Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Related Inflammation: A Single-Center Case Series Analysis
Abstract
1. Background and Rationale
2. Case Summaries
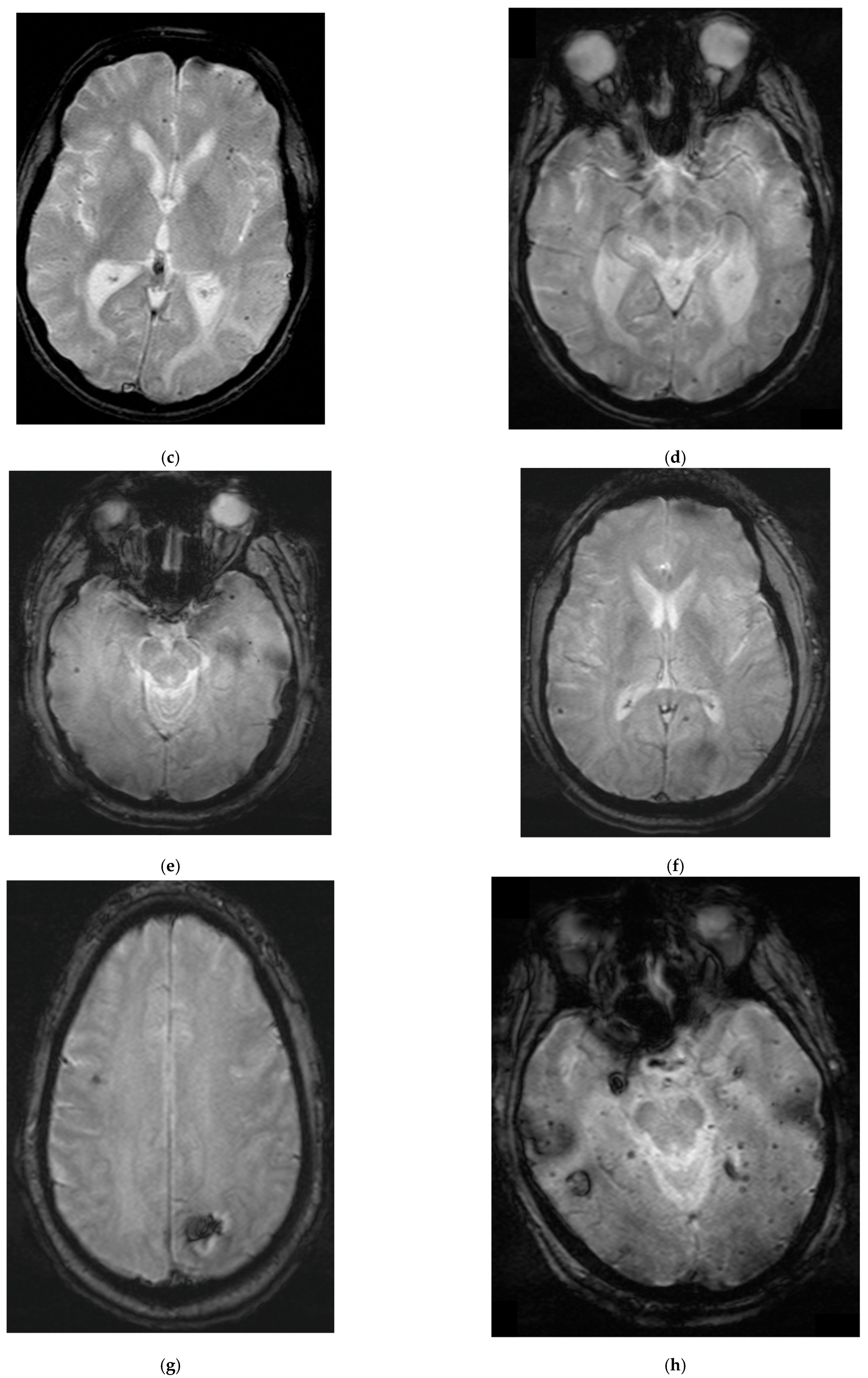
2.1. Patient 1
2.2. Patient 2
2.3. Patient 3
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMP | Basic metabolic panel |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| CAA | Cerebral amyloid angiopathy |
| CAA-RI | Cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation |
| CBC | Complete blood count |
| CMBs | Cerebral microbleeds |
| CSO | Centrum semiovale |
| CSS | Cortical superficial siderosis |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| CTA | Computed tomography angiography |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| ENC2 | Mayo Clinic encephalitis panel |
| EPV | Enlarged perivascular spaces |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rate |
| GRE | Gradient recalled echo |
| IADLS | Instrumental activities of daily living |
| ICH | Intracerebral hemorrhage |
| IVIG | Intravenous immunoglobulin |
| LP | Lumbar puncture |
| MCH | Mean corpuscular hemoglobin |
| MCHC | Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration |
| MCV | Mean corpuscular volume |
| MPV | Mean platelet volume |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| PCP | Primary care practitioner |
| PLEX | Plasmapheresis |
| RBC | Red blood cell count |
| RDW | Red blood cell distribution width |
| T2 FLAIR | T2-weighted-fluid-attenuated inversion recovery |
| WBC | White blood cell count |
| WMH | White matter hyperintensities |
References
- Castro Caldas, A.; Silva, C.; Albuquerque, L.; Pimentel, J.; Silva, V.; Ferro, J.M. Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Associated with Inflammation: Report of 3 Cases and Systematic Review. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Qin, W.; Guo, Y.; Xia, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Zang, W. Clinical, laboratory, and radiological features of cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation (CAA-ri): Retrospective, observational experience of a single centre. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 44, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auriel, E.; Charidimou, A.; Gurol, M.E.; Ni, J.; Van Etten, E.S.; Martinez-Ramirez, S.; Boulouis, G.; Piazza, F.; DiFrancesco, J.C.; Frosch, M.P.; et al. Validation of Clinicoradiological Criteria for the Diagnosis of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy-Related Inflammation. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozberg, M.G.; Perosa, V.; Gurol, M.E.; van Veluw, S.J. A practical approach to the management of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Int. J. Stroke 2021, 16, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regenhardt, R.W.; Thon, J.M.; Das, A.S.; Thon, O.R.; Charidimou, A.; Viswanathan, A.; Gurol, M.E.; Chwalisz, B.K.; Frosch, M.P.; Cho, T.A.; et al. Association Between Immunosuppressive Treatment and Outcomes of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy-Related Inflammation. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szalardy, L.; Fakan, B.; Maszlag-Torok, R.; Ferencz, E.; Reisz, Z.; Radics, B.L.; Csizmadia, S.; Szpisjak, L.; Annus, A.; Zadori, D.; et al. Identifying diagnostic and prognostic factors in cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation: A systematic analysis of published and seven new cases. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2024, 50, e12946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnecom, C.; Lev, M.H.; Wendell, L.; Smith, E.E.; Rosand, J.; Frosch, M.P.; Greenberg, S.M. Course of cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation. Neurology 2007, 68, 1411–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martucci, M.; Sarria, S.; Toledo, M.; Coscojuela, P.; Vert, C.; Siurana, S.; Auger, C.; Rovira, A. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation: Imaging findings and clinical outcome. Neuroradiology 2014, 56, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, A.; Tasker, K. Inflammatory Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy: A Broad Clinical Spectrum. J. Clin. Neurol. 2023, 19, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvarani, C.; Morris, J.M.; Giannini, C.; Brown, R.D., Jr.; Christianson, T.; Hunder, G.G. Imaging Findings of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy, Abeta-Related Angiitis (ABRA), and Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy-Related Inflammation: A Single-Institution 25-Year Experience. Medicine 2016, 95, e3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nada, A.; Leiva-Salinas, C.; Mahdi, E.; Mahmoud, E.; Ahsan, H.; Cousins, J.P. Multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of cerebral amyloid angiopathy related inflammation: Case series and review of literature. Clin. Imaging 2021, 78, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasi, M.; Marini, S.; Morotti, A.; Boulouis, G.; Xiong, L.; Charidimou, A.; Ayres, A.M.; Lee, M.J.; Biffi, A.; Goldstein, J.N.; et al. Cerebellar Hematoma Location: Implications for the Underlying Microangiopathy. Stroke 2018, 49, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.K.; Anderson, N.E.; Hutchinson, D.; Synek, B.; Barber, P.A. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy related inflammation: Three case reports and a review. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savar, S.M.; Ma, B.; Hone, E.; Jahan, F.; Markovic, S.; Pedrini, S.; Shemehsavar, S.; Easwaran, V.; Taddei, K.; Gardener, S.; et al. Fluid biomarkers in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1347320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorou, A.; Palaiodimou, L.; Malhotra, K.; Zompola, C.; Katsanos, A.H.; Shoamanesh, A.; Boviatsis, E.; Dardiotis, E.; Spilioti, M.; Sacco, S.; et al. Clinical, Neuroimaging, and Genetic Markers in Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy-Related Inflammation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Stroke 2023, 54, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boncoraglio, G.B.; Piazza, F.; Savoiardo, M.; Farina, L.; DiFrancesco, J.C.; Prioni, S.; Tagliavini, F.; Parati, E.A.; Giaccone, G. Prodromal Alzheimer’s disease presenting as cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation with spontaneous amyloid-related imaging abnormalities and high cerebrospinal fluid anti-Abeta autoantibodies. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 45, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brotman, D.J.; Eberhart, C.G.; Burger, P.C.; McArthur, J.C.; Hellmann, D.B. Primary angiitis of the central nervous system and Alzheimer’s disease: Clinically and pathologically evident in a single patient. J. Rheumatol. 2000, 27, 2935–2937. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dorr, S.; Schickel, R.; Lucke-Paulig, L.; Schontag, S.; Lobmann, R. Rapid Cognitive Decline and Recurrent Falls in a 71 Year-Old Man Due to Cerebral Amyloidangiopathy-Related Inflammation (CAA-RI). Geriatrics 2019, 4, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMP | |||
| Sodium | 140 | 134 | 143 |
| Potassium | 4.3 | 3.3 | 2.9 |
| Chloride | 107 | 103 | 98 |
| CO2 | 23 | 23 | 31 |
| Anion gap | 10 | 8 | 14 |
| Glucose | 154 | 99 | 94 |
| BUN | 18 | 14 | 14 |
| Creatinine | 0.58 | 1.04 | 1.17 |
| GFR | 94.5 | 90 | 66 |
| BUN/creatinine ratio | 31 | 13.5 | 12 |
| Calcium | 9.3 | 8.9 | 9.2 |
| CBC | |||
| WBC | 21.5 | 6.5 | 8.4 |
| RBC | 4.27 | 5.23 | 4.77 |
| Hemoglobin | 12.8 | 15.8 | 14.2 |
| Hematocrit | 40.2 | 44.6 | 40.5 |
| MCV | 94.1 | 85.2 | 84.9 |
| MCH | 30 | 30.2 | 29.7 |
| MCHC | 31.9 | 35.5 | 35 |
| Platelets | 477 | 193 | 240 |
| MPV | 7 | 9.3 | 8 |
| RDW | 13.1 | 14.6 | 14.1 |
| CSF | |||
| Total nucleated cells | 0 | 1 | 44 |
| Total RBCs | 1 | 40 | 8501 |
| Neutrophils | 0 | 9 | 70 |
| Lymphocytes | 0 | 41 | 16 |
| Monocytes | 0 | 50 | 14 |
| Glucose | 125 | 62 | 72 |
| Protein | 29.7 | 34 | 91 |
| Mayo Clinic ENC2 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Grade of Probability | Criteria |
|---|---|
| Possible CAA-RI | Age ≥ 40 years. More than one of the following symptoms not directly attributable to an acute ICH: 1. Headache 2. Impaired consciousness 3. Behavioral change 4. Focal neurological deficit 5. Epileptic seizures MRI with WMH lesions that extend only to neighboring subcortical white matter. More than one of the following cortico-subcortical hemorrhagic lesions: 1. Cerebral macrobleeds 2. Cerebral microbleeds 3. Cortical superficial siderosis Absence of other infectious or neoplastic causes. |
| Probable CAA-RI | Age ≥ 40 years. More than one of the following symptoms not directly attributable to an acute ICH: 1. Headache 2. impaired consciousness 3. behavioral change 4. Focal neurological deficit 5. Epileptic seizures MRI: asymmetric, uni- or multifocal WMH-lesions in the proximate subcortical white matter. Asymmetry is not in setting of previous ICH. More than one of the following cortico-subcortical hemorrhagic lesions: 1. Cerebral macrobleeds 2. Cerebral microbleeds 3. Cortical superficial siderosis Absence of other infectious or neoplastic causes. |
| Definite CAA-RI | Criteria of probable CAA-RI plus histopathology findings:Perivascular, transmural and/or intramural inflammation. Proof of amyloid deposits in vessels of affected cortex and leptomeningeal regions. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, S.Z.; Alley, H.; Johnson, J.; Sirvisetty, H.; Sowell, M.; Glynn, A.; Hedera, P. Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Related Inflammation: A Single-Center Case Series Analysis. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15050472
Ali SZ, Alley H, Johnson J, Sirvisetty H, Sowell M, Glynn A, Hedera P. Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Related Inflammation: A Single-Center Case Series Analysis. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(5):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15050472
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Syed Zahid, Hanah Alley, James Johnson, Harshini Sirvisetty, Michael Sowell, Alex Glynn, and Peter Hedera. 2025. "Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Related Inflammation: A Single-Center Case Series Analysis" Brain Sciences 15, no. 5: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15050472
APA StyleAli, S. Z., Alley, H., Johnson, J., Sirvisetty, H., Sowell, M., Glynn, A., & Hedera, P. (2025). Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Related Inflammation: A Single-Center Case Series Analysis. Brain Sciences, 15(5), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15050472







