A Novel Neighbor Housing Environment Enhances Social Interaction and Rescues Cognitive Deficits from Social Isolation in Adolescence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Housing
2.2. Social Interaction Test
2.3. Novel Object Recognition
2.4. Anxiety-Like Behavior in the Light-Dark Box
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
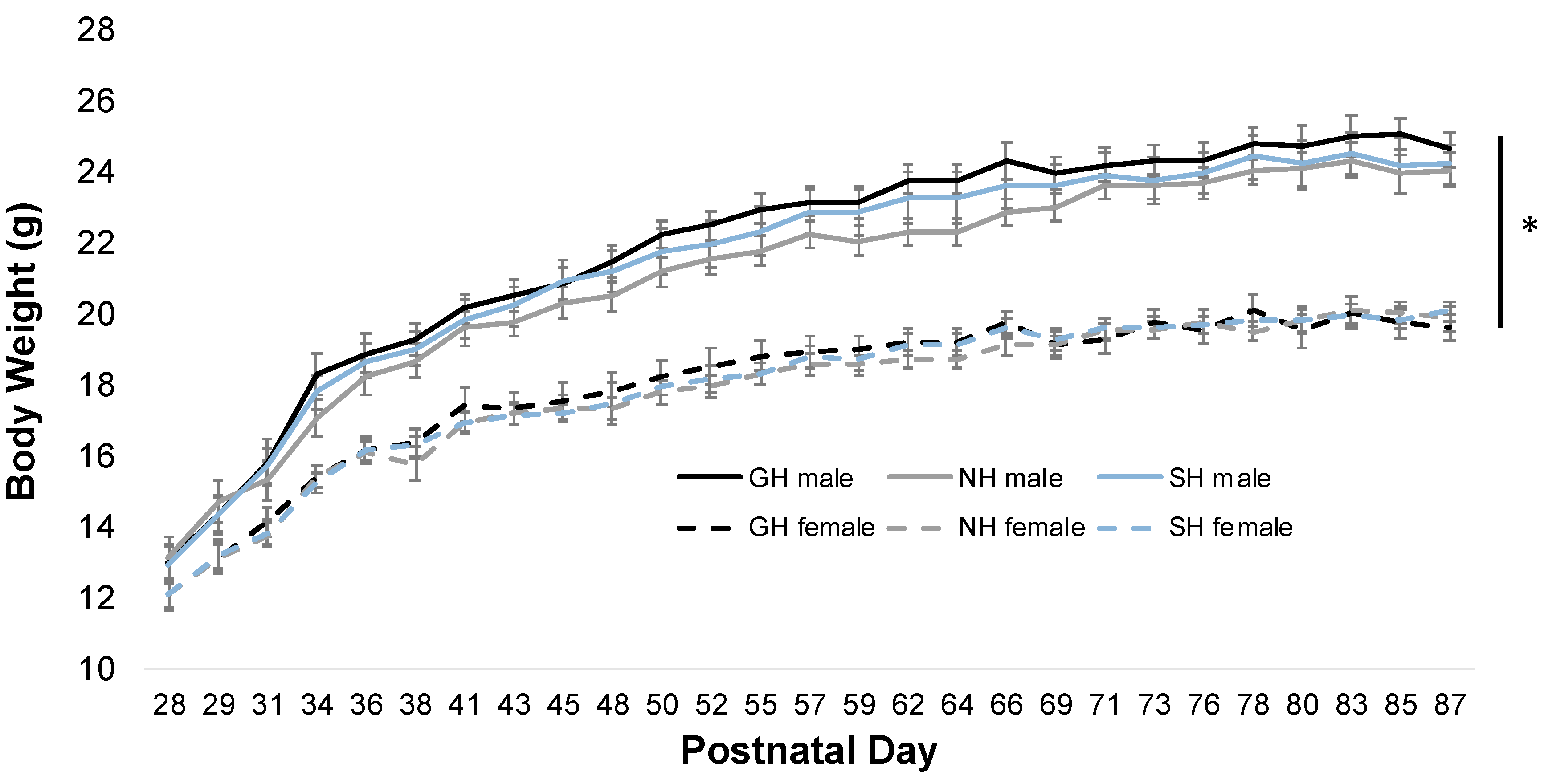
3.1. Social Housing Does not Alter Bodyweight
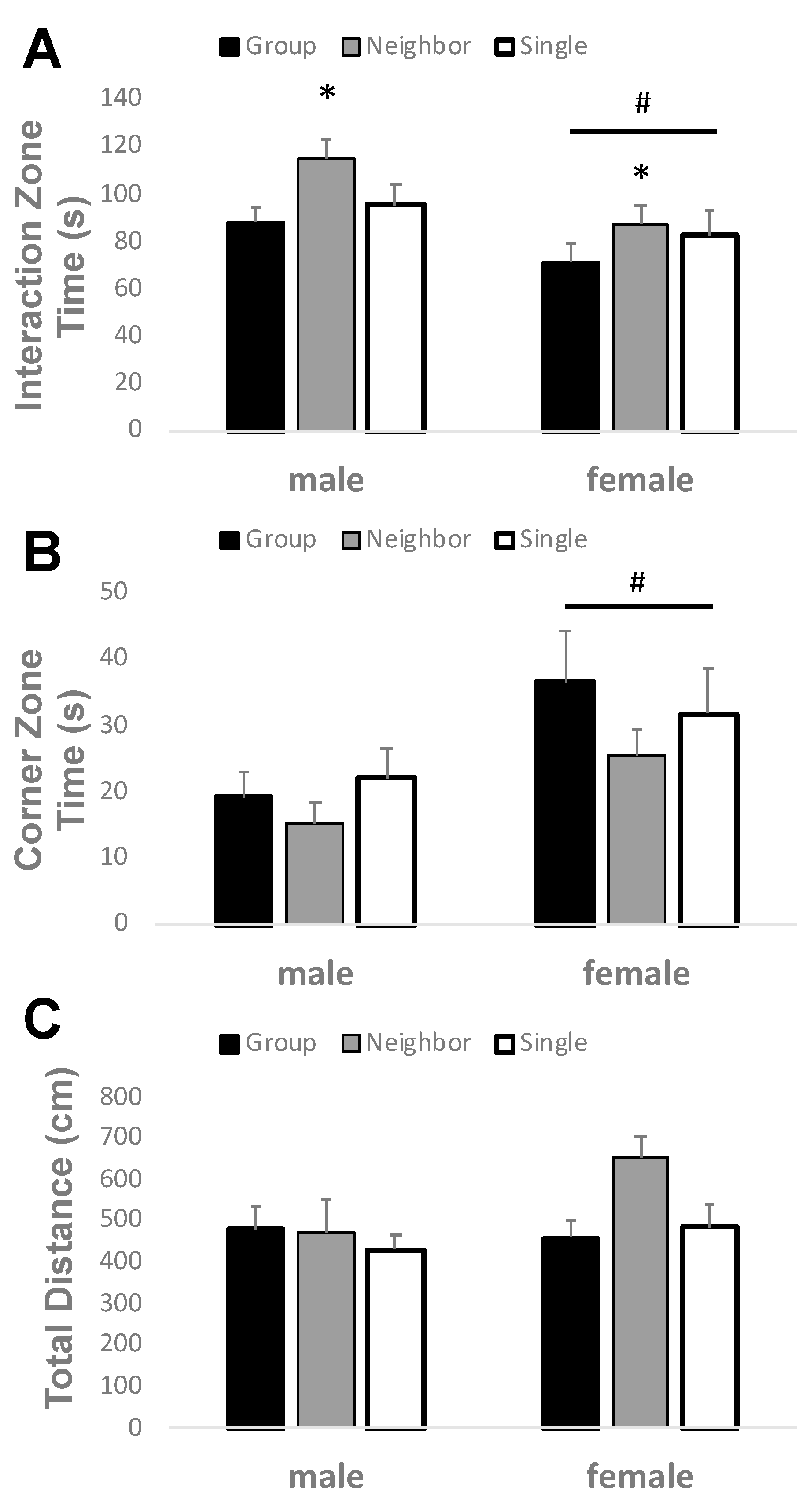
3.2. Neighbor Housing Increases Social Interaction
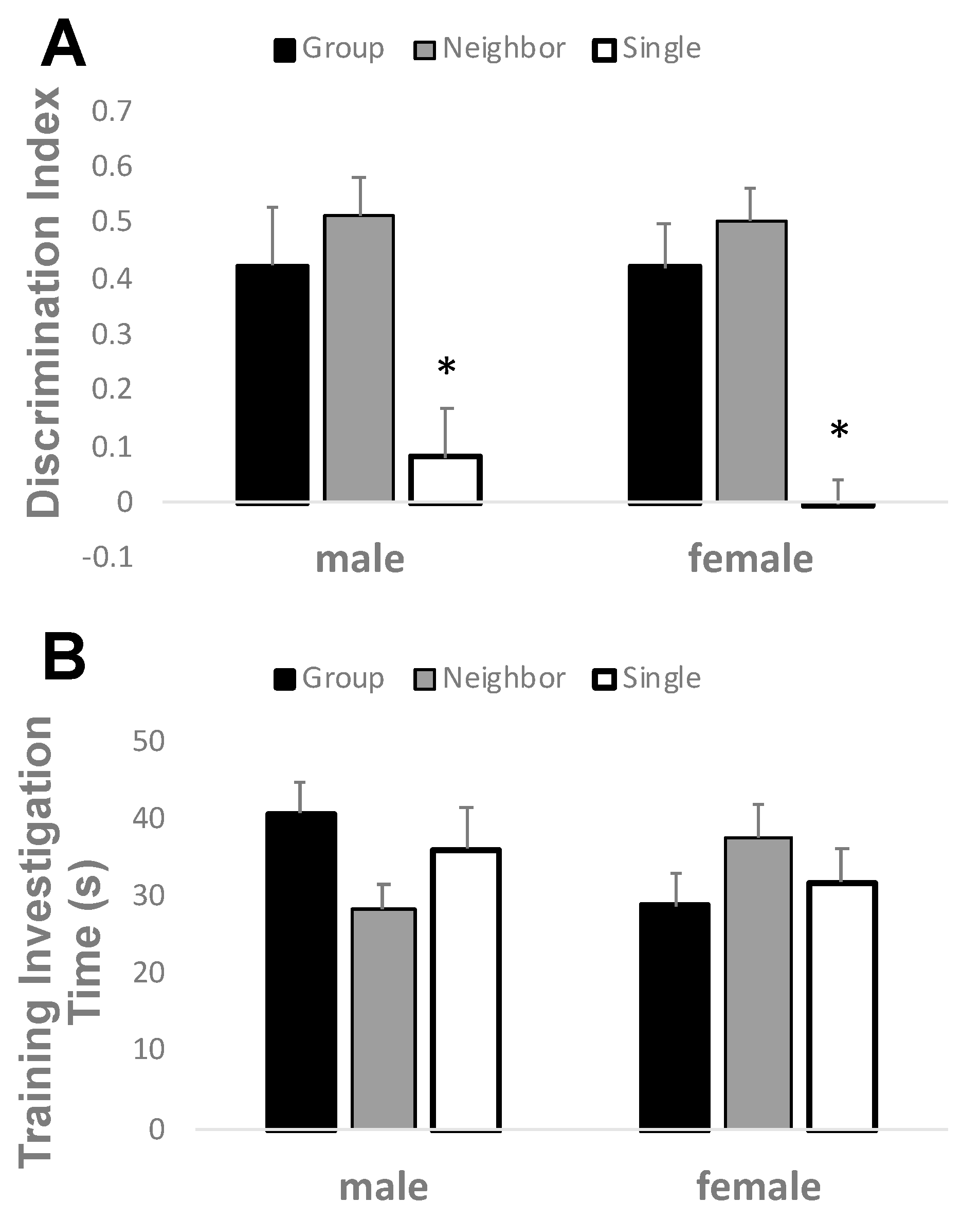
3.3. Neighbor Housing Rescues Social Isolation Deficits in Recognition Memory
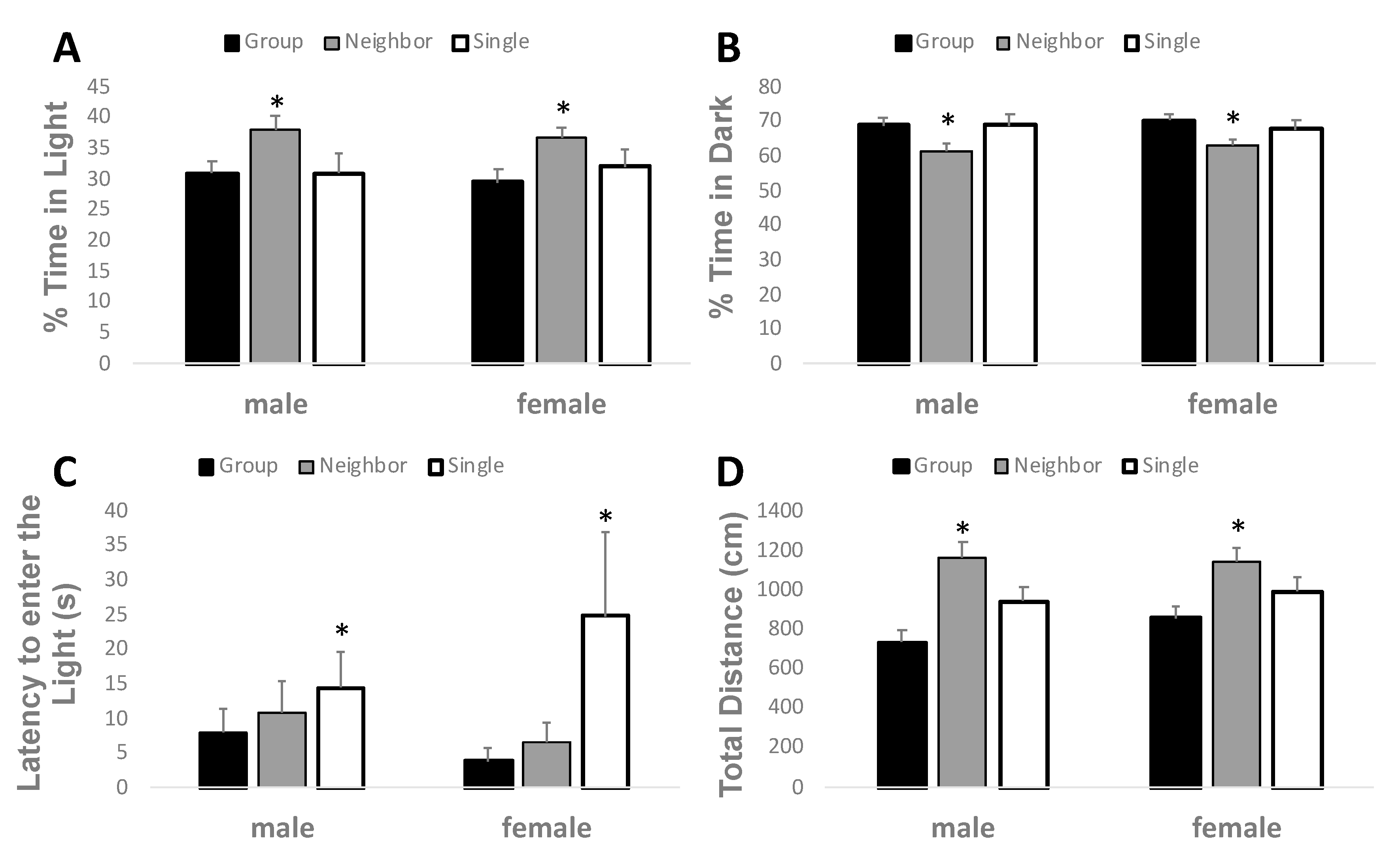
3.4. Anxiety-Like Behavior in the Light-Dark Box is Reduced by Neighbor Housing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spear, L.P. The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 417–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kerkhof, L.W.; Damsteegt, R.; Trezza, V.; Voorn, P.; Vanderschuren, L.J. Social play behavior in adolescent rats is mediated by functional activity in medial prefrontal cortex and striatum. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 1899–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panksepp, J. The ontogeny of play in rats. Dev. Psychobiol. 1981, 14, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, N.; Jenikejew, J.; Richter, S.H.; Kaiser, S.; Sachser, N. Social experiences during adolescence affect anxiety-like behavior but not aggressiveness in male mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 326, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lander, S.S.; Linder-Shacham, D.; Gaisler-Salomon, I. Differential effects of social isolation in adolescent and adult mice on behavior and cortical gene expression. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 316, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voikar, V.; Polus, A.; Vasar, E.; Rauvala, H. Long-term individual housing in C57BL/6J and DBA/2 mice: Assessment of behavioral consequences. Genes Brain Behav. 2005, 4, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.F.; Laber, K. Impact of social isolation and enriched environment during adolescence on voluntary ethanol intake and anxiety in C57BL/6J mice. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 148, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, H.; Ibi, D.; Mizoguchi, H.; Nagai, T.; Nitta, A.; Takuma, K.; Nabeshima, T.; Yoneda, Y.; Yamada, K. Behavioral abnormality and pharmacologic response in social isolation-reared mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 202, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, B.A.; Chappell, A.M. Early social isolation in male Long-Evans rats alters both appetitive and consummatory behaviors expressed during operant ethanol self-administration. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelly, M.J.; Chappell, A.E.; Carter, E.; Weiner, J.L. Adolescent social isolation increases anxiety-like behavior and ethanol intake and impairs fear extinction in adulthood: Possible role of disrupted noradrenergic signaling. Neuropharmacology 2015, 97, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, S.; Haj-Mirzaian, A.; Rahimi-Balaei, M.; Razmi, A.; Kordjazy, N.; Shirzadian, A.; Ejtemaei Mehr, S.; Sianati, H.; Dehpour, A.R. Co-occurrence of anxiety and depressive-like behaviors following adolescent social isolation in male mice; possible role of nitrergic system. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 145, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Pu, T.; Wang, L.; Marshall, C.; He, H.; Hu, G.; Xiao, M. Early enriched physical environment reverses impairments of the hippocampus, but not medial prefrontal cortex, of socially-isolated mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 64, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Yuan, S.; Shao, F.; Wang, W. Adolescent Social Defeat Induced Alterations in Social Behavior and Cognitive Flexibility in Adult Mice: Effects of Developmental Stage and Social Condition. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arain, M.; Haque, M.; Johal, L.; Mathur, P.; Nel, W.; Rais, A.; Sandhu, R.; Sharma, S. Maturation of the adolescent brain. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2013, 9, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butler, T.R.; Karkhanis, A.N.; Jones, S.R.; Weiner, J.L. Adolescent Social Isolation as a Model of Heightened Vulnerability to Comorbid Alcoholism and Anxiety Disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 1202–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, M.F.; Doremus-Fitzwater, T.L.; Becker, H.C. Chronic social isolation and chronic variable stress during early development induce later elevated ethanol intake in adult C57BL/6J mice. Alcoholic 2011, 45, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talani, G.; Biggio, F.; Licheri, V.; Locci, V.; Biggio, G.; Sanna, E. Isolation Rearing Reduces Neuronal Excitability in Dentate Gyrus Granule Cells of Adolescent C57BL/6J Mice: Role of GABAergic Tonic Currents and Neurosteroids. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talani, G.; Licheri, V.; Masala, N.; Follesa, P.; Mostallino, M.C.; Biggio, G.; Sanna, E. Increased voluntary ethanol consumption and changes in hippocampal synaptic plasticity in isolated C57BL/6J mice. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinodan, M.; Rosen, K.M.; Ito, S.; Corfas, G. A critical period for social experience-dependent oligodendrocyte maturation and myelination. Science 2012, 337, 1357–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinodan, M.; Ikawa, D.; Miyamoto, Y.; Yamauchi, J.; Yamamuro, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Toritsuka, M.; Kimoto, S.; Okumura, K.; Yamauchi, T.; et al. Social isolation impairs remyelination in mice through modulation of IL-6. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 4267–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medendorp, W.E.; Petersen, E.D.; Pal, A.; Wagner, L.M.; Myers, A.R.; Hochgeschwender, U.; Jenrow, K.A. Altered Behavior in Mice Socially Isolated During Adolescence Corresponds With Immature Dendritic Spine Morphology and Impaired Plasticity in the Prefrontal Cortex. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Gomez, E.; Perez-Rando, M.; Belles, M.; Gilabert-Juan, J.; Llorens, J.V.; Carceller, H.; Bueno-Fernandez, C.; Garcia-Mompo, C.; Ripoll-Martinez, B.; Curto, Y.; et al. Early Social Isolation Stress and Perinatal NMDA Receptor Antagonist Treatment Induce Changes in the Structure and Neurochemistry of Inhibitory Neurons of the Adult Amygdala and Prefrontal Cortex. eNeuro 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Dietz, K.; DeLoyht, J.M.; Pedre, X.; Kelkar, D.; Kaur, J.; Vialou, V.; Lobo, M.K.; Dietz, D.M.; Nestler, E.J.; et al. Impaired adult myelination in the prefrontal cortex of socially isolated mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1621–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Edwards, T.J.; Kurniawan, N.D.; Richards, L.J.; Jiang, T. Altered structural connectome in adolescent socially isolated mice. Neuroimage 2016, 139, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veenema, A.H. Early life stress, the development of aggression and neuroendocrine and neurobiological correlates: What can we learn from animal models? Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2009, 30, 497–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, E.M.; Dallaire, J.A.; Gaskill, B.N.; Pritchett-Corning, K.R.; Garner, J.P. Aggression in group-housed laboratory mice: Why can’t we solve the problem? Lab. Anim. (N. Y.) 2017, 46, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilpin, N.W.; Weiner, J.L. Neurobiology of comorbid post-traumatic stress disorder and alcohol-use disorder. Genes Brain Behav. 2017, 16, 15–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council, N.R. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals: Eighth Edition; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; p. 118. [Google Scholar]
- Golden, S.A.; Covington, H.E., 3rd; Berton, O.; Russo, S.J. A standardized protocol for repeated social defeat stress in mice. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, J.T.; Mahmood, T.; Harris, G.M.; Abbas, S.; Miles, M.F. Intermittent Ethanol during Adolescence Leads to Lasting Behavioral Changes in Adulthood and Alters Gene Expression and Histone Methylation in the PFC. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, E.C.; Brown, M.W. Neural circuitry for rat recognition memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 285, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzel, D.H.; Tovmasyan, A.; Ashcraft, K.A.; Rajic, Z.; Weitner, T.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Buckley, A.F.; Prasad, M.R.; Young, K.; et al. Radioprotection of the Brain White Matter by Mn(III) N-Butoxyethylpyridylporphyrin-Based Superoxide Dismutase Mimic MnTnBuOE-2-PyP5+. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, D.W.; Engelmann, M.; Tobin, V.A.; Meddle, S.L.; Ludwig, M. Vasopressin and social odor processing in the olfactory bulb and anterior olfactory nucleus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1220, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, L.A.; Varlinskaya, E.I.; Spear, L.P. Rewarding properties of social interactions in adolescent and adult male and female rats: Impact of social versus isolate housing of subjects and partners. Dev. Psychobiol. 2004, 45, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; You, Q.L.; Wei, M.D.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Z.Y.; Lin, S.; Huang, L.; Li, S.J.; Li, X.W.; Gao, T.M. Social Isolation During Adolescence Strengthens Retention of Fear Memories and Facilitates Induction of Late-Phase Long-Term Potentiation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kercmar, J.; Budefeld, T.; Grgurevic, N.; Tobet, S.A.; Majdic, G. Adolescent social isolation changes social recognition in adult mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 216, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naert, A.; Callaerts-Vegh, Z.; D’Hooge, R. Nocturnal hyperactivity, increased social novelty preference and delayed extinction of fear responses in post-weaning socially isolated mice. Brain Res. Bull. 2011, 85, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, L.; Jia, H.; Meng, Q.; Wu, S.; Li, N.; He, S. Isolation rearing induces social and emotional function abnormalities and alters glutamate and neurodevelopment-related gene expression in rats. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 33, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, T.D.; Dao, D.T.; Kovacsics, C.E. The Open Field Test. In Mood and Anxiety Related Phenotypes in Mice; Neuromethods, G.T., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, R.J. More haste, considerably less speed. J. Psychopharmacol. 2007, 21, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faravelli, C.; Lo Sauro, C.; Godini, L.; Lelli, L.; Benni, L.; Pietrini, F.; Lazzeretti, L.; Talamba, G.A.; Fioravanti, G.; Ricca, V. Childhood stressful events, HPA axis and anxiety disorders. World J. Psychiatry 2012, 2, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, L.; Wang, L.; Zhong, Y. Social Isolation Induces Rac1-Dependent Forgetting of Social Memory. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, W.M. The development of the three Rs concept. Altern. Lab. Anim. 1995, 23, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holgate, J.Y.; Garcia, H.; Chatterjee, S.; Bartlett, S.E. Social and environmental enrichment has different effects on ethanol and sucrose consumption in mice. Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logue, S.; Chein, J.; Gould, T.; Holliday, E.; Steinberg, L. Adolescent mice, unlike adults, consume more alcohol in the presence of peers than alone. Dev. Sci. 2014, 17, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, J.S.; Wilson, B.B.; Tan, O.; Gururajan, A.; Bowen, M.T. Acute alcohol exposure dose-dependently alleviates social avoidance in adolescent mice and inhibits social investigation in adult mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pais, A.B.; Pais, A.C.; Elmisurati, G.; Park, S.H.; Miles, M.F.; Wolstenholme, J.T. A Novel Neighbor Housing Environment Enhances Social Interaction and Rescues Cognitive Deficits from Social Isolation in Adolescence. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9120336
Pais AB, Pais AC, Elmisurati G, Park SH, Miles MF, Wolstenholme JT. A Novel Neighbor Housing Environment Enhances Social Interaction and Rescues Cognitive Deficits from Social Isolation in Adolescence. Brain Sciences. 2019; 9(12):336. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9120336
Chicago/Turabian StylePais, Alexander B., Anthony C. Pais, Gabriel Elmisurati, So Hyun Park, Michael F. Miles, and Jennifer T. Wolstenholme. 2019. "A Novel Neighbor Housing Environment Enhances Social Interaction and Rescues Cognitive Deficits from Social Isolation in Adolescence" Brain Sciences 9, no. 12: 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9120336
APA StylePais, A. B., Pais, A. C., Elmisurati, G., Park, S. H., Miles, M. F., & Wolstenholme, J. T. (2019). A Novel Neighbor Housing Environment Enhances Social Interaction and Rescues Cognitive Deficits from Social Isolation in Adolescence. Brain Sciences, 9(12), 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9120336




