The Complex of p-Tyr42 RhoA and p-p65/RelA in Response to LPS Regulates the Expression of Phosphoglycerate Kinase 1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Cultures
2.3. Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Immunoprecipitation
2.5. ROS Assay
2.6. Preparation of Cytosolic and Nuclear Fractions
2.7. Small Interference siRNA Transfection
2.8. Site-Directed Mutagenesis
2.9. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and ChIP-PCR
2.10. Confocal Microscopy
2.11. Cell Migration Assay
2.12. Purification of Recombinant Protein
2.13. Measurement of Cell Proliferation with MTT Reagents
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
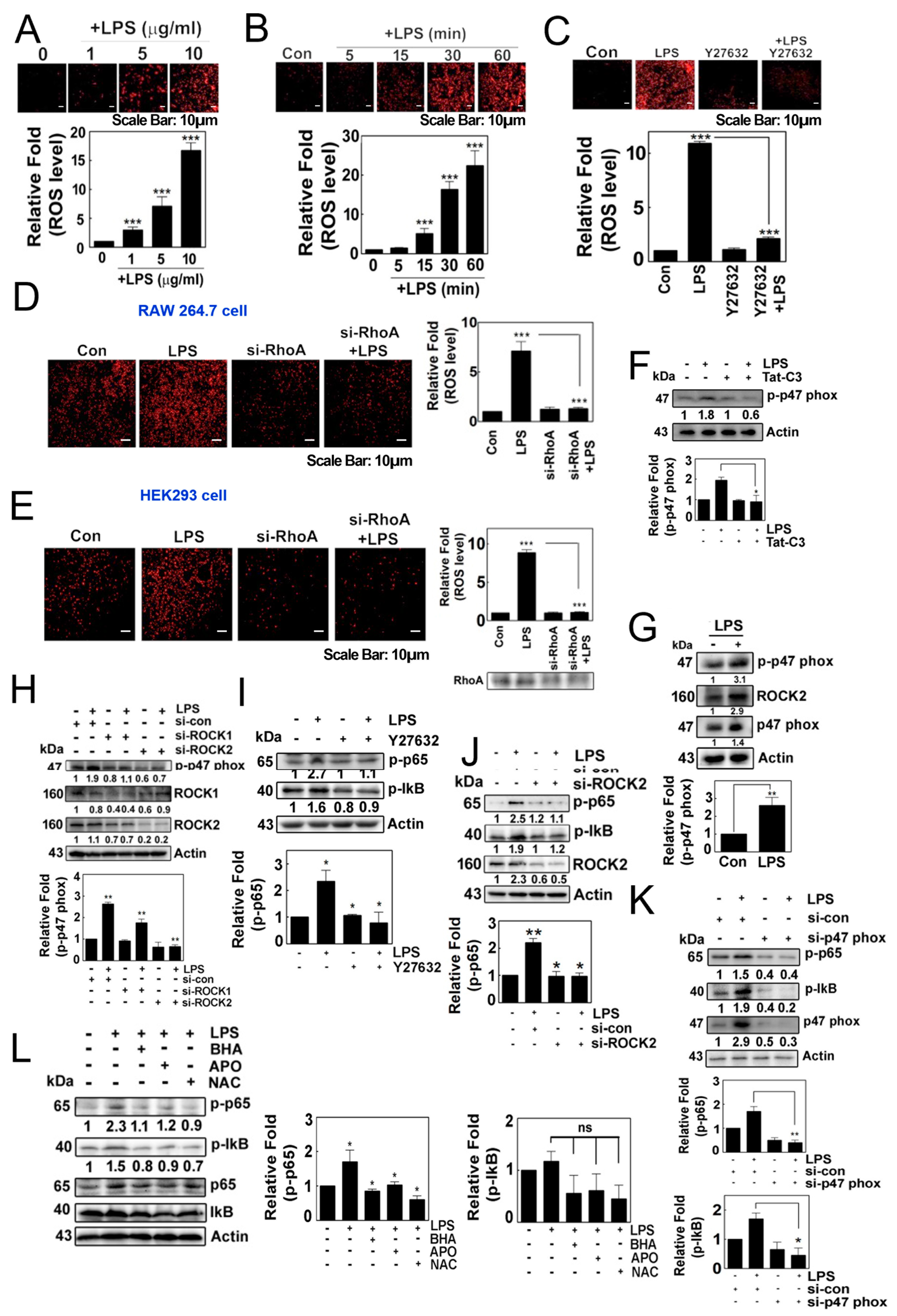
3.1. LPS Induces the Production of Superoxide through RhoA/ROCK, Leading to the Activation of NF-κB
3.2. Phosphorylated p65/RelA at the Ser536 Residue Binds with p-Tyr42 RhoA
3.3. p-Ser536 p65/RelA and p-Tyr42 RhoA Translocate to the Nucleus in Response to LPS Stimulation
3.4. LPS Induces PGK1 through p-Tyr42 RhoA and p-65
3.5. p-Ser536 p65/RelA and p-Tyr42 RhoA Bind to the Promoter of the PGK1 Gene
3.6. PGK1 Leads to the Phosphorylation of β-Catenin during the Process of Inflammation uponLPS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes. Dev. 2004, 18, 2195–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Hayden, M.S. New regulators of NF-kappaB in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxford, T.; Ghosh, G. A structural guide to proteins of the NF-kappaB signaling module. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Fu, J. NF-kappaB and cancer: A paradigm of Yin-Yang. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2011, 1, 192–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perkins, N.D. The diverse and complex roles of NF-kappaB subunits in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabe, Y.; Ando, K.; Hirao, S.; Yoshida, M.; Handa, H. Redox regulation of NF-kappaB activation: Distinct redox regulation between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Signaling to NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptors. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, O.; Bolshakov, V.N.; Raines, S.; Newham, P.; Perkins, N.D. Transcriptional profiling of the LPS induced NF-kappaB response in macrophages. BMC Immunol. 2007, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.B.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases: Biochemistry and biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 21, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perona, R.; Montaner, S.; Saniger, L.; Sanchez-Perez, I.; Bravo, R.; Lacal, J.C. Activation of the nuclear factor-kappaB by Rho, CDC42, and Rac-1 proteins. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnad, R.; Kaina, B.; Fritz, G. Rho GTPases are involved in the regulation of NF-kappaB by genotoxic stress. Exp. Cell Res. 2001, 264, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, S.; Tahara, M.; Ogata, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Morishige, K.; Tasaka, K.; Murata, Y. Involvement of nuclear factor-kB activation through RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway in LPS-induced IL-8 production in human cervical stromal cells. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 13, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.G.; Moon, M.Y.; Park, S.H.; Park, J.B. IkappaB kinase gamma/nuclear factor-kappaB-essential modulator (IKKgamma/NEMO) facilitates RhoA GTPase activation, which, in turn, activates Rho-associated KINASE (ROCK) to phosphorylate IKKbeta in response to transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.G.; Kwon, H.J.; Wu, G.; Park, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.C.; Choe, M.; Kang, S.G.; Seo, G.Y.; et al. RhoA GTPase oxidation stimulates cell proliferation via nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 103, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.G.; Choi, K.C.; Hong, C.W.; Park, H.S.; Choi, E.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, J.B. Tyr42 phosphorylation of RhoA GTPase promotes tumorigenesis through nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 112, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.G.; Mahmud, S.; Min, J.K.; Lee, Y.B.; Kim, H.; Kang, D.C.; Park, H.S.; Seong, J.; Park, J.B. RhoA GTPase phosphorylated at tyrosine 42 by src kinase binds to beta-catenin and contributes transcriptional regulation of vimentin upon Wnt3A. Redox Biol. 2021, 40, 101842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cap, K.C.; Kim, J.G.; Hamza, A.; Park, J.B. P-Tyr42 RhoA GTPase amplifies superoxide formation through p47phox, phosphorylated by ROCK. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 523, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Borgeson, B.; Phanse, S.; Tu, F.; Drew, K.; Clark, G.; Xiong, X.; Kagan, O.; Kwan, J.; Bezginov, A.; et al. Panorama of ancient metazoan macromolecular complexes. Nature 2015, 525, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbluh, J.; Mercer, J.; Shrestha, Y.; Oliver, R.; Tamayo, P.; Doench, J.G.; Tirosh, I.; Piccioni, F.; Hartenian, E.; Horn, H.; et al. Genetic and Proteomic Interrogation of Lower Confidence Candidate Genes Reveals Signaling Networks in beta-Catenin-Active Cancers. Cell Syst. 2016, 3, 302–316.e304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nishimura, D.; Wu, R.C.; Amano, M.; Iso, T.; Kedes, L.; Nishida, H.; Kaibuchi, K.; Hamamori, Y. Nuclear Rho kinase, ROCK2, targets p300 acetyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 15320–15329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.P.; Behar, M.; Birnbaum, H.A.; Hoffmann, A.; Wright, P.E.; Ghosh, G. Analysis of the RelA:CBP/p300 interaction reveals its involvement in NF-kappaB-driven transcription. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Li, H.; Ejaz, S.; Liang, S. PGK1-mediated cancer progression and drug resistance. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 2280–2302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Meisenhelder, J.; Yang, W.; Hawke, D.H.; Zheng, Y.; Xia, Y.; Aldape, K.; He, J.; Hunter, T.; et al. Mitochondria-Translocated PGK1 Functions as a Protein Kinase to Coordinate Glycolysis and the TCA Cycle in Tumorigenesis. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.S.; Glatzle, J.; Bajaeifer, K.; Buhler, S.; Lehmann, T.; Konigsrainer, I.; Vollmer, J.P.; Sipos, B.; Ahmad, S.S.; Northoff, H.; et al. Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 as a promoter of metastasis in colon cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieker, D.; Konigsrainer, I.; Tritschler, I.; Loffler, M.; Beckert, S.; Traub, F.; Nieselt, K.; Buhler, S.; Weller, M.; Gaedcke, J.; et al. Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 a promoting enzyme for peritoneal dissemination in gastric cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Al-Mathkour, M.; Cao, L.; Khalafi, S.; Chen, Z.; Poveda, J.; Peng, D.; Lu, H.; Soutto, M.; Hu, T.; et al. CDK1 bridges NF-kappaB and beta-catenin signaling in response to H. pylori infection in gastric tumorigenesis. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guetta-Terrier, C.; Karambizi, D.; Akosman, B.; Zepecki, J.P.; Chen, J.S.; Kamle, S.; Fajardo, J.E.; Fiser, A.; Singh, R.; Toms, S.A.; et al. Chi3l1 Is a Modulator of Glioma Stem Cell States and a Therapeutic Target in Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 1984–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.Q.; Chu, Z.Z.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Wu, J.R.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Y.C.; Chen, D.; Zhang, J.C.; et al. Serine/threonine kinase TBK1 promotes cholangiocarcinoma progression via direct regulation of beta-catenin. Oncogene 2023, 42, 1492–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hino, S.; Tanji, C.; Nakayama, K.I.; Kikuchi, A. Phosphorylation of beta-catenin by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase stabilizes beta-catenin through inhibition of its ubiquitination. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 9063–9072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Veelen, W.; Le, N.H.; Helvensteijn, W.; Blonden, L.; Theeuwes, M.; Bakker, E.R.; Franken, P.F.; van Gurp, L.; Meijlink, F.; van der Valk, M.A.; et al. beta-catenin tyrosine 654 phosphorylation increases Wnt signalling and intestinal tumorigenesis. Gut 2011, 60, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krejci, P.; Aklian, A.; Kaucka, M.; Sevcikova, E.; Prochazkova, J.; Masek, J.K.; Mikolka, P.; Pospisilova, T.; Spoustova, T.; Weis, M.; et al. Receptor tyrosine kinases activate canonical WNT/beta-catenin signaling via MAP kinase/LRP6 pathway and direct beta-catenin phosphorylation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltschmidt, C.; Banz-Jansen, C.; Benhidjeb, T.; Beshay, M.; Forster, C.; Greiner, J.; Hamelmann, E.; Jorch, N.; Mertzlufft, F.; Pfitzenmaier, J.; et al. A Role for NF-kappaB in Organ Specific Cancer and Cancer Stem Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Yu, Z. Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1) in cancer: A promising target for diagnosis and therapy. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, O.; Dong, H.; Gao, L.; Wang, S.; Zheng, M.; Li, X.; Lin, B. PGK1 Is a Key Target for Anti-Glycolytic Therapy of Ovarian Cancer: Based on the Comprehensive Analysis of Glycolysis-Related Genes. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 682461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Sun, L.; Kang, Y. Regulation of phosphoglycerate kinase 1 and its critical role in cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dogsom, O.; Hamza, A.; Mahmud, S.; Min, J.-K.; Lee, Y.-B.; Park, J.-B. The Complex of p-Tyr42 RhoA and p-p65/RelA in Response to LPS Regulates the Expression of Phosphoglycerate Kinase 1. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12122090
Dogsom O, Hamza A, Mahmud S, Min J-K, Lee Y-B, Park J-B. The Complex of p-Tyr42 RhoA and p-p65/RelA in Response to LPS Regulates the Expression of Phosphoglycerate Kinase 1. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(12):2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12122090
Chicago/Turabian StyleDogsom, Oyungerel, Amir Hamza, Shohel Mahmud, Jung-Ki Min, Yoon-Beom Lee, and Jae-Bong Park. 2023. "The Complex of p-Tyr42 RhoA and p-p65/RelA in Response to LPS Regulates the Expression of Phosphoglycerate Kinase 1" Antioxidants 12, no. 12: 2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12122090
APA StyleDogsom, O., Hamza, A., Mahmud, S., Min, J.-K., Lee, Y.-B., & Park, J.-B. (2023). The Complex of p-Tyr42 RhoA and p-p65/RelA in Response to LPS Regulates the Expression of Phosphoglycerate Kinase 1. Antioxidants, 12(12), 2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12122090






