Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammation and Antiaging Activities of Artocarpus altilis Methanolic Extract on Urban Particulate Matter-Induced HaCaT Keratinocytes Damage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extraction Methods of Artocarpin altilis
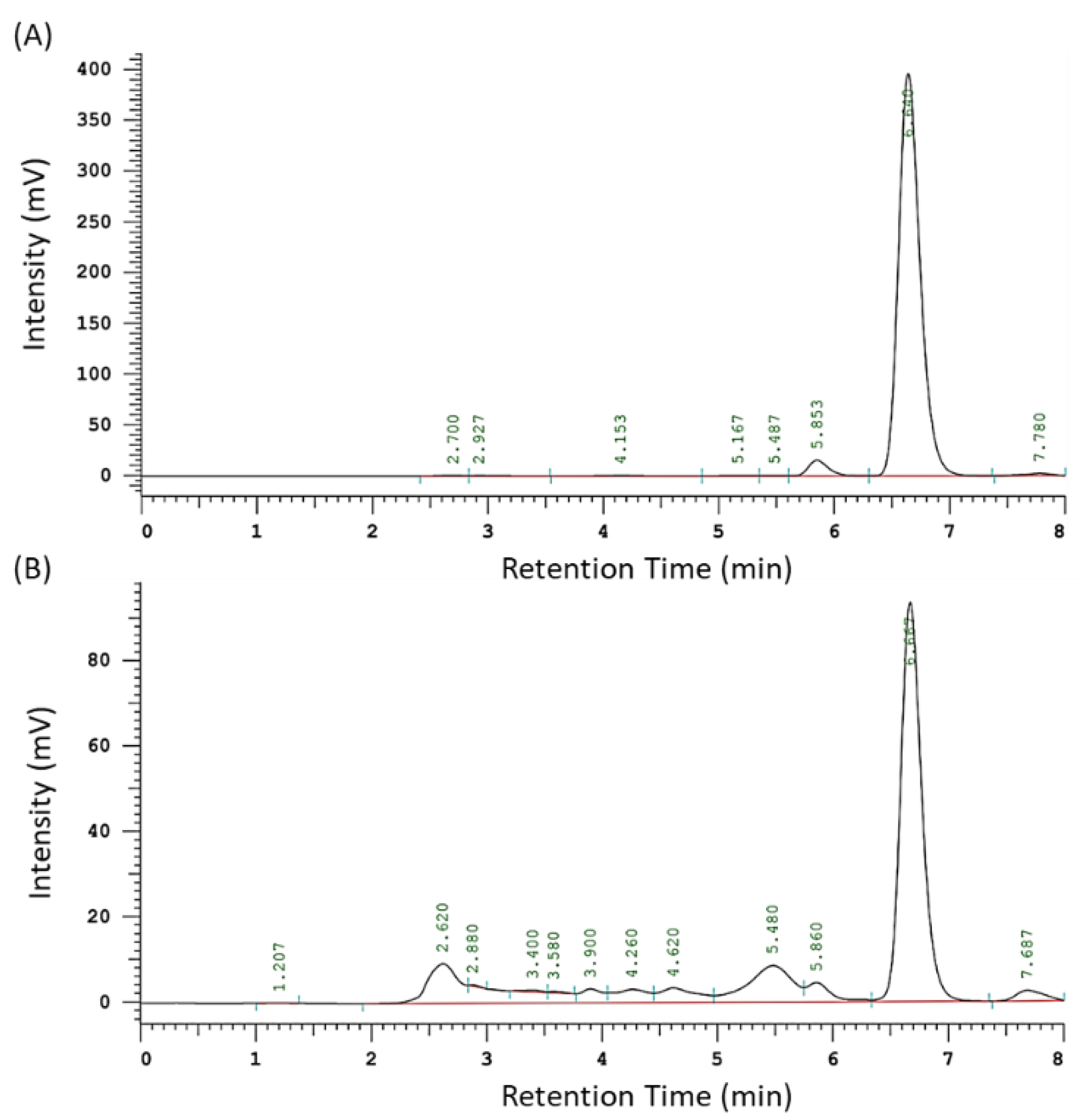
2.2. Quantification of the Index Component of AAM
2.3. Cell Line and Culture
2.4. Preparation of Particulate Matter
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
2.6. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assay
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and discussion
3.1. The Yield and Artocarpin Content of AAM
3.2. Effects of AAM on HaCaT Keratinocytes Cell Viability
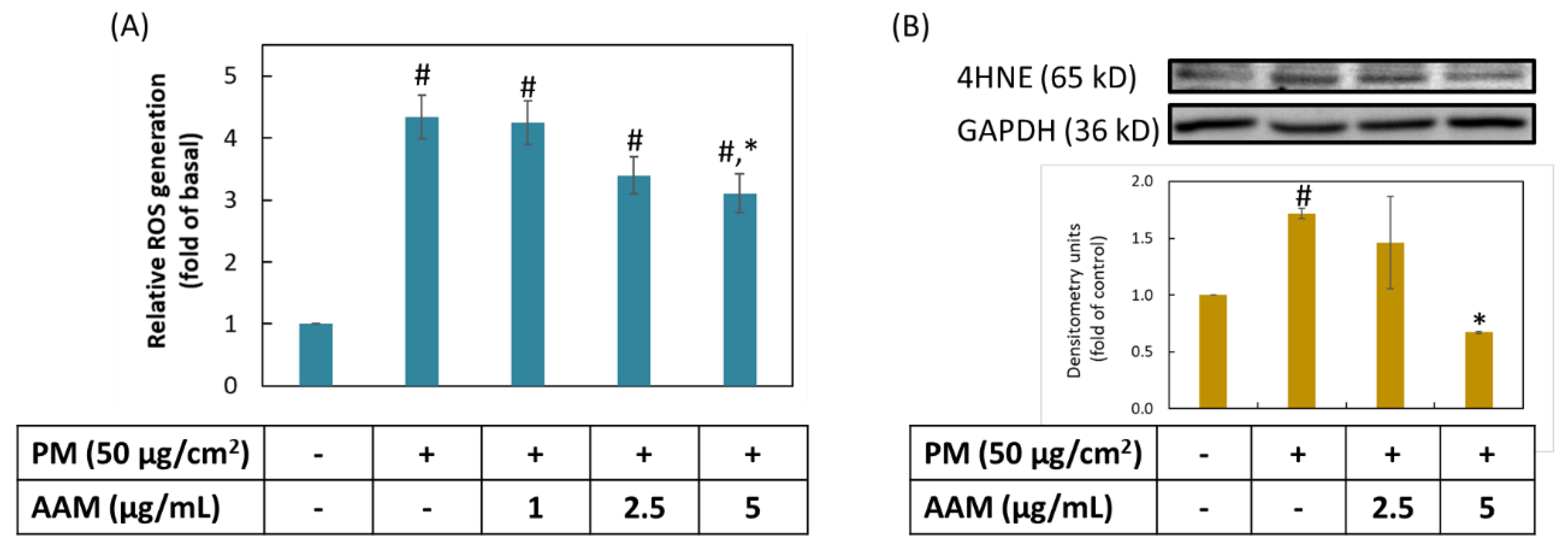
3.3. AAM Inhibited PM-Stimulated Oxidative Stress on HaCaT Cells
3.4. Inhibition of AAM on PM-Induced Inflammation in HaCaT Cells
3.5. AAM Suppressed PM-Induced Phosphorylation of MAPK Signaling Pathway
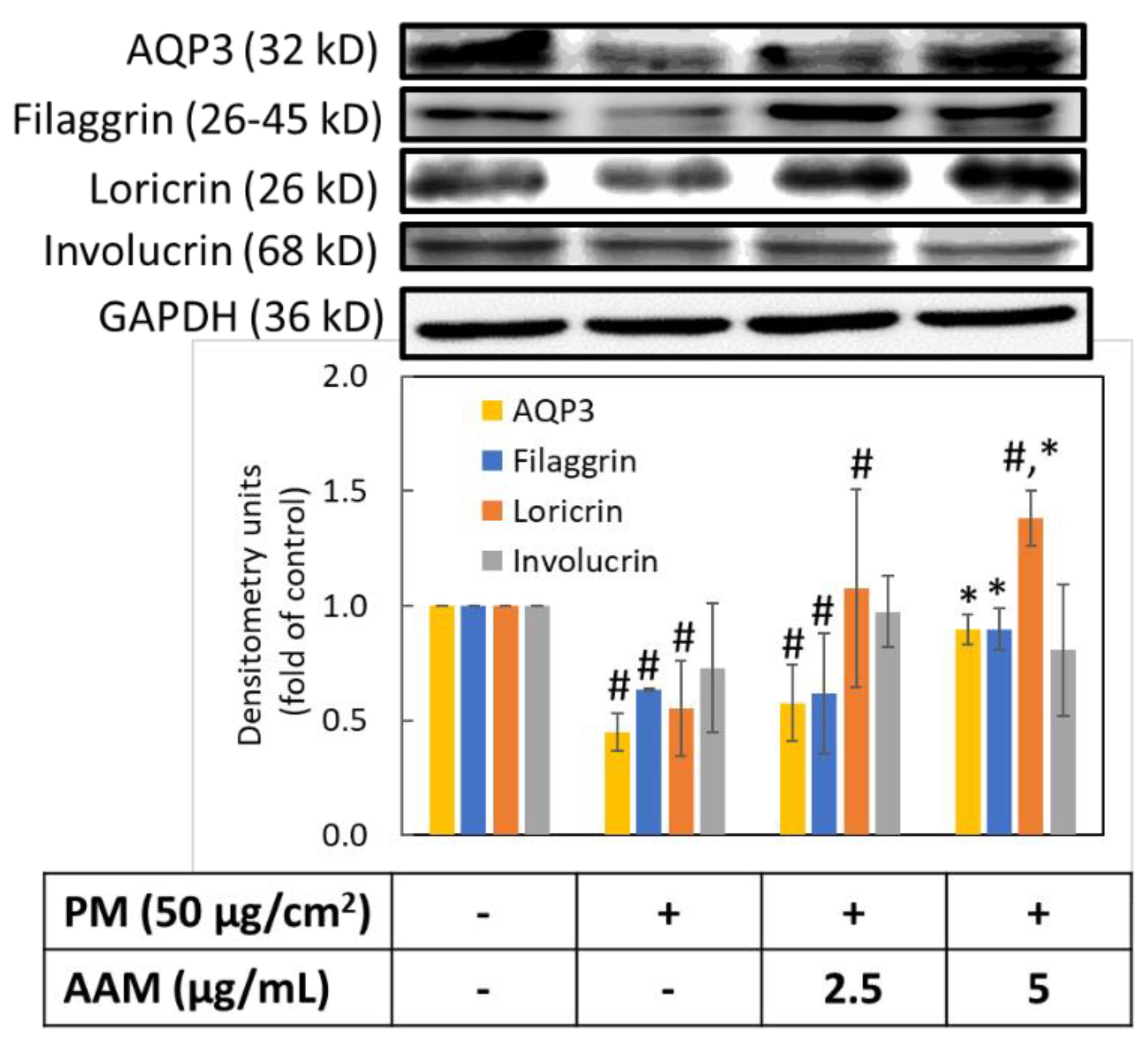
3.6. AAM Suppressed PM-Induced Aging-Related Protein Expression
3.7. AAM Prevented PM-Induced Skin Barrier Dysfunction
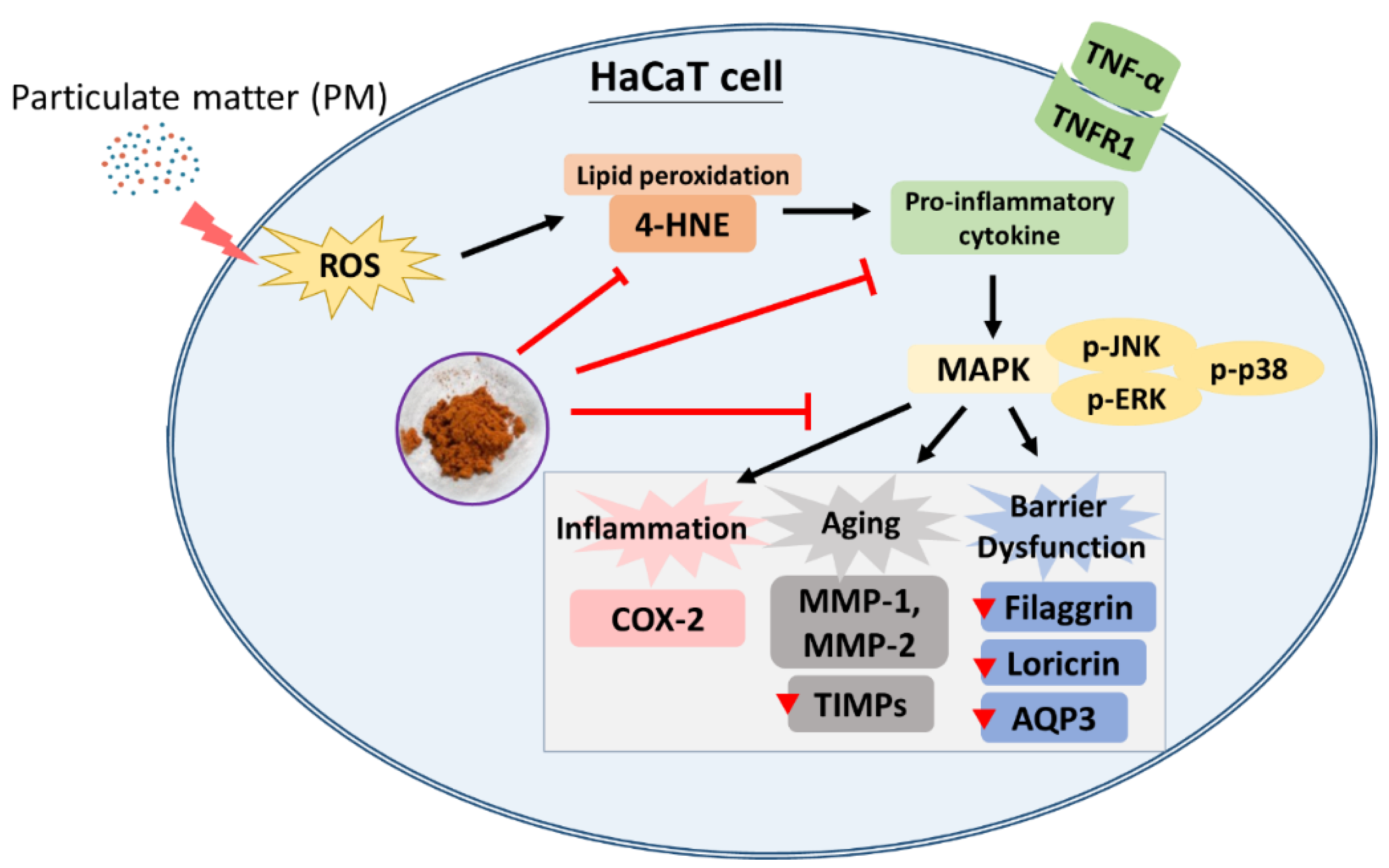
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dijkhoff, I.M.; Drasler, B.; Karakocak, B.B.; Petri-Fink, A.; Valacchi, G.; Eeman, M.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Impact of airborne particulate matter on skin: A systematic review from epidemiology to in vitro studies. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Pérez, R.D.; Taborda, N.A.; Gómez, D.M.; Narvaez, J.F.; Porras, J.; Hernandez, J.C. Inflammatory effects of particulate matter air pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 42390–42404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.E.; Kim, J.; Goleva, E.; Berdyshev, E.; Lee, J.; Vang, K.A.; Lee, U.H.; Han, S.; Leung, S.; Hall, C.F.; et al. Particulate matter causes skin barrier dysfunction. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e145185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morakinyo, O.M.; Mokgobu, M.I.; Mukhola, M.S.; Hunter, R.P. Health Outcomes of Exposure to Biological and Chemical Components of Inhalable and Respirable Particulate Matter. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Baan, R.; Mattock, H.; Straif, K. The carcinogenicity of outdoor air pollution. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1262–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bize, C.; Le Gélébart, E.; Moga, A.; Payré, B.; Garcia, C. Barrier disruption, dehydration and inflammation: Investigation of the vicious circle underlying dry skin. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 43, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.W.; Lee, H.S.; Na, J.I.; Huh, C.H.; Park, K.C.; Choi, H.R. Resveratrol Inhibits Particulate Matter-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Human Keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jeong, G.J.; Hong, J.Y.; Park, K.Y.; Lee, M.K.; Seo, S.J. Negative Air Ions Alleviate Particulate Matter-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in the Human Keratinocyte Cell Line HaCaT. Ann. Dermatol. 2021, 33, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.H.; Nguyen, U.T.; Kim, Y.H.; Shin, H.M.; Yang, I.J. Astragali Radix and its compound formononetin ameliorate diesel particulate matter-induced skin barrier disruption by regulation of keratinocyte proliferation and apoptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 228, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.E.; Howell, M.D.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Gilleaudeau, P.M.; Cardinale, I.R.; Boguniewicz, M.; Krueger, J.G.; Leung, D.Y. TNF-α downregulates filaggrin and loricrin through c-Jun N-terminal kinase: Role for TNF-α antagonists to improve skin barrier. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Lin, Z.C.; Hu, S.C.; Chiang, Y.C.; Hsu, L.F.; Lin, Y.C.; Lee, I.T.; Tsai, M.H.; Fang, J.Y. Urban particulate matter down-regulates filaggrin via COX2 expression/PGE2 production leading to skin barrier dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hieda, D.S.; Anastacio da Costa Carvalho, L.; Vaz de Mello, B.; Oliveira, E.A.; Romano de Assis, S.; Wu, J.; Du-Thumm, L.; Viana da Silva, C.L.; Roubicek, D.A.; Maria-Engler, S.S.; et al. Air Particulate Matter Induces Skin Barrier Dysfunction and Water Transport Alteration on a Reconstructed Human Epidermis Model. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 2343–2352.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.T.; Lee, C.W.; Ko, H.H.; Yen, F.L. Extracts of Artocarpus communis decrease α-melanocyte stimulating hormone-induced melanogenesis through activation of ERK and JNK signaling pathways. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 724314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.W.; Ko, H.H.; Chai, C.Y.; Chen, W.T.; Lin, C.C.; Yen, F.L. Effect of Artocarpus communis Extract on UVB Irradiation-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Hairless Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3860–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.W.; Ko, H.H.; Lin, C.C.; Chai, C.Y.; Chen, W.T.; Yen, F.L. Artocarpin attenuates ultraviolet B-induced skin damage in hairless mice by antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangpraditkun, K.; Tissot, M.; Joompang, A.; Charoensit, P.; Grandmottet, F.; Viyoch, J.; Viennet, C. Prevention by the Natural Artocarpin of Morphological and Biochemical Alterations on UVB-Induced HaCaT Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5067957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H.; Liu, J.F.; Chiang, Y.C.; Hu, S.C.; Hsu, L.F.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, Z.C.; Lee, H.C.; Chen, M.C.; Huang, C.L.; et al. Artocarpin, an isoprenyl flavonoid, induces p53-dependent or independent apoptosis via ROS-mediated MAPKs and Akt activation in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28342–28358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, C.W.; Tzeng, W.S.; Lin, L.T.; Lee, C.W.; Yen, M.H.; Yen, F.L.; Lin, C.C. Artocarpus communis Induces Autophagic Instead of Apoptotic Cell Death in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 559–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonpanya, N.; Sanookpan, K.; Sriratanasak, N.; Vinayanuwattikun, C.; Wichadakul, D.; Sritularak, B.; Chanvorachote, P. Artocarpin Targets Focal Adhesion Kinase-Dependent Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition and Suppresses Migratory-Associated Integrins in Lung Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.J.; Chen, C.C.; Leu, Y.L.; Lin, M.W.; Chiu, M.M.; Wang, S.H. The effects of artocarpin on wound healing: In vitro and in vivo studies. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Y.; Huang, P.H.; Tseng, C.H.; Yen, F.L. Topical Artocarpus communis Nanoparticles Improved the Water Solubility and Skin Permeation of Raw, A. communis Extract, Improving Its Photoprotective Effect. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.H.; Hu, S.C.S.; Yen, F.L.; Tseng, C.H. Improvement of Skin Penetration, Antipollutant Activity and Skin Hydration of 7,3’,4’-Trihydroxyisoflavone Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, A.X.; Hyun, Y.J.; Piao, M.J.; Fernando, P.; Kang, K.A.; Ahn, M.J.; Yi, J.M.; Kang, H.K.; Koh, Y.S.; Lee, N.H.; et al. Eckol Inhibits Particulate Matter 2.5-Induced Skin Keratinocyte Damage via MAPK Signaling Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.W.; Su, Y.H.; Chiang, Y.C.; Lee, I.T.; Li, S.Y.; Lee, H.C.; Hsu, L.F.; Yan, Y.L.; Li, H.Y.; Chen, M.C.; et al. Glycofullerenes Inhibit Particulate Matter Induced Inflammation and Loss of Barrier Proteins in HaCaT Human Keratinocytes. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.Y.; Ngoc, L.T.N.; Chae, M.; Tran, V.V.; Lee, Y.C. Effects of Microwave-Assisted Opuntia Humifusa Extract in Inhibiting the Impacts of Particulate Matter on Human Keratinocyte Skin Cell. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, P.; Piao, M.J.; Zhen, A.X.; Ahn, M.J.; Yi, J.M.; Choi, Y.H.; Hyun, J.W. Extract of Cornus officinalis Protects Keratinocytes from Particulate Matter-induced Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Gomez, H.; Murugan, R.; Hong, X.; Xu, D.; Jiang, F.; Peng, Z.Y. Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Ferroptosis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5080843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sticozzi, C.; Belmonte, G.; Pecorelli, A.; Arezzini, B.; Gardi, C.; Maioli, E.; Miracco, C.; Toscano, M.; Forman, H.J.; Valacchi, G. Cigarette smoke affects keratinocytes SRB1 expression and localization via H2O2 production and HNE protein adducts formation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, A.; Cervellati, C.; Muresan, X.M.; Belmonte, G.; Pecorelli, A.; Cervellati, F.; Benedusi, M.; Evelson, P.; Valacchi, G. Keratinocytes oxidative damage mechanisms related to airbone particle matter exposure. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2018, 172, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, P.; Milkovic, L.; Zarkovic, N.; Waeg, G.; Rattan, S.I. Lipid peroxidation-derived 4-hydroxynonenal-modified proteins accumulate in human facial skin fibroblasts during ageing in vitro. Biogerontology 2014, 15, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surowiak, P.; Gansukh, T.; Donizy, P.; Halon, A.; Rybak, Z. Increase in cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts in photoaged skin. J. Cosmet. Dermator. 2014, 13, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.J.; Yi, C.O.; Jeon, B.T.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Kang, G.M.; Lee, J.E.; Roh, G.S.; Lee, J.D. Curcumin attenuates radiation-induced inflammation and fibrosis in rat lungs. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 17, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, G.J.; Park, K.Y.; Lee, M.K.; Seo, S.J. Particulate matter induces pro-inflammatory cytokines via phosphorylation of p38 MAPK possibly leading to dermal inflammaging. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas-Rodríguez, S.; Folgueras, A.R.; López-Otín, C. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in aging: Tissue remodeling and beyond. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 2015–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.R.; Alam, M.B.; Park, J.H.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, S.H. Attenuation of UVB-Induced Photo-Aging by Polyphenolic-Rich Spatholobus Suberectus Stem Extract Via Modulation of MAPK/AP-1/MMPs Signaling in Human Keratinocytes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, P.M. Skin barrier function. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2008, 8, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Won, K.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, H.B.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, H.M. Positive Promoting Effects of Smilax China Flower Absolute on the Wound Healing/Skin Barrier Repair-Related Responses of HaCaT Human Skin Keratinocytes. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2001051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, S.; Sauder, D.N. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor type 1 (p55) is a main mediator for TNF-alpha-induced skin inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 1713–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.-Y.; Pan, C.-C.; Tseng, C.-H.; Yen, F.-L. Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammation and Antiaging Activities of Artocarpus altilis Methanolic Extract on Urban Particulate Matter-Induced HaCaT Keratinocytes Damage. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112304
Yang C-Y, Pan C-C, Tseng C-H, Yen F-L. Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammation and Antiaging Activities of Artocarpus altilis Methanolic Extract on Urban Particulate Matter-Induced HaCaT Keratinocytes Damage. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(11):2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112304
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Chun-Yin, Cheng-Chang Pan, Chih-Hua Tseng, and Feng-Lin Yen. 2022. "Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammation and Antiaging Activities of Artocarpus altilis Methanolic Extract on Urban Particulate Matter-Induced HaCaT Keratinocytes Damage" Antioxidants 11, no. 11: 2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112304
APA StyleYang, C.-Y., Pan, C.-C., Tseng, C.-H., & Yen, F.-L. (2022). Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammation and Antiaging Activities of Artocarpus altilis Methanolic Extract on Urban Particulate Matter-Induced HaCaT Keratinocytes Damage. Antioxidants, 11(11), 2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112304






