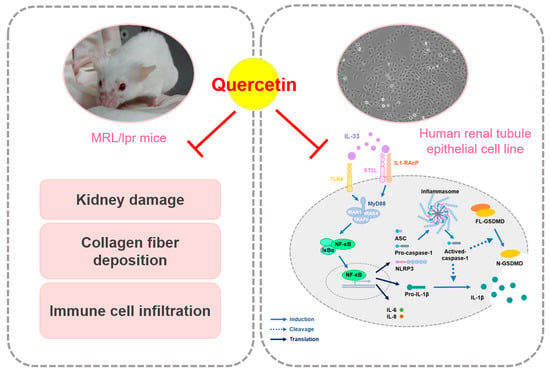
Quercetin Ameliorates Renal Injury and Pyroptosis in Lupus Nephritis through Inhibiting IL-33/ST2 Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagent Preparation
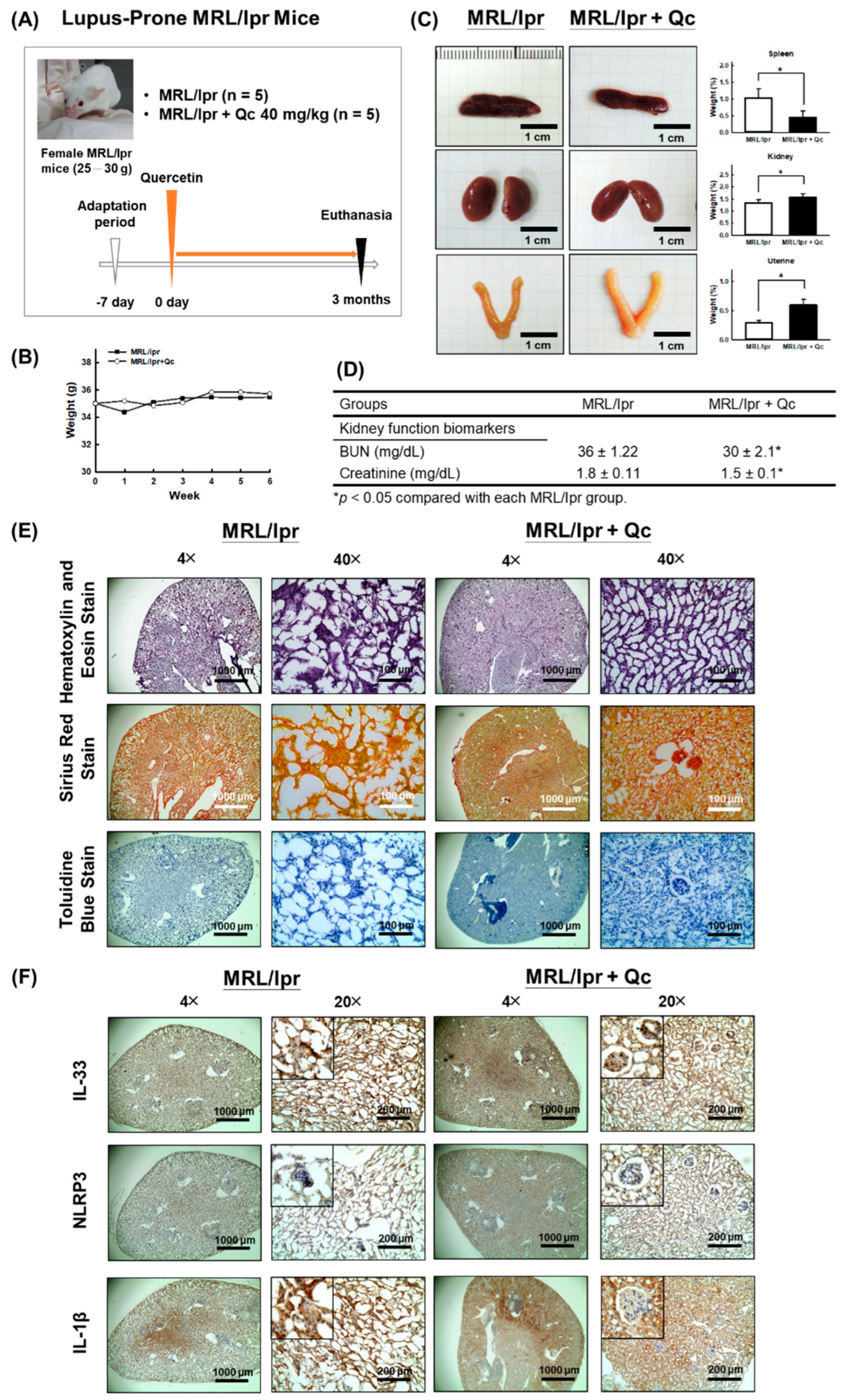
2.2. MRL/lpr Mice
2.3. Renal Function Assessment
2.4. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.5. Cell Culture and Cell Viability
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.7. Cytoplasmic and Nucleus Extraction Preparation
2.8. Western Blotting Analysis
2.9. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quercetin Relieves Symptoms of Lupus Nephritis in MRL/lpr Mice Model
3.2. Quercetin Attenuates the Pathological Changes in MRL/lpr Mice Model
3.3. Quercetin Reduces IL-33-Induced Fibrosis in Human Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Line
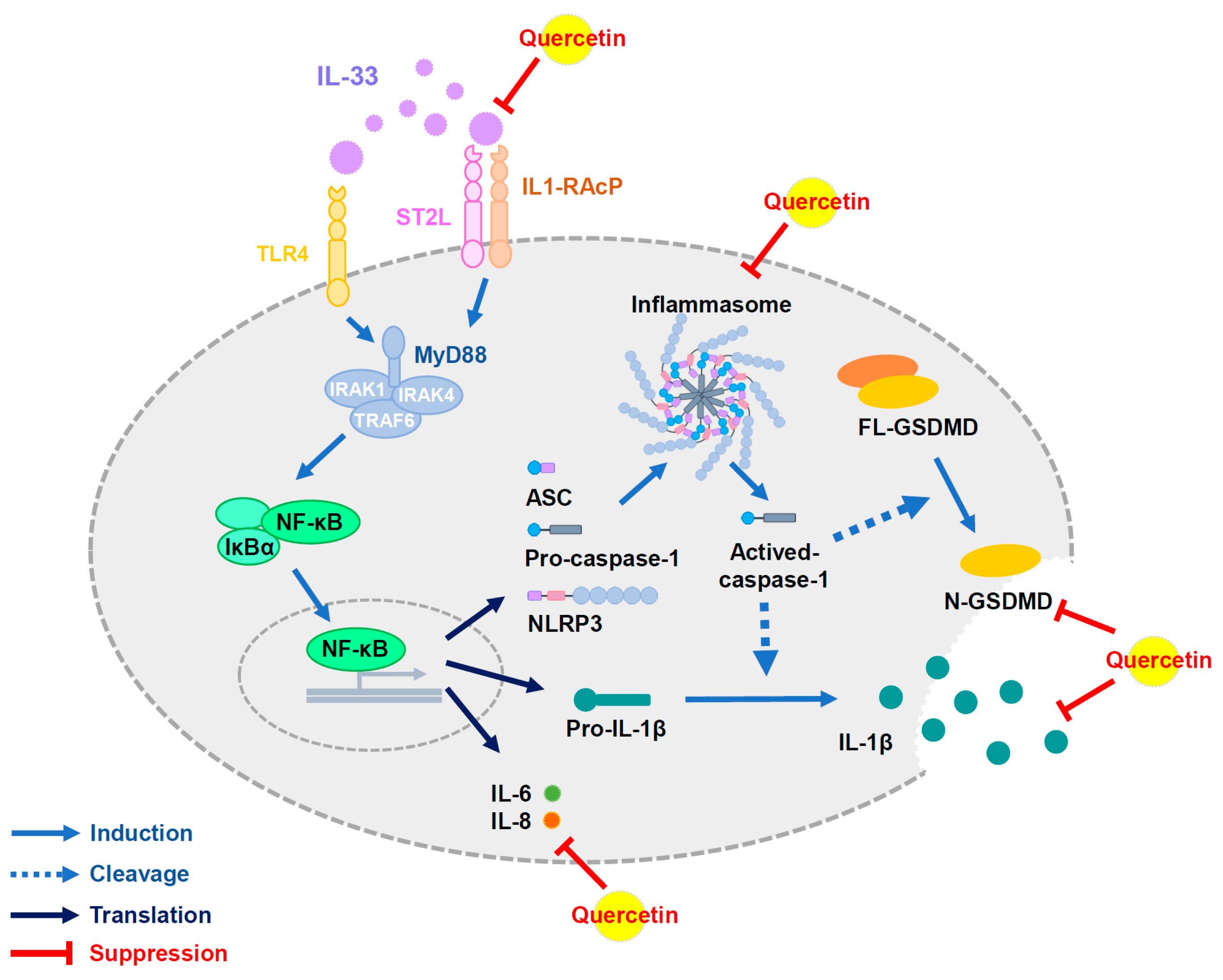
3.4. Quercetin Suppresses IL-33-Stimulated Inflammasome and Pyroptosis-Associated Protein in Human Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Line
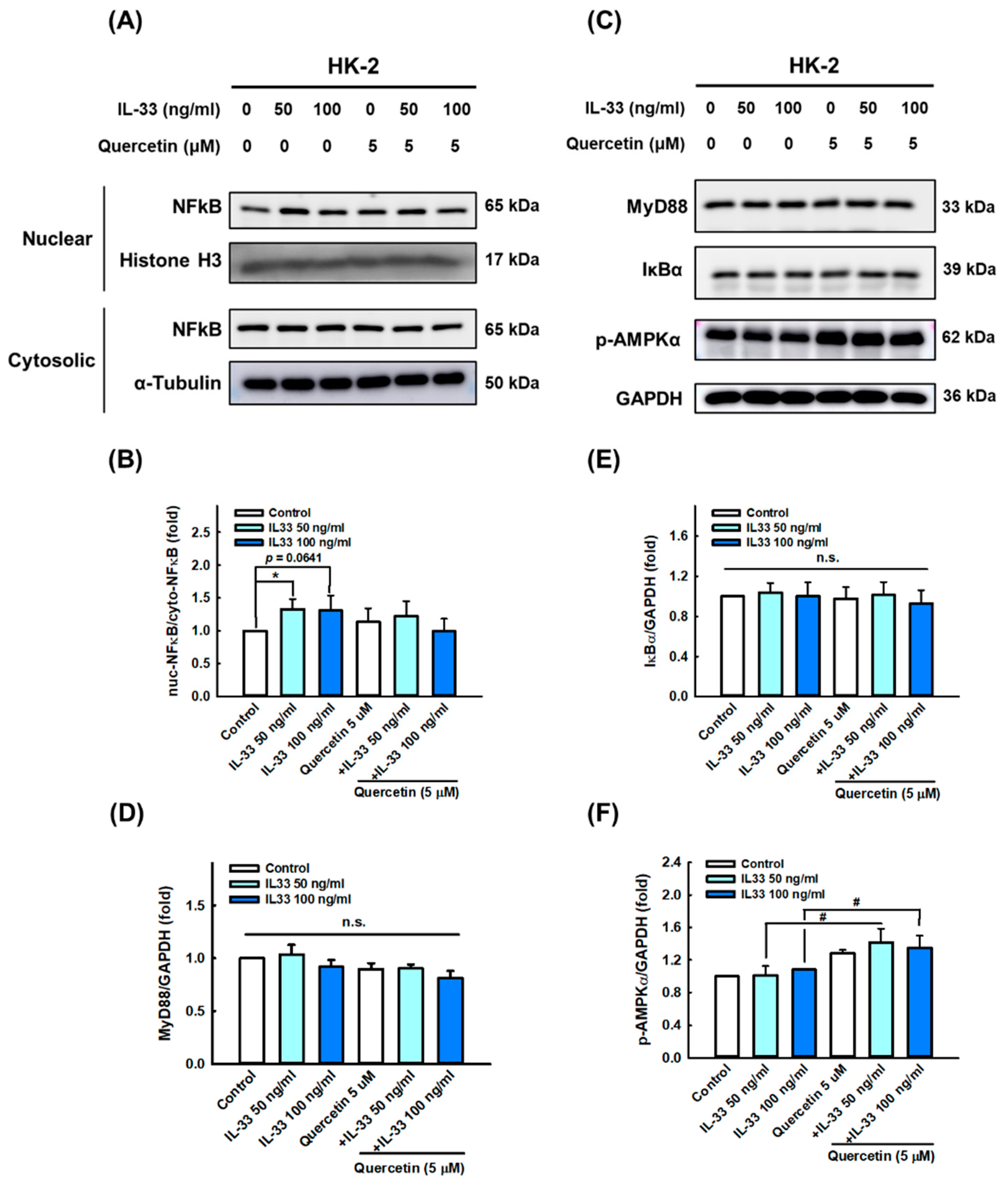
3.5. Quercetin Regulates IL-33-Stimulated Inflammatory Pathways in Human Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Line
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, A.; Isenberg, D.A. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroz, N.; Segal, M.S. Lupus nephritis and end-stage kidney disease. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 346, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, H.J.; Saxena, R.; Zhao, M.H.; Parodis, I.; Salmon, J.E.; Mohan, C. Lupus nephritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostopoulou, M.; Adamichou, C.; Bertsias, G. An update on the diagnosis and management of lupus nephritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montigny, P.M.; Houssiau, F.A. New treatment options in lupus nephritis. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2022, 70, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Kostopoulou, M.; Cheema, K.; Anders, H.J.; Aringer, M.; Bajema, I.; Boletis, J.; Frangou, E.; Houssiau, F.A.; Hollis, J.; et al. 2019 update of the joint european league against rheumatism and european renal association-european dialysis and transplant association (eular/era-edta) recommendations for the management of lupus nephritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Healy, H.; Kassianos, A.J. The emerging role of renal tubular epithelial cells in the immunological pathophysiology of lupus nephritis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 578952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.; Yang, C. Renal tubular epithelial cells: The neglected mediator of tubulointerstitial fibrosis after injury. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.-P. Interleukin-33 (il-33): A critical review of its biology and the mechanisms involved in its release as a potent extracellular cytokine. Cytokine 2022, 156, 155891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. Il-33: An alarmin cytokine with crucial roles in innate immunity, inflammation and allergy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 31, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, G. Role of il-33 and its receptor in t cell-mediated autoimmune diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 587376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefrançais, E.; Roga, S.; Gautier, V.; Gonzalez-de-Peredo, A.; Monsarrat, B.; Girard, J.P.; Cayrol, C. Il-33 is processed into mature bioactive forms by neutrophil elastase and cathepsin g. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1673–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, G.; Lipsky, B.P.; Smithgall, M.D.; Meininger, D.; Siu, S.; Talabot-Ayer, D.; Gabay, C.; Smith, D.E. The il-1 receptor accessory protein (acp) is required for il-33 signaling and soluble acp enhances the ability of soluble st2 to inhibit il-33. Cytokine 2008, 42, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkar, R.; Lee, R.T. The il-33/st2 pathway: Therapeutic target and novel biomarker. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, I.; Dieplinger, B.; Mueller, T. St2 and the st2/il-33 signalling pathway-biochemistry and pathophysiology in animal models and humans. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2019, 495, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdaca, G.; Greco, M.; Tonacci, A.; Negrini, S.; Borro, M.; Puppo, F.; Gangemi, S. Il-33/il-31 axis in immune-mediated and allergic diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarrand, J.; Soyfoo, M. Involvement of il-33 in the pathophysiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Xi, W.; Li, C.; Zhong, R. Association of increased serum il-33 levels with clinical and laboratory characteristics of systemic lupus erythematosus in chinese population. Clin. Exp. Med. 2011, 11, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Lin, W.; Zheng, X. Il-33 neutralization suppresses lupus disease in lupus-prone mice. Inflammation 2014, 37, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septembre-Malaterre, A.; Boumendjel, A.; Seteyen, A.S.; Boina, C.; Gasque, P.; Guiraud, P.; Sélambarom, J. Focus on the high therapeutic potentials of quercetin and its derivatives. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2022, 2, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Reyes, D.; Morales, A.I.; Prieto, M. Transit and metabolic pathways of quercetin in tubular cells: Involvement of its antioxidant properties in the kidney. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khayri, J.M.; Sahana, G.R.; Nagella, P.; Joseph, B.V.; Alessa, F.M.; Al-Mssallem, M.Q. Flavonoids as potential anti-inflammatory molecules: A review. Molecules 2022, 27, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, A.A.; El-Magd, M.A.; Ahmed, M.M.; Ghamry, H.I.; Alshahrani, M.Y.; Hegazy, R.A.; Magdy, A.; El-Fotoh, M.F.A. Quercetin alleviated multi-walled carbon nanotubes-induced neurotoxicity in mice through inhibition of oxidation, inflammation, and pyroptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, P.; Lin, W.; Deng, X.; Ba, X.; Han, L.; Chen, Z.; Qin, K.; Huang, Y.; Tu, S. Potential implications of quercetin in autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 689044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Wang, T.; Long, M.; Li, P. Quercetin: Its main pharmacological activity and potential application in clinical medicine. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8825387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Yue, J.; Tang, Q.; Cheng, K.W.; Chen, F.; Peng, M.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, M. The effect of quercetin on diabetic nephropathy (dn): A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 4789–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Feng, Y.; Gui, Y.; Yang, J.; He, W.; Dai, C. Quercetin inhibits fibroblast activation and kidney fibrosis involving the suppression of mammalian target of rapamycin and β-catenin signaling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.; Poletti, P.T.; Favero, G.; Stacchiotti, A.; Bonomini, F.; Montanari, C.C.; Bona, S.R.; Marroni, N.P.; Rezzani, R.; Veronese, F.V. Protective effects of quercetin treatment in a pristane-induced mouse model of lupus nephritis. Autoimmunity 2018, 51, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plüß, M.; Piantoni, S.; Tampe, B.; Kim, A.H.J.; Korsten, P. Belimumab for systemic lupus erythematosus—Focus on lupus nephritis. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2022, 18, 2072143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, F.; Yoshimasu, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kanazawa, N.; Tachibana, T. Mast cells and histamine metabolism in skin lesions from mrl/mp-lpr/lpr mice. Autoimmun. Rev. 2009, 8, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Titov, A.A.; Morel, L. An update on lupus animal models. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2017, 29, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, C.G.; Preuss, H.G. Assessment of renal function--glomerular and tubular. Clin. Lab. Med. 1993, 13, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Sharma, A.; Kaur, A.; Kaur, T.; Kaur, S.; Pathak, D.; Singh, A.P. Ameliorative role of inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitors against sodium arsenite-induced renal and hepatic dysfunction in rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 45, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.D.; Luo, J.H.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Liao, Y.J.; Li, Y. Tranilast prevents renal interstitial fibrosis by blocking mast cell infiltration in a rat model of diabetic kidney disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 7356–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Chiang, Y.F.; Huang, C.Y.; Shieh, T.M.; Kao, C.; Chang, F.K.; Huang, T.C.; Ali, M.; Chang, H.Y.; Hong, Y.H.; et al. Spirulina phycocyanin extract and its active components suppress epithelial-mesenchymal transition process in endometrial cancer via targeting tgf-beta1/smad4 signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 152, 113219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Blanco, L.P.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Nakabo, S.; Pedersen, H.L.; Yu, Z.X.; Kaplan, M.J. Effects of gasdermin d in modulating murine lupus and its associated organ damage. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halkom, A.; Wu, H.; Lu, Q. Contribution of mouse models in our understanding of lupus. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 39, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, D.; Sang, A.; Yin, Y.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Morel, L. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 271694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.C.; Tang, T.T.; Lv, L.L.; Lan, H.Y. Renal tubule injury: A driving force toward chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakis, S.; Gkirtzimanaki, K.; Papadaki, G.; Gakiopoulou, H.; Drakos, E.; Eloranta, M.-L.; Makridakis, M.; Kontostathi, G.; Zoidakis, J.; Baira, E.; et al. Nets decorated with bioactive il-33 infiltrate inflamed tissues and induce ifn-α production in patients with sle. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e147671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carew, R.M.; Wang, B.; Kantharidis, P. The role of emt in renal fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 347, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, L.; Zhuang, S. New insights into the role and mechanism of partial epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 569322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.Y.; Jing, H.Y.; Ma, Y.R. Interleukin-33/ suppression of tumorigenicity 2 in renal fibrosis: Emerging roles in prognosis and treatment. Front. Physiol. 2022, 12, 792897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Han, Z.; Zhang, W.; Tan, R.; Gu, M. Interleukin-33 levels are elevated in chronic allograft dysfunction of kidney transplant recipients and promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition of human kidney (hk-2) cells. Gene 2018, 644, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Sun, N.; Mo, N.; Lu, S.; Song, E.; Ren, C.; Li, Z. Quercetin inhibits kidney fibrosis and the epithelial to mesenchymal transition of the renal tubular system involving suppression of the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 3782–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Z.; He, Q. Quercetin improves contrast-induced acute kidney injury through the hif-1α/lncrna neat1/hmgb1 pathway. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaysane, A.; Chun, J.; Seamone, M.E.; Wang, W.; Chin, R.; Hirota, S.; Li, Y.; Clark, S.A.; Tschopp, J.; Trpkov, K.; et al. The nlrp3 inflammasome promotes renal inflammation and contributes to ckd. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2010, 21, 1732–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Han, W.; Song, S.; Du, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, N.; Wu, H.; Shi, Y.; Duan, H. Nlrp3 deficiency ameliorates renal inflammation and fibrosis in diabetic mice. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 478, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hara, H.; Núñez, G. Mechanism and regulation of nlrp3 inflammasome activation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Liang, J.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Ke, Y.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, S.; Lin, J. Novel effects of combination therapy through inhibition of caspase-1/gasdermin d induced-pyroptosis in lupus nephritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 720877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sborgi, L.; Rühl, S.; Mulvihill, E.; Pipercevic, J.; Heilig, R.; Stahlberg, H.; Farady, C.J.; Müller, D.J.; Broz, P.; Hiller, S. Gsdmd membrane pore formation constitutes the mechanism of pyroptotic cell death. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 1766–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Sun, Q.; Zhong, X.; Zeng, M.; Zeng, H.; Shi, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Shao, F.; et al. Structural mechanism for gsdmd targeting by autoprocessed caspases in pyroptosis. Cell 2020, 180, 941–955.e920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-Y.; Li, L.-C.; Yang, J.-L. Emerging roles of il-33/st2 axis in renal diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskender, H.; Dokumacioglu, E.; Sen, T.M.; Ince, I.; Kanbay, Y.; Saral, S. The effect of hesperidin and quercetin on oxidative stress, nf-κb and sirt1 levels in a stz-induced experimental diabetes model. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.W.; Tang, W.; Zuo, J.P. Toll-like receptors: Potential targets for lupus treatment. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.; Batuman, V. Aristolochic acid i induces proximal tubule injury through ros/hmgb1/mt DNA mediated activation of tlrs. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 4277–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, M.M.; Shaw, R.J. The ampk signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and metabolism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A.; Hyttinen, J.M.; Kaarniranta, K. Amp-activated protein kinase inhibits nf-κb signaling and inflammation: Impact on healthspan and lifespan. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 89, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Song, X. Quercetin attenuates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via suppressing oxidative stress-mediated er stress through activation of sirt1/ampk pathways. Cell. Signal. 2022, 96, 110363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Luo, Y.; Luo, L.; Wu, D.; Ding, X.; Zheng, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, B.; Yang, X.; Silva, F.; et al. Adiponectin restrains ilc2 activation by ampk-mediated feedback inhibition of il-33 signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20191054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Tsai, M.L.; Tsai, Y.G.; Kuo, C.H.; Hung, C.H. Il-33 regulates m1/m2 chemokine expression via mitochondrial redox-related mitophagy in human monocytes. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2022, 359, 109915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.-Y.; Chiang, Y.-F.; Hong, Y.-H.; Shieh, T.-M.; Huang, T.-C.; Ali, M.; Chang, H.-Y.; Wang, K.-L.; Hsia, S.-M. Quercetin Ameliorates Renal Injury and Pyroptosis in Lupus Nephritis through Inhibiting IL-33/ST2 Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2238. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112238
Chen H-Y, Chiang Y-F, Hong Y-H, Shieh T-M, Huang T-C, Ali M, Chang H-Y, Wang K-L, Hsia S-M. Quercetin Ameliorates Renal Injury and Pyroptosis in Lupus Nephritis through Inhibiting IL-33/ST2 Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(11):2238. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112238
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hsin-Yuan, Yi-Fen Chiang, Yong-Han Hong, Tzong-Ming Shieh, Tsui-Chin Huang, Mohamed Ali, Hsin-Yi Chang, Kai-Lee Wang, and Shih-Min Hsia. 2022. "Quercetin Ameliorates Renal Injury and Pyroptosis in Lupus Nephritis through Inhibiting IL-33/ST2 Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo" Antioxidants 11, no. 11: 2238. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112238
APA StyleChen, H.-Y., Chiang, Y.-F., Hong, Y.-H., Shieh, T.-M., Huang, T.-C., Ali, M., Chang, H.-Y., Wang, K.-L., & Hsia, S.-M. (2022). Quercetin Ameliorates Renal Injury and Pyroptosis in Lupus Nephritis through Inhibiting IL-33/ST2 Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo. Antioxidants, 11(11), 2238. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112238