B7-H3 as a Reliable Diagnostic Biomarker for the Differentiation of High-Grade Gliomas (HGGs) and Low-Grade Gliomas (LGGs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Histopathologic and Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.2.2. Follow-Up
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sociodemographic and Baseline Characteristics
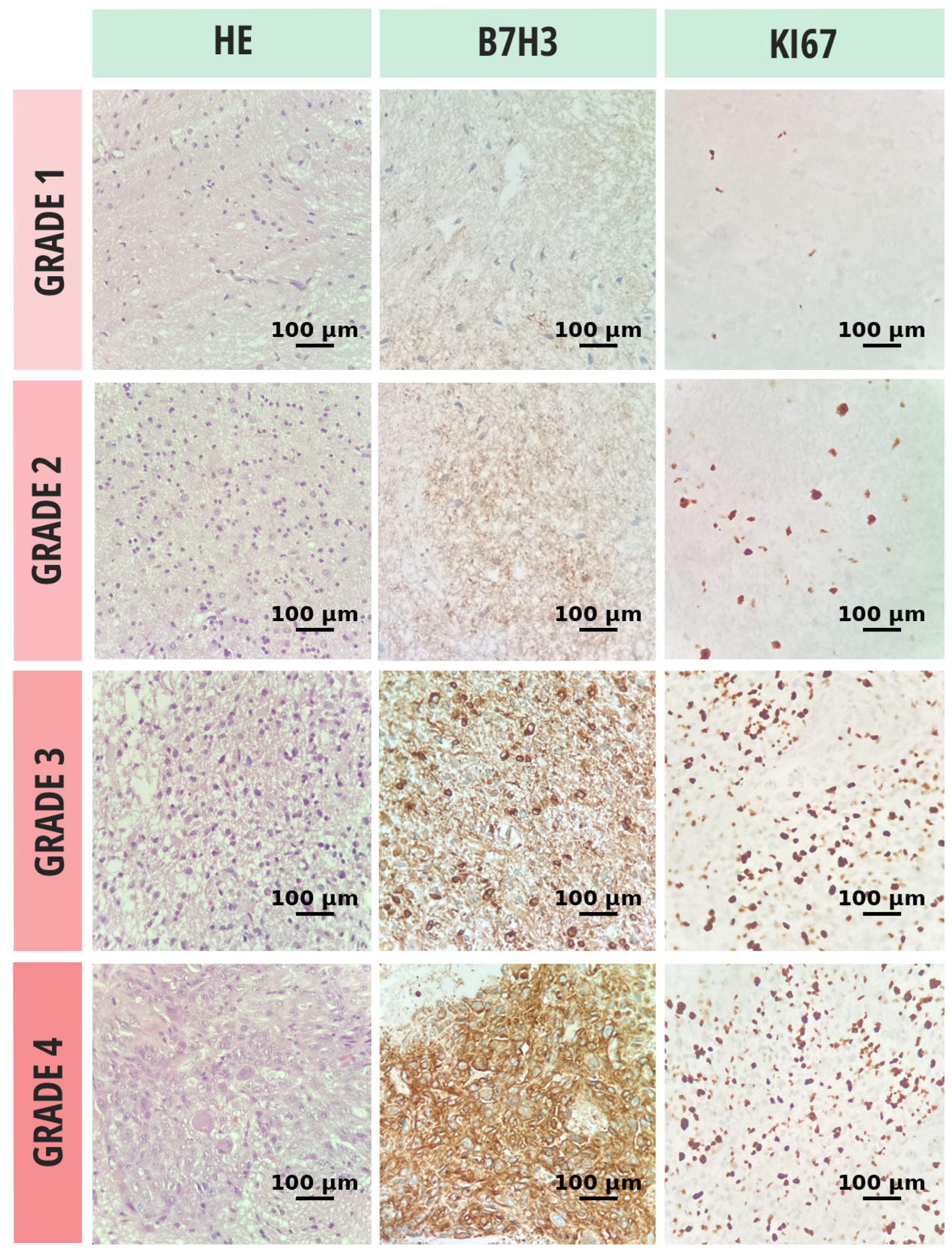
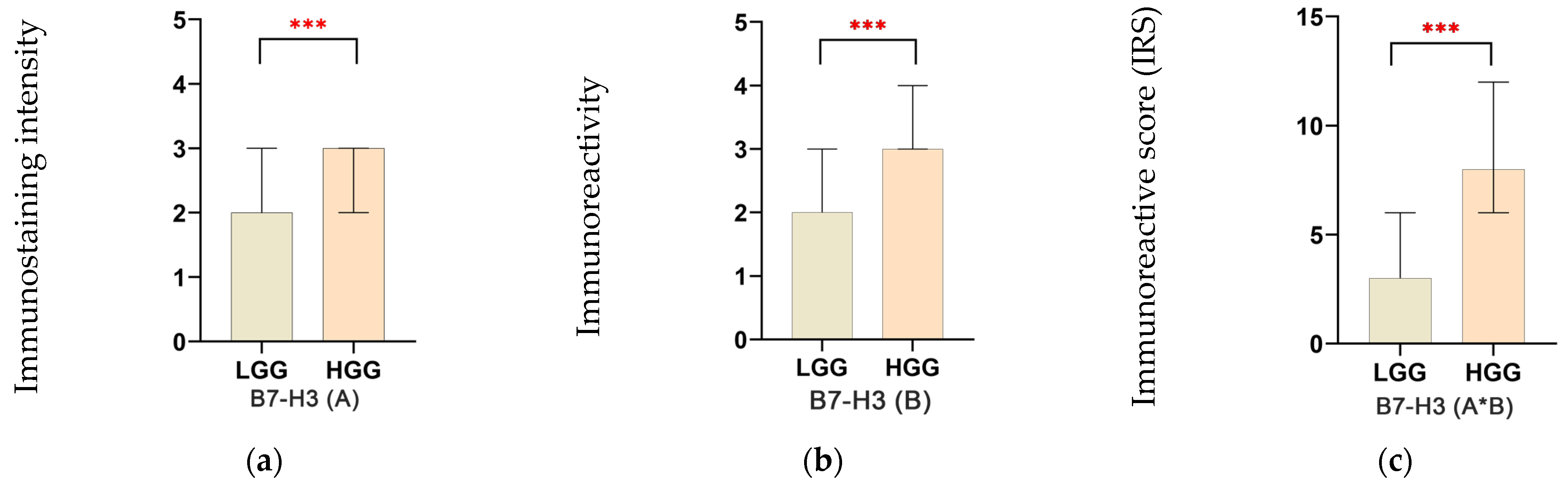
3.2. Discriminative Role of B7-H3 in Glial Neoplasms
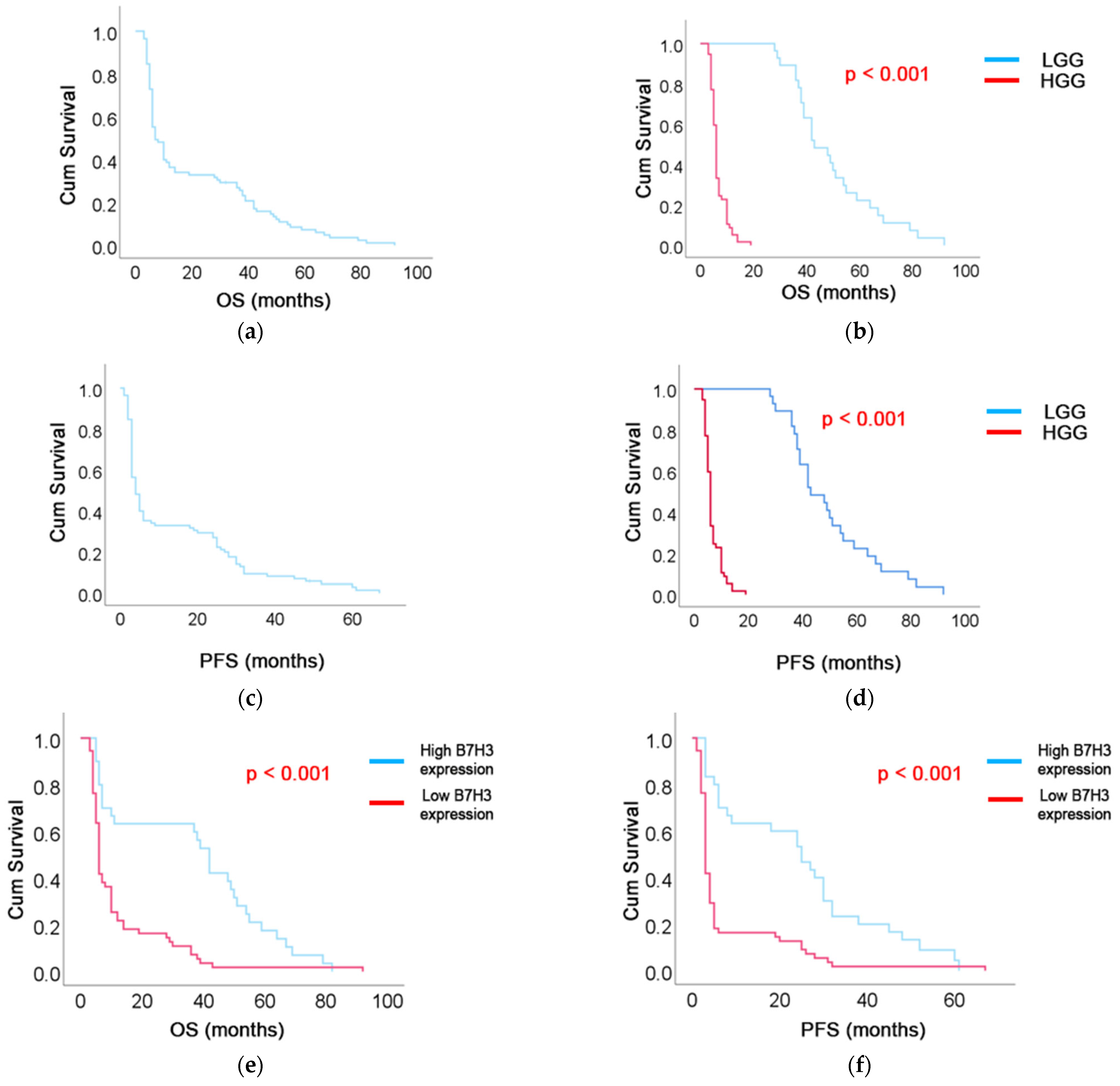
3.3. Follow-Up Data
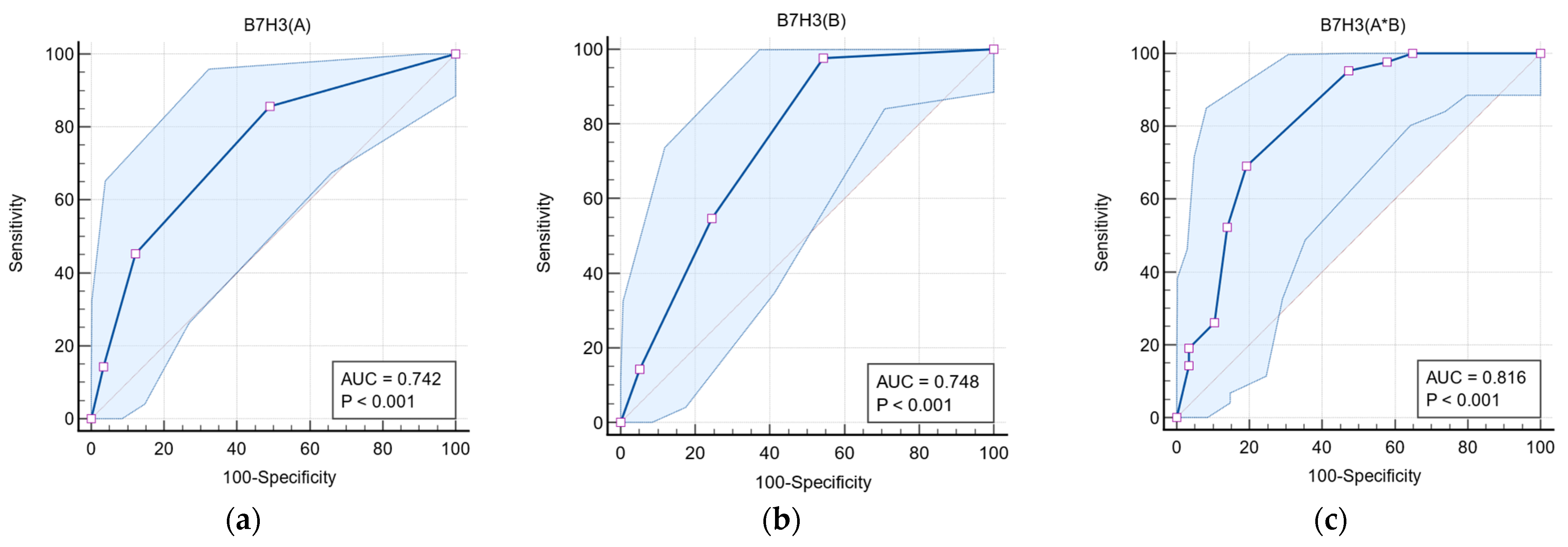
3.4. Predictive Value of B7-H3 Expression in Glial Neoplasms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; Von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Truitt, G.; Boscia, A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2011-2015. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20 (Suppl. S4), iv1–iv86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begagić, E.; Pugonja, R.; Bečulić, H.; Čeliković, A.; Lihić, L.T.; Vukas, S.K.; Čejvan, L.; Skomorac, R.; Selimović, E.; Jaganjac, B.; et al. Molecular Targeted Therapies in Glioblastoma Multiforme: A Systematic Overview of Global Trends and Findings. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüceer, R.O.; Kaya, S.; Balcı, S.N.; Eğilmez, H.R.; Yılmaz, M.; Erdıs, E. Prognostic Biomarkers in Isocitrate Dehydrogenase Wild-Type Glioblastoma: A Focus on B7-H3. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasic, P.; Jeremic, M.; Jeremic, R.; Pjevic, M.D.; Rasic, M.; Djuricic, S.M.; Milickovic, M.; Vukadin, M.; Mijovic, T.; Savic, D. Targeting B7-H3-A Novel Strategy for the Design of Anticancer Agents for Extracranial Pediatric Solid Tumors Treatment. Molecules 2023, 28, 3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontos, F.; Michelakos, T.; Kurokawa, T.; Sadagopan, A.; Schwab, J.H.; Ferrone, C.R.; Ferrone, S. B7-H3: An Attractive Target for Antibody-based Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasic, P.; Jovanovic-Tucovic, M.; Jeremic, M.; Djuricic, S.M.; Vasiljevic, Z.V.; Milickovic, M.; Savic, D. B7 homologue 3 as a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target in gastrointestinal tumors. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 13, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getu, A.A.; Tigabu, A.; Zhou, M.; Lu, J.; Fodstad, Ø.; Tan, M. New frontiers in immune checkpoint B7-H3 (CD276) research and drug development. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chang, M.; Wang, Y.; Xing, B.; Ma, W. B7-H3 in Brain Malignancies: Immunology and Immunotherapy. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 3762–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maachani, U.B.; Tosi, U.; Pisapia, D.J.; Mukherjee, S.; Marnell, C.S.; Voronina, J.; Martinez, D.; Santi, M.; Dahmane, N.; Zhou, Z.; et al. B7-H3 as a Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Pediatric central nervous system Tumors. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babič, D.; Jovčevska, I.; Zottel, A. B7-H3 in glioblastoma and beyond: Significance and therapeutic strategies. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1495283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitanza, N.A.; Ronsley, R.; Choe, M.; Seidel, K.; Huang, W.; Rawlings-Rhea, S.D.; Beam, M.; Steinmetzer, L.; Wilson, A.L.; Brown, C.; et al. Intracerebroventricular B7-H3-targeting CAR T cells for diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: A phase 1 trial. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydar, D.; Houke, H.; Chiang, J.; Yi, Z.; Odé, Z.; Caldwell, K.; Zhu, X.; Mercer, K.S.; Stripay, J.L.; Shaw, T.I.; et al. Cell-surface antigen profiling of pediatric brain tumors: B7-H3 is consistently expressed and can be targeted via local or systemic CAR T-cell delivery. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Vicente, Y.; Castillejos-López, M.d.J.; Carmona-Aparicio, L.; Coballase-Urrutia, E.; Velasco-Hidalgo, L.; Niembro-Zúñiga, A.M.; Zapata-Tarrés, M.; Torres-Espíndola, L.M. Immunotherapy for Pediatric Gliomas: CAR-T Cells Against B7H3: A Review of the Literature. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2024, 23, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.A.; Cheung, N.V. Targets and Antibody Formats for Immunotherapy of Neuroblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1836–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theruvath, J.; Sotillo, E.; Mount, C.W.; Graef, C.M.; Delaidelli, A.; Heitzeneder, S.; Labanieh, L.; Dhingra, S.; Leruste, A.; Majzner, R.G.; et al. Locoregionally administered B7-H3-targeted CAR T cells for treatment of atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alva, E.; Rubens, J.; Chi, S.; Rosenberg, T.; Reddy, A.; Raabe, E.H.; Margol, A. Recent progress and novel approaches to treating atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor. Neoplasia 2023, 37, 100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, S.; Plant-Fox, A.S.; Chi, S.N.; Narendran, A. Current advances in immunotherapy for atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor (ATRT). Neurooncol. Pract. 2023, 10, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottino, C.; Vitale, C.; Dondero, A.; Castriconi, R. B7-H3 in Pediatric Tumors: Far beyond Neuroblastoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Xu, H.; Dong, R.; Chen, C.C.; Hua, W. Survival Association and Cell Cycle Effects of B7H3 in Neuroblastoma. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2020, 63, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J. Diagnostic value of MRI radiomics in differentiating high-grade glioma from low-grade glioma: A meta-analysis. Oncol. Lett. 2023, 26, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, B.; Balla, M.; Dutton, L.; Williams, S.; Lewis, J.; Gallagher, P.; Finch, T.; Burns, R.; Araújo-Soares, V.; Menger, F.; et al. “It changes everything”: Understanding how people experience the impact of living with a lower-grade glioma. Neurooncol. Pract. 2024, 11, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ren, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Q.; Dong, B. Identification and verification of the ferroptosis- and pyroptosis-associated prognostic signature for low-grade glioma. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 22, 728–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.; Kornblum, H.I. Molecular markers in glioma. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 134, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śledzińska, P.; Bebyn, M.G.; Furtak, J.; Kowalewski, J.; Lewandowska, M.A. Prognostic and Predictive Biomarkers in Gliomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerholz, D.K.; Beck, A.P. Principles and approaches for reproducible scoring of tissue stains in research. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.D.; Lozada, J.R.; Zorko, N.A.; Elliott, A.; Makovec, A.; Radovich, M.; Heath, E.I.; Agarwal, N.; Mckay, R.R.; Garje, R.; et al. Pan-Cancer Interrogation of B7-H3 (CD276) as an Actionable Therapeutic Target Across Human Malignancies. Cancer Res. Commun. 2024, 4, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontão, P.; Teixeira, G.R.; Moreno, D.A.; Marques, R.F.; Stavale, J.N.; Malheiros, S.M.F.; Júnior, C.A.; Mançano, B.M.; Reis, R.M. High B7-H3 protein expression in Medulloblastoma is associated with metastasis and unfavorable patient outcomes. Diagn. Pathol. 2025, 20, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, B.; Parameswaran, S.; Sharma, A.; Krishnakumar, S. Clinical relevance of B7H3 expression in retinoblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, P.Y.; Bent, M.v.D.; Youssef, G.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Ellingson, B.M.; Weller, M.; Galanis, E.; Barboriak, D.P.; de Groot, J.; Gilbert, M.R.; et al. RANO 2.0: Update to the Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology Criteria for High- and Low-Grade Gliomas in Adults. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 5187–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schag, C.C.; Heinrich, R.L.; Ganz, P.A. Karnofsky performance status revisited: Reliability, validity, and guidelines. J. Clin. Oncol. 1984, 2, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, C.; Tao, B.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Z.; Yang, X.; Peng, L.; Xia, X.; Chen, L. B7-H3 Regulates Glioma Growth and Cell Invasion Through a JAK2/STAT3/Slug-Dependent Signaling Pathway. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Digregorio, M.; Coppieters, N.; Lombard, A.; Lumapat, P.N.; Scholtes, F.; Rogister, B. The expression of B7-H3 isoforms in newly diagnosed glioblastoma and recurrence and their functional role. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehama, D.; Di Ianni, N.; Musio, S.; Du, H.; Patané, M.; Pollo, B.; Finocchiaro, G.; Park, J.J.; Dunn, D.E.; Edwards, D.S.; et al. B7-H3-redirected chimeric antigen receptor T cells target glioblastoma and neurospheres. eBioMedicine 2019, 47, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Marzese, D.M.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.C.; Kelly, D.F.; et al. B7H3 regulates differentiation and serves as a potential biomarker and theranostic target for human glioblastoma. Lab. Investig. 2019, 99, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, R.; Chi, X.; Xian, N.; Chen, X.; Huang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; et al. Safety and efficacy of B7-H3 targeting CAR-T cell therapy for patients with recurrent GBM. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42 (Suppl. S16), 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, N.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, J.; Pan, C.; Zhang, P.; Ma, W.; Zhang, X.; Xi, J.J.; Chen, M.; et al. B7H3-targeting chimeric antigen receptor modification enhances antitumor effect of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells in glioblastoma. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
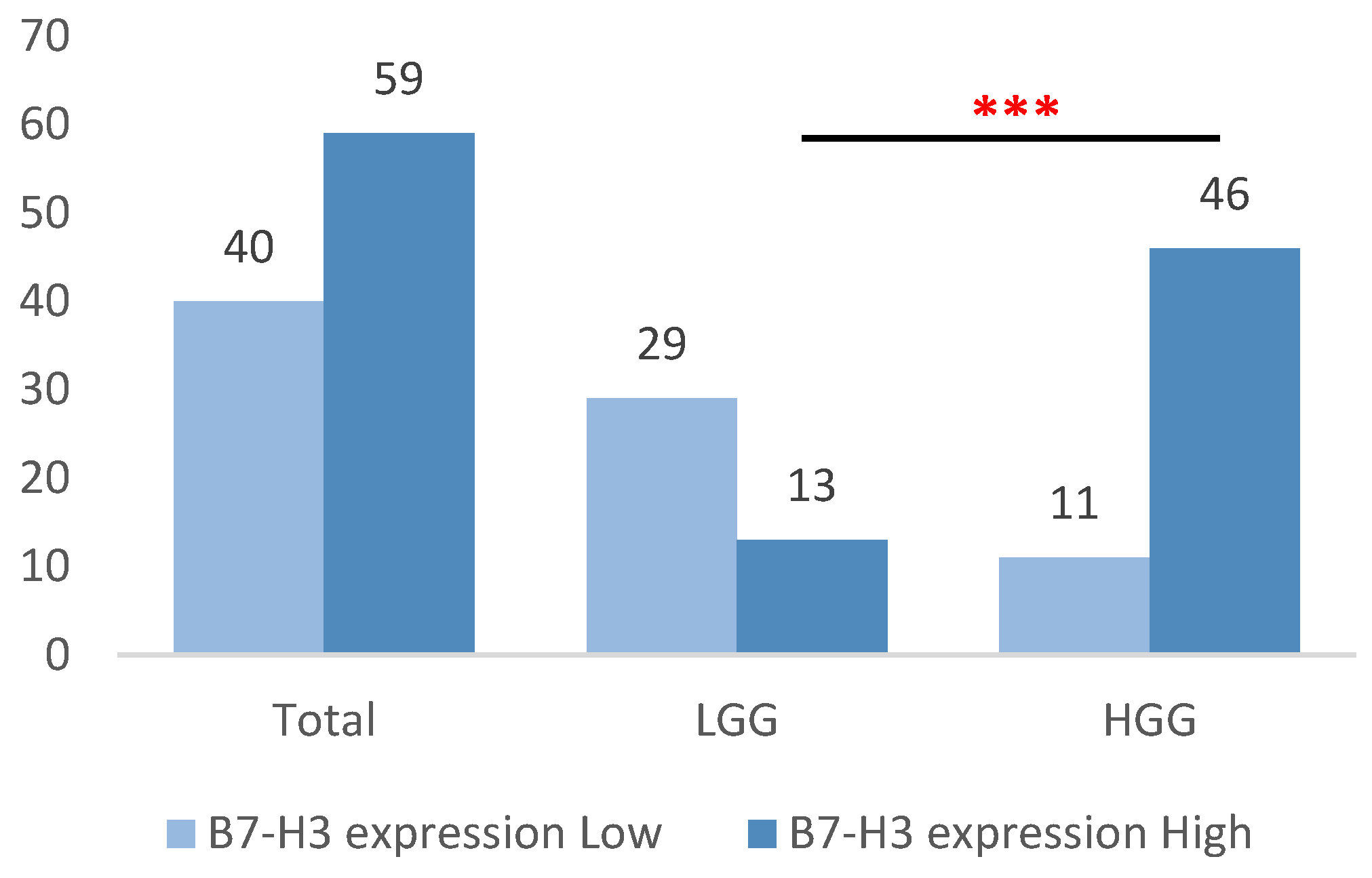
| Variable | Total (N = 99) | Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LGG (N = 42) | HGG (N = 57) | p-Value | |||
| Demographic data | |||||
| Gender N (%) | Male | 57 (57.6) | 21 (50.0) | 36 (63.2) | 0.190 |
| Female | 42 (42.4) | 21 (50.0) | 21 (36.8) | ||
| Age (years) Median (IQR) | 56 (46–63) | 55 (44–65) | 56 (47–63) | 0.899 | |
| Histopathologic data | |||||
| Grade N (%) | G1 | 12 (12.1) | 12 (28.6) | - | <0.001 |
| G2 | 30 (30.3) | 30 (71.4) | - | ||
| G3 | 21 (21.2) | - | 21 (36.8) | ||
| G4 | 36 (36.4) | - | 36 (63.2) | ||
| Ki-67 (%) Median (IQR) | 20.0 (8.0–60.0) | 5.0 (4.0–20.0) | 30.0 (25.0–60.0) | <0.001 | |
| IDH status | IDH-mutant | 55 (55.6%) | 31 (73.8%) | 9 (15.8%) | <0.001 |
| IDH-wild type | 44 (44.4%) | 11 (26.2%) | 48 (84.2%) | ||
| Variable | AUC | 95% CI | Cut-Off | Sensitivity | Specificity | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B7-H3 (A) | 0.742 | 0.645–0.825 | ≥2 | 85.71 | 50.88 | <0.001 |
| B7-H3 (B) | 0.748 | 0.651–0.830 | ≥3 | 97.62 | 45.61 | <0.001 |
| B7-H3 (A*B) | 0.816 | 0.726–0.886 | ≥5 | 73.14 | 80.70 | <0.001 |
| Variable | Total (N = 99) | Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LGG (N = 42) | HGG (N = 57) | p-Value | |||
| KPS preoperatively Median (IQR) | 40.0 (20.0–60.0) | 60.0 (40.0–80.0) | 40.0 (20.0–40.0) | <0.001 | |
| KPS first follow-up (1 month) Median (IQR) | 40.0 (20.0–100.0) | 60.0 (40.0–100.0) | 20.0 (20.0–60.0) | <0.001 | |
| Overall survival (months) Median (IQR) | 10 (5–37) | 43 (38–57) | 6 (4–10) | <0.001 | |
| RANO criteria of disease progression | Complete response | 4 (4.0) | 4 (9.5) | 0 (0) | <0.001 |
| Partial response | 17 (17.2) | 17 (40.5) | 0 (0) | ||
| Stable disease | 20 (20.2) | 15 (35.7) | 5 (8.8) | ||
| Progression | 58 (58.6) | 6 (14.3) | 52 (91.2) | ||
| PFS (months) Median (IQR) | 7 (5–28) | 30 (25–42) | 3 (3–4) | <0.001 | |
| Variable | Univariate Regression Analysis | Multivariate Regression Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age > 60 years | 2.1 (0.9–4.9) | 0.083 | - | - |
| Gender (male) | 1.2 (0.7–2.2) | 0.521 | - | - |
| KPS preoperatively < 60 | 4.3 (1.8–10.4) | <0.001 | 1.7 (0.1–29.4) | 0.718 |
| KPS postoperatively < 60 | 4.5 (1.9–10.6) | <0.001 | 2.6 (0.2–44.7) | 0.500 |
| RANO criteria = progression | 5.4 (2.7–10.6) | <0.001 | 4.9 (2.4–10.1) | <0.001 |
| IDH wild type | 3.8 (1.6–8.9) | 0.002 | 3.4 (1.3–8.5) | 0.011 |
| Ki-67 > 25% | 4.6 (2.1–10.2) | <0.001 | 3.7 (1.5–9.0) | 0.005 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juković-Bihorac, F.; Đuričić, S.; Begagić, E.; Bečulić, H.; Efendić, A.; Vranić, S.; Pojskić, M. B7-H3 as a Reliable Diagnostic Biomarker for the Differentiation of High-Grade Gliomas (HGGs) and Low-Grade Gliomas (LGGs). Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080872
Juković-Bihorac F, Đuričić S, Begagić E, Bečulić H, Efendić A, Vranić S, Pojskić M. B7-H3 as a Reliable Diagnostic Biomarker for the Differentiation of High-Grade Gliomas (HGGs) and Low-Grade Gliomas (LGGs). Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(8):872. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080872
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuković-Bihorac, Fatima, Slaviša Đuričić, Emir Begagić, Hakija Bečulić, Alma Efendić, Semir Vranić, and Mirza Pojskić. 2025. "B7-H3 as a Reliable Diagnostic Biomarker for the Differentiation of High-Grade Gliomas (HGGs) and Low-Grade Gliomas (LGGs)" Brain Sciences 15, no. 8: 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080872
APA StyleJuković-Bihorac, F., Đuričić, S., Begagić, E., Bečulić, H., Efendić, A., Vranić, S., & Pojskić, M. (2025). B7-H3 as a Reliable Diagnostic Biomarker for the Differentiation of High-Grade Gliomas (HGGs) and Low-Grade Gliomas (LGGs). Brain Sciences, 15(8), 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080872











