Neuralgic Amyotrophy and Hourglass Nerve Constriction/Nerve Torsion: Two Sides of the Same Coin? A Clinical Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Are NA, hourglass constriction and nerve torsion really a different evolution of the same pathology?
- What is the best diagnostic approach for these conditions?
- What is the best treatment approach for these conditions?
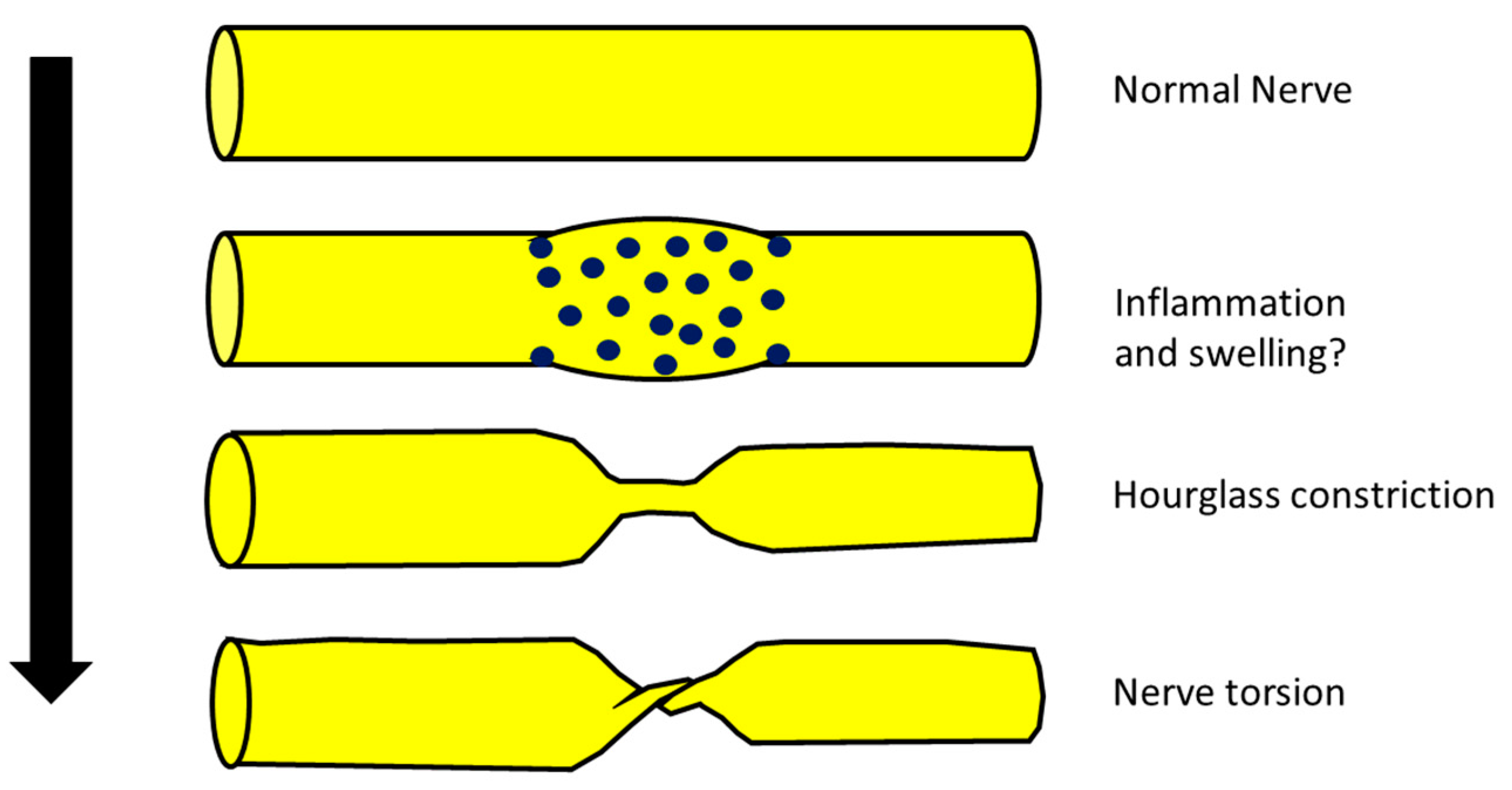
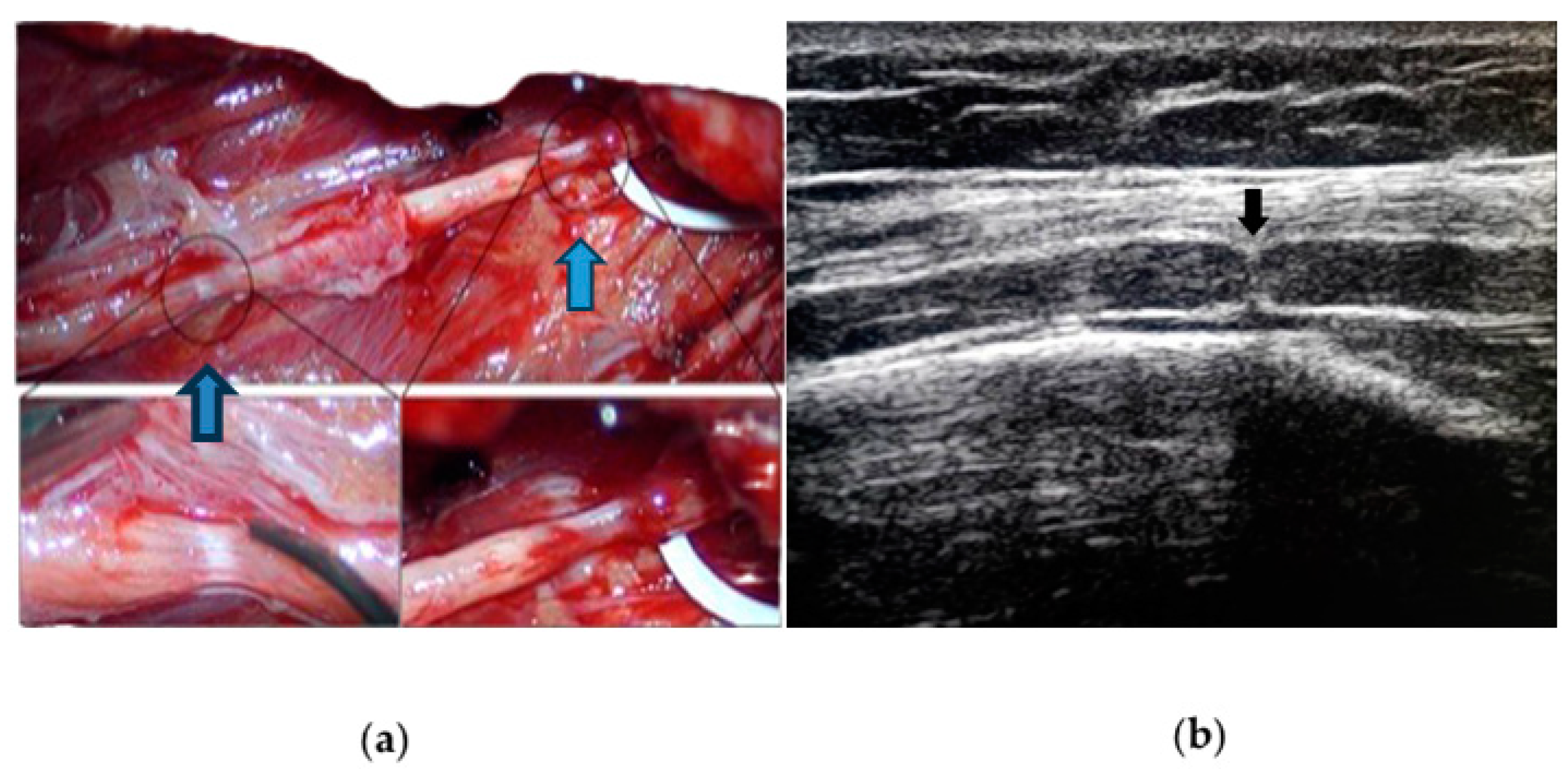
2. Are NA, Hourglass Constriction and Nerve Torsion Really a Different Evolution of the Same Pathology?
- (a)
- (b)
- (c)
- From a neurophysiological point of view, the typical picture of NA is the main or exclusive involvement of motor fibers, even in the case of mixed nerve involvement. On the other hand, hourglass constriction/nerve torsion usually affects both motor and sensory fibers at the same time and with the same severity. Motor fibers are exclusively included only in the case of pure motor nerve involvement (e.g., PIN and AIN) [25,26].
- (d)
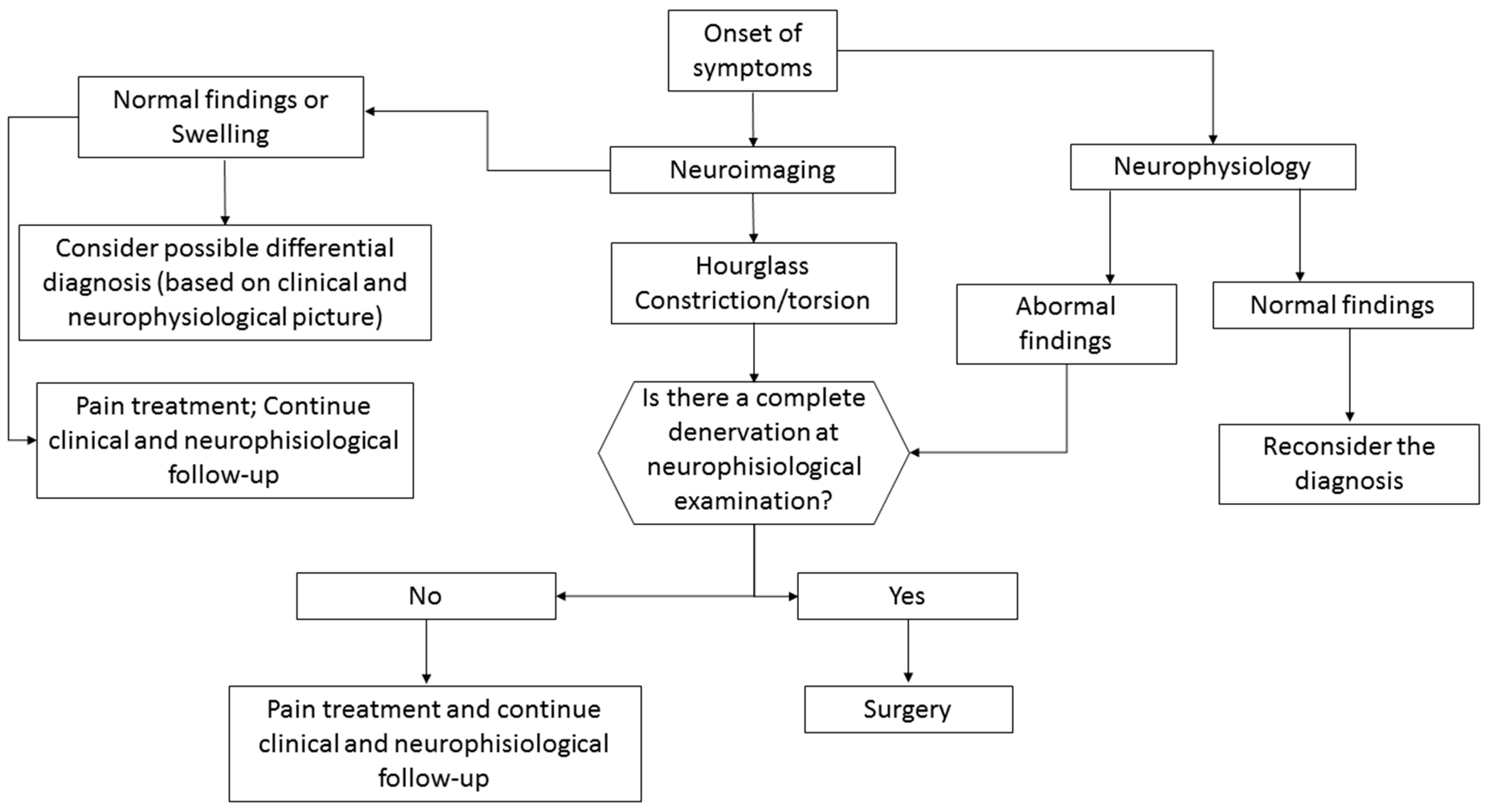
3. What Is the Best Diagnostic Approach for These Conditions?
3.1. Neuroimaging
3.2. Neurophysiology
3.3. Differential Diagnosis of Acute Mononeuropathies and Related Examinations
4. What Is the Best Treatment Approach for These Conditions?
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, C.C.; Bevelaqua, A.C. Challenging pain syndromes: Parsonage-Turner syndrome. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 25, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eijk, J.J.; Groothuis, J.T.; Van Alfen, N. Neuralgic amyotrophy: An update on diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment. Muscle Nerve 2016, 53, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seror, P. Neuralgic amyotrophy: An update. Jt. Bone Spine 2017, 2, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farr, E.; D’Andrea, D.; Franz, C.K. Phrenic Nerve Involvement in Neuralgic Amyotrophy (Parsonage-Turner Syndrome). Sleep Med. Clin. 2020, 15, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Alfen, N.; van Engelen, B.G. The clinical spectrum of neuralgic amyotrophy in 246 cases. Brain 2006, 129 Pt 2, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gstoettner, C.; Mayer, J.A.; Rassam, S.; Hruby, L.A.; Salminger, S.; Sturma, A.; Aman, M.; Harhaus, L.; Platzgummer, H.; Aszmann, O.C. Neuralgic amyotrophy: A paradigm shift in diagnosis and treatment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, S.; Zheng, D.; Tian, W.; Tian, G.; Ho, P.C.; Cheng, H.S.; Zhong, Y. Hourglass-like constrictions of peripheral nerve in the upper extremity: A clinical review and pathological study. Neurosurgery 2014, 75, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glorioso, D.; Palestini, R.; Cuccagna, C.; Lauretti, L.; Padua, L. Nerve Torsion as a Pattern of Parsonage-Turner Syndrome: Literature Review and Two Representative Cases. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarawickrama, D.; Therimadasamy, A.K.; Sebastin, S.J.; Wilder-Smith, E.P. Radial nerve torsion. Neurology 2016, 86, 1559–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Yu, J.L.; Jin, H.L.; Ng, L.; Wang, J.C.; Li, X.; Gai, T.T.; Zhou, Y.; Li, D.P. Hourglass-like constriction of the anterior interosseous nerve in the left forearm: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 2023, 11, 4194–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberlin, C.; Shafi, M.; Diverres, J.P.; Silberman, O.; Adle, H.; Belkheyar, Z. Hourglass-like constriction of the axillary nerve: Report of two patients. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2006, 31, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omura, T.; Nagano, A.; Murata, H.; Takahashi, M.; Ogihara, H.; Omura, K. Simultaneous anterior and posterior interosseous nerve paralysis with several hourglass-like fascicular constrictions in both nerves. J. Hand Surg. 2001, 26, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Li, C.; Sun, H.; Zhu, Q.; Cui, S. Hourglass-Like Constriction of the Musculocutaneous Nerve: Case Report. J. Hand Surg. 2010, 35, 1652–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretas, F.; Araújo, G.C.S.; Ugarte, O.N.; Acioly, M.A. Spontaneous radial nerve palsy with hourglass-like constriction. BMJ Case Rep. 2023, 16, e253537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Song, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, J.; Lu, L. Spontaneous peripheral nerve palsy with hourglass-like fascicular constriction in the upper extremity. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 131, 1876–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Nagano, A.; Mikami, Y.; Tajiri, Y. Multiple constrictions of the radial nerve without external compression. J. Hand Surg. 2000, 25, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongwei, P.; Guanglei, T.; Jianing, W.; Shuhuan, W.; Qingtai, L.; Wen, T. Nontraumatic paralysis of the radial nerve with multiple constrictions. J. Hand Surg. 2003, 28, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Nukada, H.; Hayashi, M.; Ochi, K.; Yamazaki, H.; Kato, H. Pathological Findings of Hourglass-Like Constriction in Spontaneous Posterior Interosseous Nerve Palsy. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2020, 45, e1–e990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arányi, Z.; Csillik, A.; Dévay, K.; Rosero, M.; Barsi, P.; Böhm, J.; Schelle, T. Ultrasonographic identification of nerve pathology in neuralgic amyotrophy: Enlargement, constriction, fascicular entwinement, and torsion. Muscle Nerve 2015, 52, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneag, D.B.; Urban, C.; Li, T.Y.; Colucci, P.G.; Pedrick, E.G.; Nimura, C.A.; Feinberg, J.H.; Milani, C.J.; Tan, E.T. Hourglass-like constrictions on MRI are common in electromyography-confirmed cases of neuralgic amyotrophy (Parsonage-Turner syndrome): A tertiary referral center experience. Muscle Nerve 2023. early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneag, D.B.; Rancy, S.K.; Wolfe, S.W.; Lee, S.C.; Kalia, V.; Lee, S.K.; Feinberg, J.H. Brachial plexitis or neuritis? MRI features of lesion distribution in Parsonage-Turner syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2018, 58, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, I. Isolated spontaneous posterior interosseous nerve palsy: A review of aetiology and management. J. Hand Surg. Eur. Vol. 2019, 44, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigamoney, K.V.; Rashid, A.; Ng, C.Y. Management of Atraumatic Posterior Interosseous Nerve Palsy. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2017, 42, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, D.I. Neuralgic amyotrophy: Clinical features and diagnostic evaluation. Neurologist 2001, 7, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Qi, H.; Ding, H.; Chen, F.; Xin, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Guan, S.; Shi, H. Electrophysiological examination and high frequency ultrasonography for diagnosis of radial nerve torsion and compression. Medicine 2018, 97, e9587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granata, G.; Coraci, D.; Erra, C.; Tsukamoto, H.; Padua, L.; Luigetti, M. Posterior interosseous nerve syndrome due to radioulnar joint cyst. Muscle Nerve. 2013, 48, 842–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.W.; Wang, S.; Tian, G.; Li, C.; Tian, W.; Tian, M. Typical brachial neuritis (Parsonage-Turner syndrome) with hourglass-like constrictions in the affected nerves. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2011, 36, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ArÁnyi, Z.; Csillik, A.; DéVay, K.; Rosero, M.; Barsi, P.; BÖhm, J.; Schelle, T. Ultrasonography in neuralgic amyotrophy: Sensitivity, spectrum of findings, and clinical correlations. Muscle Nerve 2017, 56, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripellino, P.; Arányi, Z.; van Alfen, N.; Ventura, E.; Peyer, A.K.; Cianfoni, A.; Gobbi, C.; Pedrick, E.; Sneag, D.B. Imaging of neuralgic amyotrophy in the acute phase. Muscle Nerve 2022, 66, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Lu, B.; Yin, C.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Mi, Y.; Xu, P. The Effectiveness of Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis of Spontaneous Hourglasslike Constriction of Peripheral Nerve in the Upper Extremity. World Neurosurg. 2020, 134, e103–e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiling, B.; Waschke, A.; Ceanga, M.; Grimm, A.; Witte, O.W.; Axer, H. Not your average Saturday night palsy-High resolution nerve ultrasound resolves rare cause of wrist drop. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 172, 160–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Jeon, T.; Kim, C.U. Value of ultrasound in diagnosis of radial nerve palsy with hourglass-like constrictions without extrinsic compression: A case report. J. Hand Surg. Eur. Vol. 2018, 43, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Sung, D.H.; Chang, M.C. Diagnosis of Hourglass-Like Constriction Neuropathy of the Radial Nerve Using High-Resolution Magnetic Resonance Neurography: A Report of Two Cases. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sneag, D.B.; Saltzman, E.B.; Meister, D.W.; Feinberg, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; Wolfe, S.W. MRI bullseye sign: An indicator of peripheral nerve constriction in parsonage-turner syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2017, 56, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossey-Marec, D.; Simonet, J.; Beccari, R.; Michot, C.; Bencteux, P.; Dacher, J.N.; Milliez, P.Y.; Thiebot, J. Ultrasonographic appearance of idiopathic radial nerve constriction proximal to the elbow. J. Ultrasound Med. 2004, 23, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cignetti, N.E.; Cox, R.S.; Baute, V.; McGhee, M.B.; van Alfen, N.; Strakowski, J.A.; Boon, A.J.; Norbury, J.W.; Cartwright, M.S. A standardized ultrasound approach in neuralgic amyotrophy. Muscle Nerve 2023, 67, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eder, M.; Schulte-Mattler, W.; Pöschl, P. Neurographic course Of Wallerian degeneration after human peripheral nerve injury. Muscle Nerve 2017, 56, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.K.; Kennett, R.; Smith, G. Posterior interosseous nerve palsy in rheumatoid arthritis: Case report and literature review. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2009, 62, e556–e560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, K.; Horiuchi, Y.; Tazaki, K.; Nishi, K.; Kawashima, H.; Yabe, H. Spontaneous anterior interosseous nerve palsy with Churg-Strauss syndrome. Mod. Rheumatol. 2010, 20, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadilkar, S.V.; Patil, S.B.; Shetty, V.P. Neuropathies of leprosy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 420, 117288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindic, C.J. Infectious neuropathies. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2013, 26, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.; Pinto, C.; Barbosa, A.; Borges, T.; Dias, C.; Almeida, J. New insights in cryoglobulinemic vasculitis. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 105, 102313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavee, J. Peripheral neuropathy in sarcoidosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2022, 368, 577864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, D.; van de Beek, D.; Brouwer, M.C. Clinical features, treatment and outcome in neurosarcoidosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Neurol. 2016, 16, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobile-Orazio, E.; Cappellari, A.; Meucci, N.; Carpo, M.; Terenghi, F.; Bersano, A.; Priori, A.; Barbieri, S.; Scarlato, G. Multifocal motor neuropathy: Clinical and immunological features and response to IVIg in relation to the presence and degree of motor conduction block. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 72, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beadon, K.; Guimarães-Costa, R.; Léger, J.M. Multifocal motor neuropathy. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2018, 31, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchetta, M.; Padua, L.; Granata, G.; Luigetti, M.; Campagnolo, M.; Dalla Torre, C.; Coraci, D.; Sabatelli, M.; Briani, C. Nerve ultrasound findings in neuropathy associated with anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein antibodies. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rison, R.A.; Beydoun, S.R. Paraproteinemic neuropathy: A practical review. BMC Neurol. 2016, 16, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, L.; Luigetti, M.; Florio, L.; Capone, F.; Di Lazzaro, V. Causes of chronic neuropathies: A single-center experience. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 1611–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerischer, L.M.; Scheibe, F.; Nümann, A.; Köhnlein, M.; Stölzel, U.; Meisel, A. Acute porphyrias—A neurological perspective. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attarian, S.; Fatehi, F.; Rajabally, Y.A.; Pareyson, D. Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 2198–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luigetti, M.; Del Grande, A.; Conte, A.; Lo Monaco, M.; Bisogni, G.; Romano, A.; Zollino, M.; Rossini, P.M.; Sabatelli, M. Clinical, neurophysiological and pathological findings of HNPP patients with 17p12 deletion: A single-centre experience. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 341, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuleman, J.; Timmerman, V.; Van Broeckhoven, C.; De Jonghe, P. Hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy. Neurogenetics 2001, 3, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannibal, M.C.; Ruzzo, E.K.; Miller, L.R.; Betz, B.; Buchan, J.G.; Knutzen, D.M.; Barnett, K.; Landsverk, M.L.; Brice, A.; LeGuern, E.; et al. SEPT9 gene sequencing analysis reveals recurrent mutations in hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy. Neurology 2009, 72, 1755–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Alfen, N.; van Engelen, B.G.; Hughes, R.A. Treatment for idiopathic and hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy (brachial neuritis). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009, 2009, CD006976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Shen, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yu, Y.; Yin, H.; Xu, W. Surgical treatment of hourglass-like radial nerve constrictions. Neurochirurgie 2021, 67, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizume, H.; Nishida, K.; Nanba, Y.; Shigeyama, Y.; Inoue, H.; Morito, Y. Non-traumatic paralysis of the posterior interosseous nerve. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1996, 78, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, K.R.; Sneag, D.B.; Feinberg, J.H.; Nwawka, O.K.; Lee, S.K.; Arányi, Z.; Wolfe, S.W. Outcomes of Microneurolysis of Hourglass Constrictions in Chronic Neuralgic Amyotrophy. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2021, 46, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastamäki, M. Prompt interfascicular neurolysis for the successful treatment of hourglass-like fascicular nerve compression. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Hand Surg. 2002, 36, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Yang, J.Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, C. Surgical and conservative treatments of complete spontaneous posterior interosseous nerve palsy with hourglass-like fascicular constrictions: A retrospective study of 41 cases. Neurosurgery 2014, 75, 250–257; discussion 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.; Lister, G.D. Localized constrictive radial neuropathy in the absence of extrinsic compression: Three cases. J. Hand Surg. Am. 1984, 9A, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Neuralgic Amyotrophy | Hourglass Constriction/Nerve Torsion | |
|---|---|---|
| Site | Mainly brachial plexus | Radial, anterior and posterior interosseous nerves |
| Clinical picture | Strong and invalidating pain (lasting usually more than 24 h), exclusive or main motor fiber involvement also in the case of mixed nerves | Pain that is not invalidating and of a short duration (lasting usually less than 24 h) |
| Neurophysiology | Exclusive or main motor fibers involvement also in the case of mixed nerve involvement | Same involvement of motor and sensory nerves in the case of mixed nerve involvement |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Granata, G.; Tomasello, F.; Sciarrone, M.A.; Stifano, V.; Lauretti, L.; Luigetti, M. Neuralgic Amyotrophy and Hourglass Nerve Constriction/Nerve Torsion: Two Sides of the Same Coin? A Clinical Review. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14010067
Granata G, Tomasello F, Sciarrone MA, Stifano V, Lauretti L, Luigetti M. Neuralgic Amyotrophy and Hourglass Nerve Constriction/Nerve Torsion: Two Sides of the Same Coin? A Clinical Review. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(1):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14010067
Chicago/Turabian StyleGranata, Giuseppe, Fabiola Tomasello, Maria Ausilia Sciarrone, Vito Stifano, Liverana Lauretti, and Marco Luigetti. 2024. "Neuralgic Amyotrophy and Hourglass Nerve Constriction/Nerve Torsion: Two Sides of the Same Coin? A Clinical Review" Brain Sciences 14, no. 1: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14010067
APA StyleGranata, G., Tomasello, F., Sciarrone, M. A., Stifano, V., Lauretti, L., & Luigetti, M. (2024). Neuralgic Amyotrophy and Hourglass Nerve Constriction/Nerve Torsion: Two Sides of the Same Coin? A Clinical Review. Brain Sciences, 14(1), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14010067








