Stereospecific Epoxidation of Limonene Catalyzed by Peroxygenase from Oat Seeds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General
2.2. GC (Gas-Chromatography) Analysis
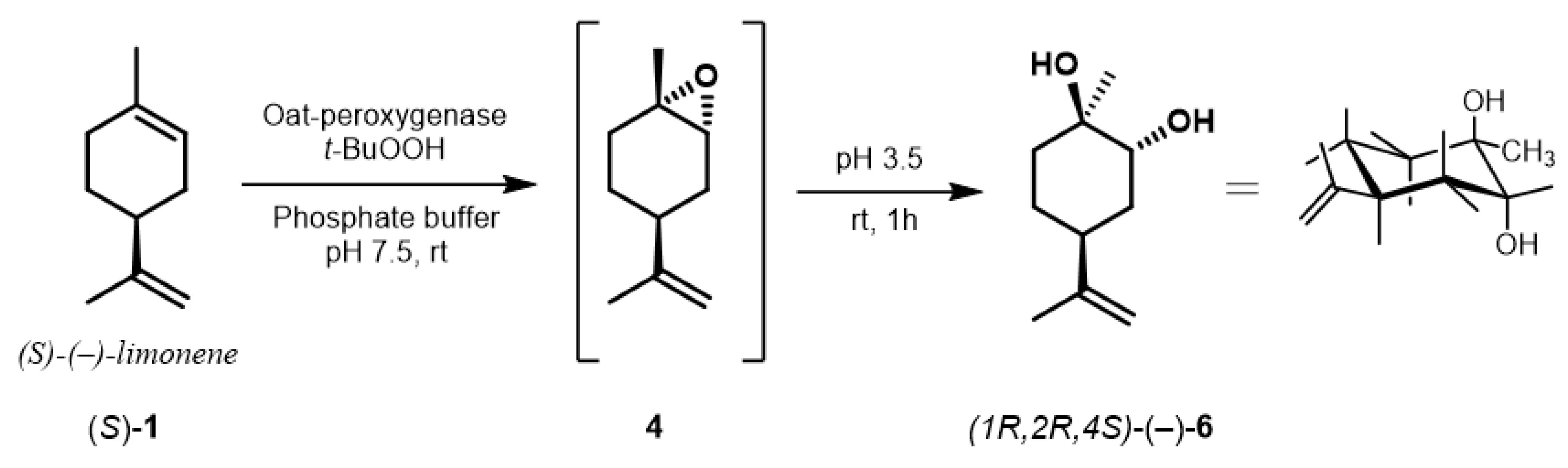
2.3. General Procedure for Biocatalyzed Epoxidation of (R)- or (S)-Limonene
2.4. Preparative Biocatalyzed Epoxidation of (R)-Limonene
2.5. Preparative Biocatalyzed Epoxidation of (S)-Limonene
2.6. Synthesis of Diepoxide (−)-5 from Monoepoxide (−)-4
2.7. Synthesis of Diols (+)-6 and (−)-7 from (R)-Limonene
2.8. Synthesis of Diol (−)-6 from (S)-Limonene
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ravichandran, C.; Badgujar, P.C.; Gundev, P.; Upadhyay, A. Review of toxicological assessment of d-limonene, a food and cosmetics additive. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 120, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, S.; Tomao, V.; Chemat, F. Limonene as green solvent for extraction of natural products. In Green Solvents I; Mohammad, A., Inamuddin, Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, K.; Bouju, E.; Suchet, P.; Berthod, A. Use of limonene in countercurrent chromatography: A green alkane substitute. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 4644–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, V.; Pispas, S.; Syriou, S.; Pournara, A.; Zoumpanioti, M.; Sotiroudis, T.G.; Xenakis, A. Biocompatible microemulsions based on limonene: Formulation, structure, and applications. Langmuir 2008, 24, 3380–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matta, G.B. D-Limonene Based Aqueous Cleaning Compositions. U.S. Patent 4,511,488, 16 April 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.A.; Kainulainen, P.; Aflatuni, A.; Tiilikkala, K.; Holopainen, J.K. Insecticidal, Repellent, Antimicrobial Activity and Phytotoxicity of Essential Oils: With Special Reference to Limonene and Its Suitability for Control of Insect Pests. Agric. Food Sci. Finl. 2001, 10, 243–259. Available online: https://jukuri.luke.fi/handle/10024/451249 (accessed on 9 February 2021). [CrossRef]
- Anandakumar, P.; Kamaraj, S.; Vanitha, M.K. D-limonene: A multifunctional compound with potent therapeutic effects. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtar, Y.M.; Adu-Frimpong, M.; Xu, X.; Yu, J. Biochemical significance of limonene and its metabolites: Future prospects for designing and developing highly potent anticancer drugs. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, J.A.; Pappan, K.; Thompson, P.A.; Want, E.J.; Siskos, A.P.; Keun, H.C.; Wulff, J.; Hu, C.; Lang, J.E.; Chow, H.-H.S. Plasma metabolomic profiles of breast cancer patients after short-term limonene intervention. Cancer Prev. Res. 2015, 8, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciriminna, R.; Lomeli-Rodriguez, M.; Demma Carà, P.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.A.; Pagliaro, M. Limonene: A versatile chemical of the bioeconomy. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15288–15296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbon, P.A.; Chu, F.; Tang, C. Progress in renewable polymers from natural terpenes, terpenoids, and rosin. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 8–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firdaus, M.; Meier, M.A.R. Renewable polyamides and polyurethanes derived from limonene. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques de Oliveira, E.R.; Vieira, R.P. Synthesis and characterization of poly(limonene) by photoinduced controlled radical polymerization. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 2931–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrino, F.; Fidalgo, A.; Palmisano, L.; Ilharco, L.M.; Pagliaro, M.; Ciriminna, R. Polymers of limonene oxide and carbon dioxide: Polycarbonates of the solar economy. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 4884–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, S.; Leitner, L.-C.; Schmalz, H.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. Unlocking the processability and recyclability of biobased poly(limonene carbonate). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 6442–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrantes, M.; Neves, P.; Antunes, M.M.; Gago, S.; Almeida Paz, F.A.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Pillinger, M.; Gonçalves, I.S.; Silva, C.M.; Valente, A.A. Microwave-assisted molybdenum-catalysed epoxidation of olefins. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2010, 320, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonon, A.J.; Kozlov, Y.N.; Bahú, J.O.; Filho, R.M.; Mandelli, D.; Shul’pin, G.B. Limonene epoxidation with H2O2 promoted by Al2O3: Kinetic study, experimental design. J. Catal. 2014, 319, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resul, M.F.M.G.; López Fernández, A.M.; Rehman, A.; Harvey, A.P. Development of a selective, solvent-free epoxidation of limonene using hydrogen peroxide and a tungsten-based catalyst. React. Chem. Eng. 2018, 3, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gottuso, A.; Köckritz, A.; Saladino, M.L.; Armetta, F.; De Pasquale, C.; Nasillo, G.; Parrino, F. Catalytic and photocatalytic epoxidation of limonene using mesoporous silica nanoparticles as functional support for a Janus-like approach. J. Catal. 2020, 391, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadi, S.; Bergeron, J.-Y.; Kaliaguine, S. Kinetic investigation of aerobic epoxidation of limonene over cobalt substituted mesoporous SBA-16. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 594–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiemann, L.O.; Faltl, C.; Sieber, V. Lipase-mediated epoxidation of the cyclic monoterpene limonene to limonene oxide and limonene dioxide. Z. Naturforsch. 2012, 67, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; Willot, S.J.-P.; Zhang, W.; Ribitsch, D.; Hae Choi, Y.; Verpoorte, R.; Zhang, T.; Hollmann, F.; et al. Natural deep eutectic solvents as multifunctional media for the valorization of agricultural wastes. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steiner, D.; Ivison, L.; Goralski, C.T.; Appell, R.B.; Gojkovic, J.R.; Singaram, B. A facile and efficient method for the kinetic separation of commercially available cis- and trans-limonene epoxide. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2002, 13, 2359–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-B.; Qu, J. Water-promoted kinetic separation of trans- and cis-limonene oxides. Chin. J. Chem. 2012, 30, 1133–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, M.; Andrews, P.C.; Fraser, C.B.H.; Forsyth, M.; Junk, P.C.; Massi, M.; Tuck, K.L. Separation of the cis- and trans-diastereoisomers trans-limonene 1,2-oxide and convenient routes to diequatorial and diaxial 1,2-diols. Synthesis 2007, 10, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Werf, M.J.; Jongejan, H.; Franssen, M.C.R. Resolution of limonene 1,2-epoxide diastereomers by mercury(II) ions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 5521–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, P.C.; Blair, M.; Fraser, B.H.; Junk, P.C.; Massi, M.; Tuck, K.L. Water soluble lanthanoid benzoate complexes for the kinetic separation of cis/trans-limonene oxide. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2006, 17, 2833–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandi, E.E.; Marchesi, C.; Annovazzi, C.; Riva, S.; Monti, D.; Wohlgemuth, R. Efficient epoxide hydrolase catalyzed resolutions of (+)- and (−)-cis/trans-limonene oxides. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 3171–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubillos, J.; Vásquez, S.; Montes de Correa, C. Salen manganese (III) complexes as catalysts for R-(+)-limonene oxidation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 373, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dariva Pinto, L.; Dupont, J.; de Souza, R.F.; Bernardo-Gusmão, K. Catalytic asymmetric epoxidation of limonene using manganese Schiff-base complexes immobilized in ionic liquids. Catal. Commun. 2008, 9, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Werf, M.J.; Keijzer, P.M.; van der Schaft, P.H. Xanthobacter sp. C20 contains a novel bioconversion pathway for limonene. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 84, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, M.; Shindo, M.; Shimada, T. Metabolism of (+)- and (−)-limonenes to respective carveols and perillyl alcohols by CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2002, 30, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hobisch, M.; Holtmann, D.; Gomez de Santos, P.; Alcalde, M.; Hollmann, F.; Kara, S. Recent developments in the use of peroxygenases—Exploring their high potential in selective oxyfunctionalisations. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 51, 107615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, C.; Carro, J.; González-Benjumea, A.; Babot, E.D.; Olmedo, A.; Linde, D.; Martínez, A.T.; Gutiérrez, A. Advances in enzymatic oxyfunctionalization of aliphatic compounds. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 51, 107703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Águila, S.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R.; Tinoco, R.; Rivera, M.; Pecchi, G.; Alderete, J.B. Stereoselective oxidation of R-(+)-limonene by chloroperoxidase from Caldariomyces fumago. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, S.; Kinne, M.; Ullrich, R.; Kayser, G.; Hofritcher, M. Epoxidation of linear, branched and cyclic alkenes catalyzed by unspecific peroxygenase. Enz. Microb. Technol. 2013, 52, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, C.; Schwab, W. Epoxidation, hydroxylation and aromatization is catalyzed by a peroxygenase from Solanum lycopersicum. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2013, 96, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanfilippo, C.; Paterna, A.; Biondi, D.M.; Patti, A. Lyophilized extracts from vegetable flours as valuable alternatives to purified oxygenases for the synthesis of oxylipins. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 93, 103325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltby, K.A.; Hutchby, M.; Plucinski, P.; Davidson, M.G.; Hintermair, U. Selective Catalytic Synthesis of 1,2- and 8,9-Cyclic Limonene Carbonates as Versatile Building Blocks for Novel Hydroxyurethanes. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 7405–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Mateos, A.; Herrero Teijón, P.; Rubio González, R. Titanocene-promoted stereoselective eliminations on epoxy alcohols derived from R-(−)-carvone. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 1611–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, H.; Yamaguchi, J.; Sugimura, S.; Minamoto, M.; Gorou, Y.; Morinaga, H.; Motokucho, S. Systematic synthetic study of four diastereomerically distinct limonene-1,2-diols and their corresponding cyclic carbonates. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karlberg, A.-T.; Shao, L.P.; Nilsson, U.; Gäfvert, E.; Nilsson, J.L.G. Hydroperoxides in oxidized d-limonene identified as potent contact allergens. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1994, 286, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimaru, A.; Yamazaki, I. Hydroperoxide-dependent hydroxylation involving “H2O2-reducible hemoprotein” in microsomes of pea seeds. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 6119–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmeester, H.J.; Konings, M.C.J.M.; Gershenzon, J.; Karp, F.; Croteau, R. Cytochrome P-450 dependent (+)-limonene-6-hydroxylation in fruits of caraway (Carum carvi). Phytochemistry 1999, 50, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lie, F.; Lim, E.; Li, K.; Li, Z. Regio- and Stereoselective Allylic Hydroxylation of D-Limonene to (+)-trans-carveol with Cellulosimicrobium cellulans EB-8-4. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009, 351, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeneveld, M.; van Beek, H.L.; Duetz, W.A.; Fraaije, M.W. Identification of a novel oxygenase capable of regiospecific hydroxylation of D-limonene into (+)-trans-carveol. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 7263–7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, R.M.; Klika, K.D. The four diepoxides of (R)-(+)-limonene. Aust. J. Chem. 1991, 44, 1803–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonneau, L.; Foster, X.; Zhao, D.; Kaliaguine, S. Catalyst-free epoxidation of limonene to limonene dioxide. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5115–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehman, A.; Russell, E.; Saleem, F.; Javed, F.; Ahmad, S.; Eze, V.C.; Harvey, A. Synthesis of trans-limonene bis-epoxide by stereoselective epoxidation of (R)-(+)-limonene. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonon, A.J.; Bahú, J.O.; Klein, B.C.; Mandelli, D.; Filho, R.M. Green production of limonene diepoxide for potential biomedical applications. Catal. Today 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royals, E.E.; Leffingwell, J.C. Reactions of the limonene 1,2-Oxides. I. The diastereospecific reactions of the (+)-cis- and (+)-trans-limonene 1,2-oxides. J. Org. Chem. 1966, 31, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biondi, D.M.; Sanfilippo, C.; Patti, A. Stereospecific Epoxidation of Limonene Catalyzed by Peroxygenase from Oat Seeds. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10091462
Biondi DM, Sanfilippo C, Patti A. Stereospecific Epoxidation of Limonene Catalyzed by Peroxygenase from Oat Seeds. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(9):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10091462
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiondi, Daniela Maria, Claudia Sanfilippo, and Angela Patti. 2021. "Stereospecific Epoxidation of Limonene Catalyzed by Peroxygenase from Oat Seeds" Antioxidants 10, no. 9: 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10091462
APA StyleBiondi, D. M., Sanfilippo, C., & Patti, A. (2021). Stereospecific Epoxidation of Limonene Catalyzed by Peroxygenase from Oat Seeds. Antioxidants, 10(9), 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10091462







