Norma Latina Neuropsychological Evaluation in Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis and Its Relationship with Disability
Abstract
1. Introduction
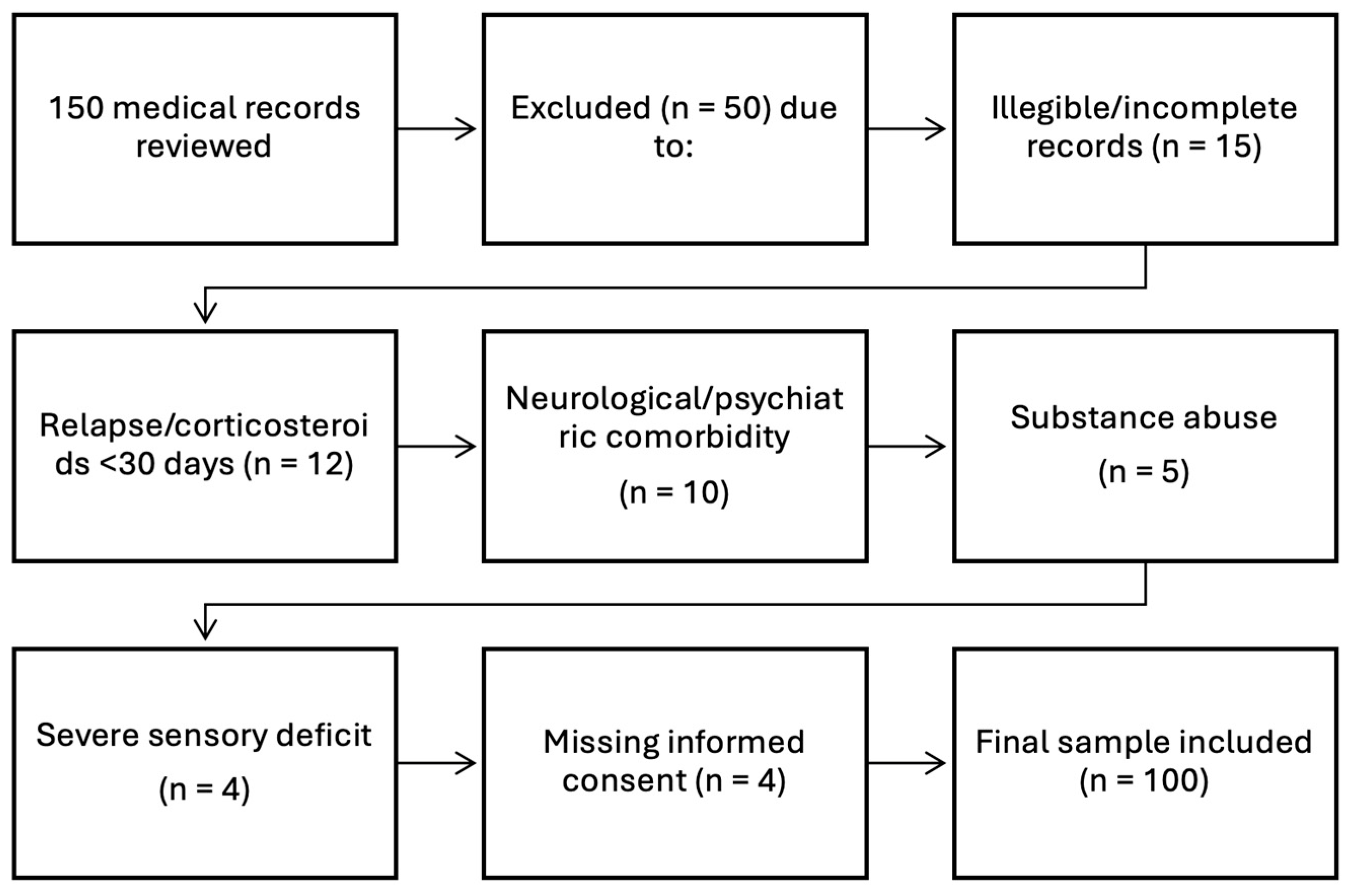
2. Materials and Methods
- Participants
- Procedure and instruments
- Neuropsychological test
- Ethics Considerations
- Data analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Korakas, N.; Tsolaki, M. Cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis: A review of neuropsychological assessments. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 2016, 29, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, J.S.; Krysko, K.M.; Hua, L.H.; Absinta, M.; Franklin, R.J.M.; Segal, B.M. Ageing and multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, T.; Moccia, M.; Coetzee, T.; A Cohen, J.; Correale, J.; Graves, J.; Marrie, R.A.; Montalban, X.; Yong, V.W.; Thompson, A.J.; et al. Multiple sclerosis progression: Time for a new mechanism-driven framework. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, S.C.; Cook, K.; De Nino, S.; Fletcher, M. The topographical model of multiple sclerosis: A dynamic visualization of disease course. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 3, e279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inojosa, H.; Schriefer, D.; Ziemssen, T. Clinical outcome measures in multiple sclerosis: A review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roxburgh, R.H.; Seaman, S.R.; Masterman, T.; Hensiek, A.E.; Sawcer, S.J.; Vukusic, S.; Achiti, I.; Confavreux, C.; Coustans, M.; Le Page, E.; et al. Multiple Sclerosis Severity Score: Using disability and disease duration to rate disease severity. Neurology 2005, 64, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meca-Lallana, V.; Gascón-Giménez, F.; Ginestal-López, R.C.; Higueras, Y.; Téllez-Lara, N.; Carreres-Polo, J.; Eichau-Madueño, S.; Romero-Imbroda, J.; Vidal-Jordana, Á.; Pérez-Miralles, F. Cognitive Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis: Diagnosis and Monitoring. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 5183–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacentini, C.; Argento, O.; Nocentini, U. Cognitive Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis: “Classic” Knowledge and Recent Acquisitions. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2023, 81, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, D.; Ramos Usuga, D.; Fuentes Mendoza, E.M.; Aguayo Arelis, A.; Rabago Barajas, B.V.; Macías Islas, M.Á.; Krch, D.; Lequerica, A.H.; Arango-Lasprilla, J.C. Validation of the Norma Latina Neuropsychological Assessment Battery in Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis in Mexico. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 59, 103685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, D.; Perrin, P.B.; Morlett-Paredes, A.; Galarza-Del-Angel, J.; Martínez, C.; Garza, M.T.; Saracho, C.P.; Rodríguez, W.; Rodríguez-Agudelo, Y.; Rábago, B.; et al. Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure—Copy and Immediate Recall: Normative Data for the Latin American Spanish Speaking Adult Population. NeuroRehabilitation 2015, 37, 677–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, D.; Perrin, P.B.; Stevens, L.F.; Garza, M.T.; Weil, C.; Saracho, C.P.; Rodríguez, W.; Rodríguez-Agudelo, Y.; Rábago, B.; Weiler, G.; et al. Stroop Color-Word Interference Test: Normative Data for the Latin American Spanish Speaking Adult Population. NeuroRehabilitation 2015, 37, 591–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango-Lasprilla, J.C.; Rivera, D.; Longoni, M.; Saracho, C.P.; Garza, M.T.; Aliaga, A.; Rodríguez, W.; Rodríguez-Agudelo, Y.; Rábago, B.; Sutter, M.; et al. Modified Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (M-WCST): Normative Data for the Latin American Spanish Speaking Adult Population. NeuroRehabilitation 2015, 37, 563–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango-Lasprilla, J.C.; Rivera, D.; Aguayo, A.; Rodríguez, W.; Garza, M.T.; Saracho, C.P.; Rodríguez-Agudelo, Y.; Aliaga, A.; Weiler, G.; Luna, M.; et al. Trail Making Test: Normative Data for the Latin American Spanish Speaking Adult Population. NeuroRehabilitation 2015, 37, 639–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango-Lasprilla, J.C.; Rivera, D.; Rodríguez, G.; Garza, M.T.; Galarza-Del-Angel, J.; Rodríguez, W.; Velázquez-Cardoso, J.; Aguayo, A.; Schebela, S.; Weil, C.; et al. Symbol Digit Modalities Test: Normative Data for the Latin American Spanish Speaking Adult Population. NeuroRehabilitation 2015, 37, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, D.; Perrin, P.B.; Aliaga, A.; Garza, M.T.; Saracho, C.P.; Rodrŕguez, W.; Justo-Guillen, E.; Aguayo, A.; Schebela, S.; Gulin, S.; et al. Brief Test of Attention: Normative Data for the Latin American Spanish Speaking Adult Population. NeuroRehabilitation 2015, 37, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabarrieta-Landa, L.; Rivera, D.; Galarza-Del-Angel, J.; Garza, M.T.; Saracho, C.P.; Rodríguez, W.; Chávez-Oliveros, M.; Rábago, B.; Leibach, G.; Schebela, S.; et al. Verbal Fluency Tests: Normative Data for the Latin American Spanish Speaking Adult Population. NeuroRehabilitation 2015, 37, 515–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabarrieta-Landa, L.; Rivera, D.; Morlett-Paredes, A.; Jaimes-Bautista, A.; Garza, M.T.; Galarza-del-Angel, J.; Rodríguez, W.; Rábago, B.; Schebela, S.; Perrin, P.B.; et al. Standard Form of the Boston Naming Test: Normative Data for the Latin American Spanish Speaking Adult Population. NeuroRehabilitation 2015, 37, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango-Lasprilla, J.C.; Rivera, D.; Garza, M.T.; Saracho, C.P.; Rodríguez, W.; Rodríguez-Agudelo, Y.; Aguayo, A.; Schebela, S.; Luna, M.; Longoni, M.; et al. Hopkins Verbal Learning Test- Revised: Normative Data for the Latin American Spanish Speaking Adult Population. NeuroRehabilitation 2015, 37, 699–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaka, M.M. Statistics Corner: A Guide to Appropriate Use of Correlation Coefficient in Medical Research. Malawi Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- de Caneda, M.A.G.; de Vecino, M.C.A. The Correlation between EDSS and Cognitive Impairment in MS Patients. Assessment of a Brazilian Population Using a BICAMS Version. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2016, 74, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botchorishvili, N.; Shiukashvili, N.; Mikeladze, N.; Dzagnidze, A.; Mikava, N.; Tighashvili, M.; Janelidze, M. Screening of Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Study in Georgia. Neurol. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5591078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechenberger, S.; Helmlinger, B.; Ropele, S.; Pirpamer, L.; Bachmaier, G.; Damulina, A.; Pichler, A.; Khalil, M.; Enzinger, C.; Pinter, D. Information Processing Speed as a Prognostic Marker of Physical Impairment and Progression in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 57, 103353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedict, R.H.B.; Carone, D.A.; Bakshi, R. Correlating Brain Atrophy with Cognitive Dysfunction, Mood Disturbances, and Personality Disorder in Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neuroimaging 2004, 14, 36S–45S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Abbasi Garravnd, N.; Feizollahi, M.; Talebi, M. The Expanded Disability Status Scale Score and Demographic Indexes Are Correlated with the Severity of Cognitive Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. J. Clin. Neurol. 2021, 17, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vleugels, L.; Lafosse, C.; van Nunen, A.; Nachtergaele, S.; Ketelaer, P.; Charlier, M.; Vandenbussche, E. Visuoperceptual Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Diagnosed with Neuropsychological Tasks. Mult. Scler. 2000, 6, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasescu, R.; Cerezo Garcia, M.; Aladro Benito, Y. Impairment of visuospatial/visuoconstructional skills in multiple sclerosis patients: The correlation with regional lesion load and subcortical atrophy. Neurología 2016, 31, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botvinick, M.M.; Braver, T.S.; Barch, D.M.; Carter, C.S.; Cohen, J.D. Conflict Monitoring and Cognitive Control. Psychol. Rev. 2001, 108, 624–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, M.; Mitchell, L.; Millist, L.; Lizak, N.; Beh, S.; Frohman, T.C.; Frohman, E.M.; White, O.B.; Fielding, J. Ocular Motor Measures of Cognitive Dysfunction in Multiple Sclerosis II: Working Memory. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covey, T.J.; Zivadinov, R.; Shucard, J.L.; Shucard, D.W. Information Processing Speed, Neural Efficiency, and Working Memory Performance in Multiple Sclerosis: Differential Relationships with Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2011, 33, 1129–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, B.; Lange, F.; Steinke, A. The Reliability of the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test in Clinical Practice. Assessment 2021, 28, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, K.T.; Beiske, A.G.; Landrø, N.I.; Hessen, E. Predictors of Executive Complaints and Executive Deficits in Multiple Sclerosis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2014, 129, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kania, K.; Pawlak, M.A.; Forycka, M.; Wiłkość-Dębczyńska, M.; Michalak, S.; Łukaszewska, A.; Wyciszkiewicz, A.; Wypych, A.; Serafin, Z.; Marcinkowska, J.; et al. Predicting Clinical Progression and Cognitive Decline in Patients with Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis: A 6-Year Follow-up Study. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2024, 58, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingo VanGilder, J.; Hengge, C.R.; Duff, K.; Schaefer, S.Y. Visuospatial Function Predicts One-Week Motor Skill Retention in Cognitively Intact Older Adults. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 664, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.G.; Kent, J.-A.; Marcopulos, B.A.; Arredondo, B.C.; Wilson, M. Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Normative Data for the Psychiatric Population. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2022, 36, 1653–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meo, E.; Portaccio, E.; Giorgio, A.; Ruano, L.; Goretti, B.; Niccolai, C.; Patti, F.; Chisari, C.G.; Gallo, P.; Grossi, P.; et al. Identifying the Distinct Cognitive Phenotypes in Multiple Sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibian, F.; Azimzadeh, K.; Shaygannejad, V.; Ashtari, F.; Adibi, I.; Sanayei, M. Patterns of Attention Deficit in Relapsing and Progressive Phenotypes of Multiple Sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreja-Guevara, C.; Ayuso Blanco, T.; Brieva Ruiz, L.; Hernández Pérez, M.Á.; Meca-Lallana, V.; Ramió-Torrentà, L. Cognitive Dysfunctions and Assessments in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri, S.; Jameie, M.; Balali, P.; Adib Moradi, S.; Sanjari Moghaddam, H.; Aghamollaii, V.; Harirchian, M.H. Trail Making Test Could Predict Impairment in Cognitive Domains in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Study of Diagnostic Accuracy. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2023, 38, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivadinov, R.; Sepcic, J.; Nasuelli, D.; De Masi, R.; Bragadin, L.M.; Tommasi, M.A.; Zambito-Marsala, S.; Moretti, R.; Bratina, A.; Ukmar, M.; et al. A Longitudinal Study of Brain Atrophy and Cognitive Disturbances in the Early Phase of Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 70, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patients Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Number of patients | 100 |
| Sex | |
| Female | 69% |
| Male | 31% |
| Years of education | 13.7 +/− 4.26 |
| Age | 39 +/− 11.1 |
| Time elapsed from first symptom to diagnosis | 2.13 +/− 2.87 |
| Years of disease evolution | 7.68 +/− 6.62 |
| Relapses during the last year | 0.57 +/− 0.79 |
| EDSS | 3.68 +/− 1.69 |
| MSSS | 1.07 +/− 1.26 |
| Clinical subtype | Relapsing–remitting: 93 Secondary progressive: 5 Primary progressive: 2 |
| Disease-modifying treatment | Glatiramer acetate: 83 Interferon: 12 Azathioprine: 3 No treatment: 2 |
| Test | p-Value | r-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Stroop Test. Words | 0.016 | −0.262 * |
| M-WCST Perseverative Error | 0.005 | 0.289 ** |
| ROCF memory | 0.005 | −0.292 ** |
| Test | p-Value | r-Value |
|---|---|---|
| M-WCST. Total error | 0.003 | 0.307 ** |
| Stroop Test. Word-color | 0.003 | −0.323 ** |
| HVLT-R. Recognition | <0.001 | −0.327 *** |
| BTA. Numbers total | <0.001 | −0.340 *** |
| HVLT-R assay 1 | <0.001 | −0.341 *** |
| HVLT-R assay 2 | <0.001 | −0.357 *** |
| BTA. Words total | <0.001 | −0.359 *** |
| Stroop Test. Colors | <0.001 | −0.362 ** |
| FV. F Word | <0.001 | −0.362 *** |
| TBA. Words and numbers total | <0.001 | −0.383 *** |
| BNT | <0.001 | −0.386 *** |
| TMT-A | <0.001 | 0.393 *** |
| Test | p-Value | r-Value |
|---|---|---|
| M-WCST. Total categories corrects | <0.001 | −0.402 *** |
| FV-Fruits | <0.001 | −0.406 *** |
| FV-Word M | <0.001 | −0.408 *** |
| FV-Animals | <0.001 | −0.411 *** |
| FV-Jobs | <0.001 | −0.419 *** |
| FV-Word S | <0.001 | −0.440 *** |
| FV-Word A | <0.001 | −0.447 *** |
| TMT-B | <0.001 | 0.449 *** |
| ROCF-copy | <0.001 | 0.458 *** |
| HVLT-R Total | <0.001 | −0.466 *** |
| Test | p-Value | r-Value |
|---|---|---|
| SDMT | <0.001 | −0.549 *** |
| HVLT-R Assay 3 | <0.001 | −0.573 *** |
| Test | p-Value | r-Value |
|---|---|---|
| HVLT-R assay 1 | 0.580 | 0.056 |
| HVLT-R assay 2 | 0.380 | −0.089 |
| HVLT-R assay 3 | 0.335 | −0.098 |
| HVLT-R Total | 0.748 | −0.033 |
| HVLT-R Recognition | 0.475 | 0.073 |
| ROCF Copy | 0.224 | −0.128 |
| ROCF Memory | 0.365 | −0.096 |
| BTA Number total | 0.339 | −0.097 |
| BTA Word total | 0.060 | −0.190 |
| TBA TOTAL | 0.116 | 0.159 |
| SDMT | 0.739 | −0.034 |
| TMT-A | 0.113 | 0.166 |
| TMT-B | 0.180 | 0.140 |
| STROOP TEST words | 0.733 | −0.038 |
| STROOP TEST colors | 0.609 | −0.057 |
| STROOP TEST PC | 0.820 | 0.025 |
| STROOP TEST interference | 0.346 | 0.104 |
| FV word F | 0.727 | −0.036 |
| FV word A | 0.119 | −0.158 |
| FV word S | 0.081 | −0.176 |
| FV word M | 0.180 | −0.136 |
| FV Animals | 0.998 | −0.000 |
| FV Fruits | 0.963 | −0.005 |
| FV Jobs | 0.119 | −0.158 |
| M-WCST complete categories | 0.102 | −0.171 |
| M-WCST Perseverative Errors | 0.361 | −0.096 |
| M-WCST Total Errors | 0.188 | 0.139 |
| M-WCST error percentage | 0.972 | 0.004 |
| BNT-long | 0.375 | 0.019 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguayo-Arelis, A.; Rabago-Barajas, B.V.; Cárdenas Gómez, A.M.; Arana Yepez, J.E.; Saldaña-Cruz, A.M.; Fragoso-Ruiz, A. Norma Latina Neuropsychological Evaluation in Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis and Its Relationship with Disability. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15121251
Aguayo-Arelis A, Rabago-Barajas BV, Cárdenas Gómez AM, Arana Yepez JE, Saldaña-Cruz AM, Fragoso-Ruiz A. Norma Latina Neuropsychological Evaluation in Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis and Its Relationship with Disability. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(12):1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15121251
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguayo-Arelis, Adriana, Brenda Viridiana Rabago-Barajas, Alina Mariela Cárdenas Gómez, Jesús Emmanuel Arana Yepez, Ana Miriam Saldaña-Cruz, and Alberto Fragoso-Ruiz. 2025. "Norma Latina Neuropsychological Evaluation in Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis and Its Relationship with Disability" Brain Sciences 15, no. 12: 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15121251
APA StyleAguayo-Arelis, A., Rabago-Barajas, B. V., Cárdenas Gómez, A. M., Arana Yepez, J. E., Saldaña-Cruz, A. M., & Fragoso-Ruiz, A. (2025). Norma Latina Neuropsychological Evaluation in Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis and Its Relationship with Disability. Brain Sciences, 15(12), 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15121251





