Age- and Sex-Specific Gut Microbiota Signatures Associated with Dementia-Related Brain Pathologies: An LEfSe-Based Metagenomic Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.2.1. Bacterial DNA Extraction
2.2.2. Analysis of Microbial Community Composition
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of Brain Pathologies by Age and Sex
3.2. Predicted Risk of Alzheimer’s Pathology, Vascular Pathology, and Dementia-Related Structural Brain Changes According to Age and Sex
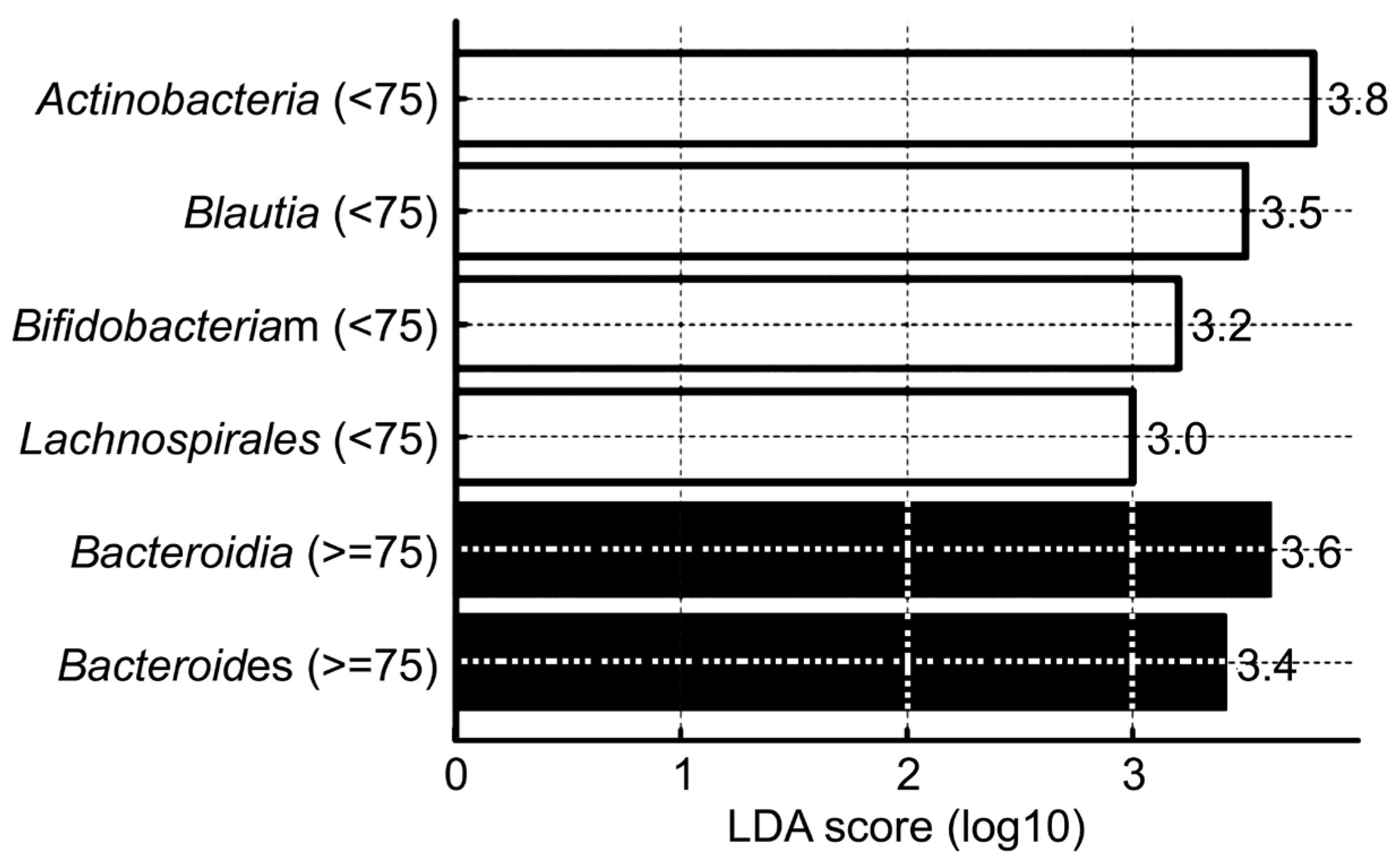
3.3. Age-Related Changes in Gut Microbial Community Composition
3.4. Sex-Related Differences in Gut Microbial Community Composition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BICWALZS | Biobank Innovations for Chronic Cerebrovascular Disease with Alzheimer’s Disease Study |
| EV | Extracellular vesicles |
| FMT | Fecal microbiota transplantation |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
| LEfSe | LDA effect size |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| OTUs | Operational taxonomic units |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
References
- Statistics Korea (KOSTAT). Future Population Projections: 2022–2072. Available online: https://kostat.go.kr/synap/skin/doc.html?fn=b64be239b900248c0e8e8a63fcee4d42840c34c570a9b86248c05847a890dd21&rs=/synap/preview/board/207/ (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- United Nations. World Population Prospects 2024: Summary of Results. Available online: https://desapublications.un.org/publications/world-population-prospects-2024-summary-results (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Hou, Y.; Dan, X.; Babbar, M.; Wei, Y.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2020 report of the Lancet Commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, M.; Wimo, A.; Guerchet, M.; Ali, G.-C.; Wu, Y.-T.; Prina, M. The Global Impact of Dementia: An Analysis of Prevalence, Incidence, Cost and Trends; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- GBD 2016 Dementia Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definitionof Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer′s Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; O’Bryant, S.E.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Zetterberg, H.; Masters, C.L.; Lista, S.; Kiddle, S.J.; Batrla, R.; Blennow, K. Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer disease: Mapping the road to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelidze, S.; Mattsson, N.; Palmqvist, S.; Smith, R.; Beach, T.G.; Serrano, G.E.; Chai, X.; Proctor, N.K.; Eichenlaub, U.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Plasma P-tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease: Relationship to other biomarkers, differential diagnosis, neuropathology and longitudinal progression to Alzheimer’s dementia. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmqvist, S.; Janelidze, S.; Quiroz, Y.T.; Zetterberg, H.; Lopera, F.; Stomrud, E.; Su, Y.; Chen, Y.; Serrano, G.E.; Leuzy, A.; et al. Discriminative accuracy of plasma phospho-tau217 for Alzheimer disease vs other neurodegenerative disorders. JAMA 2020, 324, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Jiang, J.; Alberts, I.; Wang, M.; Li, T.; Sun, X.; Rominger, A.; Zuo, C.; Shi, K. Combining PET with MRI to improve predictions of progression from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease: An exploratory radiomic analysis study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelborghs, S.; De Vreese, K.; Van de Casteele, T.; Vanderstichele, H.; Van Everbroeck, B.; Cras, P.; Martin, J.J.; Vanmechelen, E.; De Deyn, P.P. Diagnostic performance of a CSF-biomarker panel in autopsy-confirmed dementia. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 1143–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, C.; Verwey, N.A.; van der Flier, W.M.; Bouwman, F.H.; Kok, A.; van Elk, E.J.; Scheltens, P.; Blankenstein, M.A. Amyloid-beta(1–42), total tau, and phosphorylated tau as cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, G.; Sampson, T.R.; Geschwind, D.H.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Central Nervous System and the Gut Microbiome. Cell 2016, 167, 915–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Wu, L.; Peng, G.; Han, Y.; Tang, R.; Ge, J.; Zhang, L.; Jia, L.; Yue, S.; Zhou, K.; et al. Altered Microbiomes Distinguish Alzheimer’s Disease from Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment and Health in a Chinese Cohort. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 80, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, T.R.; Debelius, J.W.; Thron, T.; Janssen, S.; Shastri, G.G.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Challis, C.; Schretter, C.E.; Rocha, S.; Gradinaru, V.; et al. Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell 2016, 167, 1469–1480.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ding, Q.; Wan, X.; Wu, Q.; Ye, S.; Lou, Y. Fecal microbiota transplantation attenuates Alzheimer’s disease symptoms in APP/PS1 transgenic mice via inhibition of the TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB signaling pathway-mediated inflammation. Behav. Brain Funct. 2025, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.W.; Kim, N.-R.; Lee, D.-G.; Cheong, J.-Y.; Seo, S.W.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, E.-J.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, B.C.; Kim, S.Y.; et al. Baseline Clinical and Biomarker Characteristics of Biobank Innovations for Chronic Cerebrovascular Disease with Alzheimer’s Disease Study: BICWALZS. Psychiatry Investig. 2022, 19, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Lee, B.; Yoon, S. CASPER: Context-aware scheme for paired-end reads from high-throughput amplicon sequencing. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15 (Suppl. S9), S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Sandhu, K.; Peterson, V.; Dinan, T.G. The gut microbiome in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erny, D.; Hrabě de Angelis, A.L.; Jaitin, D.; Wieghofer, P.; Staszewski, O.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Jakobshagen, K.; Buch, T.; et al. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Parini, P.; Giuliani, C.; Santoro, A. Inflammaging: A new immune–metabolic viewpoint for age-related diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, P.W.; Jeffery, I.B. Gut microbiota and aging. Science 2015, 350, 1214–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, T.C.; Olson, C.A.; Hsiao, E.Y. Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous systems in health and disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, K.; Mulak, A. Brain-gut-Microbiota axis in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 25, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, N.M.; Kerby, R.L.; Dill-McFarland, K.A.; Harding, S.J.; Merluzzi, A.P.; Johnson, S.C.; Carlsson, C.M.; Asthana, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; et al. Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.Q.; Shen, L.L.; Li, W.W.; Fu, X.; Zeng, F.; Gui, L.; Lü, Y.; Cai, M.; Zhu, C.; Tan, Y.L.; et al. Gut microbiota is altered in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 63, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, M.J.; Jeffery, I.B.; Conde, S.; Power, S.E.; O’Connor, E.M.; Cusack, S.; Harris, H.M.B.; Coakley, M.; Lakshminarayanan, B.; O’Sullivan, O.; et al. Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature 2012, 488, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagi, E.; Candela, M.; Turroni, S.; Garagnani, P.; Franceschi, C.; Brigidi, P. Ageing and gut microbes: Perspectives for health maintenance and longevity. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.; Blacher, E.; Elinav, E.; Pettersson, S. Our gut microbiome: The evolving inner self. Cell 2017, 171, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Unno, T.; Kim, B.Y.; Park, M.S. Sex differences in gut microbiota. World J. Mens Health 2020, 38, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markle, J.G.M.; Frank, D.N.; Mortin-Toth, S.; Robertson, C.E.; Feazel, L.M.; Rolle-Kampczyk, U.; von Bergen, M.; McCoy, K.D.; Macpherson, A.J.; Danska, J.S. Sex differences in the gut microbiome drive hormone-dependent regulation of autoimmunity. Science 2013, 339, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Org, E.; Mehrabian, M.; Parks, B.W.; Shipkova, P.; Liu, X.; Drake, T.A.; Lusis, A.J. Sex differences and hormonal effects on gutmicrobiota composition in mice. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurkovetskiy, L.; Burrows, M.; Khan, A.A.; Graham, L.; Volchkov, P.; Becker, L.; Antonopoulos, D.; Umesaki, Y.; Chervonsky, A.V. Gender bias in autoimmunity is influenced by microbiota. Immunity 2013, 39, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marizzoni, M.; Mirabelli, P.; Mombelli, E.; Coppola, L.; Festari, C.; Lopizzo, N.; Luongo, D.; Mazzelli, M.; Naviglio, D.; Blouin, J.L.; et al. A peripheral signature of Alzheimer′s disease featuring microbiota-gut-brain axis markers. Alzheimer′s Res. Ther. 2023, 15, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosconi, L.; Berti, V.; Quinn, C.; McHugh, P.; Petrongolo, G.; Varsavsky, I.; Osorio, R.S.; Pupi, A.; Vallabhajosula, S.; Isaacson, R.S.; et al. Sex differences in Alzheimer risk: Brain imaging of endocrine vs chronologic aging. Neurology 2017, 89, 1382–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.; Booth, A.; Rockwood, K.; Peters, J.; D’Este, C.; Anstey, K.J. Combining modifiable risk factors and risk of dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e022846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mao, B.; Gu, J.; Wu, J.; Cui, S.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Blautia-a new functional genus with potential probiotic properties? Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1875796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, A.; van Sinderen, D. Bifidobacteria and their role as members of the human gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hagan, C.; Li, J.V.; Marchesi, J.R.; Plummer, S.; Garaiova, I.; Good, M.A. Long-term multi-species Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium dietary supplement enhances memory and changes regional brain metabolites in middle-aged rats. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2017, 144, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.L.; Xu, J.; Rong, X.Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.J.; Zhao, C. Gut microbiota alterations and health status in aging adults: From correlation to causation. Aging Med. 2021, 4, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, G.B.; Keating, D.J.; Young, R.L.; Wong, M.L.; Licinio, J.; Wesselingh, S. From gut dysbiosis to altered brain function and mental illness: Mechanisms and pathways. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Mind-altering microorganisms: The impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, R.; Wisniewski, P.J.; Alderman, B.L.; Campbell, S.C. Microbes and mental health: A review. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.L.; Inserra, A.; Lewis, M.D.; Mastronardi, C.A.; Leong, L.; Choo, J.; Kentish, S.; Xie, P.; Morrison, M.; Wesselingh, S.L.; et al. Inflammasome signaling affects anxiety- and depressive-like behavior and gut microbiome composition. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arentsen, T.; Qian, Y.; Gkotzis, S.; Femenia, T.; Wang, T.; Udekwu, K.; Forssberg, H.; Diaz Heijtz, R. The bacterial peptidoglycan-sensing molecule Pglyrp2 modulates brain development and behavior. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 This sign indicates maximum and minimum values.
This sign indicates maximum and minimum values.
 This sign indicates maximum and minimum values.
This sign indicates maximum and minimum values.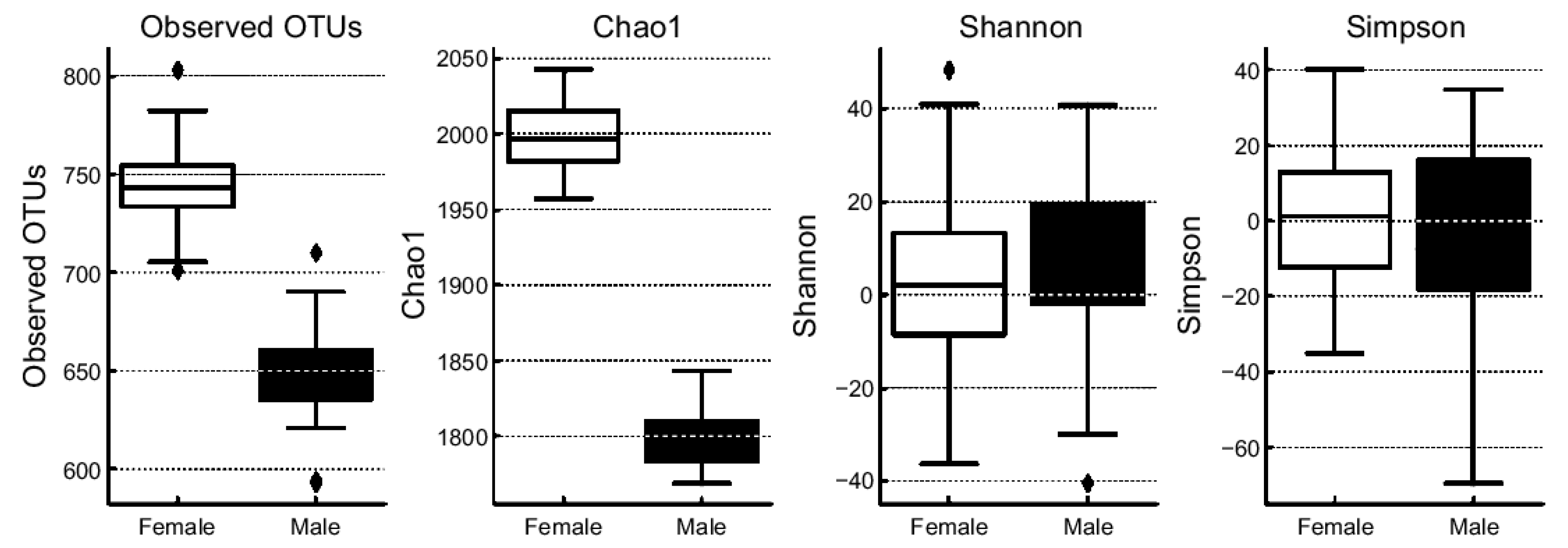

| Age Group (Years) | Sex | Alzheimer’s Pathology n, (%) | Vascular Pathology n, (%) | Dementia-Related Brain Changes n, (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Mild | Moderate to Severe | ||
| 40–59 | Male | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.7) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 2 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) |
| Female | 3 (1.0) | 4 (1.4) | 2 (0.7) | 5 (1.7) | 4 (1.4) | 3 (1.0) | |
| 60–74 | Male | 16 (5.5) | 38 (13.0) | 12 (4.1) | 42 (14.4) | 11 (3.8) | 43 (14.7) |
| Female | 25 (8.6) | 90 (30.8) | 26 (8.9) | 88 (30.0) | 56 (19.5) | 58 (19.9) | |
| ≥75 | Male | 13 (4.5) | 19 (6.5) | 14 (4.8) | 18 (6.2) | 1 (0.3) | 31 (10.6) |
| Female | 30 (10.3) | 52 (17.8) | 41 (14.0) | 41 (14.0) | 20 (6.8) | 62 (21.2) | |
| Total | 206 (70.5) | 86 (29.5) | 195 (67.0) | 96 (33.0) | 94 (32.3) | 197 (67.7) | |
| 292 (100) | 291 (100) | 291 (100) | |||||
| Outcome | Variable | OR | 95% CI (Lower) | 95% CI (Upper) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s Pathology | Intercept | 0.0016 | 0.00008 | 0.0349 | 0.00004 |
| Age | 1.0773 | 1.0341 | 1.1223 | 0.0004 | |
| Sex | 1.352 | 0.7765 | 2.3541 | 0.2864 | |
| Vascular Pathology | Intercept | 0.004 | 0.0002 | 0.0712 | 0.0002 |
| Age | 1.0688 | 1.028 | 1.1112 | 0.0008 | |
| Sex | 0.8941 | 0.5162 | 1.5486 | 0.6895 | |
| Dementia-Related Brain Changes (Moderate to Severe) | Intercept | 0.0015 | 0.00008 | 0.0279 | 0.00001 |
| Age | 1.1008 | 1.057 | 1.1464 | 0.000004 | |
| Sex | 4.0575 | 2.0834 | 7.9021 | 0.000038 |
| Variable | OR | 95% CI (Lower) | 95% CI (Upper) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.002380 | 0.000113 | 0.049988 | 0.000101 |
| Sex | 4.239421 | 2.155785 | 8.336959 | 2.836338 |
| Age | 1.086813 | 1.041521 | 1.134075 | 0.000127 |
| Alzheimer’s Pathology (Positive) | 1.385263 | 0.732585 | 2.619428 | 0.316046 |
| Vascular Pathology (Positive) | 3.555244 | 1.833334 | 6.894412 | 0.000174 |
| Taxonomic Level | Taxon | Dominant Group (Age) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phylum | Actinobacteriota | <75 | 0.004 |
| Bacteroidota | ≥75 | 0.005 | |
| Class | Actinobacteria | <75 | 0.0005 |
| Bacteroidia | ≥75 | 0.005 | |
| Order | Lachnospirales | <75 | 0.00006 |
| Genus | Bifidobacterium | <75 | 0.001 |
| Bacteroides | ≥75 | 0.0179 | |
| Species | Blautia spp. | <75 | 0.001 |
| Faecalibacterium spp. | <75 | 0.003 | |
| Bifidobacterium spp. | <75 | 0.005 | |
| Escherichia coli | ≥75 | 0.015 | |
| Bacteroides spp. | ≥75 | 0.02 |
| Taxonomic Level | Taxon | Dominant Group | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phylum | Firmicutes | Female | 0.01 |
| Bacteroidota | Male | 0.015 | |
| Class | Actinobacteria | Female | 0.002 |
| Bacteroidia | Male | 0.005 | |
| Order | Lachnospirales | Female | 0.0008 |
| Genus | Bifidobacterium | Female | 0.003 |
| Bacteroides | Male | 0.017 | |
| Species | Blautia spp. | Female | 0.002 |
| Faecalibacterium spp. | 0.003 | ||
| Bifidobacterium spp. | 0.005 | ||
| Escherichia coli | Male | 0.02 | |
| Bacteroides spp. | 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, S.H.; Roh, H.W.; Nam, Y.J.; Kim, T.W.; Cho, Y.H.; Son, S.J.; Hong, C.H. Age- and Sex-Specific Gut Microbiota Signatures Associated with Dementia-Related Brain Pathologies: An LEfSe-Based Metagenomic Study. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060611
Hong SH, Roh HW, Nam YJ, Kim TW, Cho YH, Son SJ, Hong CH. Age- and Sex-Specific Gut Microbiota Signatures Associated with Dementia-Related Brain Pathologies: An LEfSe-Based Metagenomic Study. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(6):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060611
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Sun Hwa, Hyun Woong Roh, You Jin Nam, Tae Wi Kim, Yong Hyuk Cho, Sang Joon Son, and Chang Hyung Hong. 2025. "Age- and Sex-Specific Gut Microbiota Signatures Associated with Dementia-Related Brain Pathologies: An LEfSe-Based Metagenomic Study" Brain Sciences 15, no. 6: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060611
APA StyleHong, S. H., Roh, H. W., Nam, Y. J., Kim, T. W., Cho, Y. H., Son, S. J., & Hong, C. H. (2025). Age- and Sex-Specific Gut Microbiota Signatures Associated with Dementia-Related Brain Pathologies: An LEfSe-Based Metagenomic Study. Brain Sciences, 15(6), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060611






