Role of Nitric Oxide and Protein S-Nitrosylation in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Nitric Oxide
2.1. Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
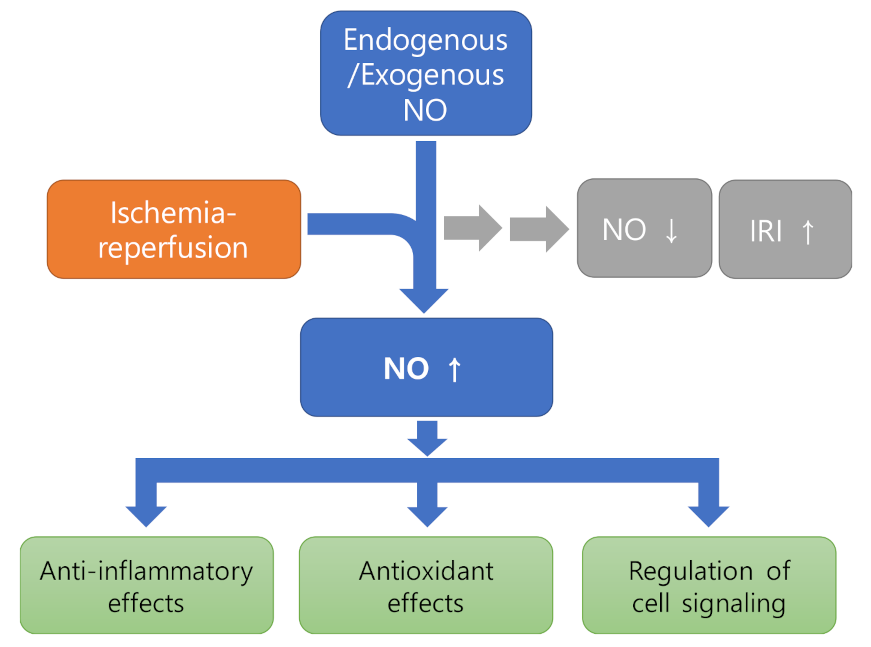
2.2. Nitric Oxide (NO) Pathophysiology in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
2.3. Role of Nitric Oxide in Protection of Ischemia Reperfusion Injury
2.3.1. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
2.3.2. Effect as Antioxidant
2.3.3. Regulation of Cell Signaling
2.4. Therapeutic Approaches
2.4.1. Direct Administration of NO
2.4.2. NO Donors
2.4.3. Advances in NO Delivery System
3. Ischemia Reperfusion Injury and Protein S-Nitrosylation
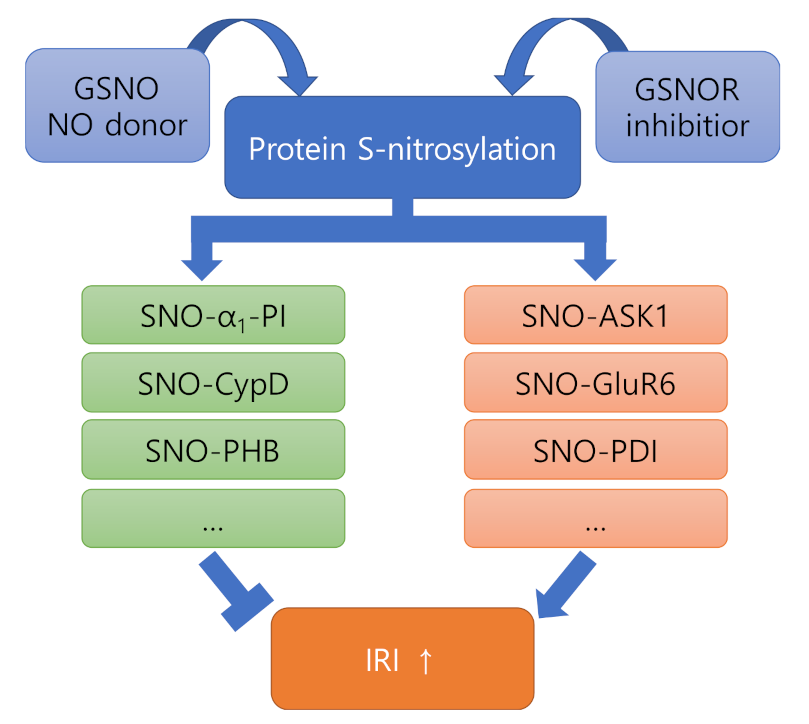
3.1. NO and Protein S-Nitrosylation
3.2. Role of SNO-Proteins in Ischemia Reperfusion Injury
3.2.1. Proteins Showing Negative Effects after Nitrosylation (ASK1, GluR6, PDI)
3.2.2. Proteins Showing Positive Effects after Nitrosylation (α1-PI, CypD, PHB)
3.3. Role of GSNOR in Ischemia Reperfusion Injury
4. Effect of NO on the Comorbidities of Ischemic Stroke
4.1. Hypertension
4.2. Atherosclerosis
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghimire, K.; Altmann, H.M.; Straub, A.C.; Isenberg, J.S. Nitric oxide: What’s new to NO? Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2017, 312, C254–C262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stomberski, C.T.; Hess, D.T.; Stamler, J.S. Protein S-Nitrosylation: Determinants of Specificity and Enzymatic Regulation of S-Nitrosothiol-Based Signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 30, 1331–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Lipton, S.A. Emerging role of protein-protein transnitrosylation in cell signaling pathways. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, T.; Oh, C.K.; Liao, L.; Zhang, X.; Lopez, K.M.; Gibbs, D.; Deal, A.K.; Scott, H.R.; Spencer, B.; Masliah, E.; et al. Noncanonical transnitrosylation network contributes to synapse loss in Alzheimer’s disease. Science 2021, 371, 253–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, S.D.; Buxton, I.L.O. The role of S-nitrosoglutathione reductase (GSNOR) in human disease and therapy. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 52, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrigan, C.L.; Stotland, M.A. Ischemia reperfusion injury: A review. Microsurgery 1993, 14, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Y.; Yiang, G.T.; Liao, W.T.; Tsai, A.P.Y.; Cheng, Y.L.; Cheng, P.W.; Li, C.Y.; Li, C.J. Current Mechanistic Concepts in Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marnett, L.J.; Riggins, J.N.; West, J.D. Endogenous generation of reactive oxidants and electrophiles and their reactions with DNA and protein. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Peña, A.; Garcia-Criado, F.J.; Eleno, N.; Arevalo, M.; Lopez-Novoa, J.M. Intrarenal administration of molsidomine, a molecule releasing nitric oxide, reduces renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Am. J. Transplant. 2004, 4, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anaya-Prado, R.; Toledo-Pereyra, L.H.; Walsh, J.; Guo, R.F.; Reuben, J.; Ward, P.A. Exogenous nitric oxide donor and related compounds protect against lung inflammatory response after hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation. J. Trauma-Inj. Infect. Crit. Care 2004, 57, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Gou, R.; Roselló-Catafau, J.; Casillas-Ramirez, A.; Massip-Salcedo, M.; Rimola, A.; Calvo, N.; Bartrons, R.; Peralta, C. How ischaemic preconditioning protects small liver grafts. J. Pathol. 2006, 208, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, B.; Smith, J.B.; Freeman, G.L. Ischemia-reperfusion of rat myocardium activates nuclear factor-κb and induces neutrophil infiltration via lipopolysaccharide-induced CXC chemokine. Circulation 2001, 103, 2296–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lefer, A.M.; Lefer, D.J. The role of nitric oxide and cell adhesion molecules on the microcirculation in ischaemia-reperfusion. Cardiovasc. Res. 1996, 32, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szabó, C.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Radi, R. Peroxynitrite: Biochemistry, pathophysiology and development of therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 662–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoudy, P.; Becker, B.F.; Gerlach, E. Nitric oxide accounts for postischemic cardioprotection resulting from angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition: Indirect evidence for a radical scavenger effect in isolated guinea pig heart. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1995, 25, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncada, S.; Erusalimsky, J.D. Does nitric oxide modulate mitochondrial energy generation and apoptosis? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G.C.; Borutaite, V. Nitric oxide inhibition of mitochondrial respiration and its role in cell death. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 1440–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.P.; Bolli, R. The ubiquitous role of nitric oxide in cardioprotection. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2006, 40, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carini, R.; De Cesaris, M.G.; Splendore, R.; Domenicotti, C.; Nitti, M.P.; Pronzato, M.A.; Albano, E. Signal pathway responsible for hepatocyte preconditioning by nitric oxide. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.R.; Botting, C.H.; Panico, M.; Morris, H.R.; Hay, R.T. Inhibition of NF-κB DNA binding by nitric oxide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 2236–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, C. Nitric oxide and the regulation of gene expression. Trends Cell Biol. 2001, 11, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melino, G.; Bernassola, F.; Catani, M.V.; Rossi, A.; Corazzari, M.; Sabatini, S.; Vilbois, F.; Green, D.R. Nitric oxide inhibits apoptosis via AP-1-dependent CD95L transactivation. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2377–2383. [Google Scholar]
- Tabuchi, A.; Oh, E.; Taoka, A.; Sakurai, H.; Tsuchiya, T.; Tsuda, M. Rapid attenuation of AP-1 transcriptional factors associated with nitric oxide (NO)-mediated neuronal cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 31061–31067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikebe, N.; Akaike, T.; Miyamoto, Y.; Hayashida, K.; Yoshitake, J.; Ogawa, M.; Maeda, H. Protective effect of S-nitrosylated α1-protease inhibitor on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 295, 904–911. [Google Scholar]
- Bibli, S.I.; Papapetropoulos, A.; Iliodromitis, E.K.; Daiber, A.; Randriamboavonjy, V.; Steven, S.; Brouckaert, P.; Chatzianastasiou, A.; Kypreos, K.E.; Hausenloy, D.J.; et al. Nitroglycerine limits infarct size through S-nitrosation of cyclophilin D: A novel mechanism for an old drug. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahl, A.; Anderson, C.J.; Qian, L.; Voss, H.; Manfredi, G.; Iadecola, C.; Zhou, P. Neuronal expression of the mitochondrial protein prohibitin confers profound neuroprotection in a mouse model of focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Konrad, C.; Anderson, C.; Qian, L.; Yin, T.; Manfredi, G.; Iadecola, C.; Zhou, P. Prohibitin S-nitrosylation is required for the neuroprotective effect of nitric oxide in neuronal cultures. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 3142–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiume, K.; Saitoh, M.; Ichijo, H. Activation of apoptosis signal-regulating Kinase 1 by the stress-induced activating phosphorylation of pre-formed oligomer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2002, 191, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.H.; Yuan, F.G.; Hu, S.Q.; Diao, F.; Wu, Y.P.; Zong, Y.Y.; Song, T.; Li, C.; Zhang, G.Y. Endogenous nitric oxide induces activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 via S-nitrosylation in rat hippocampus during cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Neuroscience 2013, 229, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, J.H.; Li, C.; Yu, H.M.; Zheng, J.N.; Zhang, G.Y. NNOS downregulation attenuates neuronal apoptosis by inhibiting nNOS-GluR6 interaction and GluR6 nitrosylation in cerebral ischemic reperfusion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 420, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.M.; Xu, J.; Li, C.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, F.; Han, D.; Zhang, G.Y. Coupling between neuronal nitric oxide synthase and glutamate receptor 6-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathway via S-nitrosylation contributes to ischemia neuronal death. Neuroscience 2008, 155, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Guan, T.; Li, C.; Shang, H.; Cui, L.; Li, X.M.; Kong, J. SOD1 aggregation in astrocytes following ischemia/reperfusion injury: A role of NO-mediated S-nitrosylation of protein disulfide isomerase (PDI). J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kietadisorn, R.; Juni, R.P.; Moens, A.L. Tackling endothelial dysfunction by modulating NOS uncoupling: New insights into its pathogenesis and therapeutic possibilities. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E481–E495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Förstermann, U.; Sessa, W.C. Nitric oxide synthases: Regulation and function. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.W.; Kong, L.B.; Li, G.Q.; Wang, X.H. Expression of iNOS in early injury in a rat model of small-for-size liver transplantation. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2009, 8, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cohen, R.A.; Adachi, T. Nitric-Oxide-Induced Vasodilatation: Regulation by Physiologic S-Glutathiolation and Pathologic Oxidation of the Sarcoplasmic Endoplasmic Reticulum Calcium ATPase. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2006, 16, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, K.; Morrell, C.N.; Cambien, B.; Yang, S.X.; Yamakuchi, M.; Bao, C.; Hara, M.R.; Quick, R.A.; Cao, W.; O’Rourke, B.; et al. Nitric oxide regulates exocytosis by S-nitrosylation of N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor. Cell 2003, 115, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murad, F.; Waldman, S.; Molina, C.; Bennett, B.; Leitman, D. Regulation and role of guanylate cyclase-cyclic GMP in vascular relaxation. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1987, 249, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Tegenge, M.A.; Bicker, G. Nitric oxide and cGMP signal transduction positively regulates the motility of human neuronal precursor (NT2) cells. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 1828–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.-J.; Heo, J.-I.; Kho, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Kang, H.-J.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Shin, J.-Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, S.C.; et al. Nitric Oxide Is an Essential Mediator for Neuronal Differentiation of Rat Primary Cortical Neuron Cells. Exp. Neurobiol. 2010, 19, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.J.; Hua, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, Q.G.; Luo, C.X.; Han, X.; Lu, Y.M.; Zhu, D.Y. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase-derived nitric oxide inhibits neurogenesis in the adult dentate gyrus by down-regulating cyclic AMP response element binding protein phosphorylation. Neuroscience 2006, 141, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béchade, C.; Pascual, O.; Triller, A.; Bessis, A. Nitric oxide regulates astrocyte maturation in the hippocampus: Involvement of NOS2. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2011, 46, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köken, T.; Inal, M. The effect of nitric oxide on ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat liver. Clin. Chim. Acta 1999, 288, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, A.; Frazzini, V.I.; Solomon, R.A.; Trifiletti, R.R. Nitric oxide production during focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 1993, 24, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malinski, T.; Bailey, F.; Zhang, Z.G.; Chopp, M. Nitric oxide measured by a porphyrinic microsensor in rat brain after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1993, 13, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugimura, T.; Sako, K.; Tohyama, Y.; Yonemasu, Y. Consecutive in vivo measurement of nitric oxide in transient forebrain ischemic rat under normothermia and hypothermia. Brain Res. 1998, 808, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassbender, K.; Fatar, M.; Ragoschke, A.; Picard, M.; Bertsch, T.; Kuehl, S.; Hennerici, M. Subacute but not acute generation of nitric oxide in focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2000, 31, 2208–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, A.; Clark, J.F.; Broderick, J.P.; Pyne-Geithman, G.J.; Wagner, K.R.; Ran, R.; Khatri, P.; Tomsick, T.; Sharp, F.R. Reperfusion activates metalloproteinases that contribute to neurovascular injury. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 210, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terpolilli, N.A.; Kim, S.W.; Thal, S.C.; Kataoka, H.; Zeisig, V.; Nitzsche, B.; Klaesner, B.; Zhu, C.; Schwarzmaier, S.; Meissner, L.; et al. Inhalation of nitric oxide prevents ischemic brain damage in experimental stroke by selective dilatation of collateral arterioles. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bolli, R. Cardioprotective Function of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase and Role of Nitric Oxide in Myocardial Ischemia and Preconditioning: An Overview of a Decade of Research. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2001, 33, 1897–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aiba, M.; Takeyoshi, I.; Ohwada, S.; Kawashima, Y.; Iwanami, K.; Sunose, Y.; Yamada, T.; Tsutsumi, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Morishita, Y. Novel nitric oxide donor (FK409) ameliorates liver damage during extended liver resection with warm ischemia in dogs. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2001, 193, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya-Prado, R.; Toledo-Pereyra, L.H.; Guo, R.F.; Reuben, J.; Ward, P.A.; Walsh, J. The attenuation of hemorrhage-induced liver injury by exogenous nitric oxide, L-Arginine, and inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase. J. Investig. Surg. 2003, 16, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Toledo-Pereyra, L.H. Interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor production as the initial stimulants of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury. J. Surg. Res. 1994, 57, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangogiannis, N.G. Chemokines in ischemia and reperfusion. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 97, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatano, E.; Bennett, B.L.; Manning, A.M.; Qian, T.; Lemasters, J.J.; Brenner, D.A. Nf-κb stimulates inducible nitric oxide synthase to protect mouse hepatocytes from TNF-α- and fas-mediated apoptosis. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Mier, G.; Toledo-Pereyra, L.H.; McDuffie, J.E.; Warner, R.L.; Hsiao, C.; Stapleton, S.R.; Ward, P.A. Exogenous nitric oxide downregulates MIP-2 and MIP-1α chemokines and MAPK p44/42 after ischemia and reperfusion of the rat kidney. J. Investig. Surg. 2002, 15, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, T.; Nagata, K.; Kobayashi, Y. A suppressive role of nitric oxide in MIP-2 production by macrophages upon coculturing with apoptotic cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 80, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Neblina, F.; Toledo-Pereyra, L.H.; Mirmiran, R.; Paez-Rollys, A.J. Time dependence of Na-nitroprusside administration in the prevention of neutrophil infiltration in the rat ischemic kidney. Transplantation 1996, 61, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakir, O.; Oruc, A.; Eren, S.; Buyukbayram, H.; Erdinc, L.; Eren, N. Does sodium nitroprusside reduce lung injury under cardiopulmonary bypass? Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2003, 23, 1040–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Pokreisz, P.; Vermeersch, P.; Marsboom, G.; Swinnen, M.; Verbeken, E.; Santos, J.; Pellens, M.; Gillijns, H.; et al. Nitric Oxide Inhalation Improves Microvascular Flow and Decreases Infarction Size after Myocardial Ischemia and Reperfusion. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chattopadhyay, P.; Verma, N.; Verma, A.; Kamboj, T.; Khan, N.A.; Wahi, A.K. L-arginine protects from pringle manoeuvere of ischemia-reperfusion induced liver injury. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 890–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Mier, G.; Toledo-Pereyra, L.H.; Ward, P.A. Adhesion molecules in liver ischemia and reperfusion. J. Surg. Res. 2000, 94, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Mier, G.; Toledo-Pereyra, L.H.; McDuffie, E.; Warner, R.L.; Ward, P.A. L-selectin and chemokine response after liver ischemia and reperfusion. J. Surg. Res. 2000, 93, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Mier, G.; Toledo-Pereyra, L.H.; McDuffie, J.E.; Warner, R.L.; Ward, P.A. P-selectin and chemokine response after liver ischemia and reperfusion. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2000, 191, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldow, T.; Witt, W.; Weber, E.; Matschke, K. Nitric oxide donor-induced persistent inhibition of cell adhesion protein expression and NFκB activation in endothelial cells. Nitric Oxide-Biol. Chem. 2006, 15, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.Z.; Tsukahara, H.; Hayakawa, K.; Todoroki, Y.; Tamura, S.; Ohshima, Y.; Hiraoka, M.; Mayumi, M. Effects of antioxidants and NO on TNF-α-induced adhesion molecule expression in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Respir. Med. 2005, 99, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toledo-Pereyra, L.H.; Toledo, A.H.; Walsh, J.; Lopez-Neblina, F. Molecular signaling pathways in ischemia/reperfusion. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2004, 2, 174–177. [Google Scholar]
- Takata, T.; Araki, S.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Watanabe, Y. Oxidative stress orchestrates mapk and nitric-oxide synthase signal. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiecker, M.; Darius, H.; Kaboth, K.; Hübner, F.; Liao, J.K. Differential regulation of endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression by nitric oxide donors and antioxidants. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1998, 63, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.; Brisbois, E.J. Clinical use of inhaled nitric oxide: Local and systemic applications. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hataishi, R.; Rodrigues, A.C.; Neilan, T.G.; Morgan, J.G.; Buys, E.; Shiva, S.; Tambouret, R.; Jassal, D.S.; Raher, M.J.; Furutani, E.; et al. Inhaled nitric oxide decreases infarction size and improves left ventricular function in a murine model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, H379–H384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zapol, W.M.; Nagasaka, Y.; Fernandez, B.O.; Garcia-Saura, M.F.; Petersen, B.; Ichinose, F.; Bloch, K.D.; Feelisch, M. Brief periods of nitric oxide inhalation protect against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Anesthesiology 2008, 109, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terpolilli, N.A.; Feiler, S.; Dienel, A.; Müller, F.; Heumos, N.; Friedrich, B.; Stover, J.; Thal, S.; Schöller, K.; Plesnila, N. Nitric oxide inhalation reduces brain damage, prevents mortality, and improves neurological outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage by resolving early pial microvasospasms. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 2096–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inglessis, I.; Shin, J.T.; Lepore, J.J.; Palacios, I.F.; Zapol, W.M.; Bloch, K.D.; Semigran, M.J. Hemodynamic effects of inhaled nitric oxide in right ventricular myocardial infarction and cardiogenic shock. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janssens, S.P.; Bogaert, J.; Zalewski, J.; Toth, A.; Adriaenssens, T.; Belmans, A.; Bennett, J.; Claus, P.; Desmet, W.; Dubois, C.; et al. Nitric oxide for inhalation in ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NOMI): A multicentre, double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 2717–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Neblina, F.; Paez, A.J.; Toledo, A.H.; Toledo-Pereyra, L.H. Role of nitric oxide in ischemia/reperfusion of the rat kidney. Circ. Shock 1994, 44, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Mizukami, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Matsumoto, I. Effect of sodium nitroprusside on ischemia-reperfusion injuries of the rat liver. Hepatogastroenterology 2004, 51, 1404–1407. [Google Scholar]
- Willmot, M.; Gray, L.; Gibson, C.; Murphy, S.; Bath, P.M.W. A systematic review of nitric oxide donors and L-arginine in experimental stroke; effects on infarct size and cerebral blood flow. Nitric Oxide-Biol. Chem. 2005, 12, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bath, P.M.W.; Woodhouse, L.; Scutt, P.; Krishnan, K.; Wardlaw, J.M.; Bereczki, D.; Sprigg, N.; Berge, E.; Beridze, M.; Caso, V.; et al. Efficacy of nitric oxide, with or without continuing antihypertensive treatment, for management of high blood pressure in acute stroke (ENOS): A partial-factorial randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woodhouse, L.; Scutt, P.; Krishnan, K.; Berge, E.; Gommans, J.; Ntaios, G.; Wardlaw, J.; Sprigg, N.; Bath, P.M. Effect of Hyperacute Administration (within 6 Hours) of Transdermal Glyceryl Trinitrate, a Nitric Oxide Donor, on Outcome after Stroke: Subgroup Analysis of the Efficacy of Nitric Oxide in Stroke (ENOS) Trial. Stroke 2015, 46, 3194–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bath, P.M.; Scutt, P.; Anderson, C.S.; Appleton, J.P.; Berge, E.; Cala, L.; Dixon, M.; England, T.M.; Godolphin, P.J.; Havard, D.; et al. Prehospital transdermal glyceryl trinitrate in patients with ultra-acute presumed stroke (RIGHT-2): An ambulance-based, randomised, sham-controlled, blinded, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulz, R.; Kelm, M.; Heusch, G. Nitric oxide in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 61, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, R.; Ray, U.; Jana, P.; Bhattacharya, R.; Banerjee, D.; Sinha, A. Reduction of death rate due to acute myocardial infarction in subjects with cancers through systemic restoration of impaired nitric oxide. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, N.; Neil, C.; Bruce, M.; MacLennan, G.; Cotton, S.; Papadopoulou, S.; Feelisch, M.; Bunce, N.; Lim, P.O.; Hildick-Smith, D.; et al. Intravenous sodium nitrite in acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction: A randomized controlled trial (NIAMI). Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.A.; Pellaton, C.; Velmurugan, S.; Rathod, K.S.; Andiapen, M.; Antoniou, S.; Van Eijl, S.; Webb, A.J.; Westwood, M.A.; Parmar, M.K.; et al. Randomized phase 2 trial of intracoronary nitrite during acute myocardial infarction. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rink, J.S.; Sun, W.; Misener, S.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, Z.J.; Kibbe, M.R.; Dravid, V.P.; Venkatraman, S.; Thaxton, C.S. Nitric Oxide-Delivering High-Density Lipoprotein-like Nanoparticles as a Biomimetic Nanotherapy for Vascular Diseases. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 6904–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navati, M.S.; Lucas, A.; Liong, C.; Barros, M.; Jayadeva, J.T.; Friedman, J.M.; Cabrales, P. Reducing Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by the Targeted Delivery of Nitric Oxide from Magnetic-Field-Induced Localization of S-Nitrosothiol-Coated Paramagnetic Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 2907–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, D.T.; Matsumoto, A.; Kim, S.-O.; Marshall, H.E.; Stamler, J.S. Protein S-nitrosylation: Purview and parameters. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 150–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, S.A.; Choi, Y.-B.; Pan, Z.-H.; Lei, S.Z.; Chen, H.-S.V.; Sucher, N.J.; Loscalzo, J.; Singel, D.J.; Stamler, J.S. A redox-based mechanism for the neuroprotective and neurodestructive effects of nitric oxide and related nitroso-compounds. Nature 1993, 364, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, D.; Stamler, J.S. The SNO-proteome: Causation and classifications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2011, 15, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benhar, M.; Forrester, M.T.; Hess, D.T.; Stamler, J.S. Regulated Protein Denitrosylation by Cytosolic and Mitochondrial Thioredoxins. Science 2008, 320, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kornberg, M.D.; Sen, N.; Hara, M.R.; Juluri, K.R.; Nguyen, J.V.K.; Snowman, A.M.; Law, L.; Hester, L.D.; Snyder, S.H. GAPDH mediates nitrosylation of nuclear proteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, D.A.; Marletta, M.A. Thioredoxin catalyzes the S-nitrosation of the caspase-3 active site cysteine. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Wang, L.; Wong, C.C.L.; Scott, F.L.; Eckelman, B.P.; Han, X.; Tzitzilonis, C.; Meng, F.; Gu, Z.; Holland, E.A.; et al. Transnitrosylation of XIAP Regulates Caspase-Dependent Neuronal Cell Death. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pawloski, J.R.; Hess, D.T.; Stamler, J.S. Export by red blood cells of nitric oxide bioactivity. Nature 2001, 409, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Nakamura, T.; Cao, G.; Holland, E.A.; McKercher, S.R.; Lipton, S.A. S-Nitrosylation activates Cdk5 and contributes to synaptic spine loss induced by beta-amyloid peptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14330–14335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Liu, T.; Chen, W.; Oka, S.; Fu, C.; Jain, M.R.; Parrott, A.M.; Baykal, A.T.; Sadoshima, J.; Li, H. Redox Regulatory Mechanism of Transnitrosylation by Thioredoxin. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 2262–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brys, R.; Gibson, K.; Poljak, T.; Van Der Plas, S.; Amantini, D. Discovery and development of ASK1 inhibitors. In Progress in Medicinal Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 59, pp. 101–179. ISBN 9780128211731. [Google Scholar]
- Christopherson, K.S.; Hillier, B.J.; Lim, W.A.; Bredt, D.S. PSD-95 assembles a ternary complex with the N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor and a bivalent neuronal NO synthase PDZ domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 27467–27473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lyles, M.M.; Gilbert, H.F. Catalysis of the Oxidative Folding of Ribonuclease A by Protein Disulfide Isomerase: Dependence of the Rate on the Composition of the Redox Buffer. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigi, F.; Gonzalez, D.R.; Minhas, K.M.; Sun, Q.-A.; Foster, M.W.; Khan, S.A.; Treuer, A.V.; Dulce, R.A.; Harrison, R.W.; Saraiva, R.M.; et al. Dynamic denitrosylation via S-nitrosoglutathione reductase regulates cardiovascular function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4314–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carver, D.J.; Gaston, B.; deRonde, K.; Palmer, L.A. Akt-Mediated Activation of HIF-1 in Pulmonary Vascular Endothelial Cells by S-Nitrosoglutathione. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, M.; Alvarez, M.N.; Peluffo, G.; Freeman, B.A.; Radi, R. Xanthine oxidase-mediated decomposition of S-nitrosothiols. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 7828–7834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, X.; Qiu, H. Post-translational S-nitrosylation of proteins in regulating cardiac oxidative stress. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, B.; Lam, G.K.W.; Xie, L.; Diesen, D.L.; Villamizar, N.; Nienaber, J.; Messina, E.; Bowles, D.; Kontos, C.D.; Hare, J.M.; et al. Endogenous S-nitrosothiols protect against myocardial injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6297–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatzistergos, K.E.; Paulino, E.C.; Dulce, R.A.; Takeuchi, L.M.; Bellio, M.A.; Kulandavelu, S.; Cao, Y.; Balkan, W.; Kanashiro-Takeuchi, R.M.; Hare, J.M. S-nitrosoglutathione reductase deficiency enhances the proliferative expansion of adult heart progenitors and myocytes post myocardial infarction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castillo, O.A.; Herrera, G.; Manriquez, C.; Rojas, A.F.; González, D.R. Pharmacological inhibition of s-nitrosoglutathione reductase reduces cardiac damage induced by ischemia–reperfusion. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa-Wagner, A.; Dumitrascu, D.; Capitanescu, B.; Petcu, E.; Surugiu, R.; Fang, W.H.; Dumbrava, D.A. Dietary habits, lifestyle factors and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, M.; Van Der Graaf, Y.; Visseren, F.L.; Mali, W.P.T.M.; Geerlings, M.I. Hypertension and longitudinal changes in cerebral blood flow: The SMART-MR study. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, L.L.; Mitchell, G.F. Aortic Stiffness, Cerebrovascular Dysfunction, and Memory. Pulse 2016, 4, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, G.F. Effects of central arterial aging on the structure and function of the peripheral vasculature: Implications for end-organ damage. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 105, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumbach, G.L.; Faraci, F.M.; Heistad, D.D. Effects of local reduction in pressure on endothelium-dependent responses of cerebral arterioles. Stroke 1994, 25, 1456–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Humphrey, J.D. Mechanisms of arterial remodeling in hypertension coupled roles of wall shear and intramural stress. Hypertension 2008, 52, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davies, P.F. Hemodynamic shear stress and the endothelium in cardiovascular pathophysiology. Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med. 2009, 6, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bender, S.B.; De Beer, V.J.; Tharp, D.L.; Van Deel, E.D.; Bowles, D.K.; Duncker, D.J.; Laughlin, M.H.; Merkus, D. Reduced contribution of endothelin to the regulation of systemic and pulmonary vascular tone in severe familial hypercholesterolaemia. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 1757–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traupe, T.; Ortmann, J.; Munter, K.; Barton, M. Endothelial Therapy of Atherosclerosis and Its Risk Factors. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2005, 1, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, H. Nitric oxide and coronary endothelial dysfunction in humans. Cardiovasc. Res. 1999, 43, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, T.J.; Gerhard, M.D.; Meredith, I.T.; Charbonneau, F.; Delagrange, D.; Creager, M.A.; Selwyn, A.P.; Ganz, P. Systemic nature of endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 1995, 75, 71B–74B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignarro, L.J.; Cirino, G.; Casini, A.; Napoli, C. Nitric oxide as a signaling molecule in the vascular system: An overview. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1999, 34, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| NO /SNO | Effect | Target | Mechanism | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO | Anti-inflammatory | TNFα (kidney, liver) | Inhibiting protein expression | [9,10] |
| IL-1 (liver) | [11] | |||
| MIP-1/2 (myocardium) | [12] | |||
| P-selectin (neutrophil) | [13] | |||
| Antioxidant | ROS (ubiquitous) | Scavenging oxygen radical | [14,15,16,17,18] | |
| Regulation of cell signaling | p38 MAPK (hepatocyte) | Activating signal pathway | [19] | |
| NF-κB (neuron) | Inhibiting signal pathway | [20,21] | ||
| AP-1 (neuron) | [22,23] | |||
| SNO | Protective | α1-PI (liver) | Inhibiting hepatocyte apoptosis | [24] |
| CypD (heart) | Inhibiting mPTP opening | [25] | ||
| PHB (neuron) | (not known) | [26,27] | ||
| Injurious | ASK1 (hippocampus) | Inducing apoptosis | [28,29] | |
| GluR6 (hippocampus) | Increasing NO excessively | [30,31] | ||
| PDI (astrocytes) | Forming protein aggregation | [32] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.-M.; Choi, J.W.; Choi, M.S. Role of Nitric Oxide and Protein S-Nitrosylation in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11010057
Lee H-M, Choi JW, Choi MS. Role of Nitric Oxide and Protein S-Nitrosylation in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(1):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11010057
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyang-Mi, Ji Woong Choi, and Min Sik Choi. 2022. "Role of Nitric Oxide and Protein S-Nitrosylation in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury" Antioxidants 11, no. 1: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11010057
APA StyleLee, H.-M., Choi, J. W., & Choi, M. S. (2022). Role of Nitric Oxide and Protein S-Nitrosylation in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Antioxidants, 11(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11010057






