Deep Brain Stimulation in Treatment-Resistant Psychiatric Disorders: Efficacy, Safety, and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
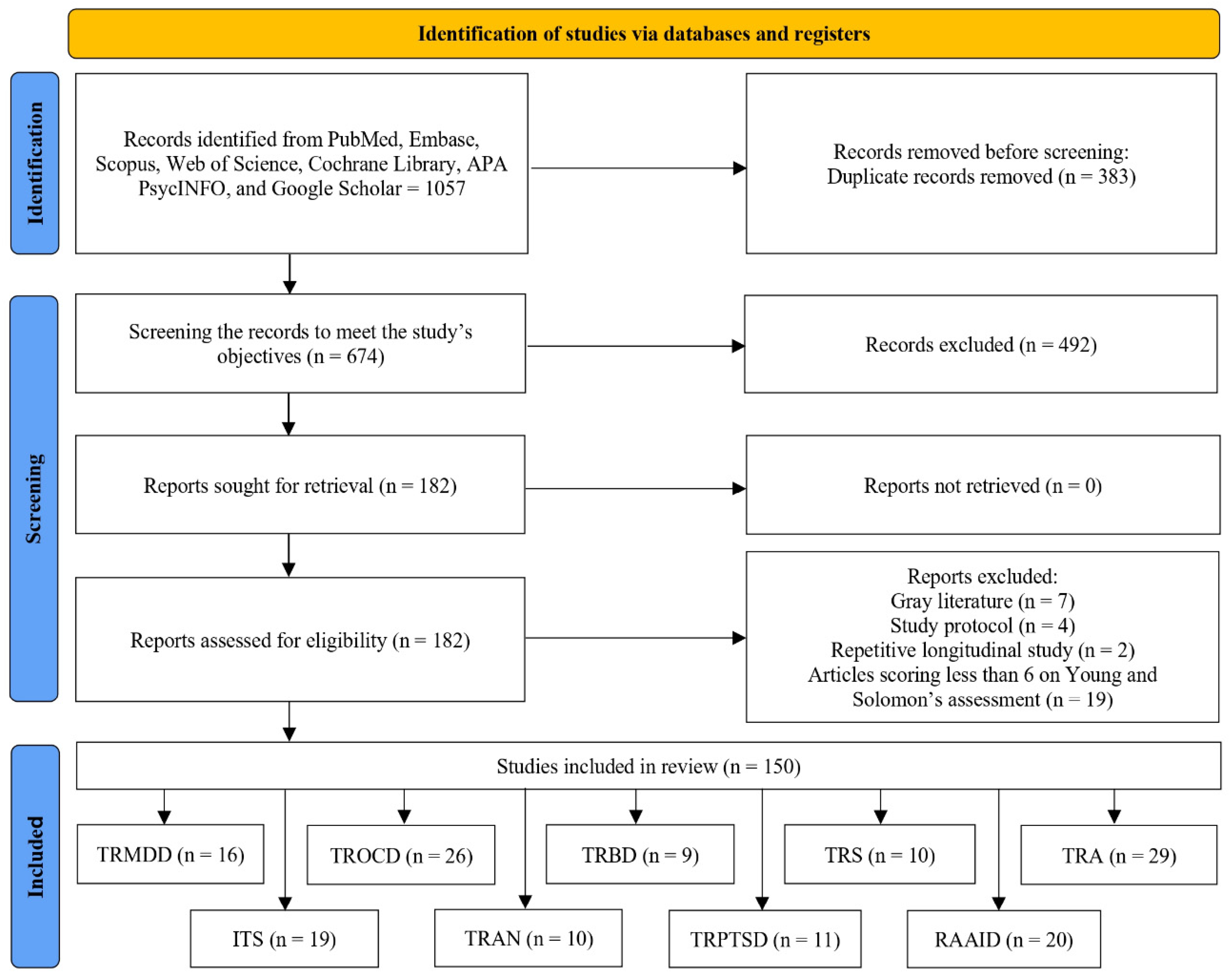
2.1. Search Strategy and Study Selection
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Appraisal of Study Quality
2.4. Synthesis of Evidence
3. Results
3.1. Treatment-Resistant Major Depressive Disorder
3.2. Treatment-Resistant Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder
3.3. Treatment-Resistant Bipolar Disorder
3.4. Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia
3.5. Treatment-Refractory Addictions
3.6. Intractable Tourette’s Syndrome
3.7. Treatment-Refractory Anorexia Nervosa
3.8. Treatment-Refractory Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
3.9. Refractory Aggression in Autistic Children with Severe Intellectual Disability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2019 Mental Disorders Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry 2022, 9, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howes, O.D.; Thase, M.E.; Pillinger, T. Treatment resistance in psychiatry: State of the art and new directions. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kranenburg, G.D.; Van den Brink, R.H.; Mulder, W.G.; Diekman, W.J.; Pijnenborg, G.H.; Mulder, C.L. Clinical effects and treatment outcomes of long-term compulsory in-patient treatment of treatment-resistant patients with severe mental illness and substance-use disorder. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, C.V.T.; Macho, C.M.; Almunia, M.L.; García, M.N.; Castro, G.J.B.; Rivas, P.P.; Fernández-Alén, J.A. Comparative experience in the development of deep brain stimulation for movement disorders and psychiatric diseases: A review. Brain Netw. Disord. 2025, 1, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widge, A.S. Closing the loop in psychiatric deep brain stimulation: Physiology, psychometrics, and plasticity. Neuropsychopharmacology 2024, 49, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, C.R.; Olsen, S.; Widge, A.S. Deep brain stimulation for psychiatric disorders: From focal brain targets to cognitive networks. Neuroimage 2021, 225, 117515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, D.; Akram, H.; Jahanshahi, M. Deep brain stimulation for psychiatric disorders: Role of imaging in identifying/confirming DBS targets, predicting, and optimizing outcome and unravelling mechanisms of action. Psychoradiology 2021, 1, 118–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koek, R.J.; Roach, J.; Athanasiou, N.; Korotinsky, A. Novel neurostimulation therapeutic approaches for treatment-resistant psychiatric disorders. In Treatment Resistance in Psychiatry; Kim, Y.K., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.P.; Ganesh, U.M.; Arumugham, S.S.; Srinivas, D.; Venkatasubramanian, G.; Reddy, Y.J. Deep brain stimulation–A primer for psychiatrists. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2025, 104, 104354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostick-Quenet, K.; Kalwani, L.; Koenig, B.; Torgerson, L.; Sanchez, C.; Munoz, K.; Hsu, R.L.; Sierra-Mercado, D.; Robinson, J.O.; Outram, S.; et al. Researchers’ ethical concerns about using adaptive deep brain stimulation for enhancement. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 813922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, F.; Lancelot, M. Incoming ethical issues for deep brain stimulation: When long-term treatment leads to a ‘new form of the disease’. J. Med. Ethics 2021, 47, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.M.; Solomon, M.J. How to critically appraise an article. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLure, M. Clarity bordering on stupidity: Where’s the quality in systematic review? J. Educ. Pol. 2005, 20, 393–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Kabotyanski, K.E.; Hirani, S.; Liu, T.; Naqvi, Z.; Giridharan, N.; Hasen, M.; Provenza, N.R.; Banks, G.P.; Mathew, S.J.; et al. Efficacy of deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2024, 9, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.J.; Yang, X.H.; Mo, Y.; Deng, C.J.; Huang, X.B.; Cai, D.B.; Zheng, W. Deep transcranial magnetic stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2024, 96, 104032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.A.; Okun, M.S.; Scangos, K.W.; Mayberg, H.S.; de Hemptinne, C. Deep brain stimulation for refractory major depressive disorder: A comprehensive review. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasubbu, R.; Lang, S.; Kiss, Z.H. Dosing of Electrical Parameters in Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for Intractable Depression: A Review of Clinical Studies. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Mo, J.; Sui, L.; Zhang, J.; Hu, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhao, B.; Wang, X.; et al. Deep brain stimulation in treatment-resistant depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis on efficacy and safety. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 655412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitti, F.L.; Yang, A.I.; Cristancho, M.A.; Baltuch, G.H. Deep brain stimulation is effective for treatment-resistant depression: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White Bradley: Treatment Resistant Depression Subcallosal Cingulate Network DBS (TRANSCEND). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT06423430. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.ucbraid.org/trial/NCT06423430 (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- Holtzheimer, P.E.; Husain, M.M.; Lisanby, S.H.; Taylor, S.F.; Whitworth, L.A.; McClintock, S.; Slavin, K.V.; Berman, J.; McKhann, G.M.; Patil, P.G.; et al. Subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: A multisite, randomised, sham-controlled trial. Lancet Psychiatry 2017, 4, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougherty, D.D.; Rezai, A.R.; Carpenter, L.L.; Howland, R.H.; Bhati, M.T.; O’Reardon, J.P.; Eskandar, E.N.; Baltuch, G.H.; Machado, A.D.; Kondziolka, D.; et al. A randomized sham-controlled trial of deep brain stimulation of the ventral capsule/ventral striatum for chronic treatment-resistant depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 78, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenen, V.A.; Bewernick, B.H.; Kayser, S.; Kilian, H.; Boström, J.; Greschus, S.; Hurlemann, R.; Klein, M.E.; Spanier, S.; Sajonz, B.; et al. Superolateral medial forebrain bundle deep brain stimulation in major depression: A gateway trial. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-dos-Santos, A.; Sales, M.; Sebastião, A.; Gusmão, R. A new viewpoint on the etiopathogenesis of depression: Insights from the neurophysiology of deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease and treatment-resistant depression. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 607339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Sanchez, S.; Perez-Caballero, L.; Berrocoso, E. Cellular and molecular mechanisms triggered by deep brain stimulation in depression: A preclinical and clinical approach. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 73, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergfeld, I.O.; Mantione, M.; Figee, M.; Schuurman, P.R.; Lok, A.; Denys, D. Treatment-resistant depression and suicidality. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 235, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, K.B.; Plana-Ripoll, O.; Musliner, K.L.; Debost, J.C.; Petersen, L.V.; Munk-Olsen, T. Cause-specific life years lost in individuals with treatment-resistant depression: A Danish nationwide register-based cohort study. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 280 Pt A, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, D.M.; Canuso, C.M.; Daly, E.; Johnson, J.C.; Fu, D.J.; Doherty, T.; Blauer-Peterson, C.; Cepeda, M.S. Suicide-specific mortality among patients with treatment-resistant major depressive disorder, major depressive disorder with prior suicidal ideation or suicide attempts, or major depressive disorder alone. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reutfors, J.; Andersson, T.M.; Tanskanen, A.; DiBernardo, A.; Li, G.; Brandt, L.; Brenner, P. Risk factors for suicide and suicide attempts among patients with treatment-resistant depression: Nested case-control study. Arch. Suicide Res. 2021, 25, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, P.E.; Windels, F.; Morris, J.; Coyne, T.; Marsh, R.; Giorni, A.; Mohan, A.; Sachdev, P.; O’lEary, E.; Boschen, M.; et al. A randomised, double-blind, sham-controlled trial of deep brain stimulation of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis for treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchón, J.M.; Real, E.; Alonso, P.; Aparicio, M.A.; Segalas, C.; Plans, G.; Luyten, L.; Brunfaut, E.; Matthijs, L.; Raymakers, S.; et al. A prospective international multi-center study on safety and efficacy of deep brain stimulation for resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 1234–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, L.; Saryyeva, A.; Schwabe, K.; Heissler, H.E.; Runge, J.; Alam, M.; Heitland, I.; Kahl, K.G.; Krauss, J.K. Long-term deep brain stimulation in treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: Outcome and quality of life at four to eight years follow-up. Neuromodulation 2021, 24, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Vlis, T.A.; Ackermans, L.; Mulders, A.E.; Vrij, C.A.; Schruers, K.; Temel, Y.; Duits, A.; Leentjens, A.F. Ventral capsule/ventral striatum stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder: Toward a unified connectomic target for deep brain stimulation? Neuromodulation 2021, 24, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naesström, M.; Hariz, M.; Strömsten, L.; Bodlund, O.; Blomstedt, P. Deep brain stimulation in the bed nucleus of stria terminalis in obsessive-compulsive disorder—1-year follow-up. World Neurosurg. 2021, 149, e794–e802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, L.; Sutton, B.; Winston, H.R.; Abosch, A.; Thompson, J.A.; Davis, R.A. Deep brain stimulation for obsessive-compulsive disorder: Real world experience post-FDA-humanitarian use device approval. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 568932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, C.V.; Treu, S.; Strange, B.; Lara, M.; Navas, M.; Ezquiaga, E.; Zazo, E.S.; Vicente, J.S.; Muñiz, I.; Fernandez, F.S. Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens, ventral striatum, or internal capsule targets for medication-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: A multicenter study. World Neurosurg. 2021, 155, e168–e176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luyten, L.; Hendrickx, S.; Raymaekers, S.; Gabriëls, L.; Nuttin, B. Electrical stimulation in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis alleviates severe obsessive-compulsive disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcia, J.A.; Avecillas-Chasín, J.M.; Nombela, C.; Arza, R.; García-Albea, J.; Pineda-Pardo, J.A.; Reneses, B.; Strange, B.A. Personalized striatal targets for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, L.; Franzini, A.; Messina, G.; Scarone, S.; Gambini, O. Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens and bed nucleus of stria terminalis for obsessive-compulsive disorder: A case series. World Neurosurg. 2015, 83, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarouf, M.; Neudorfer, C.; El Majdoub, F.; Lenartz, D.; Kuhn, J.; Sturm, V. Deep brain stimulation of medial dorsal and ventral anterior nucleus of the thalamus in OCD: A retrospective case series. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenen, V.A.; Schlaepfer, T.E.; Goll, P.; Reinacher, P.C.; Voderholzer, U.; Van Elst, L.T.; Urbach, H.; Freyer, T. The medial forebrain bundle as a target for deep brain stimulation for obsessive-compulsive disorder. CNS Spectr. 2017, 22, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voon, V.; Droux, F.; Morris, L.; Chabardes, S.; Bougerol, T.; David, O.; Krack, P.; Polosan, M. Decisional impulsivity and the associative-limbic subthalamic nucleus in obsessive-compulsive disorder: Stimulation and connectivity. Brain 2017, 140, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooms, P.; Blankers, M.; Figee, M.; Bergfeld, I.O.; van den Munckhof, P.; Schuurman, P.R.; Denys, D. Cost-effectiveness of deep brain stimulation versus treatment as usual for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Brain Stimul. 2017, 10, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrand, S.; Evans, A.H.; Mangelsdorf, S.; Loi, S.M.; Mocellin, R.; Borham, A.; Bevilacqua, J.; Blair-West, S.; Walterfang, M.A.; Bittar, R.G.; et al. Deep brain stimulation for severe treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: An open-label case series. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2018, 52, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Dallapiazza, R.F.; De Vloo, P.; Elias, G.J.; Fomenko, A.; Boutet, A.; Giacobbe, P.; Lozano, A.M. Inferior thalamic peduncle deep brain stimulation for treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: A phase 1 pilot trial. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huys, D.; Kohl, S.; Baldermann, J.C.; Timmermann, L.; Sturm, V.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Kuhn, J. Open-label trial of anterior limb of internal capsule–nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation for obsessive-compulsive disorder: Insights gained. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Khanna, S.; Jain, R. Deep brain stimulation of ventral internal capsule for refractory obsessive–compulsive disorder. Indian J. Psychiatry 2019, 61, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beszłej, J.A.; Siwicki, D.; Fila-Witecka, K.; Wieczorek, T.; Piotrowski, P.; Weiser, A.; Tabakow, P.; Rymaszewska, J. Deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder-case report of two patients. Psychiatr. Pol. 2019, 53, 807–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denys, D.; Graat, I.; Mocking, R.; de Koning, P.; Vulink, N.; Figee, M.; Ooms, P.; Mantione, M.; Munckhof, P.v.D.; Schuurman, R. Efficacy of deep brain stimulation of the ventral anterior limb of the internal capsule for refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: A clinical cohort of 70 patients. Am. J. Psychiatry 2020, 177, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, M.T.; Trapp, N.T.; McCormick, L.M.; Jareczek, F.J.; Zanaty, M.; Close, L.N.; Beeghly, J.; Greenlee, J.D. Deep brain stimulation for obsessive–compulsive disorder: A long term naturalistic follow up study in a single institution. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabardes, S.; Krack, P.; Piallat, B.; Bougerol, T.; Seigneuret, E.; Yelnik, J.; Vidal, S.F.; David, O.; Mallet, L.; Benabid, A.-L.; et al. Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in obsessive–compulsives disorders: Long-term follow-up of an open, prospective, observational cohort. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, H.; Apergis-Schoute, A.M.; Akram, H.; Foltynie, T.; Limousin, P.; Drummond, L.M.; Fineberg, N.A.; Matthews, K.; Jahanshahi, M.; Robbins, T.W.; et al. A randomized trial directly comparing ventral capsule and anteromedial subthalamic nucleus stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder: Clinical and imaging evidence for dissociable effects. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnaim, M.A.; Lang-Hambauer, V.; Hebel, T.; Schoisswohl, S.; Schecklmann, M.; Deuter, D.; Schlaier, J.; Langguth, B. Deep brain stimulation for treatment resistant obsessive compulsive disorder; an observational study with ten patients under real-life conditions. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1242566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadot, R.; Najera, R.; Hirani, S.; Anand, A.; Storch, E.; Goodman, W.K.; Shofty, B.; Sheth, S.A. Efficacy of deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 93, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hariz, M.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Zrinzo, L.; Coenen, V.A.; Sheth, S.A.; Bervoets, C.; Naesström, M.; Blomstedt, P.; Coyne, T.; et al. Deep brain stimulation for refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD): Emerging or established therapy? Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gippert, S.M.; Switala, C.; Bewernick, B.H.; Kayser, S.; Bräuer, A.; Coenen, V.A.; Schlaepfer, T.E. Deep brain stimulation for bipolar disorder—Review and outlook. CNS Spectr. 2017, 22, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzheimer, P.E.; Kelley, M.E.; Gross, R.E.; Filkowski, M.M.; Garlow, S.J.; Barrocas, A.; Wint, D.; Craighead, M.C.; Kozarsky, J.; Chismar, R.; et al. Subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant unipolar and bipolar depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2012, 69, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, C.V.; Ezquiaga, E.; Navas, M.; Sola, R.G. Deep brain stimulation of the subcallosal cingulate for medication-resistant type I bipolar depression: Case report. Bipolar Disord. 2013, 15, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harel, E.V.; Zangen, A.; Roth, Y.; Reti, I.; Braw, Y.; Levkovitz, Y. H-coil repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for the treatment of bipolar depression: An add-on, safety and feasibility study. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 12, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutz, J. Brain stimulation treatment for bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2023, 25, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, I.U.; Foote, K.D.; Goodman, W.K.; Ricciuti, N.; Ward, H.; Sudhyadhom, A.; Jacobson, C.E.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Okun, M.S. A case of mania following deep brain stimulation for obsessive compulsive disorder. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2010, 88, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funkiewiez, A.; Ardouin, C.; Caputo, E.; Krack, P.; Fraix, V.; Klinger, H.; Chabardes, S.; Foote, K.; Benabid, A.; Pollak, P. Long term effects of bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation on cognitive function, mood, and behaviour in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewernick, B.H.; Hurlemann, R.; Matusch, A.; Kayser, S.; Grubert, C.; Hadrysiewicz, B.; Axmacher, N.; Lemke, M.; Cooper-Mahkorn, D.; Cohen, M.X.; et al. Nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation decreases ratings of depression and anxiety in treatment-resistant depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisely, S.; Li, A.; Warren, N.; Siskind, D. A systematic review and meta-analysis of deep brain stimulation for depression. Depress. Anxiety 2018, 35, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, H.; Li, J.; Jin, H.; Li, D.; Liu, D.; Sun, B. Habenula deep brain stimulation for intractable schizophrenia: A pilot study. Neurosurg. Focus 2020, 49, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioque, M.; Rumià, J.; Roldán, P.; Hidalgo-Mazzei, D.; Montejo, L.; Benabarre, A.; Gil-Badenes, J.; Tercero, J.; Parellada, E.; Vieta, E. Deep brain stimulation and digital monitoring for patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: A case series. Span. J. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2025, 18, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascella, N.; Butala, A.A.; Mills, K.; Kim, M.J.; Salimpour, Y.; Wojtasievicz, T.; Hwang, B.; Cullen, B.; Figee, M.; Moran, L.; et al. Deep brain stimulation of the substantia nigra pars reticulata for treatment-resistant schizophrenia: A case report. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 90, e57–e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corripio, I.; Roldán, A.; Sarró, S.; McKenna, P.J.; Alonso-Solís, A.; Rabella, M.; Díaz, A.; Puigdemont, D.; Pérez-Solà, V.; Álvarez, E.; et al. Deep brain stimulation in treatment resistant schizophrenia: A pilot randomized cross-over clinical trial. EBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibar-Durán, J.Á.; Collado, I.C.; Bejarano, A.R.; Nevado, R.S.; Bolanos, I.A.; García-Cornet, J.; Alonso-Solís, A.; Bello, E.M.G.; Schmidt, C.d.Q.; Hernández, F.M.; et al. Long-term outcomes of deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant schizophrenia: Exploring potential targets. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 163, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendi, M.S.; Zendehrouh, E.; Ellis, C.A.; Liang, Z.; Fu, Z.; Mathalon, D.H.; Ford, J.M.; Preda, A.; van Erp, T.G.M.; Miller, R.L.; et al. Aberrant dynamic functional connectivity of default mode network in schizophrenia and links to symptom severity. Front. Neural Circuits 2021, 15, 649417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.L.; Zong, X.F.; Mann, J.J.; Zheng, J.J.; Liao, Y.H.; Li, Z.C.; He, Y.; Chen, X.-G.; Tang, J.-S. A review of the functional and anatomical default mode network in schizophrenia. Neurosci. Bull. 2017, 33, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macpherson, T.; Hikida, T. Role of basal ganglia neurocircuitry in the pathology of psychiatric disorders. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 73, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Minzenberg, M.J.; Raouf, S.; D’Esposito, M.; Carter, C.S. Impaired prefrontal-basal ganglia functional connectivity and substantia nigra hyperactivity in schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhoury, M. The habenula in psychiatric disorders: More than three decades of translational investigation. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 83, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, N.; Shaheen, A.; Sarica, C.; Singh, A.; Zanaty, M.; Johari, K.; Yang, A.; Zesiewicz, T.; Dalm, B.; Bezchlibnyk, Y.; et al. Deep brain stimulation for substance use disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1231760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luigjes, J.V.; Van Den Brink, W.; Feenstra, M.V.; Van Den Munckhof, P.; Schuurman, P.R.; Schippers, R.; Mazaheri, A.; De Vries, T.J.; Denys, D. Deep brain stimulation in addiction: A review of potential brain targets. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 17, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves-Ferreira, A.; Do Couto, F.S.; Campos, A.R.; Neto, L.P.; Gonçalves-Ferreira, D.; Teixeira, J. Deep brain stimulation for refractory cocaine dependence. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, e87–e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, S.L.; Glue, P.; Manning, P.; Vanneste, S.; Lim, L.J.; Mohan, A.; De Ridder, D. Anterior cingulate cortex implants for alcohol addiction: A feasibility study. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorspan, F.; Domenech, P.; Grabli, D.; Yelnik, J.; Delavest, M.; Dauré, C.; Bellivier, F.; Pelissolo, A.; Belaid, H.; Baunez, C.; et al. A single case report of STN-DBS for severe crack-cocaine dependence: Double-blind ON vs. SHAM randomized controlled assessment. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1146492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zammit Dimech, D.; Zammit Dimech, A.A.; Hughes, M.; Zrinzo, L. A systematic review of deep brain stimulation for substance use disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, N.; Qu, L.; Li, Y.; Jing, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Deep brain stimulation of nucleus accumbens for methamphetamine addiction: Two case reports. World Neurosurg. 2019, 122, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, J.; Bauer, R.; Pohl, S.; Lenartz, D.; Huff, W.; Kim, E.H.; Klosterkoetter, J.; Sturm, V. Observations on unaided smoking cessation after deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens. Eur. Addict. Res. 2009, 15, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, J.; Gründler, T.O.; Bauer, R.; Huff, W.; Fischer, A.G.; Lenartz, D.; Maarouf, M.; Bührle, C.; Klosterkötter, J.; Ullsperger, M.; et al. Successful deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens in severe alcohol dependence is associated with changed performance monitoring. Addict. Biol. 2011, 16, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, J.; Möller, M.; Treppmann, J.F.; Bartsch, C.; Lenartz, D.; Gründler, T.O.; Maarouf, M.; Brosig, A.; Barnikol, U.B.; Klosterkötter, J.; et al. Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens and its usefulness in severe opioid addiction. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 145–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Li, N.; Ge, S.; Lozano, A.M.; Lee, D.J.; Yang, C.; Li, L.; Bai, Q.; Lu, H.; Wang, J.; et al. Long-term results after deep brain stimulation of nucleus accumbens and the anterior limb of the internal capsule for preventing heroin relapse: An open-label pilot study. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, F.; Zeljic, K.; Pan, J.; Sun, B. Death from opioid overdose after deep brain stimulation: A case report. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, e9–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, U.J.; Sturm, V.; Voges, J.; Heinze, H.J.; Galazky, I.; Heldmann, M.; Scheich, H.; Bogerts, B. Successful treatment of chronic resistant alcoholism by deep brain stimulation of nucleus accumbens: First experience with three cases. Pharmacopsychiatry 2009, 42, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voges, J.; Müller, U.; Bogerts, B.; Münte, T.; Heinze, H.J. Deep brain stimulation surgery for alcohol addiction. World Neurosurg. 2013, 80, S28.e21–S28.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, J.J., III; Haut, M.W.; Hodder, S.L.; Zheng, W.; Lander, L.R.; Berry, J.H.; Farmer, D.L.; Marton, J.L.; Ranjan, M.; Brandmeir, N.J.; et al. Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens/ventral capsule for severe and intractable opioid and benzodiazepine use disorder. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2021, 29, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezai, A.R.; Mahoney, J.J.; Ranjan, M.; Haut, M.W.; Zheng, W.; Lander, L.R.; Berry, J.H.; Farmer, D.L.; Marton, J.L.; Tirumalai, P.; et al. Safety and feasibility clinical trial of nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation for treatment-refractory opioid use disorder. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 140, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, U.J.; Sturm, V.; Voges, J.; Heinze, H.J.; Galazky, I.; Büntjen, L.; Heldmann, M.; Frodl, T.; Steiner, J.; Bogerts, B. Nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation for alcohol addiction–safety and clinical long-term results of a pilot trial. Pharmacopsychiatry 2016, 49, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Geng, X.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Oscillatory local field potentials of the nucleus accumbens and the anterior limb of the internal capsule in heroin addicts. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 1242–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, B.; Giacobbe, P.; George, T.P.; Nestor, S.M.; Rabin, J.S.; Goubran, M.; Nyman, A.J.; Baskaran, A.; Meng, Y.; Pople, C.B.; et al. Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens in the treatment of severe alcohol use disorder: A phase I pilot trial. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 3992–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, P.; Luderer, M.; Müller, U.J.; Jakobs, M.; Baldermann, J.C.; Voges, J.; Kiening, K.; Lux, A.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; the DeBraSTRA study group; et al. Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens in treatment-resistant alcohol use disorder: A double-blind randomized controlled multi-center trial. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantione, M.; van de Brink, W.; Schuurman, P.R.; Denys, D. Smoking cessation and weight loss after chronic deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens: Therapeutic and research implications: Case report. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, E218; discussion E218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Wei, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, D.; Zhan, S.; Sun, B. Deep brain stimulation of nucleus accumbens with anterior capsulotomy for drug addiction: A case report. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2020, 98, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Y.; Du, J.; Liu, W.; Zhan, S.; Voon, V.; Sun, B. Increased dopamine transporter levels following nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation in methamphetamine use disorder: A case report. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 1055–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, J.; Lenartz, D.; Huff, W.; Lee, S.; Koulousakis, A.; Klosterkoetter, J.; Sturm, V. Remission of alcohol dependency following deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens: Valuable therapeutic implications? J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 1152–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, G. Therapeutic Effect of Deep Brain Stimulation of the Nucleus Accumbens on Refractory Drug Addiction: A Case Report. Available online: https://www.neuromodulation.com/assets/documents/2007-ins-nans-conference-poster-abstracts-part1_107.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2007).
- Zhou, H.; Xu, J.; Jiang, J. Deep brain stimulation of nucleus accumbens on heroin-seeking behaviors: A case report. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 69, e41–e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia-Alfonso, C.E.; Luigjes, J.; Smolders, R.; Cohen, M.X.; Levar, N.; Mazaheri, A.; van den Munckhof, P.; Schuurman, P.R.; van den Brink, W.; Denys, D. Effective deep brain stimulation in heroin addiction: A case report with complementary intracranial electroencephalogram. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 71, e35–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldmann, M.; Berding, G.; Voges, J.; Bogerts, B.; Galazky, I.; Müller, U.; Baillot, G.; Heinze, H.-J.; Münte, T.F. Deep brain stimulation of nucleus accumbens region in alcoholism affects reward processing. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Sun, B. Deep brain stimulation removal after successful treatment for heroin addiction. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2020, 54, 543–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloufi, A.K.; Zahhar, J.A.; Bader, M.W.; Almutairi, M.B.; Alaaldeen, A.; Hetta, O.E.; Gammash, A.M.; Almuntashiri, S.; Binrabaa, I.S.; Alsaleh, A.; et al. Tourette syndrome and brain stimulation therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of current evidence. Front. Psychiatry 2025, 16, 1478503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarian-Tefaghi, L.; Zrinzo, L.; Foltynie, T. The use of deep brain stimulation in Tourette syndrome. Brain Sci. 2016, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehmeyer, L.; Schueller, T.; Kiess, J.; Heiden, P.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Baldermann, J.C.; Andrade, P. Target-specific effects of deep brain stimulation for Tourette syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 769275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldermann, J.C.; Schueller, T.; Huys, D.; Becker, I.; Timmermann, L.; Jessen, F.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Kuhn, J. Deep brain stimulation for Tourette-syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Stimul. 2016, 9, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Ramirez, D.; Jimenez-Shahed, J.; Leckman, J.F.; Porta, M.; Servello, D.; Meng, F.G.; Kuhn, J.; Huys, D.; Baldermann, J.C.; Foltynie, T.; et al. Efficacy and safety of deep brain stimulation in Tourette syndrome: The international Tourette syndrome deep brain stimulation public database and registry. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, C.; Deeb, W.; Patel, B.; Wu, Y.; Voon, V.; Okun, M.S.; Sun, B. Deep brain stimulation for Tourette’s syndrome. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrock, L.E.; Mink, J.W.; Woods, D.W.; Porta, M.; Servello, D.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Silburn, P.A.; Foltynie, T.; Walker, H.C.; Shahed-Jimenez, J.; et al. Tourette syndrome deep brain stimulation: A review and updated recommendations. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 448–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welter, M.L.; Mallet, L.; Houeto, J.L.; Karachi, C.; Czernecki, V.; Cornu, P.; Navarro, S.; Pidoux, B.; Dormont, D.; Bardinet, E.; et al. Internal pallidal and thalamic stimulation in patients with Tourette syndrome. Arch. Neurol. 2008, 65, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Torres, I.; Hariz, M.I.; Zrinzo, L.; Foltynie, T.; Limousin, P. Improvement of tics after subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation. Neurology 2009, 72, 1787–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedimonte, F.; Andreani, J.C.; Piedimonte, L.; Graff, P.; Bacaro, V.; Micheli, F.; Vilela Filho, O. Behavioral and motor improvement after deep brain stimulation of the globus pallidus externus in a case of Tourette’s syndrome. Neuromodulation 2013, 16, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceglia, S.; Rosa, M.; Servello, D.; Porta, M.; Barbieri, S.; Moro, E.; Priori, A. Adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS) for Tourette syndrome. Brain Sci. 2017, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjan, R.; Chourey, A.; Kabir, Y.; Mata, H.D.; Tiepolo, E.; Vinueza, I.L.; Mohammed, C.; Mohammed, S.F.; Thottakurichi, A.A. Role of Neurosurgical Interventions in the Treatment of Movement Disorders Like Parkinson’s Disease, Dystonia, and Tourette Syndrome. Cureus 2024, 16, e72613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huys, D.; Bartsch, C.; Koester, P.; Lenartz, D.; Maarouf, M.; Daumann, J.; Mai, J.K.; Klosterkötter, J.; Hunsche, S.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; et al. Motor improvement and emotional stabilization in patients with Tourette syndrome after deep brain stimulation of the ventral anterior and ventrolateral motor part of the thalamus. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedad, J.C.P.; Rickards, H.E.; Cavanna, A.E. What patients with Gilles de la Tourette syndrome should be treated with deep brain stimulation and what is the best target? Neurosurgery 2012, 71, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlagh, M.G.; Smith, M.E.; Landeros-Weisenberger, A.; Kobets, A.J.; King, R.A.; Miravite, J.; de Lotbinière, A.C.J.; Alterman, R.L.; Mogilner, A.Y.; Pourfar, M.H.; et al. Lessons learned from open-label deep brain stimulation for Tourette syndrome: Eight cases over 7 years. Tremor Other Hyperkinetic Mov. 2013, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefalopoulou, Z.; Zrinzo, L.; Jahanshahi, M.; Candelario, J.; Milabo, C.; Beigi, M.; Akram, H.; Hyam, J.; Clayton, J.; Kass-Iliyya, L.; et al. Bilateral globus pallidus stimulation for severe Tourette’s syndrome: A double-blind, randomised crossover trial. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servello, D.; Sassi, M.; Gaeta, M.; Ricci, C.; Porta, M. Tourette syndrome (TS) bears a higher rate of inflammatory complications at the implanted hardware in deep brain stimulation (DBS). Acta Neurochir. 2011, 153, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawikova, I.; Leckman, J.F.; Kronig, H.; Katsovich, L.; Bessen, D.E.; Ghebremichael, M.; Bothwell, A.L. Decreased numbers of regulatory T cells suggest impaired immune tolerance in children with tourette syndrome: A preliminary study. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, M.; Termine, C.; Franciotta, D.; Castiglioni, E.; Pagani, A.; Lanzi, G.; Marino, F.; Lecchini, S.; Cosentino, M.; Balottin, U. Dopaminergic receptor D5 mRNA expression is increased in circulating lymphocytes of Tourette syndrome patients. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2008, 43, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaszewska, D.; Cleintuar, P.; Oudijn, M.; Lok, A.; van Elburg, A.; Denys, D.; Mocking, R. Efficacy and safety of deep brain stimulation for treatment-refractory anorexia nervosa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.I.; Nguyen, A.; Gupta, N.; Godbole, N.; Perisetla, N.; Hatter, M.J.; Beyer, R.S.; Bui, N.E.; Jagan, J.; Yang, C.; et al. Effectiveness of deep brain stimulation in treatment of anorexia nervosa and obesity: A systematic review. World Neurosurg. 2022, 168, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, A.; Naik, A.; Bederson, M.; Arnold, P.M.; Hassaneen, W. Efficacy of deep brain stimulation for the treatment of anorexia nervosa: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of patient-level data. Neurosurg. Focus 2023, 54, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhan, S.; Li, D.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, T.; Pan, S.; Zhang, J.; Cao, C.; Jin, H.; et al. Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens for treatment-refractory anorexia nervosa: A long-term follow-up study. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oudijn, M.S.; Mocking, R.J.; Wijnker, R.R.; Lok, A.; Schuurman, P.R.; Van Den Munckhof, P.; van Elburg, A.; Denys, D. Deep brain stimulation of the ventral anterior limb of the capsula interna in patients with treatment-refractory anorexia nervosa. Brain Stimul. 2021, 14, 1528–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba Martínez, G.; Justicia, A.; Salgado, P.; Ginés, J.M.; Guardiola, R.; Cedrón, C.; Polo, M.; Delgado-Martínez, I.; Medrano, S.; Manero, R.M.; et al. A randomized trial of deep brain stimulation to the subcallosal cingulate and nucleus accumbens in patients with treatment-refractory, chronic, and severe anorexia nervosa: Initial results at 6 months of follow up. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsman, N.; Lam, E.; Volpini, M.; Sutandar, K.; Twose, R.; Giacobbe, P.; Sodums, D.J.; Smith, G.S.; Woodside, D.B.; Lozano, A.M. Deep brain stimulation of the subcallosal cingulate for treatment-refractory anorexia nervosa: 1 year follow-up of an open-label trial. Lancet Psychiatry 2017, 4, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israël, M.; Steiger, H.; Kolivakis, T.; McGregor, L.; Sadikot, A.F. Deep brain stimulation in the subgenual cingulate cortex for an intractable eating disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, e53–e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsman, N.; Woodside, B.; Lozano, A.M. Evaluating the potential of deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant anorexia nervosa. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 116, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsman, N.; Woodside, D.B.; Giacobbe, P.; Hamani, C.; Carter, J.C.; Norwood, S.J.; Sutandar, K.; Staab, R.; Elias, G.; Lyman, C.H.; et al. Subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-refractory anorexia nervosa: A phase 1 pilot trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etkin, A.; Wager, T.D. Functional neuroimaging of anxiety: A meta-analysis of emotional processing in PTSD, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2007, 164, 1476–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeres, J.; Hariz, M. Deep brain stimulation for post-traumatic stress disorder: A review of the experimental and clinical literature. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2022, 100, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, J.P.; Koek, R.J.; Schwartz, H.N.; Chen, J.W.; Sultzer, D.L.; Mandelkern, M.A.; Kulick, A.D.; Krahl, S.E. Deep brain stimulation of the basolateral amygdala for treatment-refractory posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, e82–e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langevin, J.P.; Chen, J.W.; Koek, R.J.; Sultzer, D.L.; Mandelkern, M.A.; Schwartz, H.N.; Krahl, S.E. Deep brain stimulation of the basolateral amygdala: Targeting technique and electrodiagnostic findings. Brain Sci. 2016, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koek, R.J.; Langevin, J.P.; Krahl, S.E.; Chen, J.W.; Kulick, A.D.; Schwartz, H.N.; Mandelkern, M.; Sultzer, D. Amygdala DBS for PTSD: 2 years of observations on the first case. Brain Stimul. 2017, 10, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koek, R.; Langevin, J.; Krahl, S.; Chen, J.; Sultzer, D.; Mandelkern, M. Basolateral amygdala deep brain stimulation for treatment refractory combat PTSD: Data from the first two cases. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestor, S.M.; Giacobbe, P.; Abrahao, A.; Davidson, B.; Rabin, J.S.; Lipsman, N.; Hamani, C. Advances in deep brain stimulation for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder. Expert. Rev. Med. Devices 2023, 20, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koek, R.J.; Roach, J.; Athanasiou, N.; van’t Wout-Frank, M.; Philip, N.S. Neuromodulatory treatments for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 92, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamani, C.; Davidson, B.; Levitt, A.; Meng, Y.; Corchs, F.; Abrahao, A. Patient with posttraumatic stress disorder successfully treated with deep brain stimulation of the medial prefrontal cortex and uncinate fasciculus. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 88, e57–e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reznikov, R.; Bambico, F.R.; Diwan, M.; Raymond, R.J.; Nashed, M.G.; Nobrega, J.N.; Hamani, C. Prefrontal cortex deep brain stimulation improves fear and anxiety-like behavior and reduces basolateral amygdala activity in a preclinical model of posttraumatic stress disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznikov, R.; Hamani, C. Posttraumatic stress disorder: Perspectives for the use of Deep brain stimulation. Neuromodulation 2017, 20, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Pino, J.; Benedetti-Isaac, J.; Ripoll-Cordoba, D.; Camargo, L.; Castillo-Tamara, E.E.; Morales-Asencio, B. Effectiveness of deep brain stimulation on refractory aggression in pediatric patients with autism and severe intellectual disability: Meta-analytic review. BMC Pediatr. 2024, 24, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, F.; Cavallo, M.; Spacca, B.; Pallanti, S.; Tomaiuolo, F.; Pieraccini, F.; Fagiolini, A.; Grandoni, M.; Melani, F.; Zicca, A.; et al. Deep brain stimulation of the anterior limb of the internal capsule may be efficacious for explosive aggressive behaviour. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2016, 94, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, C.V.; Sola, R.G.; Pastor, J.; Pedrosa, M.; Navas, M.; Garcia-Navarrete, E.; Ezquiaga, E.; García-Camba, E. Long-term results of posteromedial hypothalamic deep brain stimulation for patients with resistant aggressiveness. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 119, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzini, A.; Broggi, G.; Cordella, R.; Dones, I.; Messina, G. Deep-brain stimulation for aggressive and disruptive behavior. World Neurosurg. 2013, 80, S29.e11–S29.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti-Isaac, J.; Camargo, L.; Cardenas, F.P.; Lopez, N. Effectiveness of deep brain stimulation in refractory and drug-resistant aggressiveness in autism spectrum disorder. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2023, 102, 102131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti-Isaac, J.C.; Camargo, L.; Gargiulo, P.; López, N. Deep brain stimulation in the posteromedial hypothalamic nuclei in refractory aggressiveness: Post-surgical results of 19 cases. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 24, 977–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti-Isaac, J.C.; Torres-Zambrano, M.; Vargas-Toscano, A.; Perea-Castro, E.; Alcalá-Cerra, G.; Furlanetti, L.L.; Reithmeier, T.; Tierney, T.S.; Anastasopoulos, C.; Fonoff, E.T.; et al. Seizure frequency reduction after posteromedial hypothalamus deep brain stimulation in drug-resistant epilepsy associated with intractable aggressive behavior. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, V.; Fricke, O.; Bührle, C.P.; Lenartz, D.; Maarouf, M.; Treuer, H.; Mai, J.K.; Lehmkuhl, G. DBS in the basolateral amygdala improves symptoms of autism and related self-injurious behavior: A case report and hypothesis on the pathogenesis of the disorder. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 6, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti-Isaac, J.C.; Camargo, L.; Torres Zambrano, M.; Perea-Castro, E.; Castillo-Tamara, E.; Caldichoury, N.; Herrera-Pino, J.; Flórez, Y.; Porto, M.; López, N. Deep brain stimulation may be a viable option for resistant to treatment aggression in children with intellectual disability. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 2010–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar Vidarte, O.A.; Griswold, D.P.; Orozco Mera, J.; Arango Uribe, G.J.; Salcedo, J.C. Deep brain stimulation for severe and intractable aggressive behavior. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2022, 100, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López Ríos, A.L.; Germann, J.; Hutchison, W.D.; Botero Posada, L.F.; Ahunca Velasquez, L.F.; Garcia Jimenez, F.A.; Gloria Escobar, J.M.; Chacon Ruiz Martinez, R.; Hamani, C.; Lebrun, I.; et al. Long-term follow-up on bilateral posterior hypothalamic deep brain stimulation for treating refractory aggressive behavior in a patient with Cri du chat syndrome: Analysis of clinical data, intraoperative microdialysis, and imaging connectomics. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2022, 100, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micieli, R.; Rios, A.L.; Aguilar, R.P.; Posada, L.F.; Hutchison, W.D. Single-unit analysis of the human posterior hypothalamus and red nucleus during deep brain stimulation for aggressivity. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 126, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.R.; Kim, I.H.; Kang, H.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, B.N.; Kim, D.G.; Paek, S.H. Nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation for a patient with self-injurious behavior and autism spectrum disorder: Functional and structural changes of the brain: Report of a case and review of literature. Acta Neurochir. 2017, 159, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harat, M.; Kiec, M.; Rudaś, M.; Birski, M.; Furtak, J. Treating aggression and self-destructive behaviors by stimulating the nucleus accumbens: A case series. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 706166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocco, A.; Baizabal-Carvallo, J.F. Deep brain stimulation for severe secondary stereotypies. Park. Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 1035–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiden, P.; Weigel, D.T.; Loução, R.; Hamisch, C.; Gündüz, E.M.; Ruge, M.I.; Kuhn, J.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Andrade, P. Connectivity in deep brain stimulation for self-injurious behavior: Multiple targets for a common network? Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 958247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maley, J.H.; Alvernia, J.E.; Valle, E.P.; Richardson, D. Deep brain stimulation of the orbitofrontal projections for the treatment of intermittent explosive disorder. Neurosurg. Focus 2010, 29, E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, C.V.; Blasco, G.; García, M.N.; Ezquiaga, E.; Pastor, J.; Vega-Zelaya, L.; Rivas, P.P.; Rodrigo, S.P.; Manzanares, R. Deep brain stimulation for aggressiveness: Long-term follow-up and tractography study of the stimulated brain areas. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 134, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakko, K.; Bjelogrlic-Laakso, N.; Pihlakoski, L.; Lehtimäki, K.; Järventausta, K. Tardive dyskinesia should not be overlooked. J. Child. Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Gong, C.; Wang, B.; Sun, J.; Jiang, Z. Non-invasive brain stimulation for patient with autism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1147327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Disorder | Main Target (s) | Response Rate (%) | Remission Rate (%) | Mean Follow-Up Duration | Main Outcome Measure(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRMDD | mFB, VC/VS, NAc, SCG, BNST, etc. | ~48% | ~35% | 21 months | MADRS, HDRS |
| TROCD | VC/VS, NAc, ALIC, STN, BNST | ~66% | N/A | Up to 24 months | Y-BOCS |
| TRBD | VC/VS, mFB, SCG | ~48% | N/A | Up to 9 months | MADRS, HDRS |
| TRS | sgACC, NAc, habenula, SNr | Variable (~40%) | N/A | Up to 36 months | PANSS, BPRS |
| TRA | NAc, BNST, ACC, STN | Up to 56% (craving) | N/A | Up to 8 years | Craving Scores, Relapse Rate |
| ITS | CM-Pf, GPi, NAc, Vo thalamus | >66% (tic reduction > 50%) | N/A | 12 months (median) | YGTSS |
| TRAN | NAc, SCG, vALIC | Significant BMI increase | N/A | 6–24 months | BMI, QOL, Psychiatric Scales |
| TRPTSD | BLA, mPFC/uncinate fasciculus | >30–100% (case reports) | N/A | Up to 4 years | CAPS |
| RAAID | PMH, other hypothalamic targets | >90% (aggression reduction) | N/A | 42.5 months (mean) | OAS, MOAS |
| Disease/Indication | Device-Related SE(s) | Neurological SE(s) | Psychiatric SE(s) | Other/Procedure-Related SE(s) | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRMDD | ~7–10% (infection/device), battery failure < 5% | Seizure: rare; hemorrhage: very rare | Suicidal ideation: ~1% per 100 person-years | Wound issues | No increased suicide risk |
| TROCD | 5–10% (infection, lead damage/explant) | Seizure: rare; hemorrhage: <2% | New OCD symptoms (rare), suicidality | Dysarthria, paresis | Device can become OCD focus |
| TRBD | Sparse data | Not systematically reported | Hypomania/mania (case reports; reversible) | – | Risk of affective switching |
| TRS | Device infection, hemorrhage (2 cases) | Seizure, confusion, akathisia | Mood lability (esp. withdrawal of meds) | Weight change | Most AEs reversible |
| TRA | Infection, battery depletion | Seizure (very rare), insomnia | Hypomania, anxiety, depression | Device malfunction | SEs often parameter-dependent |
| ITS | Infection: ~18% (higher than other DBS) | Paresthesia, dysarthria, gaze/visual disturbance | Anxiety, depression, memory changes | Hardware malfunction | Compulsive wound picking risk |
| TRAN | | Infection, device discomfort (rare explant) | Transient mood change, wound problems | No major psychiatric worsening | – | No new psychopathology |
| TRPTSD | Not specified | Not specified | Suicidality (case report) | – | Longest follow-up: 4 years |
| RAAID | Infection, device failure, hemorrhage | Hemorrhage (rare), not systematically reported | Not specified (communication limited) | Device removal | Device-related relapse |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khosravi, M. Deep Brain Stimulation in Treatment-Resistant Psychiatric Disorders: Efficacy, Safety, and Future Directions. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111244
Khosravi M. Deep Brain Stimulation in Treatment-Resistant Psychiatric Disorders: Efficacy, Safety, and Future Directions. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(11):1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111244
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhosravi, Mohsen. 2025. "Deep Brain Stimulation in Treatment-Resistant Psychiatric Disorders: Efficacy, Safety, and Future Directions" Brain Sciences 15, no. 11: 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111244
APA StyleKhosravi, M. (2025). Deep Brain Stimulation in Treatment-Resistant Psychiatric Disorders: Efficacy, Safety, and Future Directions. Brain Sciences, 15(11), 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111244







