The Combined Effects of Toxic Microcystis aeruginosa and Thermal Stress on the Edible Clam (Corbicula fluminea): Insights into Oxidative Stress Responses and Molecular Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Clam Acclimation and Algae Culture
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Determination of Biochemical Parameters
2.4. The IBR Index Analysis
2.5. Transcriptome Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
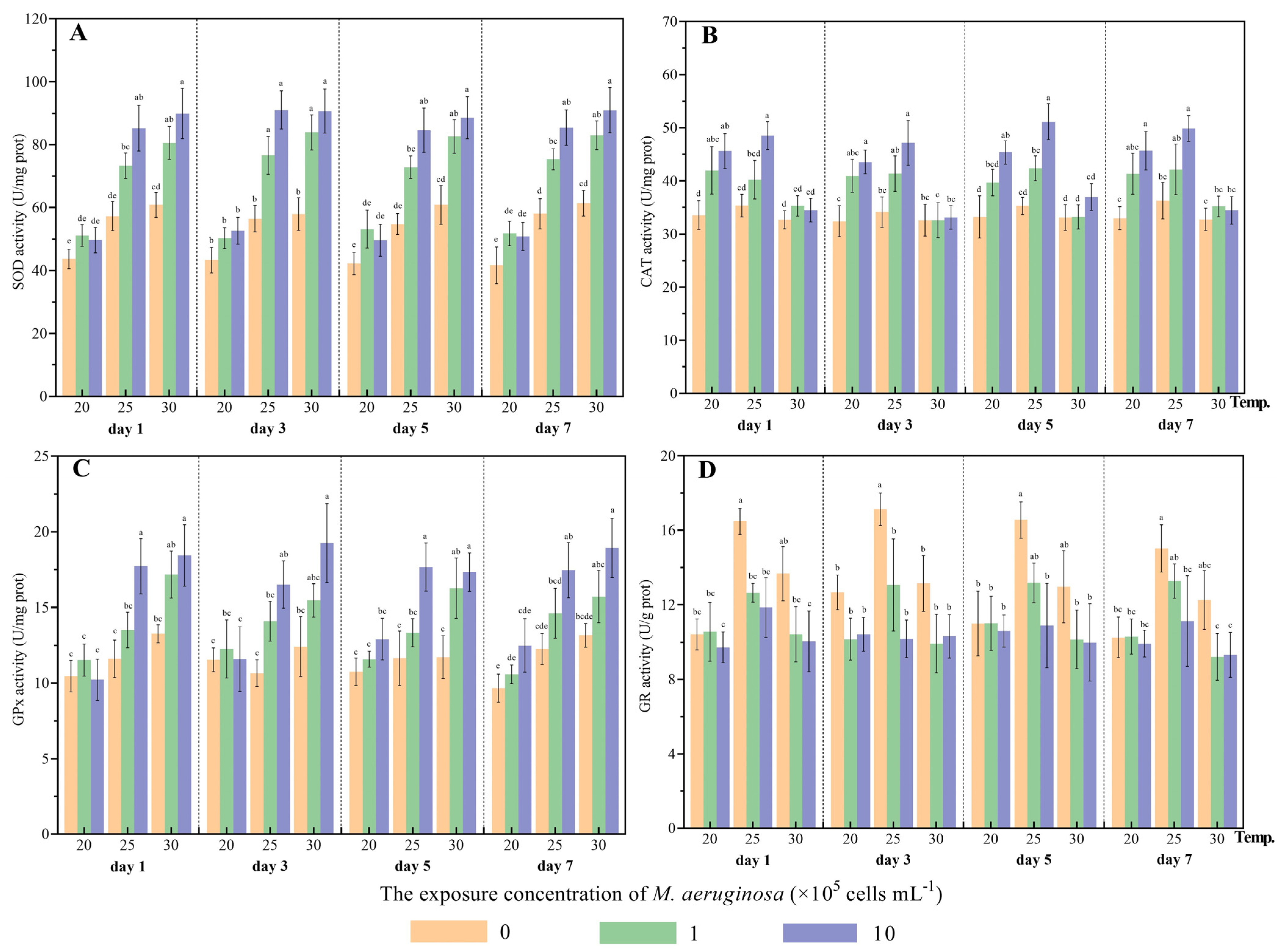
3.1. Oxidative Stress Induced by Thermal Stress and Toxic M. aeruginosa
3.1.1. Activation of Detoxification
3.1.2. Influence on Antioxidant Defense Systems
3.1.3. Assessment of ROS Levels and Lipid Oxidation
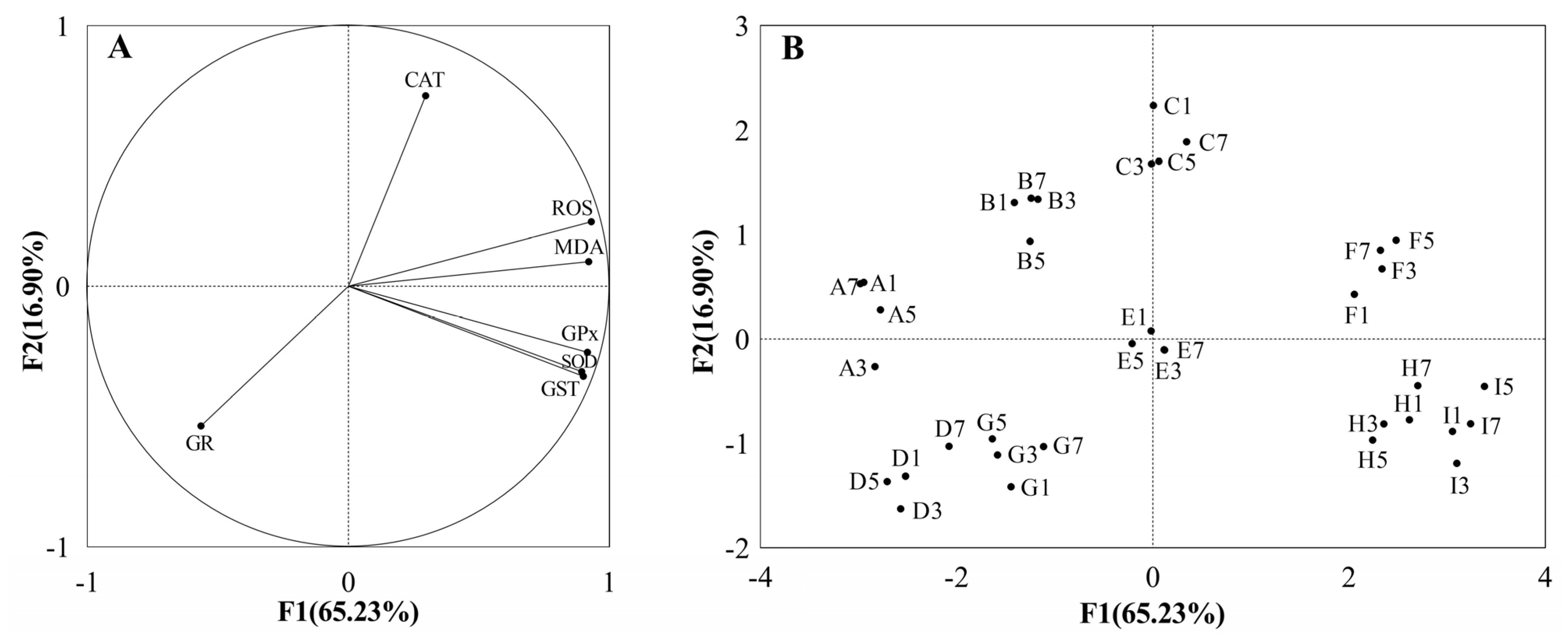
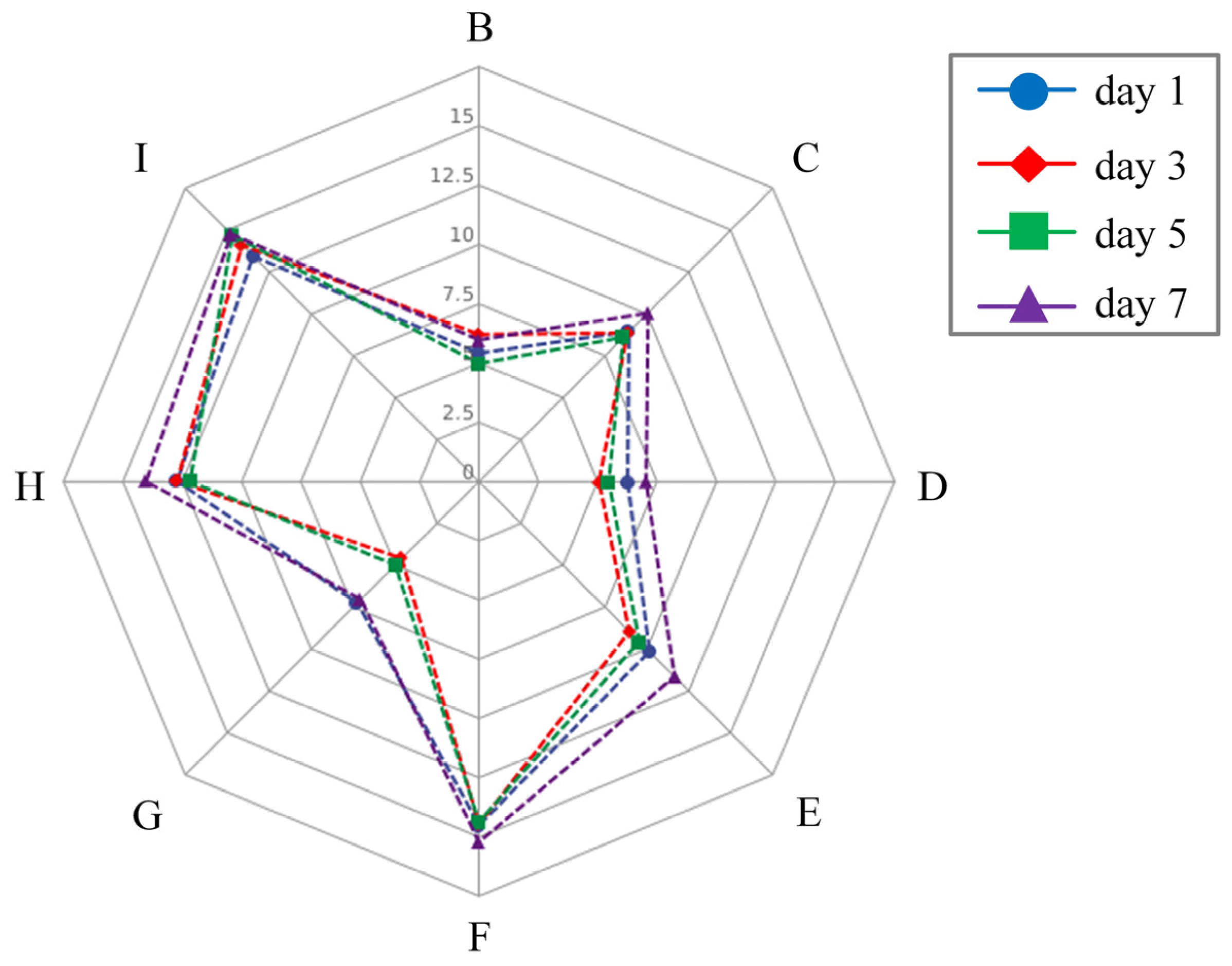
3.1.4. Integrated Analysis of Biochemical Parameters
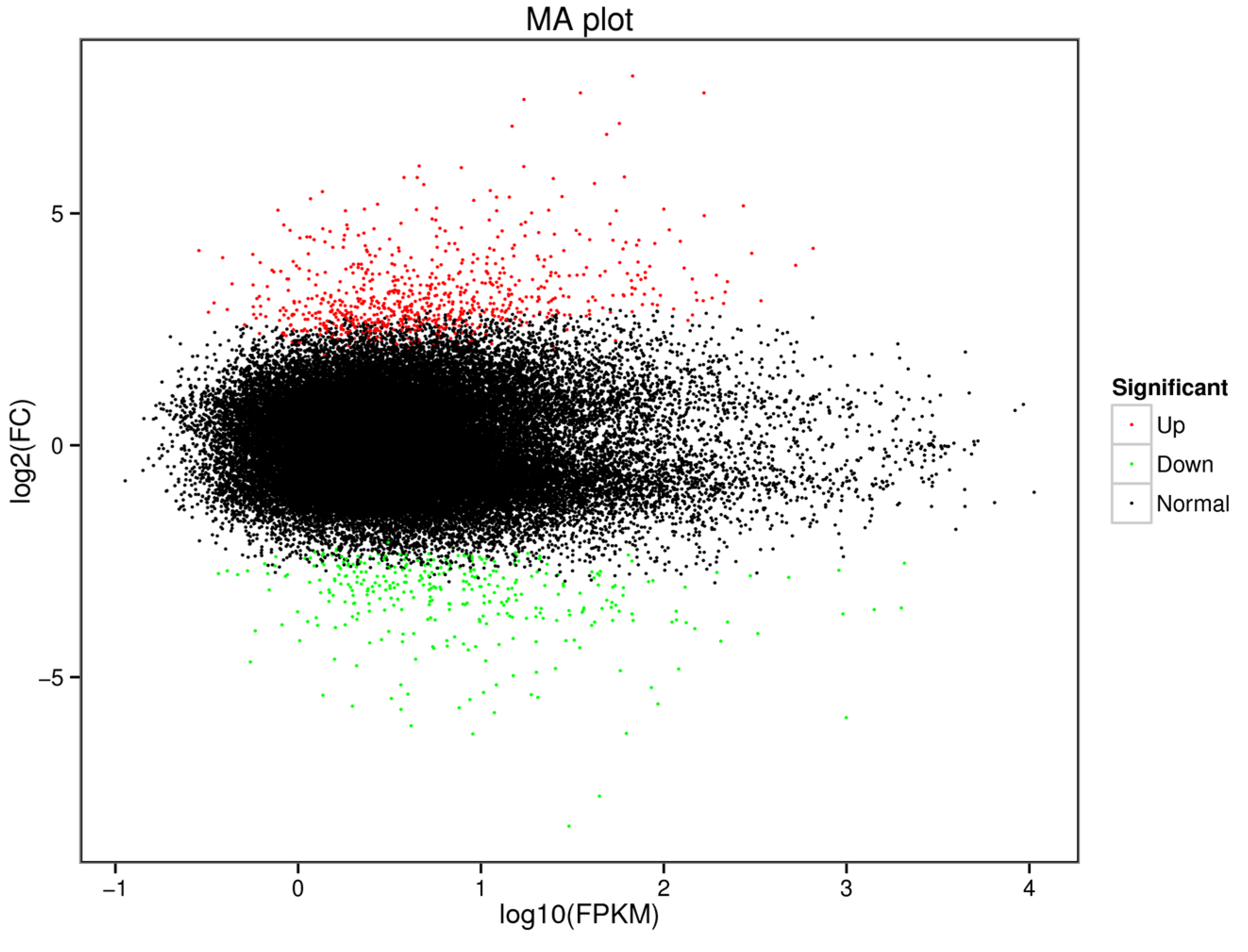
3.2. Molecular Processes Revealed via Transcriptome Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Z. Microcystin pollution in lakes and reservoirs: A nationwide meta-analysis and assessment in China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Du, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, R.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, S.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H. Update on the adverse effects of microcystins on the liver. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez-Quijada, L.; Prieto, A.I.; Guzmán-Guillén, R.; Jos, A.; Cameán, A.M. Occurrence and toxicity of microcystin congeners other than MC-LR and MC-RR: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 106–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobler, C.J.; Doherty, O.M.; Hattenrath-Lehmann, T.K.; Griffith, A.W.; Kang, Y.; Litaker, R.W. Ocean warming since 1982 has expanded the niche of toxic algal blooms in the North Atlantic and North Pacific oceans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4975–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.C.; Michalak, A.M.; Pahlevan, N. Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s. Nature 2019, 574, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobler, C.J. Climate change and harmful algal blooms: Insights and perspective. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, A.W.; Gobler, C.J. Harmful algal blooms: A climate change co-stressor in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Zheng, L.; Nguyen, H.; Ni, L.; Song, S.; Sui, Y. Antioxidant responses of triangle sail mussel Hyriopsis cumingii exposed to toxic Microcystis aeruginosa and thermal stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ji, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Xie, P. Studies on the toxic effects of microcystin-LR on the zebrafish (Danio rerio) under different temperatures. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Liang, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, X. Apoptotic responses of zebrafish (Danio rerio) after exposure with microcystin-LR under different ambient temperatures. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Seo, J.K.; Yoon, H.; Kim, P.J.; Choi, K. Combined effects of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin-LR and environmental factors on life-history traits of indigenous cladoceran Moina macrocopa. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 2560–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Gao, T.; Shao, L.; Min, Y.; Yang, J. Effects of microcystin-LR and nitrite on the lifespan, reproduction, and heat shock responses of rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus at different temperatures. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 82, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.N.; Zanden, M.V. What a difference a species makes: A meta-analysis of dreissenid mussel impacts on freshwater ecosystems. Ecol. Monogr. 2010, 80, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lance, E.; Lepoutre, A.; Savar, V.; Robert, E.; Bormans, M.; Amzil, Z. In situ use of bivalves and passive samplers to reveal water contamination by microcystins along a freshwater-marine continuum in France. Water Res. 2021, 204, 117620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haag, W.R.; Culp, J.; Drayer, A.N.; McGregor, M.A.; White, D.E.; Price, S.J. Abundance of an invasive bivalve, Corbicula fluminea, is negatively related to growth of freshwater mussels in the wild. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.L.; Shimizu, K.; Dao, T.S.; Motoo, U. First report on free and covalently bound microcystins in fish and bivalves from Vietnam: Assessment of risks to humans. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 2953–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burket, S.R.; White, M.; Ramirez, A.J.; Stanley, J.K.; Banks, K.E.; Waller, W.T.; Chambliss, C.K.; Brooks, B.W. Corbicula fluminea rapidly accumulate pharmaceuticals from an effluent dependent urban stream. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Yan, S.; Hong, X.; Zha, J.; Qin, J. Effect of imidacloprid on the behavior, antioxidant system, multixenobiotic resistance, and histopathology of Asian freshwater clams (Corbicula fluminea). Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 218, 105333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Zha, J. Comparison of the toxicity effects of tris (1, 3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate (TDCIPP) with tributyl phosphate (TNBP) reveals the mechanism of the apoptosis pathway in Asian freshwater clams (Corbicula fluminea). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6850–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Gu, X.; Chen, H.; Mao, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Jeppesen, E. Combining bivalve (Corbicula fluminea) and filter-feeding fish (Aristichthys nobilis) enhances the bioremediation effect of algae: An outdoor mesocosm study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, R.; Gu, X.; Li, K.; Chen, H.; He, H.; Mao, Z.; Johnson, R.K. Simultaneous increases of filter-feeding fish and bivalves are key for controlling cyanobacterial blooms in a shallow eutrophic lake. Water Res. 2023, 245, 120579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañeda, R.A.; Cvetanovska, E.; Hamelin, K.M.; Simard, M.A.; Ricciardi, A. Distribution, abundance and condition of an invasive bivalve (Corbicula fluminea) along an artificial thermal gradient in the St. Lawrence River. Aquat. Invasions 2018, 13, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penk, M.R.; Williams, M.A. Thermal effluents from power plants boost performance of the invasive clam Corbicula fluminea in Ireland’s largest river. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Dong, J.; Li, M.; Li, X. Feeding behavior, microcystin accumulation, biochemical response, and ultramicrostructure changes in edible freshwater bivalve Corbicula fluminea exposed to Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 13560–13570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amado, L.L.; Monserrat, J.M. Oxidative stress generation by microcystins in aquatic animals: Why and how. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Wu, Q.; Liu, C.; Shen, J.; Yan, W. Microcystin-LR exposure induced nephrotoxicity by triggering apoptosis in female zebrafish. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Kholodkevich, S.; Sharov, A.; Feng, Y.; Ren, N.; Sun, K. Microcystin-LR-induced changes of hepatopancreatic transcriptome, intestinal microbiota, and histopathology of freshwater crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, W.; Burgeot, T.; Porcher, J.M. A novel “Integrated Biomarker Response” calculation based on reference deviation concept. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2721–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chang, X.; Hu, M.; Fang, J.K.H.; Sokolova, I.M.; Huang, W.; Xu, E.G.; Wang, Y. Is microplastic an oxidative stressor? Evidence from a meta-analysis on bivalves. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.D.; Kim, W.J.; Shin, Y.K.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.K.; Rhee, J.S. Microcystin-LR bioconcentration induces antioxidant responses in the digestive gland of two marine bivalves Crassostrea gigas and Mytilus edulis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 188, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmester, V.; Nimptsch, J.; Wiegand, C. Adaptation of freshwater mussels to cyanobacterial toxins: Response of the biotransformation and antioxidant enzymes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 78, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyaneder-Terrazas, J.; Figueroa, D.; Araneda, O.F.; García, C. Saxitoxin group toxins accumulation induces antioxidant responses in tissues of Mytilus chilensis, Ameghinomya antiqua, and Concholepas concholepas during a bloom of Alexandrium pacificum. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.D.; Yunes, J.S.; Mckenzie, D.J.; Rantin, F.T.; Kalinin, A.L.; Monteiro, D.A. Microcystin-LR exposure causes cardiorespiratory impairments and tissue oxidative damage in trahira, Hoplias malabaricus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 173, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.M.; Haque, M.N.; Lee, D.H.; Nam, S.E.; Rhee, J.S. Comparative toxicokinetics and antioxidant response in the microcystin-LR-exposed gill of two marine bivalves, Crassostrea gigas and Mytilus edulis. J. Shellfish Res. 2018, 37, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, I.M. Energy-limited tolerance to stress as a conceptual framework to integrate the effects of multiple stressors. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2013, 53, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, Z.; Qiao, H.; Liu, F. Assessment of eutrophication and water quality in the estuarine area of Lake Wuli, Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravo, A.; Pereira, C.; Gomes, T.; Cardoso, C.; Serafim, A.; Almeida, C.; Rocha, T.; Lopes, B.; Company, R.; Medeiros, A.; et al. A multibiomarker approach in the clam Ruditapes decussatus to assess the impact of pollution in the Ria Formosa lagoon, South Coast of Portugal. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 75, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Feng, C.; Wu, Y.; Guo, X. Impacts of nanoplastics on bivalve: Fluorescence tracing of organ accumulation, oxidative stress and damage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pan, L.; Guo, R.; Cao, Y.; Sun, J.A. verification of correlation between chemical monitoring and multi-biomarker approach using clam Ruditapes philippinarum and scallop Chlamys farreri to assess the impact of pollution in Shandong coastal area of China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 155, 111155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aouini, F.; Trombini, C.; Sendra, M.; Blasco, J. Biochemical response of the clam Ruditapes philippinarum to silver (AgD and AgNPs) exposure and application of an integrated biomarker response approach. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 152, 104783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta-Cepas, J.; Szklarczyk, D.; Heller, D.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Forslund, S.K.; Cook, H.; Mende, D.R.; Letunic, I.; Rattei, T.; Jensen, L.J.; et al. eggNOG 5.0: A hierarchical, functionally and phylogenetically annotated orthology resource based on 5090 organisms and 2502 viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D309–D314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Xiong, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J. Toxic effects of ammonia and thermal stress on the intestinal microbiota and transcriptomic and metabolomic responses of Litopenaeus vannamei. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 141867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Maity, S.; Guchhait, R.; Chatterjee, A.; Biswas, C.; Adhikari, M.; Pramanick, K. Toxic effects of cyanotoxins in teleost fish: A comprehensive review. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 240, 105971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausfeldt, L.E.; Steffen, M.M.; McKay, R.M.; Bullerjahn, G.S.; Boyer, G.L.; Wilhelm, S.W. Insight into the molecular mechanisms for microcystin biodegradation in Lake Erie and Lake Taihu. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Factor | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Square | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GST | ||||
| Temp | 2 | 4416.781 | 133.277 | <0.001 |
| Time | 3 | 12.904 | 0.389 | 0.761 |
| M | 2 | 1910.061 | 57.636 | <0.001 |
| Temp × Time | 6 | 11.485 | 0.347 | 0.91 |
| Temp × M | 4 | 165.007 | 4.979 | 0.001 |
| Time × M | 6 | 9.835 | 0.297 | 0.937 |
| Temp × Time × M | 12 | 7.466 | 0.225 | 0.997 |
| SOD | ||||
| Temp | 2 | 8814.217 | 330.075 | <0.001 |
| Time | 3 | 13.086 | 0.49 | 0.69 |
| M | 2 | 4884.743 | 182.924 | <0.001 |
| Temp × Time | 6 | 8.155 | 0.305 | 0.932 |
| Temp × M | 4 | 498.276 | 18.659 | <0.001 |
| Time × M | 6 | 11.935 | 0.447 | 0.845 |
| Temp × Time × M | 12 | 4.756 | 0.178 | 0.999 |
| CAT | ||||
| Temp | 2 | 629.899 | 73.301 | <0.001 |
| Time | 3 | 12.074 | 1.405 | 0.248 |
| M | 2 | 781.737 | 90.97 | <0.001 |
| Temp × Time | 6 | 2.91 | 0.339 | 0.914 |
| Temp × M | 4 | 130.706 | 15.21 | <0.001 |
| Time × M | 6 | 4.371 | 0.509 | 0.8 |
| Temp × Time × M | 12 | 1.838 | 0.214 | 0.997 |
| GPx | ||||
| Temp | 2 | 185.395 | 84.353 | <0.001 |
| Time | 3 | 0.162 | 0.074 | 0.974 |
| M | 2 | 165.223 | 75.176 | <0.001 |
| Temp × Time | 6 | 3.211 | 1.461 | 0.204 |
| Temp × M | 4 | 22.769 | 10.36 | <0.001 |
| Time × M | 6 | 0.794 | 0.361 | 0.901 |
| Temp × Time × M | 12 | 2.008 | 0.914 | 0.538 |
| GR | ||||
| Temp | 2 | 87.409 | 44.326 | <0.001 |
| Time | 3 | 2.804 | 1.422 | 0.243 |
| M | 2 | 93.35 | 47.339 | <0.001 |
| Temp × Time | 6 | 0.828 | 0.42 | 0.863 |
| Temp × M | 4 | 16.357 | 8.295 | <0.001 |
| Time × M | 6 | 1.441 | 0.731 | 0.626 |
| Temp × Time × M | 12 | 0.922 | 0.468 | 0.927 |
| ROS | ||||
| Temp | 2 | 1.325 | 64.356 | <0.001 |
| Time | 3 | 0.02 | 0.949 | 0.421 |
| M | 2 | 11.049 | 536.777 | <0.001 |
| Temp × Time | 6 | 0.01 | 0.473 | 0.826 |
| Temp × M | 4 | 0.064 | 3.112 | 0.02 |
| Time × M | 6 | 0.029 | 1.391 | 0.23 |
| Temp × Time × M | 12 | 0.015 | 0.715 | 0.732 |
| MDA | ||||
| Temp | 2 | 62.491 | 28.094 | <0.001 |
| Time | 3 | 1.125 | 0.506 | 0.68 |
| M | 2 | 242.191 | 108.883 | <0.001 |
| Temp × Time | 6 | 1.093 | 0.491 | 0.813 |
| Temp × M | 4 | 25.154 | 11.309 | <0.001 |
| Time × M | 6 | 0.496 | 0.223 | 0.968 |
| Temp × Time × M | 12 | 1.221 | 0.549 | 0.875 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Dong, J.; Gao, X.; Yuan, H.; Li, X. The Combined Effects of Toxic Microcystis aeruginosa and Thermal Stress on the Edible Clam (Corbicula fluminea): Insights into Oxidative Stress Responses and Molecular Networks. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1901. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12111901
Zhang J, Wang N, Zhang Z, Gao Y, Dong J, Gao X, Yuan H, Li X. The Combined Effects of Toxic Microcystis aeruginosa and Thermal Stress on the Edible Clam (Corbicula fluminea): Insights into Oxidative Stress Responses and Molecular Networks. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(11):1901. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12111901
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jingxiao, Ning Wang, Zehao Zhang, Yunni Gao, Jing Dong, Xiaofei Gao, Huatao Yuan, and Xuejun Li. 2023. "The Combined Effects of Toxic Microcystis aeruginosa and Thermal Stress on the Edible Clam (Corbicula fluminea): Insights into Oxidative Stress Responses and Molecular Networks" Antioxidants 12, no. 11: 1901. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12111901
APA StyleZhang, J., Wang, N., Zhang, Z., Gao, Y., Dong, J., Gao, X., Yuan, H., & Li, X. (2023). The Combined Effects of Toxic Microcystis aeruginosa and Thermal Stress on the Edible Clam (Corbicula fluminea): Insights into Oxidative Stress Responses and Molecular Networks. Antioxidants, 12(11), 1901. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12111901






