Protective Effect of Pentoxifylline on the Development of Acute Gastric Mucosal Injury in a Model of LPS-Induced Sepsis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design
- (1)
- Group 1: animals treated with LPS for 30 min followed by treatment of saline for 120 min (early treatment).
- (2)
- Group 2: animals treated with LPS for 30 min followed by treatment of PTX for 120 min (early treatment).
- (3)
- Group 3: animals treated with LPS for 120 min followed by treatment of saline for 120 min (late treatment).
- (4)
- Group 4: animals treated with LPS for 120 min followed by treatment of PTX for 120 min (late treatment).
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Phosphatidylcholine (PC) and Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC)
2.5. Myeloperoxidase (MPO)
2.6. Arachidonic Acid Metabolites: Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), Prostaglandin I2 (PGI2), Thromboxane B2 (TXB2), and Leukotriene B4 (LTB4)
2.7. Proteins
2.8. Phospholipase A2 (PLA2)
2.9. Lipid Peroxidation
2.10. NO, Nitrate Synthase (NOS) Activity, Nitrosothiols, cGMP, and CO
2.11. Somatostatin
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
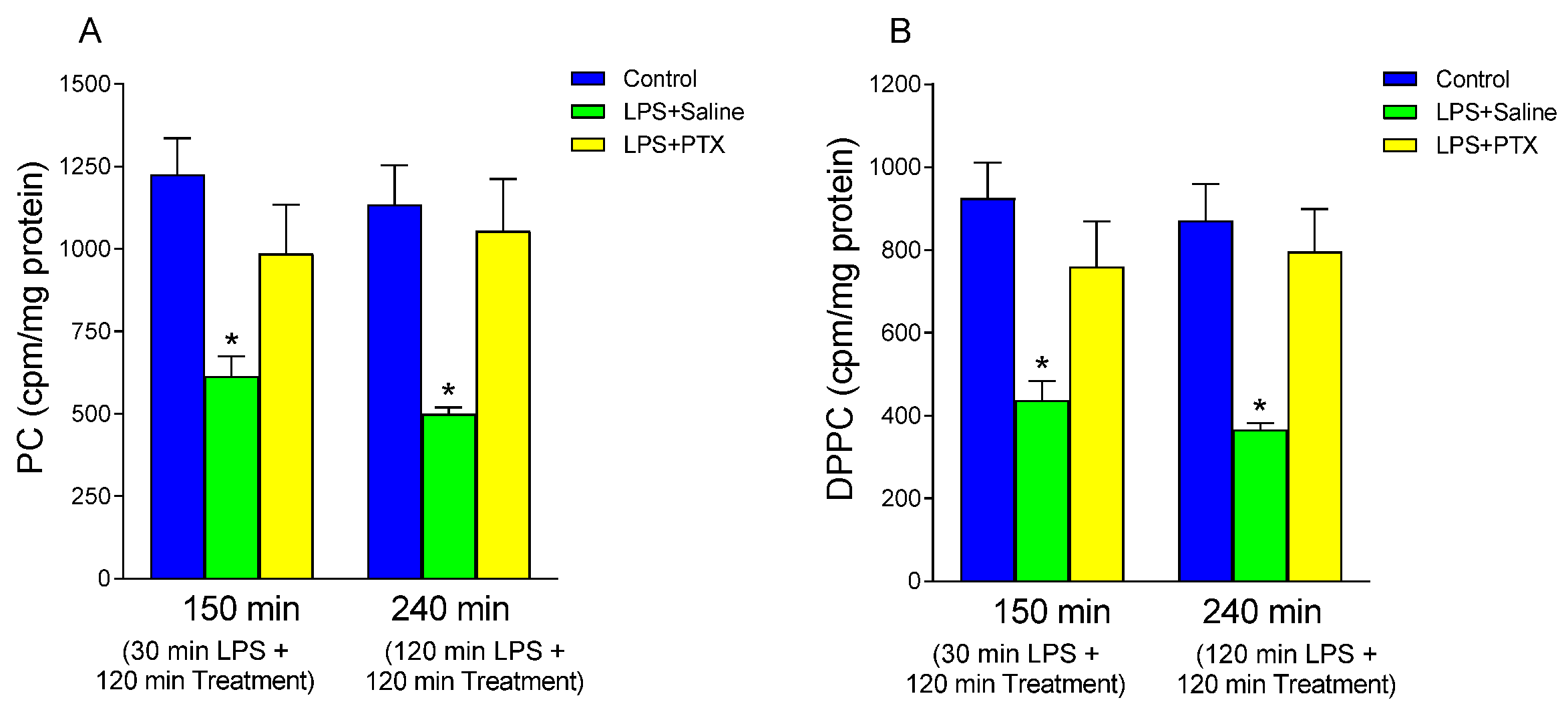
3.1. Effect of LPS and PTX Treatment on PC Synthesis
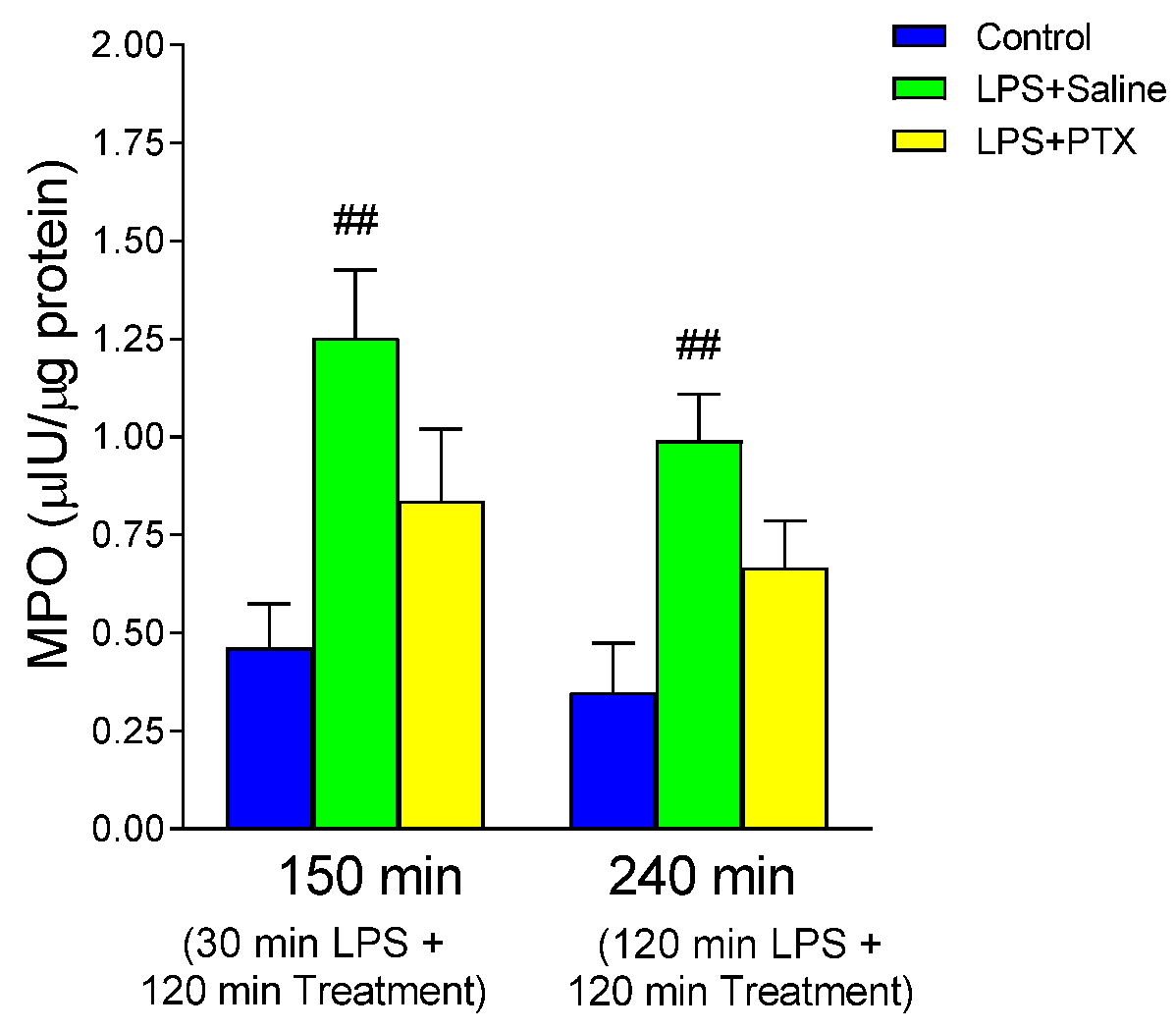
3.2. Effect of LPS and PTX Treatment on MPO
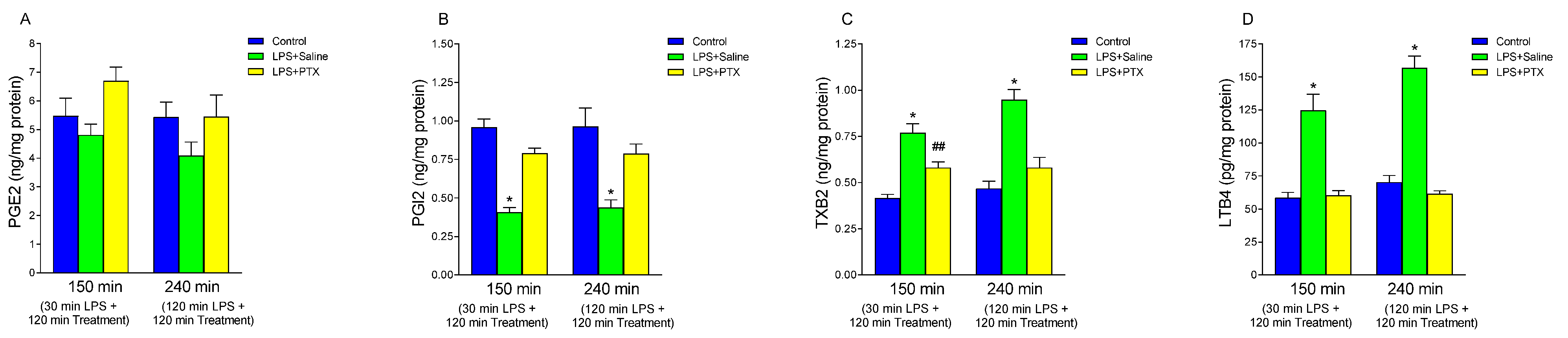
3.3. Effect of LPS and PTX Treatment on Arachidonic Acid Metabolites
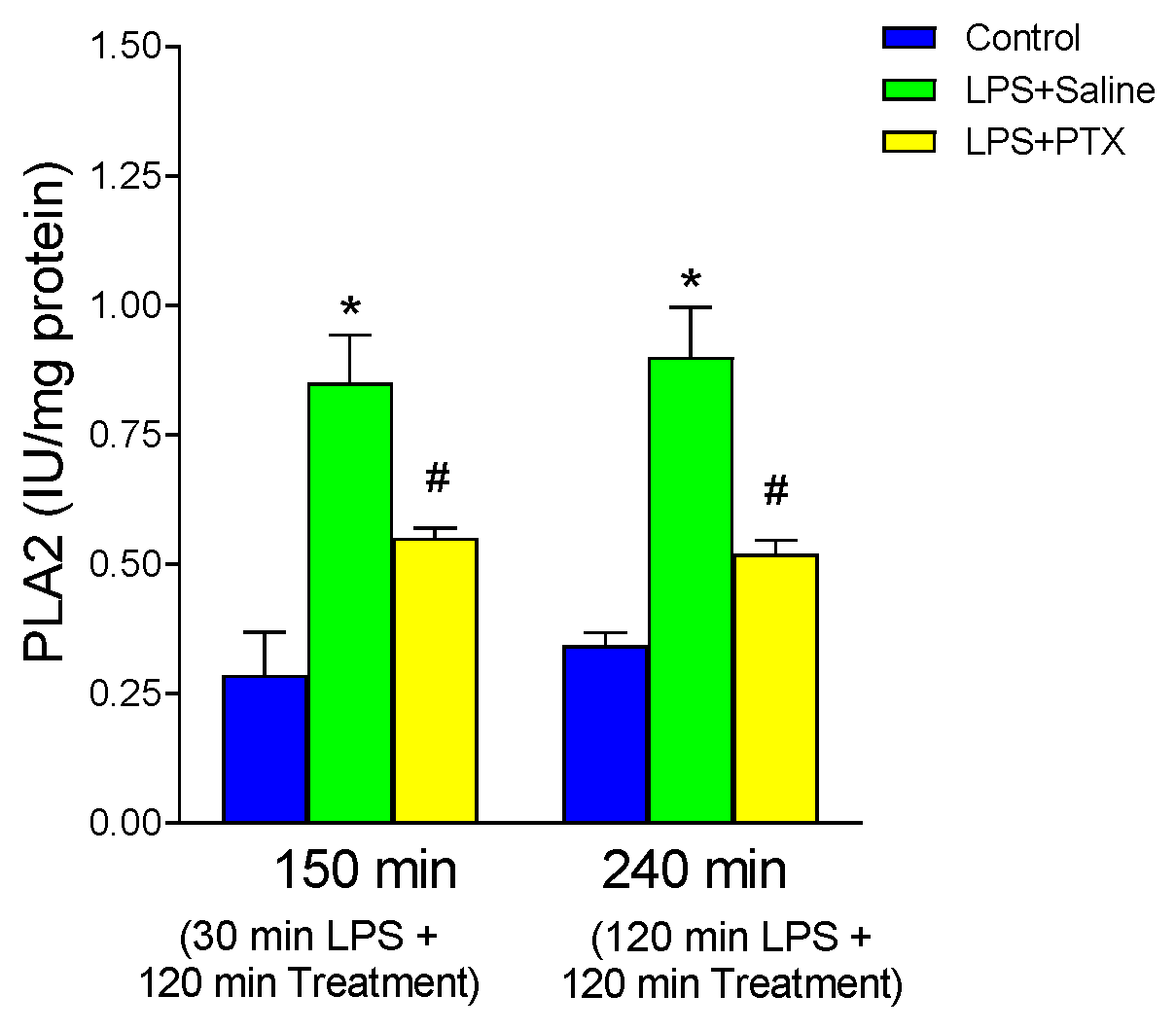
3.4. Effect of LPS and PTX Treatment on PLA2
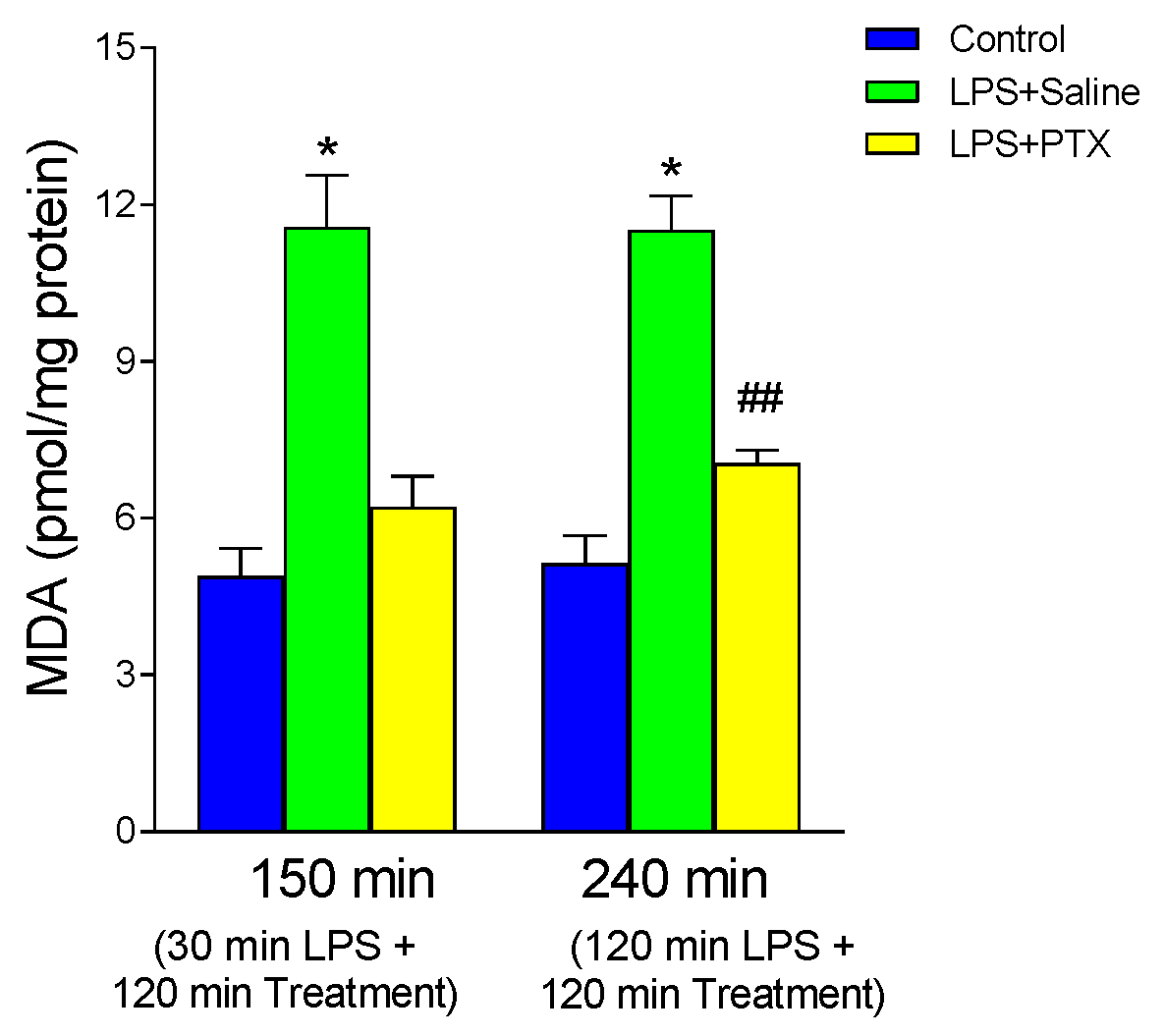
3.5. Effect of LPS and PTX Treatment on MDA
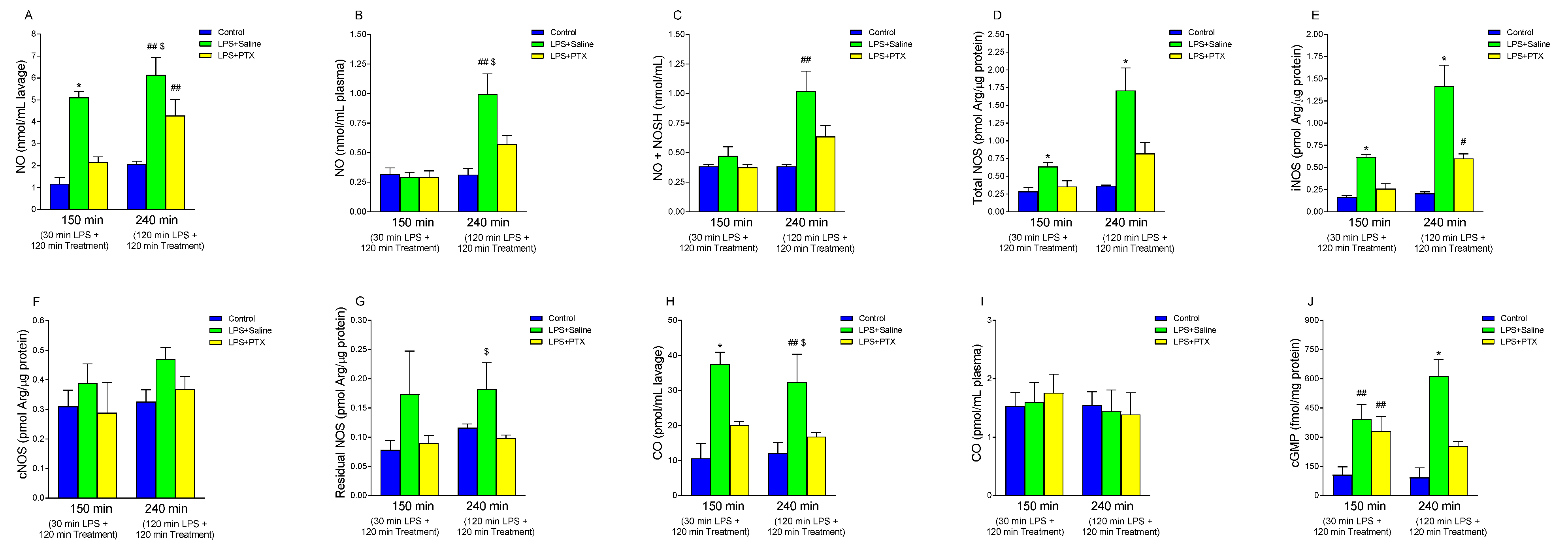
3.6. Effect of LPS and PTX Treatment on NO, NOS Activity, Nitrosothiols, cGMP, and CO
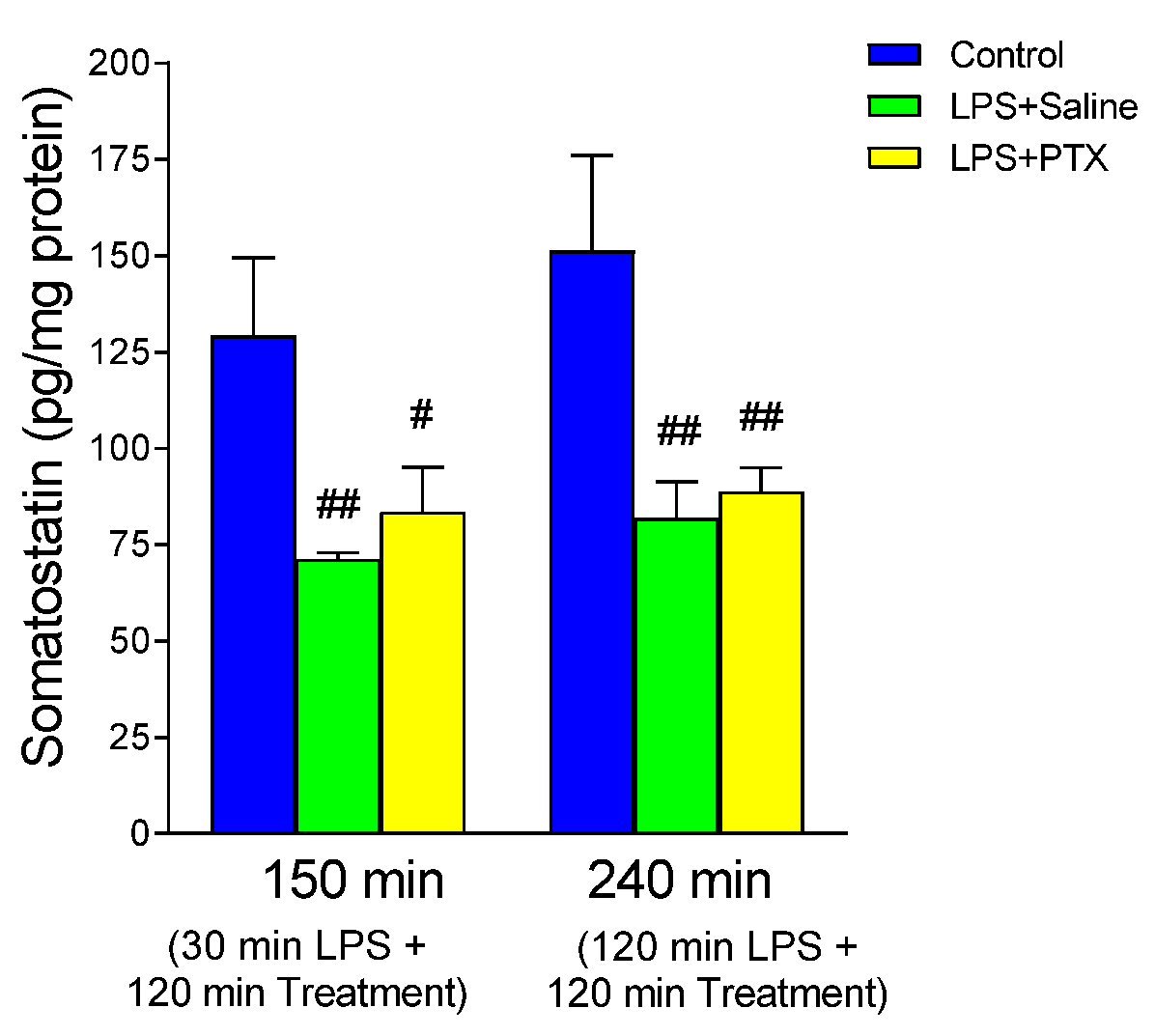
3.7. Effect of LPS and PTX Treatment on Somatostatin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blumlein, D.; Griffiths, I. Shock: Aetiology, pathophysiology and management. Br. J. Nurs. 2022, 31, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Feng, J.; Zhou, D.; Wang, J. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial activation and dysfunction: A new predictive and therapeutic paradigm for sepsis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Levy, M.; Vincent, J.-L.; Ramsay, G.; Angus, D.C.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecconi, M.; Evans, L.; Levy, M.; Rhodes, A. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet 2018, 392, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, M.P.; Blaser, A.R.; Deane, A.M. Stress ulceration: Prevalence, pathology and association with adverse outcomes. Crit. Care. 2014, 18, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Cao, K.; Zhao, Y.; Du, J. Targeting Neutrophils in Sepsis: From Mechanism to Translation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 644270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, C.; Caprani, A.; Dufaux, J.; Flaud, P. Interactions between neutrophils and endothelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 1993, 106 Pt 2, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyska, E. Pretreatment with R(+)-verapamil significantly reduces mortality and cytokine expression in murine model of septic shock. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.; Wang, W.; Falk, S.; Schrier, R. Combination therapy with albumin and pentoxifylline protects against acute kidney injury during endotoxemic shock in mice. Ren. Fail. 2009, 31, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, M.F.; O’Keefe, J.H.; DiNicolantonio, J.J. Pentoxifylline for vascular health: A brief review of the literature. Open Heart 2016, 3, e000365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacher, A.; Eggensperger, E.; Koppensteiner, R.; Mayer, N.; Klimscha, W. Pentoxifylline attenuates the increase in whole blood viscosity after transfusion. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2005, 49, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Al Haleem, E.N.; Ibrahim, F.A.M.; Zaytoon, S.A.B.; Arafa, H.M.M. Possible protective effect of TNF-α inhibition and triad NO/cGMP/VEGF activation on gastric ulcer in rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 99, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallingová, Z.; Kohút, A. Pentoxifylline-associated reduction of indomethacin-induced rat gastric mucosal injury is supported by decreased lipid peroxidation. Physiol. Res. 1994, 43, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Luo, M.; Shang, B. Pentoxifylline induces apoptosis of HepG2 cells by reducing reactive oxygen species production and activating the MAPK signaling. Life Sci. 2017, 183, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.C.; Deitch, E.; Moldawer, L.L.; Opal, S.; Redl, H.; van der Poll, T. Preclinical models of shock and sepsis: What can they tell us? Shock 2005, 24 (Suppl. S1), 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichterman, K.A.; Baue, A.E.; Chaudry, I.H. Sepsis and septic shock—A review of laboratory models and a proposal. J. Surg. Res. 1980, 29, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Poll, T. Preclinical sepsis models. Surg. Infect. 2012, 13, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Diaz, J.; Garcia-Verdugo, I.; Casals, C.; Sanchez-Rico, N.; Vara, E.; Balibrea, J.L. Effect of surfactant protein A (SP-A) on the production of cytokines by human pulmonary macrophages. Shock 2000, 14, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asvadi, I.; Hajipour, B.; Asvadi, A.; Asl, N.A.; Roshangar, L.; Khodadadi, A. Protective effect of pentoxyfilline in renal toxicity after methotrexate administration. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 15, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Yuan, X.; Xie, W. Pentoxifylline exerts anti-inflammatory effects on cerebral ischemia reperfusion-induced injury in a rat model via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, P.P.; Priebat, D.A.; Christensen, R.D.; Rothstein, G. Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: Estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1982, 78, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, P.; Scott, K.; Smith, G.; Rajkovic, I.; Stefanski, E.; Schouten, B.D.; Singh, R.; Pruzanski, W. Serum phospholipase A2 enzyme activity and immunoreactivity in a prospective analysis of patients with septic shock. Life Sci. 1992, 50, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saville, B. A scheme for the colorimetric determination of microgram amounts of thiols. Analyst 1958, 83, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamarit-Rodriguez, J.; Vara, E.; Tamarit, J. Antigenic specificity of a new and potent somatostatin antiserum. Horm. Metab. Res. 1985, 17, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, L.; Jensen, D.M. Management of patients with ulcer bleeding. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 345–360; quiz 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stremmel, W.; Ehehalt, R.; Staffer, S.; Stoffels, S.; Mohr, A.; Karner, M.; Braun, A. Mucosal protection by phosphatidylcholine. Dig. Dis. 2012, 30 (Suppl. S3), 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenberger, L.M. Role of phospholipids in protection of the GI mucosa. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donate-Correa, J.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; González-Luis, A.; Ferri, C.; Martín-Olivera, A.; Martín-Núñez, E.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Tagua, V.G.; Mora-Fernández, C.; Ortiz, A.; et al. Repurposing drugs for highly prevalent diseases: Pentoxifylline, an old drug and a new opportunity for diabetic kidney disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 2200–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-González, J.F.; Sánchez-Niño, M.D.; Donate-Correa, J.; Martín-Núñez, E.; Ferri, C.; Pérez-Delgado, N.; Górriz, J.L.; Martínez-Castelao, A.; Ortiz, A.; Mora-Fernández, C. Effects of Pentoxifylline on Soluble Klotho Concentrations and Renal Tubular Cell Expression in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1817–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsiouli, E.; Tenopoulou, M.; Papadopoulos, S.; Lekka, M.E. Phospholipases A2 as biomarkers in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Biomed. J. 2021, 44, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.N. Infection, Inflammation, and Immunity in Sepsis. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.D.; Wang, S.F.; Wang, B.T.; Yang, Z.A.; Zhou, X.R.; Lei, N.N.; Yue, W.N. Ischemic preconditioning ameliorates intestinal injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8081–8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Kim, N.; Lee, J.Y.; Nam, R.H.; Seo, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, D.H. Gastroprotective Effects of PMK-S005 against Ethanol-Induced Acute Gastric Damage in Rats. Gut Liver. 2016, 10, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Song, L.; Yang, L.; Li, C.; Ma, Y.; Xue, M.; Shi, D. Panax quinquefolius saponins combined with dual antiplatelet therapy enhanced platelet inhibition with alleviated gastric injury via regulating eicosanoids metabolism. BMC Complement Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Furusawa, S. Oxidative stress and septic shock: Metabolic aspects of oxygen-derived free radicals generated in the liver during endotoxemia. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 47, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, T.R., Jr.; Cordero, J.A., Jr.; Mercer, D.W.; Ritchie, W.P., Jr.; Dempsey, D.T. Selective lipoxygenase inhibitor reduces bile acid-induced gastric mucosal injury. J. Surg. Res. 1992, 53, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Force, T.; Milani, R.; Hibberd, P.; Lorenz, R.; Uedelhoven, W.; Leaf, A.; Weber, P. Aspirin-induced decline in prostacyclin production in patients with coronary artery disease is due to decreased endoperoxide shift. Analysis of the effects of a combination of aspirin and n-3 fatty acids on the eicosanoid profile. Circulation 1991, 84, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanas, A. Role of nitric oxide in the gastrointestinal tract. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10 (Suppl. S2), S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yandrapu, H.; Sarosiek, J. Protective Factors of the Gastric and Duodenal Mucosa: An Overview. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2015, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, N.K.; Cruz, R.J., Jr.; Aikawa, P.; Correia, C.J.; Cruz, J.W.; Mauad, T.; Zhang, H.; Rocha-e-Silva, M.; Sannomiya, P. Pentoxifylline attenuates leukocyte-endothelial interactions in a two-hit model of shock and sepsis. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 193, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruuse, C.; Jacobsen, T.B.; Thomsen, L.L.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Frandsen, E.K.; Dige-Petersen, H.; Olesen, J. Effects of the non-selective phosphodiesterase inhibitor pentoxifylline on regional cerebral blood flow and large arteries in healthy subjects. Eur. J. Neurol. 2000, 7, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, D.G.; Ozdemir, F.; Birben, E.; Keskin, O.; Ekşioğlu-Demiralp, E.; Celikel, C.; Kalayci, O.; Kalayci, C. Effects of pentoxifylline on TNF-alpha production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 2520–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.L.; de Oliveira, R.T.D.; Mamoni, R.L.; Coelho, O.R.; Nicolau, J.C.; Blotta, M.H.S.L.; Serrano, C.V., Jr. Pentoxifylline reduces pro-inflammatory and increases anti-inflammatory activity in patients with coronary artery disease—A randomized placebo-controlled study. Atherosclerosis 2008, 196, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ommati, M.M.; Hojatnezhad, S.; Abdoli, N.; Manthari, R.K.; Jia, Z.; Najibi, A.; Akbarizadeh, A.R.; Sadeghian, I.; Farshad, O.; Azarpira, N.; et al. Pentoxifylline mitigates cholestasis-related cholemic nephropathy. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2021, 7, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendawy, N. Pentoxifylline attenuates cytokine stress and Fas system in syngeneic liver proteins induced experimental autoimmune hepatitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, G.A. Gastric anti-ulcerogenic drug effect. A possible mechanism of its molecular basis. Acta Physiol. Hung. 1992, 80, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Matzky, R.; Darius, H.; Schrör, K. The release of prostacyclin (PGI2) by pentoxifylline from human vascular tissue. Arzneimittelforschung 1982, 32, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Rossignol, L.; Plantavid, M.; Chap, H.; Douste-Blazy, L. Effects of two methylxanthines, pentoxifylline and propentofylline, on arachidonic acid metabolism in platelets stimulated by thrombin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1988, 37, 3229–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paredes, S.D.; Hernández-Cortés, J.; Falahat, F.; Rancan, L.; Arias-Díaz, J.; Vara, E. Protective Effect of Pentoxifylline on the Development of Acute Gastric Mucosal Injury in a Model of LPS-Induced Sepsis. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13121481
Paredes SD, Hernández-Cortés J, Falahat F, Rancan L, Arias-Díaz J, Vara E. Protective Effect of Pentoxifylline on the Development of Acute Gastric Mucosal Injury in a Model of LPS-Induced Sepsis. Antioxidants. 2024; 13(12):1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13121481
Chicago/Turabian StyleParedes, Sergio D., Jorge Hernández-Cortés, Farzin Falahat, Lisa Rancan, Javier Arias-Díaz, and Elena Vara. 2024. "Protective Effect of Pentoxifylline on the Development of Acute Gastric Mucosal Injury in a Model of LPS-Induced Sepsis" Antioxidants 13, no. 12: 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13121481
APA StyleParedes, S. D., Hernández-Cortés, J., Falahat, F., Rancan, L., Arias-Díaz, J., & Vara, E. (2024). Protective Effect of Pentoxifylline on the Development of Acute Gastric Mucosal Injury in a Model of LPS-Induced Sepsis. Antioxidants, 13(12), 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13121481






