OR2AT4, an Ectopic Olfactory Receptor, Suppresses Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence in Human Keratinocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) and Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) Analyses
2.3. Immunoblot Analysis
2.4. Immunocytochemistry
2.5. Cre-Luciferase Assay
2.6. cAMP Assay
2.7. Inositol Phosphate Assay
2.8. Calcium Assay
2.9. Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) Transfection
2.10. Induction of Senescence in HaCaT Cells
2.11. Senescence-Associated β-Galactosidase (SA-β-gal) Staining
2.12. Cell Counting and Proliferation Assay
2.13. Monodansylcadaverine (MDC) Staining
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. OR2AT4 and OR Signaling Components Are Expressed in Human Keratinocytes
3.2. Activation of OR2AT4 by Sandalore in Human Keratinocytes
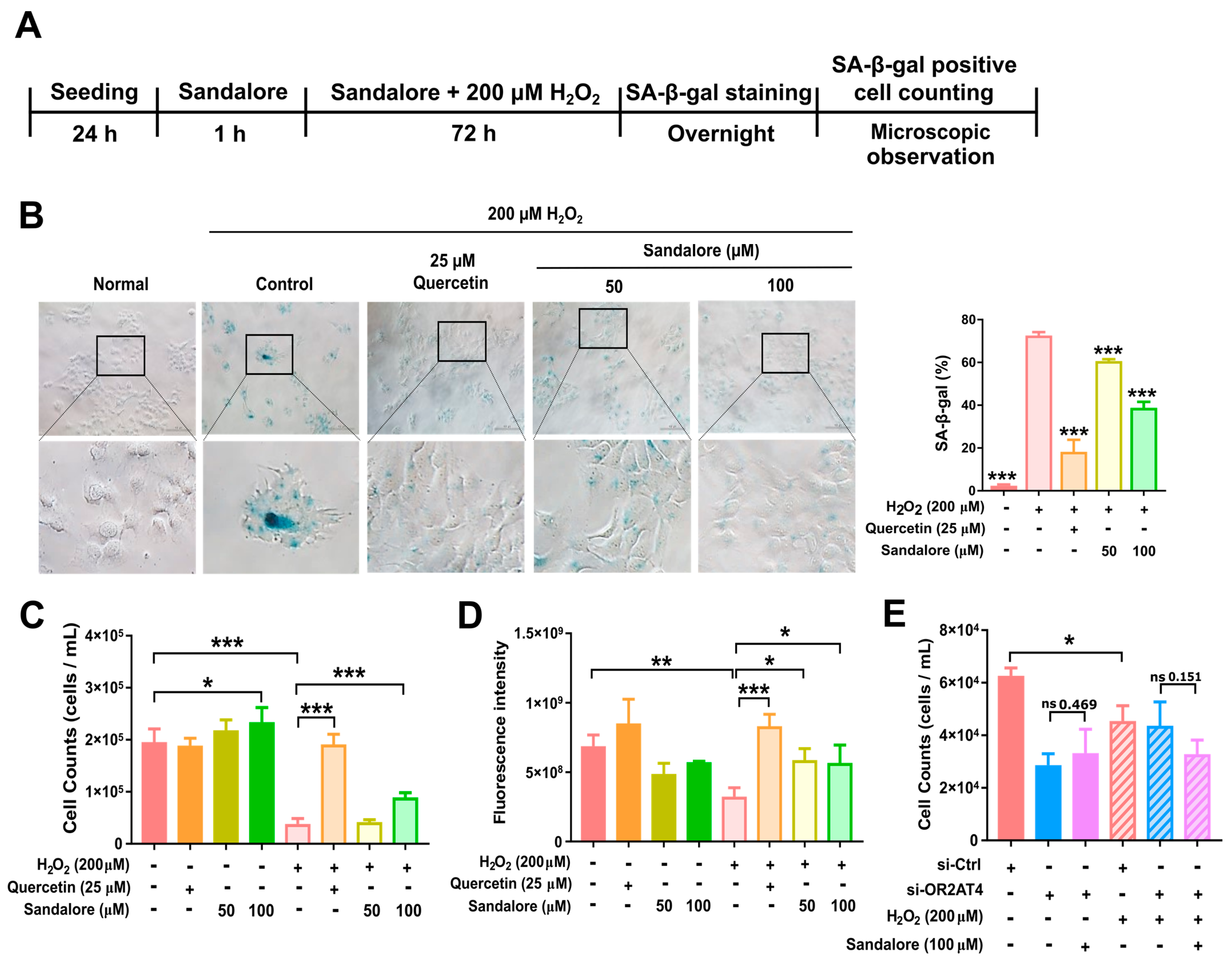
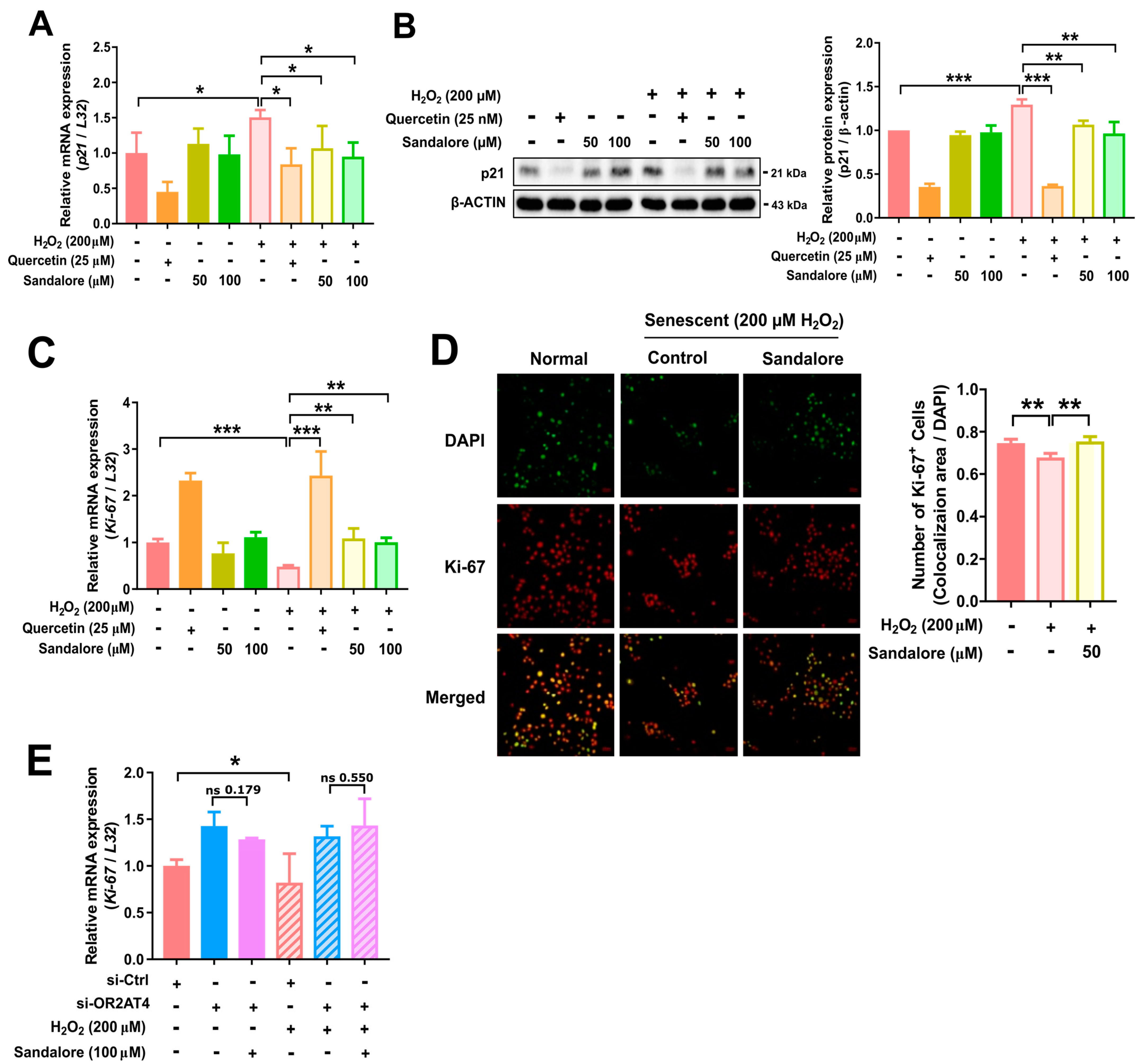
3.3. OR2AT4 Activation by Sandalore Recovers the Proliferation Capacity of H2O2-Induced Senescent HaCaT Cells
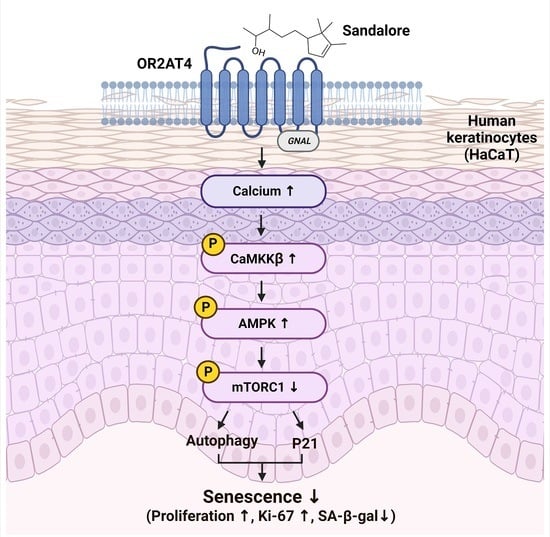
3.4. OR2AT4 Activation by Sandalore Stimulates the CaMKKβ/AMPK/mTORC1 Signaling Pathway to Suppress Senescence in HaCaT Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Höhn, A.; Weber, D.; Jung, T.; Ott, C.; Hugo, M.; Kochlik, B.; Kehm, R.; König, J.; Grune, T.; Castro, J.P. Happily (n)ever after: Aging in the context of oxidative stress, proteostasis loss and cellular senescence. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 482–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrado, C.; Mercado-Saenz, S.; Perez-Davó, A.; Gilaberte, Y.; Gonzalez, S.; Juarranz, A. Environmental Stressors on Skin Aging. Mechanistic Insights. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puizina-Ivic, N. Skin Aging. Acta Dermatovenerol. Alp. Panon. Adriat. 2008, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammeyer, A.; Luiten, R.M. Oxidation events and skin aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 21, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Thach, T.T.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-J. Olfactory receptor 43 reduces hepatic lipid accumulation and adiposity in mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, D.; Kudella, P.; Grüning, N.-M.; Gisselmann, G.; Ständer, S.; Luger, T.; Jacobsen, F.; Steinsträßer, L.; Paus, R.; Gkogkolou, P.; et al. A Synthetic Sandalwood Odorant Induces Wound-Healing Processes in Human Keratinocytes via the Olfactory Receptor OR2AT4. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, M.; Libert, F.; Schurmans, S.; Schiffmann, S.; Lefort, A.; Eggerickx, D.; Ledent, C.; Mollereau, C.; Gérard, C.; Perret, J.; et al. Expression of members of the putative olfactory receptor gene family in mammalian germ cells. Nature 1992, 355, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhaeghen, P.; Schurmans, S.; Vassart, G.; Parmentier, M. Olfactory receptors are displayed on dog mature sperm cells. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 1441–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belluscio, L.; Gold, G.H.; Nemes, A.; Axel, R. Mice Deficient in Golf Are Anosmic. Neuron 1998, 20, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluznick, J. A novel SCFA receptor, the microbiota, and blood pressure regulation. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Hwang, S.H.; Jia, Y.; Choi, J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Choi, D.; Pathiraja, D.; Choi, I.-G.; Koo, S.-H.; Lee, S.-J. Olfactory receptor 544 reduces adiposity by steering fuel preference toward fats. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 127, 4118–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thach, T.T.; Wu, C.; Hwang, K.Y.; Lee, S.-J. Azelaic Acid Induces Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Skeletal Muscle by Activation of Olfactory Receptor 544. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Jeong, M.-Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, G.; Kim, J.-S.; Cheong, Y.E.; Kang, H.; Cho, C.H.; Kim, J.; Park, M.K.; et al. Activation of ectopic olfactory receptor 544 induces GLP-1 secretion and regulates gut inflammation. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1987782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, R.; Wang, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Kang, S.-G.; Huang, K.; Tong, T. Ectopic odorant receptors responding to flavor compounds in skin health and disease: Current insights and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcik, S.; Weidinger, D.; Ständer, S.; Luger, T.; Hatt, H.; Jovancevic, N. Functional characterization of the extranasal OR2A4/7 expressed in human melanocytes. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chéret, J.; Bertolini, M.; Ponce, L.; Lehmann, J.; Tsai, T.; Alam, M.; Hatt, H.; Paus, R. Olfactory receptor OR2AT4 regulates human hair growth. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duroux, R.; Mandeau, A.; Quesnel, Y.; Loing, E. Discovery of new olfactory receptors in human keratinocytes: A potential role on skin stress response. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Son, B.; Park, S.; Choi, D.; Park, T. UV-Irradiation- and Inflammation-Induced Skin Barrier Dysfunction Is Associated with the Expression of Olfactory Receptor Genes in Human Keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, E.H.; Dyjack, N.; Kim, B.E.; Rios, C.; Seibold, M.A.; Leung, D.Y.; Goleva, E. Expression and function of the ectopic olfactory receptor OR10G7 in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1838–1848.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Depoortere, I.; Hatt, H. Therapeutic potential of ectopic olfactory and taste receptors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 116–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimozi, A.; Mavrogonatou, E.; Sklirou, A.; Kletsas, D. Oxidative stress inhibits the proliferation, induces premature senescence and promotes a catabolic phenotype in human nucleus pulposus intervertebral disc cells. Eur. Cells Mater. 2015, 30, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, H.; Kubota, M.; Roberts, R.W.; Chi, Q.; Matsunami, H. RTP Family Members Induce Functional Expression of Mammalian Odorant Receptors. Cell 2004, 119, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.D.; Jang, C.-Y.; Choe, J.M.; Sohn, J.; Kim, J. Phenylbutyric acid induces the cellular senescence through an Akt/p21WAF1 signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 422, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMullen, T.P.; Brown, E.A.; Ausrafuggaman, N.; Sahu, A.; Güler, A.D.; Deppmann, C.D. GPCR Signal Transduction: Evolution by Gene Duplication. In eLS; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A.S.; Attwood, M.M.; Rask-Andersen, M.; Schiöth, H.B.; Gloriam, D.E. Trends in GPCR drug discovery: New agents, targets and indications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, D.; Xiao, H. Methods of Cellular Senescence Induction using Oxidative Stress. In Biological Aging; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tong, T. Irreversible cellular senescence induced by prolonged exposure to H2O2 involves DNA-damage-and-repair genes and telomere shortening. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, G. p21WAF1/Cip1: More than a break to the cell cycle? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1471, M43–M56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholzen, T.; Gerdes, J. The Ki-67 protein: From the known and the unknown. J. Cell. Physiol. 2000, 182, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Kaufman, P.D. Ki-67: More than a proliferation marker. Chromosoma 2018, 127, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauson, E.M.; Dbouk, H.A.; Ghosh, A.B.; Cobb, M.H. G protein-coupled receptors and the regulation of autophagy. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racioppi, L.; Means, A.R. Calcium/Calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase Kinase 2: Roles in Signaling and Pathophysiology. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 31658–31665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kundu, M.; Viollet, B.; Guan, K.-L. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihaylova, M.M.; Shaw, R.J. The AMPK signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and metabolism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Angeline, J.; Tan, K.S.W. Autophagy is involved in starvation response and cell death in Blastocystis. Microbiology 2010, 156, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N.; Yoshimori, T. How to Interpret LC3 Immunoblotting. Autophagy 2007, 3, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, S.K.; Gonit, M.; Salotti, J.; Chen, J.; Bhat, A.; Gorospe, M.; Viollet, B.; Claffey, K.P.; Johnson, P.F. A RAS-CaMKKβ-AMPKα2 pathway promotes senescence by licensing post-translational activation of C/EBPβ through a novel 3′UTR mechanism. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3528–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhou, M.; Chen, C.; Wu, X.; Wang, X. Role of AMPK mediated pathways in autophagy and aging. Biochimie 2022, 195, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farage, M.A.; Miller, K.W.; Elsner, P.; Maibach, H.I. Intrinsic and extrinsic factors in skin ageing: A review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2008, 30, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denda, M.; Nakatani, M.; Ikeyama, K.; Tsutsumi, M.; Denda, S. Epidermal keratinocytes as the forefront of the sensory system. Exp. Dermatol. 2007, 16, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.; Veitinger, S.; Peek, I.; Busse, D.; Eckardt, J.; Vladimirova, D.; Jovancevic, N.; Wojcik, S.; Gisselmann, G.; Altmüller, J.; et al. Two olfactory receptors-OR2A4/7 and OR51B5-differentially affect epidermal proliferation and differentiation. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, F.; López, E.; Bertolini, M.; Alam, M.; Chéret, J.; Westgate, G.; Rinaldi, F.; Marzani, B.; Paus, R. Topical odorant application of the specific olfactory receptor OR2AT4 agonist, Sandalore®, improves telogen effluvium-associated parameters. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 20, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurahashi, T.; Menini, A. Mechanism of odorant adaptation in the olfactory receptor cell. Nature 1997, 385, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, J.L.; Kelly, K. Prevention and Treatment of Skin Aging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1067, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, G. Molecular mechanisms of skin ageing. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2002, 123, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, G.H.; Dulic, V. Origins of G1 arrest in senescent human fibroblasts. BioEssays 1995, 17, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Deiry, W.S.; Tokino, T.; Velculescu, V.E.; Levy, D.B.; Parsons, R.; Trent, J.M.; Lin, D.; Mercer, W.E.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 1993, 75, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, J. Aging, Cellular Senescence, and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 685–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietenpol, J.A.; Stewart, Z.A. Cell cycle checkpoint signaling: Cell cycle arrest versus apoptosis. Toxicology 2002, 181, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Bell, C.M.; Rothbart, S.B.; Moran, R.G. AMP-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) Control of mTORC1 Is p53- and TSC2-independent in Pemetrexed-treated Carcinoma Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 27473–27486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewirtz, D.A. Autophagy and senescence: A partnership in search of definition. Autophagy 2013, 9, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laberge, R.-M.; Sun, Y.; Orjalo, A.V.; Patil, C.K.; Freund, A.; Zhou, L.; Curran, S.C.; Davalos, A.R.; Wilson-Edell, K.A.; Liu, S.; et al. MTOR regulates the pro-tumorigenic senescence-associated secretory phenotype by promoting IL1A translation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 1049–1061, Correction in Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 23, 564–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, A.; Del Pilar Sosa Idelchik, M.; Melendez, J.A. Redox control of senescence and age-related disease. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Genes 1 | Accession No. | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OR2AT4 | NM_001005285.2 | CACTGTCCCCAAGATGCTGT | GTGGGTTCATGAGGACAGGG |
| GNAL | NM_182978.4 | GGCCAACCCTGAAAACCAAT | GGTCTGTGGGTGTGTAGTCA |
| GNAS | NM_001410913.1 | TGCTTCAACGATGTGACTGC | CAAGGACTTTCTCAGCGAGC |
| GNAQ | NM_002072.5 | GCCACTGGCCTCCTATTGTT | TGCTTGCCTTGGTATGCTGA |
| GNAI1 | NM_002069.6 | AAGGGTGCCACATGGTGTAG | TAGTGGCTGCTGTGTCTGTG |
| GNA12 | NM_007353.3 | CACCCTTGGCTTGTTTTCCG | CAAGCCCAGCAAACACTGAC |
| GNA13 | NM_001282425.2 | AGGGAACTTTTTGCCCGAGA | ACCCTCATACCTGACCGTGA |
| ADCY3 | NM_001320613.2 | TCAAAACCATTGGCAGCACG | TGTCGTAGTGTGGTTTCCGG |
| P21 | NM_000389.5 | ACTTCCTCCTCCCCACTTGT | CACCCTGCCCAACCTTAGAG |
| Ki-67 | NM_002417.5 | GCCCCTAAAGTAGAACCCGT | GGGTTCGGATGATTTGCCTC |
| L32 | NM_000994.4 | AGAAGTTCATCCGGCACCAG | CACTTCCAGCTCCTTGACGT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-S.; Lee, H.L.; Jeong, J.H.; Yoon, Y.E.; Lee, I.-R.; Kim, J.M.; Wu, C.; Lee, S.-J. OR2AT4, an Ectopic Olfactory Receptor, Suppresses Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence in Human Keratinocytes. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2180. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112180
Kim J-S, Lee HL, Jeong JH, Yoon YE, Lee I-R, Kim JM, Wu C, Lee S-J. OR2AT4, an Ectopic Olfactory Receptor, Suppresses Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence in Human Keratinocytes. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(11):2180. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112180
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ji-Sun, Ha Lim Lee, Ji Hyun Jeong, Ye Eun Yoon, In-Ryeong Lee, Ji Min Kim, Chunyan Wu, and Sung-Joon Lee. 2022. "OR2AT4, an Ectopic Olfactory Receptor, Suppresses Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence in Human Keratinocytes" Antioxidants 11, no. 11: 2180. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112180
APA StyleKim, J.-S., Lee, H. L., Jeong, J. H., Yoon, Y. E., Lee, I.-R., Kim, J. M., Wu, C., & Lee, S.-J. (2022). OR2AT4, an Ectopic Olfactory Receptor, Suppresses Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence in Human Keratinocytes. Antioxidants, 11(11), 2180. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112180