Risk Factors for Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Extraction
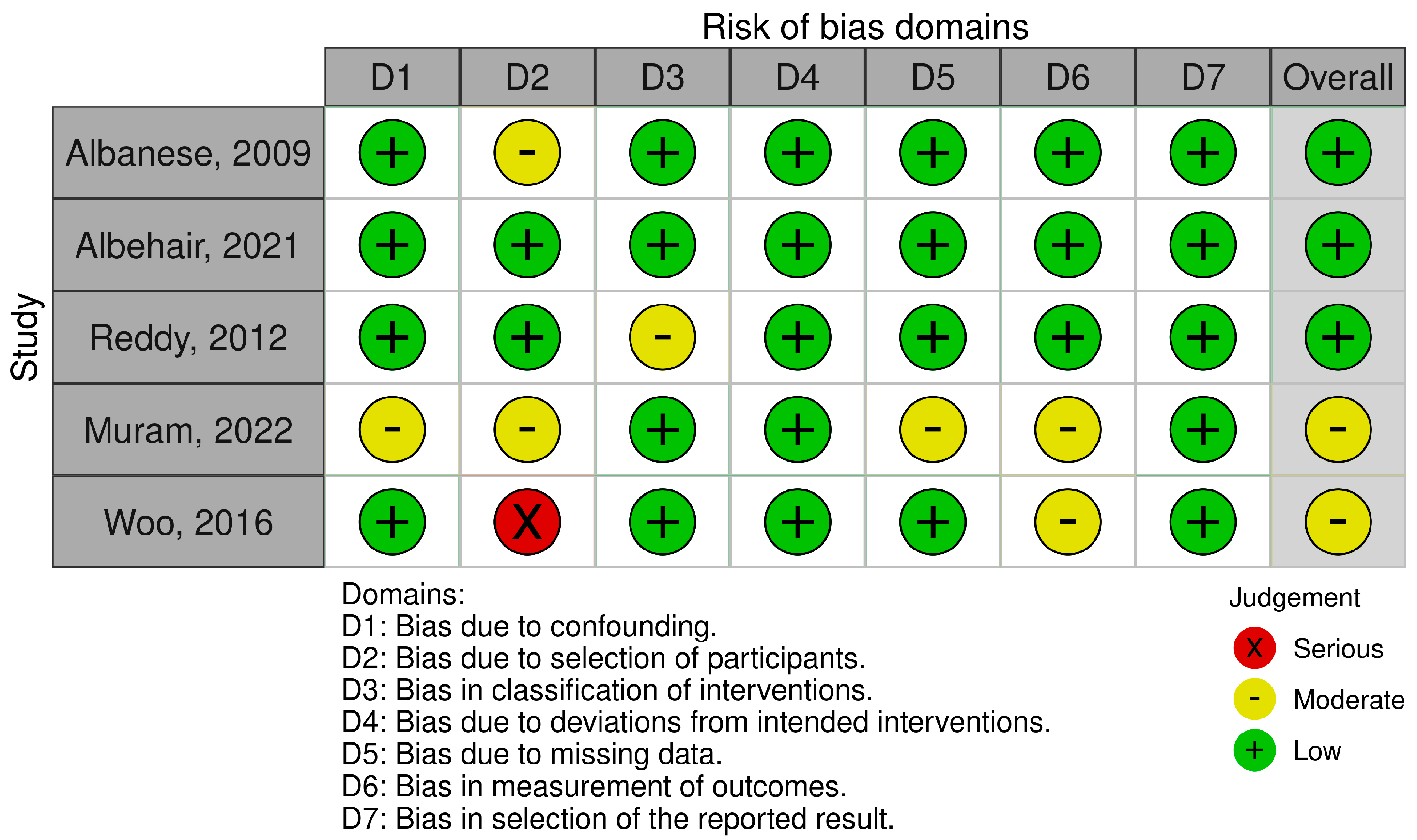
2.2. Risk of Bias
2.3. Statistical Analysis
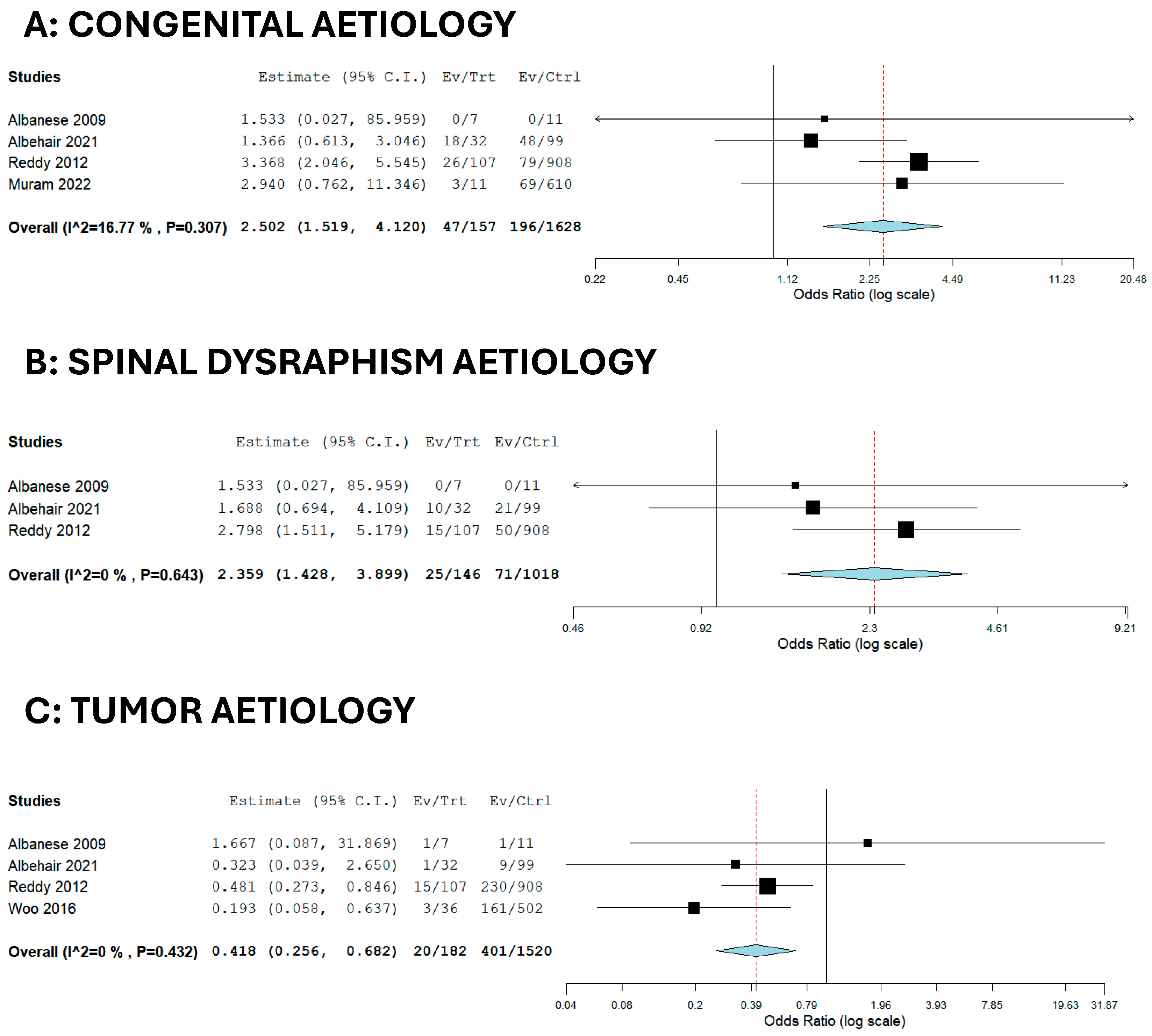
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis |
| NPH | Normal pressure hydrocephalus |
| VPS | Ventriculoperitoneal shunt |
| VPSI | Ventriculoperitoneal shunt infection |
References
- Bondurant, C.P.; Jimenez, D.F. Epidemiology of Cerebrospinal Fluid Shunting. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1995, 23, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.J.; Walker, C.T.; Jacobson, M.; Phillips, V.; Silberstein, H.J. Revision rate of pediatric ventriculoperitoneal shunts after 15 years. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2013, 11, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, V.D.; Richtmann, R.; Singh, S.; Apisarnthanarak, A.; Kübler, A.; Viet-Hung, N.; Ramírez-Wong, F.M.; Portillo-Gallo, J.H.; Toscani, J.; Gikas, A.; et al. Surgical Site Infections, International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium (INICC) Report, Data Summary of 30 Countries, 2005–2010. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2013, 34, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenbaum, S.C.; Gardner, P.; Shillito, J. Infections of Cerebrospinal Fluid Shunts: Epidemiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 1975, 131, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kestle, J.R.W.; Garton, H.J.L.; Whitehead, W.E.; Drake, J.M.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Cochrane, D.D.; Muszynski, C.; Walker, M.L. Management of shunt infections: A multicenter pilot study. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2006, 105, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadduck, W.; Adametz, J. Incidence of seizures in patients with myelomeningocele: A multifactorial analysis. Surg. Neurol. 1988, 30, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, J.M.; Kulkarni, A.V. Cerebrospinal fluid shunt infections. Neurosurg. Q. 1993, 3, 283–294. [Google Scholar]
- Kontny, U.; Höfling, B.; Gutjahr, P.; Schmitt, H.J.; Voth, D.; Schwarz, M. CSF shunt infections in children. Infection 1993, 21, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, S.C.; Guo, W. Have we made progress in preventing shunt failure? A critical analysis. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2008, 1, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwardhan, R.V.; Nanda, A. Implanted Ventricular Shunts in the United States: The Billion-dollar-a-year Cost of Hydrocephalus Treatment. Neurosurgery 2005, 56, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, H.E.; Walsh, J.W.; Wilson, H.D.; Connor, J.D.; Bean, J.R.; Tibbs, P.A. Prospective Randomized Study of Therapy in Cerebrospinal Fluid Shunt Infection. Neurosurgery 1980, 7, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronan, A.M.; Hogg, G.G.F.; Klug, G.L.F. Cerebrospinal fluid shunt infections in children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1995, 14, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelegrín, I.; Lora-Tamayo, J.; Gómez-Junyent, J.; Sabé, N.; García-Somoza, D.; Gabarrós, A.; Ariza, J.; Viladrich, P.F.; Cabellos, C. Management of Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infections in Adults: Analysis of Risk Factors Associated with Treatment Failure. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoor, N.; Solheim, O.; Fredriksli, O.A.; Gulati, S. Revision and complication rates in adult shunt surgery: A single-institution study. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 163, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Palermo, M.; Trevisi, G.; Signorelli, F.; Doglietto, F.; Albanese, A.; Olivi, A.; Sturiale, C.L. Advancing treatment strategies for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A systematic review on studies comparing ventricular and lumbo-peritoneal shunts. Neurosurg. Rev. 2025, 48, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kestle, J.R.W.; Hoffman, H.J.; Soloniuk, D.; Humphreys, R.P.; Drake, J.M.; Hendrick, E.B. A concerted effort to prevent shunt infection. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 1993, 9, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renier, D.; Lacombe, J.; Pierre-Kahn, A.; Sainte-Rose, C.; Hirsch, J.-F. Factors causing acute shunt infection. J. Neurosurg. 1984, 61, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, B.; Duff, P. The effect of double gloving on frequency of glove perforations. Obstet. Gynecol. 1991, 78, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097-269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Albanese, A.; De Bonis, P.; Sabatino, G.; Capone, G.; Marchese, E.; Vignati, A.; Maira, G. Antibiotic-impregnated ventriculo-peritoneal shunts in patients at high risk of infection. Acta Neurochir. 2009, 151, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albehair, M.A.; Alosail, M.A.; Albulwi, N.M.; AlAssiry, A.; Alzahrani, F.A.; Bukhamsin, A.; Ammar, A. A Retrospective Study on the Avoidability of Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infections in a University Hospital in Al-Khobar, Saudi Arabia. Cureus 2021, 13, e13135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Reddy, G.K.; Bollam, P.; Caldito, G. Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Surgery and the Risk of Shunt Infection in Patients with Hydrocephalus: Long-Term Single Institution Experience. World Neurosurg. 2012, 78, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.Y.; Working Group on Neurosurgical Outcomes Monitoring; Wong, H.; Pu, J.K.; Wong, W.; Wong, L.Y.; Lee, M.W.; Yam, K.; Lui, W.; Poon, W. Primary ventriculoperitoneal shunting outcomes: A multicentre clinical audit for shunt infection and its risk factors. Hong Kong Med. J. 2016, 22, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muram, S.; Isaacs, A.M.; Sader, N.; Holubkov, R.; Fong, A.; Conly, J.; Hamilton, M.G. A standardized infection prevention bundle for reduction of CSF shunt infections in adult ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery performed without antibiotic-impregnated catheters. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 138, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Wan, X.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Optimally estimating the sample mean from the sample size, median, mid-range, and/or mid-quartile range. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2018, 27, 1785–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, T. Prevention options for ventriculoperitoneal shunt infections: A retrospective analysis during a five-year period. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 19775–19780. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alkosha, H.M.; Mohammed, M.I.; El Shokhaiby, U.M.; Amen, M.M. A Proposed Protective Protocol Predicting Reduction of Shunt Infection. World Neurosurg. 2022, 164, e1049–e1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shurtleff, D.B.; Foltz, E.L.; Weeks, R.D.; Loeser, J. Therapy of Staphylococcus Epidermidis: Infections Associated with Cerebrospinal Fluid Shunts. Pediatrics 1974, 53, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choux, M.; Genitori, L.; Lang, D.; Lena, G. Shunt implantation: Reducing the incidence of shunt infection. J. Neurosurg. 1992, 77, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinchon, M.; Dhellemmes, P. Cerebrospinal fluid shunt infection: Risk factors and long-term follow-up. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2006, 22, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.V.; Drake, J.M.; Lamberti-Pasculli, M. Cerebrospinal fluid shunt infection: A prospective study of risk factors. J. Neurosurg. 2001, 94, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, M.; Aycan, A.; Gulsen, I.; Akyol, M.E.; Kuyumcu, F. Relationship between hydrocephalus etiology and ventriculoperitoneal shunt infection in children and review of literature. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2018, 68, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laeke, T.; Tirsit, A.; Biluts, H.; Murali, D.; Wester, K. Pediatric Hydrocephalus in Ethiopia: Treatment Failures and Infections: A Hospital-Based, Retrospective Study. World Neurosurg. 2017, 100, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, M.; Eseoglu, M.; Gudu, B.O.; Demir, I.; Kozan, A.; Gokalp, A.; Sosuncu, E.; Kiymaz, N. Comparison of simultaneous shunting to delayed shunting in infants with myelomeningocele in terms of shunt infection rate. Turk. Neurosurg. 2011, 21, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammirati, M.; Raimondi, A.J. Cerebrospinal fluid shunt infections in children. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 1987, 3, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montano, N.; D’ALessandris, Q.G.; Bianchi, F.; Lauretti, L.; Doglietto, F.; Fernandez, E.; Maira, G.; Pallini, R. Communicating hydrocephalus following surgery and adjuvant radiochemotherapy for glioblastoma. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, C.M.; Neidert, M.C.; Péus, D.; Ulrich, N.H.; Regli, L.; Krayenbühl, N.; Woernle, C.M. Hydrocephalus after resection and adjuvant radiochemotherapy in patients with glioblastoma. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2014, 120, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoefnagel, D.; Dammers, R.; Ter Laak-Poort, M.P.; Avezaat, C.J.J. Risk factors for infections related to external ventricular drainage. Acta Neurochir. 2008, 150, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korinek, A.-M.; Fulla-Oller, L.; Boch, A.-L.; Golmard, J.-L.; Hadiji, B.; Puybasset, L. Morbidity of Ventricular Cerebrospinal Fluid Shunt Surgery in Adults: An 8-Year Study. Neurosurgery 2011, 68, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozier, A.P.; Sciacca, R.R.; Romagnoli, M.F.; Connolly, E.S. Ventriculostomy-related Infections: A Critical Review of the Literature. Neurosurgery 2002, 51, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germanwala, A.V.; Huang, J.; Tamargo, R.J. Hydrocephalus After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 21, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.-H.; Park, J.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Hwang, S.-K.; Hamm, I.-S. Early Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Placement After Severe Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGirt, M.J.; Zaas, A.; Fuchs, H.E.; George, T.M.; Kaye, K.; Sexton, D.J. Risk Factors for Pediatric Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infection and Predictors of Infectious Pathogens. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Author | Year | Type of Study | N of Patients (Non-Infected/Infected) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albanese et al. [20] | 2009 | Retrospective | 28 (11/7) |
| Reddy et al. [22] | 2012 | Retrospective | 1015 (908/107) |
| Woo et al. [23] | 2016 | Retrospective | 538 (502/36) |
| Albehair et al. [21] | 2021 | Retrospective | 131 (99/32) |
| Muram et al. [24] | 2022 | Retrospective | 621 (610/11) |
| Factor | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor | 0.418 | 0.256–0.682 | <0.001 | 0 |
| Congenital | 2.502 | 1.519–4.120 | <0.001 | 16.77 |
| Spinal dysraphism | 2.359 | 1.428–3.899 | <0.001 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Signorelli, F.; Palermo, M.; Onorati, F.; Zeoli, F.; Romozzi, M.; Marziali, G.; Sturiale, C.L.; Trevisi, G.; Visocchi, M. Risk Factors for Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101055
Signorelli F, Palermo M, Onorati F, Zeoli F, Romozzi M, Marziali G, Sturiale CL, Trevisi G, Visocchi M. Risk Factors for Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(10):1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101055
Chicago/Turabian StyleSignorelli, Francesco, Matteo Palermo, Francesco Onorati, Fabio Zeoli, Marina Romozzi, Giammaria Marziali, Carmelo Lucio Sturiale, Gianluca Trevisi, and Massimiliano Visocchi. 2025. "Risk Factors for Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Brain Sciences 15, no. 10: 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101055
APA StyleSignorelli, F., Palermo, M., Onorati, F., Zeoli, F., Romozzi, M., Marziali, G., Sturiale, C. L., Trevisi, G., & Visocchi, M. (2025). Risk Factors for Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sciences, 15(10), 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101055