Prevalent Cardiovascular Disease and Atrial Fibrillation in Relation to Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Burden
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
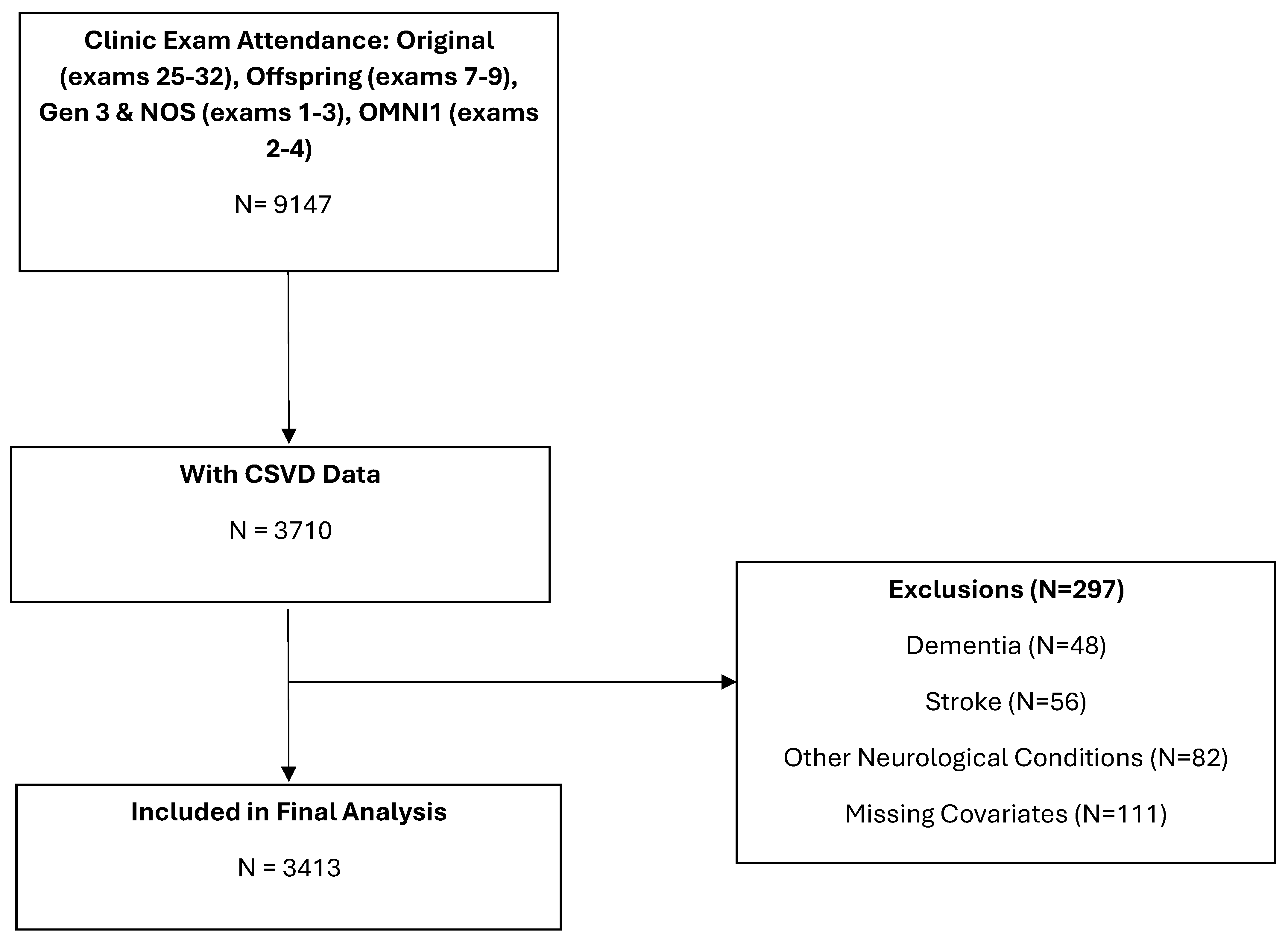
2.1. Sample
2.2. Exposure
2.3. Brain MRI
2.4. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Markers
2.5. Multi-Marker CSVD Score
2.6. Covariates
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Multivariable Regression Analyses (Table 2)
| Predictor | Model a | Multi-Maker CSVD Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (N = 2336) | 1 (N = 773) OR (95% CI) | ≥2 (N = 304) OR (95% CI) | ||
| Prevalent cardiovascular disease or AF | 1 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.46 (1.12, 1.90) *# | 1.19 (0.84, 1.69) |
| 2 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.38 (1.05, 1.84) *# | 1.25 (0.87, 1.81) | |
| Prevalent AF | 1 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.78 (1.19, 2.66) *# | 1.25 (0.74, 2.11) |
| 2 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.86 (1.24, 2.80) *# | 1.37 (0.80, 2.34) | |
| Prevalent cardiovascular disease | 1 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.43 (1.06, 1.93) *# | 1.18 (0.80, 1.73) |
| 2 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.31 (0.96, 1.79) | 1.22 (0.81, 1.83) | |
| Prevalent coronary heart disease | 1 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.29 (0.91, 1.83) | 1.06 (0.67, 1.66) |
| 2 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.19 (0.83, 1.71) | 1.09 (0.68, 1.73) | |
| Prevalent heart failure | 1 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.76 (0.74, 4.21) | 2.00 (0.78, 5.10) |
| 2 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.77 (0.74, 4.23) | 2.29 (0.85, 5.94) | |
3.2. Prevalent CVD and Individual CSVD Markers (Figure 2)
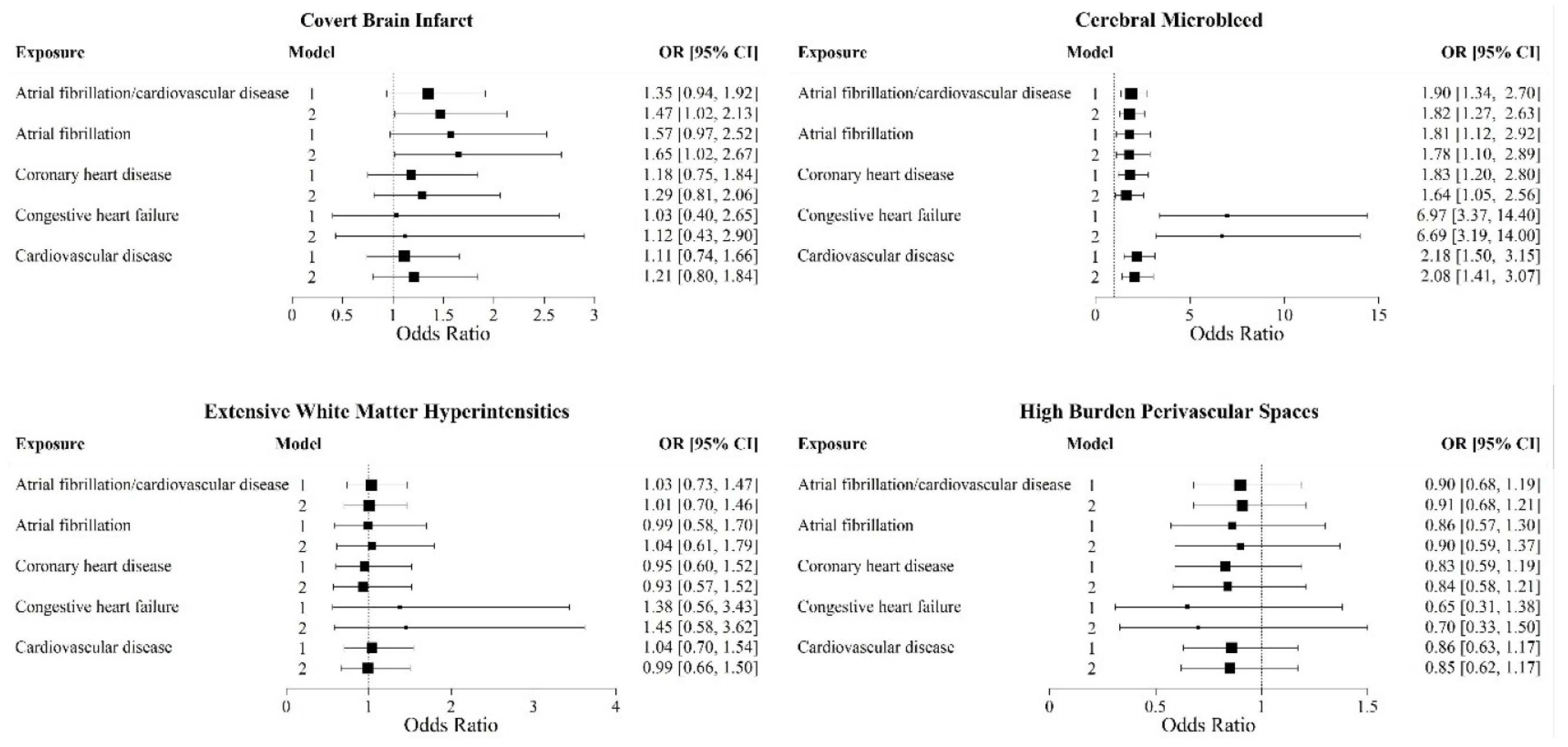
3.3. Exploratory Analyses (Supplementary Table S2)
4. Discussion
5. Limitations and Strengths of Our Study
6. Conclusions
7. Clinical Perspective
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, S.S.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Anderson, C.A.; Arora, P.; Avery, C.L.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Barone Gibbs, B.; Beaton, A.Z.; Boehme, A.K.; et al. 2024 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics: A Report of US and Global Data from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2024, 149, e347–e913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piechocki, M.; Przewlocki, T.; Pieniazek, P.; Trystula, M.; Podolec, J.; Kablak-Ziembicka, A. A Non-Coronary, Peripheral Arterial Atherosclerotic Disease (Carotid, Renal, Lower Limb) in Elderly Patients-A Review: Part I-Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Atherosclerosis-Related Diversities in Elderly Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomassen, J.Q.; Tolstrup, J.S.; Benn, M.; Frikke-Schmidt, R. Type-2 diabetes and risk of dementia: Observational and Mendelian randomisation studies in 1 million individuals. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2020, 29, e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitmer, R.A.; Sidney, S.; Selby, J.; Johnston, S.C.; Yaffe, K. Midlife cardiovascular risk factors and risk of dementia in late life. Neurology 2005, 64, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryden, L.; Sacuiu, S.; Wetterberg, H.; Najar, J.; Guo, X.; Kern, S.; Zettergren, A.; Shams, S.; Pereira, J.B.; Wahlund, L.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation, Stroke, and Silent Cerebrovascular Disease: A Population-based MRI Study. Neurology 2021, 97, e1608–e1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryden, L.; Zettergren, A.; Seidu, N.M.; Guo, X.; Kern, S.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Sacuiu, S.; Skoog, I. Atrial fibrillation increases the risk of dementia amongst older adults even in the absence of stroke. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 286, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Wang, R.; Kalpouzos, G.; Laukka, E.J.; Li, Y.; Johnell, K.; Fratiglioni, L.; Qiu, C. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Associated with Atrial Fibrillation Among Older Adults: A Population-Based Study. Stroke 2021, 52, 2685–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestre, H.; Kostrikov, S.; Mehta, R.I.; Nedergaard, M. Perivascular spaces, glymphatic dysfunction, and small vessel disease. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 2257–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannistraro, R.J.; Badi, M.; Eidelman, B.H.; Dickson, D.W.; Middlebrooks, E.H.; Meschia, J.F. CNS small vessel disease: A clinical review. Neurology 2019, 92, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.R.; Beiser, A.; Himali, J.J.; Shoamanesh, A.; DeCarli, C.; Seshadri, S. Cerebral microbleeds and risk of incident dementia: The Framingham Heart Study. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 54, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, E.E.; Biessels, G.J.; Cordonnier, C.; Fazekas, F.; Frayne, R.; Lindley, R.I.; T O’Brien, J.; Barkhof, F.; Benavente, O.R.; et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 822–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, P.; Ikram, M.K.; Niessen, W.J.; Ikram, M.A.; Vernooij, M.W. Practical Small Vessel Disease Score Relates to Stroke, Dementia, and Death. Stroke 2018, 49, 2857–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, C.W.; Vasan, R.S. Cohort Profile: The Framingham Heart Study (FHS): Overview of milestones in cardiovascular epidemiology. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 1800–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeerakathil, T.; Wolf, P.A.; Beiser, A.; Massaro, J.; Seshadri, S.; D’Agostino, R.B.; DeCarli, C. Stroke risk profile predicts white matter hyperintensity volume: The Framingham Study. Stroke 2004, 35, 1857–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, S.M.; Vernooij, M.W.; Cordonnier, C.; Viswanathan, A.; Salman, R.A.-S.; Warach, S.; Launer, L.J.; Van Buchem, M.A.; Breteler, M.M. Cerebral microbleeds: A guide to detection and interpretation. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doubal, F.N.; MacLullich, A.M.; Ferguson, K.J.; Dennis, M.S.; Wardlaw, J.M. Enlarged perivascular spaces on MRI are a feature of cerebral small vessel disease. Stroke 2010, 41, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, R.; Massaro, J.M.; Wolf, P.A.; Young, M.E.; Beiser, A.; Seshadri, S.; D’Agostino, R.B.; DeCarli, C. Association of white matter hyperintensity volume with decreased cognitive functioning: The Framingham Heart Study. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charidimou, A.; Jager, R.H.; Fox, Z.; Peeters, A.; Vandermeeren, Y.; Laloux, P.; Baron, J.-C.; Werring, D.J. Prevalence and mechanisms of cortical superficial siderosis in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology 2013, 81, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chobanian, A.V.; Bakris, G.L.; Black, H.R.; Cushman, W.C.; Green, L.A.; Izzo, J.L., Jr.; Jones, D.W.; Materson, B.J.; Oparil, S.; Wright, J.T., Jr.; et al. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2003, 42, 1206–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, J.D. A direct approach to false discovery rates. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 2002, 64, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noubiap, J.J.; Tang, J.J.; Teraoka, J.T.; Dewland, T.A.; Marcus, G.M. Minimum National Prevalence of Diagnosed Atrial Fibrillation Inferred from California Acute Care Facilities. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 84, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, D.; Gawalko, M.; Betz, K.; Hendriks, J.M.; Lip, G.Y.; Vinter, N.; Guo, Y.; Johnsen, S. Atrial fibrillation: Epidemiology, screening and digital health. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 37, 100786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstmann, S.; Mohlenbruch, M.; Wegele, C.; Rizos, T.; Laible, M.; Rauch, G.; Veltkamp, R. Prevalence of atrial fibrillation and association of previous antithrombotic treatment in patients with cerebral microbleeds. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoamanesh, A.; Hart, R.G.; Connolly, S.J.; Kasner, S.E.; Smith, E.E.; Martí-Fàbregas, J.; Liu, Y.Y.; Uchiyama, S.; Mikulik, R.; Veltkamp, R.; et al. Microbleeds and the Effect of Anticoagulation in Patients with Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source: An Exploratory Analysis of the NAVIGATE ESUS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, M.C.; Nyquist, P.; Sullivan, K.J.; Fornage, M.; Gottesman, R.F.; Becker, D.M. Cerebral Small-Vessel Disease in Individuals with a Family History of Coronary Heart Disease: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Neuroepidemiology 2021, 55, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhne, M.; Krisai, P.; Coslovsky, M.; Rodondi, N.; Müller, A.; Beer, J.H.; Ammann, P.; Auricchio, A.; Moschovitis, G.; Hayoz, D.; et al. Silent brain infarcts impact on cognitive function in atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 2127–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheibani, N.; Wong, K.H.; Turan, T.N.; Yeatts, S.D.; Gottesman, R.F.; Prabhakaran, S.; Rost, N.S.; Havenon, A.d. White Matter Hyperintensity and Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes in the SPRINT MIND Trial. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 30, 105764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahoz, C.; Schaefer, E.J.; Cupples, L.A.; Wilson, P.W.; Levy, D.; Osgood, D.; Parpos, S.; Pedro-Botet, J.; Daly, J.A.; Ordovas, J.M. Apolipoprotein E genotype and cardiovascular disease in the Framingham Heart Study. Atherosclerosis 2001, 154, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhi, L.; Lu, Y. The effect of apolipoprotein E gene polymorphism and Lp(a) levels on coronary artery disease with atrial fibrillation. J. Int. Med. Res. 2022, 50, 3000605221109387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumsden, A.L.; Mulugeta, A.; Zhou, A.; Hypponen, E. Apolipoprotein E (APOE) genotype-associated disease risks: A phenome-wide, registry-based, case-control study utilising the UK Biobank. eBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clinical Characteristics | No CSVD Marker (N = 2336) | 1 CSVD Marker (N = 773) | ≥2 CSVD Markers (N = 304) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male, n (%) | 1089 (47) | 366 (47) | 134 (44) |
| Age at clinic exam, years, mean (SD) | 53.3 (12.5) | 61.3 (14.1) | 69.8 (11) |
| Age at MRI, years, mean (SD) | 55.4 (12.3) | 63.2 (13.8) | 71.4 (10.8) |
| FHS Cohort, n (%) | |||
| Original | 13 (1) | 30 (4) | 26 (9) |
| Offspring | 761 (33) | 399 (52) | 223 (73) |
| Gen 3 and NOS | 1491 (64) | 308 (40) | 54 (18) |
| Omni 1 | 71 (3) | 36 (5) | 7 (2) |
| Time between clinic exam and MRI, years, mean (SD) | 1.6 (1.0) | 1.4 (1.1) | 1.2 (1.1) |
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg, mean (SD) | 120 (16) | 124 (18) | 132 (19) |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg, mean (SD) | 74 (10) | 74(10) | 72 (11) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2, mean (SD) | 27.9 (5.4) | 28.2 (5.5) | 27.8 (5) |
| APOE-ε4+, n (%) | 514 (22) | 171 (22) | 86 (28) |
| Smoking, n (%) | 194 (8) | 58 (8) | 17 (6) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 721 (31) | 377 (49) | 200 (66) |
| Hypertension treatment, n (%) | 573 (25) | 321 (42) | 161 (53) |
| Statin use, n (%) | 577 (25) | 277 (36) | 118 (39) |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 181 (8) | 100 (13) | 47 (15) |
| Prevalent cardiovascular disease or atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 172 (7) | 132 (17) | 68 (22) |
| Prevalent cardiovascular disease, n (%) | 128 (5) | 104 (13) | 54 (18) |
| Prevalent atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 58 (2) | 56 (7) | 26 (9) |
| Prevalent coronary heart disease, n (%) | 90 (4) | 71 (9) | 37 (12) |
| Prevalent heart failure, n (%) | 10 (<1) | 13 (2) | 11 (4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ekenze, O.; Pinheiro, A.; Beiser, A.S.; Lioutas, V.-A.; Aparicio, H.J.; Benjamin, E.J.; Vasan, R.S.; DeCarli, C.; Seshadri, S.; Demissie, S.; et al. Prevalent Cardiovascular Disease and Atrial Fibrillation in Relation to Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Burden. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080813
Ekenze O, Pinheiro A, Beiser AS, Lioutas V-A, Aparicio HJ, Benjamin EJ, Vasan RS, DeCarli C, Seshadri S, Demissie S, et al. Prevalent Cardiovascular Disease and Atrial Fibrillation in Relation to Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Burden. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(8):813. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080813
Chicago/Turabian StyleEkenze, Oluchi, Adlin Pinheiro, Alexa S. Beiser, Vasileios-Arsenios Lioutas, Hugo J. Aparicio, Emelia J. Benjamin, Ramachandran S. Vasan, Charles DeCarli, Sudha Seshadri, Serkalem Demissie, and et al. 2025. "Prevalent Cardiovascular Disease and Atrial Fibrillation in Relation to Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Burden" Brain Sciences 15, no. 8: 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080813
APA StyleEkenze, O., Pinheiro, A., Beiser, A. S., Lioutas, V.-A., Aparicio, H. J., Benjamin, E. J., Vasan, R. S., DeCarli, C., Seshadri, S., Demissie, S., & Romero, J. R. (2025). Prevalent Cardiovascular Disease and Atrial Fibrillation in Relation to Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Burden. Brain Sciences, 15(8), 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080813






