Speech Production Intelligibility Is Associated with Speech Recognition in Adult Cochlear Implant Users
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Auditory Feedback Influences Speech Production
1.2. Phonological Processing for Speech Perception and Production
1.3. Acoustic and Perceptual Measures of Speech Production in CI Users and Their Relation to Speech Perception
1.4. The Current Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants: Cochlear Implant Users
2.2. Participants: Normal Hearing Listeners
2.3. Speech Production: Word Reading and Acoustic Analysis
2.3.1. Materials
2.3.2. Procedure
2.3.3. Acoustic Analysis
2.4. Intelligibility Ratings of Cochlear Implant Users’ Speech
2.4.1. Materials
2.4.2. Procedure
2.5. Speech Perception Tasks (Outcome Measures)
2.5.1. Phonological Processing: Word and Nonword Reading Efficiency
2.5.2. Sentence Recognition Accuracy
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
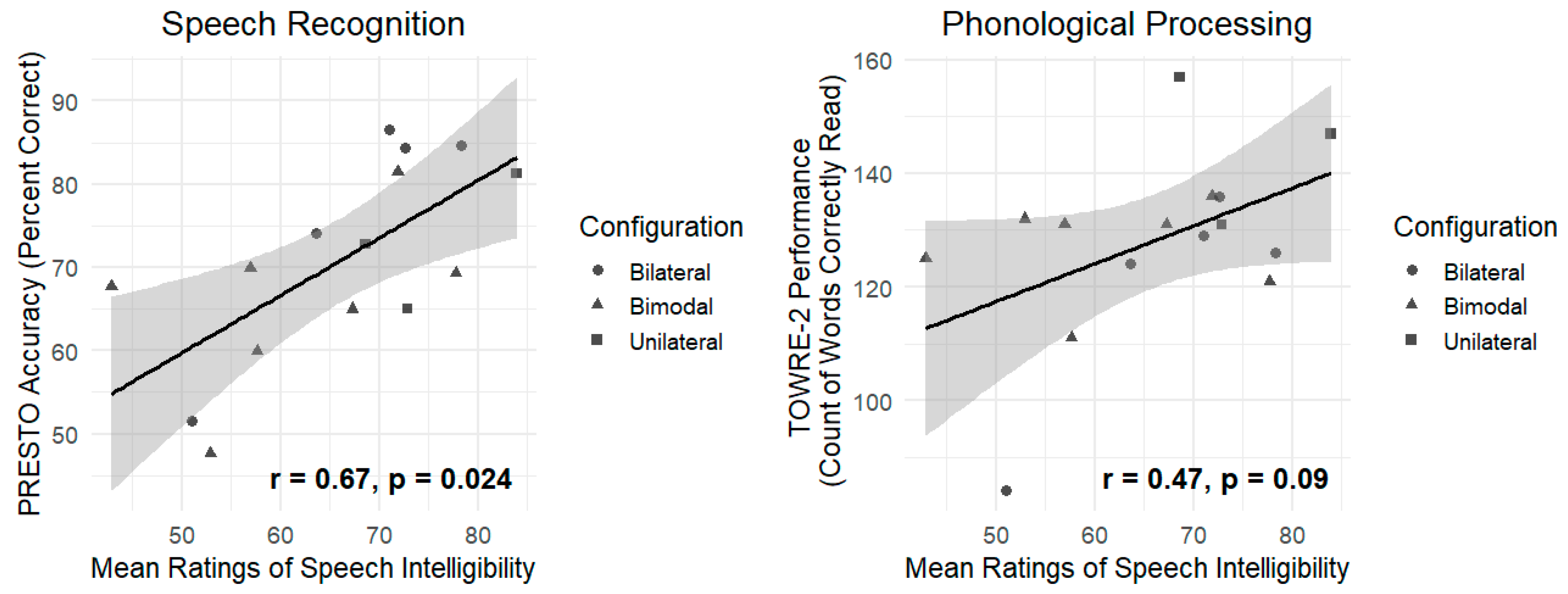
3.1. The Association Between Intelligibility Ratings and Speech Perception Outcomes
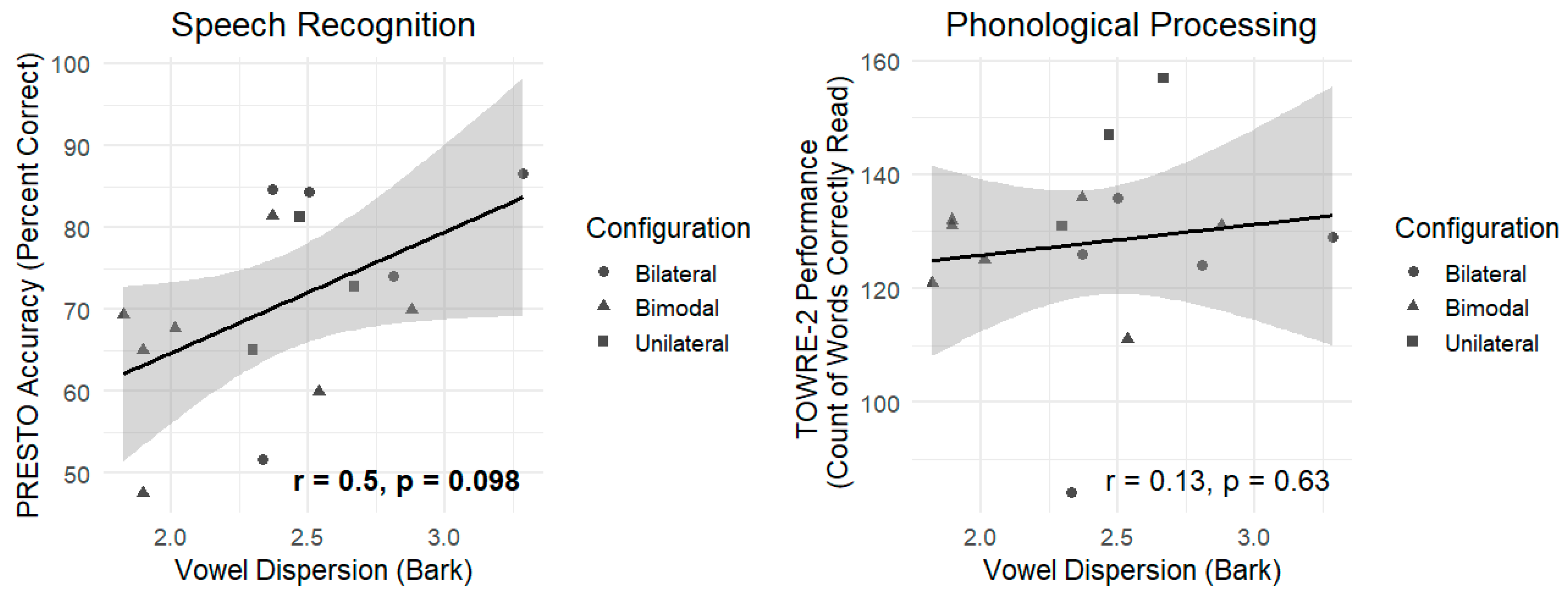
3.2. The Association Between Vowel Dispersion and Speech Perception Outcomes
3.3. The Relationship Between the Two Measures of Speech Production
4. Discussion
4.1. Subjective Ratings of Speech Intelligibility Are Associated with Speech Recognition
4.2. Vowel Dispersion Is Not Associated with Speech Recognition, Phonological Processing, or Intelligibility Ratings
4.3. Limitations
4.4. Future Directions: Other Factors That May Influence Speech Production and Intelligibility Ratings
4.5. Clinical Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blamey, P.; Artieres, F.; Başkent, D.; Bergeron, F.; Beynon, A.; Burke, E.; Dillier, N.; Dowell, R.; Fraysse, B.; Gallégo, S.; et al. Factors Affecting Auditory Performance of Postlinguistically Deaf Adults Using Cochlear Implants: An Update with 2251 Patients. Audiol. Neurotol. 2013, 18, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisvert, I.; Reis, M.; Au, A.; Cowan, R.; Dowell, R.C. Cochlear Implantation Outcomes in Adults: A Scoping Review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazard, D.S.; Vincent, C.; Venail, F.; van de Heyning, P.; Truy, E.; Sterkers, O.; Skarzynski, P.H.; Skarzynski, H.; Schauwers, K.; O’Leary, S.; et al. Pre-, Per- and Postoperative Factors Affecting Performance of Postlinguistically Deaf Adults Using Cochlear Implants: A New Conceptual Model over Time. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamati, T.N.; Pisoni, D.B.; Moberly, A.C. Speech and Language Outcomes in Adults and Children with Cochlear Implants. Annu. Rev. Linguist. 2022, 8, 299–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Fried, J.; Nguyen, S.A.; Schvartz-Leyzac, K.C.; Camposeo, E.L.; Meyer, T.A.; Dubno, J.R.; McRackan, T.R. Longitudinal Speech Recognition Changes After Cochlear Implant: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskent, D.; Gaudrain, E.; Tamati, T.N.; Wagner, A. Perception and Psychoacoustics of Speech in Cochlear Implant Users. In Scientific Foundations of Audiology: Perspectives from Physics, Biology, Modeling, and Medicine; Plural Publishing, Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 185–320. [Google Scholar]
- Tamati, T.N.; Ray, C.; Vasil, K.J.; Pisoni, D.B.; Moberly, A.C. High- and Low-Performing Adult Cochlear Implant Users on High-Variability Sentence Recognition: Differences in Auditory Spectral Resolution and Neurocognitive Functioning. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2020, 31, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomsky, N.; Halle, M. The Sound Pattern of English; Harper & Row Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1968; pp. 295–298. [Google Scholar]
- Luce, P.A.; Pisoni, D.B. Recognizing Spoken Words: The Neighborhood Activation Model. Ear Hear. 1998, 19, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R. Factors of Lexical Competition in Vowel Articulation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, J.-L.; Basirat, A.; Ménard, L.; Sato, M. The Perception-for-Action-Control Theory (PACT): A Perceptuo-Motor Theory of Speech Perception. J. Neurolinguistics 2012, 25, 336–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberman, A.M.; Cooper, F.S.; Shankweiler, D.P.; Studdert-Kennedy, M. Perception and the Speech Code. Psychol. Rev. 1967, 74, 431–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesters, J.; Baghai-Ravary, L.; Möttönen, R. The Effects of Delayed Auditory and Visual Feedback on Speech Production. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 137, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houde, J.F.; Jordan, M.I. Sensorimotor Adaptation in Speech Production. Science 1998, 279, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.A.; Munhall, K.G. Perceptual Calibration of F0 Production: Evidence from Feedback Perturbation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 108, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Xiao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yan, Y. The Role of Auditory Feedback in Speech Production: Implications for Speech Perception in the Hearing Impaired. In Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Integrated Circuits, ISIC 2014, Singapore, 10–12 December 2014; pp. 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuya, T.; MacDonald, E.N.; Munhall, K.G.; Purcell, D.W. Formant Compensation for Auditory Feedback with English Vowels. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiller, D.M.; Sato, M.; Gracco, V.L.; Baum, S.R. Perceptual Recalibration of Speech Sounds Following Speech Motor Learning. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyea, J.A.; McMullen, K.P.; Harris, M.S.; Houston, D.M.; Martin, J.M.; Bolster, V.A.; Adunka, O.F.; Moberly, A.C. Cochlear Implants in Adults: Effects of Age and Duration of Deafness on Speech Recognition. Otol. Neurotol. 2016, 37, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, U. Deterioration of the Phonological Processing Skills in Adults with an Acquired Severe Hearing Loss. Eur. J. Cogn. Psychol. 2002, 14, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, U.; Lyxell, B. Phonological Deterioration in Adults with an Acquired Severe Hearing Impairment. Scand. Audiol. Suppl. 1998, 27, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyxell, B.; Andersson, J.; Andersson, U.; Arlinger, S.; Bredberg, G.; Harder, H. Phonological Representation and Speech Understanding with Cochlear Implants in Deafened Adults. Scand. J. Psychol. 1998, 39, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, U.; Lyxell, B. Phonological Deterioration in Adults with an Acquired Severe Hearing Impairment: A Deterioration in Long-Term Memory or Working Memory? Scand. Audiol. 1999, 28, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moberly, A.C.; Lowenstein, J.H.; Nittrouer, S. Word Recognition Variability with Cochlear Implants: The Degradation of Phonemic Sensitivity. Otol. Neurotol. 2016, 37, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moberly, A.C.; Harris, M.S.; Boyce, L.; Nittrouer, S. Speech Recognition in Adults With Cochlear Implants: The Effects of Working Memory, Phonological Sensitivity, and Aging. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2017, 60, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, H.; Denny, M.; Guenther, F.H.; Hanson, H.M.; Marrone, N.; Matthies, M.L.; Perkell, J.S.; Stockmann, E.; Tiede, M.; Vick, J.; et al. On the Structure of Phoneme Categories in Listeners with Cochlear Implants. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2007, 50, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, H.; Denny, M.; Guenther, F.; Matthies, M.; Ménard, L.; Perkell, J.; Stockmann, E.; Tiede, M.; Vic, J.; Zandipour, M. Effects of Bite Blocks and Hearing Status on Vowel Production. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 118, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, H.; Matthies, M.L.; Guenther, F.H.; Denny, M.; Perkell, J.S.; Stockmann, E.; Tiede, M.; Vick, J.; Zandipour, M. Effects of Short- and Long-Term Changes in Auditory Feedback on Vowel and Sibilant Contrasts. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2007, 50, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langereis, M.C.; Bosman, A.J.; van Olphen, A.F.; Smoorenburg, G.F. Changes in Vowel Quality in Post-Lingually Deafened Cochlear Implant Users. Int. J. Audiol. 1997, 36, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langereis, M.C.; Bosman, A.J.; van Olphen, A.F.; Smoorenburg, G.F. Intelligibility of Vowels Produced by Post-Lingually Deafened Cochlear Implant Users. Audiology 1999, 38, 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménard, L.; Polak, M.; Denny, M.; Burton, E.; Lane, H.; Matthies, M.L.; Marrone, N.; Perkell, J.S.; Tiede, M.; Vick, J. Interactions of Speaking Condition and Auditory Feedback on Vowel Production in Postlingually Deaf Adults with Cochlear Implantsa. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 121, 3790–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkell, J.S.; Lane, H.; Denny, M.; Matthies, M.L.; Tiede, M.; Zandipour, M.; Vick, J.; Burton, E. Time Course of Speech Changes in Response to Unanticipated Short-Term Changes in Hearing State. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 121, 2296–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, F.H.; Hampson, M.; Johnson, D. A Theoretical Investigation of Reference Frames for the Planning of Speech Movements. Psychol. Rev. 1998, 105, 611–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, F.H.; Ghosh, S.S.; Tourville, J.A. Neural Modeling and Imaging of the Cortical Interactions Underlying Syllable Production. Brain Lang. 2006, 96, 280–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, F.H.; Hickok, G. Role of the Auditory System in Speech Production. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 129, pp. 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Baese-Berk, M.M. Interactions between Speech Perception and Production during Learning of Novel Phonemic Categories. Atten Percept Psychophys 2019, 81, 981–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baese-Berk, M.M.; Kapnoula, E.C.; Samuel, A.G. The Relationship of Speech Perception and Speech Production: It’s Complicated. Psychon. Bull Rev. 2025, 32, 226–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, S.-C.; Ochoa, D.; Daliri, A. Production Variability and Categorical Perception of Vowels Are Strongly Linked. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flege, J.E. Production and Perception of a Novel, Second-language Phonetic Contrast. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 93, 1589–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flege, J.E.; MacKay, I.R.A.; Meador, D. Native Italian Speakers’ Perception and Production of English Vowels. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 106, 2973–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, R.S. Using Links between Speech Perception and Speech Production to Evaluate Different Acoustic Metrics: A Preliminary Report. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 113, 2850–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkell, J.S.; Guenther, F.H.; Lane, H.; Matthies, M.L.; Stockmann, E.; Tiede, M.; Zandipour, M. The Distinctness of Speakers’ Productions of Vowel Contrasts Is Related to Their Discrimination of the Contrasts. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 116, 2338–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vick, J.C.; Perkell, J.S.; Matthies, M.L.; Gould, J. Covariation of Cochlear Implant Users’ Perception and Production of Vowel Contrasts and Their Identification by Listeners with Normal Hearing. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2001, 44, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Classon, E.; Rudner, M.; Rönnberg, J. Working Memory Compensates for Hearing Related Phonological Processing Deficit. J. Commun. Disord. 2013, 46, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classon, E.; Löfkvist, U.; Rudner, M.; Rönnberg, J. Verbal Fluency in Adults with Postlingually Acquired Hearing Impairment. Speech Lang. Hear. 2014, 17, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudner, M.; Foo, C.; Sundewall-Thorén, E.; Lunner, T.; Rönnberg, J. Phonological Mismatch and Explicit Cognitive Processing in a Sample of 102 Hearing-Aid Users. Int. J. Audiol. 2008, 47, S91–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudner, M.; Danielsson, H.; Lyxell, B.; Lunner, T.; Rönnberg, J. Visual Rhyme Judgment in Adults with Mild-to-Severe Hearing Loss. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnsberger, J.D.; Svirsky, M.A.; Kaiser, A.R.; Pisoni, D.B.; Wright, R.; Meyer, T.A. Perceptual “Vowel Spaces” of Cochlear Implant Users: Implications for the Study of Auditory Adaptation to Spectral Shift. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2001, 109, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazard, D.S.; Lee, H.J.; Gaebler, M.; Kell, C.A.; Truy, E.; Giraud, A.L. Phonological Processing in Post-Lingual Deafness and Cochlear Implant Outcome. NeuroImage 2010, 49, 3443–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevich, V.A.; Moberly, A.C.; Tamati, T.N. Lexical Difficulty Affects Vowel Articulation in Adult Cochlear Implant Users. Proc. Meet. Acoust. 2022, 50, 060003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamati, T.N.; Vasil, K.J.; Kronenberger, W.G.; Pisoni, D.B.; Moberly, A.C.; Ray, C. Word and Nonword Reading Efficiency in Postlingually Deafened Adult Cochlear Implant Users. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, e272–e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddeley, A.; Logie, R.; Nimmo-Smith, I.; Brereton, N. Components of Fluent Reading. J. Mem. Lang. 1985, 24, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.D.; McClelland, J.L. Processing Determinants of Reading Speed. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 1979, 108, 151–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; Katzir-Cohen, T. Reading Fluency and Its Intervention. In The Role of Fluency in Reading Competence, Assessment, and Instruction; Routledge: London, UK, 2001; ISBN 978-1-4106-0824-6. [Google Scholar]
- Moberly, A.C.; Reed, J. Making Sense of Sentences: Top-down Processing of Speech by Adult Cochlear Implant Users. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2019, 62, 2895–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, B.S.; Baumgartner, W.-D.; Hamzavi, J.S. Changes in Vowel Quality after Cochlear Implantation. ORL 2003, 65, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishon-Rabin, L.; Taitelbaum, R.; Tobin, Y.; Hildesheimer, M. The Effect of Partially Restored Hearing on Speech Production of Postlingually Deafened Adults with Multichannel Cochlear Implants. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 106, 2843–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldstein, R.S. Effects of Postlingual Deafness on Speech Production: Implications for the Role of Auditory Feedback. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1990, 88, 2099–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkell, J.; Lane, H.; Svirsky, M.; Webster, J. Speech of Cochlear Implant Patients: A Longitudinal Study of Vowel Production. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 91, 2961–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, P.W.; Blarney, P.J.; Dettman, S.J.; Rowland, L.C.; Barker, E.J.; Tobey, E.A.; Busby, P.A.; Cowan, R.C.; Clark, G.M. A Clinical Report on Speech Production of Cochlear Implant Users. Ear Hear. 1995, 16, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Monsen, R.B. Normal and Reduced Phonological Space: The Production of English Vowels by Deaf Adolescents. J. Phon. 1976, 4, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsen, R.B.; Shaughnessy, D.H. Improvement in Vowel Articulation of Deaf Children. J. Commun. Disord. 1978, 11, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, B.S.; Baumgartner, W.D.; Hamzavi, J.S. Effect of the Loss of Auditory Feedback on Segmental Parameters of Vowels of Postlingually Deafened Speakers. Auris Nasus Larynx 2003, 30, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradlow, A.R.; Torretta, G.M.; Pisoni, D.B. Intelligibility of Normal Speech I: Global and Fine-Grained Acoustic-Phonetic Talker Characteristics. Speech Commun. 1996, 20, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clopper, C.G.; Mitsch, J.F.; Tamati, T.N. Effects of Phonetic Reduction and Regional Dialect on Vowel Production. J. Phon. 2017, 60, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munson, B.; Solomon, N.P. The Effect of Phonological Neighborhood Density on Vowel Articulation. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2004, 47, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.; Naples, J.G.; Eliades, S.J. Control of Speech and Voice in Cochlear Implant Patients. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 2158–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashjaei, S.; Behroozmand, R.; Fozdar, S.; Farrar, R.; Arjmandi, M. Vocal Control and Speech Production in Cochlear Implant Listeners: A Review within Auditory-Motor Processing Framework. Hear. Res. 2024, 453, 109132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijkhuizen, J.N.; Boermans, P.P.B.M.; Briaire, J.J.; Frijns, J.H.M. Intelligibility of the Patient’s Speech Predicts the Likelihood of Cochlear Implant Success in Prelingually Deaf Adults. Ear Hear. 2016, 37, e302–e310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijkhuizen, J.N.; Beers, M.; Boermans, P.-P.B.M.; Briaire, J.J.; Frijns, J.H.M. Speech Intelligibility as a Predictor of Cochlear Implant Outcome in Prelingually Deafened Adults. Ear Hear. 2011, 32, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwyl-Irvine, A.; Massonnie, J.; Flitton, A.; Kirkham, N.; Evershed, J.K. Gorilla in Our Midst: An Online Behavioral Experiment Builder. Behav. Res. Methods 2020, 52, 388–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, A.E.; Bianco, R.; Poole, K.C.; Zhao, S.; Oxenham, A.J.; Billig, A.J.; Chait, M. An Online Headphone Screening Test Based on Dichotic Pitch. Behav. Res. Methods 2020, 53, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitevitch, M.S.; Luce, P.A. A Web-Based Interface to Calculate Phonotactic Probability for Words and Nonwords in English. Behav. Res. Methods 2004, 36, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelman, J.S.; Brown, G.D.A.; Quesada, J.F. Contextual Diversity, Not Word Frequency, Determines Word-Naming and Lexical Decision Times. Psychol. Sci. 2006, 17, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brysbaert, M.; New, B. Moving Beyond Kučera And Francis: A Critical Evaluation of Current Word Frequency Norms and the Introduction of a New and Improved Word Frequency Measure for American English. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiel, F. Automatic Phonetic Transcription of Nonprompted Speech. In Proceedings of the XIVth International Congress of Phonetic Sciences, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–7 August 1999; pp. 607–610. [Google Scholar]
- Praat: Doing Phonetics by Computer. Available online: https://www.fon.hum.uva.nl/praat/ (accessed on 22 August 2025).
- Jadoul, Y.; Thompson, B.; de Boer, B. Introducing Parselmouth: A Python Interface to Praat. J. Phon. 2018, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traunmüller, H. Analytical Expressions for the Tonotopic Sensory Scale. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1990, 88, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarborough, R.; Zellou, G. Clarity in Communication: “Clear” Speech Authenticity and Lexical Neighborhood Density Effects in Speech Production and Perception. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 3793–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellou, G.; Scarborough, R. Lexically Conditioned Phonetic Variation in Motherese: Age-of-Acquisition and Other Word-Specific Factors in Infant- and Adult-Directed Speech. Lab. Phonol. 2015, 6, 305–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santurette, S.; Dau, T. Binaural Pitch Perception in Normal-Hearing and Hearing-Impaired Listeners. Hear. Res. 2007, 223, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TOWRE-2-Test of Word Reading Efficiency|Second Edition|Pearson Assessments US. Available online: https://www.pearsonassessments.com/en-us/Store/Professional-Assessments/Speech-%26-Language/Test-of-Word-Reading-Efficiency-%7C-Second-Edition/p/100000451?srsltid=AfmBOopJ28erRVKHx5I1aQ5YtHUY62pPljE_JOzAFqv7KLig3hXyHt6N (accessed on 22 August 2025).
- Moberly, A.C.; Afreen, H.; Schneider, K.J.; Tamati, T.N. Preoperative Reading Efficiency as a Predictor of Adult Cochlear Implant Outcomes. Otol. Neurotol. 2022, 43, e1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.L.; Tamati, T.N.; Pisoni, D.B. Development, Reliability, and Validity of PRESTO: A New High-Variability Sentence Recognition Test. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2013, 24, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamati, T.N.; Sevich, V.A.; Clausing, E.M.; Moberly, A.C. Lexical Effects on the Perceived Clarity of Noise-Vocoded Speech in Younger and Older Listeners. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 837644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, D.J.; Levy, R.; Scheepers, C.; Tily, H.J. Random Effects Structure for Confirmatory Hypothesis Testing: Keep It Maximal. J. Mem. Lang. 2013, 68, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M.; Walker, S.C. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, J.; Lane, H.; Vick, J.; Perkell, J.S.; Matthies, M.L.; Zandipour, M. Changes in Speech Intelligibility of Postlingually Deaf Adults after Cochlear Implantation. Ear Hear. 2001, 22, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, S.; Bocklet, T.; Nöth, E.; Müller, J.; Hoster, E.; Schuster, M. Speech Production Quality of Cochlear Implant Users with Respect to Duration and Onset of Hearing Loss. ORL 2017, 79, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagle, C.L. Examining the Temporal Structure of the Perception–Production Link in Second Language Acquisition: A Longitudinal Study. Lang. Learn. 2018, 68, 234–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borden, G.; Gerber, A.; Milsark, G. Production and perception of the /r/-/l/ contrast in Korean adults learning English. Lang. Learn. 1983, 33, 499–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M.; Moorman, C. Can Perception Training Improve the Production of Second Language Phonemes? A Meta-Analytic Review of 25 Years of Perception Training Research. Appl. Psycholinguist. 2018, 39, 187–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönnberg, J.; Lunner, T.; Zekveld, A.; Sörqvist, P.; Danielsson, H.; Lyxell, B.; Dahlström, Ö.; Signoret, C.; Stenfelt, S.; Pichora-Fuller, M.K.; et al. The Ease of Language Understanding (ELU) Model: Theoretical, Empirical, and Clinical Advances. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, C.; Prémont, A.; Trudeau-Fisette, P.; Ménard, L. Exploring Consequences of Short- and Long-Term Deafness on Speech Production: A Lip-Tube Perturbation Study. Clin. Linguist Phonet. 2015, 29, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourville, J.A.; Reilly, K.J.; Guenther, F.H. Neural Mechanisms Underlying Auditory Feedback Control of Speech. NeuroImage 2008, 39, 1429–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, S.H.; Kewley-Port, D. Vowel Intelligibility in Clear and Conversational Speech for Normal-Hearing and Hearing-Impaired Listeners. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 112, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, S.; Kewley-Port, D. Talker Differences in Clear and Conversational Speech: Acoustic Characteristics of Vowels. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2007, 50, 1241–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradlow, A.R.; Kraus, N.; Hayes, E. Speaking Clearly for Children With Learning Disabilities: Sentence Perception in Noise. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2003, 46, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Picheny, M.A.; Durlach, N.I.; Braida, L.D. Speaking Clearly for the Hard of Hearing II. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1986, 29, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahl, S.; Yao, Y.; Johnson, K. Why Reduce? Phonological Neighborhood Density and Phonetic Reduction in Spontaneous Speech. J. Mem. Lang. 2012, 66, 789–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derwing, T.M.; Munro, M.J. Accent, Intelligibility, and Comprehensibility: Evidence from Four L1s. Stud. Second Lang. Acquis. 1997, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Munro, M.J.; Derwing, T.M. Processing Time, Accent, and Comprehensibility in the Perception of Native and Foreign-Accented Speech. Lang. Speech 1995, 38, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, M.J.; Derwing, T.M. Modeling Perceptions of the Accentedness and Comprehensibility of L2 Speech the Role of Speaking Rate. Stud. Second Lang. Acquis. 2001, 23, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, C.; Trudeau-Fisette, P.; Lepore, F.; Lippé, S.; Ménard, L. Impact of Visual and Auditory Deprivation on Speech Perception and Production in Adults. Clin. Linguist. Phon. 2020, 34, 1061–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.; Tinnemore, A.R.; Nguyen, N.; Goupell, M.J. On the Difficulty of Defining Duration of Deafness for Adults With Cochlear Implants. Ear Hear. 2025, 46, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munson, B. Lexical Characteristic Mediate the Influence of Sex and Sex Typicality on Vowel-Space Size. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Phonetic Sciences, Saarbrucken, Germany, 6–10 August 2007; pp. 885–888. [Google Scholar]
- Munson, B.; Babel, M. The Phonetics of Sex and Gender. In The Routelidge Handbook of Phonetics; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2019; pp. 499–525. [Google Scholar]
- Smiljanic, R.; Gilbert, R.C. Intelligibility of Noise-Adapted and Clear Speech in Child, Young Adult, and Older Adult Talkers. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2017, 60, 3069–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahò, M.; Monzani, D. The Multifaceted Nature of Inner Speech: Phenomenology, Neural Correlates, and Implications for Aphasia and Psychopathology. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 2025, 3, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, J.R. An Adaptive Orienting Theory of Error Processing. Psychophysiology 2018, 55, e13041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarr, N.S. The Intelligibility of Deaf Speech to Experienced and Inexperienced Listeners. J. Speech Hear. Res. 1983, 26, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baese-Berk, M.M.; Levi, S.V.; Van Engen, K.J. Intelligibility as a Measure of Speech Perception: Current Approaches, Challenges, and Recommendations. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 153, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bent, T.; Baese-Berk, M.; Borrie, S.A.; McKee, M. Individual Differences in the Perception of Regional, Nonnative, and Disordered Speech Varieties. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 140, 3775–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, D.J.; Baese-Berk, M.M.; Bent, T.; Borrie, S.A.; Van Engen, K.J. Coping with Adversity: Individual Differences in the Perception of Noisy and Accented Speech. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2018, 80, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baese-Berk, M.M.; McLaughlin, D.J.; McGowan, K.B. Perception of Non-Native Speech. Lang. Linguist. Compass 2020, 14, e12375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossey, E.; Clopper, C.G.; Wagner, L. The Development of Sociolinguistic Competence across the Lifespan: Three Domains of Regional Dialect Perception. Lang. Learn. Dev. 2020, 16, 330–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, K.B. Social Expectation Improves Speech Perception in Noise. Lang. Speech 2015, 58, 502–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, D.L. Nonlanguage Factors Affecting Undergraduates’ Judgments of Nonnative English-Speaking Teaching Assistants. Res High Educ 1992, 33, 511–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, E.; Lybaert, C.; Plevoets, K. Social Attitudes, Intelligibility and Comprehensibility: The Role of the Listener in the Perception of Non-Native Speech. Vigo Int. J. Appl. Linguist. 2022, 19, 177–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, V. Speech Intelligibility and Personality Peer-Ratings of Young Adults with Cochlear Implants. J. Deaf Stud. Deaf Educ. 2018, 23, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, V. Attitudes toward Deafness Affect Impressions of Young Adults with Cochlear Implants. J. Deaf Stud. Deaf Educ. 2018, 23, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuda, D.; Manrique, M.; Ramos, Á.; Marx, M.; Bovo, R.; Khnifes, R.; Hilly, O.; Belmin, J.; Stripeikyte, G.; Graham, P.L.; et al. Improving Quality of Life in the Elderly: Hearing Loss Treatment with Cochlear Implants. BMC Geriatr 2024, 24, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawton, A.; Green, C.; Dickens, A.P.; Richards, S.H.; Taylor, R.S.; Edwards, R.; Greaves, C.J.; Campbell, J.L. The Impact of Social Isolation on the Health Status and Health-Related Quality of Life of Older People. Qual Life Res 2011, 20, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, B.; Lindbæk, M.; Harris, S. Cochlear Implants and Quality of Life: A Prospective Study. Ear Hear. 2005, 26, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Subject | Gender | Age (YR) | Side of Implant | HA in Contra-Lateral Ear | Etiology of HL | Age at First CI (YR) | Duration of Deafness (YR) | Years of CI Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI1 | Woman | 65 | Bilateral | N/A | Genetic | 54 | 13 | 11 |
| CI2 | Woman | 57 | Left | Yes | Genetic | 48 | 41 | 9 |
| CI3 | Woman | 69 | Bilateral | N/A | Otosclerosis | 56 | 41 | 13 |
| CI4 | Woman | 76 | Left | No | Autoimmune | 68 | 23 | 8 |
| CI5 | Man | 59 | Bilateral | N/A | Sudden (idiopathic) | 57 | 2 | 2 |
| CI6 | Woman | 62 | Right | Yes | Sudden (idiopathic) | 56 | 29 | 6 |
| CI7 | Man | 66 | Left | No | Meniere’s | 60 | 46 | 6 |
| CI8 | Woman | 35 | Left | No | Physical trauma | 31 | 18 | 4 |
| CI9 | Woman | 64 | Left | Yes | Genetic | 59 | 50 | 5 |
| CI10 | Man | 56 | Bilateral | N/A | Unknown | 45 | Unknown | 11 |
| CI11 | Woman | 24 | Bilateral | N/A | Unknown | 19 | Unknown | 5 |
| CI12 | Man | 67 | Right | Yes | Physical trauma | 60 | 48 | 7 |
| CI13 | Man | 73 | Right | Yes | Genetic | 60 | 20 | 13 |
| CI14 | Woman | 49 | Right | Yes | Genetic | 39 | Unknown | 10 |
| CI15 | Woman | 56 | Right | Yes | Unknown | 48 | Unknown | 8 |
| Vowel | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Talker | æ | ɑ | i | u | Total |
| CI1 | 18 | 23 | 18 | 15 | 74 |
| CI2 | 18 | 26 | 21 | 16 | 81 |
| CI3 | 15 | 19 | 20 | 13 | 67 |
| CI4 | 13 | 22 | 19 | 16 | 70 |
| CI5 | 15 | 24 | 21 | 16 | 76 |
| CI6 | 15 | 18 | 17 | 14 | 64 |
| CI7 | 15 | 22 | 17 | 14 | 68 |
| CI8 | 17 | 21 | 21 | 13 | 72 |
| CI9 | 15 | 23 | 17 | 14 | 69 |
| CI10 | 15 | 23 | 17 | 13 | 68 |
| CI11 | 16 | 20 | 21 | 16 | 73 |
| CI12 | 16 | 23 | 22 | 15 | 76 |
| CI13 | 12 | 22 | 20 | 15 | 69 |
| CI14 | 15 | 23 | 18 | 12 | 68 |
| CI15 | 15 | 24 | 20 | 14 | 73 |
| Total | 230 | 333 | 289 | 216 | 1068 |
| Subject | Intelligibility Rating | Vowel Dispersion (Bark) | PRESTO Accuracy (Percent Correct) | TOWRE-2 Score (Total Words + Nonwords Correctly Reported) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI1 | 71.0 (27.6) | 3.29 (0.74) | 86.6 | 129 |
| CI2 | 71.9 (26.5) | 2.37 (0.46) | 81.4 | 136 |
| CI3 | 63.6 (27.8) | 2.81 (0.44) | 74.1 | 124 |
| CI4 | 72.9 (25.4) | 2.30 (0.63) | 65.0 | 131 |
| CI5 | 72.7 (26.3) | 2.50 (0.59) | 84.4 | 136 |
| CI6 | 77.8 (21.7) | 1.82 (0.36) | 69.4 | 121 |
| CI7 | 84.0 (19.2) | 2.47 (0.32) | 81.2 | 147 |
| CI8 | 68.6 (27.1) | 2.67 (0.91) | 72.8 | 157 |
| CI9 | 56.9 (32.6) | 2.88 (0.81) | 69.9 | 131 |
| CI10 | 51.0 (32.0) | 2.33 (0.58) | 51.6 | 84 |
| CI11 | 78.4 (23.5) | 2.37 (0.37) | 84.7 | 126 |
| CI12 | 52.9 (31.5) | 1.89 (0.41) | 47.6 | 132 |
| CI13 | 42.9 (31.2) | 2.01 (0.52) | 67.7 | 125 |
| CI14 | 57.6 (33.2) | 2.54 (0.87) | 60.2 | 111 |
| CI15 | 67.3 (27.5) | 1.89 (0.57) | 64.9 | 131 |
| Mean | 65.9 (11.5) | 2.41 (0.41) | 70.8 (11.9) | 128.1 (16.2) |
| Sentence Recognition (PRESTO) Accuracy | Phonological Processing (TOWRE-2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Intelligibility Ratings | r = 0.67 | r = 0.47 |
| p = 0.024 | p = 0.090 | |
| Vowel Dispersion | r = 0.50 | r = 0.13 |
| p = 0.098 | p = 0.63 |
| Effect | Estimate | Error | T-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 55.56 | 8.83 | 6.30 | <0.0001 * |
| Vowel Dispersion | −0.32 | 0.46 | −0.69 | 0.49 |
| Lexical Frequency | 4.60 | 1.74 | 2.65 | 0.009 * |
| Neighborhood Density | 0.001 | 0.23 | 0.001 | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sevich, V.A.; Williams, D.J.; Moberly, A.C.; Tamati, T.N. Speech Production Intelligibility Is Associated with Speech Recognition in Adult Cochlear Implant Users. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101066
Sevich VA, Williams DJ, Moberly AC, Tamati TN. Speech Production Intelligibility Is Associated with Speech Recognition in Adult Cochlear Implant Users. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(10):1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101066
Chicago/Turabian StyleSevich, Victoria A., Davia J. Williams, Aaron C. Moberly, and Terrin N. Tamati. 2025. "Speech Production Intelligibility Is Associated with Speech Recognition in Adult Cochlear Implant Users" Brain Sciences 15, no. 10: 1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101066
APA StyleSevich, V. A., Williams, D. J., Moberly, A. C., & Tamati, T. N. (2025). Speech Production Intelligibility Is Associated with Speech Recognition in Adult Cochlear Implant Users. Brain Sciences, 15(10), 1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101066







