R.; Malphurs, J.; et al. Effect of Vitamin E and Memantine on Functional Decline in Alzheimer Disease: The TEAM-AD VA Cooperative Randomized Trial. JAMA 2014, 311, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Yamagishi, K.; Maruyama, K.; Kishida, R.; Ikeda, A.; Umesawa, M.; Renzhe, C.; Kubota, Y.; Hayama-Terada, M.; Shimizu, Y.; et al. Dietary Intake of Tocopherols and Risk of Incident Disabling Dementia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.J.; Vishwanathan, R.; Johnson, M.A.; Hausman, D.B.; Davey, A.; Scott, T.M.; Green, R.C.; Miller, L.S.; Gearing, M.; Woodard, J.; et al. Relationship between Serum and Brain Carotenoids, α-Tocopherol, and Retinol Concentrations and Cognitive Performance in the Oldest Old from the Georgia Centenarian Study. J. Aging Res. 2013, 2013, 951786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanprasertsuk, J.; Scott, T.M.; Johnson, M.A.; Poon, L.W.; Nelson, P.T.; Davey, A.; Woodard, J.L.; Vishwanathan, R.; Barbey, A.K.; Barger, K.; et al. Brain A-Tocopherol Concentration Is Inversely Associated with Neurofibrillary Tangle Counts in Brain Regions Affected in Earlier Braak Stages: A Cross-Sectional Finding in the Oldest Old. JAR Life 2021, 10, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, K.; Gearing, M.; Davey, A.; Burgess, M.; Poon, L.W.; Martin, P.; Green, R.C. Successful Recruitment of Centenarians for Post-Mortem Brain Donation: Results from the Georgia Centenarian Study. J. Biosci. Med. 2012, 2, 124. [Google Scholar]
- Poon, L.W.; Jazwinski, M.; Green, R.C.; Woodard, J.L.; Martin, P.; Rodgers, W.L.; Johnson, M.A.; Hausman, D.; Arnold, J.; Davey, A.; et al. Methodological Considerations in Studying Centenarians: Lessons Learned from the Georgia Centenarian Studies. Annu. Rev. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2007, 27, 231. [Google Scholar]
- Reisberg, B.; Ferris, S.; de Leon, M.; Crook, T. The Global Deterioration Scale for Assessment of Primary Degenerative Dementia. Am. J. Psychiatry 1982, 139, 1136–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.A.; Davey, A.; Hausman, D.B.; Park, S.; Poon, L.W. Dietary Differences between Centenarians Residing in Communities and in Skilled Nursing Facilities: The Georgia Centenarian Study. Age 2006, 28, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranard, K.M.; Kuchan, M.J.; Bruno, R.S.; Juraska, J.M.; Erdman, J.W. Synthetic α-Tocopherol, Compared with Natural α-Tocopherol, Downregulates Myelin Genes in Cerebella of Adolescent Ttpa-Null Mice. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchan, M.J.; Ranard, K.M.; Dey, P.; Jeon, S.; Sasaki, G.Y.; Schimpf, K.J.; Bruno, R.S.; Neuringer, M.; Erdman, J.W. Infant Rhesus Macaque Brain α-Tocopherol Stereoisomer Profile Is Differentially Impacted by the Source of α-Tocopherol in Infant Formula. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2305–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanprasertsuk, J.; Mohn, E.S.; Matthan, N.R.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Barger, K.; Vishwanathan, R.; Johnson, M.A.; Poon, L.W.; Johnson, E.J. Serum Carotenoids, Tocopherols, Total n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and n-6/n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Ratio Reflect Brain Concentrations in a Cohort of Centenarians. J. Gerontol. Ser. A. 2019, 3, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, M.C.; Schneider, J.A.; Li, H.; Tangney, C.C.; Nag, S.; Bennett, D.A.; Honer, W.G.; Barnes, L.L. Brain Tocopherols Related to Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropathology in Humans. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leeuw, F.A.; Schneider, J.A.; Agrawal, S.; Leurgans, S.E.; Morris, M.C. Brain Tocopherol Levels Are Associated with Lower Activated Microglia Density in Elderly Human Cortex. Alzheimers Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2020, 6, e12021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyose, C.; Muramatsu, R.; Kameyama, Y.; Ueda, T.; Igarashi, O. Biodiscrimination of Alpha-Tocopherol Stereoisomers in Humans after Oral Administration. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novotny, J.A.; Fadel, J.G.; Holstege, D.M.; Furr, H.C.; Clifford, A.J. This Kinetic, Bioavailability, and Metabolism Study of RRR-α-Tocopherol in Healthy Adults Suggests Lower Intake Requirements than Previous Estimates. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 2105–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatt, D.H.; Pryor, W.A.; Mata, J.E.; Rodriguez-Proteau, R. Re-Evaluation of the Relative Potency of Synthetic and Natural α-Tocopherol: Experimental and Clinical Observations. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2004, 15, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, S.K.; Lauridsen, C. α-Tocopherol Stereoisomers. Vitam. Horm. 2007, 76, 281–308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Traber, M.G.; Burton, G.W.; Ingold, K.U.; Kayden, H.J. RRR- and SRR-Alpha-Tocopherols Are Secreted without Discrimination in Human Chylomicrons, but RRR-Alpha-Tocopherol Is Preferentially Secreted in Very Low Density Lipoproteins. J. Lipid Res. 1990, 31, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, P.; González-Fuentes, J.; Castro-Vázquez, L.; Lozano, M.V.; Santander-Ortega, M.J.; Rodríguez-Robledo, V.; Villaseca-González, N.; Arroyo-Jiménez, M.M. Vitamin Transporters in Mice Brain with Aging. J. Anat. 2018, 232, 699–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulatowski, L.; Parker, R.; Warrier, G.; Sultana, R.; Butterfield, D.A.; Manor, D. Vitamin E Is Essential for Purkinje Neuron Integrity. Neuroscience 2014, 260, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, J.; Iwamoto, T.; Kida, S.; Masushige, S.; Yamada, K.; Esashi, T. Tocopherol-Associated Protein Is a Ligand-Dependent Transcriptional Activator. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 285, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, J.S.; Rendeiro, C.; Mun, J.G.; Du, K.; Thaman, P.; Snyder, A.; Pinardo, H.; Drnevich, J.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Lai, C.-S.; et al. Brain α-Tocopherol Concentration and Stereoisomer Profile Alter Hippocampal Gene Expression in Weanling Mice. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 3075–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traber, M.G.; Atkinson, J. Vitamin E, Antioxidant and Nothing More. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Zhao, B.; Shen, S.; Hou, J.; Hu, J.; Xin, W. ESR Study on the Structure-Antioxidant Activity Relationship of Tea Catechins and Their Epimers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1427, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliandolo, A.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Role of Vitamin E in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: Evidence from Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley-Whitman, M.A.; Lovell, M.A. Biomarkers of Lipid Peroxidation in Alzheimer Disease (AD): An Update. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Bautista, C.; Baquero, M.; Vento, M.; Cháfer-Pericás, C. Free Radicals in Alzheimer’s Disease: Lipid Peroxidation Biomarkers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 491, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterfield, D.A. Brain Lipid Peroxidation and Alzheimer Disease: Synergy between the Butterfield and Mattson Laboratories. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 64, 101049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Fata, G.; Weber, P.; Mohajeri, M.H. Effects of Vitamin E on Cognitive Performance during Ageing and in Alzheimer’s Disease. Nutrients 2014, 6, 5453–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangialasche, F.; Solomon, A.; Kåreholt, I.; Hooshmand, B.; Cecchetti, R.; Fratiglioni, L.; Soininen, H.; Laatikainen, T.; Mecocci, P.; Kivipelto, M. Serum Levels of Vitamin E Forms and Risk of Cognitive Impairment in a Finnish Cohort of Older Adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2013, 48, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeidler, J.; Mastrogiacomo, C.N.; Beeri, M.S.; Rosendorff, C.; Silverman, J.M. Distinct Age-Related Associations for Body Mass Index and Cognition in Cognitively Healthy Very Old Veterans. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2019, 31, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Walsh, C.E.; Johnson, M.P.; Belsky, D.W.; Reason, M.; Curran, P.; Aiello, A.E.; Chanti-Ketterl, M.; Harris, K.M. Life-Course Trajectories of Body Mass Index from Adolescence to Old Age: Racial and Educational Disparities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2021, 118, e2020167118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escourrou, E.; Durrieu, F.; Chicoulaa, B.; Dupouy, J.; Oustric, S.; Andrieu, S.; Gardette, V. Cognitive, Functional, Physical, and Nutritional Status of the Oldest Old Encountered in Primary Care: A Systematic Review. BMC Fam. Pract. 2020, 21, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, P.R.; Webb, K.L.; Neumann, J.T.; Thao, L.T.P.; Beilin, L.J.; Ernst, M.E.; Fitzgibbon, B.; Gasevic, D.; Nelson, M.R.; Newman, A.B.; et al. Associations of Body Size with All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in Healthy Older Adults. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Klimentidis, Y.C.; Bea, J.W.; Ernst, K.C.; Hu, C.; Jackson, R.; Thomson, C.A. Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, and Mortality in a Large Multiethnic Postmenopausal Cohort-Results from the Women’s Health Initiative. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 65, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Mean ± SD or Count (%) |
|---|---|
| Age, in years | 102.2 ± 2.5 |
| Sex | |
| Male | 5 (11%) |
| Female | 42 (89%) |
| Race | |
| Caucasian | 42 (89%) |
| Black | 5 (11%) |
| Body mass index, in kg/m2 | 22.1 ± 3.9 |
| Education | |
| Lower than high school | 23 (51%) |
| High school | 12 (27%) |
| Higher than high school | 10 (22%) |
| No data | 2 |
| Residence | |
| Community dwelling | 33 (70%) |
| Institutionalized | 14 (30%) |
| Diabetes | 3 (6%) |
| Hypertension | 25 (53%) |
| Alcohol status | |
| Never | 21 (60%) |
| Past | 6 (17%) |
| Present | 8 (23%) |
| No data | 12 |
| Smoking status | |
| Never | 30 (86%) |
| Past | 4 (11%) |
| Present | 1 (3%) |
| No data | 12 |
| Apo E genotype | |
| ε3/ε3 | 32 (68%) |
| ε2/ε3 | 7 (15%) |
| ε3/ε4 | 7 (15%) |
| ε2/ε4 | 1 (2%) |
| Global Deterioration Scale | |
| 1–3 (no dementia) | 23 (49%) |
| 4–7 (dementia) | 24 (51%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chan, J.P.; Tanprasertsuk, J.; Johnson, E.J.; Dey, P.; Bruno, R.S.; Johnson, M.A.; Poon, L.W.; Davey, A.; Woodard, J.L.; Kuchan, M.J. Associations between Brain Alpha-Tocopherol Stereoisomer Profile and Hallmarks of Brain Aging in Centenarians. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13080997
Chan JP, Tanprasertsuk J, Johnson EJ, Dey P, Bruno RS, Johnson MA, Poon LW, Davey A, Woodard JL, Kuchan MJ. Associations between Brain Alpha-Tocopherol Stereoisomer Profile and Hallmarks of Brain Aging in Centenarians. Antioxidants. 2024; 13(8):997. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13080997
Chicago/Turabian StyleChan, Jia Pei, Jirayu Tanprasertsuk, Elizabeth J. Johnson, Priyankar Dey, Richard S. Bruno, Mary Ann Johnson, Leonard W. Poon, Adam Davey, John L. Woodard, and Matthew J. Kuchan. 2024. "Associations between Brain Alpha-Tocopherol Stereoisomer Profile and Hallmarks of Brain Aging in Centenarians" Antioxidants 13, no. 8: 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13080997
APA StyleChan, J. P., Tanprasertsuk, J., Johnson, E. J., Dey, P., Bruno, R. S., Johnson, M. A., Poon, L. W., Davey, A., Woodard, J. L., & Kuchan, M. J. (2024). Associations between Brain Alpha-Tocopherol Stereoisomer Profile and Hallmarks of Brain Aging in Centenarians. Antioxidants, 13(8), 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13080997








