Therapeutic Advances in Targeting the Amyloid-β Pathway for Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction of AD
1.1. The Aβ Hypothesis
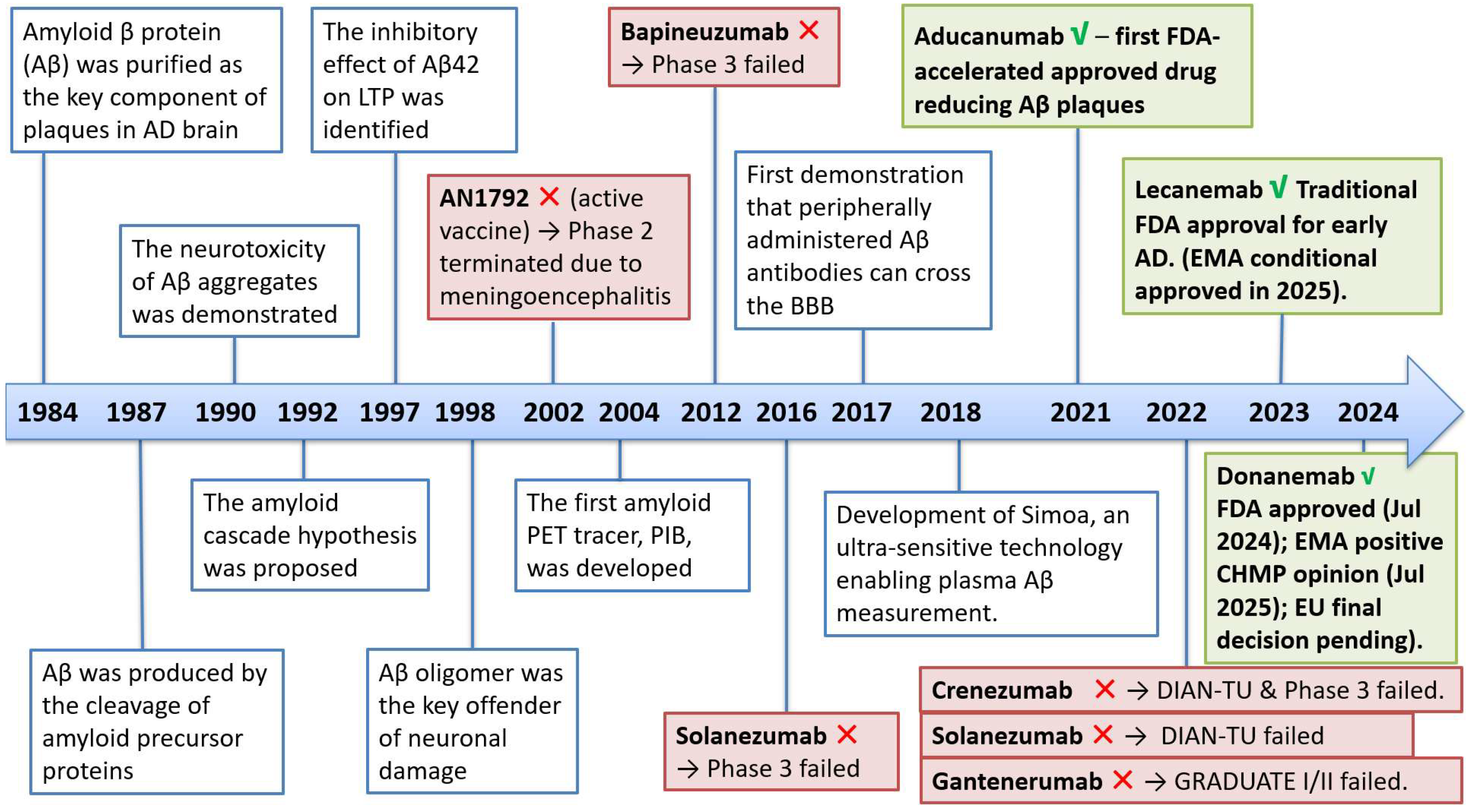
1.1.1. The Development of the Aβ Hypothesis [21]
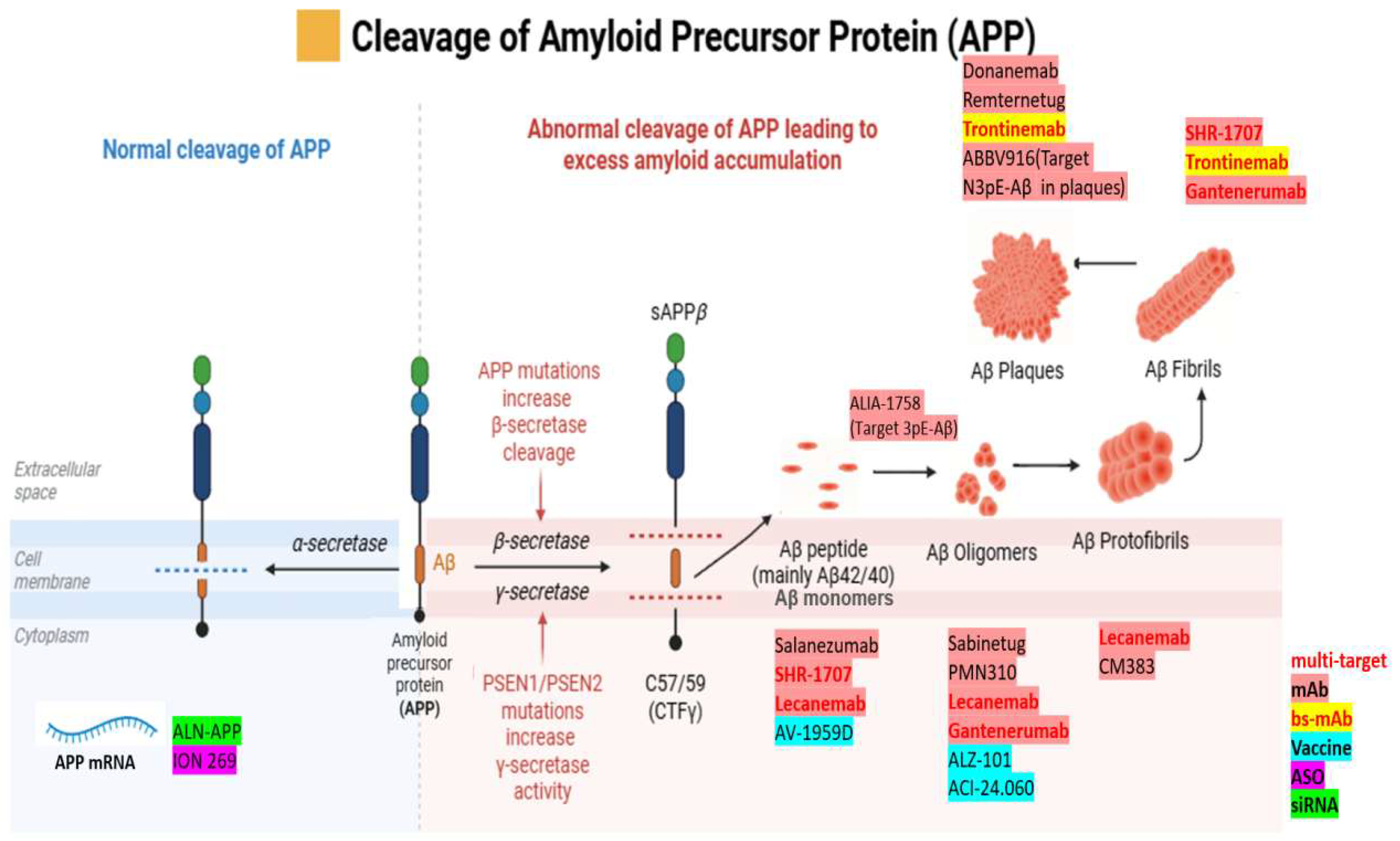
1.1.2. APP Processing: Amyloidogenic and Non-amyloidogenic Pathways
1.1.3. Biomarkers in Clinical Trials and Therapy
2. Small-Molecule Therapeutics in AD: Symptomatic Treatments and Aβ-Targeting Agents
2.1. Agents for Symptomatic Treatment
2.2. β-Secretase (BACE1) Inhibitors
2.3. γ-Secretase Inhibitors/Modulators
3. Small-Molecular Drugs in Human Clinical Trials
3.1. Aβ Aggregation Modulators
3.2. Aβ–Receptor/Synapse Modulators
3.3. Metabolic/Antioxidant Modalities
4. The Advances in Anti-Aβ Biologics Therapeutics
4.1. Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs)
4.2. Vaccine
4.3. Gene Therapy and RNAi
5. Future Perspectives
5.1. The “Next Milestone” of Biologics in Aβ Therapy
5.2. Aβ Pathways for Future Therapies
5.3. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, W.V.; Bonito-Oliva, A.; Sakmar, T.P. Update on Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy and Prevention Strategies. Annu. Rev. Med. 2017, 68, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hock, C.; Konietzko, U.; Streffer, J.R.; Tracy, J.; Signorell, A.; Müller-Tillmanns, B.; Lemke, U.; Henke, K.; Moritz, E.; Garcia, E.; et al. Antibodies against β-Amyloid Slow Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuron 2003, 38, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Institute on Aging and Reagan Institute Working Group on Diagnostic Criteria for the Neuropathological Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Consensus Recommendations for the Postmortem Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 1997, 18, S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näslund, J.; Haroutunian, V.; Mohs, R.; Davis, K.L.; Davies, P.; Greengard, P.; Buxbaum, J.D. Correlation Between Elevated Levels of Amyloid β-Peptide in the Brain and Cognitive Decline. JAMA 2000, 283, 1571–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Götz, J.; Chen, F.; van Dorpe, J.; Nitsch, R.M. Formation of Neurofibrillary Tangles in P301L Tau Transgenic Mice Induced by Aβ42 Fibrils. Science 2001, 293, 1491–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, R.; Mormino, E.; Johnson, K. The Evolution of Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease: Implications for Prevention Trials. Neuron 2014, 84, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Allsop, D. Amyloid deposition as the central event in the aetiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1991, 12, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyreuther, K.; Masters, C.L. Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) and ΒZA4 Amyloid in the Etiology of Alzheimer’s Disease: Precursor—Product Relationships in the Derangement of Neuronal Function. Brain Pathol. 1991, 1, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J. The molecular pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 1991, 6, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Lemaire, H.-G.; Unterbeck, A.; Salbaum, J.M.; Masters, C.L.; Grzeschik, K.-H.; Multhaup, G.; Beyreuther, K.; Müller-Hill, B. The precursor of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature 1987, 325, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardena, S.; Yang, G.; Goldstein, L.S.B. Presenilin controls kinesin-1 and dynein function during APP-vesicle transport in vivo. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 3828–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolata, G. Down Syndrome—Alzheimer’s Linked: Down syndrome adults get Alzheimer-like changes in their brains and many become demented, leading researchers to ask about the connection. Science 1985, 230, 1152–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.-K.; Kuan, Y.-C.; Lin, H.-W.; Hu, C.-J. Clinical trials of new drugs for Alzheimer disease: A 2020–2023 update. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, R.J.; Jamshidi, P.; Plascencia-Villa, G.; Perry, G. The Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis: A Conclusion in Search of Support. Am. J. Pathol. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, B.; Stein, P.; Cavazzoni, P. Approval of aducanumab for Alzheimer disease—The FDA’s perspective. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 1276–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullard, A. FDA approves third anti-amyloid antibody for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2024, 23, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canady, V.A. FDA approves new treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Ment. Health Wkly. 2023, 33, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA Converts Novel Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment to Traditional Approval. 2023. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-converts-novel-alzheimers-disease-treatment-traditional-approval#:~:text=FDA%20Converts%20Novel%20Alzheimer’s%20Disease%20Treatment%20to%20Traditional%20Approval,-Action%20Follows%20Confirmatory&text=Today%2C%20the%20U.S.%20Food%20and,confirmatory%20trial%20verified%20clinical%20benefit (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Kim, B.-H.; Kim, S.; Nam, Y.; Park, Y.H.; Shin, S.M.; Moon, M. Second-generation anti-amyloid monoclonal antibodies for Alzheimer’s disease: Current landscape and future perspectives. Transl. Neurodegener. 2025, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzforum. Cognitive Decline Trips API Trials of BACE Inhibitor. 2019. Available online: https://www.alzforum.org/news/research-news/cognitive-decline-trips-api-trials-bace-inhibitor (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Glenner, G.G.; Wong, C.W. Alzheimer’s disease: Initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1984, 120, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.A.; Higgins, G.A. Alzheimer’s Disease: The Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis. Science 1992, 256, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisoni, G.B.; Altomare, D.; Thal, D.R.; Ribaldi, F.; van der Kant, R.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Blennow, K.; Cummings, J.; van Duijn, C.; Nilsson, P.M.; et al. The probabilistic model of Alzheimer disease: The amyloid hypothesis revised. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2022, 23, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzi, R.E.; Gusella, J.F.; Watkins, P.C.; Bruns, G.A.P.; George-Hyslop, P.S.; Van Keuren, M.L.; Patterson, D.; Pagan, S.; Kurnit, D.M.; Neve, R.L. Amyloid β Protein Gene: cDNA, mRNA Distribution, and Genetic Linkage Near the Alzheimer Locus. Science 1987, 235, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klunk, W.E.; Engler, H.; Nordberg, A.; Wang, Y.; Blomqvist, G.; Holt, D.P.; Bergström, M.; Savitcheva, I.; Huang, G.F.; Estrada, S.; et al. Imaging brain amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease with Pittsburgh Compound-B. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, A.; Kaneko, N.; Villemagne, V.L.; Kato, T.; Doecke, J.; Doré, V.; Fowler, C.; Li, Q.X.; Martins, R.; Rowe, C.; et al. High performance plasma amyloid-β biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2018, 554, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, S.; Koller, M.; Black, R.S.; Jenkins, L.; Griffith, S.G.; Fox, N.C.; Eisner, L.; Kirby, L.; Rovira, M.B.; Forette, F.; et al. Clinical effects of Aβ immunization (AN1792) in patients with AD in an interrupted trial. Neurology 2005, 64, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salloway, S.; Sperling, R.; Fox, N.C.; Blennow, K.; Klunk, W.; Raskind, M.; Sabbagh, M.; Honig, L.S.; Porsteinsson, A.P.; Ferris, S.; et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Bapineuzumab in Mild-to-Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honig, L.S.; Vellas, B.; Woodward, M.; Boada, M.; Bullock, R.; Borrie, M.; Hager, K.; Andreasen, N.; Scarpini, E.; Liu-Seifert, H.; et al. Trial of Solanezumab for Mild Dementia Due to Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloway, S.; Farlow, M.; McDade, E.; Clifford, D.B.; Wang, G.; Llibre-Guerra, J.J.; Hitchcock, J.M.; Mills, S.L.; Santacruz, A.M.; Aschenbrenner, A.J.; et al. A trial of gantenerumab or solanezumab in dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eli Lilly and Company. Lilly Announces Topline Results of Solanezumab Phase 3 Clinical Trial. 2016. Available online: https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lilly-announces-top-line-results-solanezumab-phase-3-clinical (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Bateman, R.J.; Smith, J.; Donohue, M.C.; Delmar, P.; Abbas, R.; Salloway, S.; Wojtowicz, J.; Blennow, K.; Bittner, T.; Black, S.E.; et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Gantenerumab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1862–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citron, M. Alzheimer’s disease: Treatments in discovery and development. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 1055–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, H.L.; Selkoe, D.J. Inflammation and therapeutic vaccination in CNS diseases. Nature 2002, 420, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurdsson, E.M.; Wisniewski, T.; Frangione, B. A safer vaccine for Alzheimer’s disease? Neurobiol. Aging 2002, 23, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R.; Barcikowska, M.; Misicka, A.; Lipkowski, A.W.; Spisacka, S.; Januszewski, S. Ischemic rats as a model in the study of the neurobiological role of human β-amyloid peptide. Time-dependent disappearing diffuse amyloid plaques in brain. Neuroreport 1999, 10, 3615–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, D.; Barbour, R.; Dunn, W.; Gordon, G.; Grajeda, H.; Guido, T.; Hu, K.; Huang, J.; Johnson-Wood, K.; Khan, K.; et al. Immunization with amyloid-β attenuates Alzheimer-disease-like pathology in the PDAPP mouse. Nature 1999, 400, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bard, F.; Cannon, C.; Barbour, R.; Burke, R.-L.; Games, D.; Grajeda, H.; Guido, T.; Hu, K.; Huang, J.; Johnson-Wood, K.; et al. Peripherally administered antibodies against amyloid β-peptide enter the central nervous system and reduce pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janus, C.; Pearson, J.; McLaurin, J.; Mathews, P.M.; Jiang, Y.; Schmidt, S.D.; Chishti, M.A.; Horne, P.; Heslin, D.; French, J.; et al. Aβ peptide immunization reduces behavioural impairment and plaques in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2000, 408, 979–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.; Diamond, D.M.; Gottschall, P.E.; Ugen, K.E.; Dickey, C.; Hardy, J.; Duff, K.; Jantzen, P.; DiCarlo, G.; Wilcock, D.; et al. Aβ peptide vaccination prevents memory loss in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2000, 408, 982–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMattos, R.B.; Bales, K.R.; Cummins, D.J.; Dodart, J.-C.; Paul, S.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Peripheral anti-Aβ antibody alters CNS and plasma Aβ clearance and decreases brain Aβ burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8850–8855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoll, J.A.R.; Wilkinson, D.; Holmes, C.; Steart, P.; Markham, H.; Weller, R.O. Neuropathology of human Alzheimer disease after immunization with amyloid-β peptide: A case report. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granzotto, A.; Sensi, S.L. Once upon a time, the Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 93, 102161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.L.; Hinrich, A.J.; Roman, B.; Norrbom, M.; Rigo, F.; Marr, R.A.; Norstrom, E.M.; Hastings, M.L. Targeting Amyloid-β Precursor Protein, APP, Splicing with Antisense Oligonucleotides Reduces Toxic Amyloid-β Production. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 1539–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampel, H.; Hardy, J.; Blennow, K.; Chen, C.; Perry, G.; Kim, S.H.; Villemagne, V.L.; Aisen, P.; Vendruscolo, M.; Iwatsubo, T.; et al. The Amyloid-beta Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5481–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-W.; Thompson, R.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H. APP processing in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Brain 2011, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roda, A.R.; Serra-Mir, G.; Montoliu-Gaya, L.; Tiessler, L.; Villegas, S. Amyloid-beta peptide and tau protein crosstalk in Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 1666–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Strooper, B.; Saftig, P.; Craessaerts, K.; Vanderstichele, H.; Guhde, G.; Annaert, W.; Von Figura, K.; Van Leuven, F. Deficiency of presenilin-1 inhibits the normal cleavage of amyloid precursor protein. Nature 1998, 391, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisodia, S.S. Beta-amyloid precursor protein cleavage by a membrane-bound protease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 6075–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, K.; Sopher, B.L.; Rydel, R.E.; Begley, J.G.; Pham, D.G.; Martin, G.M.; Fox, M.; Mattson, M.P. Increased activity-regulating and neuroprotective efficacy of α-secretase-derived secreted amyloid precursor protein conferred by a C-terminal heparin-binding domain. J. Neurochem. 1996, 67, 1882–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Goldstein, L.E.; Lahiri, D.K.; Rogers, J.T. Role of the APP Non-Amyloidogenic Signaling Pathway and Targeting α -Secretase as an Alternative Drug Target for Treatment of Alzheimers Disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 2848–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, S.; Jain, S. Aducanumab: A review of the first approved amyloid-targeting antibody for Alzheimer’s disease. Drugs Ther. Perspect. 2022, 38, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisai R&D Management Co., Ltd. Mechanism of Action—Leqembi (Lecanemab-Irmb). 2025. Available online: https://www.leqembihcp.com/about-leqembi/mechanism-of-action (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Lowe, S.L.; Willis, B.A.; Hawdon, A.; Natanegara, F.; Chua, L.; Foster, J.; Shcherbinin, S.; Ardayfio, P.; Sims, J.R. Donanemab (LY3002813) dose-escalation study in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2021, 7, e12112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.; Osse, A.M.L.; Cammann, D.; Powell, J.; Chen, J. Anti-Amyloid Monoclonal Antibodies for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. BioDrugs 2024, 38, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa-Pacha, N.M.; Abdin, S.M.; Omar, H.A.; Alniss, H.; Al-Tel, T.H. BACE1 inhibitors: Current status and future directions in treating Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 339–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-f.; Xu, T.-h.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, Y.-r.; Jiang, Y.; Melcher, K.; Xu, H.E. Amyloid beta: Structure, biology and structure-based therapeutic development. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 1205–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.-B.; Lindholm, K.; Yan, R.; Citron, M.; Xia, W.; Yang, X.-L.; Beach, T.; Sue, L.; Wong, P.; Price, D.; et al. Elevated β-secretase expression and enzymatic activity detected in sporadic Alzheimer disease. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Lindholm, K.; Yang, L.-B.; Yue, X.; Citron, M.; Yan, R.; Beach, T.; Sue, L.; Sabbagh, M.; Cai, H.; et al. Amyloid β peptide load is correlated with increased β-secretase activity in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3632–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, M.; Cole, S.L.; Yasvoina, M.; Zhao, J.; Citron, M.; Berry, R.; Disterhoft, J.F.; Vassar, R. BACE1 gene deletion prevents neuron loss and memory deficits in 5XFAD APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 26, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasugi, N.; Tomita, T.; Hayashi, I.; Tsuruoka, M.; Niimura, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Thinakaran, G.; Iwatsubo, T. The role of presenilin cofactors in the γ-secretase complex. Nature 2003, 422, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberly, W.T.; LaVoie, M.J.; Ostaszewski, B.L.; Ye, W.; Wolfe, M.S.; Selkoe, D.J. γ-Secretase is a membrane protein complex comprised of presenilin, nicastrin, aph-1, and pen-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6382–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, S.F.; Tschirner, S.K.; Steiner, H. Secretases in Alzheimer’s disease: Novel insights into proteolysis of APP and TREM2. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2022, 72, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, R.; Sterling, K.; Song, W. Amyloid β-based therapy for Alzheimer’s disease: Challenges, successes and future. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, S.L.; Doody, R.S.; Mohs, R.C.; Friedhoff, L.T.; Donepezil Study Group. Donepezil improves cognition and global function in Alzheimer disease: A 15-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rösler, M.; Bayer, T.; Anand, R.; Cicin-Sain, A.; Gauthier, S.; Agid, Y.; Dal-Bianco, P.; Stähelin, H.B.; Hartman, R.; Gharabawi, M. Efficacy and safety of rivastigmine in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: International randomised controlled trialCommentary: Another piece of the Alzheimer’s jigsaw. BMJ 1999, 318, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariot, P.N.; Solomon, P.; Morris, J.; Kershaw, P.; Lilienfeld, S.; Ding, C.; Galantamine USA-Study Group. A 5-month, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of galantamine in AD. Neurology 2000, 54, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisberg, B.; Doody, R.; Stöffler, A.; Schmitt, F.; Ferris, S.; Möbius, H.J. Memantine in moderate-to-severe Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhong, R.-j.; Cheng, C.; Li, S.; Le, W.-d. New therapeutics beyond amyloid-β and tau for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, J.R.M.; Resende, R.; Custódio, J.B.A.; Salvador, J.A.R.; Santos, A.E. BACE1 Inhibitors for Alzheimer’s Disease: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2024, 101, S53–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.D.; Li, S.W.; Brunskill, A.P.J.; Chen, X.; Cox, K.; Cumming, J.N.; Forman, M.; Gilbert, E.J.; Hodgson, R.A.; Hyde, L.A.; et al. Discovery of the 3-Imino-1,2,4-thiadiazinane 1,1-Dioxide Derivative Verubecestat (MK-8931)–A β-Site Amyloid Precursor Protein Cleaving Enzyme 1 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 10435–10450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, M.F.; Kost, J.; Tariot, P.N.; Aisen, P.S.; Cummings, J.L.; Vellas, B.; Sur, C.; Mukai, Y.; Voss, T.; Furtek, C.; et al. Randomized trial of verubecestat for mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, J.A.; Shcherbinin, S.; Devous Sr, M.D.; Bragg, S.M.; Selzler, K.J.; Wessels, A.M.; Shering, C.; Mullen, J.; Landry, J.; Andersen, S.W.; et al. Lanabecestat: Neuroimaging results in early symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2021, 7, e12123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henley, D.; Raghavan, N.; Sperling, R.; Aisen, P.; Raman, R.; Romano, G. Preliminary Results of a Trial of Atabecestat in Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1483–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisai Co., Ltd.; Biogen Inc. Eisai and Biogen to Discontinue Phase III Clinical Studies of BACE Inhibitor Elenbecestat in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. 2019. Available online: https://www.eisai.com/news/2019/pdf/enews201965pdf.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Doody, R.S.; Raman, R.; Farlow, M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Vellas, B.; Joffe, S.; Kieburtz, K.; He, F.; Sun, X.; Thomas, R.G.; et al. A phase 3 trial of semagacestat for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coric, V.; Salloway, S.; van Dyck, C.H.; Dubois, B.; Andreasen, N.; Brody, M.; Curtis, C.; Soininen, H.; Thein, S.; Shiovitz, T.; et al. Targeting Prodromal Alzheimer Disease with Avagacestat: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, G.; Fan, X.; Juan, D.; Wenxue, Z.; Sijia, W.; Meinei, C.; Xiaolong, D.; Yiming, Q. The manipulator behind “Scissors”: γ -secretase and its modulators in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2025, 17, 1637671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushakra, S.; Porsteinsson, A.P.; Sabbagh, M.; Watson, D.; Power, A.; Liang, E.; MacSweeney, E.; Boada, M.; Flint, S.; McLaine, R.; et al. APOLLOE4 Phase 3 study of oral ALZ-801/valiltramiprosate in APOE ε4/ε4 homozygotes with early Alzheimer’s disease: Trial design and baseline characteristics. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2024, 10, e12498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, J.A.; Abushakra, S.; Blennow, K.; Reiman, E.M.; Hort, J.; Prins, N.D.; Sheardova, K.; Kesslak, P.; Shen, L.; Zhu, X.; et al. Effects of Oral ALZ-801/Valiltramiprosate on Plasma Biomarkers, Brain Hippocampal Volume, and Cognition: Results of 2-Year Single-Arm, Open-Label, Phase 2 Trial in APOE4 Carriers with Early Alzheimer’s Disease. Drugs 2024, 84, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Groen, T.; Schemmert, S.; Brener, O.; Gremer, L.; Ziehm, T.; Tusche, M.; Nagel-Steger, L.; Kadish, I.; Schartmann, E.; Elfgen, A.; et al. The Aβ oligomer eliminating D-enantiomeric peptide RD2 improves cognition without changing plaque pathology. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzsche, J.; Cosma, N.C.; Kauselmann, G.; Fenski, F.; Bieniek, C.; Bujnicki, T.; Pils, M.; Bannach, O.; Willbold, D.; Peters, O. Oral PRI-002 treatment in patients with MCI or mild AD: A randomized, double-blind phase 1b trial. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meglio, M. Synapse-Targeting Agent ALX-001 Ready for Phase 2 Following Early-Stage Progress. 2024. Available online: https://www.neurologylive.com/view/synapse-targeting-agent-alx-001-ready-phase-2-early-stage-progress?utm_source (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Pencina, K.M.; Lavu, S.; Dos Santos, M.; Beleva, Y.M.; Cheng, M.; Livingston, D.; Bhasin, S. MIB-626, an Oral Formulation of a Microcrystalline Unique Polymorph of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, Increases Circulating Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide and its Metabolome in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2023, 78, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knepper, P.A.; Pfahler, N.; Aman, S.; Zaparackas, Z. The Effect of Resveratrol, Quercetin, and Curcumin (RQC) on Superactivated Platelets (SAPs) in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2024, 65, 5700. [Google Scholar]
- National Library of Medicine (NLoM). RQC for the Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease and Retinal Amyloid-β. 2024. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06470061?rank=3&term=AREA%5BBasicSearch%5D(resveratrol%20alzheimer%27s)&utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Synapse. RO-7269162—Drug Targets, Indications, R&D Status and Clinical Trials. Available online: http://synapse.patsnap.com/drug/1f06948da17c4690b137c86452ec4870?utm_source= (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Cummings, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lee, G.; Zhong, K.; Fonseca, J.; Cheng, F. Alzheimer’s disease drug development pipeline: 2023. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2023, 9, e12385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevigny, J.; Chiao, P.; Bussière, T.; Weinreb, P.H.; Williams, L.; Maier, M.; Dunstan, R.; Salloway, S.; Chen, T.; Ling, Y.; et al. The antibody aducanumab reduces Aβ plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2016, 537, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitek, G.E.; Decourt, B.; Sabbagh, M.N. Lecanemab (BAN2401): An anti-beta-amyloid monoclonal antibody for the treatment of Alzheimer disease. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2023, 32, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovici, G.D.; Selkoe, D.J.; Schindler, S.E.; Aisen, P.; Apostolova, L.G.; Atri, A.; Greenberg, S.M.; Hendrix, S.B.; Petersen, R.C.; Weiner, M.; et al. Donanemab: Appropriate use recommendations. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2025, 12, 100150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.; Rasool, A.; Shaheryar, M.; Sarfraz, A.; Sarfraz, Z.; Robles-Velasco, K.; Cherrez-Ojeda, I. Donanemab for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trials. Healthcare 2022, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzforum. Remternetug. 2025. Available online: https://www.alzforum.org/therapeutics/remternetug (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- Bateman, R.J.; Cummings, J.; Schobel, S.; Salloway, S.; Vellas, B.; Boada, M.; Black, S.E.; Blennow, K.; Fontoura, P.; Klein, G.; et al. Gantenerumab: An anti-amyloid monoclonal antibody with potential disease-modifying effects in early Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, B.A.; Sundell, K.; Lachno, D.R.; Ferguson-Sells, L.R.; Case, M.G.; Holdridge, K.; DeMattos, R.B.; Raskin, J.; Siemers, E.R.; Dean, R.A. Central pharmacodynamic activity of solanezumab in mild Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2018, 4, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krafft, G.A.; Jerecic, J.; Siemers, E.; Cline, E.N. ACU193: An Immunotherapeutic Poised to Test the Amyloid β Oligomer Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 848215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemers, E.; Feaster, T.; Sethuraman, G.; Sundell, K.; Skljarevski, V.; Cline, E.N.; Zhang, H.; Jerecic, J.; Honig, L.S.; Salloway, S.; et al. INTERCEPT-AD, a phase 1 study of intravenous sabirnetug in participants with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 2025, 12, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qiu, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a single intravenous dose of SHR-1707 in healthy adult subjects: Two randomized, double-blind, single-ascending-dose, phase 1 studies. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, S.; Hu, Y. Current Anti-Amyloid-β Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment: From Clinical Research to Nanomedicine. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 7825–7845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Library of Medicine. A study to Assess Safety of ABBV-916 and How Intravenous ABBV-916 Moves Through the Body and Affects Brain Amyloid Plaque Clearance in Adult Participants Aged 50–90 Years with Early Alzheimer’s Disease (NCT05291234); NLOF: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05291234 (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Davtyan, H.; Ghochikyan, A.; Petrushina, I.; Hovakimyan, A.; Davtyan, A.; Poghosyan, A.; Marleau, A.M.; Movsesyan, N.; Kiyatkin, A.; Rasool, S.; et al. Immunogenicity, Efficacy, Safety, and Mechanism of Action of Epitope Vaccine (Lu AF20513) for Alzheimer’s Disease: Prelude to a Clinical Trial. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 4923–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Association, A.s. Active immunotherapy, ACI-24.060, induces anti-Abeta antibodies with binding profiles mirroring clinically validated monoclonal antibodies. In Proceedings of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference 2024, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 30 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, S.; Ducharme, S.; Brosch, J.R.; Vijverberg, E.G.B.; Sostelly, A.; Goteti, S.; Farrugia, L.; Avbersek, A.; Kaspar, C.; Mummery, C.J. Single ascending dose results from an ongoing Phase 1 study of mivelsiran (ALN-APP), the first investigational RNA interference therapeutic targeting amyloid precursor protein for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, e084521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumalai, S.; Patani, R.; Hung, C. Therapeutic potential of APP antisense oligonucleotides for Alzheimer’s disease and down syndrome-related Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2024, 19, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MedPath. A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Trial to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of ALIA-1758 Following Single Ascending Doses in Healthy Participants (NCT06406348). 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06406348?rank=1 (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Petrushina, I.; Hovakimyan, A.; Harahap-Carrillo, I.S.; Davtyan, H.; Antonyan, T.; Chailyan, G.; Kazarian, K.; Antonenko, M.; Jullienne, A.; Hamer, M.M.; et al. Characterization and preclinical evaluation of the cGMP grade DNA based vaccine, AV-1959D to enter the first-in-human clinical trials. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 139, 104823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. A Study of CM383 in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease (NCT06619613); NLOF: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06619613 (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Sandberg, A.; Luheshi, L.M.; Söllvander, S.; de Barros, T.P.; Macao, B.; Knowles, T.P.J.; Biverstål, H.; Lendel, C.; Ekholm-Petterson, F.; Dubnovitsky, A.; et al. Stabilization of neurotoxic Alzheimer amyloid-β oligomers by protein engineering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15595–15600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetterberg, H.; Rinne, J.O.; Sandberg, A.; Lovró, Z.; Scheinin, M.; Pierrou, S.; Harting, K. Phase 1b trial on the safety, tolerability and immunogenicity of anti-amyloid vaccine ALZ-101 in subjects with MCI or mild AD. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, e095440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. A Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of ION269 in Participants with Down Syndrome at Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease (NCT06673069); NLOF: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06673069 (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Gibbs, E.; Silverman, J.M.; Zhao, B.; Peng, X.; Wang, J.; Wellington, C.L.; Mackenzie, I.R.; Plotkin, S.S.; Kaplan, J.M.; Cashman, N.R. A Rationally Designed Humanized Antibody Selective for Amyloid Beta Oligomers in Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doody, R.S.; Thomas, R.G.; Farlow, M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Vellas, B.; Joffe, S.; Kieburtz, K.; Raman, R.; Sun, X.; Aisen, P.S.; et al. Phase 3 trials of solanezumab for mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, R.; Rinne, J.O.; Boada, M.; Katayama, S.; Scheltens, P.; Vellas, B.; Tuchman, M.; Gass, A.; Fiebach, J.B.; Hill, D.; et al. Bapineuzumab for mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease in two global, randomized, phase 3 trials. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2016, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowitzki, S.; Bittner, T.; Sink, K.M.; Mackey, H.; Rabe, C.; Honig, L.S.; Cassetta, E.; Woodward, M.; Boada, M.; van Dyck, C.H. Evaluating the safety and efficacy of crenezumab vs placebo in adults with early Alzheimer disease: Two phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled trials. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withington, C.G.; Turner, R.S. Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities with anti-amyloid antibodies for the treatment of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 862369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Elhage, A.; Cho, M.; Apostolova, L.G.; Nicoll, J.A.R.; Atri, A. Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA): Radiological, biological and clinical characteristics. Brain 2023, 146, 4414–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, S.; Merrick, R.; Milne, R.; Brayne, C. Aducanumab for Alzheimer’s disease? BMJ 2021, 374, n1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero, J.; Williams, L.; Stella, H.; Leitermann, K.; Mikulskis, A.; O’Gorman, J.; Sevigny, J. First-in-human, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-dose escalation study of aducanumab (BIIB037) in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2016, 2, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- University of Zurich. Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Research: Approval of First Drug to Slow Disease Progression. 2021. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20211117041052/https://www.media.uzh.ch/en/Press-Releases/2021/Approval.html (accessed on 17 November 2021).
- Sevigny, J.; Chiao, P.; Williams, L.; Chen, T.; Ling, Y.; O’Gorman, J.; Hock, C.; Nitsch, R.M.; Sandrock, A. O4-04-05: Aducanumab (BIIB037), an anti-amyloid beta monoclonal antibody, in patients with prodromal or mild Alzheimer’s disease: Interim results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1b study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2015, 11, P277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlawish, J. If the FDA Approves Biogen’s Alzheimer’s Treatment, I Won’t Prescribe It. 2021. Available online: https://www.statnews.com/2021/05/30/if-the-fda-approves-biogens-alzheimers-treatment-i-wont-prescribe-it/ (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Viglietta, V.; O’Gorman, J.; Williams, L.; Tian, Y.; Sandrock, A.; Doody, R.; Salloway, S.; Barkhof, F.; Vellas, B.; Sano, M.; et al. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Studies to Evaluate Treatment with Aducanumab (BIIB037) in Patients with Early Alzheimer’s Disease: Phase 3 Study Design (S1.003). Neurology 2016, 86, S1.003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BrightFocus, F. Alzheimer’s Drug Aduhelm to be Discontinued. BrightFocus News. 2024. Available online: https://www.brightfocus.org/news/alzheimers-drug-aduhelm-to-be-discontinued/ (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Englund, H.; Sehlin, D.; Johansson, A.-S.; Nilsson, L.N.G.; Gellerfors, P.; Paulie, S.; Lannfelt, L.; Pettersson, F.E. Sensitive ELISA detection of amyloid-β protofibrils in biological samples. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logovinsky, V.; Satlin, A.; Lai, R.; Swanson, C.; Kaplow, J.; Osswald, G.; Basun, H.; Lannfelt, L. Safety and tolerability of BAN2401—A clinical study in Alzheimer’s disease with a protofibril selective Aβ antibody. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2016, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, C.J.; Zhang, Y.; Dhadda, S.; Wang, J.; Kaplow, J.; Lai, R.Y.K.; Lannfelt, L.; Bradley, H.; Rabe, M.; Koyama, A.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, phase 2b proof-of-concept clinical trial in early Alzheimer’s disease with lecanemab, an anti-Aβ protofibril antibody. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, C.H.v.; Swanson, C.J.; Aisen, P.; Bateman, R.J.; Chen, C.; Gee, M.; Kanekiyo, M.; Li, D.; Reyderman, L.; Cohen, S.; et al. Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amano, A.; Sanjo, N.; Araki, W.; Anraku, Y.; Nakakido, M.; Matsubara, E.; Tomiyama, T.; Nagata, T.; Tsumoto, K.; Kataoka, K.; et al. Peripheral administration of nanomicelle-encapsulated anti-Aβ oligomer fragment antibody reduces various toxic Aβ species in the brain. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhaya, A.R.; Kosterin, I.; Kumar, S.; von Arnim, C.A.F.; Yamaguchi, H.; Fändrich, M.; Walter, J.; Thal, D.R. Biochemical stages of amyloid-β peptide aggregation and accumulation in the human brain and their association with symptomatic and pathologically preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2014, 137, 887–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, S.L.; Evans, C.D.; Shcherbinin, S.; Cheng, Y.J.; Willis, B.A.; Gueorguieva, I.; Lo, A.C.; Fleisher, A.S.; Dage, J.L.; Ardayfio, P.; et al. Donanemab (LY3002813) Phase 1b Study in Alzheimer’s Disease: Rapid and Sustained Reduction of Brain Amyloid Measured by Florbetapir F18 Imaging. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 8, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintun, M.A.; Lo, A.C.; Evans, C.D.; Wessels, A.M.; Ardayfio, P.A.; Andersen, S.W.; Shcherbinin, S.; Sparks, J.; Sims, J.R.; Brys, M.; et al. Donanemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1691–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherbinin, S.; Evans, C.D.; Lu, M.; Andersen, S.W.; Pontecorvo, M.J.; Willis, B.A.; Gueorguieva, I.; Hauck, P.M.; Brooks, D.A.; Mintun, M.A.; et al. Association of Amyloid Reduction After Donanemab Treatment With Tau Pathology and Clinical Outcomes: The TRAILBLAZER-ALZ Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohrmann, B.; Baumann, K.; Benz, J.; Gerber, F.; Huber, W.; Knoflach, F.; Messer, J.; Oroszlan, K.; Rauchenberger, R.; Richter, W.F.; et al. Gantenerumab: A Novel Human Anti-Aβ Antibody Demonstrates Sustained Cerebral Amyloid-β Binding and Elicits Cell-Mediated Removal of Human Amyloid-β. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 28, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrowitzki, S.; Deptula, D.; Thurfjell, L.; Barkhof, F.; Bohrmann, B.; Brooks, D.J.; Klunk, W.E.; Ashford, E.; Yoo, K.; Xu, Z.-X.; et al. Mechanism of Amyloid Removal in Patients With Alzheimer Disease Treated With Gantenerumab. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowitzki, S.; Lasser, R.A.; Dorflinger, E.; Scheltens, P.; Barkhof, F.; Nikolcheva, T.; Ashford, E.; Retout, S.; Hofmann, C.; Delmar, P.; et al. A phase III randomized trial of gantenerumab in prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G.; Delmar, P.; Voyle, N.; Rehal, S.; Hofmann, C.; Abi-Saab, D.; Andjelkovic, M.; Ristic, S.; Wang, G.; Bateman, R.; et al. Gantenerumab reduces amyloid-β plaques in patients with prodromal to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: A PET substudy interim analysis. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2019, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G.; Delmar, P.; Kerchner, G.A.; Hofmann, C.; Abi-Saab, D.; Davis, A.; Voyle, N.; Baudler, M.; Fontoura, P.; Doody, R. Thirty-Six-Month Amyloid Positron Emission Tomography Results Show Continued Reduction in Amyloid Burden with Subcutaneous Gantenerumab. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 8, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, H.P.; Schumacher, V.; Schäfer, M.; Imhof-Jung, S.; Freskgård, P.-O.; Brady, K.; Hofmann, C.; Rüger, P.; Schlothauer, T.; Göpfert, U.; et al. Delivery of the Brainshuttle™ amyloid-beta antibody fusion trontinemab to non-human primate brain and projected efficacious dose regimens in humans. mAbs 2023, 15, 2261509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benilova, I.; Karran, E.; De Strooper, B. The toxic Aβ oligomer and Alzheimer’s disease: An emperor in need of clothes. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Fu, X.; Quan, S.; Ren, Z.; Chu, C.; Jia, L. Amyloid-β-targeted therapies for Alzheimer’s disease: Currently and in the future. Ageing Neurodegener. Dis. 2023, 3, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Vukicevic, M.; Fiorini, E.; Siegert, S.; Carpintero, R.; Rincon-Restrepo, M.; Lopez-Deber, P.; Piot, N.; Ayer, M.; Rentero, I.; Babolin, C.; et al. An amyloid beta vaccine that safely drives immunity to a key pathological species in Alzheimer’s disease: Pyroglutamate amyloid beta. Brain Commun. 2022, 4, fcac022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Shi, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, R.; Wang, H.; Chen, H. Immunotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease: Targeting β-amyloid and beyond. Transl. Neurodegener. 2022, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, I.; Rovira, M.B.; Guerra, M.L.S.; Rey, M.J.; Costa-Jussá, F. Neuropathology and pathogenesis of encephalitis following amyloid β immunization in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol. 2004, 14, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellas, B.; Black, R.; Thal, L.J.; Fox, N.C.; Daniels, M.; McLennan, G.; Tompkins, C.; Leibman, C.; Pomfret, M.; Grundman, M. Long-term follow-up of patients immunized with AN1792: Reduced functional decline in antibody responders. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2009, 6, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winblad, B.; Andreasen, N.; Minthon, L.; Floesser, A.; Imbert, G.; Dumortier, T.; Maguire, R.P.; Blennow, K.; Lundmark, J.; Staufenbiel, M.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and antibody response of active Aβ immunotherapy with CAD106 in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, first-in-human study. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.B.; Bhardwaj, S.; Roychoudhury, S.; Kumar, D.; Alexiou, A.; Kumar, P.; Ambasta, R.K.; Prasher, P.; Shukla, S.; Upadhye, V.; et al. Immunotherapy for Alzheimer’s Disease: Current Scenario and Future Perspectives. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 8, 534–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.J.; Dickson, S.P.; Wang, P.N.; Chiu, M.J.; Huang, C.C.; Chang, C.C.; Liu, H.; Hendrix, S.B.; Dodart, J.C.; Verma, A.; et al. Safety, tolerability, immunogenicity, and efficacy of UB-311 in participants with mild Alzheimer’s disease: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2a study. EBioMedicine 2023, 94, 104665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.L.; Zhou, Y.; Lee, G.; Zhong, K.; Fonseca, J.; Leisgang-Osse, A.M.; Cheng, F. Alzheimer’s disease drug development pipeline: 2025. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2025, 11, e70098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movsesyan, N.; Ghochikyan, A.; Mkrtichyan, M.; Petrushina, I.; Davtyan, H.; Olkhanud, P.B.; Head, E.; Biragyn, A.; Cribbs, D.H.; Agadjanyan, M.G. Reducing AD-like pathology in 3xTg-AD mouse model by DNA epitope vaccine—A novel immunotherapeutic strategy. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derhovanessian, E.; Solana, R.; Larbi, A.; Pawelec, G. Immunity, ageing and cancer. Immun. Ageing 2008, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davtyan, H.; Ghochikyan, A.; Petrushina, I.; Hovakimyan, A.; Davtyan, A.; Cribbs, D.H.; Agadjanyan, M.G. The MultiTEP platform-based Alzheimer’s disease epitope vaccine activates a broad repertoire of T helper cells in nonhuman primates. Alzheimers Dement. 2014, 10, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davtyan, H.; Hovakimyan, A.; Zagorski, K.; Davtyan, A.; Petrushina, I.; Agdashian, D.; Murthy, V.; Cribbs, D.H.; Agadjanyan, M.G.; Ghochikyan, A. BTX AgilePulse TM system is an effective electroporation device for intramuscular and intradermal delivery of DNA vaccine. Curr. Gene Ther. 2014, 14, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinicaltrials.gov. A Phase I, Randomized, Double-Blind Study to Evaluate Safety and Tolerability of Amyloid-β Vaccine, AV-1959D, in Patients with Early Alzheimer’s Disease. 2023. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05642429 (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Vassilakopoulou, V.; Karachaliou, C.-E.; Evangelou, A.; Zikos, C.; Livaniou, E. Peptide-Based Vaccines for Neurodegenerative Diseases: Recent Endeavors and Future Perspectives. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setten, R.L.; Rossi, J.J.; Han, S.-p. The current state and future directions of RNAi-based therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 421–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfrum, C.; Shi, S.; Jayaprakash, K.N.; Jayaraman, M.; Wang, G.; Pandey, R.K.; Rajeev, K.G.; Nakayama, T.; Charrise, K.; Ndungo, E.M.; et al. Mechanisms and optimization of in vivo delivery of lipophilic siRNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.M.; Nair, J.K.; Janas, M.M.; Anglero-Rodriguez, Y.I.; Dang, L.T.H.; Peng, H.; Theile, C.S.; Castellanos-Rizaldos, E.; Brown, C.; Foster, D.; et al. Expanding RNAi therapeutics to extrahepatic tissues with lipophilic conjugates. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinicaltrials.gov. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Single Ascending Dose and Open-Label Multi-Dose Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Intrathecally Administered ALN-APP in Adult Patients with Early-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease (EOAD). 2023. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05231785 (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Alnylam and Regeneron Report Positive Interim Phase 1 Clinical Data on ALN-APP, an Investigational RNAi Therap. 2023. Available online: https://investors.alnylam.com/press-release?id=27441 (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Teunissen, C.E.; Kolster, R.; Triana-Baltzer, G.; Janelidze, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Kolb, H.C. Plasma p-tau immunoassays in clinical research for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 21, e14397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremani, M.; Leon, R.; Smith, E.E.; Ismail, Z. Exploring the association between mild behavioral impairment and plasma p-tau217: Implications for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2025, 17, e70119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha Rao, M.; David Weisman, M. ARIA with Monoclonal Antibody Treatments for Alzheimer Disease. 2025. Available online: https://www.neurologylive.com/view/aria-with-monoclonal-antibody-treatments-for-alzheimer-disease? (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Niazi, S.K. Non-Invasive Drug Delivery across the Blood—Brain Barrier: A Prospective Analysis. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Shen, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, Z. Biologics as Therapeutical Agents Under Perspective Clinical Studies for Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2025, 30, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.-G.; Shen, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.-W.; Zhao, R.-C.; Zhang, T.-L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X. Nucleic acid drug vectors for diagnosis and treatment of brain diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Agent | Route | Mechanism of Action | Clinical Status (2025) | Reported Efficiency | ClinicalTrials.gov ID | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALX-001 | Oral | Blocks Aβ–mGluR5 interaction, prevents synapse loss | Phase 1b/2 ongoing | Improved synaptic biomarkers, early safety data | NCT05804383 | [85] |
| RD2 or PRI-002 | Oral | Stabilizes Aβ42 monomers, prevents oligomerization | Phase 1/2 ongoing | Preclinical efficacy; early human safety | NCT04711486 | [83,84] |
| Vallitramiprosate (ALZ-801) | Oral | Homotaurine prodrug, inhibits Aβ42 oligomerization | Phase 3 (APOE4/4 AD, ongoing) | Phase 2 showed biomarker benefit; Phase 3 readout 2025 | NCT04770220 | [81,82] |
| MIB-626 (NAD+ booster) | Oral | Sirtuin-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide stimulator to enhance alpha-secretase | Phase 2 ongoing | Early biomarker effects | NCT05040321 | [86,90] |
| RQC (Resveratrol Quinone Conjugate) | Oral | Antioxidant + anti-amyloid activity | Phase 1 ongoing | Preclinical efficacy | NCT06470061 | [87,88] |
| RO7269162 (Roche) | Oral | Modulator of amyloid/tau pathways (MOA undisclosed) | Phase 1 ongoing | None yet | NCT06076723 | [89] |
| Program (Canonical) | Modality | Prevention_or_Treatment and Disease Stage | Primary Target/Epitope | Trial_IDs (NCT No.) | Trial_Status and Regulatory_Status | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 3 | ||||||
| Lecanemab | Humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody (IV) | Treatment of early symptomatic AD (MCI/mild dementia); separate prevention in preclinical amyloid+ individuals | Aβ protofibrils (soluble aggregates) | NCT03887455 (CLARITY AD, P3); NCT04468659 (AHEAD 3-45, P3 prevention) | FDA approved (US, July 2023); EU marketing authorisation (April 2025); OLE/real-world and prevention trials ongoing | [55,92] |
| Donanemab | Humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody (monthly IV) | Treatment of early symptomatic AD; separate prevention in preclinical amyloid+ individuals | Pyroglutamate Aβ at position 3 (pGlu3-Aβ) on plaques | NCT04437511 (TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2, P3); NCT05026866 (TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 3, prevention) | FDA approved (US, July 2024); EU CHMP positive opinion (July 2025), EC decision pending (August 2025) | [93,94] |
| Remternetug | Humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody (IV) | Treatment of early symptomatic AD | pGlu3-Aβ (N3pE-Aβ) on plaques | NCT05463731 (TRAILRUNNER-ALZ 1, P2); NCT06653153 (TRAILRUNNER-ALZ 3, P3) | Phase 3 active; no marketing approvals | [57,95] |
| Gantenerumab | Human IgG1 monoclonal antibody (subcutaneous) | Treatment of early symptomatic AD | Conformational epitope spanning Aβ N-terminus + mid-region in fibrils/plaques | NCT03444870 (GRADUATE I, P3); NCT03443973 (GRADUATE II, P3) | Phase 3 (GRADUATE I and II, 2022): failed primary endpoints. Development discontinued; no approvals | [31,57,96] |
| Solanezumab | Humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody (IV) | Treatment trials in mild-to-moderate AD; prevention in preclinical amyloid + older adults (A4) | Aβ mid-domain; monomer-preferring | NCT00905372/73 (EXPEDITION 1/2, P3); NCT01900665 (EXPEDITION 3, P3); NCT02008357 (A4 prevention, P3) | Phase 2/3: autosomal-dominant AD trials ongoing; AD efficacy stopped; no approvals | [30,97] |
| Trontinemab | Bispecific mAb with transferrin-receptor ‘Brainshuttle’ (IV) | Treatment of early symptomatic AD | Aβ fibrils/plaques + transferrin receptor for blood–brain barrier (BBB) transport | NCT04639050 (P1b/2) | Phase 1b/2 multiple-ascending dose; Phase 2 active (China/Australia); no approvals | |
| Phase 2 | ||||||
| Sabirnetug ACU193 | Humanized monoclonal antibody (IV) | Treatment of early symptomatic AD | Aβ oligomers (AβO) (globular soluble species) | NCT06335173 (INTERCEPT-AD, P2); NCT04931459 (P1 completed) | Phase 2 randomized DBPC ongoing; no approvals; FDA Fast Track (2022) | [98,99] |
| SHR-1707 | Humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody (IV) | Treatment of early symptomatic AD (MCI/mild AD) | Aβ fibrils + monomers | NCT04973189 (retrospectively registered on 21 July 2021) NCT04745104 (registered on 6 February 2021) | Phase 1 and 1b completed; Phase 2 planned; no approvals; development ongoing. | [100] |
| ABBV-916 | Humanized monoclonal antibody (IV) | Treatment of early AD | N3pE-Aβ (pyroglutamate-Aβ) in plaques | NCT05291234 (Phase 2) | Phase 2 started August 2022 (active–not recruiting; est. completion October 2025); no approvals; development ongoing. | [101,102] |
| ACI-24.060 | Liposomal peptide vaccine (active Aβ immunization) | Treatment of prodromal/early AD; separate Down syndrome cohorts | Misfolded Aβ; induces antibodies to oligomers and pGlu-Aβ | NCT05462106 (ABATE, P1b/2) | Phase 1b/2 ongoing; FDA Fast Track; promising preclinical/early clinical results; not discontinued | [103,104] |
| Phase 1 | ||||||
| ALN-APP | RNA interference (siRNA) delivered intrathecally | Treatment; early symptomatic AD (dose-finding) | APP mRNA | NCT05231785 (Phase 1) | Phase 1 ongoing (active–recruiting; single and multiple dose); no approvals; development ongoing. | [105,106] |
| ALIA-1758 | Anti-pGlu3-Aβ monoclonal antibody with BBB-shuttle (IV/SC) | Therapeutic; early AD (future patient studies) | Aβ aggregates; TfR-mediated BBB transport | NCT06406348 (Phase 1 healthy volunteers) | Phase 1 completed (HVs, May 2024–April 2025; confirmed July 2025); no approvals; development ongoing under AbbVie. | [107] |
| AV-1959D | DNA vaccine (plasmid) | Treatment of early AD/MCI (dose-escalation) | Aβ1-11 N-terminal epitope (B-cell) | NCT05642429 (Phase 1) | Phase 1 completed in HVs; Phase 1b ongoing in AD patients. no approvals | [108] |
| CM383 | Humanized monoclonal antibody (IV) | Treatment of MCI due to AD/mild AD | Aβ (reported) | NCT06619613 (Phase 1b) | Phase 1 ongoing (HVs; single ascending dose RCT, May 2024–est. June 2025); no approvals | [109] |
| ALZ-101 | Peptide vaccine (AβO-selective) | Treatment of early AD | Aβ oligomers (oligomer-specific) | NCT05328115 (Phase 1b) | Phase 1b completed (mild AD/MCI); safety and immunogenicity endpoints met; no ARIA-E/meningoencephalitis; no approvals; early clinical stage | [110,111] |
| ION269 | Antisense oligonucleotide (intrathecal) | Treatment; early AD | APP mRNA | NCT06673069 (Phase 1/2a) | Phase 1b ongoing (active–recruiting, started December 2024; est. completion March 2027); no approvals; early clinical development | [112] |
| PMN310 | Humanized monoclonal antibody (IV) | Treatment of early AD | Aβ oligomers (AβO) | NCT06105528 (P1a HV); NCT06750432 (P1b AD) | Phase 1b (PRECISE-AD) ongoing (early AD, started 2025); no approvals; development ongoing | [113] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, X.; Zhu, Z. Therapeutic Advances in Targeting the Amyloid-β Pathway for Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101101
Zhang B, Li Y, Li H, Shen X, Zhu Z. Therapeutic Advances in Targeting the Amyloid-β Pathway for Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(10):1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101101
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Beiyu, Yunan Li, Huan Li, Xinai Shen, and Zheying Zhu. 2025. "Therapeutic Advances in Targeting the Amyloid-β Pathway for Alzheimer’s Disease" Brain Sciences 15, no. 10: 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101101
APA StyleZhang, B., Li, Y., Li, H., Shen, X., & Zhu, Z. (2025). Therapeutic Advances in Targeting the Amyloid-β Pathway for Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sciences, 15(10), 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101101






