Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis Compared to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Fatigue and Fast Disease Progression Interferes with the Ability to Psychosocially Adjust
Abstract
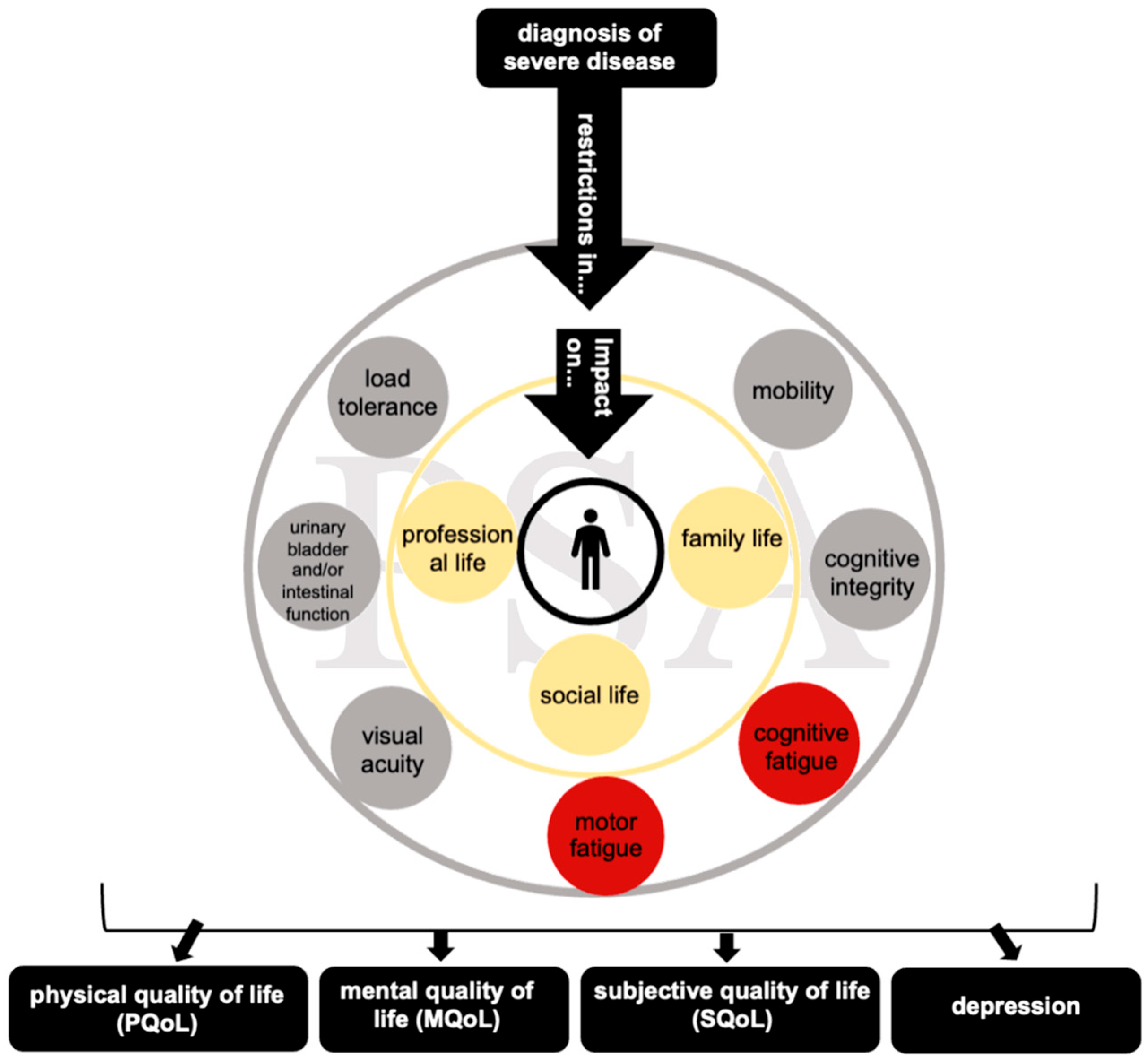
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Participants
2.2. Quality of Life and Depression as Outcome Measures of PSA
2.3. Fatigue
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Clinical Data
3.2. Indicators of Psychosocial Adjustment in MS: CFA
3.3. Predictors of Psychosocial Adjustment in MS: Regression Analyses
3.4. Psychosocial Adjustment Comparison to ALS
4. Discussion
4.1. Psychosocial Adjustment in MS
4.2. Psychosocial Adjustment Compared to ALS
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MS | Multiple sclerosis |
| ALS | Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis |
| PSA | Psychosocial adjustment |
| QoL | Quality of life |
| PQoL | Physical quality of life |
| MQoL | Mental quality of life |
| SQoL | Subjective quality of life |
| EDSS | Expanded Disability Status Scale |
| RRMS | Relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis |
| PPMS | Primary progressive multiple sclerosis |
| SPMS | Secondary progressive multiple sclerosis |
| ALS-FRS-R | ALS Functional Rating Scale—Revised |
| ACSA | Anamnestic Comparative Self-Assessment |
| SF-12 | Short-Form Survey 12 Questionnaire |
| MCS | Mental component score |
| PCS | Physical component score |
| HADS-D | Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale—Depression |
| ADI-12 | ALS Depression Inventory |
| FSMC | Fatigue Scale for Motor and Cognitive Functions |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| CFA | Confirmatory factor analysis |
| CFI | Comparative Fit Index |
| SRMR | Standardized Root Mean Square Residual |
| RMSEA | Root Mean Square Error of Approximation |
References
- Pugliatti, M.; Rosati, G.; Carton, H.; Riise, T.; Drulovic, J.; Vecsei, L.; Milanov, I. The epidemiology of multiple sclerosis in Europe. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13, 700–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogosian, A.; Day, F.; Norton, S.; Silber, E.; Sakel, M.; Sharrack, B.; Moss-Morris, R. Key demographics and psychological skills associated with adjustment to progressive Multiple Sclerosis early in the diagnosis. Front. Rehabil. Sci. 2022, 3, 966133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.R.; Silva, S.; Lencastre, L.; Guerra, M.P. Biopsychosocial Correlates of Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senders, A.; Bourdette, D.; Hanes, D.; Yadav, V.; Shinto, L. Perceived stress in multiple sclerosis: The potential role of mindfulness in health and well-being. J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 19, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lysandropoulos, A.P.; Havrdova, E.; Paradig, M.S.G. ‘Hidden’ factors influencing quality of life in patients with multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22 (Suppl. S2), 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwibel, H.L.; Smrtka, J. Improving quality of life in multiple Sclerosis: An unmet need. Am. J. Manag. Care 2011, 17, S139–S145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sehanovic, A.; Kunic, S.; Ibrahimagic, O.C.; Smajlovic, D.; Tupkovic, E.; Mehicevic, A.; Zoletic, E. Contributing Factors to the Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis. Med. Arch. 2020, 74, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernheim, J.L. How to get serious answers to the serious question: “How have you been?”: Subjective Quality of Life (QOL) as an individual experiental emergent construct. Bioethics 1999, 13, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, A.; Power, M. Development of the World Health Organization WHOQOL-BREF Quality of Life Assessment. Psychol. Med. 1998, 28, 551–558. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, Z.; Homayuni, A.; Etemadifar, M. Barriers to quality of life in patients with multiple sclerosis: A qualitative study. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strober, L.B. Quality of life and psychological well-being in the early stages of multiple sclerosis (MS): Importance of adopting a biopsychosocial model. Disabil. Health J. 2018, 11, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szilasiova, J.; Krokavcova, M.; Gdovinova, Z.; Rosenberger, J.; van Dijk, J.P. Quality of life in patients with multiple sclerosis in Eastern Slovakia. Disabil. Rehabil. 2011, 33, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lulé, D.; Pauli, S.; Altintas, E.; Singer, U.; Merk, T.; Uttner, I.; Birbaumer, N.; Ludolph, A.C. Emotional adjustment in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez Medrano, C.R.; Aho-Ozhan, H.E.A.; Weiland, U.; Uttner, I.; Ludolph, A.C.; Lule, D. Disease progression but not physical state per se determines mental wellbeing in ALS. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 3593–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, A.; Sayao, A.; Yousefi, M.; Devonshire, V.; Traboulsee, A.; Tremlett, H. Health-related quality of life in patients with longstanding ‘benign multiple sclerosis’. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2015, 4, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrie, R.A.; Cohen, J.; Stuve, O.; Trojano, M.; Sorensen, P.S.; Reingold, S.; Cutter, G.; Reider, N. A systematic review of the incidence and prevalence of comorbidity in multiple sclerosis: Overview. Mult. Scler. J. 2015, 21, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.A.; Langdon, D.; Rog, D.; Chhetri, S.K.; Tanasescu, R.; Kalra, S.; Webster, G.; Nicholas, R.; Ford, H.L.; Woolmore, J.; et al. Prevalence, treatment and correlates of depression in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2024, 87, 105648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, D.B.; Dyrud, J.; House, R.M.; Beresford, T.P. Psychiatric manifestations of autoimmune disorders. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2005, 7, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, A.C.J.W.; van Doorn, P.A.; de Boer, J.B.; van der Meché, F.G.A.; Passchier, J.; Hintzen, R.Q. Impact of recently diagnosed multiple sclerosis on quality of life, anxiety, depression and distress of patients and partners. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2003, 108, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Weinshenker, B.; Mikail, S.; Edgley, K. Depression before and after diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 1995, 1, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possa, M.F.; Minacapelli, E.; Canale, S.; Comi, G.; Martinelli, V.; Falautano, M. The first year after diagnosis: Psychological impact on people with multiple sclerosis. Psychol. Health Med. 2017, 22, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrie, R.A.; Patten, S.B.; Berrigan, L.I.; Tremlett, H.; Wolfson, C.; Warren, S.; Leung, S.; Fiest, K.M.; McKay, K.A.; Fisk, J.D.; et al. Diagnoses of Depression and Anxiety Versus Current Symptoms and Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. MS Care 2018, 20, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, D.S.; Foliart, R.H. Increased depression in multiple sclerosis patients. A meta-analysis. Psychosomatics 1993, 34, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeschoten, R.E.; Braamse, A.M.J.; Beekman, A.T.F.; Cuijpers, P.; van Oppen, P.; Dekker, J.; Uitdehaag, B.M.J. Prevalence of depression and anxiety in Multiple Sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 372, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva Ramirez, A.; Keenan, A.; Kalau, O.; Worthington, E.; Cohen, L.; Singh, S. Prevalence and burden of multiple sclerosis-related fatigue: A systematic literature review. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broch, L.; Flemmen, H.O.; Simonsen, C.S.; Berg-Hansen, P.; Ormstad, H.; Brunborg, C.; Celius, E.G. Fatigue in multiple sclerosis is associated with socioeconomic factors. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 64, 103955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradsson, D.; Ytterberg, C.; von Koch, L.; Johansson, S. Changes in disability in people with multiple sclerosis: A 10-year prospective study. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya Aygunoglu, S.; Celebi, A.; Vardar, N.; Gursoy, E. Correlation of Fatigue with Depression, Disability Level and Quality of Life in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2015, 52, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opara, J.A.; Jaracz, K.; Brola, W. Quality of life in multiple sclerosis. J. Med. Life. 2010, 3, 352–358. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, S.; Jöstingmeyer, P. Depression, fatigue and disability are independently associated with quality of life in patients with multiple Sclerosis: Results of a cross-sectional study. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2019, 35, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margoni, M.; Preziosa, P.; Rocca, M.A.; Filippi, M. Depressive symptoms, anxiety and cognitive impairment: Emerging evidence in multiple sclerosis. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, R.; Shaikh, Z.A.; Miletich, R.S.; Czarnecki, D.; Dmochowski, J.; Henschel, K.; Janardhan, V.; Dubey, N.; Kinkel, P.R. Fatigue in multiple sclerosis and its relationship to depression and neurologic disability. Mult. Scler. J. 2000, 6, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, M.P.; Ponziani, G.; Rossi, F.; Liedl, C.L.; Stefanile, C.; Rossi, L. Quality of life in multiple sclerosis: The impact of depression, fatigue and disability. Mult. Scler. J. 2001, 7, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maybury, C.P.; Brewin, C.R. Social relationships, knowledge and adjustment to multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1984, 47, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuz, T.; Birbaumer, N.; Hautzinger, M.; Kubler, A. Psychosocial adjustment to ALS: A longitudinal study. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.J.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Carroll, W.M.; Coetzee, T.; Comi, G.; Correale, J.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Freedman, M.S.; et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludolph, A.; Drory, V.; Hardiman, O.; Nakano, I.; Ravits, J.; Robberecht, W.; Shefner, J.; for The WFN Research Group On ALS/MND. A revision of the El Escorial criteria–2015. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2015, 16, 291–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Peyrodie, L.; Agnani, O.; Cavillon, F.; Hautecoeur, P.; Donzé, C. Evaluation of an Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) modeling strategy in multiple sclerosis. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2015, 53, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedarbaum, J.M.; Stambler, N.; Malta, E.; Fuller, C.; Hilt, D.; Thurmond, B.; Nakanishi, A., III; Bdnf Als Study Group and 1A Complete Listing of the BDNF Study Group. The ALSFRS-R: A revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. J. Neurol. Sci. 1999, 169, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernheim, J.L.; Theuns, P.; Mazaheri, M.; Hofmans, J.; Fliege, H.; Rose, M. The Potential of Anamnestic Comparative Self-Assessment (ACSA) to Reduce Bias in the Measurement of Subjective Well-Being. J. Happiness Stud. 2006, 7, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J.E.; Kosinski, M.; Keller, S.D. SF-12: How to Score the SF-12 Physical and Mental Health Summary Scales; Health Institute, New England Medical Center: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Snaith, R.P. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2003, 1, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kübler, A.; Winter, S.; Kaiser, J.; Birbaumer, N.; Hautzinger, M. Das ALS-Depressionsinventar (ADI). Z. Klin. Psychol. Psychother. 2005, 34, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, I.K.; Raselli, C.; Stöcklin, M.; Opwis, K.; Kappos, L.; Calabrese, P. The Fatigue Scale for Motor and Cognitive Functions (FSMC): Validation of a new instrument to assess multiple sclerosis-related fatigue. Mult. Scler. J. 2009, 15, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.T.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff Criteria for Fit Indexes in Covariance Structure Analysis: Conventional Criteria versus New Alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. Multidiscip. J. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, E.R. t Test, Independent Samples. In Encyclopedia of Research Design; Salkind, N.J.E., Ed.; SAGE: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 1551–1556. [Google Scholar]
- Lix, L.M.; Keselman, J.C.; Keselman, H.J. Consequences of Assumption Violations Revisited: A Quantitative Review of Alternatives to the One-Way Analysis of Variance F Test. Rev. Educ. Res. 1996, 66, 579–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.E.; Thomas, J. A study of the clinical characteristics and severity of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from North India. CHRISMED J. Health Res. 2021, 8, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twork, S.; Wiesmeth, S.; Spindler, M.; Wirtz, M.; Schipper, S.; Pohlau, D.; Klewer, J.; Kugler, J. Disability status and quality of life in multiple sclerosis: Non-linearity of the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS). Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2010, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaem, H.; Haghighi, A.B. The impact of disability, fatigue and sleep quality on the quality of life in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Indian. Acad. Neurol. 2008, 11, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshubaili, A.F.; Ohaeri, J.U.; Awadalla, A.W.; Mabrouk, A.A. Quality of life in multiple sclerosis: A Kuwaiti MSQOL-54 experience. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2008, 117, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Dishon, S. Health-related quality of life in multiple sclerosis: The impact of disability, gender and employment status. Qual. Life Res. 2006, 15, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymerich, M.; Guillamón, I.; Jovell, A.J. Health-related quality of life assessment in people with multiple sclerosis and their family caregivers. A multicenter study in Catalonia (southern Europe). Patient Prefer. Adherence 2009, 3, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Marrie, R.A.; Horwitz, R.; Cutter, G.; Tyry, T. Cumulative impact of comorbidity on quality of life in MS. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2012, 125, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainone, N.; Chiodi, A.; Lanzillo, R.; Magri, V.; Napolitano, A.; Brescia Morra, V.; Valerio, P.; Freda, M.F. Affective disorders and Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) in adolescents and young adults with Multiple Sclerosis (MS): The moderating role of resilience. Qual. Life Res. 2017, 26, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kever, A.; Buyukturkoglu, K.; Riley, C.S.; De Jager, P.L.; Leavitt, V.M. Social support is linked to mental health, quality of life, and motor function in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 1827–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajska, A.; Glanz, B.I.; Chitnis, T.; Weiner, H.L.; Healy, B.C. Social support in multiple sclerosis: Associations with quality of life, depression, and anxiety. J. Psychosom. Res. 2020, 138, 110252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-González, I.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Conrad, R.; Pérez-San-Gregorio, M.Á. Quality of life in adults with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e041249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidao, A.; De Livera, A.; Nag, N.; Neate, S.; Jelinek, G.A.; Simpson-Yap, S. Depression mediates the relationship between fatigue and mental health-related quality of life in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 47, 102620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergesheimer, R.; Lanznaster, D.; Vourc‘h, P.; Andres, C.; Bakkouche, S.; Beltran, S.; Blasco, H.; Corcia, P.; Couratier, P. Advances in disease-modifying pharmacotherapies for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2020, 21, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorst, J.; Ludolph, A.C.; Huebers, A. Disease-modifying and symptomatic treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2018, 11, 1756285617734734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaravalloti, N.D.; De Luca, J. Cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, R.H.B.; Amato, M.P.; DeLuca, J.; Geurts, J.J.G. Cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis: Clinical management, MRI, and therapeutic avenues. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, M.P.; Zipoli, V.; Portaccio, E. Multiple sclerosis-related cognitive changes: A review of cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 245, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauder, T.; Hansen, S.; Bauswein, C.; Muller, R.; Jaruszowic, S.; Keune, J.; Schenk, T.; Oschmann, P.; Keune, P.M. Mindfulness training during brief periods of hospitalization in multiple sclerosis (MS): Beneficial alterations in fatigue and the mediating role of depression. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardison, M.E.; Roll, S.C. Mindfulness Interventions in Physical Rehabilitation: A Scoping Review. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2016, 70, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, R.; Posa, S.; Langer, L.; Bruno, T.; Simpson, S.; Lawrence, M.; Booth, J.; Mercer, S.W.; Feinstein, A.; Bayley, M. A systematic review and meta-analysis exploring the efficacy of mindfulness-based interventions on quality of life in people with multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 726–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Rumrill, P.; Tansey, T.N. Examining the Role of Resilience and Hope in Grit in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 875133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
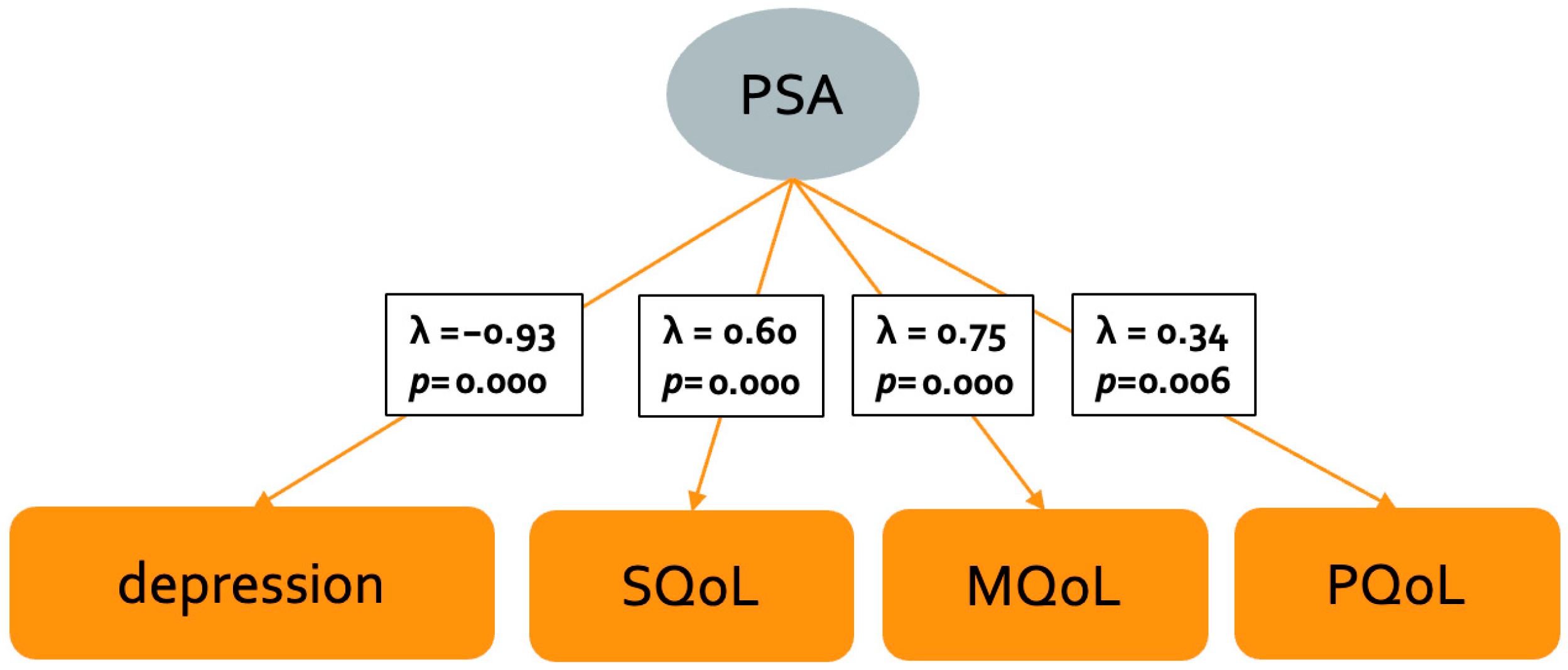
| Characteristics | MS Patients (N = 77) | ALS Patients (N = 30) | Statistics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | N (%) | Mean (SD) | N (%) | |||
| Age (years) | 46.83 (13.64) | 56.60 (11.45) | t(105) = −3.47, p < 0.001 | |||
| Female/Male | 45/32 (58.4/41.6) | 10/20 (33.3/66.7) | χ2(1) = 5.45, p = 0.020 | |||
| Years of education | 14.50 (2.82) | 14.60 (3.33) | t(105) = −0.16, p = 0.876 | |||
| EDSS * | 2.90 (1.84) | |||||
| ALS-FRS-R * | 35.97 (9.02) | |||||
| Time since onset (years) | 10.34 (9.30) | 1.62 (0.87) | t(104) = 5.11, p < 0.001 | |||
| PPMS * | 11 (14.3) | |||||
| SPMS * | 16 (20.8) | |||||
| RRMS * | 50 (64.9) | |||||
| Fit Index | Observed Value | Cut-off Criterion | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| χ2 * | 8.29, p = 0.016 | p > 0.05 | poor fit (interpretation based on p-value) |
| RMSEA * | 0.202 | <0.05 (good), <0.08 (acceptable) | poor fit (interpretation based on index value) |
| SRMR * | 0.059 | <0.08 | good fit (interpretation based on index value) |
| CFI * | 0.933 | >0.95 | marginal fit (interpretation based on index value) |
| Patient-Reported Outcome Measures | MS Patients (N = 77) | ALS Patients (N = 30) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | N (%) | Mean (SD) | |
| HADS-D * | 5.58 (4.21) | ||
| ADI-12 * | 24.97 (7.91) | ||
| Level of depression (%) | 26.59 (20.05) | 52.01 (16.48) | |
| ACSA * | 0.75 (2.01) | −0.40 (2.74) | |
| SF-12 MCS * | 45.79 (11.36) | 47.98 (11.41) | |
| SF-12 PCS * | 42.64 (10.67) | 33.74 (13.01) | |
| FSMC motor * | 30.60 (11.67) | ||
| mild (≥22) | 9 (11.7) | ||
| moderate (≥27) | 10 (13) | ||
| severe (≥32) | 38 (49.4) | ||
| FSMC cognition * | 29.05 (12.12) | ||
| mild (≥22) | 7 (9.1) | ||
| moderate (≥28) | 14 (18.2) | ||
| severe (≥34) | 31 (40.3) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balz, L.T.; Uttner, I.; Weishaupt, J.; Ludolph, A.C.; Taranu, D.; Vardakas, I.; Jung, S.; Fangerau, T.; Erhart, D.K.; Senel, M.; et al. Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis Compared to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Fatigue and Fast Disease Progression Interferes with the Ability to Psychosocially Adjust. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070745
Balz LT, Uttner I, Weishaupt J, Ludolph AC, Taranu D, Vardakas I, Jung S, Fangerau T, Erhart DK, Senel M, et al. Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis Compared to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Fatigue and Fast Disease Progression Interferes with the Ability to Psychosocially Adjust. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(7):745. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070745
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalz, Luisa T., Ingo Uttner, Jochen Weishaupt, Albert C. Ludolph, Daniela Taranu, Ioannis Vardakas, Stefanie Jung, Tanja Fangerau, Deborah K. Erhart, Makbule Senel, and et al. 2025. "Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis Compared to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Fatigue and Fast Disease Progression Interferes with the Ability to Psychosocially Adjust" Brain Sciences 15, no. 7: 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070745
APA StyleBalz, L. T., Uttner, I., Weishaupt, J., Ludolph, A. C., Taranu, D., Vardakas, I., Jung, S., Fangerau, T., Erhart, D. K., Senel, M., Tumani, H., & Lulé, D. E. (2025). Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis Compared to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Fatigue and Fast Disease Progression Interferes with the Ability to Psychosocially Adjust. Brain Sciences, 15(7), 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070745






