Cognitive Control and Prefrontal Neural Efficiency in Experienced and Novice E-Gamers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.2.1. Digit–Symbol Substitution Task
2.2.2. Dual Visual Search Task
2.2.3. Stroop Task
2.3. fNIRS Neuroimaging
2.3.1. Data Collection
2.3.2. Preprocessing
2.3.3. Analysis
3. Results
3.1. DSST Results
3.1.1. Response Time
3.1.2. Number of Correct Responses
3.1.3. fNIRS
3.1.4. Neural Efficiency
3.2. Single-Search DVST Results
3.2.1. Response Time
3.2.2. Accuracy
3.2.3. fNIRS
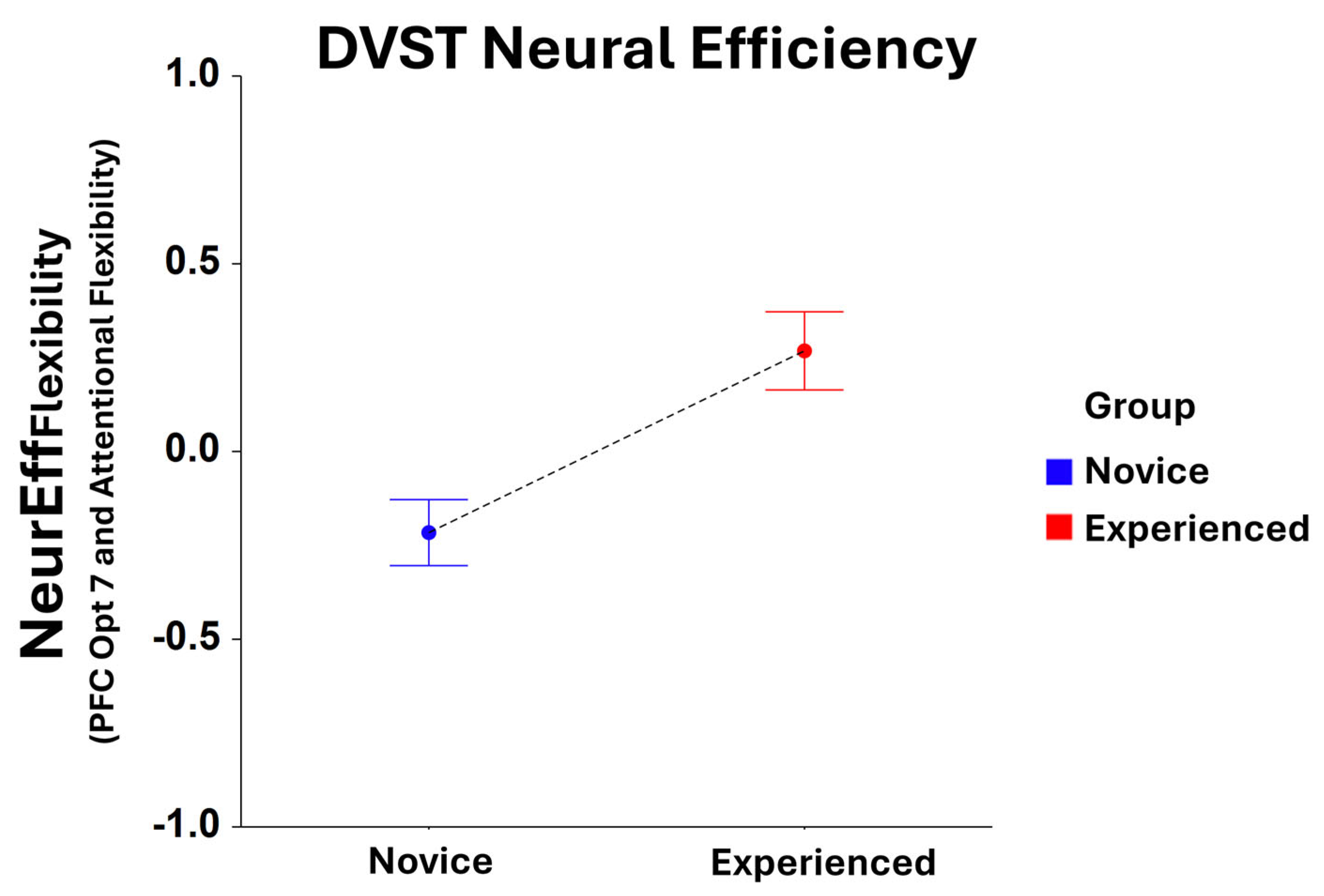
3.2.4. Neural Efficiency
3.3. Dual-Search DVST Results
3.3.1. Response Time
3.3.2. Accuracy
3.3.3. Attentional Delay
3.3.4. fNIRS
3.3.5. Neural Efficiency
3.4. Stroop Task
3.4.1. Response Time
3.4.2. Accuracy
3.4.3. fNIRS
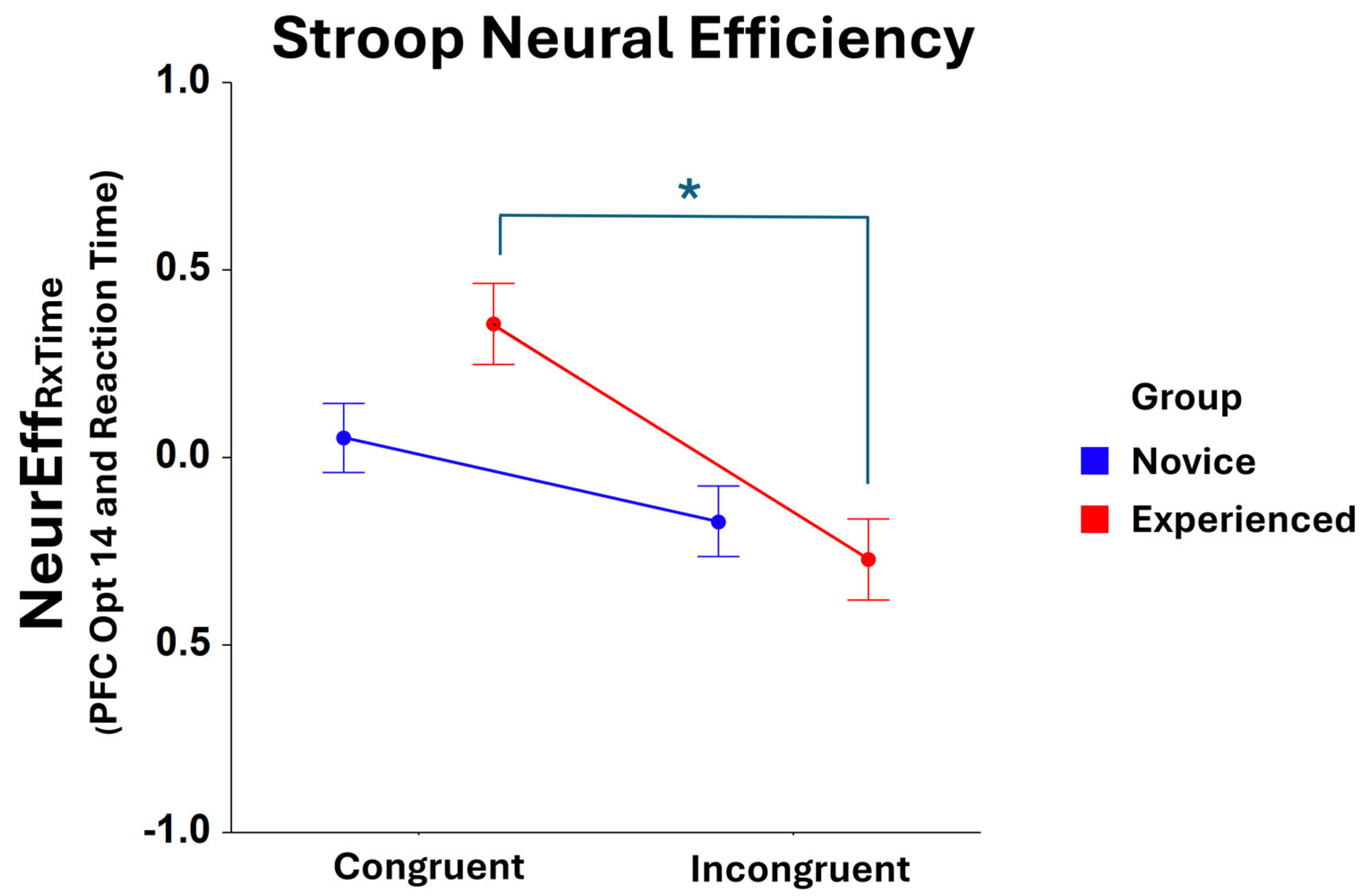
3.4.4. Neural Efficiency
4. Discussion
4.1. Updating and the DSST
4.2. Attentional Flexibility and the DVST
4.3. Inhibition and the Stroop Task
4.4. Implications
4.5. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, E.K.; Cohen, J.D. An integrative theory of prefrontal cortex function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 167–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, N.P.; Robbins, T.W. The role of prefrontal cortex in cognitive control and executive function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2022, 47, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorenko, E.; Duncan, J.; Kanwisher, N. Broad domain generality in focal regions of frontal and parietal cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16616–16621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, A.; Friedman, N.P.; Emerson, M.J.; Witzki, A.H.; Howerter, A.; Wager, T.D. The unity and diversity of executive functions and their contributions to complex “frontal lobe” tasks: A latent variable analysis. Cogn. Psychol. 2000, 41, 49–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.S.; Braver, T.S.; Barch, D.M.; Botvinick, M.M.; Noll, D.; Cohen, J.D. Anterior cingulate cortex, error detection, and the online monitoring of performance. Science 1998, 280, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerns, J.G.; Cohen, J.D.; MacDonald, A.W., III; Cho, R.Y.; Stenger, V.A.; Carter, C.S. Anterior cingulate conflict monitoring and adjustments in control. Science 2004, 303, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Spence, I. Playing shooter and driving videogames improves top-down guidance in visual search. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2013, 75, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrfuss, J.; Brass, M.; Von Cramon, D.Y. Cognitive control in the posterior frontolateral cortex: Evidence from common activations in task coordination, interference control, and working memory. Neuroimage 2004, 23, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.W.; Yarkoni, T.; Repovš, G.; Anticevic, A.; Braver, T.S. Global connectivity of prefrontal cortex predicts cognitive control and intelligence. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 8988–8999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schad, D.J.; Jünger, E.; Sebold, M.; Garbusow, M.; Bernhardt, N.; Javadi, A.-H.; Zimmermann, U.S.; Smolka, M.N.; Heinz, A.; Rapp, M.A. Processing speed enhances model-based over model-free reinforcement learning in the presence of high working memory functioning. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colzato, L.S.; van den Wildenberg, W.P.; Zmigrod, S.; Hommel, B. Action video gaming and cognitive control: Playing first person shooter games is associated with improvement in working memory but not action inhibition. Psychol. Res. 2013, 77, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colzato, L.S.; Van Leeuwen, P.J.; Van Den Wildenberg, W.; Hommel, B. DOOM’d to switch: Superior cognitive flexibility in players of first person shooter games. Front. Psychol. 2010, 1, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenbergen, L.; Sellaro, R.; Stock, A.-K.; Beste, C.; Colzato, L.S. Action video gaming and cognitive control: Playing first person shooter games is associated with improved action cascading but not inhibition. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleuze, J.; Christiaens, M.; Nuyens, F.; Billieux, J. Shoot at first sight! First person shooter players display reduced reaction time and compromised inhibitory control in comparison to other video game players. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 72, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzetoglu, K.; Bunce, S.; Onaral, B.; Pourrezaei, K.; Chance, B. Functional optical brain imaging using near-infrared during cognitive tasks. Int. J. Hum. -Comput. Interact. 2004, 17, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, G.; Hiraki, K. Prefrontal cortex deactivation during video game play. In Gaming, Simulations, and Society: Research Scope and Perspective; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2005; pp. 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, C.; Voss, M.W.; Erickson, K.I.; Boot, W.R.; Kramer, A.F. Regional differences in brain volume predict the acquisition of skill in a complex real-time strategy videogame. Brain Cogn. 2011, 76, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, G.J.; Shin, Y.W.; Kim, B.-N.; Cheong, J.H.; Jin, S.N.; Han, D.H. Increased cortical thickness in professional on-line gamers. Psychiatry Investig. 2013, 10, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.A.; Emory, E. Executive function and the frontal lobes: A meta-analytic review. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2006, 16, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.E.; Jonides, J. Storage and executive processes in the frontal lobes. Science 1999, 283, 1657–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanko, D. The health effects of video games in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Rev. 2023, 44, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rypma, B.; Prabhakaran, V. When less is more and when more is more: The mediating roles of capacity and speed in brain-behavior efficiency. Intelligence 2009, 37, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert-Wallander, B.; Green, C.S.; Sugarman, M.; Bavelier, D. Changes in search rate but not in the dynamics of exogenous attention in action videogame players. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2011, 73, 2399–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanRullen, R.; Reddy, L.; Koch, C. Visual search and dual tasks reveal two distinct attentional resources. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2004, 16, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, E.; Sherman, E.M.; Spreen, O. A Compendium of Neuropsychological Tests: Administration, Norms, and Commentary; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chance, B.; Anday, E.; Nioka, S.; Zhou, S.; Hong, L.; Worden, K.; Li, C.; Murray, T.; Ovetsky, Y.; Pidikiti, D. A novel method for fast imaging of brain function, non-invasively, with light. Opt. Express 1998, 2, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzetoglu, M.; Izzetoglu, K.; Bunce, S.; Ayaz, H.; Devaraj, A.; Onaral, B.; Pourrezaei, K. Functional near-infrared neuroimaging. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2005, 13, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, H.; Shewokis, P.A.; Curtin, A.; Izzetoglu, M.; Izzetoglu, K.; Onaral, B. Using MazeSuite and functional near infrared spectroscopy to study learning in spatial navigation. JoVE (J. Vis. Exp.) 2011, 56, e3443. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Piazza, E.A.; Simony, E.; Shewokis, P.A.; Onaral, B.; Hasson, U.; Ayaz, H. Measuring speaker–listener neural coupling with functional near infrared spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, H.; Izzetoglu, M.; Izzetoglu, K.; Onaral, B. The use of functional near-infrared spectroscopy in neuroergonomics. In Neuroergonomics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ayaz, H.; Izzetoglu, M.; Shewokis, P.A.; Onaral, B. Sliding-window motion artifact rejection for functional near-infrared spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cope, M.; Delpy, D.; Reynolds, E.; Wray, S.; Wyatt, J.; Van der Zee, P. Methods of quantitating cerebral near infrared spectroscopy data. In Oxygen Transport to Tissue X; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, C.; Tian, L. A comparison of the general linear mixed model and repeated measures ANOVA using a dataset with multiple missing data points. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2004, 6, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, J.A.; Curtin, A.; Kraft, A.E.; Ziegler, M.D.; Ayaz, H. Mental workload assessment by monitoring brain, heart, and eye with six biomedical modalities during six cognitive tasks. Front. Neuroergon. 2024, 5, 1345507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Soares, R.; Ramirez-Chavez, K.L.; Tufanoglu, A.; Barreto, C.; Sato, J.R.; Ayaz, H. Cognitive Effort during Visuospatial Problem Solving in Physical Real World, on Computer Screen, and in Virtual Reality. Sensors 2024, 24, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Dan, I. Exploring the false discovery rate in multichannel NIRS. Neuroimage 2006, 33, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, S.; Ye, J.C. Statistical analysis of fNIRS data: A comprehensive review. Neuroimage 2014, 85, 72–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, A.; Ayaz, H. Neural efficiency metrics in neuroergonomics: Theory and applications. In Neuroergonomics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Tuovinen, J.E.; Paas, F. Exploring multidimensional approaches to the efficiency of instructional conditions. Instr. Sci. 2004, 32, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Weedon, B.D.; Esser, P.; Liu, Y.-C.; Springett, D.N.; Meaney, A.; Inacio, M.; Delextrat, A.; Kemp, S.; Ward, T.; et al. Neuroergonomic assessment of developmental coordination disorder. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.; Miller, A.J.; Ayaz, H.; Brown, J.D. Haptic shared control improves neural efficiency during myoelectric prosthesis use. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, A.; Ayaz, H.; Tang, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Tong, S. Enhancing neural efficiency of cognitive processing speed via training and neurostimulation: An fNIRS and TMS study. NeuroImage 2019, 198, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavelier, D.; Green, C.S. Enhancing attentional control: Lessons from action video games. Neuron 2019, 104, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watson, J.; Curtin, A.; Topoglu, Y.; Suri, R.; Ayaz, H. Cognitive Control and Prefrontal Neural Efficiency in Experienced and Novice E-Gamers. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060568
Watson J, Curtin A, Topoglu Y, Suri R, Ayaz H. Cognitive Control and Prefrontal Neural Efficiency in Experienced and Novice E-Gamers. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(6):568. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060568
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatson, Jan, Adrian Curtin, Yigit Topoglu, Rajneesh Suri, and Hasan Ayaz. 2025. "Cognitive Control and Prefrontal Neural Efficiency in Experienced and Novice E-Gamers" Brain Sciences 15, no. 6: 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060568
APA StyleWatson, J., Curtin, A., Topoglu, Y., Suri, R., & Ayaz, H. (2025). Cognitive Control and Prefrontal Neural Efficiency in Experienced and Novice E-Gamers. Brain Sciences, 15(6), 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060568






