Sustainable Utilization of Food Biowaste (Papaya Peel) Extract for Gold Nanoparticle Biosynthesis and Investigation of Its Multi-Functional Potentials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. C. papaya Extract Preparation
2.2. Phytochemical Analysis of the VPP Extract
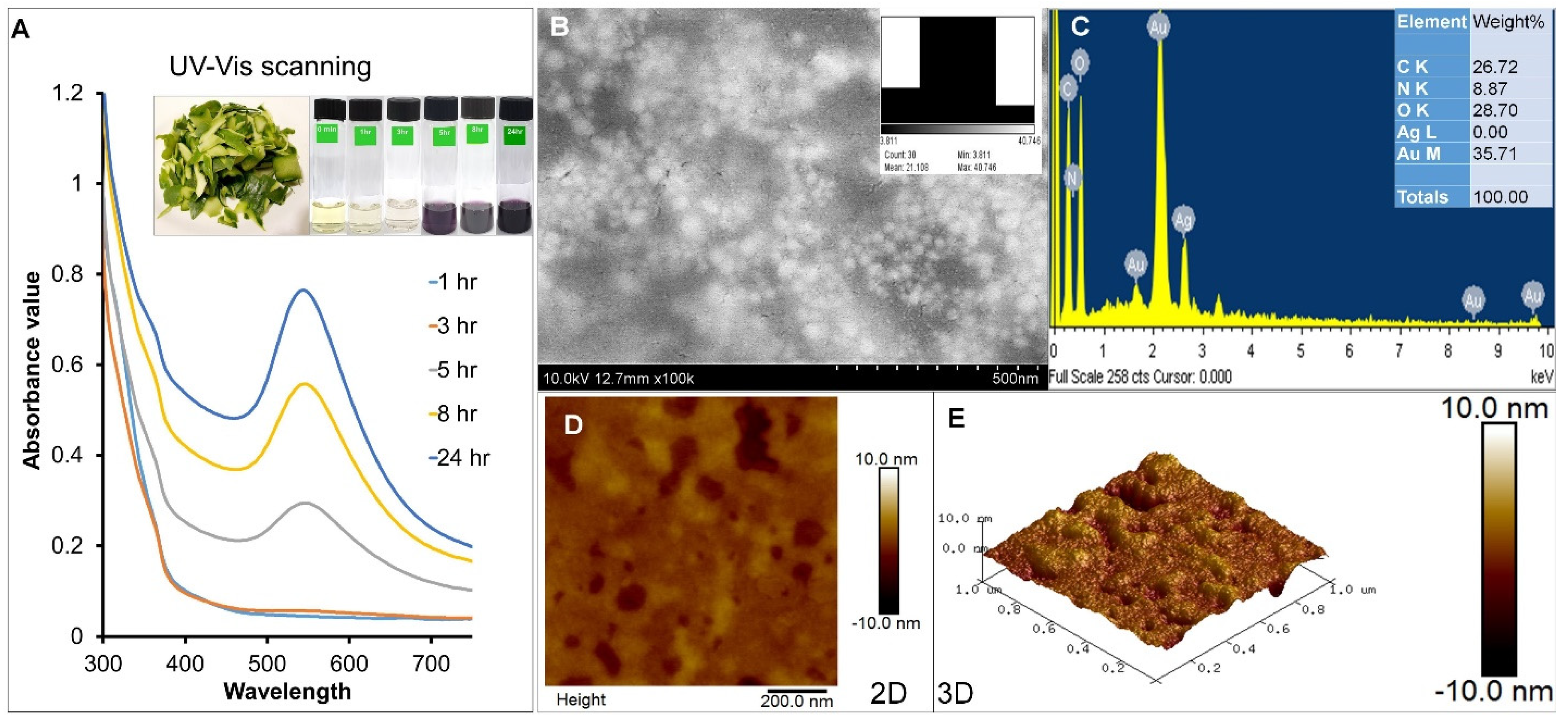
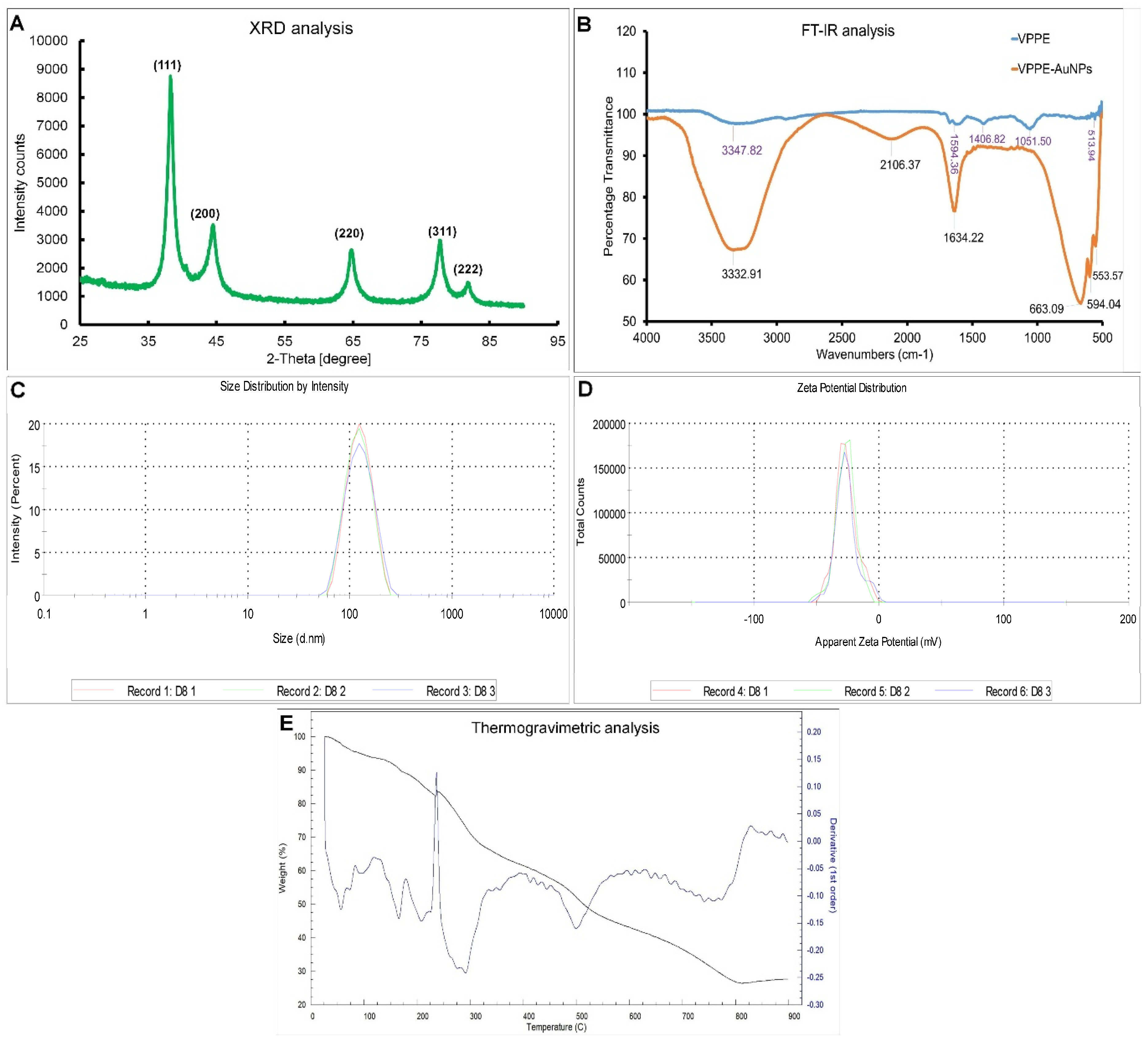
2.3. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Synthesized VPPE-AuNPs
2.4. Assessment of Multiple Biological Potential of the Synthesized VPPE-AuNPs
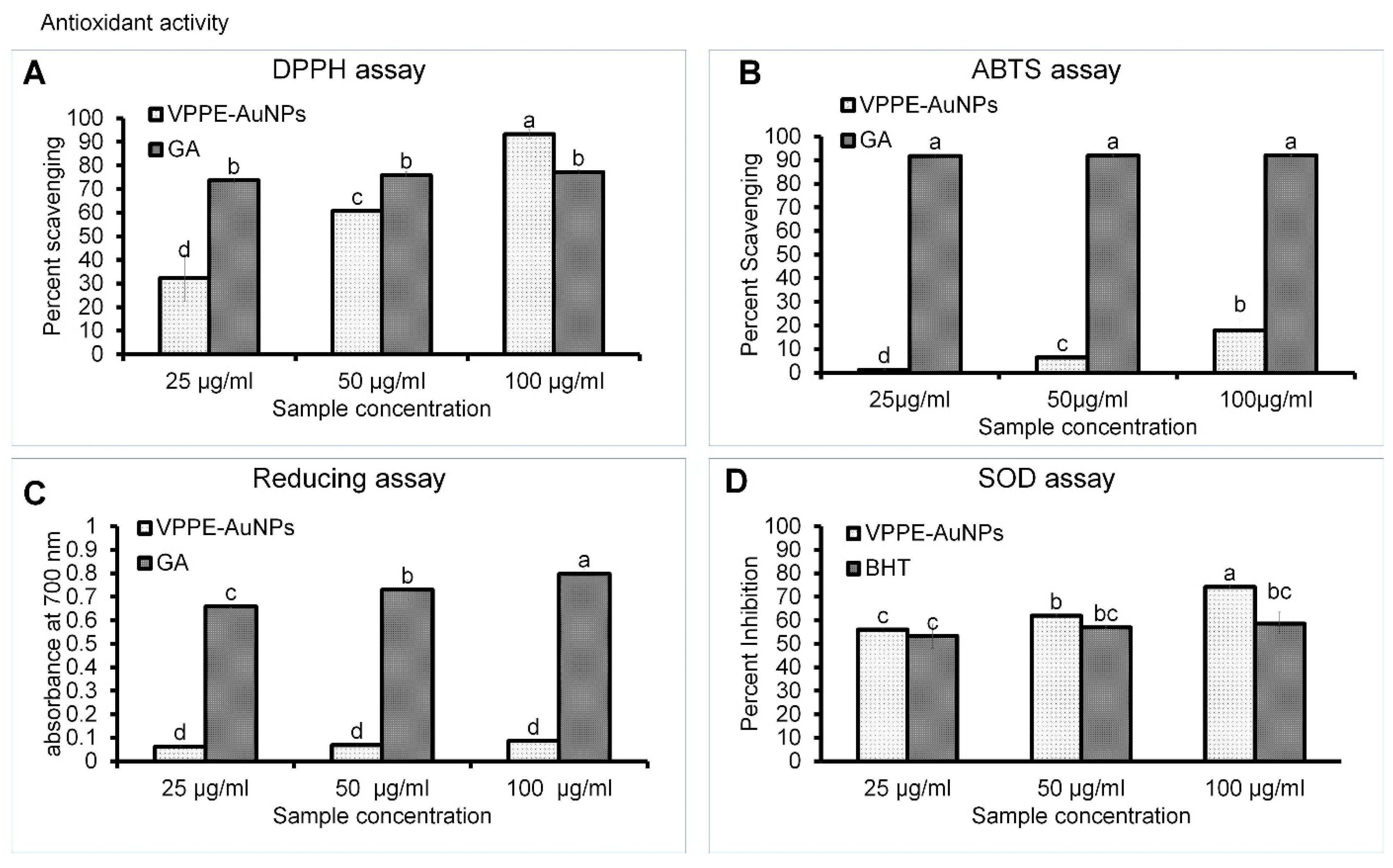
2.4.1. Evaluation of Antioxidant Potential of VPPE-AuNPs
2.4.2. Evaluation of Tyrosinase Inhibitory Potential of VPPE-AuNPs
2.4.3. Antidiabetic Potential of VPPE-AuNPs
2.4.4. Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Potential of VPPE-AuNPs
Cell Viability
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Test (ELISA)
2.4.5. Evaluation of Antibacterial Potential of VPPE-AuNPs
2.4.6. Evaluation of Photocatalytic Dye Degradation Potential of VPPE-AuNPs
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. VPPE-AuNP Manufacture and Analysis
3.2. The Multi-Biofunctional Potential of VPPE-AuNPs
3.2.1. Antioxidant Effect of VPPE-AuNPs
3.2.2. The Antityrosinase Potential of VPPE-AuNPs
3.2.3. α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase Assay of VPPE-AuNPs
3.2.4. Anti-Inflammatory Prospects of VPPE-AuNPs
3.2.5. Antibacterial Potential of VPPE-AuNPs
3.2.6. Photocatalytic Dye Degradation Effect of VPPE-AuNPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ray, P.C. Size and shape dependent second order nonlinear optical properties of nanomaterials and their application in biological and chemical sensing. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 5332–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, K.; Chopra, C.; Bhardwaj, P.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Singh, R.; Najda, A.; Cruz-Martins, N.; Singh, S.; Sharma, R.; Kuča, K. Biogenic Metallic Nanoparticles from Seed Extracts: Characteristics, Properties, and Applications. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 2271278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vundela, S.R.; Kalagatur, N.K.; Nagaraj, A.; Kadirvelu, K.; Chandranayaka, S.; Kondapalli, K.; Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Poda, S. Multi-biofunctional properties of phytofabricated selenium nanoparticles from Carica papaya fruit extract: Antioxidant, antimicrobial, antimycotoxin, anticancer, and biocompatibility. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 769891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Shahid, S.; Lee, C.-S. Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Clerodendrum inerme; characterization, antimicrobial, and antioxidant activities. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angel, R.-G.M.; Francisco, R.-F.; Enrique, M.-R.; Antonio, A.J.; Arturo, B.-R.; Jacobo, A.-M. Applications of Nanotechnology in The Agriculture, Food, and Pharmaceuticals. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, S.; Guan, Z.; Ofoegbu, P.C.; Clubb, P.; Rico, C.; He, F.; Hong, J. Green synthesis of nanoparticles: Current developments and limitations. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwat, D.; Zakharov, D.; Endrino, J.; Soldera, F.; Anders, A.; Migot, S.; Karoum, R.; Vernoux, P.; Pierson, J. Chemistry, phase formation, and catalytic activity of thin palladium-containing oxide films synthesized by plasma-assisted physical vapor deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, S171–S177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsammarraie, F.K.; Wang, W.; Zhou, P.; Mustapha, A.; Lin, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using turmeric extracts and investigation of their antibacterial activities. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 171, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, H.S.; Boda, M.A.; Shah, M.A.; Parveen, S.; Wani, A.H. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Platanus orientalis leaf extract for antifungal activity. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaram, S.; Razafindralambo, H.; Sun, Y.Z.; Vasantharaj, S.; Ghafarifarsani, H.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Raeeszadeh, M. Applications of Green Synthesized Metal Nanoparticles—A Review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 202, 360–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Dutta, T.; Kim, K.-H.; Rawat, M.; Samddar, P.; Kumar, P. ‘Green’ synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: Applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E.A.; Ballen, F.H.; Crane, J.H. An overview of US papaya production, trade, and consumption. EDIS 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.S.B. Papaya (Carica papaya L.) By-Products: Characterization and Valorisation of Bioactive and Energetic Potential. Master’s Thesis, Faculdade de Farmácia da Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Morais, D.R.; Rotta, E.M.; Sargi, S.C.; Schmidt, E.M.; Bonafe, E.G.; Eberlin, M.N.; Sawaya, A.C.; Visentainer, J.V. Antioxidant activity, phenolics and UPLC–ESI (–)–MS of extracts from different tropical fruits parts and processed peels. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.; Rasul, M.G.; Ashwath, N.; Nabi, M.N. The potential of utilising papaya seed oil and stone fruit kernel oil as non-edible feedstock for biodiesel production in Australia—A review. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinha, A.F.; Costa, A.S.; Espírito Santo, L.; Ferreira, D.M.; Sousa, C.; Pinto, E.; Almeida, A.; Oliveira, M.B.P. High-Value Compounds in Papaya By-Products (Carica papaya L. var. Formosa and Aliança): Potential Sustainable Use and Exploitation. Plants 2024, 13, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahunsi, S.; Oranusi, S.; Efeovbokhan, V.; Adesulu-Dahunsi, A.; Ogunwole, J. Crop performance and soil fertility improvement using organic fertilizer produced from valorization of Carica papaya fruit peel. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydia, E.; John, S.; Mohammed, R.; Sivapriya, T. Investigation on the Phytochemicals present in the Fruit peel of Carica papaya and evaluation of its Antioxidant and Antimicrobial property. Res. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2016, 8, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martial-Didier, A.K.; Hubert, K.K.; Parfait, K.E.J.; Kablan, T. Phytochemical properties and proximate composition of papaya (Carica papaya L. var solo 8) peels. Turk. J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 5, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, L.E.G.-G.; Yahia, E.M.; González-Aguilar, G.A. Identification and quantification of phenols, carotenoids, and vitamin C from papaya (Carica papaya L., cv. Maradol) fruit determined by HPLC-DAD-MS/MS-ESI. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canini, A.; Alesiani, D.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Tagliatesta, P. Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis of phenolic compounds from Carica papaya L. leaf. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2007, 20, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarkan, M.; Clantin, B.; Bompard, C.; Belrhali, H.; Baeyens-Volant, D.; Looze, Y.; Villeret, V.; Wintjens, R. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of the glutaminyl cyclase from Carica papaya latex. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2005, 61, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winterhalter, P.; Katzenberger, D.; Schreier, P. 6,7-Epoxy-linalool and related oxygenated terpenoids from Carica papaya fruit. Phytochemistry 1986, 25, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olafsdottir, E.S.; Jørgensen, L.B.; Jaroszewski, J.W. Cyanogenesis in glucosinolate-producing plants: Carica papaya and Carica quercifolia. Phytochemistry 2002, 60, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Agar, O.T.; Barrow, C.; Dunshea, F.; Suleria, H.A. Screening and characterization of phenolic compounds by LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS and their antioxidant potentials in papaya fruit and their by-products activities. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parniakov, O.; Roselló-Soto, E.; Barba, F.J.; Grimi, N.; Lebovka, N.; Vorobiev, E. New approaches for the effective valorization of papaya seeds: Extraction of proteins, phenolic compounds, carbohydrates, and isothiocyanates assisted by pulsed electric energy. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomás, G.-E.; Rodolfo, H.-G.; Juan, M.-D.; Georgina, S.-F.; Luis, C.-G.; Ingrid, R.-B.; Santiago, G.-T. Proteolytic activity in enzymatic extracts from Carica papaya L. cv. Maradol harvest by-products. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, M.C.; Jorge, N. Fatty acids and bioactive compounds of the pulps and kernels of Brazilian palm species, guariroba (Syagrus oleraces), jerivá (Syagrus romanzoffiana) and macaúba (Acrocomia aculeata). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavithra, C.S.; Devi, S.S.; Suneetha, W.J.; Rani, C.V. Nutritional Profiling of Papaya Peel Incorporated Chapathis. Chem. Sci. Rev. Lett. 2018, 7, 686–691. [Google Scholar]
- Balavijayalakshmi, J.; Ramalakshmi, V. Carica papaya peel mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity against human pathogens. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2017, 15, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, J.M.; Abihudi, S.A. Nutraceutical value of Carica papaya: A review. Sci. Afr. 2021, 13, e00933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huet, J.; Looze, Y.; Bartik, K.; Raussens, V.; Wintjens, R.; Boussard, P. Structural characterization of the papaya cysteine proteinases at low pH. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 341, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordănescu, O.A.; Băla, M.; Gligor, D.; Zippenfening, S.E.; Cugerean, M.I.; Petroman, M.I.; Hădărugă, D.I.; Hădărugă, N.G.; Riviş, M. A DPPH· Kinetic Approach on the Antioxidant Activity of Various Parts and Ripening Levels of Papaya (Carica papaya L.) Ethanolic Extracts. Plants 2021, 10, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahia, E.M. Postharvest Biology and Technology of Tropical and Subtropical Fruits: Mangosteen to White Sapote; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Insanu, M.; NMDMW, N.; Solihin, L.; Wirasutisna, K. Antioxidant activities and phytochemicals of polar, semi-polar, and nonpolar extracts of used and unused parts of Carica papaya fruit. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 102270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogiraj, V.; Goyal, P.K.; Chauhan, C.S.; Goyal, A.; Vyas, B. Carica papaya Linn: An overview. Int. J. Herb. Med. 2014, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Bachheti, A.; Sharma, P.; Bachheti, R.K.; Husen, A. Phytochemistry, pharmacological activities, nanoparticle fabrication, commercial products and waste utilization of Carica papaya L.: A comprehensive review. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2020, 2, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarilaleh, V.; Fisher, D.; Henkel, R. Carica papaya seed extract slows human sperm. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 241, 111972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lv, J.; Yu, J.; Xiong, H.; Chen, P.; Cao, H.; John Martin, J.J. Antioxidant Analysis of Different Parts of Several Cultivars of Papaya (Carica papaya L.). Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2022, 22, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Ma, Y.; Yi, G.; Wu, J.; Zhou, L.; Guo, H. Chemical composition and antifungal activity of Carica papaya Linn. seed essential oil against Candida spp. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanesan, S.; Jayamala, M.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Umamaheshwari, S.; Ranjitsingh, A.J.A. Antimicrobial and anticancer properties of Carica papaya leaves derived di-methyl flubendazole mediated silver nanoparticles. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.A.; Chung, S.W.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, Y.J. Comprehensive assessment of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of papaya extracts. Foods 2022, 11, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.D.; Mandavgane, S.A.; Kulkarni, B.D. Waste to wealth: A case study of papaya peel. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, R.; Jan, S.U.; Faridullah, S.; Sherani, S.; Jahan, N. Preliminary phytochemical screening, quantitative analysis of alkaloids, and antioxidant activity of crude plant extracts from Ephedra intermedia indigenous to Balochistan. Sci. World J. 2017, 2017, 5873648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofowora, A. Medicinal Plants and Medicine in Africa; John Willey Spectrum: Ibadan, Nigeria, 1993; pp. 281–285. [Google Scholar]
- Patra, J.K.; Baek, K.-H. Comparative study of proteasome inhibitory, synergistic antibacterial, synergistic anticandidal, and antioxidant activities of gold nanoparticles biosynthesized using fruit waste materials. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 4691. [Google Scholar]
- Das, G.; Seo, S.; Yang, I.-J.; Nguyen, L.T.H.; Shin, H.-S.; Patra, J.K. Synthesis of Biogenic Gold Nanoparticles by Using Sericin Protein from Bombyx mori Silk Cocoon and Investigation of Its Wound Healing, Antioxidant, and Antibacterial Potentials. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Itoh, H.; Uemura, T.; Naka, K.; Chujo, Y. Preparation of π-conjugated polymer-protected gold nanoparticles in stable colloidal form. Chem. Commun. 2001, 613–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.; Shin, H.S.; Patra, J.K. Multitherapeutic Efficacy of Curly Kale Extract Fabricated Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J.K.; Kim, S.H.; Hwang, H.; Choi, J.W.; Baek, K.-H. Volatile Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity of the Bio-Oil Obtained by Pyrolysis of Japanese Red Pine (Pinus Densiflora Siebold and Zucc.). Molecules 2015, 20, 3986–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekennia, A.; Uduagwu, D.; Olowu, O.; Nwanji, O.; Oje, O.; Daniel, B.; Mgbii, S.; Emma-Uba, C. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Alchornea laxiflora and its tyrosinase inhibition and catalytic studies. Micron 2021, 141, 102964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Houghton, P.; Soumyanath, A. α-Amylase inhibitory activity of some Malaysian plants used to treat diabetes; with particular reference to Phyllanthus amarus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 107, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowri, P.M.; Tiwari, A.K.; Ali, A.Z.; Rao, J.M. Inhibition of α-glucosidase and amylase by bartogenic acid isolated from Barringtonia racemosa Roxb. seeds. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Baek, K.-H. Novel green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Citrullus lanatus rind and investigation of proteasome inhibitory activity, antibacterial, and antioxidant potential. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 7253. [Google Scholar]
- Kubo, I.; Fujita, K.-I.; Kubo, A.; Nihei, K.-I.; Ogura, T. Antibacterial activity of coriander volatile compounds against Salmonella choleraesuis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3329–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvam, K.; Albasher, G.; Alamri, O.; Sudhakar, C.; Selvankumar, T.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Vennila, L. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of novel Canthium coromandelicum leaves based copper oxide nanoparticles for the degradation of textile dyes. Environ. Res. 2022, 211, 113046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshni, A.; Lubaina, A. Phytochemical investigation, FT-IR profiling and antibacterial activity of papaya (var. red lady) peel—A rich source of bioactive chemicals. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 2023, 14, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Dada, F.A.; Nzewuji, F.A.; Esan, A.M.; Oyeleye, S.I.; Adegbola, V.B. Phytochemical and antioxidant analysis of aqueous extracts of unripe pawpaw (Carica papaya Linn.) fruit’s peel and seed. Int. J. Recent Res. Appl. Stud. 2016, 27, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- David, H. The New Holistic Herbal; Findhorn Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Pandit, S.; Garnaes, J.; Tunjic, S.; Mokkapati, V.R.S.S.; Sultan, A.; Thygesen, A.; Mackevica, A.; Mateiu, R.V.; Daugaard, A.E. Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles from Cannabis sativa (industrial hemp) and their capacity for biofilm inhibition. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3571–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Deeb, N.M.; Khattab, S.M.; Abu-Youssef, M.A.; Badr, A. Green synthesis of novel stable biogenic gold nanoparticles for breast cancer therapeutics via the induction of extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmanyar, Z.; Mohammadi, F.; Gholami, A.; Khoshneviszadeh, M. Effect of different physical factors on the synthesis of spherical gold nanoparticles towards cost-effective biomedical applications. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.C.; Kalra, R.; Dilawari, R.; Goel, M.; Barrow, C.J. Bio-Synthesis of Aspergillus terreus Mediated Gold Nanoparticle: Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, Antifungal and In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies. Materials 2022, 15, 3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunkar, S.; Nachiyar, V. Endophytes as potential nanofactories. Int. J. Chem. Environ. Biol. Sci 2013, 1, 488–491. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Raouf, N.; Al-Enazi, N.M.; Ibraheem, I.B. Green biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Galaxaura elongata and characterization of their antibacterial activity. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3029–S3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawazeer, S.; Khan, I.; Rauf, A.; Aljohani, A.S.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Khalil, A.A.; Qureshi, M.N.; Ahmad, L.; Khan, S.A. Black pepper (Piper nigrum) fruit-based gold nanoparticles (BP-AuNPs): Synthesis, characterization, biological activities, and catalytic applications–A green approach. Green Process. Synth. 2022, 11, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokila, T.; Ramesh, P.; Geetha, D. Biosynthesis of AgNPs using Carica Papaya peel extract and evaluation of its antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 134, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J.; Pu, Y.; Bao, Y. Green synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles from Pholiota adiposa and their anticancer effects on hepatic carcinoma. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- XRD Crystallite (Grain) Size Calculator (Scherrer Equation)-InstaNANO. Available online: https://instanano.com/all/characterization/xrd/crystallite-size/ (accessed on 28 April 2024).
- Coates, J. Interpretation of infrared spectra, a practical approach. Encycl. Anal. Chem. 2000, 12, 10815–10837. [Google Scholar]
- Aina, A.; Owolo, O.; Adeoye-Isijola, M.; Olukanni, O.; Lateef, A.; Egbe, T.; Aina, F.; Asafa, T.; Abbas, S. Ecofriendly production of silver nanoparticles from the seeds of Carica papaya and its larvicidal and antibacterial efficacy against some selected bacterial pathogens. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Hangzhou, China, 18–20 April 2020; p. 012038. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, A.; Ismail, A.; Jumbianti, D.; Magdalena, S.; Sudrajat, H. Synthesis of copper oxide nano particles by using Phormidium cyanobacterium. Indones. J. Chem. 2009, 9, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phang, Y.-K.; Aminuzzaman, M.; Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Muhammad, G.; Ogawa, S.; Watanabe, A.; Tey, L.-H. Green synthesis and characterization of CuO nanoparticles derived from papaya peel extract for the photocatalytic degradation of palm oil mill effluent (POME). Sustainability 2021, 13, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, C.; Srinivasulu, K.; Venkateswarlu, P. Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol using biogenic silver nanoparticles derived from papaya (Carica papaya) peel extract. Ind. Chem. 2015, 1, 1000104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaraj, C.; Karthi, S.; Reegan, A.D.; Balasubramani, G.; Ramkumar, G.; Kalaivani, K.; Zahir, A.A.; Deepak, P.; Senthil-Nathan, S.; Rahman, M.M. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Gracilaria crassa leaf extract and their ecotoxicological potential: Issues to be considered. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Du, J.; Yi, T.-H. Green and rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Borago officinalis leaf extract: Anticancer and antibacterial activities. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sagar, A.; Rana, J.; Rani, R. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity using fungus Talaromyces purpureogenus isolated from Taxus baccata Linn. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2022, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Mehrdel, B. Sonochemical-assisted synthesis of highly stable gold nanoparticles catalyst for decoloration of methylene blue dye. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 127, 108551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.S.H.; Miah, M.Y.; Paul, S.C.; Aka, T.D.; Saha, O.; Rahaman, M.M.; Sharif, M.J.I.; Habiba, O.; Ashaduzzaman, M. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticle using Carica papaya leaf extract: Application for photocatalytic degradation of remazol yellow RR dye and antibacterial activity. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamelian, M.; Varmira, K.; Veisi, H. Green synthesis and characterizations of gold nanoparticles using Thyme and survey cytotoxic effect, antibacterial and antioxidant potential. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 184, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielo, I.; Rando, G.; Giacobello, F.; Sfameni, S.; Castellano, A.; Galletta, M.; Drommi, D.; Rosace, G.; Plutino, M.R. Synthesis, Chemical-Physical Characterization, and Biomedical Applications of Functional Gold Nanoparticles: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, T.; Mughal, P.; Shahzadi, T.; Shahid, S.; Abbasi, M.A. Green synthesis of silver nickel bimetallic nanoparticles using plant extract of Salvadora persica and evaluation of their various biological activities. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 6, 1250k1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boomi, P.; Ganesan, R.; Poorani, G.P.; Jegatheeswaran, S.; Balakumar, C.; Prabu, H.G.; Anand, K.; Prabhu, N.M.; Jeyakanthan, J.; Saravanan, M. Phyto-engineered gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) with potential antibacterial, antioxidant, and wound healing activities under in vitro and in vivo conditions. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anadozie, S.O.; Adewale, O.B.; Fadaka, A.O.; Afolabi, O.B.; Roux, S. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles using extract of Carica papaya fruit: Evaluation of its antioxidant properties and effect on colorectal and breast cancer cells. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 102348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easmin, S.; Bhattacharyya, M.; Pal, K.; Das, P.; Sahu, R.; Nandi, G.; Dewanjee, S.; Paul, P.; Haydar, M.S.; Roy, S. Papaya peel extract-mediated green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and determination of their antioxidant, antibacterial, and photocatalytic properties. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 47, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salla, S.; Sunkara, R.; Walker, L.T.; Verghese, M. Antioxidant and apoptotic activity of papaya peel extracts in HepG2 cells. Food Nutr. Sci. 2016, 7, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Mello, S.A.; Finlay, G.J.; Baguley, B.C.; Askarian-Amiri, M.E. Signaling pathways in melanogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorz, L.R.; Yoo, B.C.; Kim, M.-Y.; Cho, J.Y. Anti-wrinkling and anti-melanogenic effect of Pradosia mutisii methanol extract. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, N.; Vicanova, J.; Pavel, S. The hunt for natural skin whitening agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 5326–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Shah, S.W.A.; Qureshi, M.T.; Hussain, Z.; Ullah, I.; Kalsoom, U.-E.; Rahim, F.; Rahman, S.S.U.; Sultana, N.; Khan, M.K. Antidiabetic and Hypolipidemic Potential of Green AgNPs against Diabetic Mice. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 3433–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnasamy, G.; Chandrasekharan, S.; Bhatnagar, S. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Melia azedarach: Enhancement of antibacterial, wound healing, antidiabetic and antioxidant activities. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsedek, A.; Majewska, I.; Redzynia, M.; Sosnowska, D.; Koziołkiewicz, M. In vitro inhibitory effect on digestive enzymes and antioxidant potential of commonly consumed fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 4610–4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solikhah, T.I.; Setiawan, B.; Ismukada, D.R. Antidiabetic activity of papaya leaf extract (Carica papaya L.) isolated with maceration method in alloxan-induces diabetic mice. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 774–778. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Perumalsamy, H.; Lee, S.; Hwang, E.; Yi, T.-H. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Euphrasia officinalisleaf extract to inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation through NF-κB and JAK/STAT pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phukan, K.; Devi, R.; Chowdhury, D. Insights into Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Internalization Pathway of Onion Peel-Derived Gold Nano Bioconjugates in RAW 264.7 Macrophages. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 7606–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Cabot, P.J.; Shaw, P.N.; Hewavitharana, A.K. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties of Carica papaya. J. Immunotoxicol. 2016, 13, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, N.; Khan, S.; Bhargava, A.; Raghuram, G.V.; Jain, D.; Panwar, H.; Samarth, R.M.; Jain, S.K.; Maudar, K.K.; Mishra, D.K.; et al. Cancer Chemopreventive Effects of the Flavonoid-Rich Fraction Isolated from Papaya Seeds. Nutr. Cancer 2014, 66, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, T.; Parmar, K.A.; Kotval, S.C.; Jadhav, J. Synthesis, characterization, antibacterial and anticancer properties of silver nanoparticles synthesized from carica papaya peel extract. Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2021, 17, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.; Garg, N.; Kashyap, S.R.; Chauhan, R. Antibacterial finish of textile using papaya peels derived silver nanoparticles. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. (IJFTR) 2015, 40, 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- Sikkema, J.; de Bont, J.A.; Poolman, B. Interactions of cyclic hydrocarbons with biological membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 8022–8028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.; Prabhune, A.; Perry, C.C. Antibiotic mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles with potent antimicrobial activity and their application in antimicrobial coatings. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 6789–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velusamy, P.; Das, J.; Pachaiappan, R.; Vaseeharan, B.; Pandian, K. Greener approach for synthesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles using aqueous solution of neem gum (Azadirachta indica L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 66, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardillo, D.; Weiss, M.; Tehei, M.; Devers, T.; Rosenfeld, A.; Konstantinov, K. Multifunctional Fe2O3/CeO2 nanocomposites for free radical scavenging ultraviolet protection. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 65397–65402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljevic, Z.; Dojcinovic, M.; Vujancevic, J.; Jankovic-Castvan, I.; Ognjanovic, M.; Tadic, N.; Stojadinovic, S.; Brankovic, G.; Nikolic, M. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue under natural sunlight using iron titanate nanoparticles prepared by a modified sol–gel method. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 200708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorekine, G.; Anduwan, G.; Waimbo, M.N.; Osora, H.; Velusamy, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Charles, J. Photocatalytic studies of copper oxide nanostructures for the degradation of methylene blue under visible light. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1248, 131487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, A.; Vasantharaj, S.; Jagadeesan, N.L.; Shankar, S.N.; Pannerselvam, B.; Bose, V.G.; Arumugam, G.; Shanmugavel, M. Studies on phytomolecules mediated synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for biomedical and environmental applications. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 33, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name | Result |
|---|---|
| Tannin | +ve |
| Protein, amino acids | +ve |
| Saponin | +ve |
| Cardiac steroidal glycoside | +ve |
| Carbohydrates | +ve |
| Steroids | +ve |
| Antioxidant Assays | IC50 Value (µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| VPPE-AuNPs | GA | |
| DPPH free radical scavenging | 44.54 | 24.96 |
| ABTS free radical scavenging | 566.39 | 31.71 |
| SOD inhibition | 43.34 | 50.86 (BHT) |
| Reducing power (IC0.5) | 580.91 | 38.62 |
| TAC (µM Trolox equivalent) | 45.64 ± 1.38 | 47.48 ± 1.76 |
| Tyrosinase inhibitory activity | 222.04 | 218.68 (Kojic acid) |
| α-glucosidase inhibition | 44.29 | |
| α-amylase inhibition | 84.87 | |
| Infective Strains | Measurement of Inhibition (mm) | IC and BC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VPPE-AuNPs | Kanamycin | |||||
| Sample | Standard | IC | BC | IC | BC | |
| Pediococcus sp. | 10.00 ± 0.18 | 12.00 ± 0.05 | 100 | >100 | 5 | 10 |
| Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 33090 | 8.74 ± 0.03 | 13.04 ± 0.14 | 100 | >100 | 5 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patra, J.K.; Shin, H.-S.; Yang, I.-J.; Nguyen, L.T.H.; Das, G. Sustainable Utilization of Food Biowaste (Papaya Peel) Extract for Gold Nanoparticle Biosynthesis and Investigation of Its Multi-Functional Potentials. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050581
Patra JK, Shin H-S, Yang I-J, Nguyen LTH, Das G. Sustainable Utilization of Food Biowaste (Papaya Peel) Extract for Gold Nanoparticle Biosynthesis and Investigation of Its Multi-Functional Potentials. Antioxidants. 2024; 13(5):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050581
Chicago/Turabian StylePatra, Jayanta Kumar, Han-Seung Shin, In-Jun Yang, Ly Thi Huong Nguyen, and Gitishree Das. 2024. "Sustainable Utilization of Food Biowaste (Papaya Peel) Extract for Gold Nanoparticle Biosynthesis and Investigation of Its Multi-Functional Potentials" Antioxidants 13, no. 5: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050581
APA StylePatra, J. K., Shin, H.-S., Yang, I.-J., Nguyen, L. T. H., & Das, G. (2024). Sustainable Utilization of Food Biowaste (Papaya Peel) Extract for Gold Nanoparticle Biosynthesis and Investigation of Its Multi-Functional Potentials. Antioxidants, 13(5), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050581











