Bilirubin as a Therapeutic Molecule: Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
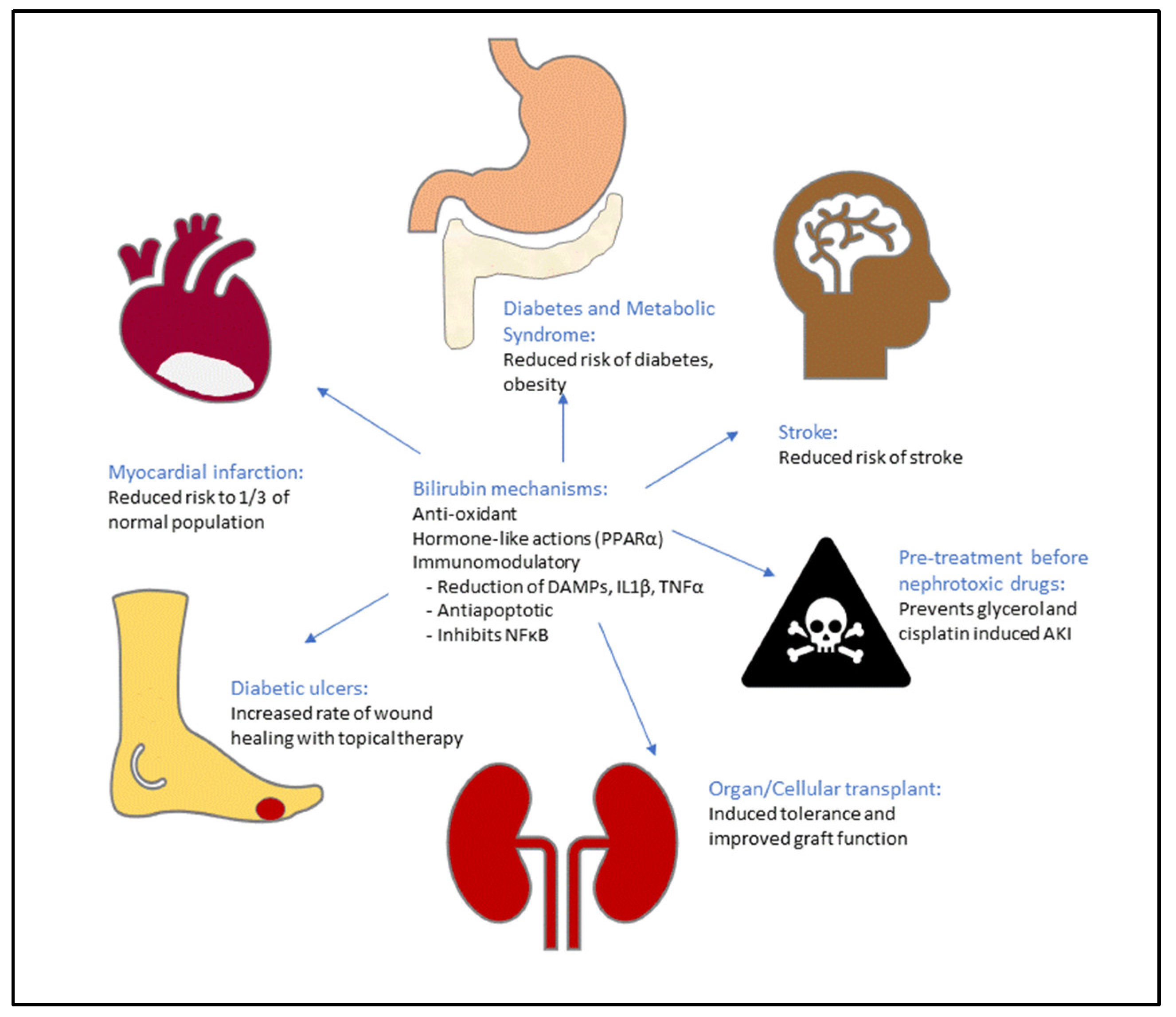
2. Evidence for the Protective Effects of Bilirubin
3. Bilirubin Chemistry
4. Physiology
5. Mechanisms of Action
5.1. Antioxidant Activity
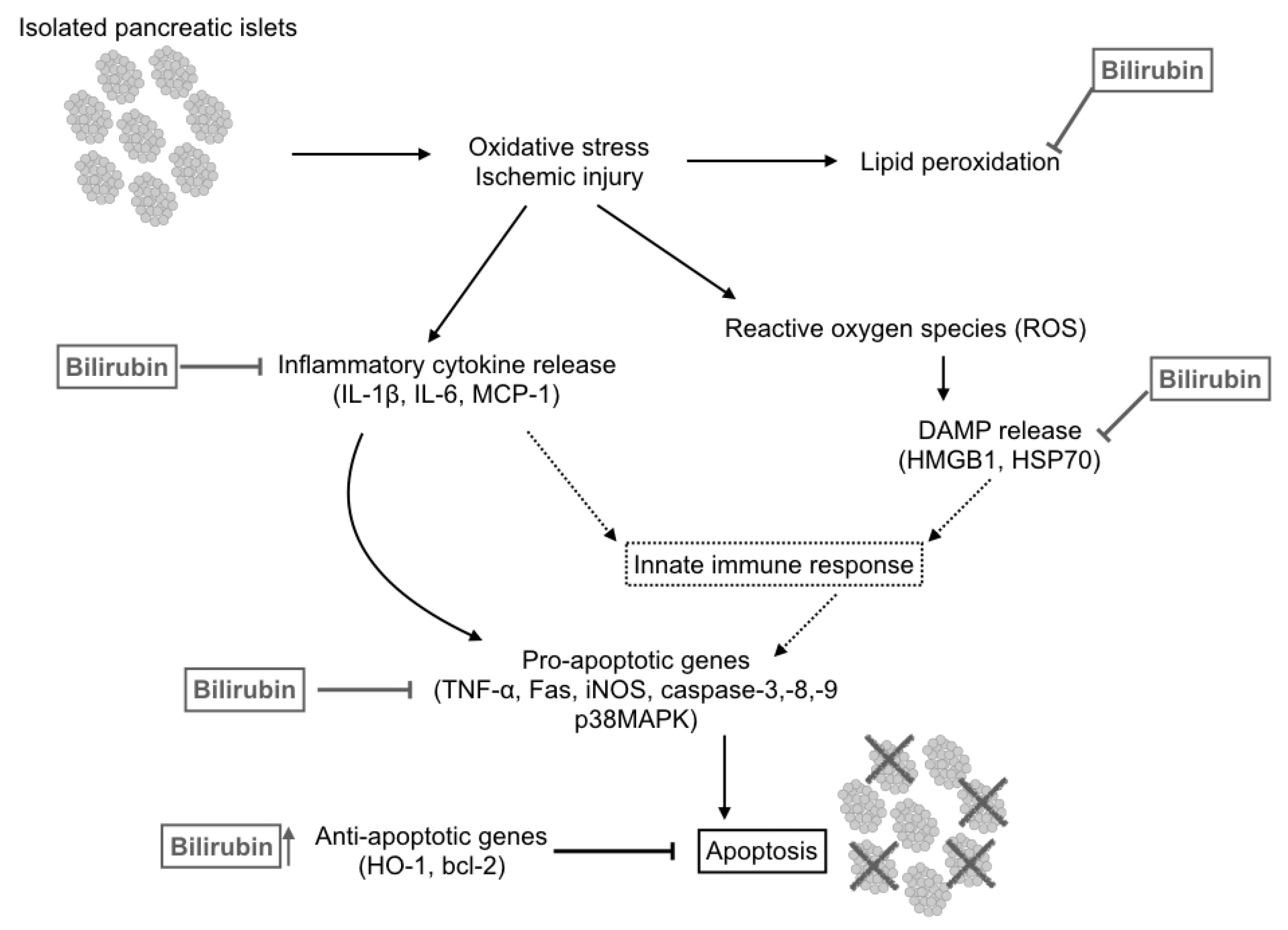
5.2. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory
5.3. Hormone-Like Effects and Signaling
6. Potential Therapeutic Applications
6.1. Cardiovascular Disease
6.2. Acute Kidney Injury
6.3. Transplantation
6.4. Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome
6.5. Non-Healing Wounds
7. Therapeutic Dose Range
8. Delivery Methods
8.1. HO-1 Induction
8.2. Biliverdin Administration
8.3. Inhibition of Bilirubin Conjugation by UGT
8.4. Natural Bilirubin Administration
8.5. Nanoparticle Encapsulation
8.6. Synthetic Analogues
9. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCandless, D.W. (Ed.) History of Bilirubin. In Kernicterus; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, R. Direct-Reacting Bilirubin, Bilirubin Glucuronide, in Serum, Bile, and Urine. Science 1956, 124, 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odell, G.B. The dissociation of bilirubin from albumin and its clinical implications. J. Pediatr. 1959, 55, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, J.; Ferreiro, M.; Hewitt, J. 59 Prevention of Hyperbilirubinemia of Prematurity by Phototherapy. Pediatr. Res. 1967, 1, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stocker, R.; Yamamoto, Y.; McDonagh, A.F.; Glazer, A.N.; Ames, B.N. Bilirubin is an antioxidant of possible physiological importance. Science 1987, 235, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkby, K.A.; Adin, C.A. Products of heme oxygenase and their potential therapeutic applications. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2006, 290, F563–F571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nam, J.; Lee, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jeong, S.; Kim, W.; Yoo, J.-W.; Moon, J.-O.; Lee, C.; Chung, H.Y.; Kim, M.-S.; et al. Is it worth expending energy to convert biliverdin into bilirubin? Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 124, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dullaart, R.P.F.; Boersema, J.; Lefrandt, J.D.; Wolffenbuttel, B.H.; Bakker, S.J.L. The inverse association of incident cardiovascular disease with plasma bilirubin is unaffected by adiponectin. Atherosclerosis 2014, 235, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, P.N.; Wu, L.L.; Hunt, S.C.; James, B.C.; Vincent, G.M.; Williams, R.R. Higher Serum Bilirubin Is Associated With Decreased Risk for Early Familial Coronary Artery Disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1996, 16, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djouss, L. Total serum bilirubin and risk of cardiovascular disease in the Framingham offspring study. Am. J. Cardiol. 2001, 87, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlstein, T.S.; Pande, R.L.; Beckman, J.A.; Creager, M.A. Serum Total Bilirubin Level and Prevalent Lower-Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perlstein, T.S.; Pande, R.L.; Creager, M.A.; Weuve, J.; Beckman, J.A. Serum Total Bilirubin Level, Prevalent Stroke, and Stroke Outcomes: NHANES 1999–2004. Am. J. Med. 2008, 121, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheriyath, P. High Total Bilirubin as a Protective Factor for Diabetes Mellitus: An Analysis of NHANES Data From 1999–2006. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2010, 2, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwon, K.-M.; Kam, J.-H.; Kim, M.-Y.; Kim, M.-Y.; Chung, C.; Kim, J.-K.; Linton, J.; Eom, A.; Koh, S.-B.; Kang, H.-T. Inverse Association Between Total Bilirubin and Metabolic Syndrome in Rural Korean Women. J. Women’s Health 2011, 20, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creeden, J.F.; Gordon, D.M.; Stec, D.E.; Hinds, T.D. Bilirubin as a metabolic hormone: The physiological relevance of low levels. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2021, 320, E191–E207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertner, H.A.; Vítek, L. Gilbert syndrome, UGT1A1*28 allele, and cardiovascular disease risk: Possible protective effects and therapeutic applications of bilirubin. Atherosclerosis 2008, 198, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosma, P.J. Inherited disorders of bilirubin metabolism. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiddarwar, A.S.; D’Silva, S.Z.; Colah, R.B.; Ghosh, K.; Mukherjee, M.B. Genetic Variations in Bilirubin Metabolism Genes and Their Association with Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia in Adults. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2017, 81, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakrania, B.; Du Toit, E.F.; Ashton, K.; Wagner, K.-H.; Headrick, J.P.; Bulmer, A.C. Chronically elevated bilirubin protects from cardiac reperfusion injury in the male Gunn rat. Acta Physiol. 2017, 220, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulmer, A.C.; Bakrania, B.; Du Toit, E.F.; Boon, A.-C.; Clark, P.; Powell, L.W.; Wagner, K.-H.; Headrick, J.P. Bilirubin acts as a multipotent guardian of cardiovascular integrity: More than just a radical idea. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2018, 315, H429–H447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, J.; Yun, J.E.; Lee, H.; Kimm, H.; Jee, S.H. Total, direct, and indirect serum bilirubin concentrations and metabolic syndrome among the Korean population. Endocrine 2010, 39, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.H.; Lee, M.J.; Kang, Y.M.; Hwang, J.Y.; Jang, J.E.; Leem, J.; Park, J.-Y.; Kim, H.-K.; Lee, W.J. Higher serum bilirubin level as a protective factor for the development of diabetes in healthy Korean men: A 4 year retrospective longitudinal study. Metabolism 2014, 63, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppannasamy, D.; Venkatesan, R.; Thankappan, L.; Andavar, R.; Devisundaram, S. Inverse Association between Serum Bilirubin Levels and Retinopathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, NC09–NC12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, E.J.; Lee, J.G.; Kim, B.S.; Huh, K.H.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, Y.S.; Joo, D.J. Clinical impact of serum bilirubin levels on kidney transplant outcomes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.P.; Kim, D.H.; Yang, S.H.; Hwang, J.H.; An, J.N.; Min, S.I.; Ha, J.; Oh, Y.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Lim, C.S. Serum Bilirubin Affects Graft Outcomes through UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase Sequence Variation in Kidney Transplantation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-E.; Lee, Y.-B.; Jun, J.; Jin, S.-M.; Jee, J.H.; Bae, J.; Kim, J. Increment of serum bilirubin as an independent marker predicting new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Korean population. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 27, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leníček, M.; Ďuricová, D.; Hradsky, O.; Dušátková, P.; Jirásková, A.; Lukas, M.; Nachtigal, P.; Vítek, L. The Relationship Between Serum Bilirubin and Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spetzler, V.N.; Goldaracena, N.; Kaths, J.M.; Marquez, M.; Selzner, N.; Cattral, M.S.; Greig, P.D.; Lilly, L.; McGilvray, I.; Levy, G.A.; et al. High preoperative bilirubin values protect against reperfusion injury after live donor liver transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2015, 28, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenhunen, R.; Marver, H.S.; Schmid, R. The enzymatic conversion of heme to bilirubin by microsomal heme oxygenase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1968, 61, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostrow, J.D.; Mukerjee, P.; Tiribelli, C. Structure and binding of unconjugated bilirubin: Relevance for physiological and pathophysiological function. J. Lipid Res. 1994, 35, 1715–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucker, S.D.; Goessling, W. Mechanism of hepatocellular uptake of albumin-bound bilirubin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2000, 1463, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brito, M.A.; Palmela, I.; Cardoso, F.L.; Sá-Pereira, I.; Brites, D. Blood-brain barrier and bilirubin: Clinical aspects and experimental data. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 660–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, A.R.; Brito, M.A.; Bolanos, J.P.; Brites, R.; Almeida, A.; Delgado-Esteban, M. Bilirubin selectively inhibits cytochromecoxidase activity and induces apoptosis in immature cortical neurons: Assessment of the protective effects of glycoursodeoxycholic acid. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Solá, S.; Brites, D. Bilirubin induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway in developing rat brain neurons. Hepatology 2002, 35, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, M.; Agarwal, A. New insights into the role of heme oxygenase-1 in acute kidney injury. Kidney Res. Clin. Pr. 2020, 39, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, K.A.; Grande, J.P.; Croatt, A.J.; Likely, S.; Hebbel, R.P.; Enright, H. Intracellular targets in heme protein-induced renal injury. Kidney Int. 1998, 53, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baranano, D.E.; Rao, M.; Ferris, C.D.; Snyder, S.H. Biliverdin reductase: A major physiologic cytoprotectant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16093–16098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McDonagh, A.F. The biliverdin–bilirubin antioxidant cycle of cellular protection: Missing a wheel? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maines, M.D.; Raju, V.S.; Panahian, N. Spin trap (N-t-butyl-alpha-phenylnitrone)-mediated suprainduction of heme oxygenase-1 in kidney ischemia/reperfusion model: Role of the oxygenase in protection against oxidative injury. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 291, 911–919. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, J.E.; Foresti, R.; Sarathchandra, P.; Kaur, H.; Green, C.J.; Motterlini, R. Heme oxygenase-1-derived bilirubin ameliorates postischemic myocardial dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H643–H651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foresti, R.; Green, C.J.; Motterlini, R. Generation of bile pigments by haem oxygenase: A refined cellular strategy in response to stressful insults. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 2004, 71, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, S.; Snyder, S.H. Neuroprotective Action of Bilirubin against Oxidative Stress in Primary Hippocampal Cultures. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 890, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dore, S.; Takahashi, M.; Ferris, C.D.; Hester, L.D.; Guastella, D.; Snyder, S.H. Bilirubin, formed by activation of heme oxygenase-2, protects neurons against oxidative stress injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 2445–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaur, H.; Hughes, M.N.; Green, C.J.; Naughton, P.; Foresti, R.; Motterlini, R. Interaction of bilirubin and biliverdin with reactive nitrogen species. FEBS Lett. 2003, 543, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minetti, M.; Mallozzi, C.; Di Stasi, A.M.M.; Pietraforte, D. Bilirubin Is an Effective Antioxidant of Peroxynitrite-Mediated Protein Oxidation in Human Blood Plasma. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1998, 352, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Gengaro, P.E.; Niederberger, M.; Burke, T.J.; Schrier, R.W. Nitric oxide: A mediator in rat tubular hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boon, A.; Hawkins, C.; Coombes, J.; Wagner, K.-H.; Bulmer, A. Bilirubin scavenges chloramines and inhibits myeloperoxidase-induced protein/lipid oxidation in physiologically relevant hyperbilirubinemic serum. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 86, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adin, C.A.; VanGundy, Z.C.; Papenfuss, T.L.; Xu, F.; Ghanem, M.; Lakey, J.; Hadley, G.A. Physiologic Doses of Bilirubin Contribute to Tolerance of Islet Transplants by Suppressing the Innate Immune Response. Cell Transplant. 2017, 26, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Ma, Y.; Pan, S.; Reddy, S.; Sun, X. Bilirubin protects grafts against nonspecific inflammation-induced injury in syngeneic intraportal islet transplantation. Exp. Mol. Med. 2010, 42, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Gao, Y.; Guo, H.; Kong, Q.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Pan, S.; Jiang, H.; Dai, W. Pretreatment with Bilirubin Protects Islet against Oxidative Injury During Isolation and Purification. Transplant. Proc. 2011, 43, 1810–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Vishnubhakat, J.M.; Bloom, O.; Zhang, M.; Ombrellino, M.; Sama, A.; Tracey, K.J. Proinflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1) stimulate release of high mobility group protein-1 by pituicytes. Surgery 1999, 126, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondevila, C.; Shen, X.-D.; Tsuchiyashi, S.; Yamashita, K.; Csizmadia, E.; Lassman, C.; Busuttil, R.W.; Kupiec-Weglinski, J.W.; Bach, F.H. Biliverdin therapy protects rat livers from ischemia and reperfusion injury. Hepatology 2004, 40, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullagar, B.; Rao, W.; Gilor, C.; Xu, F.; He, X.; Adin, C.A. Nano-Encapsulation of Bilirubin in Pluronic F127–Chitosan Improves Uptake in β Cells and Increases Islet Viability and Function after Hypoxic Stress. Cell Transplant. 2017, 26, 1703–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Q.; Jiang, X.; Zhai, Y.-Y.; Luo, L.-Z.; Xu, H.-L.; Xiao, J.; Kou, L.; Zhao, Y.-Z. Protective effects and mechanisms of bilirubin nanomedicine against acute pancreatitis. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, A.; Otterbein, L.E.; Overhaus, M.; Sarady, J.K.; Tsung, A.; Kimizuka, K.; Nalesnik, M.A.; Kaizu, T.; Uchiyama, T.; Liu, F.; et al. Biliverdin protects the functional integrity of a transplanted syngeneic small bowel. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, K.; McDaid, J.; Öllinger, R.; Tsui, T.; Berberat, P.O.; Usheva, A.; Csizmadia, E.; Smith, R.N.; Soares, M.; Bach, F.H. Biliverdin, a natural product of heme catabolism, induces tolerance to cardiac allografts. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 765–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, B.; Archer, F.E.; Kathiravan, S.; Hirsch, D.S.; Kleinfeld, A.M.; Vetrano, A.M.; Hegyi, T. Effects of Bilirubin on Neutrophil Responses in Newborn Infants. Neonatology 2013, 103, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwak, J.Y.; Takeshige, K.; Cheung, B.S.; Minakami, S. Bilirubin inhibits the activation of superoxide-producing NADPH oxidase in a neutrophil cell-free system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Protein Struct. Mol. Enzym. 1991, 1076, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, T.; Hortmann, M.; Oelze, M.; Opitz, B.; Steven, S.; Schell, R.; Knorr, M.; Karbach, S.; Schuhmacher, S.; Wenzel, P.; et al. Conversion of biliverdin to bilirubin by biliverdin reductase contributes to endothelial cell protection by heme oxygenase-1—evidence for direct and indirect antioxidant actions of bilirubin. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2010, 49, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Takamiya, R.; Yamaguchi, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Tojo, S.J.; Tamatani, T.; Kitajima, M.; Makino, N.; Ishimura, Y.; Suematsu, M. Induction of Heme Oxygenase-1 Suppresses Venular Leukocyte Adhesion Elicited by Oxidative Stress. Circ. Res. 1999, 85, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hinds, T.D.J.; Creeden, J.F.; Gordon, D.M.; Stec, D.F.; Donald, M.C.; Stec, D.E. Bilirubin Nanoparticles Reduce Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis, Improve Fat Utilization, and Increase Plasma β-Hydroxybutyrate. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 594574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, J.T.D.; Creeden, J.F.; Gordon, D.M.; Spegele, A.C.; Britton, S.L.; Koch, L.G.; Stec, D.E. Rats Genetically Selected for High Aerobic Exercise Capacity Have Elevated Plasma Bilirubin by Upregulation of Hepatic Biliverdin Reductase-A (BVRA) and Suppression of UGT1A1. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020, 9, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, D.; Adeosun, S.O.; Ngwudike, S.I.; Anderson, C.D.; Hall, J.; Hinds, T.D.; Stec, D.E. CRISPR Cas9-mediated deletion of biliverdin reductase A (BVRA) in mouse liver cells induces oxidative stress and lipid accumulation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 672, 108072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stec, D.E.; Gordon, D.; Nestor-Kalinoski, A.L.; Donald, M.C.; Mitchell, Z.L.; Creeden, J.F.; Hinds, J.T.D. Biliverdin Reductase A (BVRA) Knockout in Adipocytes Induces Hypertrophy and Reduces Mitochondria in White Fat of Obese Mice. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, D.; Blomquist, T.M.; Miruzzi, S.A.; McCullumsmith, R.; Stec, D.E.; Hinds, T.D. RNA sequencing in human HepG2 hepatocytes reveals PPAR-α mediates transcriptome responsiveness of bilirubin. Physiol. Genom. 2019, 51, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, D.; Hong, S.; Kipp, Z.; Hinds, T. Identification of Binding Regions of Bilirubin in the Ligand-Binding Pocket of the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-A (PPARalpha). Molecules 2021, 26, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, D.M.; Neifer, K.L.; Hamoud, A.-R.A.; Hawk, C.F.; Nestor-Kalinoski, A.L.; Miruzzi, S.A.; Morran, M.P.; Adeosun, S.O.; Sarver, J.G.; Erhardt, P.W.; et al. Bilirubin remodels murine white adipose tissue by reshaping mitochondrial activity and the coregulator profile of peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor α. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 9804–9822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, B.; Barrabés, J.A.; Figueras, J.; Pineda, V.; Rodríguez-Palomares, J.; Lidón, R.-M.; Sambola, A.; Bañeras, J.; Otaegui, I.; García-Dorado, D. Plasma bilirubin values on admission and ventricular remodeling after a first anterior ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction. Ann. Med. 2016, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, M. Association of Serum Bilirubin Concentration with Risk of Coronary Artery Disease. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwertner, H.A.; Fischer, J.R., Jr. Comparison of various lipid, lipoprotein, and bilirubin combinations as risk factors for predicting coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 2000, 150, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-P.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Schwaiger, J.; Cupples, L.A.; Lingenhel, A.; Hunt, S.C.; Yang, S.; Kronenberg, F. Association Between the UGT1A1*28 Allele, Bilirubin Levels, and Coronary Heart Disease in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2006, 114, 1476–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bulmer, A.; Verkade, H.J.; Wagner, K.-H. Bilirubin and beyond: A review of lipid status in Gilbert’s Syndrome and its relevance to cardiovascular disease protection. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kundur, A.R.; Bulmer, A.C.; Singh, I. Unconjugated bilirubin inhibits collagen induced platelet activation. Platelets 2013, 25, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundur, A.R.; Santhakumar, A.B.; Bulmer, A.C.; Singh, I. Mildly elevated unconjugated bilirubin is associated with reduced platelet activation-related thrombogenesis and inflammation in Gilbert’s Syndrome. Platelets 2017, 28, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tosevska, A.; Heiß, E.H.; Ladurner, A.; Mölzer, C.; Wallner, M.; Bulmer, A.; Wagner, K.; Dirsch, V.M.; Atanasov, A.G. Bilirubin Decreases Macrophage Cholesterol Efflux and ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter A1 Protein Expression. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Amotz, R.; Bonagura, J.; Velayutham, M.; Hamlin, R.; Burns, P.; Adin, C.A. Intraperitoneal bilirubin administration decreases infarct area in a rat coronary ischemia/reperfusion model. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, N.; Croatt, A.J.; Haggard, J.J.; Grande, J.P.; Nath, K.A. Acute cholestatic liver disease protects against glycerol-induced acute renal failure in the rat. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barabas, K.; Milner, R.; Farese, J.; Baylis, C.; Croker, B.; Archer, L.; Adin, C. Hyperbilirubinemia’s protective effect against cisplatin nephrotoxicity in the Gunn rat. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2008, 19, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bösch, F.; Thomas, M.; Kogler, P.; Oberhuber, R.; Sucher, R.; Aigner, F.; Semsroth, S.; Wiedemann, D.; Yamashita, K.; Troppmair, J.; et al. Bilirubin rinse of the graft ameliorates ischemia reperfusion injury in heart transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2014, 27, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Shimazu, M.; Kondo, M.; Uchida, K.; Kumamoto, Y.; Wakabayashi, G.; Kitajima, M.; Suematsu, M. Bilirubin rinse: A simple protectant against the rat liver graft injury mimicking heme oxygenase-1 preconditioning. Hepatology 2003, 38, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Lee, S.S.; Dell’Agnello, C.; Tchipashvili, V.; D’Avilla, J.; Czismadia, E.; Chin, B.Y.; Bach, F.H. Bilirubin Can Induce Tolerance to Islet Allografts. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Tian, X.Y.; Liu, L.; Wong, W.T.J.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Q.; Ho, H.-M.; Wang, N.; Wong, S.L.; et al. Unconjugated Bilirubin Mediates Heme Oxygenase-1–Induced Vascular Benefits in Diabetic Mice. Diabetes 2014, 64, 1564–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dekker, D.; Dorresteijn, M.J.; Pijnenburg, M.; Heemskerk, S.; Rasing-Hoogveld, A.; Burger, D.M.; Wagener, F.A.; Smits, P. The Bilirubin-Increasing Drug Atazanavir Improves Endothelial Function in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soneja, A.; Drews, M.; Malinski, T. Role of nitric oxide, nitroxidative and oxidative stress in wound healing. Pharmacol. Rep. 2005, 57, 108–119. [Google Scholar]
- Ahanger, A.; Leo, M.D.; Gopal, A.; Kant, V.; Tandan, S.K.; Kumar, D. Pro-healing effects of bilirubin in open excision wound model in rats. Int. Wound J. 2014, 13, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, M.; Singh, V.; Kumar, D.; Kumawat, S.; Gopalakrishnan, A.; Lingaraju, M.C.; Gupta, P.; Tandan, S.K.; Kumar, D. Antioxidant potential of bilirubin-accelerated wound healing in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2014, 387, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Xia, X.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, Y.-W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, R.; Kou, L. Bioadhesive hydrogel comprising bilirubin/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes promote diabetic wound healing. Pharm. Biol. 2021, 59, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, M.; Singh, V.; Kumawat, S.; Kant, V.; Tandan, S.K.; Kumar, D. Bilirubin modulated cytokines, growth factors and angiogenesis to improve cutaneous wound healing process in diabetic rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 30, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.M.; Poduval, T.B. Immunomodulatory and immunotoxic effects of bilirubin: Molecular mechanisms. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 997–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavan, P.; Schwemberger, S.J.; Smith, D.L.; Babcock, G.F.; Zucker, S.D. Unconjugated bilirubin induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells by triggering mitochondrial depolarization. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 112, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adin, C.A.; Croker, B.P.; Agarwal, A. Protective effects of exogenous bilirubin on ischemia-reperfusion injury in the isolated, perfused rat kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2005, 288, F778–F784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerman, C.; Goldschmidt, D.; Caplan, M.S.; Kaplan, M.; Bromiker, R.; Eidelman, A.I.; Gartner, L.M.; Hochman, A. Protective Effect of Bilirubin in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in the Rat Intestine. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2002, 35, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkby, K.; Baylis, C.; Agarwal, A.; Croker, B.; Archer, L.; Adin, C. Intravenous bilirubin provides incomplete protection against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2007, 292, F888–F894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, M.F.; Lerner, A. Nutraceutical induction and mimicry of heme oxygenase activity as a strategy for controlling excitotoxicity in brain trauma and ischemic stroke: Focus on oxidative stress. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2021, 21, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, B.; Liu, Y.; You, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, L. Intraperitoneally administered biliverdin protects against UVB-induced skin photo-damage in hairless mice. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 144, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Brown, J.D.; Kawasaki, Y.; Bommer, J.; Takemoto, J.Y. Scalable production of biliverdin IXα by Escherichia coli. BMC Biotechnol. 2012, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, L.; Hosick, P.A.; John, K.; Stec, D.E.; Hinds, T.D. Biliverdin reductase isozymes in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rochette, L.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Redox Functions of Heme Oxygenase-1 and Biliverdin Reductase in Diabetes. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, M.F. “Iatrogenic Gilbert syndrome”—A strategy for reducing vascular and cancer risk by increasing plasma unconjugated bilirubin. Med. Hypotheses 2007, 69, 974–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croom, K.F.; Dhillon, S.; Keam, S.J. Atazanavir. Drugs 2009, 69, 1107–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, N.K.; Kole, L.; Basu, M.; Chakraborty, K.; Mitra, P.S.; Owens, I.S. The Major Chemical-detoxifying System of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases Requires Regulated Phosphorylation Supported by Protein Kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 23048–23061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medical Devices Containing Materials Derived from Animal Sources (Except for In Vitro Diagnostic Devices), Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff. 15 March 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/87251/download (accessed on 8 January 2021).
- Yao, Q.; Chen, R.; Ganapathy, V.; Kou, L. Therapeutic application and construction of bilirubin incorporated nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luckring, E.J.; Parker, P.D.; Hani, H.; Grace, M.; Lila, M.A.; Pierce, J.G.; Adin, C.A. In Vitro Evaluation of a Novel Synthetic Bilirubin Analog as an Antioxidant and Cytoprotective Agent for Pancreatic Islet Transplantation. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 963689720906417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mccarty, M.F. Serum bilirubin may serve as a marker for increased heme oxygenase activity and inducibility in tissues—A rationale for the versatile health protection associated with elevated plasma bilirubin. Med. Hypotheses 2013, 81, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adin, C.A. Bilirubin as a Therapeutic Molecule: Challenges and Opportunities. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10101536
Adin CA. Bilirubin as a Therapeutic Molecule: Challenges and Opportunities. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(10):1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10101536
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdin, Christopher A. 2021. "Bilirubin as a Therapeutic Molecule: Challenges and Opportunities" Antioxidants 10, no. 10: 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10101536
APA StyleAdin, C. A. (2021). Bilirubin as a Therapeutic Molecule: Challenges and Opportunities. Antioxidants, 10(10), 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10101536





