Schaftoside Reduces Depression- and Anxiogenic-like Behaviors in Mice Depression Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Reagents and Drugs
2.3. Experimental Design
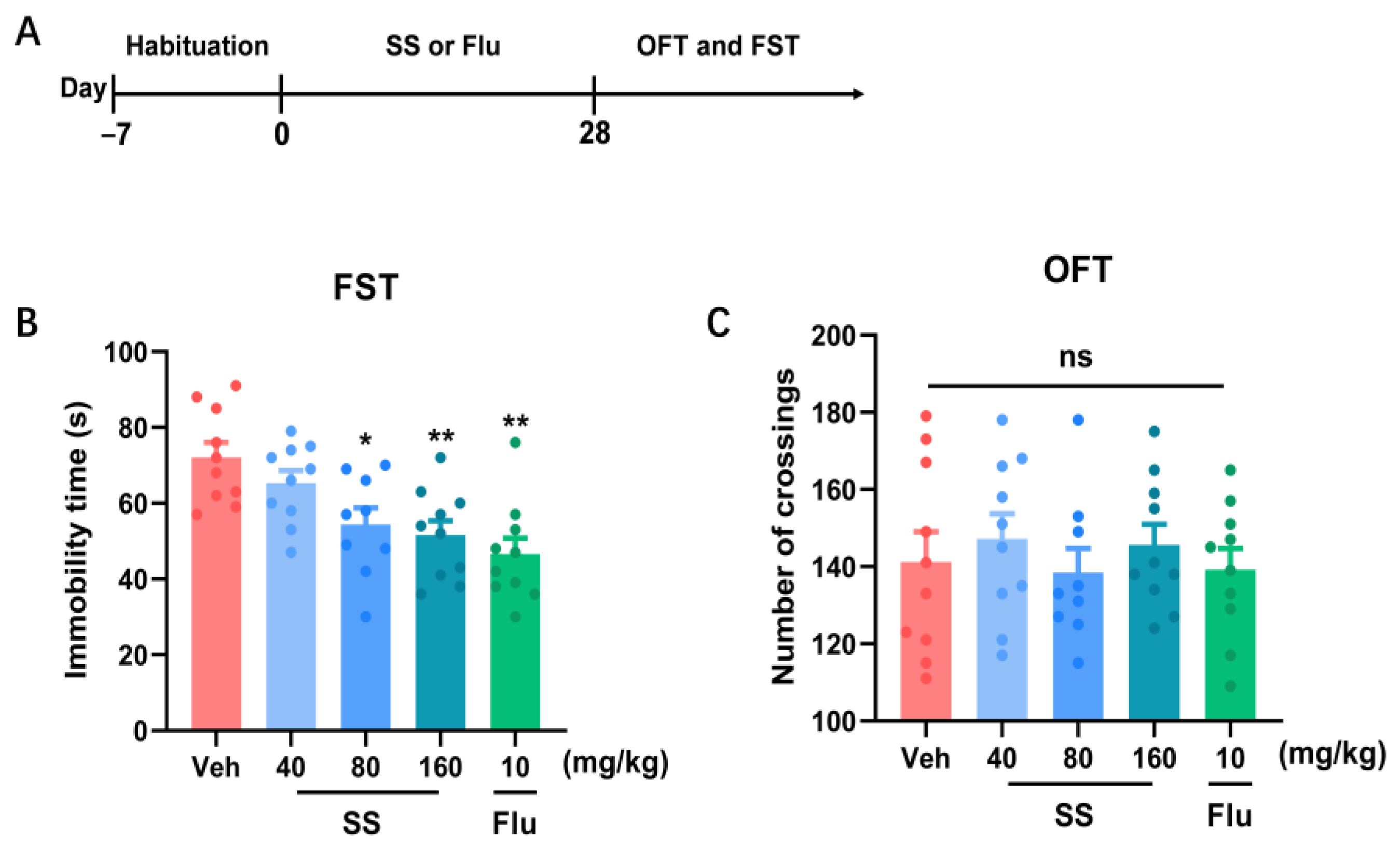
2.3.1. Experiment 1: Effects of SS Treatment on Locomotor Activity in Open Field Test and Immobility Time in the Forced Swim Test (FST) in Mice for 28 Days
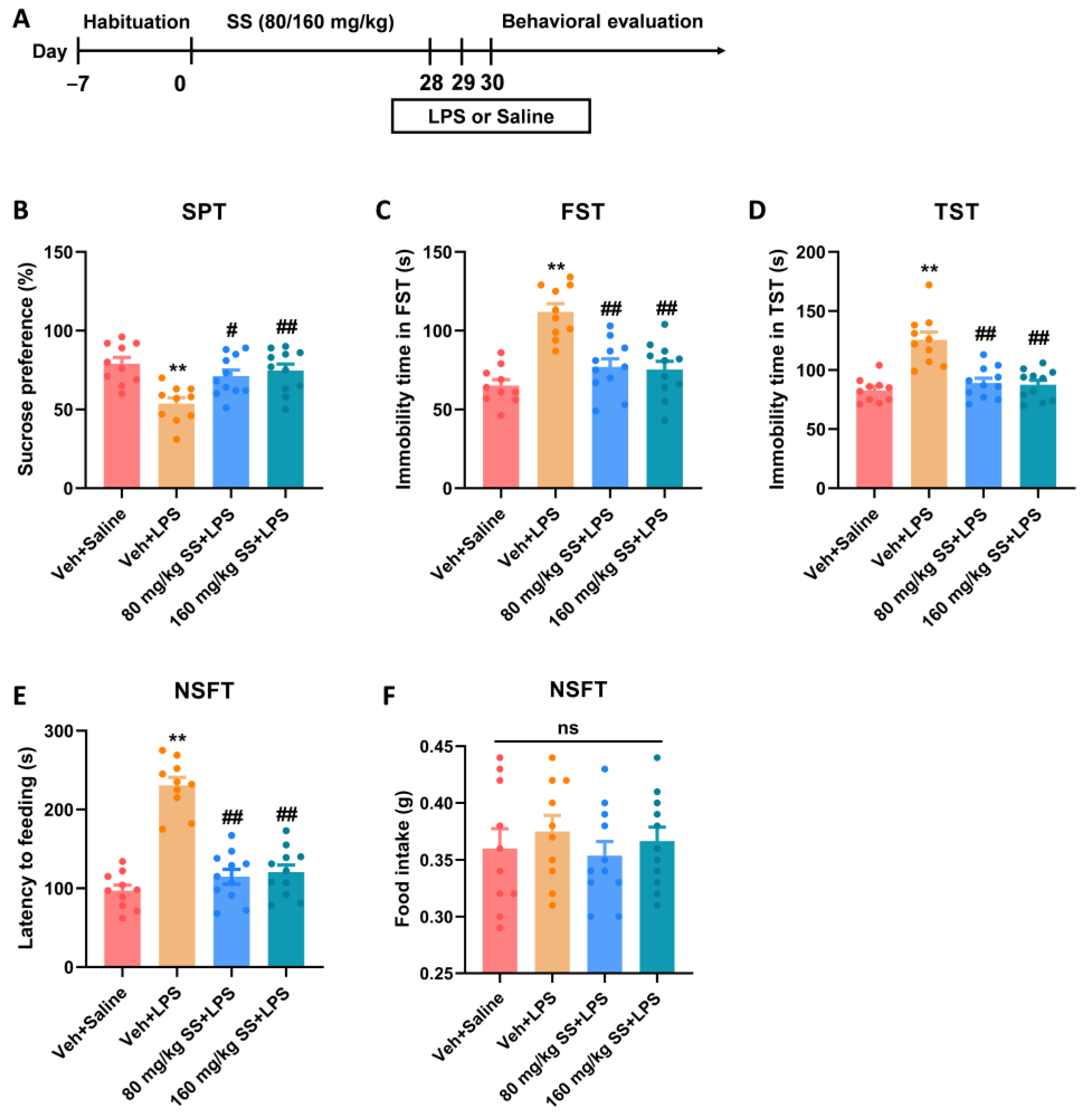
2.3.2. Experiment 2: Effects of SS Treatment on Depression- and Anxiety-like Behaviors Induced by LPS for 28 Days
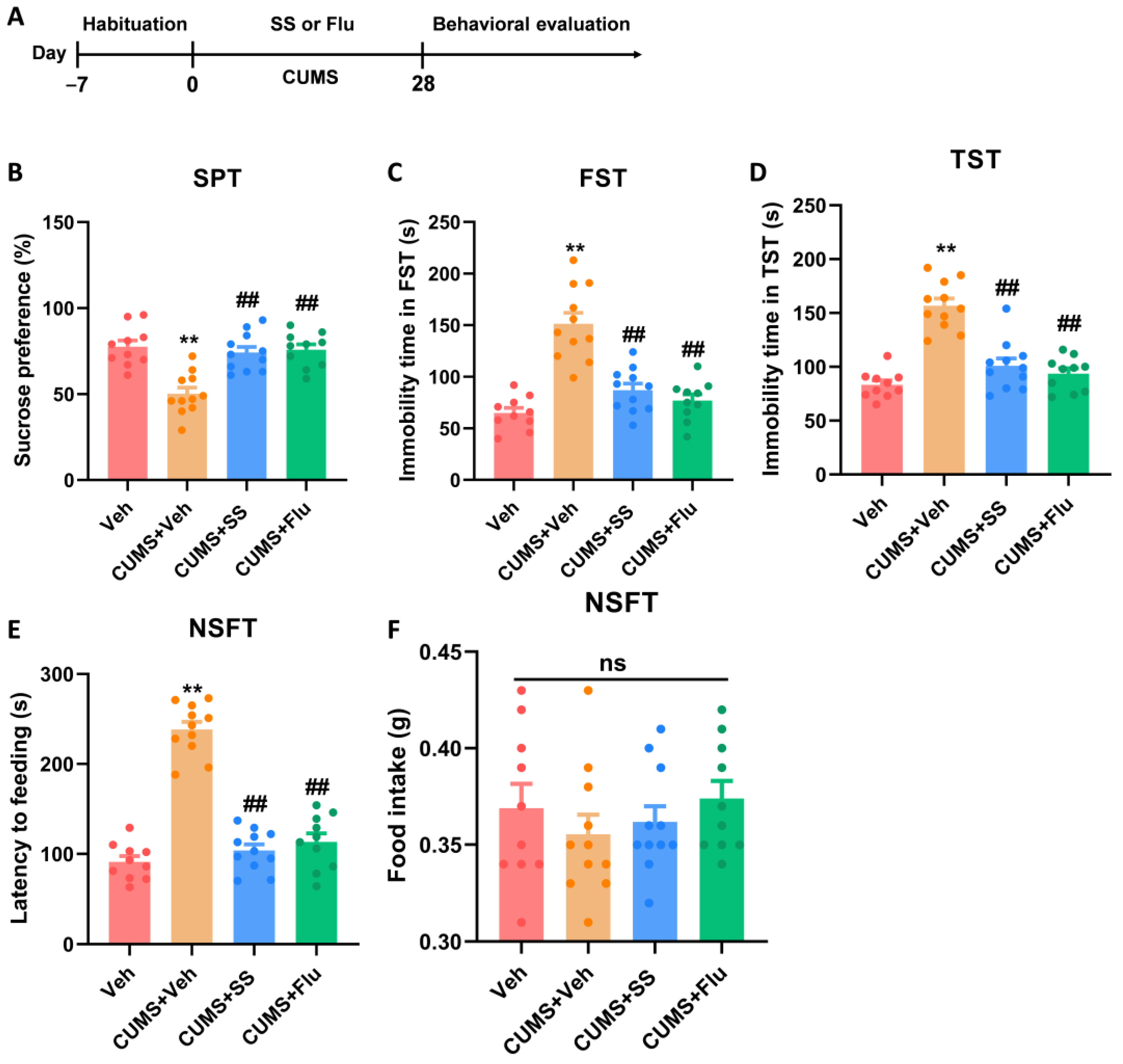
2.3.3. Experiment 3: Effects of SS Treatment on Depression- and Anxiety-like Behaviors Induced by CUMS for 28 Days
2.4. CUMS
2.5. Behavioral Assays
2.5.1. FST
2.5.2. Sucrose Preference Test (SPT)
2.5.3. Tail Suspension Test (TST)
2.5.4. Open Field Test (OFT)
2.5.5. Novelty-Suppressed Feeding Test (NSFT)
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. A 28-Day Treatment with SS Yielded an Antidepressant Effect in the FST
3.2. Prolonged Treatment of SS Improved Depression- and Anxiety-like Behaviors Caused by LPS
3.3. Prolonged Treatment of SS Improved Depression- and Anxiety-like Behaviors in CUMS Mice
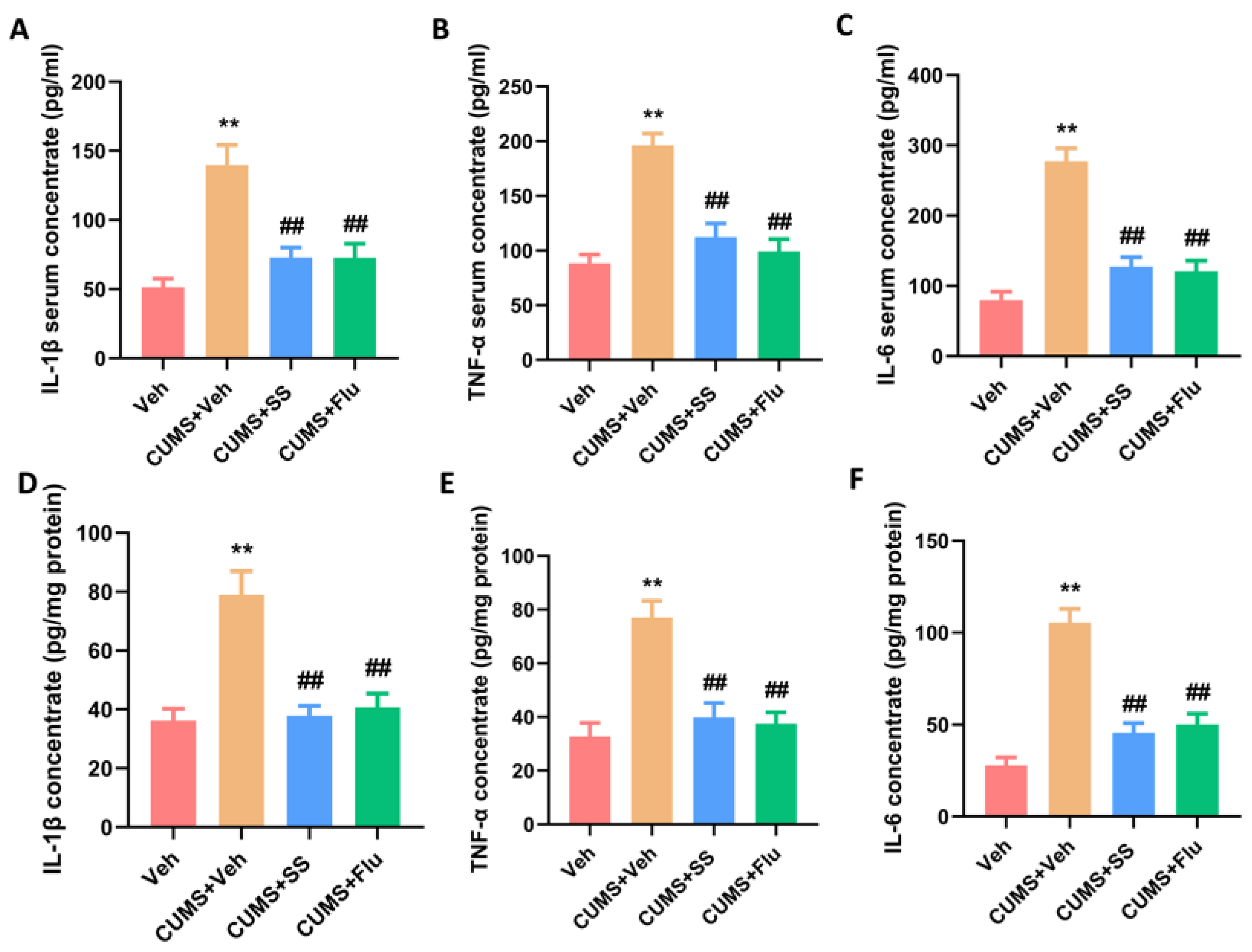
3.4. Chronic Administration of SS Reduced Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Concentrations in the Serum and Hippocampus of CUMS Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Namiot, E.D.; Smirnovova, D.; Sokolov, A.V.; Chubarev, V.N.; Tarasov, V.V.; Schioth, H.B. Depression clinical trials worldwide: A systematic analysis of the ICTRP and comparison with ClinicalTrials.gov. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators, C.-M.D. Global prevalence and burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in 204 countries and territories in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2021, 398, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar]
- Bitter, I.; Szekeres, G.; Cai, Q.; Feher, L.; Gimesi-Orszagh, J.; Kunovszki, P.; El Khoury, A.C.; Dome, P.; Rihmer, Z. Mortality in patients with major depressive disorder: A nationwide population-based cohort study with 11-year follow-up. Eur. Psychiatry 2024, 67, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadkhah, M.; Jafarzadehgharehziaaddin, M.; Molaei, S.; Akbari, M.; Gholizadeh, N.; Fathi, F. Major depressive disorder: Biomarkers and biosensors. Clin. Chim. Acta 2023, 547, 117437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.T.; Wang, X.L.; Lei, L.; Guo, Z.Y.; Kan, F.F.; Hu, D.; Gai, C.; Zhang, Y. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy of ketamine and esketamine on suicidal ideation in treatment-resistant depression. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 80, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Lei, L.; Zhang, Y. Impacts of microbiota and its metabolites through gut-brain axis on pathophysiology of major depressive disorder. Life Sci. 2024, 351, 122815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.S.; Wang, Y.M.; Liu, H.; Ning, B.; Yu, H.B.; Li, S.L.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhao, M.J.; Ma, J. Hyperactivity in the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis: An Invisible Killer for Anxiety and/or Depression in Coronary Artherosclerotic Heart Disease. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2024, 23, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Yu, C.; Mao, Q.; Han, F.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Pires, N.; Wei, X.; Jing, W.; Lin, Q.; et al. Advances in biosensors for major depressive disorder diagnostic biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 258, 116291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afridi, R.; Suk, K. Neuroinflammatory Basis of Depression: Learning From Experimental Models. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 691067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Chen, C.Y.; Lei, L.; Zhang, Y. Regulation of the microglial polarization for alleviating neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis and therapeutics of major depressive disorder. Life Sci. 2025, 362, 123373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Giuliani, F. The Role of Inflammation in Depression and Fatigue. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.S. The macrophage theory of depression. Med. Hypotheses 1991, 35, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beurel, E.; Toups, M.; Nemeroff, C.B. The Bidirectional Relationship of Depression and Inflammation: Double Trouble. Neuron 2020, 107, 234–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.J.; Wei, Y.B.; Strawbridge, R.; Bao, Y.; Chang, S.; Shi, L.; Que, J.; Gadad, B.S.; Trivedi, M.H.; Kelsoe, J.R.; et al. Peripheral cytokine levels and response to antidepressant treatment in depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Wang, Y.T.; Hu, D.; Gai, C.; Zhang, Y. Astroglial Connexin 43-Mediated Gap Junctions and Hemichannels: Potential Antidepressant Mechanisms and the Link to Neuroinflammation. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 43, 4023–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, V.; Daly, E.J.; Trivedi, M.; Cooper, K.; Lane, R.; Lim, P.; Mazzucco, C.; Hough, D.; Thase, M.E.; Shelton, R.C.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Flexibly Dosed Esketamine Nasal Spray Combined With a Newly Initiated Oral Antidepressant in Treatment-Resistant Depression: A Randomized Double-Blind Active-Controlled Study. Am. J. Psychiatry 2019, 176, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Pan, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Xing, Y.; Xiao, G.; He, Y.; et al. Reveal the potent antidepressant effects of Zhi-Zi-Hou-Pu Decoction based on integrated network pharmacology and DDI analysis by deep learning. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jazvinscak Jembrek, M.; Orsolic, N.; Karlovic, D.; Peitl, V. Flavonols in Action: Targeting Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Major Depressive Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.W.; Yang, L.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, J.S.; Meng, X.L. Pivotal regulatory roles of traditional Chinese medicine in ischemic stroke via inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 294, 115316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.W.; Feng, N.; Liu, Y.C.; Guo, Q.; Wang, J.K.; Bai, Y.Z.; Ye, X.M.; Yang, Z.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Neuroinflammation inhibition by small-molecule targeting USP7 noncatalytic domain for neurodegenerative disease therapy. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo0789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, G.O.; Muzitano, M.F.; Legora-Machado, A.; Almeida, T.A.; De Oliveira, D.B.; Kaiser, C.R.; Koatz, V.L.; Costa, S.S. C-glycosylflavones from the aerial parts of Eleusine indica inhibit LPS-induced mouse lung inflammation. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 362–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.S.; Shin, J.H.; Jo, D.S.; Shin, D.W.; Choi, D.H.; Kim, W.J.; Park, K.; Kim, J.K.; Joo, C.G.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Anti-melanogenic activity of schaftoside in Rhizoma Arisaematis by increasing autophagy in B16F1 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, G.; Song, M.; Wang, J.; Shen, C.; Chen, Z.; Huang, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, C.; Lin, C.; et al. Activation of Farnesoid X Receptor by Schaftoside Ameliorates Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2020, 33, 87–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, J.; Paudel, Y.N.; Yang, X.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, S.; Ji, X.; Liu, K.; Jin, M. Schaftoside Suppresses Pentylenetetrazol-Induced Seizures in Zebrafish via Suppressing Apoptosis, Modulating Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 2542–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xue, H.; Yu, R.; Bao, Y.O.; Kuang, Y.; Chai, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, J.; Shi, X.; et al. Schaftoside inhibits 3CL(pro) and PL(pro) of SARS-CoV-2 virus and regulates immune response and inflammation of host cells for the treatment of COVID-19. Acta Pharm. Sinica B 2022, 12, 4154–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.L.; Han, Q.Q.; Gong, W.Q.; Pan, D.H.; Wang, L.Z.; Hu, W.; Yang, M.; Li, B.; Yu, J.; Liu, Q. Microglial activation mediates chronic mild stress-induced depressive- and anxiety-like behavior in adult rats. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, T.C.; Wohleb, E.S.; Zhang, Y.; Fogaça, M.; Hare, B.; Duman, R.S. Persistent Increase in Microglial RAGE Contributes to Chronic Stress-Induced Priming of Depressive-like Behavior. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tynan, R.J.; Naicker, S.; Hinwood, M.; Nalivaiko, E.; Buller, K.M.; Pow, D.V.; Day, T.A.; Walker, F.R. Chronic stress alters the density and morphology of microglia in a subset of stress-responsive brain regions. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachiller, S.; Jiménez-Ferrer, I.; Paulus, A.; Yang, Y.; Swanberg, M.; Deierborg, T.; Boza-Serrano, A. Microglia in Neurological Diseases: A Road Map to Brain-Disease Dependent-Inflammatory Response. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Barres, B.A. Microglia and macrophages in brain homeostasis and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.N.; Greenwald, M.S.; Henter, I.D.; Kraus, C.; Mkrtchian, A.; Clark, N.G.; Park, L.T.; Gold, P.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; Kadriu, B. Inflammation, stress and depression: An exploration of ketamine’s therapeutic profile. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majd, M.; Saunders, E.F.H.; Engeland, C.G. Inflammation and the dimensions of depression: A review. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2020, 56, 100800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soczynska, J.K.; Mansur, R.B.; Brietzke, E.; Swardfager, W.; Kennedy, S.H.; Woldeyohannes, H.O.; Powell, A.M.; Manierka, M.S.; McIntyre, R.S. Novel therapeutic targets in depression: Minocycline as a candidate treatment. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 235, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderi, Y.; Panahi, Y.; Barreto, G.E.; Sahebkar, A. Neuroprotective effects of minocycline on focal cerebral ischemia injury: A systematic review. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Jiang, T.; Shan, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Qi, X.; Bian, Y.; Zhao, L. Pro-inflammatory cytokines in stress-induced depression: Novel insights into mechanisms and promising therapeutic strategies. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 131, 110931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Ju, T.; Zeng, D.; Duan, F.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, W. “Inflamed” depression: A review of the interactions between depression and inflammation and current anti-inflammatory strategies for depression. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 207, 107322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, M.; Lv, H.; Li, K.; Hao, X.; Xing, X.; et al. Application of lipopolysaccharide in establishing inflammatory models. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florescu, D.N.; Boldeanu, M.V.; Șerban, R.E.; Florescu, L.M.; Serbanescu, M.S.; Ionescu, M.; Streba, L.; Constantin, C.; Vere, C.C. Correlation of the Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, Inflammatory Markers, and Tumor Markers with the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer. Life 2023, 13, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yang, Y.; Fan, X.W.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Shi, Y.J.; Hu, W.J.; Wang, C.X. Impacts of inflammatory cytokines on depression: A cohort study. BMC Psychiatry 2024, 24, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Corbi, G.; Maes, M.; Scapagnini, G.; Davinelli, S. Exploring the Impact of Flavonoids on Symptoms of Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micek, A.; Jurek, J.; Owczarek, M.; Guerrera, I.; Torrisi, S.A.; Castellano, S.; Grosso, G.; Alshatwi, A.A.; Godos, J. Polyphenol-Rich Beverages and Mental Health Outcomes. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Liang, C.; Huang, K.; Luo, J.; Lu, R.; Lai, Y.; Zheng, D.; Lin, Z.; Zhong, J.; Dai, J.; et al. Curcumin prevents neurodegeneration by blocking HDAC6-NLRP3 pathway-dependent neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 146, 113928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Quan, T.; Leng, Y.; Chang, E.; Bai, Y.; Bian, Y.; Hou, Y. Advances of curcumin in nervous system diseases: The effect of regulating oxidative stress and clinical studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1496661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Liang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, A.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. Bioactive compound schaftoside from Clinacanthus nutans attenuates acute liver injury by inhibiting ferroptosis through activation the Nrf2/GPX4 pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 328, 118135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Zeng, M.J.; Zhou, L.P.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhao, F.; Shang, Z.Y.; Deng, X.Y.; Ma, Z.Q.; Fu, Q.; Ma, S.P.; et al. Baicalin exerts neuroprotective effects via inhibiting activation of GSK3β/NF-κB/NLRP3 signal pathway in a rat model of depression. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 64, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.T.; Wang, S.Q.; Su, J.; Xu, L.X.; Ji, Z.Y.; Zhang, R.Y.; Zhao, Q.W.; Ma, Z.Q.; Deng, X.Y.; Ma, S.P. Baicalin ameliorates neuroinflammation-induced depressive-like behavior through inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 expression via the PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 pathway. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Li, H.R.; Chen, X.X.; Gao, X.R.; Huang, L.L.; Du, A.Q.; Jiang, C.; Li, H.; Ge, J.F. Quercetin Alleviates LPS-Induced Depression-Like Behavior in Rats via Regulating BDNF-Related Imbalance of Copine 6 and TREM1/2 in the Hippocampus and PFC. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1544. [Google Scholar]
- Pannu, A.; Sharma, P.C.; Thakur, V.K.; Goyal, R.K. Emerging Role of Flavonoids as the Treatment of Depression. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Liu, W.; Yang, H.; Zong, Y.; Sun, J.; Sun, X.; Song, S.; Liu, M.; Kan, J.; Che, C. Schaftoside reduces inflammation in Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis through the inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88 pathway. Cytokine 2024, 175, 156483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Tu, W.; Lou, X.; Yang, G.; et al. Schaftoside ameliorates oxygen glucose deprivation-induced inflammation associated with the TLR4/Myd88/Drp1-related mitochondrial fission in BV2 microglia cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 139, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Luo, T. Isoschaftoside Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in Microglia through Regulation of HIF-1α-Mediated Metabolic Reprogramming. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2022, 2022, 5227335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, L.N.; Cheng, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Deng, Q.E.; et al. Escin ameliorates CUMS-induced depressive-like behavior via BDNF/TrkB/CREB and TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathways in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 984, 177063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.X.; Sun, W.Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, Q.; Li, L.N.; Yu, X.; Wang, S.Y.; Fan, A.R.; Xu, X.Q.; Chang, H.S. Honokiol improves depression-like behaviors in rats by HIF-1α- VEGF signaling pathway activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 968124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roddy, D.W.; Farrell, C.; Doolin, K.; Roman, E.; Tozzi, L.; Frodl, T.; O’Keane, V.; O’Hanlon, E. The Hippocampus in Depression: More Than the Sum of Its Parts? Advanced Hippocampal Substructure Segmentation in Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Wu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wan, C.; Yuan, N.; Chen, J.; Hao, W.; Mo, X.; Guo, X.; et al. Roles of microglia in adult hippocampal neurogenesis in depression and their therapeutics. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1193053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yang, W.; Ge, T.; Wang, Y.; Cui, R. Stress induced microglial activation contributes to depression. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 179, 106145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, Y.; Sun, Z.; Ren, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Yang, J. Microglia in depression: An overview of microglia in the pathogenesis and treatment of depression. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Gan, Y.; Lei, J.; Cai, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, Y. Schaftoside Reduces Depression- and Anxiogenic-like Behaviors in Mice Depression Models. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030238
Hu Y, Gan Y, Lei J, Cai J, Zhou Y, Chen H, Zhang Q, Shi Y. Schaftoside Reduces Depression- and Anxiogenic-like Behaviors in Mice Depression Models. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(3):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030238
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yue, Yaoxue Gan, Jia Lei, Jinhui Cai, Yecheng Zhou, Hao Chen, Qian Zhang, and Yan Shi. 2025. "Schaftoside Reduces Depression- and Anxiogenic-like Behaviors in Mice Depression Models" Brain Sciences 15, no. 3: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030238
APA StyleHu, Y., Gan, Y., Lei, J., Cai, J., Zhou, Y., Chen, H., Zhang, Q., & Shi, Y. (2025). Schaftoside Reduces Depression- and Anxiogenic-like Behaviors in Mice Depression Models. Brain Sciences, 15(3), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030238



