Effect of Copper Nanoparticles in the Diet of WKY and SHR Rats on the Redox Profile and Histology of the Heart, Liver, Kidney, and Small Intestine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drug and Chemicals
2.2. Experimental Protocol
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. Biochemical Analyses of Plasma
2.5. Analysis of Redox Status
2.6. Histological Examination of Organs
2.7. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Blood Pressure (R)
3.2. Effect of Cu Source (C)
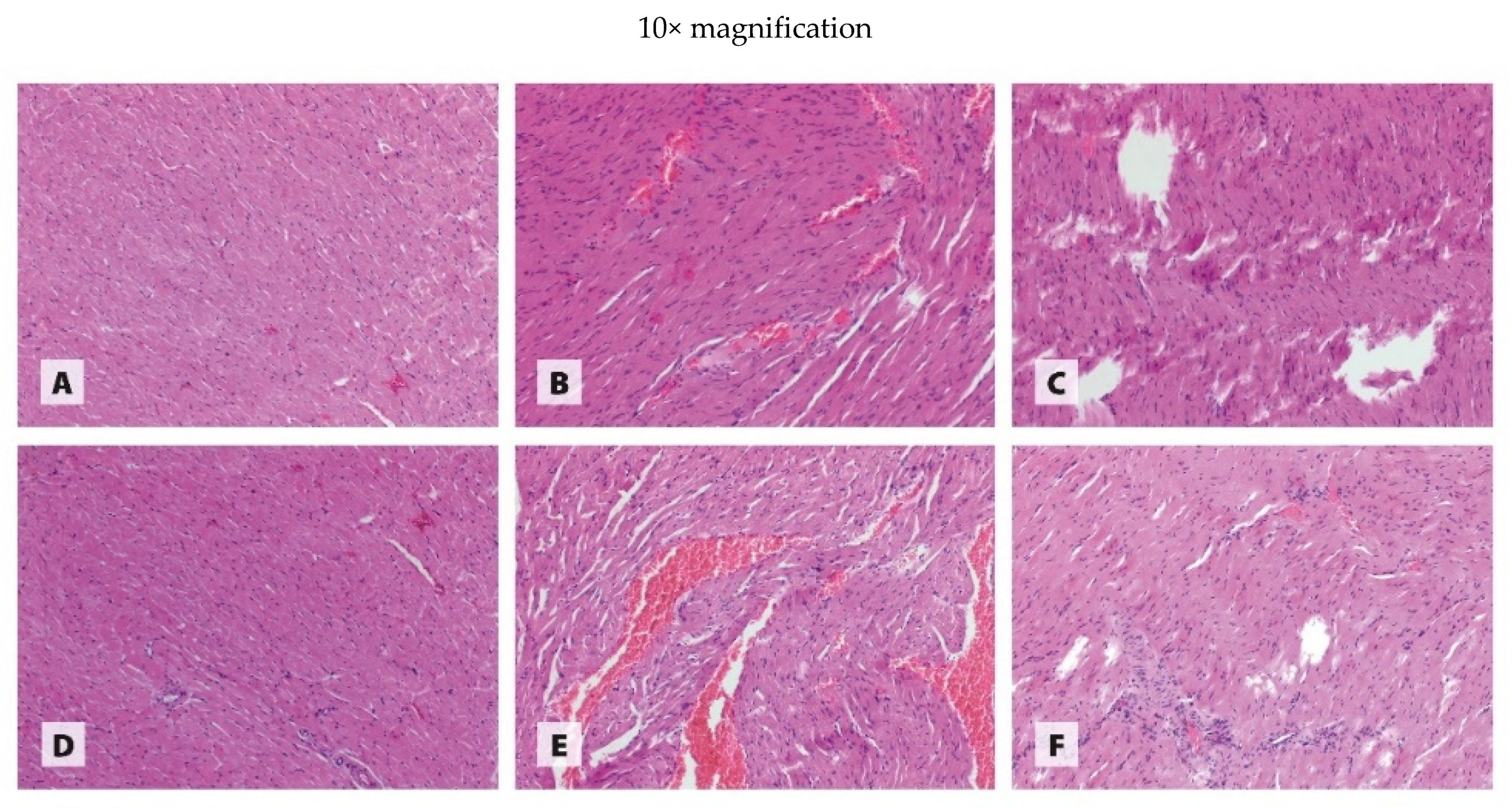
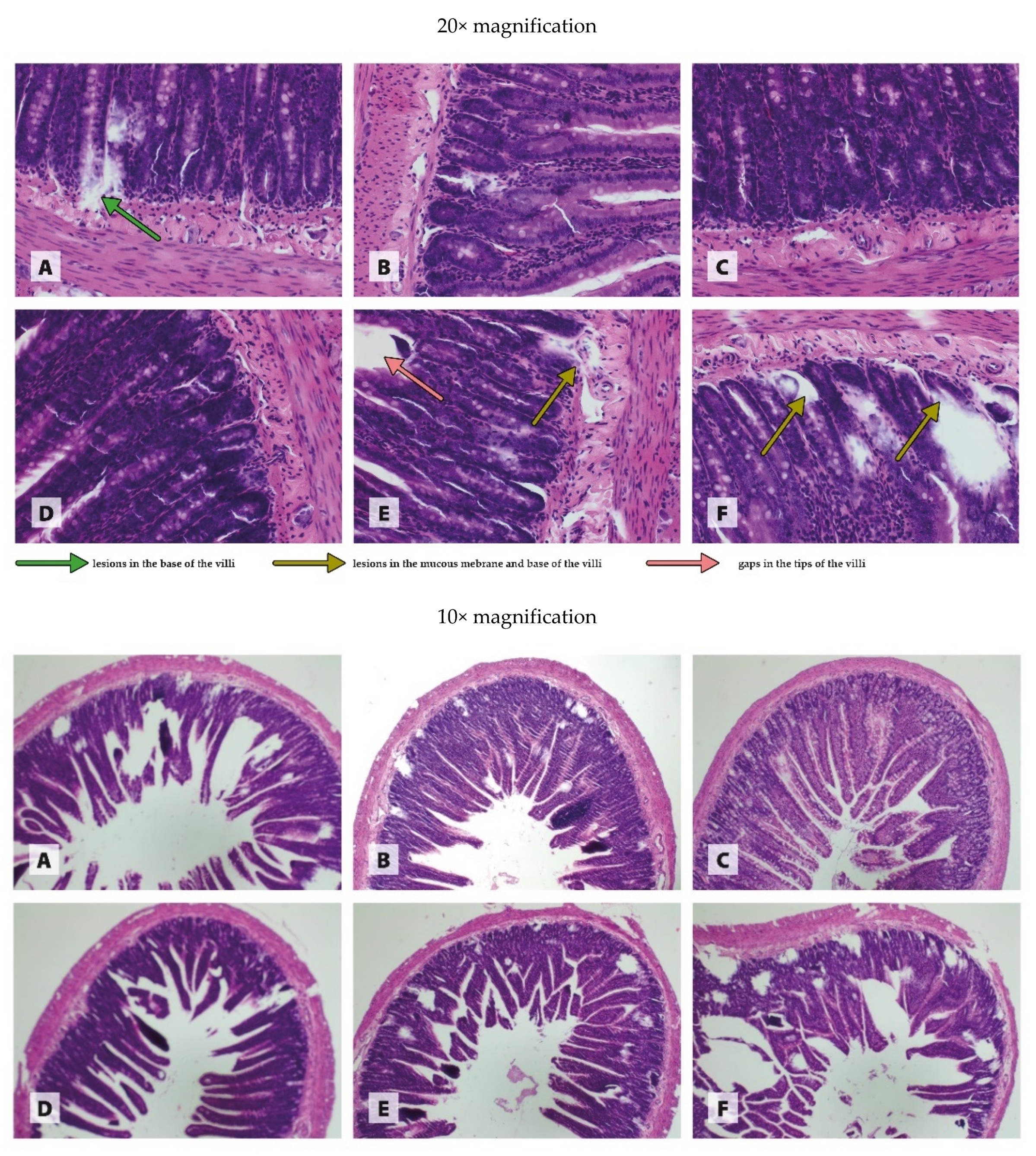
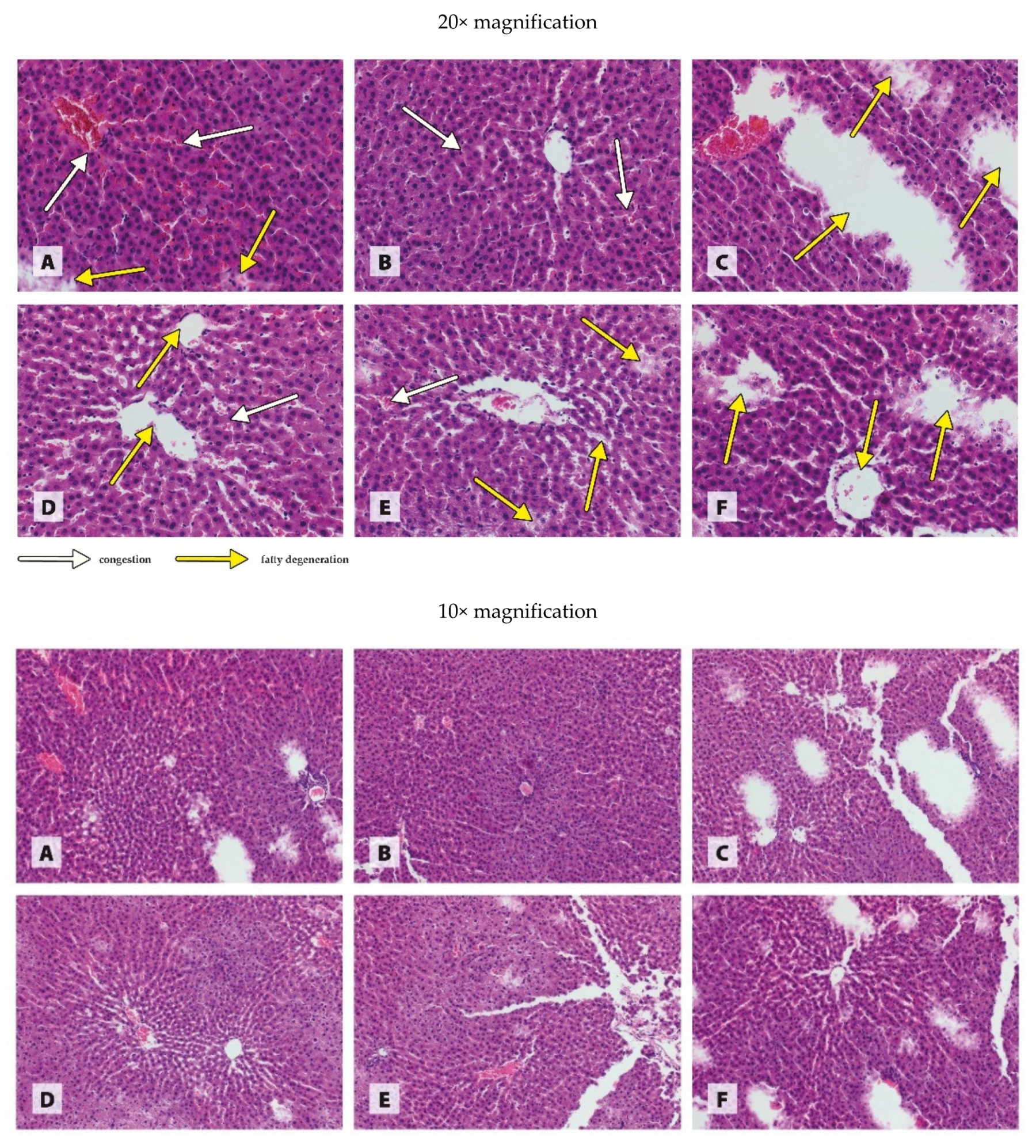
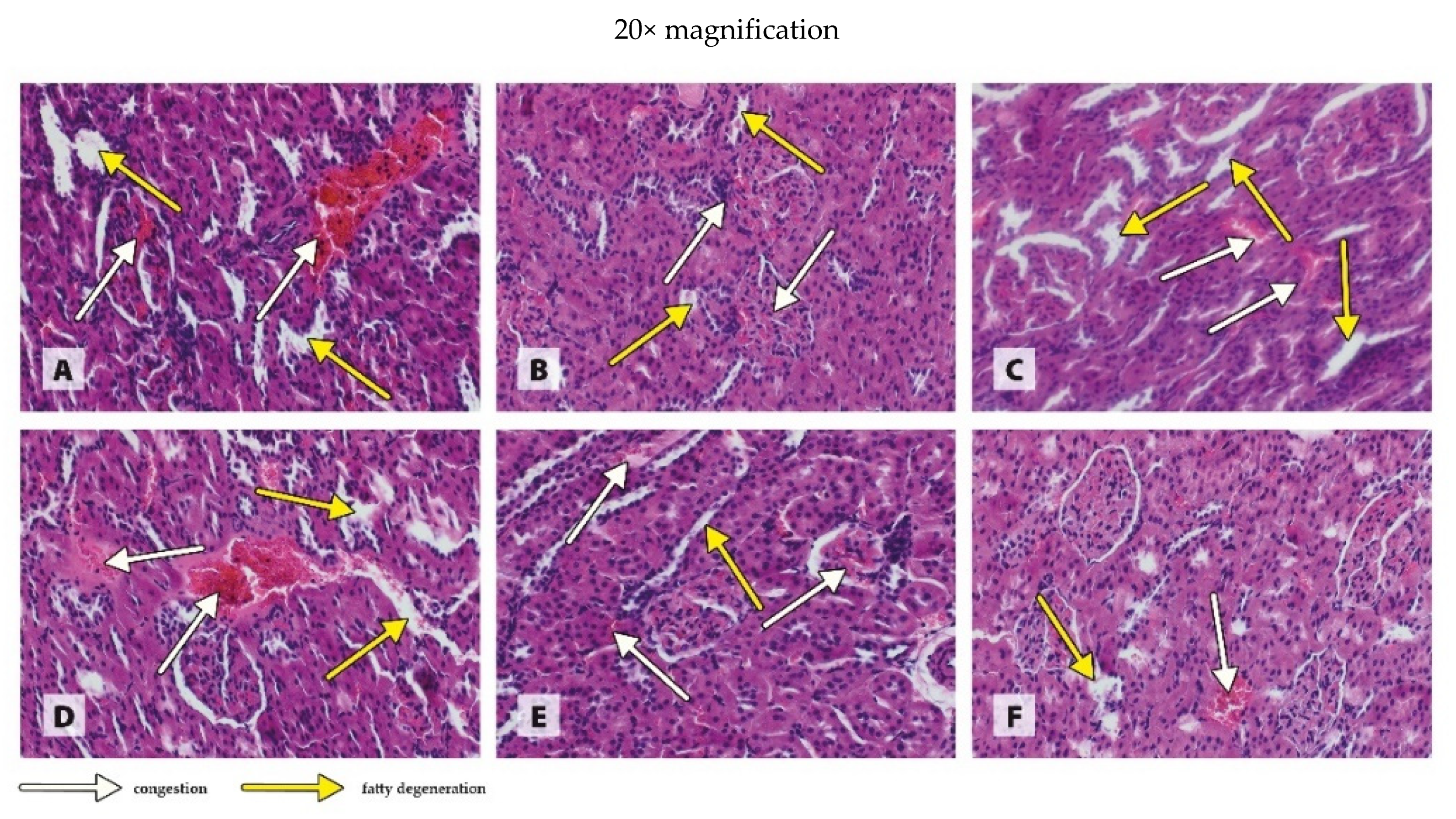
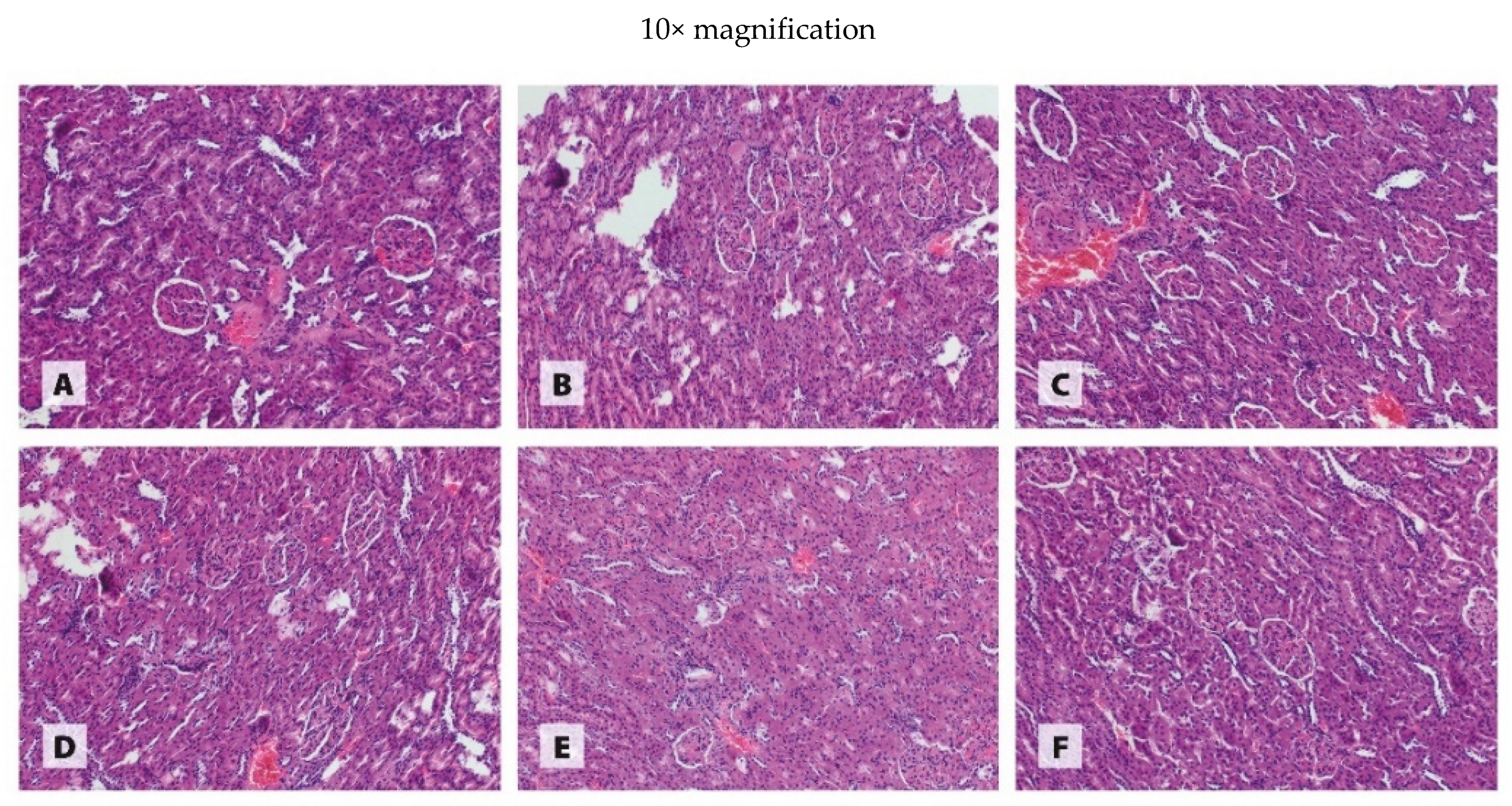
3.3. Histology of Organs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brewster, L.M. Creatine kinase, energy reserve, and hypertension: From bench to bedside. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmieder, R.E. End organ damage in hypertension. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2010, 107, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; He, X.; Lei, S.S.; Zhou, F.C.; Zhang, N.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, Y.Z.; Su, J.; Yu, J.J.; Li, L.Z.; et al. Hypertensive rats treated chronically with Nω-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) induced disorder of hepatic fatty acid metabolism and intestinal pathophysiology. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baradaran, A.; Nasri, H.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Oxidative stress and hypertension: Possibility of hypertension therapy with antioxidants. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2014, 19, 358–367. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Shankar, R.; Singh, G.P. Prevalence and associated risk factors of hypertension: A cross-sectional study in urban varanasi. Int. J. Hypertens. 2017, 2017, 5491838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Pino-García, R.; Rivero-Pérez, M.D.; González-SanJosé, M.L.; Croft, K.D.; Muñiz, P. Antihypertensive and antioxidant effects of supplementation with red wine pomace in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 2444–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touyz, R.M.; Chen, X.; Tabet, F.; Yao, G.; He, G.; Quinn, M.T.; Pagano, P.J.; Schiffrin, E.L. Expression of a gp91phox-containing leukocyte-type NADPH oxidase in human vascular smooth muscle cells: Modulation by Ang II. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feairheller, D.L.; Brown, M.D.; Park, J.Y.; Brinkley, T.E.; Basu, S.; Hagberg, J.M.; Ferrell, R.E.; Fenty-Stewart, N.M. Exercise training, NADPH oxidase p22phox gene polymorphisms, and hypertension. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedro-Botet, J.; Covas, M.I.; Martin, S.; Rubies-Prat, J. Decreased endogenous antioxidant enzymatic status in essential hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2000, 14, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angelova, M.; Asenova, S.; Nedkova, V.; Koleva-Kolarova, R. Copper in the human organism. Trakia J. Sci. 2011, 9, 88–98. [Google Scholar]
- Bost, M.; Houdart, S.; Oberli, M.; Kalonji, E.; Huneau, J.F.; Margaritis, I. Dietary copper and human health: Current evidence and unresolved issues. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2016, 35, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ognik, K.; Stępniowska, A.; Cholewińska, E.; Kozłowski, K. The effect of administration of copper nanoparticles to chickens in drinking water on estimated intestinal absorption of iron, zinc, and calcium. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2045–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tishchenko, K.I.; Beloglazkina, E.K.; Mazhuga, A.G.; Zyk, N.V. Copper-containing enzymes: Site types and low-molecular-weight model compounds. Ref. J. Chem. 2016, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kalita, J.; Bora, H.K.; Misra, U.K. Temporal kinetics of organ damage in copper toxicity: A histopathological correlation in rat model. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 81, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cholewińska, E.; Ognik, K.; Fotschki, B.; Zduńczyk, Z.; Juśkiewicz, J. Comparison of the effect of dietary copper nanoparticles and one copper (II) salt on the copper biodistribution and gastrointestinal and hepatic morphology and function in a rat model. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ognik, K.; Cholewińska, E.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Zduńczyk, Z.; Tutaj, K.; Szlązak, R. The effect of copper nanoparticles and copper (II) salt on redox reactions and epigenetic changes in a rat model. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 103, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ognik, K.; Cholewińska, E.; Tutaj, K.; Cendrowska-Pinkosz, M.; Dworzański, W.; Dworzańska, A.; Juśkiewicz, J. The effect of the source and dosage of dietary Cu on redox status in rat tissues. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaye, R.; Zhao, J.; Bowman, L.; Ding, M. Genotoxicity and carcinogenicity of cobalt-, nickel- and copper-based nanoparticles. Exp. Ther. Med. 2012, 4, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elhussainy, E.M.A.; El-Shourbagy, S. Protective effect of multivitamin complex on copper oxide nanoparticles (nanoCuO) induced toxicity in rats. Bull. Egypt. Soc. Physiol. Sci. 2015, 34, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.C.; Ko, J.W.; Park, S.H.; Shin, N.R.; Shin, I.S.; Moon, C.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, J.C. Comparative toxicity and biodistribution assessments in rats following subchronic oral exposure to copper nanoparticles and microparticles. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, I.C.; Ko, J.W.; Park, S.H.; Lim, J.O.; Shin, I.S.; Moon, C.; Kim, S.H.; Heo, J.D.; Kim, J.C. Comparative toxicity and biodistribution of copper nanoparticles and cupric ions in rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2883–2900. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Weiss, J.; Shahidi, F. Nanotechnology in nutraceuticals and functional foods. Food. Technol. 2006, 3, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Majewski, M.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Krajewska-Włodarczyk, M.; Gromadziński, L.; Socha, K.; Cholewińka, E.; Ognik, K. The Role of 20-HETE, COX, Thromboxane Receptors, and Blood Plasma Antioxidant Status in Vascular Relaxation of Copper-Nanoparticle-Fed WKY Rats. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, P.G. Components of the AIN-93 diets as improvements in the AIN-76A diet. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 838–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ognik, K.; Wertelecki, T. Effect of different vitamin E sources and levels on selected oxidative status indices in blood and tissues as well as on rearing performance of slaughter turkey hens. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2012, 21, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, G.A.; Croft, J.B.; Giles, W.H. The heart, kidney, and brain as target organs in hypertension. Cardiol. Clin. 2002, 20, 225–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskorz, D. Hypertensive mediated organ damage and hypertension management. how to assess beneficial effects of antihypertensive treatments? High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2020, 27, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Gill, M.R. The past and present of serum aminotransferases and the future of liver injury biomarkers. EXCLI J. 2016, 15, 817–828. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, C.; Yan, C.J.; Yuan, X.T.; Zhu, L.P. Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and their potential synergistic effect on alloxan induced oxidative stress conditions during cardiac injury in Sprague–Dawley rats. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 198, 111557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, R.S.; Hussein, M.M.; Soliman, A.H. Effect of naringenin and hesperidin in amelioration of copper oxid nanoparticles toxicity in rat liver. Arabian J. Med. Sci. 2018, 1, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadyari, A.; Razavipour, S.T.; Mohammadbeigi, M.; Negahdary, M.; Ajdary, M. Explore in vivo toxicity assessment of copper oxide nanoparticle in Wistar rats. J. Biol. Today’s World. 2014, 3, 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, M.; Liu, H. Gene expression profiling of nephrotoxicity from copper nanoparticles in rats after repeated oral administration. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 34, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighodaro, O.M.; Akinloye, O.A. First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): Their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anreddy, R.N.R. Copper oxide nanoparticles induces oxidative stress and liver toxicity in rats following oral exposure. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 903–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R.H.; Wu, C.Q.; Yang, B.H.; Ma, H.Z.; Shi, C.; Wang, Q.J.; Wang, Q.X.; Yuan, Y.; Liao, M.Y. Integrated metabolomic analysis of the nano-sized copper particle induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats: A rapid in vivo screening method for nanotoxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2008, 232, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, T.; Afonso, J.; Carvalho, F.; Albino-Teixeira, A. Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidants in Arterial Hypertension. In Lipid Peroxidation; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kulak, E.; Ognik, K.; Stępniowska, A.; Sembratowicz, I. The effect of administration of silver nanoparticles on silver accumulation in tissues and the immune and antioxidant status of chickens. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2018, 27, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, H.C.; Wang, T.; Liao, C.Y.; Cui, L.; Zhou, Q.F.; Yan, B.; Jiang, G.B. Impact of silver nanoparticles on human cells: Effect of particle size. Nanotoxicology 2010, 4, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.; Hu, L.; Qu, G.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, G. Exposure, tissue biodistribution, and biotransformation of nanosilver. NanoImpact 2016, 2, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dietary Treatment 1 | AST U/L | ALT U/L | GGT U/L | CREAT umol/L | UA umol/L | CK U/L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WKY CuCO3 6.5 | 159.85 | 4.14 | 0.93 | 76.54 | 44.20 c | 1124.2 | |
| SHR CuCO3 6.5 | 138.27 | 6.27 | 0.80 | 72.95 | 77.68 b | 1173.4 | |
| WKY CuCO3 3.25 + CuNP3.25 | 207.58 | 5.61 | 0.89 | 77.74 | 70.31 b | 1019.8 | |
| SHR CuCO3 3.25 + CuNP3.25 | 185.84 | 7.54 | 0.92 | 64.58 | 31.47 c | 1792.5 | |
| WKY CuNP6.5 | 195.62 | 4.99 | 0.61 | 96.87 | 118.53 a | 1551.4 | |
| SHR CuNP6.5 | 175.21 | 4.64 | 0.94 | 41.86 | 69.64 b | 1754.2 | |
| SEM | 0.645 | 0.024 | 0.089 | 0.866 | 0.985 | 0.766 | |
| Blood pressure (R) | |||||||
| WKY | 187.69 | 4.91 b | 0.81 | 83.72 a | 77.68 | 1231.8 b | |
| SHR | 166.44 | 6.15 a | 0.89 | 59.80 b | 59.60 | 1573.4 a | |
| Cu source (C) | |||||||
| CuCO3 6.5 | 149.06 b | 5.20 ab | 0.87 | 74.75 | 60.94 | 1148.8 c | |
| CuCO3 3.25 + CuNP3.25 | 196.71 a | 6.57 a | 0.90 | 71.16 | 50.89 | 1406.2 b | |
| CuNP6.5 | 185.41 a | 4.82 b | 0.78 | 69.36 | 94.08 | 1652.8 a | |
| p value | |||||||
| R effect | 0.062 | 0.035 | 0.876 | 0.014 | 0.006 | 0.027 | |
| C effect | 0.002 | 0.023 | 0.072 | 0.681 | <0.001 | 0.003 | |
| R × C interaction | 0.077 | 0.052 | 0.135 | 0.357 | 0.048 | 0.244 | |
| Dietary Treatment 1 | MDA µmol/g | GSH + GSG umol/kg | SOD U/g | CAT U/g | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WKY CuCO3 6.5 | 0.984 ab | 13.237 c | 16.89 | 219.32 | |
| SHR CuCO3 6.5 | 0.787 c | 12.615 c | 26.30 | 234.69 | |
| WKY CuCO3 3.25 + CuNP3.25 | 0.942 b | 20.361 a | 37.01 | 173.76 | |
| SHR CuCO3 3.25 + CuNP3.25 | 0.976 ab | 17.411 b | 37.01 | 176.36 | |
| WKY CuNP6.5 | 1.209 a | 15.767 b | 38.53 | 227.07 | |
| SHR CuNP6.5 | 1.095 ab | 18.655 ab | 32.83 | 293.46 | |
| SEM | 0.048 | 0.145 | 0.231 | 0.645 | |
| Blood pressure (R) | |||||
| WKY | 0.963 | 16.46 | 26.95 a | 196.54 | |
| SHR | 0.881 | 16.23 | 31.65 b | 205.52 | |
| Cu source (C) | |||||
| CuCO3 6.5 | 0.885 | 12.926 | 21.59 b | 227.01 b | |
| CuCO3 3.25 + CuNP3.25 | 0.959 | 18.886 | 37.01 a | 175.06 c | |
| CuNP6.5 | 1.152 | 17.211 | 35.68 a | 260.27 a | |
| p value | |||||
| R effect | 0.042 | 0.752 | 0.024 | 0.974 | |
| C effect | 0.006 | 0.014 | <0.001 | 0.007 | |
| R × C interaction | 0.033 | 0.047 | 0.054 | 0.258 | |
| Dietary Treatment 1 | MDA µmol/g | GSH + GSG umol/kg | SOD U/g | CAT U/g | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WKY CuCO3 6.5 | 2.014 | 18.427 | 20.058 | 909.17 | |
| SHR CuCO3 6.5 | 1.471 | 17.313 | 23.621 | 1453.96 | |
| WKY CuCO3 3.25 + CuNP3.25 | 1.605 | 20.706 | 25.272 | 342.32 | |
| SHR CuCO3 3.25 + CuNP3.25 | 1.504 | 15.903 | 47.646 | 549.53 | |
| WKY CuNP6.5 | 1.993 | 22.078 | 14.240 | 517.79 | |
| SHR CuNP6.5 | 2.253 | 25.816 | 16.657 | 535.09 | |
| SEM | 0.036 | 0.108 | 0.078 | 0.364 | |
| Blood pressure (R) | |||||
| WKY | 1.809 | 19.566 | 22.665 b | 625.74 b | |
| SHR | 1.488 | 16.608 | 35.633 a | 1001.75 a | |
| Cu source (C) | |||||
| CuCO3 6.5 | 1.742 b | 17.870 b | 21.839 b | 1181.56 a | |
| CuCO3 3.25 + CuNP3.25 | 1.555 b | 18.305 b | 36.459 a | 445.92 b | |
| CuNP6.5 | 2.123 a | 23.947 a | 15.448 c | 526.44 b | |
| p value | |||||
| R effect | 0.058 | 0.259 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| C effect | 0.047 | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| R × C interaction | 0.057 | 0.069 | 0.693 | 0.386 | |
| Dietary Treatment 1 | MDA µmol/g | GSH + GSG umol/kg | SOD U/g | CAT U/g | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WKY CuCO3 6.5 | 1.665c | 0.709 | 16.65 | 531.44 | |
| SHR CuCO3 6.5 | 2.625 b | 0.323 | 13.31 | 629.08 | |
| WKY CuCO3 3.25 + CuNP3.25 | 3.059 a | 2.677 | 49.49 | 583.92 | |
| SHR CuCO3 3.25 + CuNP3.25 | 2.081 b | 2.381 | 31.78 | 602.38 | |
| WKY CuNP6.5 | 2.252 b | 5.798 | 27.52 | 758.54 | |
| SHR CuNP6.5 | 2.325 a | 5.386 | 36.42 | 975.24 | |
| SEM | 0.037 | 0.071 | 0.112 | 0.416 | |
| Blood pressure (R) | |||||
| WKY | 2.362 | 1.693 a | 33.07 a | 557.68 b | |
| SHR | 2.353 | 1.352 b | 22.54 b | 615.73 a | |
| Cu source (C) | |||||
| CuCO3 6.5 | 2.145 | 0.516c | 14.98 c | 580.26 b | |
| CuCO3 3.25 + CuNP3.25 | 2.570 | 2.529b | 40.63 a | 593.15 b | |
| CuNP6.5 | 2.289 | 5.592a | 31.97 b | 866.89 a | |
| p value | |||||
| R effect | 0.384 | 0.031 | 0.012 | 0.047 | |
| C effect | 0.008 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.008 | |
| R × C interaction | 0.044 | 0.749 | 0.052 | 0.174 | |
| Dietary Treatment 1 | MDA µmol/g | GSH + GSG umol/kg | SOD U/g | CAT U/g | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WKY CuCO3 6.5 | 5.603 a | 19.564 | 11.068 | 1892.28 a | |
| SHR CuCO3 6.5 | 4.135 b | 7.037 | 11.163 | 1700.45 b | |
| WKY CuCO3 3.25 + CuNP3.25 | 6.429 a | 10.811 | 10.618 | 1263.13 d | |
| SHR CuCO3 3.25 + CuNP3.25 | 6.855 a | 18.109 | 10.551 | 1478.23 c | |
| WKY CuNP6.5 | 4.988 ab | 8.679 | 11.362 | 1756.64 b | |
| SHR CuNP6.5 | 5.075 ab | 8.552 | 10.769 | 1443.23 c | |
| SEM | 0.026 | 0.044 | 0.124 | 0.892 | |
| Blood pressure (R) | |||||
| WKY | 6.016 | 15.188 | 10.843 | 1577.71 | |
| SHR | 5.495 | 12.573 | 10.857 | 1589.34 | |
| Cu source (C) | |||||
| CuCO3 6.5 | 4.869 | 13.301 a | 11.115 | 1796.37 | |
| CuCO3 3.25 + CuNP3.25 | 6.642 | 14.460 a | 10.584 | 1370.68 | |
| CuNP6.5 | 5.032 | 8.616 b | 11.065 | 1599.93 | |
| p value | |||||
| R effect | 0.072 | 0.477 | 0.647 | 0.824 | |
| C effect | 0.048 | <0.001 | 0.068 | 0.006 | |
| R × C interaction | 0.049 | 0.062 | 0.077 | 0.004 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cholewińska, E.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Majewski, M.; Smagieł, R.; Listos, P.; Fotschki, B.; Godycka-Kłos, I.; Ognik, K. Effect of Copper Nanoparticles in the Diet of WKY and SHR Rats on the Redox Profile and Histology of the Heart, Liver, Kidney, and Small Intestine. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050910
Cholewińska E, Juśkiewicz J, Majewski M, Smagieł R, Listos P, Fotschki B, Godycka-Kłos I, Ognik K. Effect of Copper Nanoparticles in the Diet of WKY and SHR Rats on the Redox Profile and Histology of the Heart, Liver, Kidney, and Small Intestine. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(5):910. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050910
Chicago/Turabian StyleCholewińska, Ewelina, Jerzy Juśkiewicz, Michał Majewski, Radosław Smagieł, Piotr Listos, Bartosz Fotschki, Irena Godycka-Kłos, and Katarzyna Ognik. 2022. "Effect of Copper Nanoparticles in the Diet of WKY and SHR Rats on the Redox Profile and Histology of the Heart, Liver, Kidney, and Small Intestine" Antioxidants 11, no. 5: 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050910
APA StyleCholewińska, E., Juśkiewicz, J., Majewski, M., Smagieł, R., Listos, P., Fotschki, B., Godycka-Kłos, I., & Ognik, K. (2022). Effect of Copper Nanoparticles in the Diet of WKY and SHR Rats on the Redox Profile and Histology of the Heart, Liver, Kidney, and Small Intestine. Antioxidants, 11(5), 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050910







